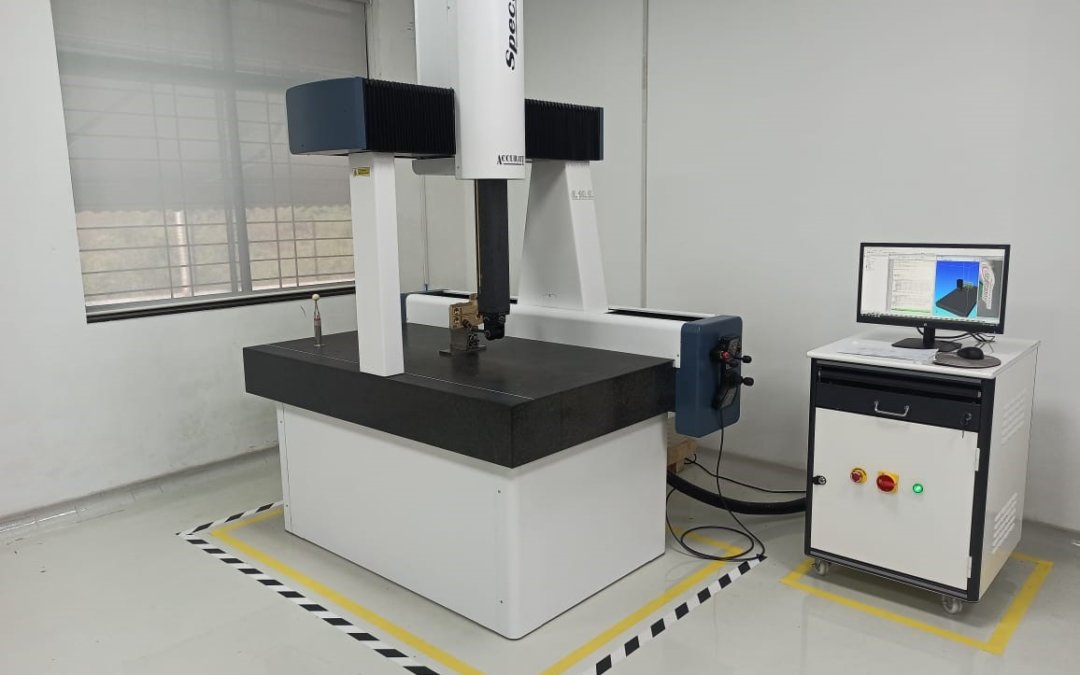
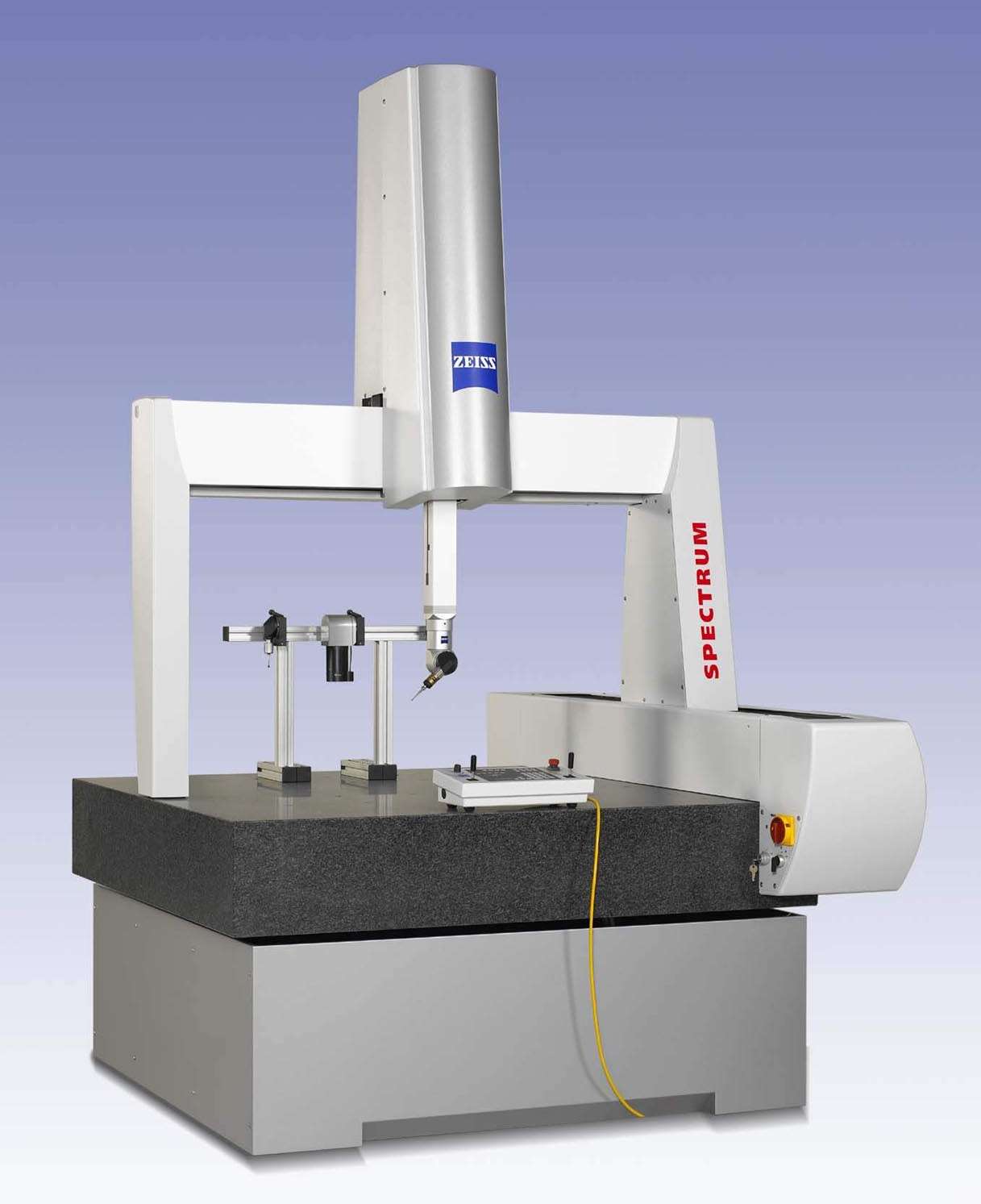
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for used coordinate measuring machine
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and quality assurance, sourcing a reliable used coordinate measuring machine (CMM) can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexity of these machines, combined with the need for precise calibration and performance assurance, makes the procurement process daunting. This guide aims to demystify the global market for used CMMs by providing insights into various types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when making a purchase. Whether you are a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia seeking to enhance your production capabilities or a quality control manager in Nigeria looking for cost-effective solutions, understanding the nuances of used CMMs is essential for informed decision-making.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different categories of CMMs, their applications across diverse industries, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality and reliability. Additionally, we will address cost considerations and maintenance practices that can significantly affect your investment’s longevity and performance. By equipping you with the necessary knowledge and actionable insights, this guide empowers international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to navigate the used CMM market confidently, ensuring that your organization can achieve optimal efficiency and precision in your operations.
Understanding used coordinate measuring machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge CMM | Fixed structure with a bridge-like design; ideal for precision measurements in small to medium parts. | Aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. | Pros: High accuracy, versatile for various parts. Cons: Limited to smaller workpieces; requires significant floor space. |
