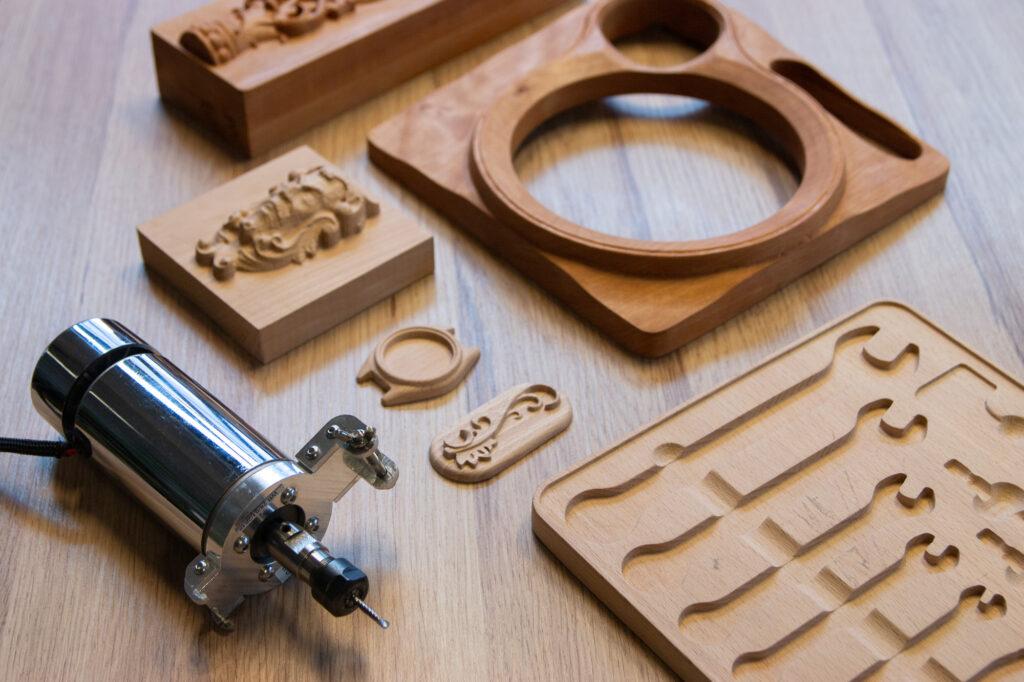
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wood work cnc
In the rapidly evolving woodworking industry, sourcing high-quality CNC machinery can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. With diverse options available, from entry-level machines to advanced multi-axis routers, understanding how to select the right wood work CNC solution for your specific needs is essential for enhancing productivity and maintaining competitive advantage. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into various types of CNC machines, their applications in different woodworking sectors, and crucial factors for supplier vetting.
Whether you are a furniture manufacturer in Brazil, a cabinet maker in Saudi Arabia, or a craftsman in Europe, making informed purchasing decisions is paramount. The guide will cover cost considerations, financing options, and best practices for integrating CNC technology into your operations, ensuring that you can navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence. By equipping you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers you to streamline your sourcing process, optimize your production capabilities, and ultimately elevate your business in an increasingly competitive landscape.
As you explore the intricacies of wood work CNC, let this guide be your trusted partner in achieving operational excellence and fostering sustainable growth across diverse markets.
Understanding wood work cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Routers | Multi-axis cutting capabilities, high-speed spindles | Furniture manufacturing, cabinetry | Pros: Versatile, high precision; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| CNC Lathes | Rotational cutting for cylindrical objects | Decorative woodturning, custom parts | Pros: Excellent for complex shapes; Cons: Limited to round objects. |
| Desktop CNC Machines | Compact size, user-friendly design | Small workshops, hobbyists | Pros: Affordable, space-saving; Cons: Limited capacity and power. |
| 5-Axis CNC Routers | Capability to cut from multiple angles | Aerospace components, intricate designs | Pros: High versatility, detailed work; Cons: More complex to operate. |
| Laser Engravers | Uses laser technology for cutting and engraving | Sign making, personalized gifts | Pros: High detail, fast processing; Cons: Material limitations. |
What Are CNC Routers and Their Applications in B2B?
