Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vacuum casting metal
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing high-quality vacuum casting metal can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The process, while offering superior precision and reduced porosity, requires a deep understanding of various casting methods, materials, and supplier capabilities. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the complexities of vacuum casting metal, providing valuable insights into different types, applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
From automotive components to intricate aerospace parts, vacuum casting has become essential in producing high-performance, reliable metal parts across multiple industries. Buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find actionable strategies for evaluating costs and understanding the nuances of the vacuum casting process.
By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge needed to navigate supplier landscapes and assess product quality, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain or seeking to innovate your production processes, understanding the intricacies of vacuum casting metal is critical for achieving operational excellence and staying ahead in the global market.
Understanding vacuum casting metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Die Casting | Utilizes a vacuum to eliminate air during metal injection; reduces porosity | Automotive parts, aerospace components | Pros: High-quality, consistent parts; suitable for mass production. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Vacuum Investment Casting | Employs a two-piece mold in a vacuum chamber; ideal for intricate designs | Medical devices, jewelry, precision parts | Pros: Excellent surface finish; complex geometries. Cons: Longer lead times compared to traditional casting. |
| High Vacuum Die Casting (HVDC) | Enhanced vacuum levels for superior metal flow and reduced defects | Aerospace, high-performance automotive parts | Pros: Exceptional mechanical properties; minimal defects. Cons: More expensive due to advanced technology. |
| Centrifugal Vacuum Casting | Combines centrifugal force with vacuum; effective for small, intricate parts | Jewelry, small precision components | Pros: High detail and accuracy; efficient for small runs. Cons: Limited to specific shapes and sizes. |
| Ultra-High Vacuum Die Casting (UHVDC) | Achieves extreme vacuum conditions for the most demanding applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, specialty applications | Pros: Superior quality and purity; ideal for critical applications. Cons: Very high cost and complex setup. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Vacuum Die Casting?
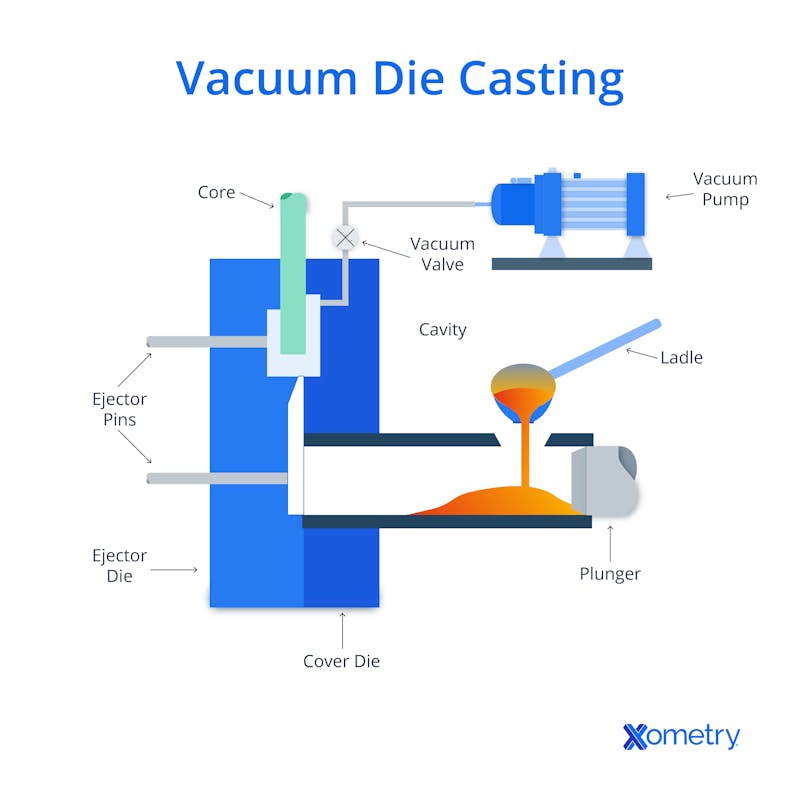
Vacuum Die Casting is a widely adopted method in industries requiring high-volume production of identical parts, particularly in the automotive sector. This technique uses a vacuum to remove air from the die, significantly reducing porosity and enhancing the mechanical properties of the final product. Suitable for metals like aluminum and magnesium, this method is ideal for producing components that require high strength and durability. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment in machinery and tooling, but the long-term benefits of reduced defects and higher production rates often justify the costs.
