Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, understanding the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel is crucial for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of material sourcing. This high-performance alloy, known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, presents a unique challenge: how to select the right grade and supplier to meet specific application needs across diverse industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing.
This guide delves deep into the various types of 17-4 stainless steel, highlighting their properties, typical applications, and the critical role of yield strength in determining material performance. Buyers will gain insights into supplier vetting processes, ensuring quality and compliance with international standards. Additionally, we address cost considerations and provide strategies for negotiating favorable terms while maintaining product integrity.
Designed specifically for international B2B buyers from regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Saudi Arabia—this comprehensive resource empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. By equipping you with the necessary knowledge and tools, we aim to streamline your procurement process, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately contribute to your business’s success in a competitive market.
Understanding yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
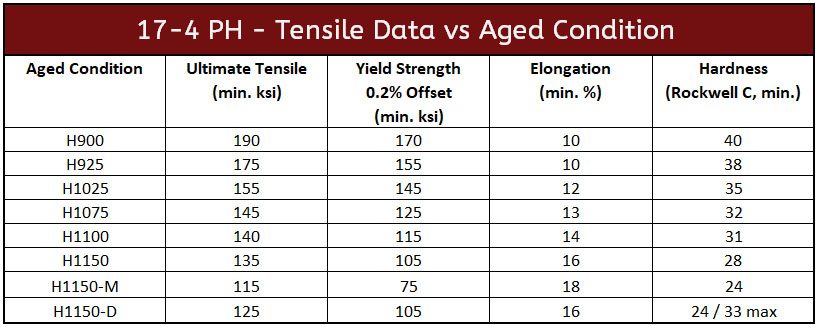
| H900 | High yield strength (170 ksi), excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace components, oil and gas applications | Pros: Exceptional strength and toughness; Cons: Limited ductility at high temperatures. |
| H1025 | Moderate yield strength (145 ksi), improved toughness | Mechanical seals, pump shafts | Pros: Better formability; Cons: Slightly lower strength compared to H900. |
| H1075 | Yield strength of 125 ksi, enhanced ductility | Food processing equipment, chemical processing | Pros: Good weldability; Cons: Lower hardness than higher grades. |
| H1150 | Yield strength of 105 ksi, higher elongation (16%) | Heavy machinery, structural applications | Pros: Enhanced machinability; Cons: Reduced strength in comparison to H900. |
| H1150D | Yield strength of 105 ksi with specific heat treatment | Aerospace and military applications | Pros: Tailored properties for specific uses; Cons: Complex heat treatment process. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of H900 Yield Strength in 17-4 Stainless Steel?
The H900 condition of 17-4 stainless steel is characterized by its high yield strength of approximately 170 ksi, making it suitable for applications that require exceptional strength and toughness. This variant is commonly utilized in aerospace components and oil and gas applications where both mechanical integrity and corrosion resistance are crucial. Buyers should consider the limitations in ductility at elevated temperatures, which may affect its performance in certain applications.
How Does H1025 Differ from Other Variants?
H1025 stainless steel offers a moderate yield strength of about 145 ksi, providing improved toughness compared to H900. It is particularly well-suited for applications like mechanical seals and pump shafts, where formability is essential. While it maintains a good balance of strength and ductility, buyers should be aware that it does not reach the peak strength of H900, potentially limiting its use in ultra-high-stress environments.
What Advantages Does H1075 Offer for Food Processing?
The H1075 condition features a yield strength of 125 ksi and is recognized for its enhanced ductility, making it ideal for food processing and chemical equipment. This grade offers good weldability, allowing for easier fabrication and assembly. Buyers should note, however, that while it provides excellent formability, its hardness and strength are lower than the higher-grade variants, which could be a consideration for more demanding applications.
What Are the Benefits of Using H1150 in Heavy Machinery?
H1150 stainless steel has a yield strength of 105 ksi and is known for its higher elongation, which makes it suitable for heavy machinery and structural applications. Its enhanced machinability allows for more efficient production processes. However, potential buyers should be cautious of its reduced strength compared to H900, as it may not be suitable for all high-stress environments.
Why Choose H1150D for Aerospace and Military Applications?