CNC routers are versatile machines that utilize multi-axis cutting capabilities, making them ideal for various woodworking applications. They are commonly used in furniture manufacturing and cabinetry, providing high-speed spindles that enhance production efficiency. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and the machine’s capacity to handle diverse materials, ensuring that it aligns with production needs.
How Do CNC Lathes Benefit Woodworking Businesses?
CNC lathes specialize in producing cylindrical objects, making them invaluable for decorative woodturning and custom part fabrication. These machines excel in creating complex shapes and designs that require rotational cutting. While they offer high precision and efficiency, buyers must note their limitation to round objects, which may not suit all woodworking applications.
Why Choose Desktop CNC Machines for Small Workshops?
Desktop CNC machines are compact and designed for ease of use, making them perfect for small workshops and hobbyists. They provide an affordable entry point into CNC technology, allowing businesses to experiment with various designs. However, their limited capacity and power may restrict larger-scale production, necessitating careful consideration for businesses looking to expand.
What Advantages Do 5-Axis CNC Routers Offer?
5-axis CNC routers offer unparalleled versatility by enabling cutting from multiple angles, which is essential for intricate designs and aerospace components. These machines are capable of producing highly detailed work, making them a favorite among industries that require precision. However, their complexity can pose a challenge for operators, which is a critical factor for B2B buyers focusing on training and operational efficiency.
How Do Laser Engravers Enhance Customization in Woodworking?
Laser engravers utilize advanced technology to cut and engrave materials with high detail and speed. They are particularly popular in sign making and the production of personalized gifts, allowing businesses to meet customer demands for customization. While they excel in detail and processing speed, buyers should consider the material limitations and ensure that the engraver can handle the specific types of wood and other materials they intend to use.
Key Industrial Applications of wood work cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wood work cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture production | Enhanced design flexibility and reduced lead times | Machine precision, software compatibility, and support |
| Signage and Graphics | Engraving and cutting custom signs | High-quality finishes and unique designs | Material compatibility, cutting speed, and durability |
| Construction and Carpentry | Fabrication of structural wood components | Increased efficiency and waste reduction | Machine size, power requirements, and tooling options |
| Musical Instrument Making | Crafting intricate parts for instruments | Precision in sound quality and design aesthetics | Material handling, tooling accuracy, and machine stability |
| Arts and Crafts | Production of decorative wood items | Ability to scale production while maintaining quality | Versatility in design software and ease of use |
How is Wood Work CNC Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, wood work CNC machines are pivotal for producing custom furniture pieces. These machines allow manufacturers to create intricate designs with high precision, significantly reducing lead times compared to traditional methods. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing CNC machines that can handle diverse wood types and provide robust software integration is essential. The ability to quickly adapt designs to meet local tastes and preferences also enhances market competitiveness.
What Role Does Wood Work CNC Play in Signage and Graphics?
CNC technology is widely utilized in the signage and graphics industry for engraving and cutting custom signs. This application enables businesses to produce high-quality finishes and unique designs that stand out. For B2B buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, it is crucial to consider factors such as material compatibility and the machine’s cutting speed to ensure efficiency. Additionally, sourcing machines that can handle various substrates, including acrylic and wood, will expand the range of products that can be offered.
How Does Wood Work CNC Benefit Construction and Carpentry?
In construction and carpentry, CNC machines are employed to fabricate structural wood components like beams and panels. This application not only increases production efficiency but also minimizes material waste, a critical consideration for environmentally conscious buyers. For international clients, especially in developing markets, understanding the power requirements and machine size is vital for seamless integration into existing workflows. Additionally, robust after-sales support and training can enhance operational efficiency.
In What Ways is Wood Work CNC Used in Musical Instrument Making?
The musical instrument manufacturing industry relies on CNC technology to craft intricate parts that affect sound quality and design aesthetics. Wood work CNC machines enable manufacturers to produce components with exceptional precision, ensuring consistency in tone and craftsmanship. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing machines that offer advanced tooling options to accommodate various wood types. Furthermore, understanding the intricacies of material handling is essential for achieving optimal results in this specialized market.
