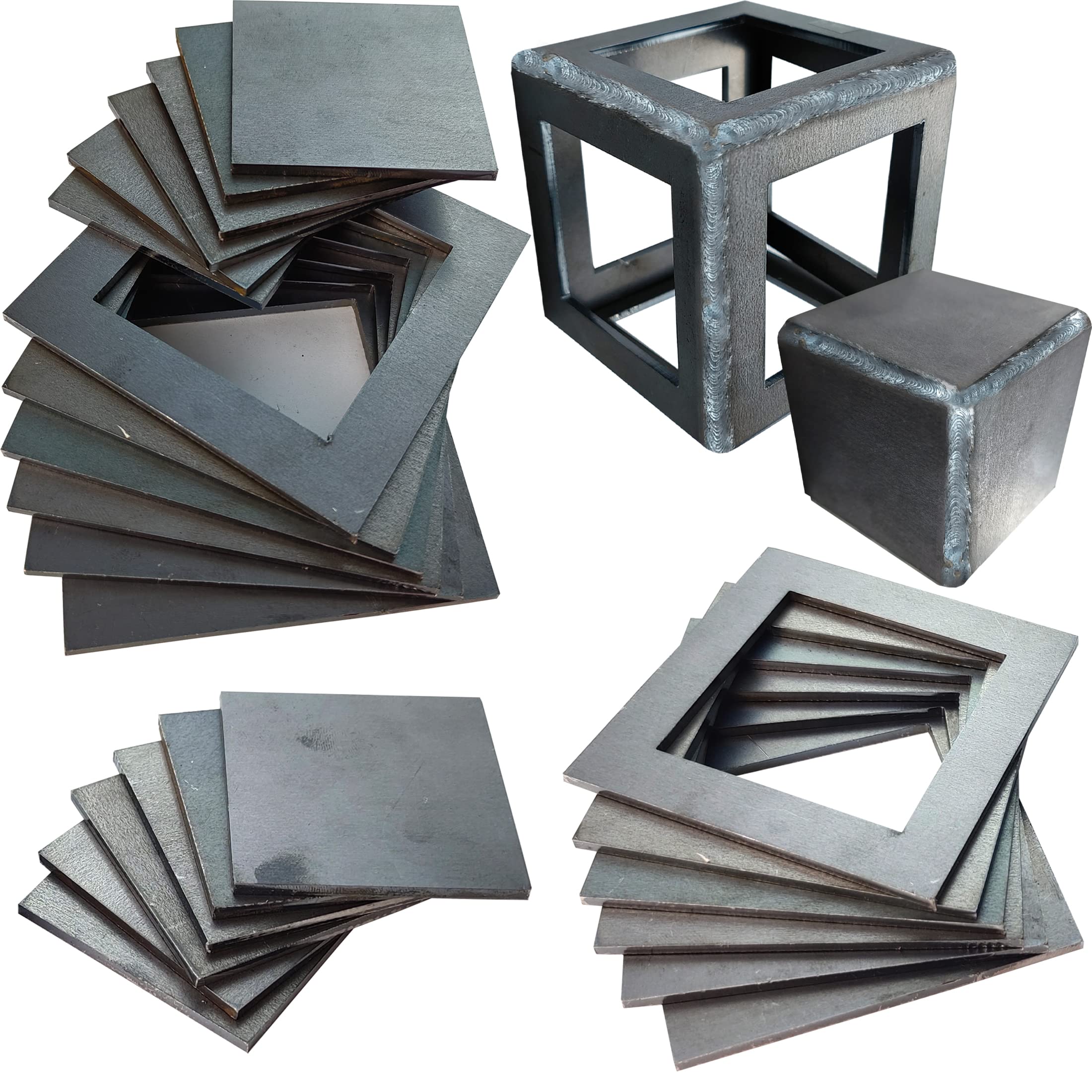
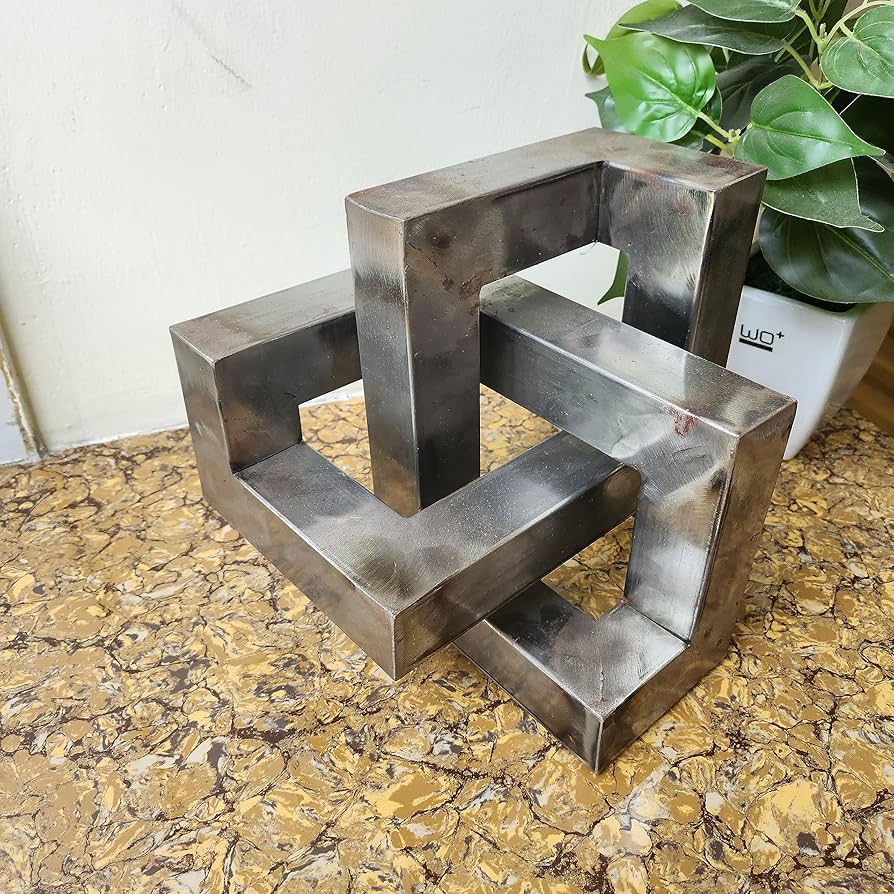
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for welding practice metal
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and fabrication, sourcing high-quality welding practice metal poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in Nigeria, Brazil, or across Europe and the Middle East, identifying reliable suppliers for welding practice materials is crucial to ensure both skill development and project success. This guide aims to illuminate the global market for welding practice metal, providing insights into various types of metals, their applications, and the most effective strategies for sourcing them.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into the distinct categories of welding practice metals—ranging from carbon steel to aluminum and titanium—each with unique properties suited for different welding techniques. You’ll learn how to assess supplier credibility, evaluate costs, and navigate shipping logistics, ensuring that your procurement process is both efficient and cost-effective.
Moreover, the guide emphasizes the importance of understanding the specific needs of your operations, whether you’re in heavy industry, construction, or smaller-scale fabrication. By equipping yourself with the knowledge and tools presented here, you can make informed purchasing decisions that enhance your welding capabilities and ultimately drive business growth. Join us as we explore the intricate world of welding practice metal, empowering you to secure the best resources for your welding projects.
Understanding welding practice metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Affordable, widely available, strong and durable | Construction, automotive, machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Prone to rust if not treated. |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing | Food processing, medical devices | Pros: Long-lasting, low maintenance; Cons: Higher cost, requires specialized welding techniques. |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, packaging | Pros: Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: Difficult to weld without proper skills and equipment. |
| Titanium | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, medical implants | Pros: Extremely durable, biocompatible; Cons: Expensive, requires specialized techniques and equipment. |