| Gantry CMM | Larger, often floor-mounted design; capable of handling oversized components and materials. | Heavy machinery, aerospace components, and large assemblies. | Pros: Excellent for large parts; robust design. Cons: Higher initial investment; may require specialized installation. |
| Portable CMM | Compact and lightweight; can be used in various locations, including shop floors. | Field measurements, quality control in diverse environments. | Pros: Flexibility and mobility; cost-effective. Cons: Generally less accurate than fixed CMMs; may require skilled operators. |
| Horizontal Arm CMM | Features a horizontal arm structure; suited for measuring large, flat parts. | Sheet metal fabrication, automotive, and large assemblies. | Pros: Good for flat and large components; less floor space needed. Cons: Limited to specific shapes; may have lower accuracy than bridge types. |
| Optical CMM | Utilizes laser or optical technology for non-contact measurements; ideal for delicate parts. | Electronics, optics, and precision engineering. | Pros: Non-contact measurement; suitable for fragile components. Cons: Higher operational costs; sensitive to environmental conditions. |
What are the Characteristics of Bridge CMMs and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Bridge coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are characterized by their fixed structure, which consists of a bridge supported by vertical columns. This design allows for precise measurements of small to medium-sized parts, making them suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. When considering a bridge CMM, buyers should evaluate the machine’s calibration history and the types of probes available, as these factors significantly influence measurement accuracy and versatility in various applications.