How Does Vacuum Investment Casting Differ from Traditional Methods?
Vacuum Investment Casting stands out due to its ability to produce highly intricate parts with excellent surface finishes. This process involves creating a two-piece mold placed in a vacuum chamber, allowing molten metal to be drawn into complex shapes. It’s particularly useful for applications in the medical device and jewelry industries, where precision is paramount. Buyers should weigh the advantages of superior detail against potentially longer lead times and higher costs compared to traditional casting methods.
What Advantages Do High Vacuum Die Casting and Ultra-High Vacuum Die Casting Offer?
High Vacuum Die Casting (HVDC) and Ultra-High Vacuum Die Casting (UHVDC) are specialized techniques that push the boundaries of casting quality. HVDC achieves enhanced vacuum levels to minimize gas entrapment, making it suitable for high-performance automotive and aerospace parts. UHVDC takes this further, ensuring extreme purity and quality, which is crucial in semiconductor manufacturing. While these methods provide exceptional mechanical properties and defect resistance, buyers must consider the significant investment and complexity involved in their implementation.
In What Scenarios is Centrifugal Vacuum Casting Most Effective?
Centrifugal Vacuum Casting combines centrifugal force with vacuum technology, making it particularly effective for creating small, intricate components like jewelry. This method excels in producing high-detail items with a smooth finish, making it a favorite among jewelers and precision manufacturers. However, its application is somewhat limited to specific shapes and sizes, so B2B buyers should assess whether their production needs align with the capabilities of this casting method.
Key Industrial Applications of vacuum casting metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vacuum casting metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of engine and transmission components | Enhanced mechanical properties and reduced porosity | Supplier reliability, compliance with industry standards |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of lightweight structural components | High precision and predictable mechanical behavior | Certifications, quality assurance processes |
| Electronics | Creation of intricate housings and heat sinks | Improved thermal conductivity and reduced defects | Material specifications, lead times, and cost efficiency |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility and precision in complex geometries | Regulatory compliance, material sourcing |
| Jewelry | Crafting intricate designs and custom settings | High-quality finishes and the ability to create detailed features | Artisanal craftsmanship, material quality, and design flexibility |
How is Vacuum Casting Metal Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, vacuum casting metal is primarily utilized for producing critical engine and transmission components. This method mitigates porosity, ensuring that parts can withstand high pressure and temperature during operation. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing components that adhere to stringent quality standards is essential. They should seek suppliers who can guarantee consistent production quality and timely delivery to meet the demands of mass production.
What Role Does Vacuum Casting Metal Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Vacuum casting is vital in aerospace for creating lightweight structural components that require exceptional precision and reliability. The method allows for the production of complex geometries that are essential for aerospace applications, where mechanical failure can have catastrophic consequences. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East must prioritize suppliers with the necessary certifications and a proven track record in quality assurance to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
How is Vacuum Casting Metal Beneficial for Electronics?
In the electronics sector, vacuum casting is employed to manufacture intricate housings and heat sinks that require precise dimensions and excellent thermal properties. The reduced porosity from vacuum casting leads to improved performance and longevity of electronic components. B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Vietnam should focus on suppliers who can provide materials that meet specific thermal and electrical conductivity requirements while also ensuring competitive pricing.
Why is Vacuum Casting Metal Important for Medical Devices?
The medical device industry relies on vacuum casting for producing surgical instruments and implants that demand high precision and biocompatibility. The ability to create complex shapes without defects is crucial for ensuring patient safety and device efficacy. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East must ensure that their suppliers adhere to strict regulatory compliance and can provide documentation to support the safety and effectiveness of their products.
How Does Vacuum Casting Metal Enhance Jewelry Production?
In jewelry making, vacuum casting allows artisans to create intricate designs and custom settings with a high-quality finish. This method is particularly advantageous for producing detailed features and unique shapes that traditional casting may struggle to replicate. Buyers, especially in Europe, should consider suppliers that offer artisanal craftsmanship and high-quality materials to ensure the final products meet their design specifications and market expectations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vacuum casting metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Porosity in Cast Parts
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in industries such as automotive and aerospace is the issue of porosity in cast metal parts. Porosity not only affects the structural integrity of components but also leads to failures in subsequent processes like welding and heat treatment. Buyers often find that traditional casting methods do not yield the level of quality they require, resulting in increased scrap rates and rework, which can be both costly and time-consuming.
