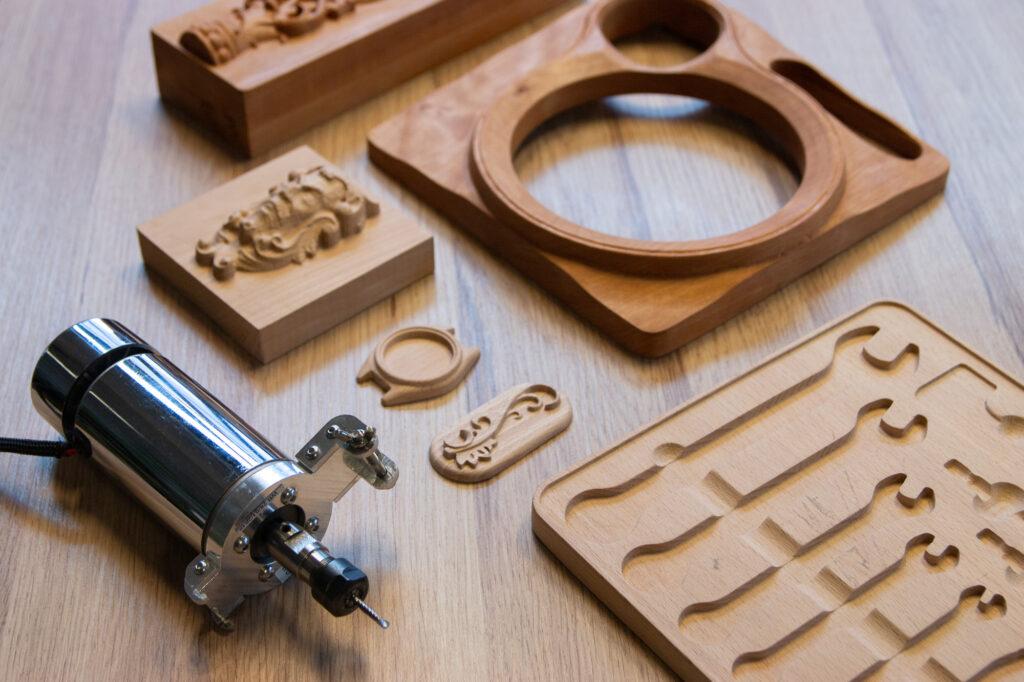
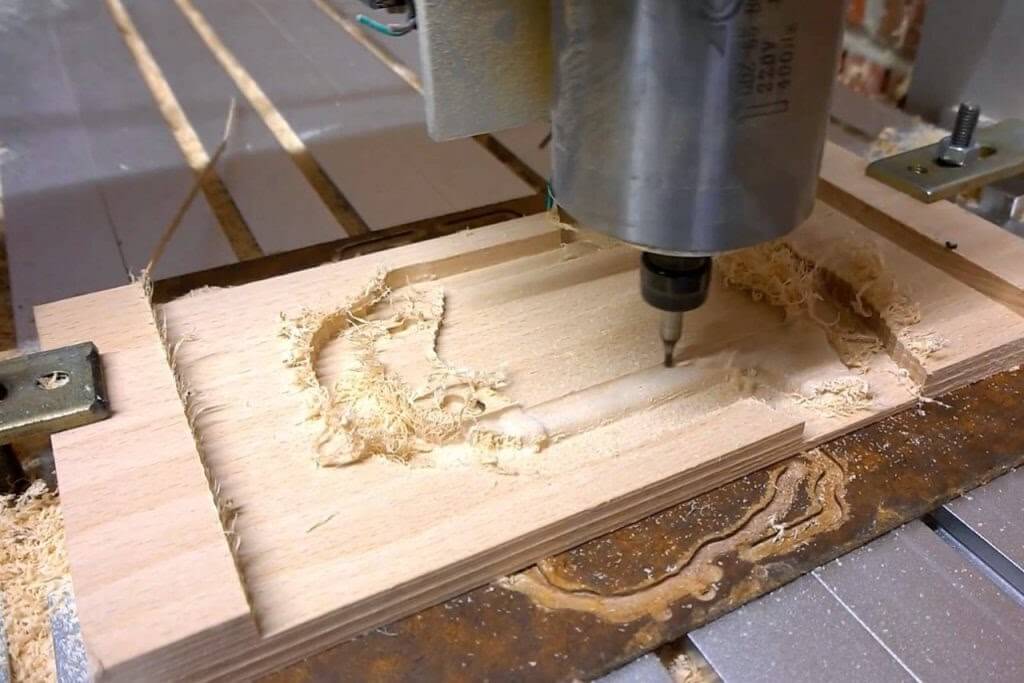
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wood working cnc
Navigating the global market for woodworking CNC machinery presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses strive to enhance productivity and meet diverse customer demands, the need for reliable, high-quality CNC routers becomes paramount. This guide is designed to facilitate informed purchasing decisions by offering a comprehensive overview of woodworking CNC options available in the market.