H1150D is a specific heat-treated variant of 17-4 stainless steel with a yield strength of 105 ksi, tailored for aerospace and military applications. Its properties can be customized through precise heat treatment processes, providing flexibility for specific use cases. However, the complexity of its heat treatment may pose challenges for procurement and processing, requiring buyers to ensure they have the right capabilities in place.
Key Industrial Applications of yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components such as landing gear and brackets | High strength-to-weight ratio enhances fuel efficiency | Certifications (e.g., AS9100), compliance with aerospace standards |
| Oil & Gas | Pump shafts and mechanical seals in drilling equipment | Durability under extreme conditions reduces downtime | Resistance to corrosion and wear, availability of various sizes |
| Chemical Processing | Components for reactors and pressure vessels | Excellent corrosion resistance ensures safety and longevity | Material certification, compatibility with specific chemicals |
| Defense | Structural components in military vehicles and equipment | High strength and toughness improve operational reliability | Compliance with military specifications, sourcing from certified suppliers |
| Food Processing | Equipment parts like valves and fittings | Non-reactive properties ensure product safety and quality | Compliance with food safety regulations, availability in hygienic designs |
How is Yield Strength of 17-4 Stainless Steel Applied in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, yield strength is crucial for components like landing gear and brackets, where structural integrity is paramount. The high yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel allows manufacturers to create lightweight yet durable parts, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. International buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that suppliers comply with aerospace standards such as AS9100, which guarantees quality and reliability in high-stakes applications.
What Role Does Yield Strength Play in Oil & Gas Applications?
In the oil and gas sector, 17-4 stainless steel is widely used for pump shafts and mechanical seals that operate under high pressures and corrosive environments. The alloy’s exceptional yield strength ensures that these components can withstand the rigors of drilling operations, minimizing the risk of failure and costly downtime. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that offer corrosion resistance and are available in various sizes to meet specific operational needs.
Why is Yield Strength Important in Chemical Processing?
Chemical processing facilities often require materials that can endure aggressive environments. The yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel makes it an ideal choice for components in reactors and pressure vessels, where safety and longevity are critical. For international buyers, it is essential to obtain material certifications that confirm compatibility with specific chemicals, ensuring safe and effective operation.
How Does Yield Strength Enhance Defense Applications?
In defense applications, the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel is vital for structural components in military vehicles and equipment. High strength and toughness provide operational reliability in challenging conditions, making it a preferred material for various applications. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with military specifications and source from certified suppliers to guarantee the quality and performance of their materials.
What Advantages Does Yield Strength Provide in Food Processing?
In food processing, the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel is leveraged in equipment parts like valves and fittings, where non-reactive properties are essential for product safety. The alloy’s ability to withstand harsh cleaning processes without compromising structural integrity is a significant advantage. Buyers should seek suppliers who comply with food safety regulations and offer hygienic designs to maintain product quality and safety standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Yield Strength Measurements Affecting Quality Control
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive often face challenges with inconsistent yield strength measurements of 17-4 stainless steel. These inconsistencies can lead to product failures, resulting in costly recalls or warranty claims. Additionally, the lack of standardized testing procedures across suppliers can make it difficult for manufacturers to ensure that the materials they are sourcing meet the necessary specifications for their applications. This concern is particularly acute for international buyers, who may have different testing protocols or quality assurance standards in their respective countries.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish clear communication with their suppliers regarding testing protocols and quality assurance measures. Requesting detailed material test reports (MTRs) that include yield strength data as well as certification to relevant standards (such as ASTM A564) can provide assurance of the material’s properties. Additionally, conducting independent third-party testing can further validate the yield strength of the materials sourced. Buyers should also consider developing long-term relationships with suppliers who have a proven track record of consistency and reliability in their products, ensuring that they receive high-quality materials that meet their specific requirements.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Desired Mechanical Properties
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with achieving the desired mechanical properties of 17-4 stainless steel for their specific applications, particularly when it comes to balancing yield strength with ductility and toughness. This challenge is often compounded by the complexities of the heat treatment process, where improper temperature control or timing can lead to suboptimal material performance. In industries such as oil and gas or aerospace, where equipment operates under extreme conditions, these mechanical property challenges can compromise safety and performance.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should work closely with metallurgists or materials engineers to fully understand the heat treatment options available for 17-4 stainless steel. Understanding the different tempering conditions (e.g., H900, H1025) and their corresponding yield strength and toughness profiles will allow for better customization of material properties. Buyers can also collaborate with suppliers who offer tailored heat treatment services to achieve the desired mechanical properties. Implementing rigorous quality control measures during the heat treatment process, such as monitoring temperature and duration, will ensure that the final product meets the required specifications.