| Alloy Steel | Enhanced properties through alloying elements | Oil & gas, construction, automotive | Pros: Improved strength and toughness; Cons: More costly than carbon steel, may require specific welding processes. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Carbon Steel for Welding Practice?
Carbon steel is a popular choice for welding practice due to its affordability and availability. It is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including construction and automotive industries. When purchasing carbon steel, buyers should consider the grade and thickness required for their specific projects, as these factors can influence the welding process and the final product’s performance. Additionally, while carbon steel is cost-effective, it is susceptible to rusting, which necessitates proper surface treatment or protective coatings.
How Does Stainless Steel Differ in Welding Applications?
Stainless steel is distinguished by its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred material in industries such as food processing and medical device manufacturing. It is available in various grades, each offering unique properties, which allows for tailored applications. Buyers should be aware that welding stainless steel often requires specialized techniques and equipment, which can increase overall costs. However, the long-term durability and low maintenance requirements of stainless steel make it an attractive investment for many B2B applications.
Why Choose Aluminum for Welding Practice?
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for sectors like aerospace and automotive. While it offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, aluminum can be challenging to weld, necessitating skilled personnel and appropriate equipment. B2B buyers should evaluate their capacity for handling aluminum welding, including the acquisition of specialized tools and training. Despite these challenges, the advantages of aluminum in reducing overall weight and enhancing performance make it a compelling choice for many applications.
What Are the Benefits of Using Titanium in Welding?
Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, often utilized in aerospace and medical implants. However, the material’s cost and the complexity of the welding process can be significant barriers for some buyers. When considering titanium for welding, businesses should assess their project requirements and ensure they have access to the necessary expertise and equipment. Despite the higher initial investment, titanium’s long-term performance and durability can lead to substantial cost savings in critical applications.