The Solution: To combat porosity, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing suppliers who specialize in vacuum die casting. This method removes air and other gases from the die before the molten metal is introduced, significantly reducing the risk of porosity. When selecting a supplier, ask for detailed information on their vacuum systems and their capabilities. It’s also beneficial to request samples of previous work to assess quality. Implementing a robust quality control process that includes non-destructive testing methods, such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing, can further ensure that the parts meet stringent specifications before they are deployed in critical applications.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Complex Geometries
The Problem: As products become more sophisticated, the demand for complex geometries in cast components has increased. B2B buyers often find that traditional casting methods struggle to produce intricate designs with high precision. This limitation can lead to longer lead times and increased costs due to the need for additional machining or redesigns to fit existing manufacturing processes.
The Solution: Buyers should consider utilizing vacuum casting methods that excel in producing intricate designs. This technique allows molten metal to be drawn into every crevice of the mold, ensuring that even the most complex geometries are accurately filled. To maximize the benefits, engage with design engineers during the early stages of product development to optimize the casting design. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in advanced simulation software can also help visualize and resolve potential issues before production, thus reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Quality Across Production Batches
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is experiencing inconsistent quality in metal castings across different production batches. Variability can arise from numerous factors, including changes in material properties, fluctuations in process conditions, or lack of stringent quality controls. This inconsistency can lead to significant challenges, especially for businesses that rely on high-volume production for critical components.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, it’s essential to work with suppliers who have established a standardized process for vacuum casting. Look for manufacturers who utilize automated systems to monitor and control key parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vacuum levels throughout the casting process. Implementing a comprehensive quality management system (QMS) that includes regular audits, material traceability, and detailed documentation can help maintain uniformity across batches. Additionally, forming long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to better collaboration and improved understanding of your specific quality requirements over time, ultimately resulting in more consistent outcomes.
By addressing these common pain points with targeted solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies for vacuum casting metal, resulting in improved product quality and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vacuum casting metal
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum Alloys in Vacuum Casting Metal?
Aluminum alloys, particularly A380, are among the most commonly used materials in vacuum casting due to their excellent mechanical properties and versatility. They exhibit moderate melting temperatures (around 660°C) and good fluidity, which allows for intricate designs and thin-walled components. Aluminum alloys also offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications in automotive and aerospace industries where durability is essential.
However, while they are lightweight and have a high strength-to-weight ratio, aluminum alloys can be more expensive compared to some other metals. Their manufacturing complexity is moderate, as they require precise control during the casting process to avoid defects like porosity. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with standards such as ASTM B85 and DIN EN 1706 is crucial, as these ensure product quality and performance.
How Do Magnesium Alloys Perform in Vacuum Casting Applications?
Magnesium alloys, such as AZ91D, are favored for their low density and high strength, making them ideal for lightweight applications. They typically have a melting point of about 650°C and exhibit good mechanical properties, especially in terms of tensile strength and fatigue resistance. The use of magnesium alloys is particularly advantageous in automotive applications where weight reduction is critical.
On the downside, magnesium alloys are more susceptible to corrosion and may require protective coatings, which can increase costs and manufacturing complexity. Additionally, they can be challenging to work with due to their flammability when molten. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, understanding the specific corrosion resistance requirements and ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM B93 is essential for successful applications.
What Advantages Do Zinc Alloys Offer for Vacuum Casting Metal?
Zinc alloys, particularly those in the Zamak series, are known for their excellent casting properties and versatility. They have a relatively low melting point (around 385°C), which allows for efficient energy use during the casting process. Zinc alloys provide good corrosion resistance and can be easily plated or painted, making them suitable for decorative applications as well as functional components in the automotive and electronics industries.
However, the main limitation of zinc alloys is their lower mechanical strength compared to aluminum and magnesium alloys. This can restrict their use in high-stress applications. For international buyers, especially in regions like Brazil and Vietnam, it’s important to consider local market preferences and standards, such as JIS H 5302, to ensure compatibility with regional manufacturing practices.
What Are the Considerations for Using Stainless Steel in Vacuum Casting?
Stainless steel, particularly grades like 316L, is often selected for vacuum casting when high corrosion resistance and strength are required. With a melting point around 1400°C, stainless steel can withstand high temperatures and is suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as marine and chemical processing industries. Its durability and ability to maintain structural integrity under stress make it a preferred choice for critical components.
