Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for workholding fixtures
Navigating the global market for workholding fixtures presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and productivity. With an increasing demand for precision and speed in manufacturing, sourcing the right workholding solutions is critical. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering various types of workholding fixtures, their applications across industries, and insights on supplier vetting. Additionally, it delves into cost considerations and the latest innovations that can streamline your manufacturing processes.
As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Nigeria and Vietnam—look to optimize their operations, understanding the nuances of workholding fixtures becomes essential. This guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by offering actionable insights into selecting the best solutions tailored to your specific needs. By addressing key factors such as compatibility with existing machinery, ease of use, and long-term cost efficiency, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate this complex market successfully.
In an era where manufacturing competitiveness hinges on quick turnaround times and reliability, this guide will be your go-to resource for ensuring that your workholding fixtures not only meet but exceed operational demands. Unlock the potential of your production capabilities with the right fixtures, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving global market.
Understanding workholding fixtures Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular Workholding | Flexible configurations, interchangeable components | CNC machining, assembly processes | Pros: Customizable, scalable; Cons: Initial setup complexity. |
| Pneumatic Workholding | Utilizes compressed air for clamping, fast actuation | High-volume production, automotive | Pros: Quick setup, reduced manual effort; Cons: Requires air supply. |
| Vacuum Workholding | Uses suction to hold workpieces, ideal for flat surfaces | Woodworking, sheet metal fabrication | Pros: Non-damaging hold, versatile; Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Hydraulic Workholding | Employs hydraulic pressure for clamping, high clamping force | Heavy machining, aerospace components | Pros: Strong holding force, consistent pressure; Cons: Higher maintenance needs. |
| Quick Change Fixtures | Allows rapid swapping of workpieces or tools | High-mix low-volume production | Pros: Reduces downtime, enhances flexibility; Cons: May require additional investment. |
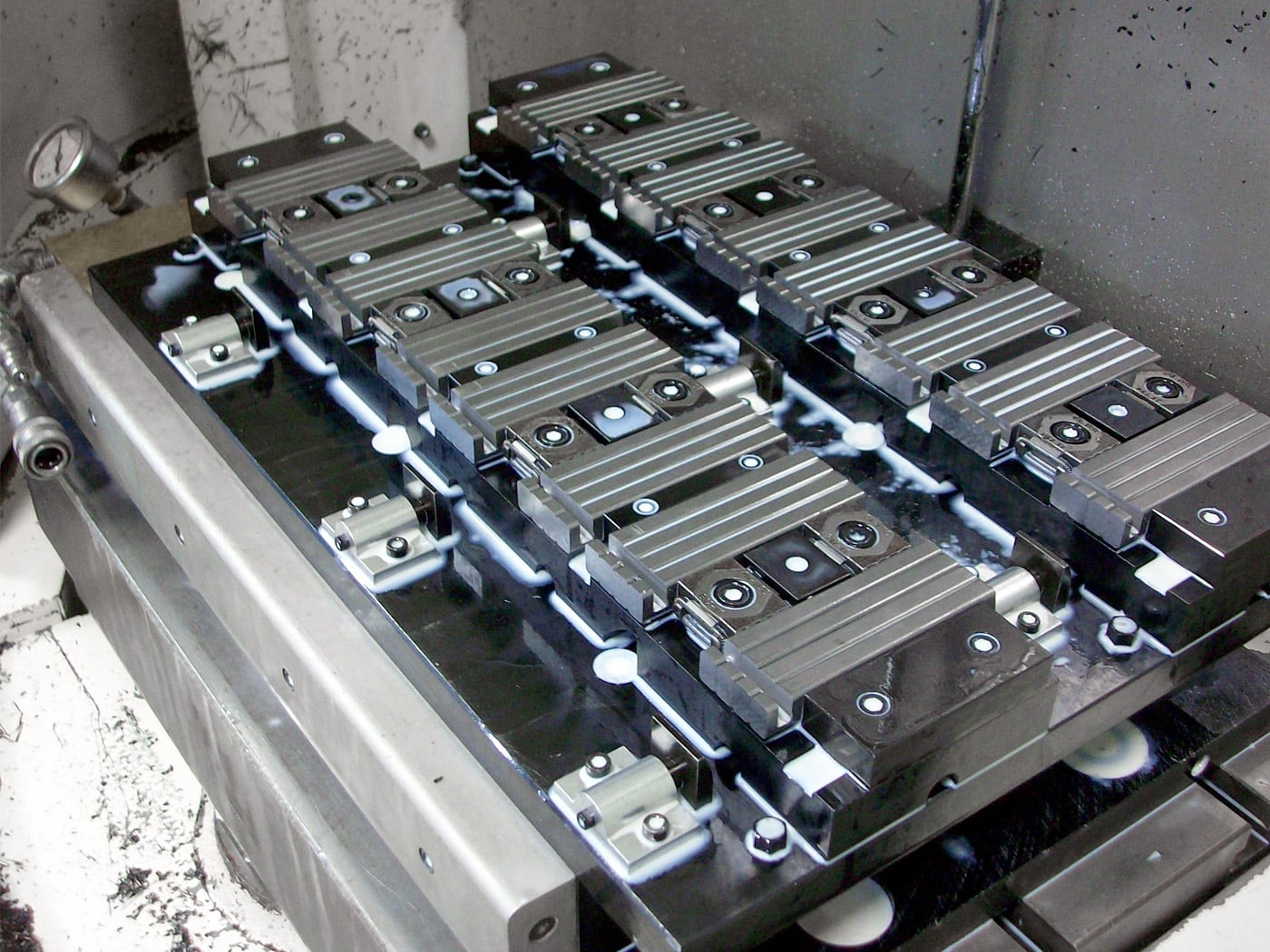
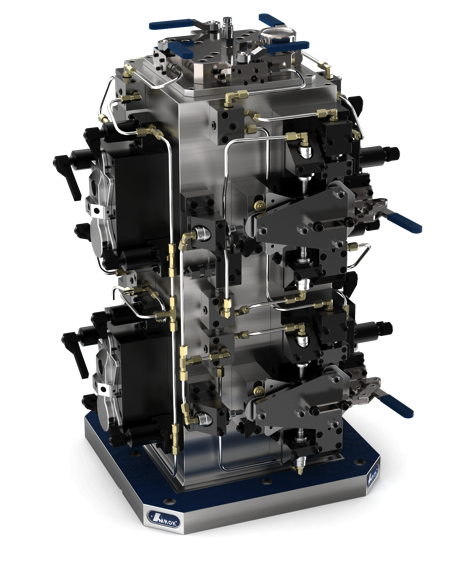
What are the Characteristics of Modular Workholding Fixtures?
Modular workholding fixtures are designed for maximum flexibility in manufacturing environments. They consist of various subplates, risers, and quick-change pallets that can be reconfigured to accommodate different workpieces. This adaptability makes them ideal for CNC machining and assembly processes where multiple parts are handled. Buyers should consider their specific production needs and whether the initial complexity of setup aligns with their operational capabilities.
How Do Pneumatic Workholding Fixtures Enhance Efficiency?