How Do Alloy Steels Enhance Welding Performance?
Alloy steels are engineered to provide enhanced properties through the addition of alloying elements, making them suitable for demanding applications in the oil and gas, construction, and automotive sectors. These steels offer improved strength and toughness compared to standard carbon steels, which can be crucial in high-stress environments. Buyers should consider the specific alloy composition and its implications for welding techniques, as different alloys may require distinct approaches. While alloy steels can be more expensive than carbon steels, their performance benefits often justify the investment for B2B applications.
Key Industrial Applications of welding practice metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Welding Practice Metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Production of Structural Components | Enhances structural integrity and reliability | Ensure compliance with international quality standards |
| Construction | Fabrication of Steel Frameworks | Reduces construction time and costs | Availability of diverse metal types and sizes |
| Automotive | Repair and Maintenance of Vehicle Chassis | Extends vehicle lifespan and performance | Access to specialized alloys and welding techniques |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline Construction and Repair | Ensures safety and efficiency in resource transport | Sourcing metals with high corrosion resistance |
| Art & Design | Creation of Metal Sculptures and Installations | Unique aesthetic value and market differentiation | Ability to source custom metal shapes and sizes |
How Is Welding Practice Metal Utilized in Manufacturing Processes?
In the manufacturing sector, welding practice metal is integral for the production of structural components, such as beams and frames. By using practice metal, companies can refine their welding techniques, ensuring that the final products meet stringent quality and safety standards. This practice not only enhances the structural integrity of components but also reduces the likelihood of costly reworks or failures. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that offer a variety of metal types and comply with international standards, particularly in regions where quality assurance is critical.
What Role Does Welding Practice Metal Play in Construction?
In construction, welding practice metal is commonly used for fabricating steel frameworks that serve as the backbone of buildings and infrastructure. The ability to practice and perfect welding skills on various metals can significantly reduce construction timelines and costs, leading to increased project efficiency. For international buyers, especially in developing regions like Africa and South America, sourcing local or regional suppliers can minimize transportation costs and ensure quicker delivery times, which is vital for project success.
How Is Welding Practice Metal Essential in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, welding practice metal is vital for the repair and maintenance of vehicle chassis. It allows technicians to practice and master techniques that enhance the durability and safety of vehicles. The proper application of welding skills ensures that repairs are reliable, extending the lifespan and performance of vehicles. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing high-quality alloys that can withstand stress and corrosion, and they should consider suppliers who provide training and support for welding practices.
Why Is Welding Practice Metal Important for Oil & Gas Industries?
The oil and gas sector relies heavily on welding practice metal for pipeline construction and repair. The ability to effectively weld practice metals ensures that pipelines are both safe and efficient, minimizing the risk of leaks and failures that could lead to environmental disasters. B2B buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing metals with high corrosion resistance and consider suppliers who can provide materials that meet specific industry certifications and standards.
How Does Welding Practice Metal Benefit Art & Design Industries?
In the art and design sectors, welding practice metal is used to create unique metal sculptures and installations. Artists and designers can practice their welding techniques on various metals, allowing for the creation of intricate designs that offer aesthetic value and market differentiation. For B2B buyers in this field, sourcing custom metal shapes and sizes is crucial, and they should seek suppliers who can accommodate unique design requirements while maintaining quality and craftsmanship.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘welding practice metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Access to Quality Welding Practice Metal
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in regions with developing infrastructure such as parts of Africa and South America, struggle with sourcing high-quality welding practice metal. Local suppliers may offer limited options, and the quality may not meet industry standards, resulting in ineffective training and wasted resources. This scarcity can lead to frustration, as businesses aim to train their workforce efficiently but find themselves constrained by subpar materials that fail to simulate real-world welding conditions.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should establish partnerships with reputable international suppliers who specialize in welding practice materials. These suppliers often provide a diverse range of high-quality metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel, specifically designed for practice. Buyers can request bulk orders to reduce shipping costs and ensure a consistent supply. Additionally, utilizing online platforms that specialize in welding coupons can provide cost-effective and high-quality practice materials. Engaging with these platforms not only broadens the available options but also allows buyers to access valuable resources like tutorials and welding tips, enhancing training outcomes.
Scenario 2: High Costs of Welding Practice Materials
The Problem: Cost is a significant concern for many businesses, especially smaller welding shops or training facilities that need to manage tight budgets. The expense associated with purchasing various types of metals for practice can quickly add up, limiting the ability to provide comprehensive training programs. This situation can hinder the growth of skills within the workforce, ultimately affecting productivity and service quality.