The drawbacks include higher costs and increased manufacturing complexity, as stainless steel requires more energy to melt and can be more difficult to cast due to its viscosity. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM A351 or DIN 17440 is essential, as these standards dictate the quality and performance of stainless steel components in demanding applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Vacuum Casting Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for vacuum casting metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive and aerospace components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to some metals | High |
| Magnesium Alloys | Lightweight structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Zinc Alloys | Decorative and functional parts | Good casting properties and versatility | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine and chemical processing | High corrosion resistance | Higher melting point increases cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for vacuum casting metal, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vacuum casting metal
What Are the Main Stages in the Vacuum Casting Metal Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process for vacuum casting metal involves several critical stages, each aimed at ensuring the production of high-quality components. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure vacuum cast products.
Material Preparation: How Is the Metal Alloy Readied for Casting?
The initial stage involves selecting and preparing the appropriate metal alloy, often aluminum, magnesium, or zinc-based. The choice of alloy impacts the final properties of the cast product, including strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. The alloy is melted in a controlled environment, ensuring it reaches the necessary temperature to maintain fluidity. This step is crucial as improper melting can lead to inconsistencies in the final product.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create the Casting?
Once the metal is melted, it is transferred into a vacuum chamber equipped with a two-part mold. The vacuum chamber is essential as it removes almost all air and gases, minimizing the risk of porosity in the final casting. The molten metal is then injected into the mold under high pressure, allowing it to fill intricate designs and features. This process can vary slightly depending on whether a hot or cold chamber die-casting machine is used.
Assembly: How Are Cast Components Joined or Finalized?
After the metal solidifies, the mold is opened, and the cast part is ejected. If the component requires further assembly, such as the integration of additional parts or finishing processes, this is the stage where it occurs. The assembly must be executed with precision to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications.
Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied to the Castings?
Finishing processes can include machining, surface treatment, and coating to enhance the aesthetic appeal and functional properties of the cast part. Machining may be necessary to achieve tight tolerances, while surface treatments can provide additional protection against wear and corrosion. This stage is vital for ensuring that the final product meets the specific needs of the customer.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Vacuum Casting Metal?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the vacuum casting process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers must be aware of the QA practices that suppliers implement.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Key international standards for quality assurance in vacuum casting include ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles, and industry-specific standards such as CE for European markets and API for the oil and gas sector. Compliance with these standards ensures that suppliers maintain a consistent quality level and can deliver reliable products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure adherence to specifications. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. Ensuring that the metal alloys meet specified standards is critical for maintaining quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the casting process, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vacuum levels are monitored. Any deviations can lead to defects that impact the final product’s quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the casting is completed, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify their properties and dimensions. This step often includes visual inspections, dimensional checks, and mechanical property testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify a supplier’s quality control practices. Here are some actionable strategies:
What Types of Audits and Reports Can Buyers Request?
Buyers should request copies of the supplier’s quality management system documentation, including their ISO 9001 certification and any industry-specific certifications. Conducting site audits is also advisable to assess the manufacturing environment and quality control processes firsthand.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an additional layer of assurance. These agencies can conduct independent audits and testing, offering unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Nuances in Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers must be cognizant of certain nuances:
Are There Regional Standards to Consider?
Different regions may have specific quality standards and regulations that suppliers must adhere to. For example, European suppliers often comply with CE marking requirements, while suppliers in the Middle East may need to meet Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional requirements to ensure compliance.
How Do Cultural Differences Impact Quality Control Practices?