Why Choose Gantry CMMs for Large-Scale Measurements?
Gantry CMMs are distinguished by their large, floor-mounted frameworks, which enable them to accommodate oversized components and assemblies. They are particularly beneficial in sectors that require the measurement of heavy machinery or aerospace components. Buyers should consider the installation requirements and the potential need for specialized training, as these machines often involve complex operations due to their size and capabilities.
How Do Portable CMMs Enhance Flexibility in Measurement?
Portable CMMs offer the advantage of being lightweight and easily transportable, making them ideal for field measurements and quality control in diverse environments. Their versatility allows for on-site inspections, which can save time and reduce the need for transporting parts to a fixed location. Buyers should assess the accuracy requirements of their applications since portable CMMs may not achieve the same precision as stationary models.
What Are the Advantages of Horizontal Arm CMMs for Flat Parts?
Horizontal arm CMMs are designed with a horizontal arm structure, making them particularly effective for measuring large, flat components. This type of CMM is commonly used in sheet metal fabrication and automotive assembly. When purchasing a horizontal arm CMM, buyers should consider the machine’s ability to handle specific shapes and its overall accuracy, as these factors can impact production efficiency.
Why Consider Optical CMMs for Delicate Measurements?
Optical CMMs use laser or optical technology to perform non-contact measurements, making them ideal for delicate parts found in electronics and precision engineering. Their non-invasive approach minimizes the risk of damaging sensitive components. Buyers should evaluate the operational costs and environmental factors that could affect the performance of optical CMMs, as these machines require specific conditions to maintain measurement integrity.
Key Industrial Applications of used coordinate measuring machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of used coordinate measuring machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision measurement of aircraft components and assemblies | Enhanced safety and compliance with strict regulations | Calibration history and previous usage environment |
| Automotive | Quality control of automotive parts and assembly lines | Improved product quality and reduced rework costs | Compatibility with existing systems and software |
| Electronics | Inspection of circuit boards and electronic components | Increased accuracy in production and reduced defects | Probing systems and software capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Measurement of surgical instruments and implants | Ensured compliance with regulatory standards | Certification and calibration records |
| Oil & Gas | Inspection of drilling equipment and components | Increased operational efficiency and safety | Previous operational environment and maintenance history |
How Are Used Coordinate Measuring Machines Applied in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, used coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are essential for the precision measurement of aircraft components and assemblies. These machines ensure that parts meet stringent safety and regulatory standards, which is critical in a sector where even minor discrepancies can lead to significant safety risks. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing CMMs with a documented calibration history and knowledge of the machine’s previous operational environment to ensure reliability and accuracy.
What Role Do Used CMMs Play in Automotive Quality Control?
In automotive manufacturing, used CMMs are employed for rigorous quality control of parts and assembly lines. They help in measuring complex geometries and ensuring that components fit together correctly, thereby enhancing product quality and minimizing rework costs. For international buyers, it is vital to assess the compatibility of the CMM with existing systems and software to facilitate seamless integration into their quality assurance processes.
How Are Used CMMs Beneficial in Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics sector utilizes used CMMs to inspect circuit boards and various electronic components. These machines provide increased accuracy in production, significantly reducing defects and enhancing product reliability. When sourcing used CMMs for electronics manufacturing, buyers should focus on the probing systems and software capabilities, ensuring they can handle the specific requirements of electronic component measurement.
Why Are Used CMMs Important for Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, used CMMs are crucial for measuring surgical instruments and implants to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Accurate measurements are vital for patient safety and product efficacy. Buyers in this field should look for CMMs that come with certification and calibration records, confirming their ability to meet the high standards required in medical manufacturing.