How is Wood Work CNC Transforming Arts and Crafts?
In the arts and crafts sector, wood work CNC machines facilitate the production of decorative wood items, allowing artisans to scale their operations without compromising on quality. This capability is particularly beneficial for small businesses looking to expand their product lines. For B2B buyers, especially in South America and Africa, sourcing versatile machines that integrate with design software is crucial for maintaining creative freedom. The ease of use and adaptability of the technology can significantly enhance productivity and innovation in this vibrant sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘wood work cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Precision and Consistency in Production
The Problem: For B2B buyers in the woodworking industry, maintaining precision and consistency across multiple projects is a critical challenge. Small variances in measurements can lead to significant issues down the line, such as mismatched components or increased material waste. Buyers often face difficulties in achieving the desired accuracy due to equipment limitations, operator skill levels, or software misconfigurations, which can impact overall production efficiency and client satisfaction.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should invest in high-quality CNC machines known for their precision, such as those from reputable brands that offer robust calibration tools and software. When sourcing a CNC router, look for models that include advanced features like automatic tool calibration and high-resolution encoders, which can significantly enhance cutting accuracy. Additionally, integrating CAD/CAM software tailored for CNC operations can streamline design-to-production workflows, ensuring that every piece produced meets exact specifications. Regular training for operators on machine settings and maintenance can further enhance performance and reduce the risk of errors.
Scenario 2: Managing Material Compatibility and Versatility
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the versatility of their CNC machines when working with different types of wood and other materials. Each material can have unique properties, requiring specific cutting speeds, tooling, and settings to achieve optimal results. Buyers may find that their existing equipment is not adaptable enough, leading to production delays or subpar quality, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction and profitability.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should opt for CNC machines that are designed for multi-material compatibility. When selecting equipment, ensure it can handle various wood types, composites, and even non-wood materials, thus providing the flexibility needed for diverse projects. Investing in a machine with adjustable spindle speeds and torque settings allows users to tailor operations according to material specifications. Moreover, collaborating with suppliers to obtain guidance on the best tooling and settings for different materials can enhance overall productivity. Implementing a testing phase with new materials can also help identify optimal settings before full-scale production begins.
Scenario 3: Overcoming High Initial Costs and Financing Options
The Problem: The initial investment required for high-quality CNC machines can be a significant barrier for B2B buyers, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in developing markets. This financial strain can limit their ability to upgrade equipment, invest in advanced technology, or even expand their production capabilities. Without access to affordable financing options, these businesses may miss out on potential growth opportunities.
The Solution: Buyers should actively seek out suppliers that offer flexible financing solutions tailored to the woodworking industry. When evaluating CNC machines, inquire about leasing options, installment plans, or financing through third-party providers. Many manufacturers also provide trade-in programs that allow businesses to upgrade their existing machinery while offsetting costs. Additionally, buyers can explore government grants or subsidies aimed at supporting manufacturing innovation in their region, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America. By leveraging these financial tools, businesses can acquire the necessary technology to enhance production without overwhelming their budgets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wood work cnc
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Wood Work CNC?
When selecting materials for woodworking CNC applications, understanding the properties of each material is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials: solid wood, plywood, MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), and laminated veneer lumber (LVL). Each material has distinct characteristics that influence performance, cost, and suitability for various applications.
Solid Wood: The Traditional Choice
Solid wood is often favored for its natural beauty and strength. Key properties include excellent durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for high-end furniture and cabinetry. However, solid wood can be affected by temperature and humidity changes, leading to warping or cracking.
Pros: Solid wood offers superior aesthetics and structural integrity. It is also easier to repair and refinish than other materials.
Cons: The cost of high-quality solid wood can be substantial, and its availability may vary by region. Additionally, machining solid wood requires skilled operators to avoid defects.
For international buyers, compliance with local standards is essential. In regions like Europe, adherence to the EU Timber Regulation ensures sustainable sourcing, while buyers in Africa and South America should consider local wood species and their market availability.
