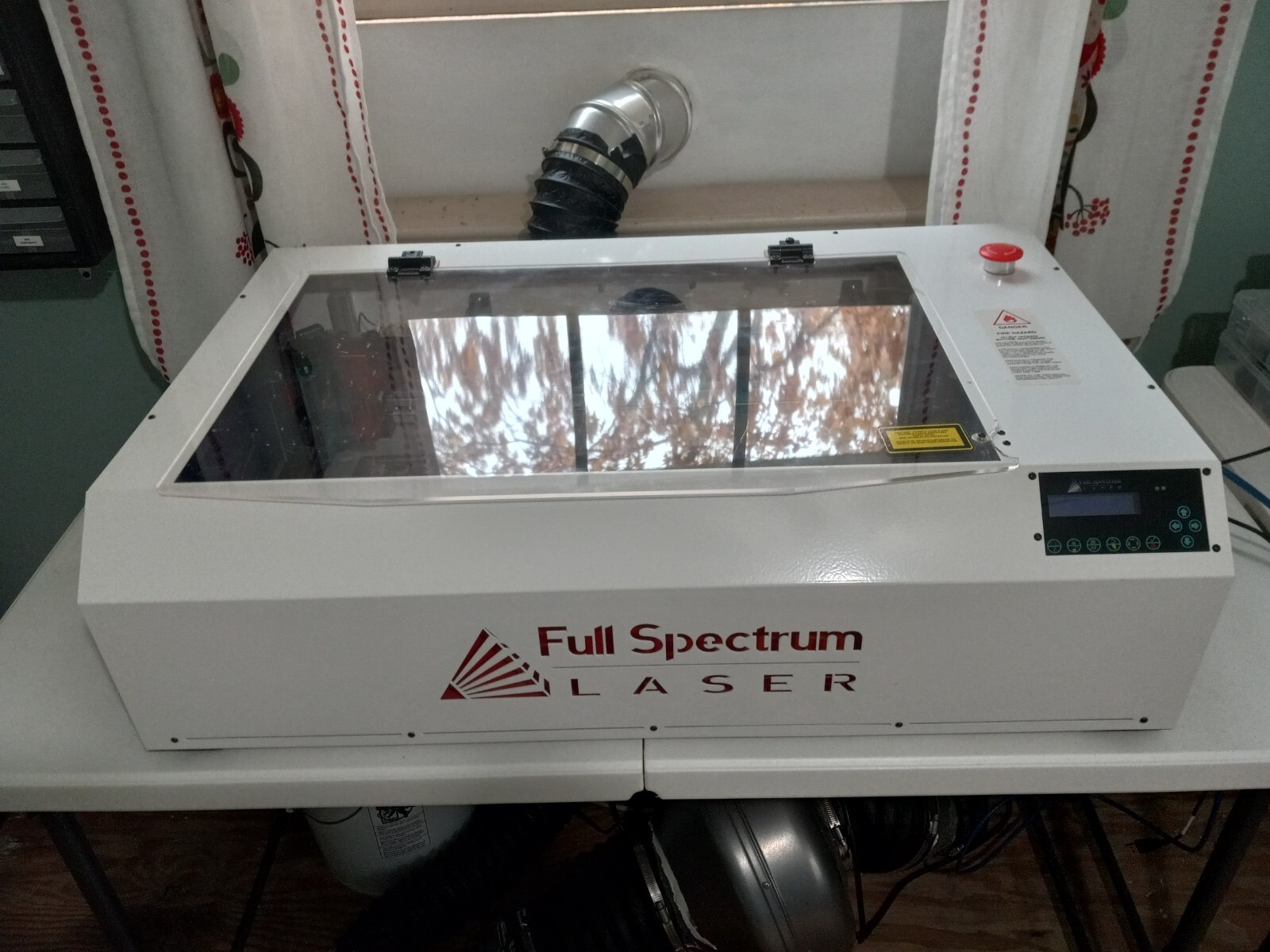
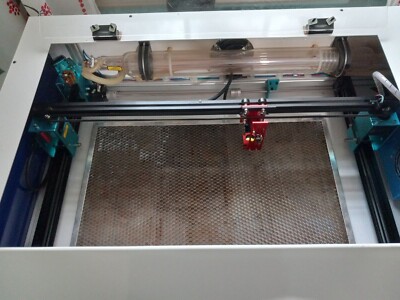
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for used laser cutters
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing used laser cutters can present a myriad of challenges, particularly for international B2B buyers navigating diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With advancements in laser cutting technology, including CO2 and fiber lasers, understanding the right type and application for your specific needs is crucial. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the used laser cutter market, detailing various types of machines, their applications across industries, and key considerations for supplier vetting and cost evaluation.
By delving into the intricacies of laser cutting technology, buyers will gain insights into the operational efficiencies and cost savings associated with each type of machine. The guide also highlights essential factors such as maintenance requirements and potential return on investment, empowering businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on the unique challenges faced by companies in emerging markets and established regions alike, this resource is designed to facilitate strategic sourcing and enhance the overall procurement process. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, or electronics sector, this guide equips you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the global market for used laser cutters.