Scenario 3: High Costs Due to Limited Availability of Custom Sizes
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter high costs associated with sourcing 17-4 stainless steel in custom sizes or shapes, which can be essential for specialized applications. When standard sizes are not available, the need for custom fabrication can lead to increased lead times and expenses. This situation is particularly frustrating for companies operating in fast-paced industries, where delays can significantly impact project timelines and budgets.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should engage suppliers who offer a wide range of standard and custom options for 17-4 stainless steel. Developing a strong partnership with these suppliers can facilitate better pricing and faster turnaround times for custom orders. Furthermore, buyers can consider consolidating their orders to maximize volume discounts and minimize shipping costs. Leveraging digital inventory platforms can also help buyers quickly identify suppliers with available stock of custom sizes, ensuring that they can procure the necessary materials without incurring excessive costs or delays.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
What are the Key Properties of 17-4 Stainless Steel?
17-4 stainless steel, also known as 17-4 PH, is a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel that offers a unique combination of high yield strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good toughness. The alloy typically contains 15% to 17.5% chromium and 3% to 5% nickel, making it suitable for high-temperature applications up to 600°F (316°C). Its mechanical properties can be tailored through heat treatment processes, allowing for a range of yield strengths from 75,000 PSI in softer conditions to 170,000 PSI in the hardened state.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 17-4 Stainless Steel?
Key Properties
- Temperature/Pressure Rating: Withstanding high temperatures and pressures, 17-4 stainless steel maintains its strength and toughness, making it suitable for applications in the aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: The alloy exhibits moderate to good corrosion resistance, particularly in environments where exposure to chemicals and moisture is prevalent.
Pros
- Durability: Its high yield strength and toughness make it ideal for demanding applications, ensuring longevity and reliability.
- Versatility: 17-4 stainless steel can be used in various forms, including bars, sheets, and custom shapes, catering to a wide range of industrial needs.
- Customizability: The material can be heat-treated to achieve specific mechanical properties, enhancing its suitability for various applications.
Cons
- Cost: Compared to standard stainless steels, 17-4 PH can be more expensive, which may impact budget-sensitive projects.
- Manufacturing Complexity: The need for precise heat treatment and machining can complicate the manufacturing process, potentially leading to longer lead times.
How Does 17-4 Stainless Steel Impact Specific Applications?
The choice of 17-4 stainless steel significantly affects application performance, particularly in sectors requiring high strength and corrosion resistance. For instance, in the aerospace industry, components made from this alloy are subject to rigorous stress and environmental conditions. Its ability to withstand corrosive media makes it suitable for oil and gas applications, where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting 17-4 Stainless Steel?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several factors should be considered:
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the material meets relevant international standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS, which can vary by region. For example, European buyers may prioritize compliance with EN standards.
- Local Sourcing and Availability: Assess the availability of 17-4 stainless steel in local markets to reduce lead times and shipping costs.
- Supplier Reputation: Partner with suppliers who have a proven track record in quality assurance and certification, particularly those with ISO certifications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Yield Strength of 17-4 Stainless Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH Stainless Steel | Aerospace components, oil and gas equipment, chemical processing | High yield strength and toughness | Higher cost compared to standard stainless steels | High |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Lower cost and good availability | Poor corrosion resistance | Low |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment | Enhanced wear resistance and toughness | May require additional heat treatment | Medium |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Marine applications, chemical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Complexity in welding and fabrication | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive understanding of the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel and its implications for various applications. By considering these factors, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Achieving Yield Strength in 17-4 Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing of 17-4 stainless steel involves several critical stages that ensure the alloy meets the desired yield strength specifications. This process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specialized techniques to maintain the integrity of the material and optimize its mechanical properties.
How Is Material Prepared for 17-4 Stainless Steel Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, which includes a precise mixture of chromium, nickel, copper, and other alloying elements. The selected materials undergo a thorough inspection to verify their chemical composition, ensuring they meet the required standards.
Once the materials are verified, they are subjected to solution treatment at high temperatures (around 1050°C) to dissolve any precipitates. This process is crucial, as it enhances the alloy’s ductility and ensures a uniform microstructure. After solution treatment, the material is rapidly quenched to lock in the desired properties, setting the stage for subsequent aging processes.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in 17-4 Stainless Steel Production?