Cultural attitudes towards quality can vary significantly across regions. In some cultures, the emphasis may be on speed and cost-effectiveness, potentially compromising quality. B2B buyers should establish clear communication channels and set explicit quality expectations to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance Is Critical for B2B Buyers
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in vacuum casting metal, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This knowledge enables them to ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements, ultimately enhancing their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vacuum casting metal’
To facilitate your procurement of vacuum casting metal, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure you select the right materials and suppliers for your business needs. By following this checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process while minimizing risks and maximizing product quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical to ensure that the vacuum casting metal meets your product requirements. This includes the type of metal alloy, dimensions, tolerances, and any specific properties such as corrosion resistance or thermal stability. Providing detailed specifications helps suppliers deliver accurate quotes and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings during production.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers specializing in vacuum casting metal. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and a portfolio showcasing similar projects. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to gather a list of potential suppliers that meet your criteria.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess each supplier’s capabilities to ensure they can meet your technical requirements. Request information on their production processes, equipment, and quality control measures. Pay particular attention to their ability to handle complex geometries and the types of metals they work with, as this directly impacts the quality of the finished product.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your choice, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Certifications indicate adherence to quality management systems and can provide peace of mind regarding the reliability of your supplier. Additionally, inquire about their experience with vacuum die casting and any specific techniques they utilize.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Quality
Request samples of the vacuum casting metal to evaluate quality before placing a large order. Conduct thorough testing to assess the material’s mechanical properties, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. This step is essential to ensure that the supplier can consistently deliver products that meet your specifications.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Pricing
Engage in discussions about lead times and pricing structures with your shortlisted suppliers. Understanding their production timelines will help you plan your project schedule effectively. Additionally, compare pricing from different suppliers while considering the quality and service level offered, as the cheapest option may not always be the best.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Ensure that clear communication channels are established with your chosen supplier. Regular updates regarding production progress, potential challenges, and delivery schedules are crucial for maintaining a smooth partnership. Establishing a strong line of communication can help resolve issues quickly and improve overall collaboration.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing vacuum casting metal, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who can meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vacuum casting metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Vacuum Casting Metal Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with vacuum casting metal, several components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of metal alloys significantly influences cost. Common materials such as aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys vary in price based on market demand and availability. Buyers should also consider the effects of material specifications on the final product, as higher-quality materials often come at a premium.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in vacuum casting, particularly for setup and quality assurance processes. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region. For example, labor in Europe may be more expensive than in parts of South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can be a significant portion of the total cost, especially for suppliers operating in regions with higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is often substantial, as high-precision molds are required for vacuum casting. Tooling costs can be amortized over a production run, making it critical to negotiate based on expected order volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the final product meets specifications is vital. QC processes require investment in equipment and personnel, which adds to the overall cost. Buyers should inquire about the quality certifications of suppliers, as these can impact pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, are significant, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local tariffs can dramatically affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing?
Pricing in vacuum casting is heavily influenced by order volume and customization requirements. Generally, higher volumes lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, small orders may incur higher costs due to setup and tooling expenses.
Customization can also increase costs. Complex geometries or specific material requirements may necessitate additional tooling or longer production times, which can inflate prices. It is advisable for buyers to clearly define their specifications and consider potential trade-offs between customization and cost.
What Pricing Influencers Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of several pricing influencers:
-
Material Availability: Local sourcing of materials can reduce costs. However, international suppliers might offer better quality or unique materials that justify higher prices.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can offer greater assurance of product reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics costs. Different terms can dictate who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks, which can significantly affect the total landed cost of goods.
What Are Some Effective Negotiation Tips for Buyers?
When negotiating prices, buyers should focus on creating long-term partnerships rather than one-off transactions. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate orders to increase volume and negotiate better pricing.
-
Explore Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also factors like maintenance, durability, and potential rework costs.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate your specifications and expectations. This can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes and avoid hidden costs later in the process.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Comparing offers from various suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value.
Conclusion
While the costs associated with vacuum casting metal can vary significantly based on multiple factors, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics can empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. By considering the outlined components and negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their procurement processes, reduce costs, and ensure they receive high-quality products tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vacuum casting metal With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Vacuum Casting Metal
In the world of manufacturing, particularly in the production of metal components, vacuum casting has gained popularity due to its ability to create high-quality parts with complex geometries. However, several alternative casting methods exist, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs, budget, and production requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Vacuum Casting Metal | Investment Casting | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, low porosity, excellent surface finish | High dimensional accuracy, good surface quality | High production speed, good mechanical properties |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to the vacuum system | Moderate, can be higher for intricate designs | Low per unit for large runs, high setup cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Moderate; requires pattern creation and mold design | Straightforward for high-volume production |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of vacuum systems needed | Mold maintenance is crucial; complex molds can wear out | Lower maintenance; simpler equipment |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, intricate designs | Complex parts, low to medium volumes | High-volume production of simpler shapes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Investment Casting?
Investment casting, often known as lost-wax casting, is a method that excels in creating complex parts with exceptional surface finishes. The process involves creating a wax model, coating it with a ceramic shell, and then melting away the wax to leave a cavity for metal pouring. While it provides excellent dimensional accuracy and surface quality, it tends to be more costly for intricate designs due to the extensive mold preparation. Additionally, the lead time for mold creation can be significant. Investment casting is ideal for low to medium production volumes where precision is paramount, such as in aerospace and medical applications.