Pneumatic workholding fixtures leverage compressed air to enable rapid clamping and unclamping of workpieces, making them particularly suitable for high-volume production environments such as automotive manufacturing. Their quick actuation capabilities significantly reduce manual effort and setup times. When purchasing, companies should evaluate their air supply infrastructure and the potential return on investment from increased throughput.
In What Scenarios Are Vacuum Workholding Fixtures Most Effective?
Vacuum workholding fixtures are especially effective for holding flat workpieces, such as sheets of metal or wood, using suction. This method provides a non-damaging hold, making it an excellent choice for delicate materials. These fixtures are commonly used in woodworking and sheet metal fabrication. Buyers should assess the material compatibility and the vacuum system’s reliability to ensure optimal performance in their production processes.
What Advantages Do Hydraulic Workholding Fixtures Offer?
Hydraulic workholding fixtures utilize hydraulic pressure to achieve high clamping forces, making them suitable for heavy machining applications and aerospace components. They provide consistent pressure and strong holding capabilities, which are critical for maintaining precision during machining. However, buyers must consider the higher maintenance requirements and potential complexity of hydraulic systems when integrating them into their operations.
How Do Quick Change Fixtures Improve Production Flexibility?
Quick change fixtures are designed to enable the rapid swapping of workpieces or tools, thereby minimizing downtime in high-mix low-volume production settings. They enhance operational flexibility and can significantly improve productivity. However, the initial investment in quick change systems can be higher, so companies should evaluate their production volume and the potential cost savings from reduced setup times when considering this option.
Key Industrial Applications of workholding fixtures
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of workholding fixtures | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machining of components for aircraft | Enhances accuracy and reduces waste, ensuring safety | Need for high tolerance and lightweight materials |
| Automotive | Assembly line fixtures for vehicle parts | Increases production efficiency and reduces assembly time | Customization for various vehicle models and parts |
| Electronics Manufacturing | PCB assembly fixtures for circuit boards | Improves handling and reduces risk of damage | Compatibility with different PCB sizes and designs |
| Medical Devices | Workholding for surgical instrument manufacturing | Ensures precision and compliance with health standards | Regulatory compliance and materials suitability |
| Energy Sector | Workholding for turbine and generator components | Supports high-volume production and reduces downtime | Durability under extreme conditions and material strength |
How Are Workholding Fixtures Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, workholding fixtures are essential for the precision machining of components such as turbine blades and fuselage parts. These fixtures ensure that parts are held securely in place, minimizing movement that can lead to inaccuracies. Buyers in this sector must prioritize high tolerance levels and lightweight materials due to stringent safety regulations and performance standards. Sourcing fixtures that meet aerospace specifications is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring the safety of aircraft.