Understanding used laser cutters Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutter | Utilizes carbon dioxide gas, effective for thicker materials. | Food packaging, textiles, and wood cutting | Pros: Excellent edge quality; versatile for various materials. Cons: Higher energy consumption; slower than fiber lasers. |
| Fiber Laser Cutter | Employs a solid-state laser, ideal for reflective materials. | Metal fabrication, automotive, and aerospace | Pros: Faster cutting speed; lower operating costs. Cons: Limited on thicker materials compared to CO2. |
| Crystal Laser Cutter | Uses neodymium or YAG technology, designed for high-power needs. | Ceramics, scribing metals, and medical devices | Pros: High precision for specialized applications; effective for hard materials. Cons: Generally more expensive; requires skilled operation. |
| Tube Laser Cutter | Specifically designed for cutting tubular materials. | Manufacturing of pipes, tubes, and structural components | Pros: Efficient for complex shapes; reduces waste. Cons: Limited versatility for flat materials; higher initial investment. |
| Laser Engraver | Focuses on engraving and marking rather than cutting. | Branding, signage, and customization | Pros: High detail and precision; ideal for small-scale projects. Cons: Not suitable for cutting thick materials; slower processing time. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of CO2 Laser Cutters for B2B Buyers?
CO2 laser cutters are characterized by their use of carbon dioxide gas to generate a powerful laser beam, making them particularly effective for cutting thicker materials such as wood, plastics, and textiles. They are widely used in industries like food packaging and textile manufacturing due to their versatility. B2B buyers should consider the energy consumption and slower cutting speeds compared to fiber lasers, but the superior edge quality and ability to handle a variety of materials make them a valuable investment for many applications.
How do Fiber Laser Cutters compare in terms of efficiency and applications?
Fiber laser cutters utilize a solid-state medium, allowing them to cut reflective materials like aluminum and copper with high efficiency. They are particularly favored in metal fabrication and the automotive sector due to their rapid cutting speeds and lower operational costs. Buyers should assess their specific material needs, as fiber lasers excel at thinner metals but may struggle with very thick materials. The initial cost may be higher, but the long-term savings in energy and maintenance make them an attractive option for B2B operations.
What are the advantages of using Crystal Laser Cutters in specialized industries?
Crystal laser cutters, often using neodymium or YAG technology, are designed for applications requiring high power and precision, such as cutting ceramics or scribing metals. These machines are particularly suitable for industries like medical devices and electronics, where accuracy is paramount. B2B buyers should note the higher upfront investment and the need for skilled operators, but the ability to handle tough materials makes them a worthwhile consideration for specialized applications.
Why should businesses consider Tube Laser Cutters for their manufacturing needs?
Tube laser cutters are engineered specifically for cutting tubular materials, making them ideal for manufacturing pipes, tubes, and structural components. They offer significant efficiency in producing complex shapes while minimizing waste. For businesses in industries like construction and automotive, investing in a tube laser cutter can streamline production processes. However, buyers should be aware of the limited versatility for flat materials and the higher initial investment required for these specialized machines.
How can Laser Engravers enhance branding and customization efforts for businesses?
Laser engravers focus on engraving and marking rather than cutting, making them perfect for branding, signage, and customization projects. They excel at producing high-detail designs and are suitable for small-scale operations. Businesses looking to enhance their branding efforts will find laser engravers beneficial; however, they should consider that these machines are not suited for cutting thick materials and may have slower processing times compared to cutting lasers.
Key Industrial Applications of used laser cutters
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of used laser cutters | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Cutting and engraving automotive parts | Enhanced precision and reduced waste | Compatibility with various materials, maintenance history |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | Improved fuel efficiency through weight reduction | Certification for aerospace standards, power capacity |
| Electronics | Production of intricate circuit boards | High accuracy and reduced production time | Ability to handle fine details, software compatibility |
| Metal Fabrication | Custom metal signage and decorative elements | Versatile applications across different metal types | Material thickness capabilities, brand reliability |
| Packaging | Cutting packaging materials for food and pharmaceuticals | Compliance with industry standards, cost efficiency | Energy consumption, ease of integration into existing lines |
How Are Used Laser Cutters Applied in the Automotive Industry?
Used laser cutters are extensively employed in the automotive sector for cutting and engraving parts such as brackets, panels, and frames. These machines deliver high precision, enabling manufacturers to minimize waste and optimize material usage. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing used laser cutters requires ensuring compatibility with various metals and understanding the machine’s maintenance history to avoid unexpected downtimes.
What Role Do Used Laser Cutters Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, used laser cutters are vital for fabricating lightweight structural components that meet stringent safety and performance standards. These machines facilitate the creation of complex shapes that contribute to weight reduction, ultimately enhancing fuel efficiency. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing machines that comply with aerospace certifications and can handle the necessary power capacities for advanced materials.
How Are Used Laser Cutters Transforming Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, used laser cutters are crucial for producing intricate circuit boards and components. Their ability to make precise cuts significantly reduces production time while maintaining the quality of the end product. International buyers, particularly from regions like Vietnam, should consider the machine’s capability to handle fine details and ensure compatibility with existing software for seamless integration into their production processes.