How Does Die Casting Compare to Vacuum Casting Metal?
Die casting is a highly efficient method for producing large quantities of parts, particularly for simple geometries. This technique involves forcing molten metal into a mold under high pressure, which allows for rapid production cycles and low per-unit costs in high-volume runs. However, die casting is less suitable for intricate designs compared to vacuum casting, as it can lead to defects like porosity and surface imperfections. The initial setup costs can be high, but once established, it offers a streamlined process for mass production, making it an excellent choice for automotive and consumer goods manufacturing.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When evaluating casting methods, B2B buyers should consider several factors: the complexity of the components, production volume, budget constraints, and desired material properties. For projects requiring high precision and low porosity, vacuum casting is often the best choice, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive where performance is critical. Conversely, for larger production runs of simpler parts, die casting may offer a more cost-effective solution. Investment casting should be considered when intricate designs are necessary, and precision is non-negotiable, despite the potentially higher costs and longer lead times. By carefully assessing these aspects, buyers can select the casting method that aligns best with their project requirements and business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vacuum casting metal
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Vacuum Casting Metal?
Understanding the technical properties of vacuum casting metal is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Here are some key specifications that significantly influence the quality and applicability of vacuum-cast products:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and quality of the metal used in the casting process. Common materials include aluminum alloys (such as A380), magnesium alloys, and zinc alloys. Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring optimal performance, strength, and durability of the final product, which directly affects the operational efficiency of the end-use applications. -
Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the casting. High precision in dimensional tolerances is vital for components that require exact fits, such as in machinery or automotive assemblies. Accurate tolerances minimize the need for secondary machining processes, thereby reducing costs and lead times for B2B buyers. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of the casted component. This property is critical for aesthetic components and those that interact with other mechanical parts, as a rough surface can lead to increased wear and failure. Understanding the required surface finish can help buyers make informed decisions about post-processing needs and associated costs. -
Porosity Levels
Porosity is the presence of tiny holes or voids within the cast material, which can compromise structural integrity. Vacuum casting significantly reduces porosity compared to traditional methods, making it crucial for applications requiring high strength and reliability. Buyers must evaluate porosity levels to ensure the castings meet their specific performance requirements. -
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material conducts heat. This property is particularly important in applications such as automotive components and electronics, where heat dissipation is critical. Understanding thermal conductivity helps buyers select materials that will perform effectively under varying temperature conditions. -
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties, including tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, define how a material behaves under stress. These properties are critical for ensuring that the vacuum-cast components can withstand operational loads and stresses without failure. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide detailed mechanical property data for their castings.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Vacuum Casting Metal?
Familiarizing yourself with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms associated with vacuum casting metal:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are then marketed by another company. In the context of vacuum casting, OEMs often require high-quality, precision cast parts that meet specific design standards. Understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure compatibility with their intended applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions, inventory management, and overall project budgets. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategies effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. For vacuum casting projects, RFQs allow buyers to obtain competitive bids, enabling informed decision-making regarding suppliers and pricing structures. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). These terms clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, especially for international buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In vacuum casting, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and timely delivery, especially in industries with strict production schedules. -
Casting Tolerance
Casting tolerance specifies the acceptable limits of deviation from the intended dimensions of a cast part. It is essential for ensuring that the finished product meets the required specifications for fit and function, which is critical for maintaining quality standards in manufacturing processes.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing vacuum-cast metal components, ultimately leading to better project outcomes and partnerships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vacuum casting metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Vacuum Casting Metal Sector?
The vacuum casting metal sector is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for precision-engineered components across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Key trends include the rise of advanced manufacturing technologies and an emphasis on customization. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer high-quality, complex geometries with reduced lead times. This shift is facilitated by digital technologies that streamline the design and production processes, enabling manufacturers to efficiently produce smaller batches of tailored components.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions. Buyers are focusing on suppliers who demonstrate responsible practices and the use of environmentally friendly materials. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is enhancing supply chain visibility and operational efficiency, allowing companies to better manage their inventories and production schedules. As a result, buyers can expect improved product quality and reduced costs, making vacuum casting a more attractive option for high-volume production.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Vacuum Casting Metal Sector?