What Role Do Workholding Fixtures Play in Automotive Assembly Lines?
Automotive assembly lines utilize workholding fixtures to streamline the manufacturing process of vehicle parts. These fixtures enable quick changes between different vehicle models, enhancing production efficiency and reducing assembly time. For international buyers, especially those in regions with varying automotive standards, customization is key. Fixtures must be adaptable to accommodate diverse vehicle designs while maintaining high levels of precision and durability.
How Are Workholding Fixtures Beneficial in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, workholding fixtures are vital for the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs). They improve handling during the soldering and assembly processes, significantly reducing the risk of damage to delicate components. Buyers should consider sourcing fixtures that are compatible with various PCB sizes and designs to ensure versatility in production. Additionally, the ability to integrate automation into these fixtures can enhance operational efficiency, a critical factor in competitive markets.
Why Are Workholding Fixtures Critical for Medical Device Production?
For the medical device industry, workholding fixtures are crucial in the manufacturing of surgical instruments and other health-related products. These fixtures ensure precision and consistency, which are paramount for compliance with health standards. Buyers in this sector must focus on regulatory compliance and the suitability of materials, as these factors directly impact product safety and effectiveness. Sourcing fixtures that can handle the specific demands of medical manufacturing is essential for success.
How Do Workholding Fixtures Support Production in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, workholding fixtures are used for machining turbine and generator components, where precision and durability are vital. These fixtures support high-volume production while reducing downtime, which is critical in energy generation operations. Buyers should prioritize sourcing fixtures that can withstand extreme conditions and have robust material strength to handle the demanding environments typical in this industry. The right workholding solutions can significantly improve operational efficiency and output quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘workholding fixtures’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Fixture Alignment During Production Runs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in manufacturing face the issue of inconsistent fixture alignment, leading to misalignment of workpieces during machining. This not only affects the quality of the final product but also leads to increased scrap rates and wasted time during setup. Buyers are often frustrated by the need to recalibrate or adjust fixtures repeatedly, which disrupts production schedules and increases operational costs.
The Solution: To address this pain point, it is crucial to invest in modular workholding systems that offer quick-change capabilities and precision alignment features. Systems like Jergens’ Ball Lock® Mounting System allow for rapid setup and consistent positioning by using a proven method for locating and locking fixtures onto machine tables. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide customizable modular components, allowing for tailored solutions to specific machining requirements. Implementing these systems will not only enhance productivity by reducing setup time but also ensure that alignment remains consistent across multiple production runs, ultimately improving product quality and reducing waste.
Scenario 2: Slow Changeover Times Impacting Production Efficiency
The Problem: A common challenge faced by manufacturers is the slow changeover times between different workholding setups. This can be especially detrimental in environments where quick production cycles are critical, such as in automotive or aerospace sectors. Slow changeovers can lead to significant downtime, resulting in lost revenue and missed deadlines. Buyers often feel pressured to improve operational efficiency but struggle to find solutions that do not compromise on quality or increase costs.
The Solution: To combat slow changeover times, manufacturers should consider investing in zero-point clamping systems, such as those offered by Jergens. These systems allow operators to fix, position, and clamp fixtures in a single step, drastically reducing setup times by up to 90%. Buyers should assess their existing workholding solutions and evaluate how zero-point systems can be integrated into their processes. Additionally, training staff on the efficient use of these systems can further enhance speed and flexibility during production. By streamlining the changeover process, businesses can significantly improve their throughput and responsiveness to market demands.
Scenario 3: Lack of Customization for Unique Workholding Needs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter limitations with standard workholding fixtures that do not accommodate their unique manufacturing processes. This lack of customization can result in inefficiencies, as standard fixtures may not securely hold specialized components, leading to defects and quality issues. Buyers often find themselves constrained by the inability to adapt their workholding setups to evolving production requirements, which can stifle innovation and growth.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, companies should seek suppliers that specialize in custom workholding solutions. For example, PAWS Workholding offers tailored fixtures designed specifically for unique applications, which can be crucial for businesses with specialized manufacturing needs. When sourcing workholding fixtures, buyers should engage in detailed consultations with manufacturers to discuss their specific requirements and explore engineering solutions that can be developed to meet those needs. Additionally, leveraging CAD capabilities in the design phase can help visualize and optimize fixture designs, ensuring they align perfectly with production goals. By embracing custom solutions, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and improve product quality, positioning themselves for future growth.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for workholding fixtures
When selecting materials for workholding fixtures, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes. This guide analyzes four common materials used in workholding fixtures, providing insights tailored to international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Workholding Fixtures?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and is suitable for various machining applications. Its low density makes it easy to handle and install, which can lead to reduced labor costs.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, resistant to rust, and offers good machinability. It is also less expensive than many other metals, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as durable as steel under extreme pressure or temperature. Additionally, it may deform under heavy loads, which could impact precision in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for light-duty workholding applications, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN when sourcing aluminum fixtures. Different regions may have specific preferences for aluminum grades based on local availability and application requirements.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Workholding Fixtures?