The Solution: B2B buyers can address this issue by exploring alternative sourcing strategies. One effective approach is to procure remnant or surplus materials from local metal suppliers or fabrication shops. These remnants are often sold at a significantly reduced price and can include various sizes and types of metals that are perfect for practice. Additionally, companies can consider forming alliances with other local businesses to share the costs of larger orders. Implementing a recycling program for scrap metal can also be beneficial, allowing businesses to repurpose materials for practice, thereby minimizing waste and maximizing resources.
Scenario 3: Lack of Standardization in Practice Metal Quality
The Problem: Inconsistent quality of welding practice metal can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in ensuring that their training programs yield reliable results. Variability in metal properties can lead to discrepancies in welding performance, affecting the skill level of trainees and potentially leading to safety hazards in real-world applications. This lack of standardization can be especially problematic for businesses operating in multiple regions where quality control measures may differ.
The Solution: To ensure uniformity and reliability, B2B buyers should establish clear specifications for the types of welding practice metals they require. This involves defining key properties such as thickness, tensile strength, and alloy composition. Buyers should communicate these specifications to suppliers and request certification documents that verify the quality and compliance of the materials with industry standards. Additionally, investing in a centralized quality control process for incoming materials can help maintain consistency. Training personnel to recognize quality indicators in welding practice metals will also empower businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring that the materials used for training consistently meet the required standards.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their welding training programs and ultimately improve the skill set of their workforce, leading to better overall business performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for welding practice metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Welding Practice Metal?
When selecting materials for welding practice, it is essential to consider the properties that will influence performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Titanium. Each material presents unique characteristics that can affect the welding process and final product.
Carbon Steel: A Versatile Choice for Welding Practice
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, with a melting point around 1425-1540°C. It generally offers good weldability and is widely available.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective option for practice. However, it is prone to rust if not properly protected, which can limit its applications in corrosive environments. Its weldability can vary based on the carbon content, with higher carbon steels being more challenging to weld.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for structural applications, automotive components, and general fabrication. Its compatibility with various welding methods, including MIG and TIG, makes it a preferred choice for beginners and professionals alike.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers should consider local availability and pricing, which can vary significantly in regions like Africa and South America.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance with Complexities
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, with a melting point of approximately 1400-1450°C. It contains chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is durable and suitable for various applications, it is more expensive than carbon steel. The welding process can be more complicated due to its tendency to warp and the need for specific filler materials.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments, stainless steel’s compatibility with TIG welding makes it a popular choice for high-quality finishes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is essential. Buyers should also be aware of local market trends that may affect the availability and cost of stainless steel, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, with a melting point of about 660°C, and offers excellent corrosion resistance. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. However, it can be more challenging to weld due to its thermal conductivity and the need for specific techniques, such as MIG welding.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in the aerospace and automotive industries, aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight materials. Its use in structural components is increasing due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 is important. Buyers should consider the local demand for aluminum products, especially in regions with growing automotive and aerospace sectors, such as Brazil.
Titanium: High-Performance Material with Unique Challenges
Key Properties: Titanium has a high melting point of approximately 1660°C and is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: While titanium is incredibly strong and lightweight, it is one of the most expensive materials, which can limit its use in practice settings. The welding process requires specialized techniques and equipment, making it less accessible for beginners.
Impact on Application: Titanium is often used in aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance engineering applications. Its unique properties make it suitable for environments that demand both strength and lightweight characteristics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B348 is critical. Buyers should be aware of the specialized nature of titanium welding and the associated costs, which can be a barrier in developing markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Welding Practice Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for welding practice metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural fabrication, automotive parts | Cost-effective and widely available | Prone to rust; variable weldability | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive; complex welding process | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Challenging to weld; requires specific techniques | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical devices | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very expensive; requires specialized welding | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, advantages, limitations, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for welding practice metal
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Welding Practice Metal?
The manufacturing process for welding practice metal involves several critical stages, each essential to ensuring the final product meets quality and performance expectations. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Welding Practice Metal?
Material preparation is the first and foremost step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the right type of metal—commonly carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum—based on the intended application. The selected materials are cut into specified dimensions, often using precision cutting tools or laser technology to ensure accuracy. This stage may also include cleaning the surfaces to remove any contaminants such as rust, oil, or dirt, which can affect the welding quality.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Welding Practice Metal?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This can involve various techniques such as bending, rolling, or stamping, depending on the specific requirements of the welding coupons or practice pieces. Advanced techniques like CNC machining may be employed for complex shapes, ensuring consistency and precision in the dimensions. This stage is crucial for creating practice metals that mimic real-world conditions and provide welders with realistic training scenarios.
How Does Assembly Fit into the Manufacturing Process?
In the assembly stage, components may be joined together if the design calls for it. For instance, multiple pieces of metal may be assembled into a more complex structure that requires welding practice. This stage often includes tack welding, where parts are temporarily joined to facilitate further processing or inspection. The assembly must be executed with precision to ensure that the practice pieces simulate actual welding conditions.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Welding Practice Metal?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing and is vital for enhancing the durability and appearance of welding practice metal. This stage may involve grinding, polishing, or coating the metal to prevent corrosion. Finishing processes can also include surface treatments that improve the metal’s resistance to wear and tear, ensuring that the practice metals have a longer lifespan and maintain their integrity during training sessions.