Plywood: Versatile and Cost-Effective
Plywood is engineered from thin layers of wood veneer, which are glued together. This construction provides excellent dimensional stability and resistance to warping. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and good resistance to moisture, making it suitable for a variety of applications, from furniture to cabinetry.
Pros: Plywood is generally more affordable than solid wood and offers versatility in design. It can be easily machined into complex shapes.
Cons: The quality of plywood can vary significantly based on the manufacturing process and the type of adhesive used, which can affect its durability.
For B2B buyers, understanding the grading standards (such as BS 6566 in Europe) is critical to ensure quality. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of formaldehyde in adhesives.
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard): Smooth and Uniform
MDF is made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a smooth, dense board. Its key properties include excellent machinability and a uniform surface that is ideal for painting and veneering.
Pros: MDF is cost-effective and provides a consistent finish, making it perfect for intricate designs and detailed carvings.
Cons: It lacks the structural strength of solid wood and can be susceptible to moisture damage if not properly sealed.
International buyers should consider the environmental impact of MDF production, particularly the use of formaldehyde. Compliance with standards like CARB (California Air Resources Board) is essential for markets in Europe and North America.
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL): Engineered for Strength
LVL is an engineered wood product made from multiple layers of thin wood veneers bonded together. Its key properties include high strength and stability, making it suitable for structural applications.
Pros: LVL is highly resistant to warping and shrinking, and its manufacturing process allows for the use of lower-quality wood, making it an economical choice.
Cons: The initial cost can be higher than traditional lumber, and its appearance may not be as appealing for finished furniture.
For B2B buyers, understanding the certification of LVL products (like APA certification in the U.S.) is crucial. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should also consider local building codes that may dictate the use of engineered wood products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Wood Work CNC
| Material | Typical Use Case for wood work cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Wood | High-end furniture, cabinetry | Superior aesthetics and durability | Expensive, can warp with humidity | High |
| Plywood | Furniture, cabinetry, flooring | Cost-effective, versatile | Quality varies, potential adhesive issues | Medium |
| MDF | Intricate designs, cabinetry | Smooth finish, easy to machine | Susceptible to moisture, less structural strength | Low |
| Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) | Structural beams, framing | High strength, stable | Higher initial cost, less aesthetic appeal | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in woodworking CNC applications, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wood work cnc
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Wood Work CNC Machines?
The manufacturing of wood work CNC machines involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-grade materials, such as aluminum, steel, and various composites, are sourced based on specific machine requirements. These materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify their quality, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications before moving to the next phase. Suppliers often provide certification documents to confirm material compliance with international standards.
Forming and Machining
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This stage includes cutting, bending, and shaping the materials using advanced CNC machining techniques. Techniques like laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and milling are commonly employed to achieve precise dimensions. For wood work CNC machines, the components must be accurately machined to ensure that they fit together seamlessly, which is crucial for the machine’s operational integrity.
Assembly
The assembly phase involves integrating various components such as spindles, motors, control systems, and the frame. During this process, skilled technicians follow detailed assembly instructions and use precision tools to ensure that every part is correctly aligned and securely fastened. This stage is critical as it directly influences the performance and durability of the CNC machine.
Finishing
The final manufacturing stage is finishing, which enhances both the aesthetic and functional qualities of the CNC machines. Processes such as painting, coating, and polishing are applied to protect the machine from wear and corrosion. Additionally, finishing touches may include the installation of user interfaces and safety features to comply with international safety standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated Into Wood Work CNC Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for wood work CNC machines. It ensures that each machine meets stringent quality and performance criteria before it reaches the end user.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should be aware of several international standards that signify quality and safety in manufacturing. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) demonstrate compliance with European safety standards, while API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may be relevant in specific industrial applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting incoming materials for quality and compliance before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly and machining stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure that components meet required specifications. This may include dimensional checks and performance testing of critical components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the entire machine undergoes rigorous testing to verify its performance. This may involve running the machine through various operational scenarios to ensure reliability and precision.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality and functionality of wood work CNC machines:
-
Functional Testing: This involves running the machine to assess its operational capabilities and identify any potential issues.