What Benefits Do Used Laser Cutters Offer in Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication companies utilize used laser cutters for creating custom metal signage and decorative elements. These machines offer versatility, allowing businesses to work with various types of metals and thicknesses. When sourcing, buyers should assess the material thickness capabilities of the machines and consider the reliability of the brand to ensure consistent performance and quality output.
How Are Used Laser Cutters Essential in the Packaging Industry?
In the packaging sector, used laser cutters are employed to cut materials for food and pharmaceutical packaging. This application not only ensures compliance with industry standards but also enhances cost efficiency through reduced waste. Buyers should focus on energy consumption rates and the ease of integrating these machines into existing production lines, particularly when operating in diverse markets across Africa and Europe.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘used laser cutters’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Assessing the Condition of Used Laser Cutters
The Problem:
When purchasing used laser cutters, B2B buyers often face the challenge of accurately assessing the condition of the equipment. Buyers may be concerned about hidden damages or wear and tear that could affect performance. This uncertainty is particularly significant for businesses in regions like Africa or South America, where access to technical support may be limited. Moreover, laser cutters are a substantial investment, and the fear of acquiring a machine that may require costly repairs can deter potential buyers.
The Solution:
To navigate this issue, buyers should prioritize thorough inspections and due diligence before making a purchase. First, request detailed maintenance records and service history from the seller to understand the machine’s operational background. Engaging a third-party technician or inspector can provide an unbiased assessment of the machine’s condition, including any potential mechanical issues or required upgrades. Additionally, it’s beneficial to test the equipment in action if possible, which allows buyers to evaluate its performance and capabilities firsthand. Utilizing platforms that offer warranties or return policies can further mitigate risks associated with purchasing used machinery.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Choosing the Right Laser Technology
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate laser technology for their specific applications when considering used laser cutters. With various types, such as CO2, fiber, and crystal lasers, each with distinct advantages and limitations, the decision can be overwhelming. For instance, while CO2 lasers may be better suited for thicker materials, fiber lasers excel in speed and efficiency for thinner sheets. This confusion can lead to misinvestments and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution:
To effectively choose the right laser technology, buyers should conduct a comprehensive needs analysis based on their specific materials and production requirements. Begin by clearly defining the types of materials you will be cutting and their thicknesses. Next, assess your production volume and desired cut quality. Engaging with experts or suppliers who specialize in laser technology can provide valuable insights tailored to your unique needs. Additionally, utilizing online resources and comparison tools can help clarify the differences between laser types. Ultimately, investing time in understanding the nuances of each technology will lead to a more informed decision, aligning the equipment with operational goals.
Scenario 3: Uncertainty About Spare Parts Availability and Support
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers of used laser cutters is the uncertainty surrounding the availability of spare parts and technical support. In regions with less robust industrial infrastructure, such as parts of the Middle East or rural Europe, the fear of prolonged downtime due to the unavailability of necessary components can be a significant deterrent. Buyers often worry about how quickly they can get their machines back up and running in case of a malfunction.
The Solution:
To address concerns about spare parts and support, it is crucial for buyers to investigate the brand reputation and availability of service networks before making a purchase. Opt for well-established brands with a proven track record in the industry, as they are more likely to have a robust supply chain for spare parts and a network of certified technicians. When evaluating used laser cutters, inquire about the specific model and its compatibility with readily available components. Joining industry forums or local trade associations can also provide insights into trusted suppliers and service providers in your region. Establishing a relationship with a reliable service partner can ensure that you have access to the necessary support when needed, thus minimizing potential downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for used laser cutters
When selecting materials for used laser cutters, it is crucial to understand how each material interacts with laser cutting technology. This understanding not only influences the efficiency and quality of the cutting process but also impacts the overall cost and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials that are frequently used in conjunction with laser cutting technology.
What Are the Key Properties of Mild Steel for Laser Cutting?
Mild steel is a widely used material in various industries due to its excellent machinability and weldability. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and exhibits moderate corrosion resistance. The key properties that make mild steel suitable for laser cutting include its ability to absorb laser energy efficiently and its relatively low melting point, which allows for quick cutting speeds.
Pros & Cons: Mild steel is durable and cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for structural applications. However, it is susceptible to rusting if not properly coated or treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time. Additionally, while it offers good strength, it may not be suitable for applications requiring higher corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Mild steel is commonly used in automotive parts, construction materials, and general fabrication. Its compatibility with various coatings and finishes allows for versatile end-product applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. Compliance with these standards ensures quality and compatibility with local regulations.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Laser Cutting Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice in industries such as food processing and medical equipment. With a temperature rating of up to 800°C, it can withstand high temperatures without losing its integrity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, which extends the lifespan of products. However, it is generally more expensive than mild steel and can be more challenging to cut due to its higher melting point, which may require more powerful laser equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as kitchen equipment and medical devices. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for intricate designs and precise cuts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for grades (e.g., 304 vs. 316) can influence purchasing decisions.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Laser Cutting?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries. It typically has a melting point around 660°C, allowing for efficient cutting with laser technology.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces shipping costs and makes it easier to handle. However, it can be more expensive than mild steel, and its reflective properties can pose challenges during laser cutting, requiring specialized equipment to manage reflections.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is frequently used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aircraft components and automotive parts. Its ability to be anodized also enhances its aesthetic appeal and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Additionally, understanding local manufacturing capabilities for aluminum can affect sourcing decisions.
