Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Yield Strength Of 17 4 Stainless Steel
Understanding Yield Strength in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel for Precision CNC Applications
17-4 precipitation hardening (PH) stainless steel is a critical material choice for demanding aerospace, medical, and industrial components due to its exceptional combination of high strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. Its yield strength—which typically ranges from 1000 MPa to 1300 MPa (145 ksi to 190 ksi) after heat treatment—is a defining characteristic enabling lightweight, high-stress part designs. However, achieving this performance in finished components requires precise control during CNC machining, as the material’s high strength and work-hardening tendencies can lead to tool wear, dimensional inaccuracies, and compromised surface integrity if not managed correctly.
At Honyo Prototype, we specialize in machining 17-4 PH stainless steel to exacting tolerances, leveraging optimized toolpaths, specialized tooling, and in-process metrology to maintain structural integrity while meeting tight geometric specifications. Our expertise ensures that the inherent yield strength of 17-4 PH translates directly into reliable, high-performance end products without sacrificing precision or repeatability. For engineers and procurement teams requiring rapid validation of manufacturability and cost, our Online Instant Quote platform delivers detailed CNC machining estimates in under 60 seconds—providing clarity on lead times, material utilization, and process feasibility before project initiation. This integration of material science proficiency and digital efficiency streamlines prototyping and low-volume production for mission-critical applications.
Technical Capabilities
Yield Strength of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel and Its Relevance in Precision Machining Applications
17-4 PH (Precipitation Hardening) stainless steel is widely used in high-precision manufacturing due to its excellent combination of high yield strength, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability after heat treatment. With a typical yield strength ranging from 1100 MPa to 1300 MPa (depending on heat treatment condition, e.g., H900, H1025, H1150), this material presents unique challenges and requirements in multi-axis CNC machining processes such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling and turning.
The high yield strength and work-hardening tendency of 17-4 PH require optimized toolpaths, rigid setups, and high-performance cutting tools to maintain tight tolerances (±0.0005″ or tighter). Compared to more machinable materials like aluminum, steel (e.g., 1018, 4140), ABS, and nylon, 17-4 PH demands higher spindle power, reduced feed rates, and specialized coolant strategies to prevent tool wear and thermal deformation.
Below is a comparative table highlighting yield strength and machining considerations across common materials used in precision CNC applications:
| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (psi) | Machinability Notes for 3/4/5-Axis Milling & Turning | Typical Use in Tight Tolerance Applications | Relative Tool Wear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH Stainless Steel (H900) | 1275–1310 | 185,000–190,000 | High work hardening; requires rigid setups, sharp carbide or ceramic tools, reduced stepovers, and high-pressure coolant. Sensitive to heat buildup affecting tolerances. | Aerospace components, medical devices, tooling | High |
| 4140 Steel (Annealed) | 415–470 | 60,000–68,000 | Moderate machinability; stable under high-speed milling. Good for tight tolerance turning with proper chip control. | Shafts, fixtures, structural parts | Moderate |
| 1018 Steel (Cold Drawn) | 370–440 | 54,000–64,000 | Easily machined; suitable for high-speed operations. Minimal thermal expansion improves tolerance control. | Prototypes, jigs, low-stress components | Low to Moderate |
| Aluminum 6061-T6 | 275–310 | 40,000–45,000 | Excellent machinability; high MRR possible. Low cutting forces allow aggressive 5-axis toolpaths. Minimal thermal distortion with proper cooling. | Enclosures, aerospace brackets, heat sinks | Low |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | 40–45 | 5,800–6,500 | Low melting point; requires sharp tools, low RPM, and chip evacuation to prevent smearing. Dimensional stability limited by moisture absorption. | Prototypes, housings, non-structural parts | Very Low |
| Nylon 6/6 | 70–80 | 10,000–11,600 | Flexible and abrasive; prone to chatter. Requires sharp tools and consistent feed. Moisture absorption affects dimensional stability. | Gears, insulators, wear components | Moderate (abrasive fillers increase wear) |
Summary for High-Precision Machining:
When machining 17-4 PH stainless steel for tight tolerance components, particularly in 4-axis and 5-axis configurations, the high yield strength necessitates conservative depth of cut, high tool rigidity, and post-machining stress relief or aging to ensure long-term dimensional stability. In contrast, materials like aluminum and ABS allow for faster cycle times and tighter surface finish control but lack the structural performance of 17-4 PH in demanding environments. Steel alloys offer a balance, while nylon and ABS are limited to non-structural, low-load applications.