From understanding the various types of CNC machines—ranging from 3-axis to advanced 5-axis routers—to exploring their applications in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and creative projects, we provide insights that cater to a wide spectrum of operational needs. Additionally, the guide delves into essential topics such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and financing options, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to make strategic investments.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the woodworking CNC landscape, this guide aims to streamline the sourcing process, mitigate risks, and ultimately drive business growth. Whether you are a small shop owner in Brazil or a large-scale manufacturer in Vietnam, the information presented here will help you navigate the complexities of the CNC market with confidence.
Understanding wood working cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Routers | 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis capabilities; versatile for various materials | Furniture making, cabinetry, signage, prototyping | Pros: High precision; versatile material handling. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| CNC Lathes | Rotational cutting; ideal for cylindrical shapes | Woodturning, decorative items, custom designs | Pros: Efficient for repetitive tasks; high-quality finish. Cons: Limited to round shapes. |
| CNC Plasma Cutters | Use of plasma for cutting; typically for metal but can handle wood | Sign making, artistic wood designs | Pros: Fast cutting speed; excellent for intricate designs. Cons: Not ideal for all wood types. |
| Desktop CNC Machines | Compact size; often entry-level; user-friendly software | Hobbyists, small-scale production | Pros: Affordable; easy to use; good for prototypes. Cons: Limited working area; lower power. |
| CNC Laser Cutters | High precision cutting and engraving using laser technology | Custom engraving, intricate designs | Pros: Exceptional detail; minimal material waste. Cons: Higher operational costs; requires maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics and Applications of CNC Routers?
CNC routers are among the most versatile woodworking machines available, capable of handling a variety of materials beyond wood, including plastics and composites. They come in different configurations, such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis systems, allowing businesses to choose based on their specific production needs. Suitable for applications ranging from furniture making to signage, these machines offer high precision and efficiency. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment against the potential for increased production capacity and versatility in product offerings.
How Do CNC Lathes Benefit Woodworking Businesses?
CNC lathes specialize in producing cylindrical shapes, making them ideal for woodturning projects such as decorative columns, bowls, and custom furniture components. They operate by rotating the material against a stationary cutting tool, providing consistent results and high-quality finishes. For businesses focused on repetitive tasks, CNC lathes can significantly enhance productivity. However, buyers should note that their functionality is limited to round shapes, which may not suit all woodworking projects.
What Advantages Do CNC Plasma Cutters Offer for Woodworking?
While primarily used for metal, CNC plasma cutters are increasingly popular for artistic wood designs and signage. They employ plasma technology to cut through materials quickly, allowing for intricate patterns and shapes. Their speed and efficiency make them attractive to businesses looking to produce large quantities of custom designs. However, B2B buyers should be aware that not all wood types are suitable for plasma cutting, and the initial setup can be complex.
Why Choose Desktop CNC Machines for Small-Scale Production?
Desktop CNC machines are compact, user-friendly, and typically more affordable than larger models, making them an excellent choice for hobbyists and small businesses. They are suitable for prototyping and small-scale production, allowing users to create detailed designs without needing extensive workspace. While their capabilities are limited compared to larger machines, they provide a low-risk entry point into CNC woodworking. Buyers should consider their specific production needs and the potential for future scaling when investing in desktop models.
What Makes CNC Laser Cutters Ideal for Intricate Designs?
CNC laser cutters utilize high-powered lasers to achieve exceptional precision in cutting and engraving, making them perfect for intricate wood designs. They are particularly effective for custom engraving and detailed patterns, offering minimal material waste and a clean finish. However, the operational costs can be higher than other CNC options, and regular maintenance is necessary to ensure performance. B2B buyers should evaluate their project requirements against the long-term operational costs when considering laser cutters.