-
Dimensional Testing: Using precision measuring tools, manufacturers verify that all components meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Load Testing: This method evaluates the machine’s ability to handle maximum operational loads without failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, especially those from international markets, should take proactive measures to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with relevant standards firsthand.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed reports on quality control practices, including inspection and testing results, can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing process and final products can add an extra layer of assurance regarding quality and compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control that may vary by region:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations concerning machinery safety and environmental impact. Buyers should ensure that the CNC machines comply with local laws in their respective markets.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing practices can help buyers establish better relationships with suppliers and ensure smoother transactions.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping and customs can complicate the quality assurance process. Buyers should account for potential delays and ensure that quality checks are performed before shipping to avoid complications upon arrival.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for wood work CNC machines are critical in ensuring that these machines meet the high standards expected by B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and the relevant international standards, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing CNC machines for their operations. This knowledge ultimately leads to enhanced productivity, reliability, and satisfaction in their woodworking endeavors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘wood work cnc’
When sourcing CNC machinery for woodworking, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape to ensure they make informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as a practical checklist, providing actionable steps to streamline the sourcing process and enhance the likelihood of a successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for identifying the right CNC machine for your woodworking needs. Consider factors such as the type of wood you’ll be working with, the desired complexity of designs, and production volume.
– Key specifications to define:
– Machine size and workspace dimensions.
– Required spindle power and RPM range.
– Number of axes (3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis) based on your project needs.
Step 2: Research Available CNC Machines
Once you have your specifications, research the various CNC machines available on the market. Look for machines that are not only high-quality but also versatile enough to handle multiple materials.
– Considerations include:
– Brand reputation and customer reviews.
– Machine capabilities (cutting, engraving, milling).
– Available features such as automatic tool changers or vacuum tables.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– What to look for:
– Certifications and compliance with international standards.
– Customer support and warranty terms.
– Availability of spare parts and maintenance services.
Step 4: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Whenever possible, request a demonstration of the CNC machine in action or ask for sample workpieces produced by the machine. This step helps validate the machine’s performance and quality.
– Focus on:
– Precision and finish of the sample products.
– Ease of use and machine operation.
– Compatibility with your existing software and workflow.
Step 5: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding the total cost of ownership goes beyond the initial purchase price. Consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, tooling, software, and electricity.
– Evaluate:
– Financing options and payment terms.
– Energy consumption rates of the machine.
– Long-term reliability and potential resale value.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety standards. This is particularly important for international transactions.
– Important certifications to check:
– ISO 9001 for quality management.
– CE marking for compliance with EU regulations.
– Other relevant industry-specific certifications.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a machine and supplier, it’s time to finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms are clearly defined, including delivery timelines, installation support, and after-sales service.
– Ensure clarity on:
– Payment schedules and financing options.
– Responsibilities for shipping and installation.
– Terms for warranty and support.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing woodworking CNC machines, ensuring they select equipment that meets their operational needs while maximizing their investment.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wood work cnc Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Wood Work CNC Machinery?
When sourcing wood work CNC machinery, understanding the cost structure is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used in manufacturing CNC machines significantly influences pricing. High-quality steel and aluminum may increase initial costs but can enhance durability and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs are a substantial part of the manufacturing overhead. Skilled labor for assembly and quality checks can vary by region, impacting the overall cost structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor. Efficient production processes can help minimize these expenses.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools required for CNC machining add to the upfront costs. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better precision and lower replacement rates.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that machinery meets performance standards, which can incur additional costs but ultimately leads to fewer operational issues.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance, mode of transportation, and the weight of the machinery. This is especially important for international buyers who must consider customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on market competition and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Wood Work CNC Machines?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC machines, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts. Buyers should consider their production needs and how they might benefit from bulk purchasing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or advanced specifications can significantly raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines made from superior materials or certified for specific quality standards (like ISO certifications) generally come at a premium but offer better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, experience, and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven reliability and service offerings.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can clarify shipping responsibilities and costs, impacting the total landed cost of machinery.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CNC Machinery?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are several strategies to enhance sourcing efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially on larger orders or repeat business.