Steel is widely regarded for its strength and durability, making it a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, with a typical temperature rating of around 1,200°F (649°C).
Pros: Steel offers exceptional strength, wear resistance, and longevity. It is suitable for high-stress applications and can be machined to precise tolerances.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can increase shipping costs and complicate handling. It is also more prone to corrosion unless treated, which may require additional maintenance.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for high-load applications, such as in the oil and gas industry or heavy manufacturing, where durability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is crucial, especially for industries with stringent safety regulations. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific steel grades in their region.
What Are the Benefits of Using Composite Materials in Workholding Fixtures?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are increasingly used in workholding fixtures due to their unique properties. They offer high strength while being lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Composites have excellent fatigue resistance and can be tailored for specific applications. They are also non-magnetic, making them suitable for sensitive electronic components.
Cons: The manufacturing complexity of composites can lead to higher costs. Additionally, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications, limiting their use in certain industries.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in industries like aerospace and electronics, where weight savings and precision are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must verify that the composite materials meet relevant international standards. There may also be specific certifications required for aerospace applications.
How Do Plastics Fit into the Workholding Fixture Material Landscape?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate or nylon, are often used in workholding fixtures for lighter applications. They are resistant to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, easy to mold, and can be produced at a lower cost than metals. They also offer good insulation properties.
Cons: Plastics may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads, which can limit their application in demanding environments. They are also less durable than metals.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used in assembly lines and for holding delicate components, particularly in the electronics and consumer goods sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastics comply with industry-specific regulations and standards, particularly in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Workholding Fixtures
| Material | Typical Use Case for workholding fixtures | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Light-duty applications in automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under heavy loads | Low |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications in manufacturing | Exceptional strength | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace and electronics | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Assembly lines and delicate components | Low cost and easy to mold | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
This material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when sourcing workholding fixtures, ensuring compatibility with their specific industry requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for workholding fixtures
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Workholding Fixtures?
Manufacturing workholding fixtures involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and functionality of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Workholding Fixtures?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which may include steel, aluminum, or specialized alloys. The choice of material is crucial, as it impacts the strength, weight, and durability of the fixture. Once the materials are selected, they undergo processes such as cutting, machining, and surface treatment to ensure they meet the required specifications. This step may also involve the use of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines for precise shaping and sizing.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Workholding Fixture Manufacturing?
Forming is the next stage, where raw materials are shaped into the desired fixture components. Common techniques include:
- Machining: Utilizing CNC machines to achieve tight tolerances and intricate designs.
- Welding: Joining different parts of the fixture together, ensuring structural integrity.
- Casting and Forging: These methods are used for creating complex shapes and enhancing material strength.
Each technique has its advantages, with machining providing high precision and forging offering improved material properties. The choice of technique often depends on the fixture’s intended application and production volume.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Workholding Fixtures?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage involves fitting the parts together, which may require the use of fasteners, adhesives, or welding. It’s essential to follow precise assembly protocols to ensure that the fixtures function correctly under operational loads. Advanced assembly techniques may also involve automation, which enhances consistency and reduces labor costs.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Workholding Fixture Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for workholding fixtures. It ensures that the products meet international standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Workholding Fixture Quality Assurance?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international standards is crucial. The ISO 9001 standard for quality management systems is widely recognized and applicable across various industries, including manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a company maintains a systematic approach to quality, focusing on continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in the oil and gas sector may apply, depending on the fixture’s application. These certifications ensure that the products meet safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
To ensure quality at every stage, manufacturers implement several quality control checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is conducted on raw materials upon arrival. It ensures that all materials meet the specified requirements before they enter the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are performed to monitor the process and detect any issues early. This may include dimensional checks and functional tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes rigorous testing to confirm it meets all quality standards and specifications. This step may include load testing, precision measurements, and surface finish evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers.
What Methods Can Be Used to Assess Supplier Quality Control?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide firsthand insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems. Audits can reveal compliance with international standards and highlight areas for improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports from suppliers can help buyers track performance metrics, defect rates, and corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations can conduct inspections at various stages of production and provide certifications that enhance trust.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers must also be aware of specific nuances related to quality control when sourcing internationally.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that impact quality assurance practices. For example, buyers in Europe may prioritize CE certification, while those in the Middle East might focus on local compliance standards. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring that the purchased fixtures meet both local and international requirements.
How Can Cultural Differences Impact Quality Control Perception?