Key Industrial Applications of wood working cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wood working cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Precision cutting and shaping of wood components | Increased production speed and accuracy | Machine size, spindle power, software compatibility |
| Cabinet Making | Custom cabinetry production | Enhanced customization and design flexibility | Material handling capabilities, tooling options, support services |
| Signage and Display | Creation of intricate signage and displays | High-quality finishes and rapid turnaround | Software ease of use, engraving capabilities, table size |
| Wood Product Export | Mass production of wood products for international markets | Streamlined operations and reduced labor costs | Compliance with international standards, maintenance support |
| Art and Craftsmanship | Detailed carvings and artistic woodworking | Ability to produce complex designs consistently | Training support, software integration, machine versatility |
How is Woodworking CNC Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, woodworking CNC machines are essential for precision cutting and shaping of various wood components. These machines enable manufacturers to produce intricate designs at scale while maintaining high accuracy. By automating the cutting process, businesses can significantly increase production speed and reduce material waste, leading to lower costs. International buyers should consider the machine’s size, spindle power, and compatibility with design software to ensure it meets their specific production needs.
What Role Does Woodworking CNC Play in Cabinet Making?
In cabinet making, woodworking CNC machines facilitate the custom production of cabinetry that meets diverse client specifications. They allow for enhanced customization, enabling artisans to produce unique designs and intricate details that would be challenging to achieve manually. This technology not only improves the quality of the finished product but also shortens lead times, making it easier to respond to market demands. Buyers should focus on material handling capabilities, tooling options, and the availability of support services when sourcing CNC machines for this application.
How is CNC Technology Transforming the Signage and Display Industry?
The signage and display industry benefits greatly from woodworking CNC machines, which are utilized to create intricate signs and displays with high-quality finishes. These machines can engrave, cut, and shape materials with precision, allowing for rapid turnaround times on custom projects. This is particularly valuable for businesses that require quick responses to client demands. When sourcing CNC equipment, companies should consider software ease of use, engraving capabilities, and the machine’s table size to accommodate various project requirements.
Why is Woodworking CNC Important for Wood Product Export?
For businesses involved in the export of wood products, woodworking CNC machines streamline production processes, enabling mass production of high-quality goods. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency. Additionally, CNC technology ensures that products meet international quality standards, which is crucial for export markets. Buyers should prioritize compliance with international standards, availability of maintenance support, and the machine’s adaptability to different wood types when selecting equipment for this sector.
How Does Woodworking CNC Support Art and Craftsmanship?
In the realm of art and craftsmanship, woodworking CNC machines empower artisans to produce detailed carvings and complex woodworking designs with consistency. These machines enable creators to push the boundaries of their craft by allowing for intricate designs that would be time-consuming or impossible to achieve by hand. Buyers in this sector should look for training support, software integration capabilities, and machine versatility to maximize their investment and enhance their creative output.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘wood working cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex CNC Machine Options
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face overwhelming choices when it comes to selecting woodworking CNC machines. With numerous models featuring varying specifications—such as spindle power, table size, and axis capabilities—deciding on the right machine can be daunting. For instance, a small furniture manufacturer in Brazil might struggle to determine whether to invest in a 3-axis or 5-axis CNC router, fearing that a poor choice could lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, or inadequate production capabilities.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate this complexity, it is crucial for buyers to conduct a thorough needs assessment before making a purchase. Start by evaluating your specific production requirements: the types of materials you will be working with, the complexity of designs, and the volume of output needed. Create a checklist that includes essential features such as maximum spindle speed, material handling capabilities, and software compatibility.
Engaging with a reliable CNC supplier is also vital. Look for vendors that offer personalized consultations, where they can provide insights based on your operational goals. Consider visiting showrooms or attending trade shows to see machines in action, which will help you gauge their performance. Finally, seek testimonials or case studies from similar businesses to understand how certain machines have met their needs. This comprehensive approach ensures that your investment aligns with your production capabilities and long-term business objectives.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistent Quality in Production
The Problem:
A significant challenge for businesses utilizing woodworking CNC machines is maintaining consistent product quality. For example, a sign-making company in Vietnam may experience discrepancies in cut quality and finish due to varying machine settings or operator skill levels. Such inconsistencies can lead to increased waste, customer dissatisfaction, and ultimately a tarnished reputation in the market.
The Solution:
Implementing a robust training program for operators is essential to ensure consistent quality. This program should cover not only the technical operation of CNC machines but also best practices in material handling and maintenance. Regularly scheduled training sessions can help reinforce skills and introduce updates on new software or tools.
Additionally, investing in quality assurance tools, such as laser measurement devices or automated inspection systems, can help detect errors before products leave the shop. These technologies can monitor dimensions and surface quality in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections. Establishing a standardized checklist for machine setup and maintenance can also minimize variability. By prioritizing training and quality assurance, businesses can enhance their production consistency and customer satisfaction.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Software Integration Challenges
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers in the woodworking CNC sector is the integration of CNC software with existing systems. A furniture manufacturer in Europe might struggle with transitioning to a new CNC machine that requires advanced design software, leading to disruptions in workflow and increased learning curves for staff. This can slow down production and impact timelines, which is particularly challenging in a competitive market.