What Quality Control Measures Are Commonly Used in Welding Practice Metal Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is critical in the manufacturing of welding practice metal, as it ensures that products meet international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Apply to Welding Practice Metal Quality Control?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards like ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. For specific applications, additional certifications such as CE marking or API specifications may be relevant. These certifications ensure that products meet safety and performance criteria, which is particularly important for B2B buyers who may operate in highly regulated industries.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. It includes inspecting materials for compliance with specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that products are within specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the finished products undergo rigorous testing and inspection to verify their overall quality, functionality, and compliance with standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Welding Practice Metal?
Several testing methods are commonly used to assess the quality of welding practice metal:
-
Visual Inspection: This involves a thorough examination of the product for any visible defects, such as cracks or surface irregularities.
-
Destructive Testing: Techniques such as tensile testing or bend testing may be employed to evaluate the metal’s strength and ductility.
-
Non-destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection help identify internal flaws without damaging the material.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for ensuring product reliability.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier QC?
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include reviewing their quality management systems, equipment, and production capabilities.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance reports that outline their QC procedures, testing methods, and compliance with international standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can conduct on-site evaluations and testing to ensure compliance with specifications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the varying quality control and certification standards that may exist across different regions. For instance, while ISO certifications are widely recognized, specific industries may have local standards that must also be considered. Buyers should engage with suppliers who understand the regulatory landscape in their target markets to ensure compliance and facilitate smoother transactions.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Crucial for Welding Practice Metal?
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for welding practice metal are integral to producing high-quality training materials. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers who meet stringent quality standards and deliver reliable products for their welding training needs. This understanding not only enhances the effectiveness of training but also ensures safety and performance in real-world applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘welding practice metal’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring welding practice metal, this practical guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Following this checklist will help you select the right materials while minimizing risks and optimizing costs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications for the welding practice metal you require. This includes dimensions, material types (such as aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon steel), and any relevant industry standards (e.g., AWS or ISO certifications). Properly defining these parameters will streamline supplier communications and ensure you receive products that meet your specific needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in welding practice metals. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry forums to gather a list of candidates. Pay attention to their geographical reach and whether they have experience serving markets similar to yours, such as those in Africa, South America, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to verify that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with industry standards. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 or specific welding qualifications that indicate quality assurance. This step not only assures you of product quality but also mitigates potential compliance issues in your supply chain.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the welding practice metal to assess their quality and compatibility with your equipment. Testing samples allows you to evaluate material properties and ensure they meet your welding techniques. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure your practice sessions yield effective results.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Keep in mind that the lowest price may not always equate to the best value. Consider additional factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and supplier reliability, which can significantly impact your overall procurement budget.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Once you’ve selected a supplier, establish clear communication channels to facilitate ongoing dialogue. This includes setting expectations for order updates, delivery schedules, and quality assurance processes. Effective communication will help resolve any issues promptly and foster a strong supplier relationship.
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance
After placing your order, continuously monitor the supplier’s performance regarding delivery timelines, product quality, and customer service. Keeping track of these metrics will help you make informed decisions for future procurement and allow you to adjust your sourcing strategy as needed. This proactive approach ensures that you maintain a reliable supply chain for your welding practice needs.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for welding practice metal, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for welding practice metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Welding Practice Metal Sourcing?
When sourcing welding practice metal, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of metal used significantly impacts costs. Common metals like mild steel or aluminum may be less expensive than specialized materials such as titanium or stainless steel. For instance, aluminum coupons can start as low as €4.95, while titanium welding coupons can reach €33.95.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for cutting, preparing, and packaging metal materials. Depending on the region and skill level, these costs can vary substantially. Skilled labor may command higher wages, which can influence the overall cost of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower these costs, making it essential to choose suppliers with optimized operations.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for cutting and shaping metals adds to the initial cost. However, these investments can lead to better-quality products and lower long-term costs if they enhance production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the metal meets specified standards is vital, particularly for international buyers. QC processes incur additional costs but are necessary to avoid compliance issues and ensure product reliability.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting metal from the supplier to the buyer’s location can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and freight rates. For international buyers, understanding the implications of Incoterms on shipping costs is essential.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s business model.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Welding Practice Metal Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the sourcing of welding practice metal:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounts. Buyers should consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can optimize their costs while meeting production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications or unique metal treatments may increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Metals that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO standards) tend to be priced higher due to the assurance of quality and compliance. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs, while established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms agreed upon (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly impact overall costs, as these terms dictate who bears the shipping costs and risks.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Welding Practice Metal Sourcing?