How Do Used CMMs Enhance Operations in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas industry, used CMMs are employed for the inspection of drilling equipment and components, contributing to increased operational efficiency and safety. Accurate measurements help in identifying potential issues before they escalate into costly problems. Buyers should consider the previous operational environment and maintenance history of the used CMMs, as these factors can significantly impact performance and longevity in demanding conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘used coordinate measuring machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Uncertainties in Machine Condition
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant uncertainty regarding the condition and reliability of used coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). When purchasing from auctions or less reputable dealers, buyers risk acquiring equipment that may not perform as expected. This can lead to operational downtime, increased costs, and compromised quality control, which is particularly concerning for manufacturers in regions with strict compliance standards.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize sourcing used CMMs from reputable dealers who provide comprehensive inspection reports and certification of the machines. Before finalizing a purchase, buyers should request detailed documentation, including maintenance history and performance evaluations. Additionally, working with a dealer that offers a warranty can provide peace of mind. It’s advisable to conduct a pre-purchase inspection where a qualified technician evaluates the machine on-site to assess its condition and functionality. This proactive approach ensures that the machine will meet production needs without unexpected failures.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Existing Systems
The Problem: Another common challenge for B2B buyers is ensuring that a used CMM is compatible with their existing software and operational processes. Buyers often discover post-purchase that the machine cannot integrate seamlessly with their current quality assurance systems, leading to inefficiencies and additional costs for upgrades or replacements.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their existing systems before purchasing a used CMM. This includes identifying the software currently in use and checking compatibility with the CMM’s software package. Engaging with the dealer to understand the software capabilities of the used machine is essential. Buyers should ask about the potential for software updates and whether the dealer can assist with integration. If necessary, consider investing in additional training for staff to familiarize them with the new system, ensuring that the transition is smooth and does not disrupt production schedules.
Scenario 3: Misjudging Technical Support and Maintenance Needs
The Problem: Many buyers underestimate the ongoing technical support and maintenance required for used CMMs. Insufficient understanding of these needs can lead to increased downtime and costly repairs, particularly in regions where access to qualified technicians is limited. This pain point is exacerbated in markets like Africa and South America, where technical support may not be readily available.
The Solution: Buyers should proactively inquire about the availability of technical support and maintenance services before purchasing a used CMM. Opting for machines from dealers who provide post-sale support is crucial. This includes access to trained technicians who can assist with calibration, repairs, and software updates. It’s beneficial to establish a maintenance schedule upon acquisition, ensuring regular checks and servicing to maintain optimal machine performance. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in training for their staff on routine maintenance tasks, empowering them to handle minor issues independently and reducing reliance on external support.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in used coordinate measuring machines, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and product quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for used coordinate measuring machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Coordinate Measuring Machines?
When selecting a used coordinate measuring machine (CMM), the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in CMM construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Versatile Choice
Aluminum is often used in the structural components of CMMs due to its lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It has good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environments, including those with high humidity or exposure to certain chemicals.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for complex designs without significantly increasing costs. Its lightweight nature facilitates easier handling and installation.
Cons: While durable, aluminum is less rigid than steel, which can lead to deformation under extreme loads or high temperatures. It may also require surface treatments to enhance durability.
Impact on Application: Aluminum CMMs are compatible with a wide range of media, but their performance may degrade in high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum alloys. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary widely, understanding local corrosion risks is essential.
Steel: The Backbone of Durability
Steel is a traditional material choice for CMMs, particularly in applications requiring high rigidity and stability. Its high temperature and pressure ratings make it suitable for heavy-duty operations.
Pros: Steel offers superior durability and resistance to deformation, ensuring long-term performance. It is also widely available and can be sourced locally in many regions.
Cons: The main drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or treatments. Additionally, steel CMMs can be heavier, complicating transportation and installation.
Impact on Application: Steel CMMs are ideal for environments where heavy parts need to be measured, but they may not be suitable for corrosive environments without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards for steel grades is crucial, especially in regions with specific regulations. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should also consider the implications of weight on shipping costs.
Granite: Precision and Stability
Granite is a favored material for the measuring surfaces of CMMs due to its inherent stability and precision. It is non-deformable and provides a stable base for measurements.
Pros: Granite’s thermal stability and resistance to wear make it an excellent choice for high-precision applications. It also has a natural ability to resist corrosion.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of granite is its brittleness; it can crack or chip under impact. Additionally, granite CMMs are typically more expensive due to the material’s cost and the complexity of manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Granite is highly suitable for environments requiring high precision, such as aerospace and automotive industries, but care must be taken to avoid physical shocks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the granite meets international standards for flatness and hardness. In regions with high humidity, additional considerations for maintenance may be necessary.