The Solution:
To mitigate software integration challenges, it is advisable to select CNC machines that come with user-friendly software that aligns with your team’s existing skills. When researching machines, inquire about the software’s compatibility with commonly used design programs such as AutoCAD or SolidWorks.
Additionally, consider investing in comprehensive training sessions led by the software provider to facilitate smoother transitions. These sessions can cover everything from basic operation to advanced techniques, ensuring that your team feels confident in utilizing the new system.
Creating a phased implementation plan can also help ease the transition. Start with a pilot project using the new machine and software, allowing your team to gain hands-on experience while minimizing disruptions to overall production. By proactively addressing software integration challenges, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and maintain productivity levels during transitions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wood working cnc
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Woodworking CNC?
When selecting materials for woodworking CNC applications, it is essential to consider their properties and how they align with the specific requirements of the project. Here, we analyze four common materials: hardwood, plywood, MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), and particleboard.
Hardwood: The Premium Choice for Quality
Key Properties: Hardwoods, such as oak, maple, and cherry, are known for their density and strength. They typically have high temperature and pressure resistance, making them suitable for intricate designs and detailed carvings.
Pros & Cons: Hardwoods offer exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal, which enhances the end product’s market value. However, they come at a higher cost and may require more complex machining due to their density. Additionally, the availability of specific hardwoods may vary by region, impacting procurement.
Impact on Application: Hardwoods are ideal for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items. Their natural beauty and strength make them suitable for applications where appearance and longevity are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of sourcing regulations and certification standards, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification, especially in Europe and North America. Compliance with local regulations regarding the import of hardwoods is crucial.
Plywood: Versatile and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Plywood consists of multiple layers of wood veneer glued together, providing strength and flexibility. It has good temperature resistance and is less prone to warping compared to solid wood.
Pros & Cons: Plywood is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a popular choice for various applications. However, the quality can vary significantly based on the grade, and lower-quality plywood may not perform well in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Plywood is commonly used for cabinetry, furniture, and structural components in woodworking projects. Its versatility allows for a wide range of uses, from decorative elements to functional structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the grading standards (such as the American Plywood Association standards) and ensure that the plywood meets local building codes, especially in regions with specific construction regulations.
MDF: The Budget-Friendly Option
Key Properties: MDF is made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a smooth surface ideal for CNC machining. It has good dimensional stability and is less likely to warp than solid wood.
Pros & Cons: MDF is cost-effective and easy to work with, making it suitable for intricate designs and detailed carvings. However, it is less durable than hardwood and can be susceptible to moisture damage.
Impact on Application: MDF is commonly used for cabinetry, moldings, and decorative panels, especially in applications where a smooth finish is desired. It is ideal for painted surfaces due to its uniform texture.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the formaldehyde emissions associated with MDF and ensure compliance with regulations such as CARB (California Air Resources Board) standards, particularly in the EU and North America.
Particleboard: Economical but Limited
Key Properties: Particleboard is made from wood chips and resin, providing a lightweight and affordable option. It has moderate strength and is suitable for low-stress applications.
Pros & Cons: Particleboard is the most economical choice among wood-based panels, making it attractive for budget-conscious projects. However, it lacks the durability and strength of hardwood or plywood, limiting its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: It is often used in furniture and cabinetry where cost is a primary concern, but it is not recommended for applications requiring high durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the quality standards for particleboard, including those related to formaldehyde emissions and moisture resistance, to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Woodworking CNC
| Material | Typical Use Case for wood working cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardwood | High-end furniture and cabinetry | Exceptional durability and aesthetics | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Plywood | Cabinetry and structural components | Cost-effective and versatile | Quality can vary significantly | Medium |
| MDF | Decorative panels and cabinetry | Smooth finish and easy to work with | Less durable and moisture-sensitive | Low |
| Particleboard | Budget furniture and cabinetry | Economical and lightweight | Limited durability and strength | Low |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for woodworking CNC applications, ensuring informed decision-making that aligns with their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wood working cnc
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Woodworking CNC Machines?
The manufacturing process of woodworking CNC machines involves several critical stages that ensure quality and performance. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in CNC Machine Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Common materials include high-grade steel for structural components, aluminum for lightweight parts, and various plastics for non-load-bearing applications. Each material is selected based on its specific properties, such as strength, weight, and resistance to wear. Precision cutting and shaping of these materials are conducted using advanced techniques like laser cutting or water jet cutting, which ensures high accuracy and minimal waste.