Cultural perceptions of quality may also differ. In some regions, emphasis may be placed on the cost of production over quality, which can lead to compromises in manufacturing standards. It is essential for international buyers to establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and to foster a relationship based on transparency and trust.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Workholding Fixture Manufacturing
In summary, the manufacturing process of workholding fixtures encompasses several critical stages, each requiring meticulous attention to detail and robust quality assurance practices. B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies by understanding these processes, verifying supplier quality control measures, and staying informed about international standards. By prioritizing quality, buyers can ensure the reliability and performance of their workholding fixtures, ultimately contributing to their operational efficiency and profitability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘workholding fixtures’
Introduction
Sourcing workholding fixtures is a critical process for businesses aiming to enhance their manufacturing efficiency and precision. This guide provides a practical checklist that helps B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procuring these essential components. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the types of materials you will be working with, the dimensions of the fixtures, and the specific clamping mechanisms needed. Understanding these specifications helps in narrowing down suitable products and suppliers that can meet your unique demands.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in workholding fixtures. Utilize online directories, industry trade shows, and referrals from peers in your sector. Look for suppliers with proven expertise in manufacturing the specific types of fixtures you require, as this can significantly impact the quality and reliability of your purchase.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001 ensure that the supplier adheres to quality management standards, which is crucial for maintaining consistency in production. Additionally, inquire about any specific certifications related to the materials or processes they use.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples or prototypes of the workholding fixtures. This allows you to assess the quality, functionality, and compatibility of the fixtures with your existing equipment. Evaluating samples firsthand can help you avoid costly mistakes later on in the procurement process.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and payment terms. While cost is an important factor, consider the overall value, including warranty, support, and after-sales service. A slightly higher price may be justified if it includes better support or superior quality.
Step 6: Check for Customization Options
Consider whether the supplier offers customization options for their workholding fixtures. Custom solutions can enhance productivity by ensuring that the fixtures are tailored to your specific processes. Discuss your requirements and explore how flexible the supplier is in accommodating unique requests.
Step 7: Review Delivery and Lead Times
Finally, confirm the delivery schedules and lead times with your chosen supplier. Understanding the timeline is crucial for planning your production schedule. Ensure that the supplier can meet your deadlines and discuss any potential delays upfront to avoid disruptions in your operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in sourcing workholding fixtures that enhance their manufacturing capabilities and drive efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for workholding fixtures Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Workholding Fixtures Sourcing?
When sourcing workholding fixtures, understanding the cost structure is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in manufacturing workholding fixtures significantly impact costs. High-grade steel, aluminum, or specialized polymers may increase upfront expenses but often lead to greater durability and performance, reducing long-term costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the location of manufacturing. In regions with higher labor rates, such as Europe, you might face increased costs compared to sourcing from countries in Africa or South America where labor is typically more affordable.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses fixed and variable costs associated with production, including utilities, equipment depreciation, and factory maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead, influencing overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment, particularly for unique fixtures. The complexity of the design directly correlates with tooling costs, and this should be factored into your total budget.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the products meet specified standards, which may add to the cost. However, investing in quality can prevent costly rework and enhance product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping mode (air vs. sea), and customs duties can all affect the final pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the industry standard for margins can aid in evaluating supplier pricing.
What Influences Pricing in Workholding Fixtures Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of workholding fixtures, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs, making it essential to assess your production needs and order strategically.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom fixtures tailored to specific applications usually command higher prices. Be clear about your requirements to avoid unnecessary customization costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also pricing. Opting for standard materials can help keep costs down, whereas specialized materials might increase expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers that provide certified products (ISO, CE, etc.) may charge a premium. However, such certifications often assure quality and compliance with industry standards, which can be invaluable.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their reliability and service, while newer entrants might be more cost-competitive.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can influence total costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Workholding Fixtures?
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and payment terms. Flexible payment options or longer payment periods can improve cash flow.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership (TCO). Consider factors like maintenance, longevity, and performance, which can affect your bottom line over time.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your operations allow, consolidate orders to achieve volume discounts. Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can also lead to better pricing and service.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the specific pricing dynamics in different regions. For instance, while sourcing from Africa or South America may present lower labor costs, logistical challenges can offset these savings.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Always seek multiple quotes from different suppliers to compare pricing and terms. This practice not only provides leverage in negotiations but also helps in identifying the best value.
Disclaimer
Prices for workholding fixtures can vary significantly based on specifications, supplier location, and market conditions. This analysis provides indicative cost structures and pricing influences, but actual prices may differ. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing workholding fixtures With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Workholding Fixtures: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of manufacturing and machining, workholding fixtures play a crucial role in ensuring precision and efficiency. However, several alternatives can also achieve similar objectives, catering to various operational needs. This analysis compares workholding fixtures against two viable alternatives: Modular Workholding Systems and Magnetic Workholding Solutions. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, B2B buyers can make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Workholding Fixtures | Modular Workholding Systems | Magnetic Workholding Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and stability for diverse applications | Flexible configurations for varied setups | Quick setup with excellent holding power |
| Cost | Typically higher initial investment | Moderate cost with scalable options | Lower initial costs but may require additional equipment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific design and setup | User-friendly with easy adjustments | Simple installation but dependent on surface material |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required for longevity | Generally low maintenance | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Complex machining tasks needing exact alignment | Versatile applications in dynamic environments | High-speed machining with non-ferrous materials |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Modular Workholding Systems?