B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can implement several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to lower prices or offer better payment terms to secure a deal.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, potential wastage, and logistics. A lower initial price may lead to higher costs later if quality is compromised.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and supplier offerings. This knowledge empowers buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate better deals.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing, priority service, and insights into future price trends.
-
Regional Considerations: Be mindful of regional economic conditions that may affect pricing, such as tariffs, currency fluctuations, and local demand for metals.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier policies, and specific buyer requirements. Always request quotes and conduct due diligence before finalizing any purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing welding practice metal With Other Solutions
When evaluating solutions for welding practice, it is essential to consider various alternatives that can serve similar purposes. In this analysis, we will compare welding practice metal, which typically refers to specific metals used for practice in welding, against other viable solutions, such as scrap metal and welding practice kits. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their unique operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Welding Practice Metal | Scrap Metal | Welding Practice Kits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, consistent results; ideal for skill building. | Variable quality; may require additional preparation. | Designed for specific skills; consistent quality. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on type and quantity. | Generally low-cost or free if sourced locally. | Higher upfront cost; includes tools and materials. |
| Ease of Implementation | Readily available from suppliers; minimal setup required. | Requires sourcing from local suppliers; may involve extra work. | Easy to use; includes instructions and all necessary components. |
| Maintenance | Low; metals are durable and reusable. | Varies; some may require cleaning or treatment before use. | Minimal; consumables need to be replaced periodically. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for dedicated practice sessions and skill enhancement. | Suitable for informal practice or experimentation. | Best for structured learning environments or workshops. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Scrap Metal as an Alternative?
Scrap Metal is a common alternative for welding practice. Its primary advantage lies in cost-effectiveness; many metal shops offer scrap at discounted prices, or it may even be available for free. This makes it an attractive option for those on a tight budget. However, the performance can be inconsistent, as the quality and type of scrap metal can vary widely. Additionally, scrap metal may require preparation, such as cleaning rust or oil, which can add time and effort to the practice process.
How Do Welding Practice Kits Compare to Welding Practice Metal?
Welding Practice Kits are designed specifically for teaching and honing welding skills. They often come with a variety of materials tailored to specific welding techniques, making them an excellent choice for structured learning environments. The downside is that these kits can be more expensive than simply purchasing welding practice metal. However, they provide a comprehensive solution, including tools, materials, and instructions, which can be beneficial for beginners or educational institutions.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Welding Practice Solution?
When selecting the appropriate welding practice solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, budget constraints, and the desired outcomes of their practice sessions. If cost is a primary concern and informal practice is acceptable, scrap metal may be the best choice. Conversely, for businesses or educational institutions seeking to provide structured training, welding practice kits offer a comprehensive and effective approach. Welding practice metal remains an excellent option for dedicated practitioners looking to refine their skills on high-quality materials. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the operational context and the goals of the welding training program.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for welding practice metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Welding Practice Metal?
Understanding the technical properties of welding practice metal is essential for B2B buyers involved in welding applications. Here are some critical specifications that influence the quality and performance of welding materials:
-
Material Grade
– Material grade indicates the specific type of metal and its mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and ductility. Common grades include A36 for carbon steel and 304 for stainless steel. Selecting the right grade ensures that the metal can withstand the required stress and environmental conditions, which is crucial for operational safety and longevity. -
Thickness Tolerance
– Thickness tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the thickness of the metal. This is critical for ensuring consistent weld quality and performance. For example, in applications that require precision, such as aerospace or automotive industries, even minor deviations can lead to failures. Establishing clear thickness tolerances in your sourcing agreements can prevent costly rework and ensure compliance with industry standards. -
Weldability
– Weldability describes how easily a material can be welded without developing defects. Factors influencing weldability include the chemical composition and microstructure of the metal. For example, high-carbon steels may be more challenging to weld due to the risk of cracking. Understanding weldability helps buyers select suitable materials that align with their welding processes and equipment, reducing the likelihood of production delays. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Corrosion resistance is a property that determines how well a metal can withstand environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals without degrading. For example, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, making it ideal for applications in marine or chemical environments. Evaluating corrosion resistance ensures the longevity and reliability of the final product, particularly in harsh conditions. -
Heat Treatment Compatibility
– This property assesses how well a metal can be heat-treated to enhance its mechanical properties. Certain metals, such as aluminum and some alloys, respond well to heat treatment, improving their strength and toughness. Buyers should consider heat treatment compatibility to optimize material performance and tailor it to specific application requirements. -
Yield Strength
– Yield strength is the amount of stress a material can withstand before it begins to deform permanently. It is a critical factor in structural applications where load-bearing capacity is essential. Knowing the yield strength of welding practice metal allows buyers to select materials that can safely support anticipated loads, ensuring structural integrity.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Welding?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and enhance decision-making in procurement. Here are essential terms commonly used in the welding sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In welding, OEMs may supply equipment, consumables, or components. Understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers identify reliable sources and ensure quality in their welding processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand as it impacts inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases to avoid excess inventory or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products or services. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they get the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Familiarity with Incoterms can help B2B buyers navigate shipping costs, insurance, and risk management, facilitating smoother transactions across borders. -
Filler Metal
– Filler metal is the material added to the weld joint to facilitate bonding. Selecting the appropriate filler metal is essential for achieving desired weld properties and ensuring compatibility with base metals. -
Flux
– Flux is a chemical cleaning agent used in welding to remove oxidation and impurities from the metal surface. Understanding the role of flux can help buyers select the right welding consumables to enhance weld quality and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing welding practice metals, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the welding practice metal Sector
What are the Key Market Drivers and Trends in the Welding Practice Metal Sector?