Why Is Acrylic a Popular Material for Laser Cutting?
Acrylic is a versatile plastic material that is often used for signage, displays, and decorative items. It has a relatively low melting point of around 100°C, making it easy to cut with lasers.
Pros & Cons: One of the main advantages of acrylic is its clarity and ability to be easily shaped, allowing for creative designs. However, it is less durable than metals and can be prone to scratching, which may limit its use in high-traffic applications.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is ideal for applications requiring transparency and aesthetic appeal, such as retail displays and lighting fixtures. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for intricate designs and smooth edges.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with local regulations regarding plastics, including recycling standards. Understanding local market demands for acrylic products can also inform purchasing strategies.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Used Laser Cutters
| Material | Typical Use Case for used laser cutters | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to rust | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, kitchen equipment | Corrosion resistant and durable | Higher cost and cutting difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | More expensive, reflective properties | Medium |
| Acrylic | Signage, decorative items | Versatile and easy to shape | Less durable, prone to scratching | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for used laser cutters, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on properties, advantages, limitations, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for used laser cutters
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Used Laser Cutters?
The manufacturing process for used laser cutters involves several critical stages that ensure the machines are reliable, efficient, and meet the demands of various industries. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: How Are Components Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting high-quality materials suitable for the laser cutter’s components. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and various alloys that can withstand high temperatures and provide durability.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo cutting, machining, and surface treatment processes. This preparation may include laser cutting or waterjet cutting for precision, followed by machining to achieve the desired dimensions. Surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming and Assembly of Laser Cutters?
Forming: What Methods Are Employed for Structural Integrity?
During the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into components using various techniques. Common methods include stamping, bending, and welding. Each technique is selected based on the specific part being manufactured. For instance, precision stamping is often used for intricate parts, while bending is crucial for creating frames and structural supports.
Welding is another vital technique employed, particularly in assembling the frame and structure of the laser cutter. Manufacturers typically use MIG or TIG welding to ensure strong, durable joints. This stage is critical for maintaining the structural integrity of the machine, as any weaknesses can lead to operational failures.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into a Complete Unit?
The assembly stage involves integrating all manufactured components into a complete laser cutting unit. This process requires skilled technicians who ensure that each part is correctly aligned and securely fastened. Key components such as the laser source, optics, and control systems are carefully assembled to minimize misalignments that could affect performance.
Quality assurance checks are performed throughout the assembly process to ensure that all components meet specified tolerances and quality standards. This stage often involves the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain precision during assembly.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for Used Laser Cutters?
Finishing processes are essential for the performance and aesthetics of used laser cutters. These processes can include surface polishing, painting, and the installation of protective coatings.
Surface polishing is often performed on critical components to ensure smooth operation and minimize friction. After polishing, parts may be painted or coated to protect against environmental factors, especially for machines intended for use in various climates, such as those found in Africa and the Middle East.
Additionally, final inspections are conducted to verify that the laser cutter meets all specifications and quality standards before it is shipped to the buyer.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Manufacturing Used Laser Cutters?
What International Standards Guide Quality Control?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for used laser cutters. Many manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for equipment used in the oil and gas industry may also be relevant. These certifications assure buyers that the products have undergone rigorous testing and meet strict safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each stage meets the required standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected for quality before they enter the production line. This may involve testing material properties or checking for physical defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, inspections are conducted to verify that components are being manufactured according to specifications. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and assembly accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the laser cutter is shipped, a comprehensive final inspection is performed. This includes testing the machine’s operational capabilities, safety features, and overall performance to ensure it meets all quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Suppliers?
What Methods Can Be Used to Assess Supplier Quality?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of suppliers when purchasing used laser cutters. One effective method is to conduct audits of the manufacturing facility. This allows buyers to assess the supplier’s adherence to quality standards, observe the manufacturing processes, and evaluate the overall work environment.
Additionally, buyers should request quality assurance reports and documentation that outline the supplier’s compliance with international standards. These documents often include test results, inspection records, and certification details.
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the equipment’s quality. These services can perform pre-shipment inspections to ensure that the laser cutter meets all specifications and is in optimal working condition.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are additional QC considerations to keep in mind. Buyers should be aware of the regulatory requirements specific to their region, as compliance with local standards is crucial for importing machinery.