Forming: How Are CNC Machines Shaped and Assembled?
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming. This involves machining operations such as milling, turning, and drilling to shape the components. CNC machining centers are typically utilized in this stage, allowing for high precision and repeatability.
Following the forming stage, assembly takes place. This can be a complex process, especially for multi-axis CNC machines, which require careful alignment of components to ensure operational accuracy. Automated assembly systems are often employed to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Finishing: What Finishing Techniques Enhance Performance and Aesthetics?
The final stage of the manufacturing process is finishing. This includes surface treatments like powder coating, anodizing, or painting, which not only enhance aesthetics but also provide protection against corrosion and wear. Finishing is vital for ensuring the longevity of CNC machines, particularly in demanding environments.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Woodworking CNC Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of woodworking CNC machines to ensure they meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with relevant international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) for specific applications can provide further assurance of quality. These certifications indicate that the products meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality control in CNC machine manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters such as dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish are monitored to ensure that the components meet required standards. This may involve the use of digital measuring tools and gauges.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing and verification against design specifications to ensure that the machine operates correctly and safely.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure the reliability of a supplier’s quality control processes, B2B buyers can take several steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities, processes, and compliance with quality standards firsthand. This also provides an opportunity to evaluate the supplier’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management practices. These reports should include data on defect rates, compliance with standards, and corrective actions taken for any identified issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These inspections can validate that the supplier’s products meet the specified quality standards and certifications.
What Are the Common Testing Methods Used in CNC Machine Manufacturing?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of woodworking CNC machines:
-
Functional Testing: Machines are tested under operational conditions to verify that they meet performance specifications. This includes testing speed, accuracy, and reliability.
-
Load Testing: This method assesses the machine’s performance under maximum load conditions to ensure it can handle the expected operational demands.
-
Durability Testing: Machines undergo extended operation cycles to evaluate wear and tear, ensuring longevity and reliability in real-world applications.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Affect International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control can significantly impact purchasing decisions. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding quality assurance.
-
Local Regulations: Buyers should be aware of local regulations and compliance requirements that may differ from international standards. This includes certifications that may be necessary for importing machinery.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary widely. Establishing clear expectations regarding quality standards and inspections is vital for successful partnerships.
-
Supply Chain Considerations: Ensuring that suppliers have robust quality control measures in place can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions, particularly in international trade.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance Critical for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in the woodworking CNC market, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, as well as the relevant quality standards and control measures, buyers can better assess potential suppliers and ensure they are investing in high-quality machinery that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘wood working cnc’
When sourcing CNC machines for woodworking, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of options, specifications, and suppliers. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that you select the right machinery for your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search for woodworking CNC machines, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will work with, the dimensions of the workpieces, and the complexity of the designs you intend to produce.
– Key specifications to define:
– Type of CNC machine (e.g., 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis)
– Maximum cutting speed and power of the spindle
– Table size and configuration
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends and technological advancements in CNC woodworking. Understanding current market offerings can help you identify features that can enhance productivity and efficiency.
– Consider:
– Automation capabilities
– Software compatibility for design and control
– Innovations that improve ease of use and maintenance
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. A reliable supplier will provide not only high-quality machines but also support and service.
– Look for:
– Company history and reputation in the market
– Customer testimonials and case studies
– After-sales support, including training and maintenance services
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have narrowed down your supplier options, request detailed quotes for the machines that meet your specifications. This step is crucial for understanding the total cost of ownership, including any additional fees for installation, training, and warranty.
– When comparing quotes:
– Ensure all quotes include the same specifications for an accurate comparison
– Look for financing options that may be available
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that your selected suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations. This verification process is essential to ensure quality and safety in your CNC machinery.
– Check for:
– ISO certifications
– Compliance with local and international safety standards
– Environmental certifications, if applicable
Step 6: Arrange for a Demonstration
If possible, arrange for a demonstration of the CNC machines you are considering. Observing the machine in action can provide valuable insights into its performance and ease of use.
– Focus on:
– The machine’s responsiveness to commands
– The quality of the cuts produced
– Overall user interface and ergonomics
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Plan for Installation
Once you have selected your CNC machine, finalize the purchase agreement and prepare for installation. Ensure that you have a clear plan for integrating the new machine into your existing workflow.