-
Cost-Efficiency Considerations: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, operational costs, and depreciation. A lower initial cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and shipping costs, which can affect the overall price. It’s advisable to get quotes in your local currency to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Research and Compare: Always compare multiple suppliers and machine specifications. This can help you find the best balance between cost and performance.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask for itemized quotes that break down all costs involved. This transparency will help in comparing offers more accurately.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC woodworking machinery can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and economic factors. The prices mentioned in various sources can serve as a reference but may not reflect the final costs upon procurement. Always consult suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing wood work cnc With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Woodworking
In the woodworking industry, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized how wood is processed, enabling precision and efficiency in production. However, various alternative solutions exist that can also meet the demands of woodworking tasks. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs, production scale, and budget.
Comparison Table of Wood Work CNC and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Wood Work CNC | Traditional Hand Tools | Laser Cutting Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Lower precision; dependent on skill | High precision; fast cutting speed |
| Cost | $1,000 – $100,000+ depending on features | Low initial investment, but variable over time | $5,000 – $200,000+ depending on size and capability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Minimal setup, training varies | Setup is complex; training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance and calibration | Low maintenance; tool sharpening required | Moderate; lens cleaning and software updates needed |
| Best Use Case | Mass production, complex designs | Custom, artisanal projects | High-volume cutting, intricate designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Hand Tools
Traditional hand tools, such as chisels, saws, and planes, have been the backbone of woodworking for centuries. They offer low initial investment costs and require minimal setup, making them accessible for small businesses and artisans. However, the performance heavily relies on the skill of the user, which can lead to inconsistencies in precision and quality. While hand tools are ideal for custom, artisanal projects where craftsmanship is paramount, they may not be suitable for high-volume production due to time constraints.
Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines provide a high level of precision and speed, making them ideal for intricate designs and detailed cuts. They can handle a variety of materials, including wood, which allows for versatility in product offerings. However, the cost of laser machines can be significant, especially for larger models or those with advanced features. The setup and operational complexity may also require specialized training, which can be a barrier for some businesses. Laser machines are best suited for high-volume production environments where speed and precision are critical.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Woodworking Needs
When selecting the right woodworking solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific production requirements, budget constraints, and desired quality of output. Wood work CNC machines are excellent for businesses looking to scale operations and achieve high precision consistently. In contrast, traditional hand tools may appeal to artisans focused on bespoke creations, while laser cutting machines are perfect for those needing speed and detail in high-volume projects. By carefully evaluating these aspects, buyers can choose a solution that aligns with their operational goals and enhances their production capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wood work cnc
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Wood Work CNC Machines?
Understanding the technical specifications of CNC machines is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in woodworking equipment. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Spindle Power and Speed
The spindle power, typically measured in horsepower (HP), affects the machine’s ability to cut through various wood types. Higher horsepower allows for cutting denser materials without stalling. Speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast the spindle can rotate. A spindle speed range of 5,000 to 24,000 RPM is common, impacting the quality of the cut and the types of materials that can be processed efficiently.
2. Cutting Area Dimensions
The cutting area defines the maximum size of the workpiece that can be processed. It is crucial for businesses that handle larger projects, such as furniture manufacturing. For example, a machine with a cutting area of 48” x 96” allows for full sheets of plywood, which is essential for reducing material waste and increasing productivity.
3. Accuracy and Tolerance
Accuracy refers to how closely a machine can reproduce a given design, while tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from the intended dimensions. High precision (e.g., ±0.001 inches) is critical in woodworking applications where fine details matter, such as in cabinetry or intricate designs. Understanding these factors helps ensure the final product meets quality standards.
4. Feed Rate
The feed rate, typically measured in inches per minute (IPM), is the speed at which the material is fed into the cutting tool. A higher feed rate can increase productivity but must be balanced with spindle speed and material type to avoid compromising cut quality. Common feed rates range from 200 IPM to 3,000 IPM, depending on the machine’s capability.
