Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Vacuum Casting Metal
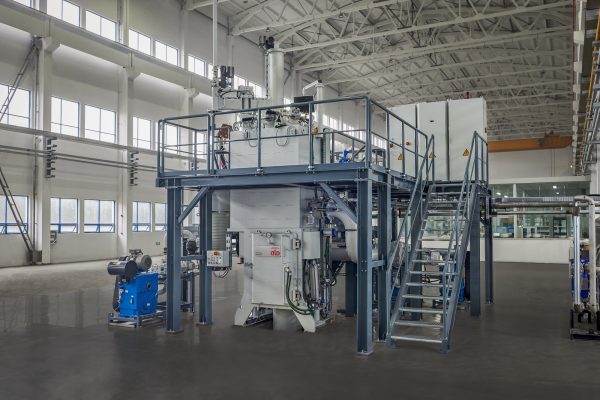

Technical Clarification and Service Introduction
Vacuum casting is a polymer-based rapid prototyping process primarily used for urethane resins, not metals. For metal component production, Honyo Prototype specializes in high-precision Sheet Metal Fabrication—a core competency distinct from vacuum casting. Our advanced metal forming capabilities deliver production-grade prototypes and low-volume runs with exceptional accuracy, repeatability, and material integrity.
Honyo’s Sheet Metal Fabrication services encompass laser cutting, CNC punching, precision bending, welding, and finishing for materials including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. We achieve tight tolerances down to ±0.05 mm, supporting complex geometries and critical applications across aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors. Every project benefits from integrated DFM analysis, in-house tooling, and rigorous quality control per ISO 9001 standards.
Accelerate your development cycle with our Online Instant Quote platform. Upload CAD files to receive detailed, transparent cost and lead time estimates within hours—not days. This digital workflow eliminates procurement delays while ensuring technical alignment with our engineering team from initial inquiry to final inspection. Partner with Honyo for seamless transition from prototype to production-ready metal components.
Technical Capabilities
Vacuum casting is a manufacturing process typically used for producing plastic parts using silicone molds and vacuum-assisted resin pouring. It is not a standard or technically accurate term for metal fabrication processes such as laser cutting, bending, and welding. However, the requested description appears to focus on metal and plastic fabrication techniques—specifically laser cutting, bending, and welding—applied to materials including aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon.
Below is a technical specification table outlining the compatibility and key parameters of laser cutting, bending, and welding for the specified materials. Note that ABS and nylon are thermoplastics and are generally not welded using traditional metal welding methods; instead, they are joined via adhesive bonding, solvent welding, or plastic welding techniques.
| Process | Material | Compatibility | Key Technical Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Aluminum | High | Wavelength: 1064 nm (fiber laser); Thickness range: 0.5–20 mm; Assist gas: N₂ or O₂; Precision: ±0.1 mm; Requires reflective laser protection |
| Steel (Mild/Stainless) | High | Wavelength: 1064 nm; Thickness range: 0.5–25 mm; Assist gas: O₂ (mild steel), N₂ (stainless); Precision: ±0.1 mm | |
| ABS | Moderate | CO₂ laser (10.6 μm); Thickness range: 0.5–10 mm; Edge may show charring; Low melting point (~105°C); Not recommended for high-precision metal-style cutting | |
| Nylon | Moderate | CO₂ laser; Thickness up to 8 mm; High moisture absorption affects cut quality; Requires pre-drying; Edge melting common | |
| Bending | Aluminum | High | Bend radius: ≥1× material thickness; Common alloys: 5052, 6061; Springback: 1–3°; Requires CNC press brake |
| Steel | High | Bend radius: ≥1× thickness; Springback: 2–5°; High-strength steels require higher tonnage; Tooling must match material yield strength | |
| ABS | Limited | Can be thermoformed; Not typically bent like sheet metal; Requires heating to glass transition (~100°C); Risk of cracking | |
| Nylon | Limited | Semi-flexible; Can be bent with heat; Prone to creep under load; Not suitable for sharp bends without heating | |
| Welding | Aluminum | High | Methods: TIG, MIG; Requires AC TIG for oxide removal; Pre-cleaning essential; High thermal conductivity; Filler alloys: 4043 or 5356 |
| Steel | High | Methods: MIG, TIG, Spot Welding; Carbon content affects weldability; Pre/post-heat may be needed for thick sections; Filler: ER70S-6 | |
| ABS | Low (Plastic Welding) | Techniques: Ultrasonic, hot plate, or solvent welding; Not compatible with arc welding; Requires clamping and precise joint design | |
| Nylon | Low (Plastic Welding) | Methods: Vibration, hot gas, or ultrasonic welding; High moisture reduces weld strength; Joint design critical; Pre-drying recommended |
Notes:
Laser cutting parameters depend on laser power (typically 1–6 kW for metals).
Bending accuracy is influenced by tooling, grain direction, and CNC programming.
Welding of plastics like ABS and nylon does not involve high-temperature fusion as in metals; instead, molecular diffusion or melting at interfaces is used.
Vacuum casting is not applicable to metal part production via laser cutting, bending, or welding. It is primarily a low-volume prototyping method for plastics.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype utilizes a specialized vacuum-assisted investment casting process for low-volume metal prototypes and bridge production, distinct from standard vacuum casting which typically refers to polyurethane resin processes. Our technical workflow ensures precision, repeatability, and metallurgical integrity for functional metal parts. Below is the detailed sequence:
CAD Upload and Initial Assessment
Clients submit 3D CAD files (STEP, IGES, or native formats) via our secure portal. Our system performs an immediate geometric validation check, confirming watertightness, unit consistency, and minimum feature recognition. This step prevents downstream errors by flagging non-manifold edges or unsupported topology before quote generation.