– Consider:
– Timeline for delivery and installation
– Training for your staff on the new equipment
– Maintenance schedules and support agreements
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing woodworking CNC machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and output quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wood working cnc Sourcing
When evaluating the cost structure and pricing for sourcing woodworking CNC machines, it is crucial to break down the various components that contribute to the overall expenditure. Understanding these elements will empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Woodworking CNC Machines?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in CNC manufacturing is the quality of materials used. High-grade metals and composites enhance machine durability and performance but may significantly increase costs. Buyers should assess the type of materials specified by suppliers and their implications on long-term maintenance and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. For instance, countries with higher wage standards may reflect these costs in the pricing of CNC machines. Understanding the local labor market can help buyers gauge the competitiveness of quotes received.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These costs are often factored into the pricing of CNC machines and can vary based on the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The expenses associated with the tools necessary for machine production can also influence pricing. Specialized tooling may be required for custom specifications, which can elevate costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that machines meet specified performance standards. Suppliers that implement comprehensive QC measures may pass these costs onto buyers, but they can also provide assurance of machine reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and the choice of Incoterms can impact overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences Pricing for Woodworking CNC Machines?
Several factors influence the pricing of woodworking CNC machines, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to price discounts. Buyers should consider their production needs to negotiate favorable pricing based on minimum order quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly affect the cost. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with certified materials and those that meet specific industry standards often command higher prices. Buyers should assess the certifications that are crucial for their operations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who bears the cost and risk at various stages of shipping. This knowledge can help buyers estimate the total landed cost more accurately.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in CNC Machine Sourcing?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in discussions about price flexibility, especially when ordering in bulk. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs, including maintenance, parts, and operational expenses. TCO analysis helps in making a more informed decision.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes can alter the effective cost of machinery. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should factor in these variables when comparing prices from European or Asian suppliers.
-
Conduct Market Research: Explore various suppliers and market trends. This research can help buyers identify competitive pricing and avoid overpaying.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for woodworking CNC machines can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. The figures provided in supplier catalogs are indicative and may not represent the final cost. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers and consider all cost components before making a purchasing decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing wood working cnc With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Wood Working CNC: Understanding Your Options
In the realm of woodworking, CNC machines have become a staple for achieving precision and efficiency. However, there are several alternative solutions that can also meet the needs of businesses looking to optimize their woodworking processes. This section delves into viable alternatives, comparing them on various aspects to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Wood Working CNC | Laser Cutting Systems | Traditional Hand Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with complex designs | Excellent for intricate cuts | Variable, depends on skill level |
| Cost | Initial investment can be high | Moderate to high, depending on size | Low initial cost, but time-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and setup | Relatively easy, requires calibration | Simple, but labor-intensive |
| Maintenance | Regular software updates and part replacement | Low, mainly lens and mirror maintenance | High, requires regular upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Mass production and complex designs | Detailed engraving and cutting | Custom, small-scale projects |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Laser Cutting Systems?
Laser cutting systems offer a strong alternative to woodworking CNC machines, especially when it comes to precision and detail. They excel in cutting intricate designs and thin materials, making them ideal for applications like signage or detailed inlays. However, the initial investment can be moderate to high, and while they are easier to operate than CNC machines, they require careful calibration and maintenance of the laser components. Additionally, laser systems might not be suitable for thicker materials, which can limit their applicability in some woodworking projects.
How Do Traditional Hand Tools Compare to Wood Working CNC?
Traditional hand tools remain a viable option, particularly for custom, small-scale projects where craftsmanship is paramount. They allow for a personal touch and can be more cost-effective in terms of initial investment. However, they demand a high level of skill and can be time-consuming, which may not align with modern production demands. Maintenance can also be more labor-intensive, as tools require regular sharpening and care. While they are not as efficient as CNC machines for mass production, hand tools can produce unique, high-quality items that appeal to niche markets.
How Should B2B Buyers Decide on the Right Solution?
When choosing between woodworking CNC machines and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific business needs, including production volume, desired precision, and budget constraints. For companies focusing on high-volume production with complex designs, CNC machines are often the best choice. On the other hand, if the focus is on detailed engraving or crafting unique pieces, laser cutting or traditional hand tools may provide better value. Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths and limitations of each solution will guide buyers toward the most suitable technology for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wood working cnc
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider in Woodworking CNC Machines?
When investing in woodworking CNC machinery, understanding key technical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specs that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Spindle Power and Speed
Spindle power, typically measured in horsepower (HP), and speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), are vital for determining a CNC machine’s cutting capabilities. Higher spindle power allows for cutting through denser materials, while increased RPM can lead to cleaner cuts and faster production. For instance, a spindle rated at 12HP operating between 5,000-24,000 RPM can handle a variety of woodworking tasks, increasing efficiency and output.