Modular Workholding Systems provide a flexible approach to workholding by allowing manufacturers to customize their setups according to specific tasks. These systems are particularly beneficial in environments where changeovers are frequent, as they can be adjusted quickly to accommodate different parts. The moderate cost associated with these systems makes them accessible for many businesses, while their low maintenance requirements add to their appeal. However, they may not provide the same level of precision as traditional workholding fixtures, particularly in complex machining tasks.
How Do Magnetic Workholding Solutions Compare?
Magnetic Workholding Solutions are an innovative alternative that offers quick setup times and strong holding power, making them ideal for high-speed machining operations. These systems can handle a variety of materials, especially non-ferrous metals, and can significantly reduce cycle times. One of the primary advantages is their lower initial investment compared to traditional workholding fixtures. However, their effectiveness can be limited by the type of material being machined, and they may not provide the same level of precision for intricate designs.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Workholding Solution?
Selecting the right workholding solution depends on a variety of factors, including the specific machining processes, the types of materials being used, and the frequency of changeovers in production. For businesses focused on high-precision tasks with a consistent part design, investing in traditional workholding fixtures may be the best choice despite the higher costs. Conversely, companies that require flexibility and speed may find Modular Workholding Systems or Magnetic Workholding Solutions more beneficial. Ultimately, understanding the operational needs and evaluating the pros and cons of each solution will guide B2B buyers toward the most suitable option for their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for workholding fixtures
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Workholding Fixtures?
When selecting workholding fixtures, understanding their critical technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Here are several key specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a workholding fixture determines its strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys. For instance, high-grade steel is often favored for its superior tensile strength and longevity in high-pressure applications. B2B buyers should prioritize material grades that align with their operational requirements to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the fixture. It is crucial for ensuring that the parts being held are machined accurately to the required specifications. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are essential in precision machining, where even minor discrepancies can lead to significant production flaws. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers select fixtures that will enhance the quality of the end products.
3. Load Capacity
Load capacity defines the maximum weight a fixture can support without failure. This property is particularly important in high-volume production settings where multiple parts may be processed simultaneously. Buyers must assess the load capacity in relation to the anticipated workload to avoid fixture deformation or breakage, which can halt production and incur additional costs.
4. Clamping Force
Clamping force is the amount of force exerted by the fixture to hold a workpiece securely in place during machining. Adequate clamping force is vital to prevent movement that could lead to inaccuracies. Understanding the required clamping force for specific materials and machining processes allows buyers to choose fixtures that ensure stability and precision.
5. Compatibility
Compatibility refers to how well a workholding fixture integrates with existing machinery and tooling systems. This includes the design of the fixture and its connection points, such as those for quick-change systems. Buyers should ensure that the fixtures they select are compatible with their current equipment to facilitate seamless integration and minimize setup times.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Workholding Fixtures?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation processes. Here are some common trade terms relevant to workholding fixtures:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of workholding fixtures, understanding OEM relationships can provide insights into the quality and reliability of the fixtures being sourced.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs effectively and ensure that their production schedules align with supplier capabilities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products. This process is essential for comparing costs and understanding the market value of workholding fixtures, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with the delivery of workholding fixtures.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order until the goods are delivered. Understanding lead times for workholding fixtures is vital for production planning and inventory management, helping businesses avoid delays that can impact their operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right workholding fixtures that meet their operational demands and contribute to overall production efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the workholding fixtures Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Workholding Fixtures Market?
The workholding fixtures market is currently experiencing significant transformation driven by global manufacturing demands, technological advancements, and evolving buyer preferences. A key trend is the increasing adoption of modular and flexible workholding systems. These solutions allow manufacturers to quickly adapt to varying production requirements, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. As manufacturers seek to optimize operations, technologies such as zero-point clamping systems and automation are becoming essential. These innovations not only improve the speed of changeovers but also significantly enhance precision in machining processes.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that offer integrated solutions combining hardware and software capabilities. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where manufacturers are investing in smart factories to boost productivity. Additionally, sustainability is emerging as a critical factor in sourcing decisions, with companies increasingly looking for eco-friendly materials and practices in their supply chains.
The current market dynamics also reflect a growing preference for local sourcing, driven by geopolitical factors and the need for supply chain resilience. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe are particularly focused on establishing partnerships with suppliers that can ensure reliable delivery and support, mitigating risks associated with global supply chain disruptions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Workholding Fixtures Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the workholding fixtures sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has prompted companies to seek solutions that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints. This includes the adoption of green materials, such as recyclable metals and environmentally friendly coatings, which align with corporate social responsibility goals.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction, as buyers increasingly demand transparency in their supply chains. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and ethical labor practices are more likely to secure contracts. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and SA8000 for social accountability are becoming essential credentials in supplier evaluations.