AI-Powered Quoting Engine
Honyo’s proprietary AI engine analyzes the validated CAD geometry against 15+ process-specific parameters including part volume, complexity factor, material selection (e.g., aluminum A356, stainless steel 316L, or Inconel 718), and required surface finish. The algorithm cross-references real-time material costs, machine utilization rates, and labor matrices to generate a technically accurate quote within 2 business hours. Critical feasibility constraints—such as maximum wall thickness deviations or undercuts exceeding 1.5° draft—are highlighted in the quote summary.
Engineering DFM Review
All quotes trigger a mandatory Design for Manufacturing review by our senior metallurgical engineers. This phase examines:
Solidification patterns to prevent shrinkage cavities
Optimal gating system placement using MAGMAsoft simulation
Thermal stress analysis for distortion prevention
Dimensional tolerance allocation per ISO 2768-mK standards
We provide actionable feedback within 24 hours, including recommended modifications to reduce porosity risks or improve yield. Typical DFM revisions address rib thickness ratios, fillet radii below 0.8mm, or insufficient draft on deep cavities.
Production Execution
Approved orders enter our controlled production sequence:
1. Pattern Creation: High-resolution SLA patterns printed with low-ash photopolymer resin
2. Ceramic Shell Building: 7-layer colloidal silica stuccoing with automated humidity control
3. Dewaxing and Firing: Steam autoclave dewaxing followed by 1000°C shell preheat
4. Vacuum-Assisted Pouring: Molten metal poured under 0.8 bar vacuum into 850°C preheated molds to eliminate gas entrapment
5. Controlled Cooling: Programmable cooling curves to minimize residual stresses
Quality Assurance and Delivery
Each batch undergoes:
100% visual inspection per ASTM E1417
Dimensional verification via CMM (report included)
Hardness testing (Rockwell/Brinell) and microstructure sampling for critical applications
Optional MPI or X-ray for aerospace/medical parts
Parts ship with full material traceability certificates, process parameter logs, and NDA-compliant documentation. Standard lead time is 10–15 business days from DFM approval.
Key process capabilities are summarized below for quick reference:
| Parameter | Capability Range | Standard Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Options | Al A356, SS 316L, Inconel 718, Ti-6Al-4V | – |
| Part Weight | 50g – 25kg | ±0.5% of nominal |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Up to 300mm linear dimension | ±0.15mm |
| Surface Finish | As-cast: Ra 3.2μm; Machined: Ra 0.8μm | – |
| Production Volume | 1–200 units per pattern | – |
This integrated workflow ensures metallurgical soundness while maintaining the agility required for prototyping. We prioritize defect prevention through physics-based simulation rather than post-process correction, resulting in first-article approval rates exceeding 92% for qualified designs. All processes comply with ISO 9001:2015 and ITAR registration for defense applications.
Start Your Project
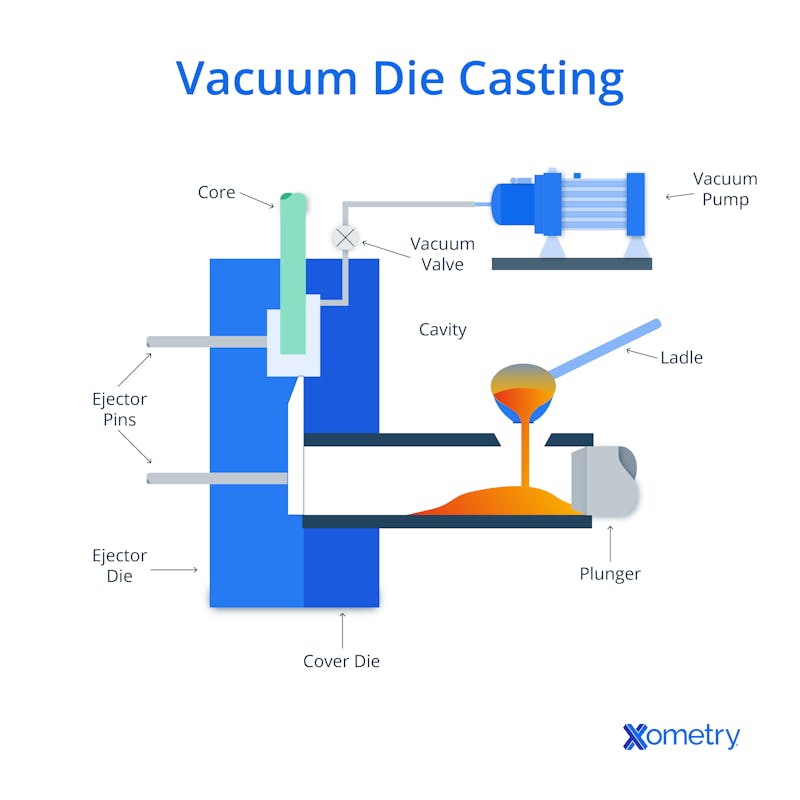
Interested in high-quality vacuum casting metal services? Contact Susan Leo today at [email protected] to discuss your project requirements. Our advanced manufacturing facility in Shenzhen ensures precision, fast turnaround, and consistent quality for prototyping and low-volume production. Let Honyo Prototype be your trusted partner for reliable vacuum casting solutions.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.