2. Cutting Area Dimensions
The cutting area defines the maximum size of material that the CNC machine can accommodate. This is crucial for businesses that work with large sheets of wood or need to create sizable products. Machines with larger cutting areas enable more extensive operations without the need for multiple setups, thus saving time and labor costs.
3. Axis Configuration
CNC machines come in various axis configurations, including 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis. A 3-axis machine allows for movement along the X, Y, and Z axes, while 4-axis and 5-axis machines offer additional rotational capabilities, enabling more complex shapes and designs. For businesses focused on intricate carvings or detailed work, investing in higher-axis machines can significantly enhance production flexibility and creativity.
4. Feed Rate
Feed rate, measured in inches per minute (IPM), indicates how quickly the machine can move the cutting tool through the material. Higher feed rates can lead to faster production times but may compromise cut quality if not balanced with the spindle speed and material type. Understanding the optimal feed rate for specific projects can help businesses improve efficiency without sacrificing quality.
5. Material Compatibility
Compatibility with various materials is essential for versatility in operations. Many CNC routers are designed to work with wood, but some can also handle composite materials, plastics, and metals. Businesses should evaluate their material requirements to ensure that the chosen machine can meet their diverse production needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Woodworking CNC?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the woodworking CNC market. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing CNC machines, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can influence the reliability and quality of the machinery. OEMs often provide better support and warranty services.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for businesses to manage inventory effectively and ensure they meet production demands without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and other details regarding specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to obtain competitive pricing and terms, which can aid in budget planning and supplier selection.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines, crucial factors in international procurement.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory management and production planning, as delays can impact overall business operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the woodworking CNC sector can make more informed decisions that enhance productivity and profitability in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the wood working cnc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Woodworking CNC Sector?
The woodworking CNC sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increased demand for customized furniture, rapid urbanization, and the rise of e-commerce are propelling the market forward. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly influenced by these trends, as they seek to enhance production efficiency and output quality. Emerging technologies like advanced CNC routing software, automation, and IoT-enabled machines are reshaping manufacturing processes, allowing for greater precision and reduced waste.
The market is also witnessing a shift toward flexible and modular CNC machines, which can easily adapt to varying production requirements. This adaptability is particularly appealing to international buyers who may operate in diverse markets with fluctuating demands. Furthermore, the incorporation of artificial intelligence in CNC operations is streamlining workflow, facilitating predictive maintenance, and minimizing downtime. As a result, businesses that harness these technological advancements can significantly enhance their competitive edge.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Woodworking CNC Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the woodworking CNC sector. The environmental impact of sourcing raw materials, particularly timber, is under scrutiny as companies strive to align with sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency in their supply chains, seeking partners who prioritize ethical sourcing and adhere to responsible forestry practices. Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) are becoming essential benchmarks for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials and processes not only meets regulatory demands but also enhances brand reputation and marketability. Companies that invest in sustainable technologies—such as energy-efficient CNC machines and waste-reduction systems—can improve their operational efficiency while minimizing their carbon footprint. This commitment to sustainability is not just beneficial for the environment; it also resonates with consumers, who increasingly prefer brands that demonstrate social responsibility.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Woodworking CNC Technologies?
The evolution of woodworking CNC technologies has been remarkable over the past few decades. Initially, CNC machines were primarily used for large-scale production and lacked the precision required for intricate designs. As technological advancements emerged, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems revolutionized the industry, allowing for more complex designs and greater accuracy.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards user-friendly interfaces and versatile machinery that cater to both small-scale artisans and large manufacturers. The rise of desktop CNC routers has democratized access to CNC technology, enabling hobbyists and small businesses to enter the market. This evolution reflects a broader trend of increased accessibility and customization, positioning woodworking CNC technology as a vital tool for modern craftsmanship and industrial production alike.
Through understanding these dynamics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with market trends, sustainability goals, and technological advancements in the woodworking CNC sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wood working cnc
-
How do I choose the right CNC machine for my woodworking business?
Selecting the right CNC machine depends on your specific production needs, material types, and budget. Start by evaluating the size and complexity of your projects. For smaller operations, a 3-axis CNC router might suffice, while larger enterprises may require 5-axis machines for more intricate designs. Additionally, consider the machine’s speed, precision, and software compatibility. It’s beneficial to consult with manufacturers or suppliers who can provide insights based on your unique requirements and offer demonstrations if possible. -
What are the key features to look for in a woodworking CNC machine?