Furthermore, understanding the nuances of warranty and service agreements can help mitigate risks associated with purchasing used equipment. Buyers should inquire about the availability of spare parts and support services in their region, as this can significantly impact the operational longevity of the laser cutter.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for used laser cutters is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, quality control standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘used laser cutters’
Introduction
When sourcing used laser cutters, a methodical approach is essential to ensure you acquire a machine that meets your operational needs while providing value for money. This guide outlines a comprehensive checklist to help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of purchasing used laser cutters. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that enhance your production capabilities.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your laser cutter. Consider factors such as the type of materials you will be cutting (e.g., metals, plastics, wood) and the thickness of those materials. Additionally, identify the necessary power output and cutting speed, as these will directly influence the efficiency and quality of your operations.
- Material Types: Different lasers excel with various materials; for example, CO2 lasers are ideal for thicker metals while fiber lasers are better for reflective materials.
- Power and Speed: Higher wattage generally means faster cutting, but also increased energy costs.
Step 2: Research Different Laser Technologies
Familiarize yourself with the different types of laser cutting technologies available, such as CO2, fiber, and crystal lasers. Each technology has its strengths and weaknesses depending on the application.
- CO2 Lasers: Best for cutting thick materials with excellent edge quality.
- Fiber Lasers: More energy-efficient and faster, suitable for engraving and cutting thin materials.
Step 3: Establish a Budget
Create a realistic budget that includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational costs such as maintenance, consumables, and energy consumption.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in potential costs for upgrades or modifications that might be necessary to meet your future production needs.
- Explore Financing Options: Investigate leasing or financing options that may make the acquisition more manageable.
Step 4: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Vet potential suppliers to ensure they are reputable and reliable. Look for suppliers who specialize in used machinery and have a proven track record in your industry.
- Request Documentation: Ask for machine history, maintenance records, and any certifications.
- Check Reviews and References: Seek testimonials or case studies from other businesses that have purchased from the supplier.
Step 5: Inspect the Equipment
If possible, conduct a physical inspection of the laser cutter before purchase. This allows you to assess the machine’s condition, functionality, and any wear and tear that may affect its performance.
- Look for Signs of Wear: Check for rust, damaged components, or any modifications that could indicate past issues.
- Test the Machine: If feasible, run a demonstration to see the machine in action and verify its performance metrics.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a machine, negotiate the terms of the purchase. This includes price, warranty, delivery terms, and after-sales support.
- Understand Warranty Options: Ensure you know what is covered and for how long, as this can save you from unexpected costs later.
- Clarify Delivery and Installation: Confirm who is responsible for transportation and whether installation support is included.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Arrange Training
After securing the best deal, finalize the purchase and arrange for necessary training for your team. Proper training can significantly enhance productivity and ensure safe operation of the equipment.
- Include Training in the Agreement: Ensure that the supplier provides training on machine operation and maintenance.
- Develop a Maintenance Schedule: Establish a routine maintenance plan to extend the lifespan of your laser cutter.
By following this structured checklist, you can confidently navigate the sourcing process for used laser cutters, ensuring that you make a sound investment that meets your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for used laser cutters Sourcing
When sourcing used laser cutters, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and buyer tips to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Used Laser Cutters?
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials used in the manufacturing of laser cutters significantly impacts pricing. High-quality components, such as optics and laser sources, contribute to the overall cost. Buyers should assess the material quality to ensure durability and performance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and maintenance. The labor cost can vary significantly based on the region and the complexity of the laser cutting technology. This factor is particularly important for buyers considering equipment from different geographical locations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with advanced facilities may charge a premium, reflecting their investment in technology and quality assurance.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can add to the cost, especially for specialized applications. Buyers should evaluate whether existing tooling can be adapted or if new tooling is required, influencing the overall investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that the equipment meets industry standards. Certifications such as ISO can add to the cost but provide assurance regarding quality and reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary depending on the origin and destination of the equipment. International shipping, customs duties, and insurance should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Influences the Price of Used Laser Cutters?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases may lead to discounts, making it essential for buyers to consider their operational needs and potential for scaling.
-
Specifications and Customization: The more specialized the equipment, the higher the price. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
-
Material Type: The type of laser cutter, whether CO2 or fiber, and its application can influence pricing. Fiber lasers, for example, often have lower operating costs but may come at a higher initial price.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment with recognized certifications or from reputable brands may command higher prices but often provide better reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and customer service can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer warranties or post-sale support, which can justify higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Deals?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage knowledge about market prices and supplier competition. Be prepared to negotiate on terms, including payment schedules and warranties.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also long-term operational costs, including energy consumption, maintenance, and potential downtime.
-
Research Pricing Nuances: Understand regional pricing variations, as costs can differ significantly based on local market conditions and availability of parts or service support.
-
Seek Value-Added Services: Look for suppliers who offer installation, training, and ongoing support as part of the purchase, enhancing the overall value of the investment.