Moreover, companies are exploring innovative approaches to reduce their environmental impact, such as using additive manufacturing techniques to produce workholding fixtures. This not only lowers material waste but also allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. In a competitive landscape, prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing is no longer just a trend but a strategic imperative for B2B buyers looking to enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements.
What Is the Historical Context of Workholding Fixtures in B2B Manufacturing?
The evolution of workholding fixtures can be traced back to the early industrial revolution when the need for precision in manufacturing became paramount. Initially, workholding devices were rudimentary, often handmade and tailored to specific tasks. However, as mass production gained momentum, the demand for standardized fixtures surged, leading to the development of more sophisticated designs.
In the latter half of the 20th century, advancements in materials science and machining technology propelled the workholding sector into a new era. The introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines necessitated more versatile and precise workholding solutions, resulting in the creation of modular systems that could adapt to various machining processes.
Today, the focus has shifted towards automation and integration with digital technologies, reflecting broader trends in manufacturing. B2B buyers now seek suppliers who not only provide high-quality fixtures but also contribute to the overall efficiency and adaptability of their manufacturing operations. This historical context highlights the ongoing transformation within the industry, positioning workholding fixtures as a critical component in modern manufacturing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of workholding fixtures
-
How do I solve the problem of inconsistent clamping with workholding fixtures?
To address inconsistent clamping, evaluate the type of workholding fixtures you are using. Opt for fixtures with adjustable clamping mechanisms or those that offer pneumatic assistance for greater precision. Additionally, consider implementing modular systems that can be customized for various workpieces. Regular maintenance and calibration of the fixtures are essential to ensure they maintain their clamping force. Partnering with suppliers who provide technical support and training can also help your team optimize the clamping process. -
What is the best type of workholding fixture for CNC machining?
The best type of workholding fixture for CNC machining typically depends on the specific application and material being machined. For general-purpose applications, modular workholding systems offer flexibility and quick setup times. If precision is crucial, consider zero-point clamping systems, which minimize setup time and enhance repeatability. For high-volume production, customized fixtures designed for specific parts can significantly improve efficiency. Engage with suppliers to explore options that align with your production needs and budget. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for workholding fixtures?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience and expertise in workholding solutions relevant to your industry. Review their product range to ensure they offer high-quality, durable fixtures that meet your specifications. Request case studies or references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service level. Additionally, consider their ability to provide technical support, customization options, and lead times. Ensuring they have a robust quality assurance process in place is crucial for maintaining production standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for workholding fixtures?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for workholding fixtures can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Standard fixtures may have lower MOQs, often ranging from 5 to 50 units, while custom fixtures could require higher MOQs due to the design and manufacturing processes involved. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as many are willing to negotiate terms for new customers or bulk orders, especially if you can commit to ongoing business. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing workholding fixtures internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of workholding fixtures can vary widely depending on the supplier and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment with the balance due upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s essential to clarify these terms before placing an order. Additionally, consider utilizing secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment during international transactions. -
How can I ensure the quality of workholding fixtures I am sourcing?
To ensure quality, request certifications such as ISO 9001 from your suppliers, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Ask for samples or prototypes before committing to larger orders. Conduct quality inspections during production and upon delivery to verify that the fixtures meet your specifications. Collaborating with suppliers who offer warranty or return policies can also provide additional assurance of product quality. Engaging third-party quality assurance services may be beneficial for larger or critical projects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing workholding fixtures?
When importing workholding fixtures, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and lead times. Choose reliable shipping partners with experience in handling industrial equipment. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as packing lists and invoices, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. It’s also wise to factor in potential delays due to customs inspections or local regulations. Establishing a clear communication channel with your supplier and logistics provider can help mitigate issues during transit. -
How can I customize workholding fixtures to meet specific production needs?