When sourcing a woodworking CNC machine, prioritize features such as spindle power, cutting speed, and the number of axes. Look for machines with robust construction for durability, advanced control systems for precision, and compatibility with various software programs. A reliable vacuum table system can enhance material handling efficiency. Additionally, consider the availability of tool changers and the machine’s ability to integrate with other equipment in your workshop to streamline production processes. -
What is the typical lead time for CNC machine orders?
Lead times for CNC machine orders can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, machine specifications, and current production schedules. Generally, expect a lead time ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Custom machines or those with specific configurations may take longer. It’s advisable to discuss timelines with your supplier upfront and request updates during the manufacturing process to ensure timely delivery and minimize disruptions to your production schedule. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC machines often depend on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may allow single-unit purchases, particularly for standard machines, while others may set MOQs for custom or specialized equipment. It’s essential to clarify this with potential suppliers during negotiations. If you’re operating in a region with limited suppliers, consider pooling orders with other businesses to meet MOQ requirements and reduce costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing CNC machinery?
Payment terms for CNC machinery can vary widely among suppliers. Many manufacturers require a deposit (typically 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping. Some may offer financing options or installment plans, especially for larger purchases. Be sure to discuss payment terms upfront, including any potential discounts for early payment or bulk orders. Understanding the terms will help you manage your cash flow effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing CNC machines internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing CNC machines from international suppliers, start by verifying their certifications and compliance with industry standards. Request samples or demonstrations of the machines to assess performance firsthand. Establish clear specifications and quality control measures in your purchase agreement. Additionally, consider hiring a third-party inspection service to evaluate the machinery before shipping, ensuring it meets your expectations and requirements. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reputable freight forwarder experienced in handling heavy machinery to streamline the shipping process. Understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your country and ensure that all documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, is in order. Plan for delivery logistics, including transportation to your facility and any necessary installation or setup services. -
How do I vet suppliers for woodworking CNC machinery?
Vetting suppliers for woodworking CNC machinery involves several steps. Start by researching potential suppliers’ reputations through reviews, testimonials, and industry ratings. Evaluate their experience and expertise in CNC machinery, and request references from previous clients. Consider visiting their facilities if possible to inspect the machines and production processes. Additionally, ensure they offer comprehensive after-sales support, including training, maintenance services, and accessible spare parts, to guarantee a reliable partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Wood Working Cnc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carbide 3D – Shapeoko Line
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Recommendations for CNC machines for woodshops include the Shapeoko line from Carbide 3D, known for excellent support, a large community, and good starter software. The Onefinity is another option, offering lower maintenance at a higher price point. Key specifications to consider are a minimum surface area of 24″x24″ and the importance of community support and company reputation.
2. Woodcraft – CNC Machines
Domain: woodcraft.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Woodcraft – CNC Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Fadal – CNC Woodworking Machines
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC woodworking machines, specifically Fadal mills, are used in the musical instrument business for solid wood parts like guitar necks and bodies. These machines can be upgraded to 10,000 rpm spindles and come with extensive tooling options, including spindle speeders and right angle heads. The rigidity of these machines compensates for lower spindle RPMs, making them suitable for woodworking desp…
4. OneFinity – CNC Machine & Tools
Domain: joeldhughes.medium.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: OneFinity Woodworker X-50 CNC machine; 1/8″ up and downcut end mills; 45 and 90-degree V bits; 3/4″ bowl bit; 1/4″ up and down cut end mills; design software: InDesign and Easel; techniques for securing material: masking tape + CA glue, wooden clamps.
5. Grizzly – Precision CNC Routers
Domain: grizzly.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: This company, Grizzly – Precision CNC Routers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wood working cnc
In today’s competitive woodworking landscape, strategic sourcing of CNC machinery is not just an operational choice but a vital strategy for growth and sustainability. By understanding the diverse range of CNC routers available—from entry-level models suitable for small shops to advanced systems capable of high-volume production—businesses can align their equipment choices with their specific operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Investing in high-quality CNC machines enhances productivity, precision, and versatility, allowing firms to respond swiftly to market demands and customer preferences. Moreover, the availability of flexible financing options makes it easier for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to acquire the necessary equipment without significant upfront capital.
As we look to the future, the woodworking industry will increasingly rely on advanced CNC technology to meet evolving consumer expectations. Now is the time for B2B buyers to embrace these innovations and strengthen their competitive edge. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you can not only enhance your production capabilities but also position your business for long-term success in an ever-changing marketplace. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore the best options tailored to your unique needs.