5. Material Compatibility
CNC machines are designed to work with various materials, including different wood types and composites. Knowing the materials your CNC can process helps businesses make informed purchasing decisions and ensures that the machine can handle specific production requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Wood Work CNC?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B environment. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality suppliers and ensure they are purchasing genuine components for their CNC machines.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC machinery, this is crucial for budget-conscious businesses, as it can affect initial investment costs. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that solicits price proposals from suppliers. It is an essential step in procurement, allowing businesses to compare costs and terms from different vendors, ensuring they get the best deal for their CNC investments.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding these terms is vital for international transactions, particularly regarding shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through computer programming. This technology is pivotal in woodworking, allowing for high precision and efficiency in cutting, carving, and engraving wood materials.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of these technical properties and trade terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when investing in woodworking CNC machinery. By grasping these concepts, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality while effectively navigating the complexities of international trade.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the wood work cnc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Wood Work CNC Sector?
The global woodworking CNC market is witnessing significant growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for customized products, and the need for enhanced production efficiency. With industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe emphasizing automation, CNC machinery is becoming indispensable. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing CNC operations, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which enhances machine uptime and reduces operational costs.
International buyers should note the trend towards modular and scalable CNC solutions. These systems allow businesses to start small and expand capabilities as demand grows, which is particularly appealing in developing markets where financial flexibility is crucial. Moreover, the rise of online marketplaces and digital platforms is simplifying the sourcing process, providing buyers with access to a wider array of products and suppliers, thus fostering competitive pricing and innovation.
Additionally, sustainability is reshaping purchasing decisions in the woodworking CNC sector. Companies are increasingly opting for machines that minimize waste and energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions where environmental regulations are becoming more stringent.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Wood Work CNC Industry?
Sustainability is a pressing concern within the woodworking CNC sector, affecting both sourcing strategies and production practices. The environmental impact of wood sourcing cannot be overlooked, as deforestation and unsustainable harvesting practices have significant repercussions on biodiversity and climate change. As such, international buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability.
The importance of ethical supply chains is becoming increasingly recognized, with many companies now seeking certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification). These certifications ensure that wood products are sourced from responsibly managed forests, fostering consumer trust and compliance with international standards.
Moreover, the trend towards using ‘green’ materials and processes is gaining traction. CNC machines that incorporate energy-efficient technology and utilize eco-friendly lubricants and coolants are becoming more prevalent. Buyers looking to differentiate themselves in the market can leverage these sustainable practices to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing their brand reputation and market competitiveness.
How Has the Wood Work CNC Sector Evolved Over Time?
The woodworking CNC sector has undergone remarkable evolution since its inception. Initially, CNC technology was limited to large-scale industrial applications, but advancements in technology have made it accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The introduction of user-friendly software and affordable machines has democratized access to CNC capabilities, allowing artisans and small businesses to harness the power of automation.
Today, CNC machines are not only used for cutting and shaping wood but also for intricate carving, engraving, and multi-material processing. This versatility has expanded the scope of what can be produced, enabling manufacturers to cater to diverse markets and consumer preferences. As the sector continues to innovate, the integration of advanced features such as automated tool changers and adaptive machining will likely redefine the standards of efficiency and precision in woodworking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wood work cnc
-
How do I select the right CNC machine for woodworking?
When choosing a CNC machine for woodworking, consider the types of projects you’ll be undertaking. Assess the machine’s capabilities, such as cutting speed, spindle power, and the number of axes (3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis). Additionally, evaluate the size of the work area and the materials you’ll be using. It’s crucial to match the machine’s specifications with your production needs and budget constraints. Don’t hesitate to request demonstrations or trial runs, and ensure the supplier offers robust customer support and training resources. -
What are the key features to look for in a wood CNC machine?
Essential features to consider include precision and repeatability, which ensure high-quality outputs. Look for machines with high spindle speeds for faster cutting and the ability to handle various materials. A robust software package for design and operation is also critical. Additionally, features like automatic tool changers, dust collection systems, and user-friendly interfaces can significantly enhance productivity and ease of use. Always verify that the machine meets your specific operational requirements and industry standards. -
What is the average cost of a wood CNC machine?