Composite Materials: The Future of CMMs
Composite materials, including carbon fiber and polymer blends, are increasingly used in CMM construction due to their unique properties. They offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to thermal expansion.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific applications, allowing for customization. They also resist corrosion and are less prone to thermal deformation.
Cons: The main limitation is the higher cost of composite materials compared to traditional options. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in industries where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace, but they may not be suitable for all environments due to cost considerations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the availability of composite materials in their region and consider compliance with international standards. For markets in Africa and South America, understanding the local supply chain for composites is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Used Coordinate Measuring Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for used coordinate measuring machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components in lightweight CMMs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less rigid, may deform under load | Low |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications requiring high rigidity | Superior durability and stability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Granite | Measuring surfaces for high-precision applications | Excellent stability and precision | Brittle, can crack under impact | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications in aerospace and automotive | Lightweight and customizable | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for used coordinate measuring machines, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for used coordinate measuring machine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Used Coordinate Measuring Machines?
When considering the procurement of a used coordinate measuring machine (CMM), understanding the manufacturing processes involved can provide valuable insights into the quality and reliability of the equipment. The production of CMMs typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for CMM Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first stage in the manufacturing of CMMs, where high-quality materials, primarily metals and composites, are selected based on their mechanical properties. Steel and aluminum are common choices due to their strength and stability, which are essential for maintaining the precision of measurements. The materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications, including hardness tests and dimensional inspections.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in CMM Production?
Forming techniques play a crucial role in shaping the components of a CMM. Techniques such as CNC machining, casting, and milling are commonly employed to create the intricate parts of the machine, such as the frame, base, and measurement arms. CNC machining, in particular, ensures high precision and repeatability, which are vital for the accuracy of the CMM. Each component is machined to tight tolerances to guarantee proper fit and function in the assembly stage.
How Are Components Assembled in CMMs?
The assembly stage is where the various components come together to form the complete CMM. This process involves skilled technicians who meticulously align and secure parts, ensuring that all mechanical and electronic systems function cohesively. During assembly, careful attention is given to the installation of the probe systems, which are essential for the measurement capabilities of the machine. The assembly area is typically kept clean and controlled to prevent contamination that could affect the machine’s performance.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Used CMMs?
Finishing processes enhance both the aesthetics and functionality of the CMM. This stage may include surface treatments, painting, and the application of protective coatings. Finishing not only contributes to the machine’s durability but also aids in corrosion resistance, which is crucial for machines used in various industrial environments. Each finishing step is closely monitored to ensure compliance with industry standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented for Used CMMs?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of used coordinate measuring machines. To ensure that these machines meet international standards, several quality control measures are implemented throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Apply to CMM Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, it is essential to be aware of international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which sets the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates that the manufacturer has established processes to ensure consistent quality in their products. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API standards may apply, depending on the intended application of the CMM.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. The typical checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that these inputs meet specified standards is crucial for the overall quality of the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various tests and inspections are conducted to monitor quality. This includes checking tolerances during machining and ensuring proper assembly techniques are followed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the CMM is fully assembled, it undergoes comprehensive testing to verify its performance and accuracy. This includes calibrating the machine and conducting functional tests to ensure it meets the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers looking to source used CMMs should actively verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. This can be achieved through:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s quality management practices and manufacturing processes firsthand. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality control and compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can provide insight into the testing procedures and results for the specific machines of interest. These reports should outline any calibration processes and performance metrics.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging a third-party inspection service can offer an unbiased evaluation of the machine’s condition and compliance with quality standards. This step is particularly beneficial for international transactions, where buyers may not have direct access to the supplier’s facilities.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding quality assurance.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and industry standards that may impact the importation and use of used CMMs. Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices can pose challenges, making it essential to establish clear communication channels with suppliers.