-
Be Cautious with Indicative Prices: Always treat listed prices as indicative. Factors such as market demand, equipment condition, and negotiation outcomes can lead to significant variations.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics for used laser cutters can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By evaluating these factors carefully, companies can optimize their procurement strategies and enhance their operational efficiencies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing used laser cutters With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Used Laser Cutters in Industrial Applications
When considering the acquisition of cutting technology, B2B buyers often evaluate various solutions to meet their manufacturing needs. While used laser cutters offer precision and versatility, alternative technologies can also fulfill similar roles in metal and material processing. This analysis compares used laser cutters with two viable alternatives: plasma cutting and waterjet cutting.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Used Laser Cutters | Plasma Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, intricate cuts; suitable for a variety of materials | Good for thick materials; less precision | Excellent for thick materials; no heat-affected zone |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; lower operational costs over time | Generally lower initial cost; higher operational costs | Higher initial investment and operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific setup and training; often integrates well with CNC systems | Easier to set up; widely available technology | More complex setup due to water management systems |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; wear on consumables | Higher maintenance; components can be costly |
| Best Use Case | Thin to medium thickness materials; intricate designs | Thick metals; less precision required | Thick materials; intricate shapes without thermal distortion |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting is a widely used method for cutting conductive materials, including steel, aluminum, and copper. The technology operates by sending a gas through a focused nozzle and generating an electric arc that ionizes the gas, creating plasma. This method is advantageous for its cost-effectiveness and speed, particularly in cutting thick materials. However, while plasma cutting is generally easier to implement, it lacks the precision of laser cutting, which may be a disadvantage for applications requiring intricate designs. Additionally, the heat generated can lead to a rougher edge quality compared to laser cutting.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through materials. This technology is unique in that it does not produce heat, thus eliminating the heat-affected zone that can distort materials. Waterjet cutting is particularly effective for thick materials and is versatile enough to cut a wide range of substances, from metals to composites and even food products. The initial investment and operational costs can be higher than those of laser and plasma cutting, and the setup can be more complex. However, its ability to maintain material integrity makes it a favorable choice for sensitive applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cutting Solution
For B2B buyers evaluating cutting technologies, the choice between used laser cutters and alternatives such as plasma and waterjet cutting hinges on specific operational requirements. If precision and intricate cutting are paramount, used laser cutters present a compelling case despite a potentially higher initial investment. Conversely, for applications involving thicker materials or where cost-effectiveness is crucial, plasma cutting may be more suitable. Waterjet cutting stands out for its versatility and ability to handle various materials without thermal distortion, making it ideal for specialized applications. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each technology will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for used laser cutters
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Buying Used Laser Cutters?
When evaluating used laser cutters, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications to consider:
1. Power Output (Wattage)
The power output of a laser cutter, measured in watts, determines its cutting capability. Higher wattage allows for cutting thicker materials and achieving faster processing times. In B2B contexts, selecting the appropriate power output is essential for optimizing production efficiency and material compatibility. For instance, a 3000W fiber laser is typically suited for cutting metals, while a 6000W laser can handle thicker sections with ease.
2. Material Compatibility
Different laser types, such as CO2 and fiber lasers, have varying capabilities when it comes to material cutting. CO2 lasers are more effective for non-metal materials (like wood and plastics), while fiber lasers excel at cutting metals, especially reflective materials. Understanding which materials your operations require helps ensure that the chosen laser cutter aligns with production needs, thereby reducing operational downtime.
3. Cutting Speed
Cutting speed refers to how quickly a laser can make cuts, usually measured in inches per minute (IPM). This metric is vital for assessing productivity levels. A machine that can cut faster without sacrificing quality can significantly enhance throughput, which is particularly important in industries with high-volume demands. For example, a faster cutting speed can lead to lower labor costs and improved delivery times for B2B transactions.
4. Precision and Tolerance
Precision is critical in laser cutting, and it is often measured in terms of tolerance, which refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. Tighter tolerances yield higher-quality parts, which is essential in sectors like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. B2B buyers must evaluate a machine’s precision capabilities to ensure they meet industry standards and customer specifications.
5. Work Area Size
The work area or bed size of a laser cutter defines the maximum dimensions of the materials that can be processed. This is particularly important for businesses that handle large or bulky materials. A larger work area can offer greater flexibility and efficiency, enabling manufacturers to cut multiple parts simultaneously, thus optimizing material usage and reducing waste.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Used Laser Cutters?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and transactions. Here are several important terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser cutters, knowing the OEM helps buyers ascertain the quality and reliability of the equipment, as established brands often offer better support and parts availability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to negotiate better pricing and ensure they can meet their production needs without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products or services. For buyers of used laser cutters, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, ensuring they receive competitive quotes and detailed specifications.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk allocation, and delivery responsibilities, which are critical when importing used machinery from overseas.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who need to manage their production schedules effectively. Understanding lead times can help businesses plan better and avoid disruptions in their supply chain.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when purchasing used laser cutters, ensuring they select machines that align with their operational requirements and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the used laser cutters Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Used Laser Cutters Sector?
The used laser cutters market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for precision cutting in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics is a significant driver. As manufacturers seek to enhance operational efficiency and reduce production costs, the adoption of laser technology, known for its speed and precision, has become a priority. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and the need for custom fabrication solutions have led to an uptick in the demand for versatile cutting equipment.