The global welding practice metal sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several key factors. The increasing demand for high-quality welding materials in manufacturing, construction, and automotive industries is significant. Additionally, the rise of advanced technologies such as automation and robotics in welding processes is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide not only traditional metals but also specialized materials like titanium and exotic alloys, which are essential for high-performance applications.
Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in industrialization, leading to heightened demand for welding materials. For instance, Nigeria and Brazil are ramping up infrastructure projects, necessitating a reliable supply chain for welding practice metals. Furthermore, the advent of e-commerce platforms is streamlining the sourcing process, allowing international buyers to access diverse product ranges efficiently. This shift is accompanied by a growing emphasis on quality assurance and certifications, which are critical for maintaining competitive advantage in global markets.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Welding Practice Metal?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the welding practice metal sector. Environmental concerns related to mining and metal production are prompting buyers to seek suppliers that prioritize ethical practices. This includes sourcing metals that are recycled or have a lower environmental impact. The importance of certifications like ISO 14001 and the use of green materials are increasingly being recognized as essential criteria for supplier selection.
B2B buyers are also exploring partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethically sourced products. In regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent, compliance with environmental standards is non-negotiable. By investing in sustainable sourcing practices, companies can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a more environmentally conscious customer base.
How Has the Welding Practice Metal Sector Evolved Over Time?
The welding practice metal sector has undergone significant evolution since its inception, transitioning from manual techniques to sophisticated automated processes. Early welding methods were rudimentary and labor-intensive, relying heavily on skilled labor. However, advancements in technology, including the introduction of MIG and TIG welding, have revolutionized the industry, allowing for greater precision and efficiency.
In recent decades, the sector has embraced digital transformation, integrating software solutions for design and workflow optimization. This evolution has not only improved productivity but also enabled better quality control and traceability in the sourcing of welding materials. As a result, today’s B2B buyers have access to a more diverse array of high-quality welding practice metals, tailored to meet the evolving demands of various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of welding practice metal
-
How do I choose the right type of welding practice metal for my needs?
When selecting welding practice metal, consider the specific welding techniques you aim to master. Common options include mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Mild steel is often the most economical and versatile choice for beginners, while stainless steel provides insights into more complex welding processes. Additionally, assess the thickness and dimensions of the metal; practice with various sizes can help you adapt to different project requirements. Establishing a relationship with a local supplier can also provide insights into the best materials for your needs. -
What is the best metal to practice welding on for beginners?
For beginners, mild steel is highly recommended due to its forgiving nature and availability. It’s affordable and can withstand various welding methods, making it ideal for practice. Many suppliers offer scrap metal or welding coupons specifically designed for training purposes. As you gain experience, consider incorporating other materials like aluminum or stainless steel to broaden your skill set and understanding of different welding characteristics. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting welding practice metal suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation, product quality, and range of offerings. Look for suppliers with positive customer reviews and those who adhere to industry standards. Certifications, such as ISO or AWS, can indicate a commitment to quality. Additionally, assess their ability to provide custom sizes or grades of metal, and inquire about lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs) to ensure they meet your operational needs. -
What are the typical payment terms offered by suppliers for welding practice metal?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include net 30 or net 60 days, where payment is due within 30 or 60 days of invoice. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or require partial upfront payments, especially for large orders. Always negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow and operational capabilities, and ensure these terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing welding practice metal?
To ensure quality, request material certifications and test reports from your supplier. Verify that the metal meets relevant industry standards, such as ASTM or EN specifications. Establish a clear QA process that includes visual inspections and, if necessary, third-party testing. Regular communication with your supplier regarding quality expectations and conducting periodic audits can further enhance the reliability of your sourced materials. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing welding practice metal?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of welding practice metal. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), which impact cost and delivery time. Ensure that your supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, factor in local regulations and duties, as these can affect overall costs. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in international trade can help streamline the process. -
What customization options are typically available for welding practice metal?