The cost of wood CNC machines can vary widely based on their capabilities and features. Entry-level models suitable for small businesses or hobbyists may start at around $1,000 to $5,000. Mid-range options for more serious enterprises typically range from $5,000 to $20,000, while high-end industrial machines can exceed $100,000. When budgeting, consider not only the initial purchase price but also potential financing options, ongoing maintenance costs, and the expected return on investment from increased productivity. -
How can I ensure the reliability of a CNC supplier?
To vet a CNC supplier effectively, research their reputation in the industry through reviews and testimonials from previous clients. Ask for references and case studies that demonstrate their experience with similar projects. Evaluate their after-sales support, warranty policies, and availability of spare parts. Additionally, visit their facility if possible, and inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. A reliable supplier will be transparent about their operations and eager to address your specific needs. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms can vary among suppliers, but commonly include options such as a deposit upfront (often 30-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing plans that allow for monthly payments over a specified period. It’s important to clarify terms before finalizing the purchase to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure that you also understand any applicable tariffs, taxes, and shipping costs that might affect the overall price. -
What kind of customization options are available for CNC machines?
Most CNC manufacturers offer a range of customization options to meet specific operational needs. This may include modifications to the machine size, spindle power, or additional features like laser engraving or 4th axis capabilities. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Customization can enhance the machine’s performance for your specific applications, so be sure to consider how these adjustments will impact your production processes. -
How is quality assurance conducted for CNC machines?
Quality assurance for CNC machines typically involves a series of checks throughout the manufacturing process. Suppliers may conduct initial inspections of components, followed by assembly testing to ensure precision and functionality. After assembly, machines are often subjected to rigorous performance tests to verify cutting accuracy and reliability. Request documentation of quality assurance protocols from your supplier to ensure that their machines meet international standards and your specific production requirements. -
What logistics should I consider when importing CNC machines?
When importing CNC machines, consider the logistics of shipping, customs clearance, and installation. Ensure that the supplier provides detailed shipping and handling information, including packaging that protects the machinery during transport. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including tariffs and duties that may apply. Additionally, plan for the logistics of installation and training, as proper setup is crucial for optimal machine performance. Collaborate with experienced logistics partners to streamline the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 2 Wood Work Cnc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carbide 3D – Shapeoko CNC
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Shapeoko CNC by Carbide 3D: Recommended for beginners, excellent support, large community, good learning resources, and free starter software. Commonly available, including used options. 2. Onefinity CNC: Newer option, claims to be lower maintenance, slightly higher price point, good support, and active community. 3. Openbuilds machines: Easily modifiable to various sizes.
2. Carbide 3D – Shapeoko Series
Domain: community.carbide3d.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Shapeoko 4 and 4 Pro are recommended starting points for beginners. The Shapeoko 5 Pro is noted for its speed and features a lit work area, making it suitable for recording projects. The machines range from the SO4 Standard (16″x16″ working area) to the SO5 Pro (4’x4′ working area). The Nomad 3 is suitable for small precision projects like jewelry and engraving but has size limitations. The Shapeo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wood work cnc
In the competitive landscape of woodworking CNC, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for success. By aligning procurement strategies with high-quality CNC machinery, international buyers can significantly enhance production efficiency and output. The versatility of modern CNC routers allows businesses to cater to diverse markets, from furniture manufacturing to intricate decorative designs. Investing in advanced technology not only optimizes operations but also ensures consistency and precision in the final products.
Moreover, as global demand for bespoke wooden items continues to rise, sourcing from reputable manufacturers becomes essential. This approach not only guarantees superior craftsmanship but also fosters long-term partnerships that can lead to innovation and shared success. With financing options becoming increasingly accessible, businesses of all sizes can invest in the right CNC solutions without straining their budgets.
Looking ahead, the woodworking industry is poised for growth, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Now is the time for international buyers to leverage strategic sourcing opportunities, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Embrace the future of woodworking CNC and elevate your business by exploring partnerships that promise quality, reliability, and innovation.