Furthermore, considering the logistics of shipping and installation is crucial. Ensuring that the used CMM arrives in optimal condition requires careful planning, including proper packing and handling during transit. Buyers should also inquire about the availability of support services, such as installation and calibration, to ensure the machine operates effectively once on-site.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with used coordinate measuring machines can significantly enhance the decision-making process for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can ensure they are investing in reliable equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘used coordinate measuring machine’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring a used coordinate measuring machine (CMM), this guide offers a clear checklist of steps to follow. By adhering to these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions, maximizing value while minimizing risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search, clarify the specific requirements for your CMM. Consider factors such as the type of measurements you need, the materials you will be working with, and the precision level required.
– Size and Capacity: Evaluate the dimensions and weight limits based on your workspace and the items you will measure.
– Measurement Range: Ensure the CMM can handle the range of measurements necessary for your applications.
Step 2: Research Market Prices
Understanding the market value of used CMMs is crucial for making a sound investment. Research prices across various platforms and suppliers to identify competitive pricing.
– Compare Listings: Utilize resources like online marketplaces and industry-specific websites to gather price data.
– Consider Additional Costs: Factor in potential costs for shipping, installation, and any required calibration services.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including years of experience and customer testimonials.
– Check Certifications: Look for suppliers with industry certifications or memberships in professional organizations, which can indicate credibility.
– Review Case Studies: Ask for examples of previous successful sales to businesses similar to yours.
Step 4: Inspect the Equipment Thoroughly
When you find a suitable CMM, prioritize a comprehensive inspection. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to assess the machine firsthand.
– Operational Testing: Verify that the CMM operates correctly and meets your specified accuracy requirements.
– Condition Reports: Request maintenance records and any previous inspection reports to understand the machine’s history.
Step 5: Verify Calibration and Software Compatibility
Ensure the used CMM is calibrated and that its software is compatible with your existing systems. Calibration is critical for maintaining measurement accuracy.
– Calibration Status: Confirm the date of the last calibration and inquire about any necessary recalibration services.
– Software Checks: Ensure the machine’s software is up to date and compatible with your operational needs.
Step 6: Assess Warranty and Support Options
A reliable warranty and support system can protect your investment. Inquire about the warranty terms and available post-purchase support.
– Warranty Coverage: Understand what is included in the warranty, such as parts and labor, and the duration of the coverage.
– Technical Support: Check if the supplier offers ongoing support, such as maintenance services or training for your team.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase with Clear Terms
Once you have selected a supplier and machine, ensure that all purchase terms are clearly defined in a contract. This should include payment terms, delivery schedules, and any conditions for returns or exchanges.
– Document Everything: Keep a record of all communications and agreements to avoid misunderstandings later.
– Clear Delivery Expectations: Set explicit expectations regarding delivery timelines and installation processes.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing a used coordinate measuring machine, ultimately ensuring a successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for used coordinate measuring machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Used Coordinate Measuring Machines?
When sourcing used coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of the machine itself, including any necessary components or accessories, plays a significant role. The type of materials used in the construction of the CMM can influence pricing. For instance, machines made from high-grade metals or specialized composites may command higher prices due to their durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with refurbishment, calibration, and maintenance of used CMMs. Skilled technicians are needed to ensure that the machines are operating correctly and accurately. Labor costs may vary significantly depending on the region and the level of expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facilities and utilities required to refurbish and maintain the machines. Overhead can vary by supplier and geographic location.
-
Tooling: The cost of any specialized tooling or probes needed for the CMM is an important consideration. Probes can be expensive, and their condition should be assessed prior to purchase.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures that the used CMM meets industry standards. This may involve additional costs for testing and certification.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, especially for large machines. International buyers must consider customs duties, taxes, and insurance when importing CMMs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Used CMMs?
Several factors influence the pricing of used coordinate measuring machines:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer lower prices for larger orders, which can be beneficial for companies looking to equip multiple facilities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific technical specifications can increase the cost of a CMM. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines with documented quality certifications and high-grade materials typically come at a premium. Buyers should verify the certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a history of reliability may charge more but often offer better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and liability. This can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Used CMMs?
To maximize value and minimize costs when sourcing used coordinate measuring machines, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Many sellers expect some negotiation, and being informed about market prices can help you secure a better deal.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may lead to higher long-term costs if the machine requires extensive repairs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import regulations. This knowledge can help in negotiating better terms and understanding the overall cost implications.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on the machine’s history, condition, and the seller’s reputation. Request maintenance records and performance reports to assess the machine’s reliability.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices for used CMMs can vary widely based on condition, specifications, and supplier. Always seek quotes tailored to your specific needs to get an accurate picture of expected costs.