Sustainability is not merely a buzzword; it is a vital component of modern B2B procurement strategies in the vacuum casting metal sector. Environmental impacts associated with traditional manufacturing processes, such as high energy consumption and waste generation, have prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers who employ sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important, with companies expected to ensure their supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices and environmental degradation.
To meet these demands, many manufacturers are adopting ‘green’ certifications and materials, focusing on recyclable and low-impact metals for vacuum casting. For example, aluminum and magnesium alloys are often preferred due to their lightweight properties and recyclability. Additionally, the use of advanced cooling systems and energy-efficient equipment during the casting process contributes to lower carbon footprints. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who can provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices and demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Vacuum Casting in the B2B Context?
The vacuum casting method has evolved significantly since its inception, initially used primarily in the aerospace sector for producing complex components. As industries expanded, so did the applications of vacuum casting, with automotive manufacturing leading the charge due to the need for lightweight and durable parts. The introduction of advanced materials and the refinement of casting techniques have allowed for greater precision and lower porosity in finished products.
In recent years, the globalization of supply chains has made vacuum casting more accessible to international B2B buyers. Innovations in technology, such as the incorporation of computer-aided design (CAD) and additive manufacturing, have further enhanced the capabilities of vacuum casting, allowing for more intricate designs and faster production times. As the demand for customized solutions continues to rise, the vacuum casting sector is well-positioned to meet these challenges and opportunities, making it a critical focus area for B2B buyers in diverse markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vacuum casting metal
-
How do I identify a reliable supplier for vacuum casting metal?
To identify a reliable supplier for vacuum casting metal, start by researching potential suppliers through industry directories and trade shows. Evaluate their experience in vacuum casting, focusing on their portfolio and client testimonials. Request certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their production capacity and ability to meet your specific requirements, including lead times and customization options. Engaging in initial conversations and requesting samples can also provide insight into their service quality and responsiveness. -
What are the key advantages of vacuum casting metal compared to traditional methods?
Vacuum casting metal offers several advantages over traditional casting methods, primarily due to its ability to minimize air entrapment, resulting in lower porosity and superior mechanical properties. This method allows for the production of complex geometries and intricate designs with high precision and excellent surface finishes. Additionally, vacuum casting is particularly beneficial for parts that will undergo further processing, such as welding or heat treatment, as it significantly reduces the risk of defects. Overall, these advantages make it ideal for high-demand industries like automotive and aerospace. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for vacuum casting metal?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for vacuum casting metal can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Factors influencing MOQ include the complexity of the part, tooling costs, and the supplier’s production capabilities. When sourcing, it’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find a mutually beneficial arrangement. If you require a lower MOQ, some suppliers may offer to combine orders or provide a prototype service to accommodate your needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vacuum casting metal internationally?
Payment terms when sourcing vacuum casting metal can differ by supplier and region. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the remainder upon delivery. International buyers should also consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. Discussing currency options and potential exchange rate fluctuations is also important for international transactions. -
How can I customize my vacuum casting metal components?
Customizing vacuum casting metal components typically involves collaborating closely with your supplier during the design phase. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, tolerances, and material requirements. Many suppliers offer design assistance and CAD modeling services to refine your concepts. Additionally, discuss any specific surface finishes or post-processing needs early in the process to ensure that your requirements are met. Regular communication throughout the production cycle is key to achieving the desired customization and quality. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for vacuum casting metal?
Quality assurance measures for vacuum casting metal should include a comprehensive inspection process at multiple stages of production. Suppliers should implement in-process inspections to monitor casting quality and dimensional accuracy. Final inspections should encompass non-destructive testing methods, such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing, to detect any internal defects. Certification to international quality standards, like ISO 9001, also indicates a commitment to quality management practices. Establishing clear quality expectations upfront can help ensure that the final products meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vacuum casting metal?
When importing vacuum casting metal, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Assess whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable for your order size and urgency. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. It’s also essential to factor in potential delays caused by customs inspections. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and minimize risks. -
What industries commonly utilize vacuum casting metal, and why?