Emerging trends include the shift towards fiber laser technology, which offers faster cutting speeds and lower operational costs compared to traditional CO2 lasers. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where cost efficiency is paramount. Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 is prompting manufacturers to invest in smart technologies, including automation and IoT, to enhance the functionality of laser cutters. For B2B buyers, sourcing equipment that integrates these technologies can lead to significant competitive advantages.
As the market evolves, geographical dynamics also play a crucial role. Regions such as Europe and the Middle East are witnessing a surge in investments in advanced manufacturing technologies, driven by government initiatives aimed at boosting industrial competitiveness. For buyers in these areas, understanding local market conditions and regulations is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Their Procurement of Used Laser Cutters?
In today’s business landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing are not just trends; they are essential components of a responsible procurement strategy. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including laser cutting, is significant, making it crucial for B2B buyers to consider the sustainability of their equipment choices. Used laser cutters often come with a reduced carbon footprint compared to new machines, as they extend the lifecycle of existing equipment and minimize waste.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical supply chains. This includes transparency in sourcing materials and adherence to environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 can indicate a supplier’s commitment to environmental management, while other ‘green’ certifications may highlight the use of sustainable practices in manufacturing and supply chain operations.
Moreover, incorporating energy-efficient technologies, such as fiber lasers, not only reduces operational costs but also lowers energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, adopting these practices can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Evolution of Laser Cutting Technology and Its Importance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of laser cutting technology has transformed the manufacturing landscape over the past few decades. Initially introduced in the 1960s for industrial applications, laser cutting was primarily limited to CO2 lasers, which were effective but less efficient compared to modern alternatives. The introduction of fiber laser technology in the early 2000s marked a significant breakthrough, offering higher efficiency, faster cutting speeds, and reduced operational costs.
For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of laser cutting technology is essential in making informed purchasing decisions. The advancements in laser technology not only improve the quality of cuts but also expand the range of materials that can be processed. This evolution has led to increased versatility in applications, making laser cutters indispensable in various sectors, from aerospace to medical device manufacturing.
As buyers navigate the used laser cutter market, recognizing these technological advancements can inform their choices, ensuring they invest in equipment that meets current and future manufacturing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of used laser cutters
-
How do I choose the right type of used laser cutter for my business needs?
Selecting the right laser cutter depends on the materials you plan to work with and the specific applications. For example, CO2 lasers are excellent for cutting thick materials like metal and are often used in industries like food packaging. In contrast, fiber lasers are more efficient for cutting thinner materials and can operate at lower costs. Consider the power requirements, cutting speed, and the intricacy of designs you need to achieve. Research the specifications and capabilities of various models to ensure they align with your production goals. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for used laser cutters?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation, industry experience, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality. Verify the supplier’s certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, assess their after-sales support, including installation, maintenance services, and warranty terms. A reputable supplier should be transparent about the machine’s history, including usage, maintenance records, and any modifications made. -
What are the typical payment terms when purchasing used laser cutters internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common arrangements include full upfront payment, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or payment through a letter of credit. It’s essential to clarify these terms before finalizing the deal. Consider negotiating terms that provide you with sufficient time to inspect the machine upon arrival, ensuring it meets your expectations and specifications. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for used laser cutters?
Minimum order quantities can vary based on the supplier and the type of machine. Many suppliers may not have a strict MOQ for used equipment, allowing buyers to purchase single units. However, for custom configurations or specialized models, there may be an MOQ to justify production or sourcing costs. Always confirm with the supplier regarding any MOQ requirements and discuss the possibility of ordering additional machinery if future needs arise. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when buying used laser cutters?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation regarding the machine’s maintenance history, including any repairs or upgrades. Conduct a thorough inspection, ideally on-site, or ask for a video demonstration of the equipment in operation. Many reputable suppliers will offer a warranty or guarantee period, providing you with additional peace of mind. Engaging a third-party inspection service can also help verify the machine’s condition before purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing used laser cutters?
Logistics is a critical aspect of importing used laser cutters. Consider shipping methods, costs, and transit times. Ensure that the supplier provides proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. Familiarize yourself with customs regulations in your country, as specific documentation may be required for import. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs clearance and arrange for local transportation once the equipment arrives. -
Can I customize a used laser cutter to fit my specific production needs?
Many used laser cutters can be customized, depending on the supplier and the machine’s design. Common modifications may include changes to the laser head, software updates, or additional attachments for different materials. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier to determine what modifications are feasible. Keep in mind that extensive customization may affect the cost and delivery timeline, so factor this into your budget and planning. -
What are the advantages of purchasing used laser cutters over new ones?