Forming processes for 17-4 stainless steel include forging, rolling, and machining. These techniques are selected based on the final application and the required mechanical properties.
- Forging is often utilized for large components, as it improves the grain structure and enhances toughness.
- Rolling is commonly used for sheets and plates, allowing for precise thickness and surface finish.
- Machining is employed for achieving intricate shapes and tolerances, particularly in aerospace and defense applications where precision is paramount.
Each forming technique impacts the alloy’s yield strength, so it’s essential to control parameters like temperature and strain rate throughout these processes.
What Are the Finishing Processes for 17-4 Stainless Steel?
Finishing processes are crucial in enhancing the surface properties of 17-4 stainless steel and ensuring it meets specific application requirements. Common finishing techniques include heat treatment, surface hardening, and polishing.
- Heat Treatment: Following forming, 17-4 stainless steel is often subjected to aging treatments at temperatures ranging from 480°C to 760°C for several hours. This aging process precipitates hardening, significantly improving the yield strength and hardness of the alloy.
- Surface Hardening: Techniques such as nitriding or shot peening may be applied to improve wear resistance and fatigue life.
- Polishing: This final step enhances surface finish, critical for applications in the food and medical industries, where hygiene and aesthetics are paramount.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for 17-4 Stainless Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for a material as versatile and widely used as 17-4 stainless steel. Implementing stringent QA measures ensures that the final product meets international standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for 17-4 Stainless Steel Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, compliance with recognized standards is crucial. ISO 9001 is the most widely adopted quality management standard globally, ensuring organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as API (American Petroleum Institute) and CE marking for European markets are essential for ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects early. The typical QC phases include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during manufacturing to ensure adherence to established parameters. This includes checking dimensions, mechanical properties, and surface finish.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including tensile tests, hardness tests, and corrosion resistance assessments, to ensure it meets all specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s QC processes is paramount.
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess compliance with quality standards. Buyers should implement a systematic audit process that includes:
- Reviewing Quality Management Systems: Ensure the supplier has documented procedures that align with international standards.
- On-Site Inspections: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe processes, equipment, and overall quality control practices firsthand.
- Requesting Documentation: Buyers should request QC reports, certifications, and test results for transparency.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct unbiased assessments of the manufacturing process, material quality, and compliance with international standards. This is particularly valuable for buyers from regions with varying regulatory environments, as it helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing materials.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Affect International B2B Transactions?
For international B2B transactions, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is critical. Buyers should be aware of regional certifications and regulatory requirements that may differ from their own. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may require compliance with local standards.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can impact the perceived importance of quality assurance. Building strong relationships with suppliers and maintaining open communication channels can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure that quality expectations are consistently met.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 17-4 stainless steel are essential for achieving the desired yield strength and meeting the diverse requirements of international B2B buyers. By understanding these processes and implementing robust QC practices, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality materials that perform reliably across various applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure 17-4 stainless steel, specifically focusing on its yield strength. Understanding yield strength is crucial for ensuring the material’s suitability for various applications, particularly in demanding industries like aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing. By following this checklist, you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your procurement process, it’s vital to outline the specific technical requirements for your project. This includes the desired yield strength, which for 17-4 stainless steel can vary significantly based on its heat treatment condition.
- Key Considerations:
- Determine the specific grade needed (e.g., H900, H1025).
- Identify other mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation that may affect performance.
Step 2: Research Market Availability
Investigate the market to understand the availability of 17-4 stainless steel across different suppliers. This includes checking for stock levels, lead times, and any regional suppliers that may have a logistical advantage.
- Actionable Tips:
- Utilize online databases or industry networks to gauge supplier reputation.
- Consider local suppliers in regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East to reduce shipping costs and time.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and service expectations. This step minimizes risks associated with material procurement.
- What to Look For:
- Request certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) to confirm quality management systems.
- Seek references or case studies from similar industries to assess their track record.
Step 4: Verify Material Specifications and Compliance
Ensure that the material specifications align with industry standards and your specific requirements. This includes verifying the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the stainless steel.
- Important Actions:
- Ask for detailed material certificates or test reports that confirm the yield strength and other properties.