Vacuum casting metal is widely utilized across various industries, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and electronics. In the automotive sector, it is favored for producing high-strength, lightweight components that require precise tolerances and surface finishes. The aerospace industry relies on vacuum casting for its ability to create complex parts with predictable mechanical properties, essential for safety and performance. Additionally, the electronics industry benefits from vacuum casting for producing intricate housings and components that demand high precision and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Vacuum Casting Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Vacuum Casting Process
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Vacuum casting involves connecting a vacuum pump to a flask before pouring molten metal. The process requires two holes: one for pouring the metal and another for vacuuming, although the second hole is often omitted in instructional videos. The investment material used is porous, allowing air to pass through while preventing molten metal from leaking. A perforated flask is essential for providing …
2. Total Materia – Vacuum Casting Solutions
Domain: totalmateria.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Vacuum casting encompasses multiple manufacturing processes utilizing vacuum technology to enhance metal casting operations. Key applications include melting reactive superalloys and titanium-based materials in oxygen-free atmospheres to prevent oxidation. Techniques include vacuum-assisted casting, which uses differential pressure for improved dimensional accuracy and surface finish, and the V-pr…
3. Ferralloy – Investment Castings
Domain: ferralloy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Investment castings, also known as lost-wax castings, are produced using an expendable mold process. They are popular for their ability to create complex parts with exceptional surface qualities and accuracy across various materials and sizes. The vacuum casting method is a specific technique used for producing vacuum castings, which involves placing a two-piece mold in a vacuum chamber to draw mo…
4. ImproPrecision – Vacuum Investment Casting
Domain: improprecision.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Vacuum investment casting yields extremely high quality metal parts with fine detail and excellent surface finish. It is more complex than conventional investment casting and requires sophisticated melting and mold-filling equipment. This process is reserved for casting parts that need very high levels of structural integrity, where defects are expensive. The vacuum process minimizes turbulence, o…
5. Xometry – Vacuum Casting Solutions
Domain: xometry.pro
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Vacuum casting (urethane casting/vacuum duplication) produces prototypes or small-series plastic parts (typically 5 to 50 pieces) with quality comparable to injection molding. It is a cost-effective alternative to injection molding, as it does not require expensive steel tooling. The process involves pouring liquid plastic into a silicone mold and curing it in an oven, using a vacuum chamber to re…
6. Formlabs – Vacuum Pouring Techniques
Domain: forum.formlabs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Formlabs – Vacuum Pouring Techniques, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Makerverse – Vacuum Casting Solutions
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Vacuum casting is a manufacturing process that produces high-quality, detailed parts with exceptional surface finish and dimensional accuracy. It is ideal for small and medium batch production and is often used for prototype projects. The process involves creating a master model using high-precision techniques like 3D printing or CNC machining, which is then surrounded by liquid silicone to create…
8. Langmuir Systems – Lost Wax Casting Solutions
Domain: forum.langmuirsystems.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Casting Methods: Lost wax investment vacuum methods for jewelry and smaller parts, including hand sculpted or printed patterns using FDM polymaker polycast or SLA printable casting wax resin. 2. Equipment: Propane melting furnace with a blower, vacuum pump, and vacuum pot. 3. Materials: Petro bond for sand casting, sodium silicate for bonded molds, and aluminum brass for casting. 4. Core and Pa…
9. Romanoff – Centrifugal Casting Machines
Domain: romanoff.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Romanoff offers a variety of centrifugal casting machines and accessories, including: 1. CCM Centrifugal Casting Machines 2. RCS Centrifugal Casting Machines 3. Crucibles & Parts for RCS & CCM 4. Casting Kits such as the Romanoff White Metal Casting Kit and RCS Casting Kit with Optical Pyrometer 5. Induction Coils for 7.5Kw Models 6. Flask Saddles in various sizes (2″ x 3″, 3″ x 3″) 7. Support Pla…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vacuum casting metal
What Are the Key Benefits of Vacuum Casting Metal for International Buyers?
In conclusion, vacuum casting metal offers significant advantages for B2B buyers seeking high-quality, precision-engineered components. The method’s ability to reduce porosity and enhance mechanical properties makes it an ideal choice for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where reliability and performance are paramount. By strategically sourcing vacuum cast components, businesses can improve product quality, reduce manufacturing costs, and expedite production timelines, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge in the global market.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain?
As international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider integrating vacuum casting into their operations, it is crucial to establish strong partnerships with reputable suppliers. Evaluating suppliers based on their technological capabilities, quality control measures, and delivery reliability will ensure that your sourcing strategy is aligned with your business objectives.
What Does the Future Hold for Vacuum Casting Metal?
Looking ahead, the demand for vacuum casting is expected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing focus on sustainability. Now is the time to invest in strategic sourcing initiatives that leverage the benefits of vacuum casting. Engage with trusted suppliers to explore innovative solutions that can propel your business forward in this evolving landscape.