For optimal results in 17-4 PH, toolpath strategies should minimize rework and thermal gradients, and in-process inspection is recommended to ensure conformance to tight geometric tolerances (e.g., GD&T).
From CAD to Part: The Process
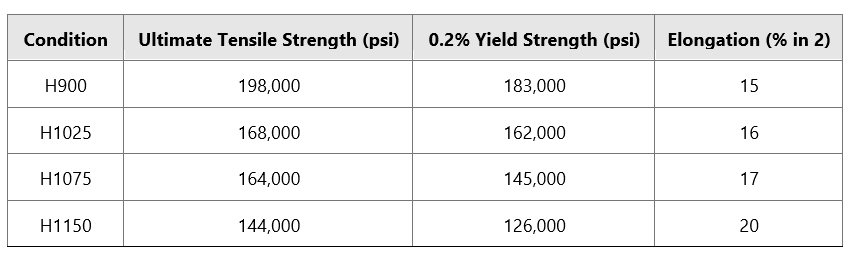
Honyo Prototype implements a rigorously controlled process to ensure the yield strength requirements for 17-4 PH stainless steel components are met at every stage from design to delivery. This process integrates material science expertise with advanced manufacturing protocols specifically for precipitation-hardening stainless steels.
Upon CAD file upload, our system immediately identifies material specifications including the designated 17-4 PH grade and required condition (e.g., H900, H1150). The AI quoting engine cross-references these parameters against ASTM A564 standards, current material certifications, and historical production data for 17-4 PH. It factors in yield strength dependencies such as heat treatment parameters, section thickness effects, and machining-induced residual stresses, generating an accurate cost projection that accounts for specialized processing needs.
During the Design for Manufacturability (DFM) phase, Honyo engineers conduct a dedicated material integrity review. We verify that geometric features will achieve uniform heat treatment penetration and avoid stress concentrations that could compromise yield strength. Critical analysis includes:
Confirming wall thicknesses align with H900/H1150 hardening kinetics to prevent core softening
Assessing surface finish requirements to eliminate stress risers below specified Ra values
Validating that all features maintain minimum 0.5mm radii to prevent localized yielding
Flagging designs requiring non-standard tempering cycles for custom yield strength targets
The following table summarizes key yield strength verification checkpoints during DFM for common 17-4 PH conditions:
| Condition | Target Yield Strength (min) | DFM Verification Focus | Critical Tolerance Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | 1310 MPa (190 ksi) | Section symmetry, quench uniformity | ±0.05mm on critical dimensions |
| H1150 | 965 MPa (140 ksi) | Distortion control, stress relief | ±0.1mm on datum features |
| Custom | Per engineering drawing | Thermal cycle validation | Drawing-specified GD&T |
Production execution follows a locked-down workflow for 17-4 PH. Material traceability begins with certified mill test reports (MTRs) for each heat number, confirming chemistry compliance with AMS 5604. Machining occurs under controlled parameters to prevent thermal work hardening, followed by solution treatment at 1040°C ±10°C with rapid quenching. Precipitation hardening uses calibrated vacuum furnaces with soak times adjusted per section thickness, validated by in-process thermocouples. Every lot undergoes hardness testing (Rockwell C-scale) with conversion to yield strength via ASTM E140 correlations, plus destructive sampling for statistical process control.
Final delivery includes comprehensive material documentation:
Certified MTRs with full chemistry and mechanical properties
Heat treatment batch records showing time-temperature profiles
Hardness test reports with location-specific measurements
Dimensional inspection data correlating to critical yield-sensitive features
Traceability matrix linking part serial numbers to furnace loads and test coupons
This integrated approach ensures Honyo Prototype consistently delivers 17-4 PH stainless steel components meeting specified yield strength requirements while maintaining full compliance with aerospace and medical industry standards. All processes are audited under AS9100/ISO 13485 frameworks with zero deviations permitted on critical material properties.
Start Your Project
For detailed technical specifications on the yield strength of 17-4 stainless steel and to discuss your custom manufacturing requirements, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Honyo Prototype offers precision machining and rapid prototyping services with a fully equipped factory located in Shenzhen, ensuring high-quality production and fast turnaround for your engineering projects.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.