- Cross-check with ASTM or AMS standards relevant to 17-4 stainless steel.
Step 5: Discuss Customization and Processing Options
Engage with suppliers about customization options that may enhance the performance of 17-4 stainless steel for your application. Understanding processing methods can also provide insights into cost and lead time.
- Explore Options:
- Inquire about available heat treatments and their impact on yield strength.
- Discuss machining and fabrication capabilities that may be necessary for your projects.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. This step can significantly impact your overall project budget and timelines.
- Key Negotiation Points:
- Discuss bulk purchasing discounts or long-term agreements for better pricing.
- Clarify payment terms, delivery schedules, and any additional costs related to shipping or processing.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Order
After reaching an agreement, finalize the purchase order with all agreed-upon specifications and terms. This step ensures that both parties are aligned and minimizes potential disputes later.
- Checklist Items:
- Review all documentation for accuracy.
- Confirm delivery timelines and any post-purchase support that may be needed.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing 17-4 stainless steel, ensuring they acquire the right material to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel Sourcing
When sourcing 17-4 stainless steel, understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances is essential for international B2B buyers. The following analysis delves into the key components that influence costs and provides actionable insights for effective sourcing.
What Are the Main Cost Components in Sourcing 17-4 Stainless Steel?
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly impacts the overall pricing of 17-4 stainless steel. The alloy’s composition includes chromium, nickel, and copper, with market fluctuations in these metals directly affecting prices. Buyers should keep abreast of commodity market trends to anticipate price changes.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing processes such as heat treatment and machining, which are critical for achieving the desired yield strength. Labor costs vary by region; therefore, buyers should consider sourcing from areas with competitive wage structures to optimize costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing practices and technological advancements can help mitigate these overhead costs, but buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, especially for custom specifications. Buyers should inquire about tooling charges and amortization over production runs to understand their impact on unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the yield strength and overall quality of 17-4 stainless steel involves rigorous QC processes. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can add to the cost but also assure buyers of consistent quality, particularly in high-stakes industries like aerospace and oil and gas.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer. International buyers should consider Incoterms that define shipping responsibilities and costs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s positioning. Buyers should assess multiple suppliers to find competitive margins while ensuring quality.
What Influences Prices for 17-4 Stainless Steel?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized specifications can increase costs due to additional processing and tooling requirements. However, tailored solutions may provide significant long-term benefits, making it vital to weigh customization against budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality and certified products typically command premium prices. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of certifications based on their application requirements, as this can impact budget allocations.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher quality but at a premium. Conducting due diligence on potential suppliers helps in making informed decisions.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed terms of delivery can significantly affect total landed costs. Buyers should clarify responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid hidden costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Prices in International B2B Transactions?
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, performance, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to better value.
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Use projected order volumes to negotiate better pricing terms. Suppliers are often willing to provide discounts for larger commitments.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers allows buyers to benchmark pricing and leverage competitive offers during negotiations.
-
Be Culturally Aware: Understanding cultural nuances in negotiation styles across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can enhance communication and lead to more favorable outcomes.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry developments and market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations, as you can argue for better pricing based on current trends.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 17-4 stainless steel can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and geopolitical factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage in direct negotiations to obtain the most accurate and beneficial pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel With Other Solutions
When evaluating materials for high-strength applications, it’s crucial to consider various alternatives to 17-4 stainless steel. While 17-4 PH stainless steel is renowned for its impressive yield strength and versatility, other materials may offer competitive or complementary properties. This analysis will compare the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel against two notable alternatives: Inconel 718 and AISI 4130 steel.
| Comparison Aspect | Yield Strength Of 17 4 Stainless Steel | Inconel 718 | AISI 4130 Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 170,000 PSI (H900) | Up to 220,000 PSI | Up to 125,000 PSI |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate (requires specific heat treatment) | High (requires specialized machining) | Easy (conventional machining) |
| Maintenance | Low (good corrosion resistance) | Moderate (good but can corrode) | Low (requires protection) |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, chemical processing | Aerospace, oil & gas, nuclear | Automotive, structural components |
Inconel 718: A High-Strength Alternative
Inconel 718 is a nickel-chromium alloy known for its exceptional yield strength and high-temperature performance. With a yield strength of up to 220,000 PSI, it outperforms 17-4 stainless steel in extreme environments, making it ideal for aerospace applications. However, the cost of Inconel 718 is significantly higher, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its machining requires specialized tools and techniques, adding complexity to the implementation process. Despite these challenges, its ability to withstand severe thermal and corrosive conditions makes it a valuable option for critical applications.