Many suppliers offer customization options such as cut-to-size metal, specific grades, or pre-drilled holes to suit particular welding projects. When discussing customization, clearly communicate your requirements, including dimensions, thickness, and any surface treatments needed. Some suppliers may also provide welding coupons designed for specific techniques, which can enhance your training and skill development. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for welding practice metal?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and type of metal. Some suppliers may have low MOQs for standard items, while specialized or customized orders may require larger quantities. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities. If your needs are below the MOQ, consider collaborating with other businesses or seeking suppliers who cater specifically to smaller orders.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Welding Practice Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Weld Metals Online – 304 2B Stainless Steel Coupons
Domain: weldmetalsonline.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: New Products: Welding Coupons, TIG Starter Kits, Pipe & Plate Coupons, Shapes, Puzzles & Kits, Torches & Consumables, Filler Wire, Welding Machines, Exotic Metals, Dabswellington TIG Art, Gloves & Gear, Merch. Key Products: 304 2B Stainless Steel 2×6 Coupons ($5.00), 6061 Aluminum 2×6 Coupons ($5.00), Cold Rolled Carbon Steel 2×6 Coupons ($6.00), Carbon Steel Flat Coupons ($6.79), 5052 Aluminum Fl…
2. Scrap Metal – Affordable Sources
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Scrap Metal: Available at steel yards and metal scrap yards, often at low prices (e.g., 28¢/lb locally, closer to 37¢/lb nationally). 2. Amazon: Offers surprisingly low prices for metal materials, especially for longer pieces, with free shipping for Amazon Prime members. 3. Local Scrappers: Can provide metal and other junk for practice, such as electric scooters and lawnmowers. 4. Mechanic Shop…
3. Garage Journal – Metal Types & Sources
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: 1. Metal Types: Cold rolled steel, scrap metal, auto body parts, 1/8″ or 3/16″ plate, 1/16″ or thicker coupons. 2. Sources: Local metal supply, metal shops, metal yards, scrap yards, body shops, FB marketplace. 3. Welding Techniques: Practice different joint methods (T, butt, lap, stitch), clean shiny metal is essential. 4. Equipment: Flux core welder, .030 Miller wire, CO2 gas recommended over fl…
4. WelderMade – Carbon Steel Scrap Box
Domain: weldermade.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “WelderMade Carbon Steel Scrap Box”, “product_type”: “Welding Material”, “price”: “$27.00 USD”, “weight”: “20 lb”, “description”: “A box of random carbon steel scrap, ideal for practice across various welding processes including MIG, TIG, Flux Core, and Stick welding. Suitable for all skill levels, providing a diverse assortment of scrap for skill development and creative explorat…
5. Move Bumpers – Practice Metal Kits
Domain: movebumpers.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Practice Metal Kits”, “type”: “Laser Cut”, “price”: “$10.00”, “available_quantities”: [“6-Pieces”, “12-Pieces”], “material”: “3/16″ US Steel”, “description”: “Select from 6 or 12-pieces of laser-cut metal to practice welding prior to building your MOVE Bumper Kit. These welding coupons are the same 3/16” metal thickness that MOVE Bumper Kits are made from. So go ahead and practic…
6. Faster Fabricator – Welding Practice Metal Strips
Domain: fasterfabricator.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Welding Practice Metal Strips”, “brand”: “Faster Fabricator”, “original_price”: “$12.20 – $84.51”, “current_price”: “$12.20”, “material_types”: [“Mild Steel”, “Aluminum”, “Stainless Steel”], “pack_sizes”: [{“size”: “10-Pack”, “price”: “$12.20 (Mild Steel), $15.00 (Aluminum), $31.30 (Stainless Steel)”}, {“size”: “20-Pack”, “price”: “$23.18 (Mild Steel), $28.50 (Aluminum), $59.47 (…
7. Weld Metals Online – Welding Practice Coupons & Kits
Domain: canadaweldingsupply.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: This company, Weld Metals Online – Welding Practice Coupons & Kits, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Etsy – Unique Welding Tools
Domain: etsy.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Etsy – Unique Welding Tools, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for welding practice metal
In summary, effective strategic sourcing for welding practice metals is pivotal for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging reliable suppliers and understanding the variety of materials available—such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel—businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and skill development.
Investing in quality welding practice materials not only supports workforce training but also fosters innovation and creativity in product development. The availability of specialized kits and consumables, coupled with competitive pricing, further empowers businesses to meet their specific needs while maintaining budget constraints.
As the global demand for skilled welding continues to grow, international buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with reputable suppliers and consider bulk purchasing strategies to optimize costs. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can secure high-quality materials that contribute to sustainable growth and improved performance in their welding practices. Engage with suppliers today to unlock the full potential of your welding operations and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.