Purchasing used laser cutters often presents significant cost savings compared to new models. Used machines can be acquired at a fraction of the price, allowing businesses to invest in additional equipment or upgrades. Moreover, many used laser cutters still have substantial operational life remaining, especially if well-maintained. Additionally, used equipment can often be delivered more quickly than new units, which may have longer lead times due to manufacturing processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Used Laser Cutters Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Laser Cutters – Key Product Details
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details:
– Types of CNC Laser Cutters: Gas Laser Cutting, Crystal Laser Cutting, Fiber Laser Cutting
– Brands Available: AMADA, MITSUBISHI, MAZAK, TRUMPF, BYSTRONIC, AP LAZER, BOSS LASER, LASERPRO, LVD STRIPPIT, TROTEC, BODOR, CINCINNATI, COHERENT, HK LASER & SYSTEMS, HYPERUSA, IPG PHOTONICS, NUKON, ROBOTEC, ROFIN
– Models Listed: ENSIS 3015, FM-D, FO3015NT, LAP4836-1808W, ML3015LVPS, …
2. Mazak – 7000 Watt Optiplex Nexus
Domain: revelationmachinery.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Used Laser Cutting Machines for Sale including CO2 Lasers, Fiber Lasers, Tube Lasers, and Laser Engravers. Brands include Cincinnati, Amada, Mazak, and more. Inventory features various lengths and capacities. Notable machines include: 7000 Watt Mazak Optiplex Nexus (2022), 4000 Watt Trumpf TruLaser 3030 (2017), 50 Watt eCobalt 50PF-LMT (2024), 12000 Watt Bodor P3 (2023), 15000 Watt Bystronic Bysta…
3. OMTech – Certified Pre-Owned Laser Engravers
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Pre-Owned Fiber, CO2 Laser Engravers Machines – OMTech Certified CO2 laser engravers and Fiber laser metal marking machines priced up to 30% below new machine purchases. Each refurbished machine is inspected by OMTech engineers, ensuring full functionality and restoration to original condition. Example product: Pre-Owned MF1624-60 – 60W CO2 Laser Engraver Cutting Machine with 16” x 24” Working Are…
4. Cloudray – 110V 100W CO2 Laser Power Supply
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Metalworking Laser Cutting Machines for sale on eBay. Key products include: 1. Cloudray 110V 100W CO2 Laser Power Supply for CO2 Engraver Cutter – $169.99 (New) 2. Cloudray 110V 80W CO2 Laser Power Supply for CO2 Cutting Machine – Price not specified 3. Creality Laser Engraver 10W Laser Cutter for Personalized Gifts – $279.00 (Brand New) 4. Ortur 20w Laser Module for Laser Engraving/Cutting – $529…
5. Used CNC Laser Cutters – KD Capital Equipment
Domain: kdcapital.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutters for Sale – KD Capital Equipment offers a variety of used laser cutting machines. The inventory includes brands such as Amada, BLM, Bystronic, Cincinnati, Mitsubishi, Trumpf, and more. Key specifications include year of manufacture, table width and length, and maximum wattage. Examples of available machines include: 2024 Bescutter BC-2000W Water Cooled Handheld Fiber Laser We…
6. Laser Cutters – High-Power Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: machinetools.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutters for sale listings on MachineTools.com include various models and specifications. Key details extracted include:
– Types: Laser Cutters
– Function: Cuts materials using a high-power laser directed by computer.
– Availability: 649 machines listed for sale.
– Brands: Notable brands include TRUMPF (96), AMADA (80), BYSTRONIC (78), MITSUBISHI (36), MAZAK (26), and others.
– Control Types:…
7. AtomStack – A5 Pro Laser Engraver
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, AtomStack – A5 Pro Laser Engraver, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. TRUMPF – Used CNC Laser Cutter
Domain: machineseeker.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutter for sale on Machineseeker.com – many listings online now. Key details include:
– Manufacturer: TRUMPF, Mazak, Gildemeister, BIESSE, Deckel Maho, DECKEL, SCM, DMG MORI, Mori Seiki, Okuma, Bystronic, DOOSAN, FLIEGL, INDEX, HERMLE.
– Model: Various models available.
– Price: Starting from €3.69 per listing/month.
– Year of manufacture: Range from 1990 to 2025.
– Condition: New,…
9. Surplex – Used Metal Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: surplex.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Used Metal Laser Cutting Machines available for auction, including brands such as FREUTEK, Bystronic, and Trumpf. Various models include CO2 and fiber laser cutting machines with power ratings ranging from 20W to 4kW. Locations include Germany, Spain, Italy, and Hungary. Auctions feature machines like the Bystronic BYTRANS CO2 Laser Cutting Machine (2008), Trumpf TruLaser 5030 (2008), and various …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for used laser cutters
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Investment in Used Laser Cutters?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of used laser cutters offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the various types of laser cutting technology—such as CO2, fiber, and crystal lasers—buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs. The ability to procure high-quality equipment at a fraction of the cost of new machines not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to sustainability goals by reducing waste and resource consumption.
As you consider your next investment, prioritize sourcing from reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive support, including maintenance and training. This can significantly mitigate risks associated with used machinery. Furthermore, leveraging advanced technologies and automation in your processes can lead to greater precision and productivity, positioning your business for long-term success.
Looking ahead, the demand for used laser cutters is expected to grow as industries continue to embrace advanced manufacturing technologies. Seize this opportunity to enhance your competitive edge by investing wisely in used laser cutting equipment. Connect with trusted suppliers today to explore your options and elevate your manufacturing capabilities.