AISI 4130 Steel: A Cost-Effective Solution
AISI 4130 steel is a low-alloy steel commonly used in manufacturing applications that require moderate strength and good weldability. With a yield strength of around 125,000 PSI, it is less robust than 17-4 stainless steel and Inconel 718. However, its lower cost and ease of machining make it an attractive choice for many structural applications, particularly in the automotive industry. AISI 4130 does require some corrosion protection, which can add to maintenance needs over time. For applications where weight and high strength are not as critical, AISI 4130 can offer a cost-effective alternative.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting a material for high-strength applications, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific conditions under which the material will be used. If maximum yield strength and high-temperature performance are paramount, Inconel 718 may be the best choice despite its higher cost. Conversely, for applications with less stringent strength requirements, AISI 4130 offers a cost-effective and easily machinable alternative. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your application will guide you in choosing the right material solution, ensuring both performance and value.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Yield Strength in 17-4 Stainless Steel?
When evaluating 17-4 stainless steel for various applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
The most common designation for 17-4 stainless steel is UNS S17400. This grade signifies that it is a martensitic precipitation-hardened stainless steel, renowned for its high strength and moderate corrosion resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the correct grade ensures the material meets the specific requirements of the application, whether it be in aerospace, chemical processing, or oil and gas industries.
2. Yield Strength
Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. For 17-4 stainless steel, yield strengths can vary significantly depending on the heat treatment condition. For instance, in the H900 condition, the yield strength can reach approximately 170,000 PSI (or 1,200 MPa). Understanding these values helps buyers select materials that can withstand operational stresses, ensuring safety and reliability.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is a measure of how much pulling force a material can withstand before breaking. For 17-4 stainless steel, tensile strength can reach up to 190,000 PSI in certain heat-treated conditions. This property is vital for applications where high mechanical loads are expected, making it an important consideration for manufacturers and engineers.
4. Elongation Percentage
Elongation refers to the amount of deformation a material can undergo before fracture, expressed as a percentage. For 17-4 stainless steel, elongation typically ranges from 10% to 18% depending on the heat treatment condition. A higher elongation percentage indicates better ductility, which can be crucial for applications requiring bending or forming.
5. Hardness
Hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to deformation and wear. In the case of 17-4 stainless steel, hardness can be quantified using different scales, such as Rockwell and Brinell. Depending on the treatment, hardness values can range from 255 to 388 HB. Understanding hardness is essential for manufacturers looking to balance strength and machinability in their production processes.
6. Heat Treatment Conditions
The heat treatment process significantly influences the mechanical properties of 17-4 stainless steel. Common conditions include H900, H1025, and H1150, each offering different yield and tensile strengths. Knowledge of these conditions allows B2B buyers to specify the right material treatment for their specific application needs, enhancing performance and durability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 17-4 Stainless Steel Yield Strength?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is vital for buyers looking to source components that meet specific performance standards, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they are making orders that align with their project requirements while managing inventory costs effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific quantities of products. B2B buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate and competitive quotes that reflect their specific needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) related to international commercial law. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for buyers to clarify responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, facilitating smoother transactions across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time taken from placing an order to delivery. Awareness of lead times helps B2B buyers plan their production schedules and inventory management, ensuring they have materials on hand when needed.
6. Certifications and Standards
Certifications such as ISO 9001 and specific ASTM standards ensure that materials meet quality and safety benchmarks. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold relevant certifications to guarantee compliance with industry standards, enhancing trust and reliability in their supply chain.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 17-4 stainless steel, ensuring that they meet their operational requirements while optimizing costs and performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Yield Strength of 17-4 Stainless Steel?
The global market for 17-4 stainless steel, particularly its yield strength, is shaped by several key drivers. As industries increasingly demand materials that combine high strength with corrosion resistance, the versatility of 17-4 makes it a preferred choice in sectors such as aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing. The shift toward lightweight yet robust materials is also gaining momentum, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations on emissions and fuel efficiency are prominent.
Emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing and precision machining are revolutionizing how 17-4 stainless steel is sourced and utilized. These advancements enable manufacturers to produce components with complex geometries while maintaining the required mechanical properties. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is leading to enhanced supply chain transparency, allowing international buyers from regions like Africa and South America to access real-time data on material availability and pricing.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and trade policies are influencing sourcing strategies. International buyers must navigate tariffs and trade agreements, particularly when sourcing from leading producers in Europe and the U.S. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing procurement strategies and ensuring cost-effectiveness.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Yield Strength of 17-4 Stainless Steel?
In the current landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount considerations for B2B buyers. The production of 17-4 stainless steel has environmental implications, including energy consumption and waste generation. Thus, suppliers are increasingly adopting practices that minimize their ecological footprint.
Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable manufacturing processes and offer certifications such as ISO 14001, which signifies a commitment to environmental management. Using recycled materials in the production of 17-4 stainless steel can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with new material extraction.
Moreover, the demand for ethical supply chains is on the rise. Buyers are looking for transparency regarding sourcing practices, labor conditions, and community impact. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Africa and South America, where local communities are often affected by industrial activities. Suppliers that can provide assurances of ethical practices and sustainability certifications will likely have a competitive edge in the market.
How Has the Yield Strength of 17-4 Stainless Steel Evolved Over Time?
The development of 17-4 stainless steel dates back to the mid-20th century when it was first introduced as a martensitic precipitation-hardening alloy. Its unique composition—containing about 17% chromium and 4% nickel—allowed for exceptional mechanical properties, including high yield strength and corrosion resistance. Initially utilized in aerospace applications, its versatility has led to widespread adoption across various industries.
Over the decades, advancements in heat treatment processes and alloying techniques have further enhanced its yield strength and overall performance. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-strength materials like 17-4 stainless steel is expected to grow, driven by the need for innovative solutions in challenging environments. Understanding the historical context of this material helps B2B buyers appreciate its value and the advancements that have made it a staple in modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
-
1. How do I determine the appropriate yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel for my application?
To select the right yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel, consider the specific demands of your application, including mechanical load, temperature range, and environmental conditions. Different heat treatment conditions (H900, H1025, etc.) provide various yield strengths, ranging from approximately 75,000 PSI to 170,000 PSI. It is crucial to consult with your supplier about the precise requirements of your project, as they can provide tailored advice based on your application’s unique challenges. -
2. What are the typical yield strengths of 17-4 stainless steel in various heat-treated conditions?
The yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel varies significantly based on its heat treatment condition. For example, in the H900 condition, the yield strength is about 170,000 PSI, while in H1150, it drops to around 105,000 PSI. Understanding these variations allows you to choose the right condition that meets your application requirements, balancing strength and other factors like ductility and toughness. -
3. How can I verify the quality of 17-4 stainless steel before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of 17-4 stainless steel, request certification documents such as ASTM compliance, mill test reports, and material safety data sheets (MSDS) from your supplier. Engaging suppliers with ISO certifications and a proven track record in the industry is also advisable. Additionally, consider third-party inspections to validate material properties, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers. -
4. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 17-4 stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities for 17-4 stainless steel can vary widely among suppliers. Many suppliers offer flexibility based on your specific needs, but typical MOQs can range from 100 to 500 pounds or more. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your purchasing strategy, especially if you need smaller quantities for prototypes or specific projects. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 17-4 stainless steel internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can differ based on supplier policies and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include advance payments, letters of credit, or net 30/60/90 days post-delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Consider working with suppliers who have established reputations in your region to facilitate smoother transactions. -
6. How does the corrosion resistance of 17-4 stainless steel affect its yield strength?
The corrosion resistance of 17-4 stainless steel is a vital consideration as it can impact its yield strength in harsh environments. While the alloy generally offers good corrosion resistance, prolonged exposure to aggressive substances can lead to material degradation and reduced mechanical properties. Ensure that your application’s environmental conditions are compatible with the alloy’s resistance capabilities, and consult with your supplier about possible coatings or treatments for enhanced protection. -
7. Can 17-4 stainless steel be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, 17-4 stainless steel is highly customizable. Suppliers often offer various heat treatment conditions, dimensions, and finishes to meet your specific needs. Depending on the application, you may also request modifications in chemical composition to enhance certain properties, such as corrosion resistance or machinability. Discuss your precise requirements with your supplier to explore available customization options. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing 17-4 stainless steel internationally?