Customizing workholding fixtures starts with a thorough understanding of your production requirements. Collaborate closely with your supplier’s engineering team to discuss your specific applications, materials, and desired outcomes. Many suppliers offer CAD design services that allow you to visualize and refine your fixture design before production. Be prepared to provide details on tolerances, clamping styles, and any unique features you need. A well-defined project scope will help ensure that the final product meets your operational demands efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Workholding Fixtures Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fixtureworks – Workholding Solutions
Domain: fixtureworks.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Workholding Solutions, Equipment & Products – Fixtureworks includes a variety of products such as Quick Release Clamps, Ball Lock Fasteners, Pneumatic Clamping Fasteners, Ball Lock Pins, Quarter-Turn Clamping Fasteners, Quick Action Sliding Locks, Wire Rope Lanyards, Spring Plungers, Locking Pins, Clamp Handles, Levers, Knobs, Grips, Equipment Handles, Hand Wheels, Cranks, Hinges, Latches, Levelin…
2. Paws Workholding – Custom Fixtures & Engineering Solutions
Domain: pawsworkholding.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Custom Workholding Fixtures for Horizontal, Trunnion, and Vertical Applications; Engineering consulting and design collaboration; Short lead times and fast turn-around; Full turnkey solutions; Low Profile Workholding Wedge Clamps for hydraulic or manual clamping; 8 Station 5C Collet; 24 Station 5C Collet; 8 Station 3J Collet Vise System; Workholding Clamps; Build Your Own Hydraulic Bases; Blank Fi…
3. Jergens Inc – Ball Lock® Zero Point System
Domain: jergensinc.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Modular Workholding system offers maximum flexibility with a variety of subplates, risers, quick-change pallets, and top tooling. Key products include: 1. Ball Lock® Zero Point System – Quick-change mounting and fixturing system for horizontal and vertical machining centers. 2. Quick-Loc™ – Modular quick change system for fast and repeatable fixture changes. 3. Power Workholding – Durable and reli…
4. AME – CNC Workholding Solutions
Domain: ame.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: CNC Workholding Systems, Precision Fixtures & Solutions, Rod Locks & Press Safety Tool Clamping Systems, Machining Automation, Machine Design Components, Custom Machine Design, Contract Manufacturing, Workholding Foundations, AMROK Tombstones, Epoxy Mineral Tombstones, Fixture Plates & Grid Plates, 4th-axis Trunnions & Rotary Tables, 5-axis Pyramids, AMROK 5th Axis, Mitee-Bite, Schunk, Triag, Vekt…
5. Raptor Workholding – Dovetail Fixtures and Adaptable Vises
Domain: raptorworkholding.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Raptor Workholding offers a variety of products including Dovetail Fixtures, Multi-Fixtures, Picatinny Rail Fixtures, and Piranha Zero-Point Adaptable Vises. Specific Dovetail Fixtures sizes include 1.5″, 0.75″, 0.50″, 0.375″, 0.281″, 2.25″, and 2.75″. The Piranha line includes Vises, Jaw Inserts, Pyramids & Tombstones, Zero Point Plates, and Vise Accessories. Additional products include Adapters …
6. Ahaus Tool & Engineering – Workholding Solutions
Domain: ahaus.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Ahaus Tool & Engineering offers a range of workholding solutions and fixtures, including machining, turning, welding, hydraulic, pneumatic, and manual options. They have built nearly 5,000 fixtures since 1995 for various industries such as automotive, machine tool, valve, and construction. Their expertise includes designing and building precise machining fixtures for CNC machines, utilizing finite…
7. CNC Cookbook – Workholding Solutions
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: The text discusses various workholding solutions for CNC milling, including jigs, fixtures, and their importance in improving production efficiency. Key components mentioned include T-Slots for positioning, keyed vises and fixtures for alignment, and fixture sub-plates (or tooling plates) that provide a repeatable method for securing workholding devices. The text emphasizes the use of a free fixtu…
8. X-Y Tool & Die – Custom Workholding Solutions
Domain: xytoolrtc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: X-Y Tool & Die, Inc. specializes in custom workholding solutions, including design and build services. They repair or rebuild existing workholding fixtures. Key capabilities include: multi-pallet milling, 4th/5th axis machining, TIG and MIG welding, friction welding, horizontal, vertical or inverted spindle turning, and ID, OD, and surface grinding. Additional offerings include quick change top to…
9. All World Machinery – ARROW Workholding Fixtures
Domain: allworldmachinery.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: ARROW Workholding Fixtures are custom engineered and assembled to fit exact specifications, capable of holding aluminum and magnesium die castings, sand castings, forgings, and bar stock. They feature innovative methods for locating, clamping, and supporting delicate parts, made with robust components and superior design techniques. The fixtures can be integrated into robotic cells or manually loa…
10. Dentech Industrial – Custom CNC Workholding Fixtures
Domain: dentechindustrial.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: CNC Workholding Fixtures & Clamping System: Custom workholding fixtures for various applications to save time and increase profitability. Applications include Milling, Turning, Grinding, and Welding. Workholding types: Hydraulic, Manual, Pneumatic, Vacuum, Robotic. Specialty features: Part confirmation, Wired or wireless pressure monitoring, Pressure confirmation, Custom control panels, Self-conta…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for workholding fixtures
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, the strategic sourcing of workholding fixtures is paramount for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. By investing in high-quality, innovative workholding solutions, businesses can enhance their machining capabilities, leading to improved throughput and profitability. The emphasis on customization and modular systems allows manufacturers to adapt to varying production demands while minimizing downtime.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that offer both standard and bespoke solutions tailored to specific operational needs. As the market evolves, embracing automation and advanced clamping technologies will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, businesses should consider leveraging data-driven insights to inform their sourcing decisions. By aligning with suppliers that provide cutting-edge solutions and exceptional service, manufacturers can not only meet current demands but also anticipate future challenges. Engage with your suppliers today to explore how strategic sourcing can elevate your workholding processes, paving the way for sustained growth and innovation.