When sourcing 17-4 stainless steel internationally, consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure your supplier has experience with international logistics to avoid delays. Additionally, assess potential duties or tariffs that may apply to your order. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding delivery timelines and shipping methods to ensure that your materials arrive on time and in good condition.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Yield Strength Of 17 4 Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Progressive Alloy – 17-4 PH Stainless Steel
Domain: progressivealloy.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 17-4 PH Stainless Steel UNS S17400 | AMS 5643 | ASTM A564 | ASTM A693 Grade 630
Type: Precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel.
Typical Usage: Applications requiring high strength and modest corrosion resistance.
Heat Treatment: Strength and toughness can be manipulated by temperature range in the heat treatment process.
Typical Applications: Pump Shafts, Oil Patch, Mechanical Seals, Ae…
2. Premium Alloys – 17-4 Stainless Steel
Domain: premiumalloys.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 17-4 stainless steel is a popular alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and versatility. It contains approximately 17% chromium and 4% nickel, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in industries such as gas, chemical, and aviation. Key properties include:
– High tensile strength (up to 190 KSI in H900 condition)
– Excellent formability and weldability
– Corrosio…
3. AK Steel – 17-4 PH® Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel
Domain: matweb.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “AK Steel 17-4 PH® Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel, Condition H 925”, “Categories”: [“Metal”, “Ferrous Metal”, “Martensitic”, “Stainless Steel”, “Precipitation Hardening Stainless”], “Material Notes”: “AK Steel 17-4 PH® provides an outstanding combination of high strength, good corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties at temperatures up to 600°F (316°C), and good t…
4. Best Stainless – 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Bar
Domain: beststainless.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “17-4 PH Stainless Steel Bar”, “UNS”: “S17400”, “AMS”: “5643”, “ASTM Standards”: [“A564”, “A693”], “Grade”: “630”, “NACE Standards”: [“MR0175”, “MR0103”], “Condition”: “H-1150D”, “Chemical Composition”: {“Carbon”: “0.070 max”, “Chromium”: “15.00 – 17.50”, “Columbian + Tantalum”: “0.15 – 0.45”, “Copper”: “3.00 – 5.00”, “Manganese”: “1.00 max”, “Nickel”: “3.00 – 5.00”, “Phosphorus”:…
5. Tech Steel – Stainless Steel 17-4PH Properties
Domain: techsteel.net
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Tech Steel – Stainless Steel 17-4PH Properties, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Aircraft Materials – Stainless Steel 17-4PH Bar
Domain: aircraftmaterials.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Stainless Steel 17-4PH Bar (AMS 5643 / AMS 5622)”, “Material Type”: “Martensitic, precipitation-hardening stainless steel”, “Key Features”: [“High strength”, “High hardness”, “Excellent corrosion resistance”, “Good fabricating characteristics”, “Can be age hardened by low temperature treatment”], “Applications”: [“Aerospace”, “Chemical”, “Petrochemical”, “Food processing”, “Paper…
7. ProtoXYZ – Stainless Steel 17-4 PH
Domain: protoxyz.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Material Type: Metals, Material Sub-Type: Stainless Steels, Material Name: Stainless Steel 17-4 PH, Note: Properties are not guaranteed. They are intended only as a basis for comparison and not for design purposes.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for yield strength of 17 4 stainless steel
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing 17-4 Stainless Steel?
The yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel, ranging from 75,000 to 170,000 PSI depending on the heat treatment condition, underscores its versatility and capability to meet demanding industrial requirements. This alloy’s excellent combination of high strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness makes it suitable for critical applications in aerospace, oil and gas, and chemical processing sectors. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the specific mechanical properties and heat treatment options is essential for optimizing performance in their respective applications.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
Strategic sourcing of 17-4 stainless steel can significantly enhance supply chain efficiency, ensuring access to high-quality materials at competitive prices. By leveraging relationships with trusted suppliers, businesses can mitigate risks associated with material shortages and fluctuating costs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications, to ensure product reliability and quality.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As industries evolve and the demand for high-performance materials increases, the strategic sourcing of 17-4 stainless steel presents an opportunity for growth and innovation. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet specific project requirements. By investing in strong partnerships and understanding the nuances of this alloy, businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive global market.