By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing used coordinate measuring machines, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing used coordinate measuring machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Used Coordinate Measuring Machines
When considering the acquisition of a used coordinate measuring machine (CMM), it’s essential to evaluate not only the merits of this solution but also viable alternatives that may suit your operational needs. This analysis compares used CMMs with other measurement technologies, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Used Coordinate Measuring Machine | Optical Measurement Systems | Laser Scanning Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy and repeatability with calibrated systems. | Good for surface measurements, but less precise than CMMs. | High detail capture for complex geometries but may require post-processing. |
| Cost | Generally lower than new CMMs, but maintenance and calibration can add to costs. | Moderate initial investment; ongoing costs for maintenance and software. | Higher upfront costs due to advanced technology and potential training needs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled technicians for setup and calibration. | Easier to integrate into existing workflows with fewer technical requirements. | May need specialized training and software setup for optimal use. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance and calibration needed to ensure accuracy. | Generally lower maintenance but still requires periodic checks. | Maintenance can be complex due to advanced technology; calibration is critical. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for precision manufacturing and quality control in various industries. | Suitable for applications where surface quality is paramount, like automotive or aerospace. | Best for complex shapes and detailed inspections, commonly used in reverse engineering. |
Understanding Optical Measurement Systems as an Alternative
Optical measurement systems utilize cameras and light to capture dimensional information about objects. These systems are often easier to implement and integrate into existing workflows compared to used CMMs. They excel in applications where surface finish and color are significant, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. However, their precision is typically lower than that of CMMs, which may limit their use in applications requiring high accuracy.
Evaluating Laser Scanning Systems as Another Option
Laser scanning systems are advanced technologies that capture high-resolution 3D data of complex geometries. They are particularly useful in reverse engineering and modeling applications. While they provide detailed information, the high upfront costs and the need for specialized training can deter some manufacturers. Additionally, post-processing of data is often required to convert the scans into usable formats, adding time and complexity to the workflow.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Measurement Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right measurement technology is crucial for optimizing production and ensuring quality control. For B2B buyers, the choice between a used coordinate measuring machine, optical measurement systems, or laser scanning systems should be guided by specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the level of precision needed. Assessing the unique demands of your manufacturing processes will lead to a more informed decision, ensuring you invest in the solution that best aligns with your business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for used coordinate measuring machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Used Coordinate Measuring Machines?
When evaluating used coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), several technical properties are essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Understanding these specifications can help buyers assess the machine’s suitability for their specific needs.
-
Measuring Range
The measuring range, typically expressed in X, Y, and Z dimensions (e.g., 500mm x 700mm x 400mm), indicates the maximum size of the object that can be measured. This property is crucial for manufacturers as it defines the operational capacity of the CMM. A machine with a larger measuring range can accommodate bigger parts, making it versatile for different applications. -
Accuracy and Tolerance
Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the actual value, while tolerance specifies the permissible limit of variation in a measured dimension. High accuracy and tight tolerances are vital for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is non-negotiable. When selecting a used CMM, buyers should verify these specifications through calibration certificates to ensure reliability. -
Probe Type and Capability
The type of probe equipped on a CMM (e.g., mechanical, optical, laser) affects the machine’s measurement capabilities. Probes determine the machine’s ability to measure different materials and geometries. Understanding the probe type helps buyers match the CMM to their specific measurement tasks, enhancing operational efficiency. -
Software Compatibility
A CMM’s software plays a crucial role in data collection and analysis. Compatibility with industry-standard software (like PC-DMIS or Calypso) ensures that the machine can integrate seamlessly into existing workflows. Buyers should evaluate the software’s features, such as user-friendliness and reporting capabilities, to determine how it can support their quality control processes. -
Condition and Maintenance History
The condition of a used CMM, including its maintenance history, can significantly impact its performance. Machines that have been regularly serviced and recalibrated are more likely to deliver consistent results. Requesting maintenance records and inspection reports can provide insights into the machine’s reliability and longevity. -
Warranty and Support
A warranty offers peace of mind, especially for used equipment. Understanding the terms of the warranty, including coverage duration and what it entails, can help buyers mitigate risks. Additionally, evaluating the support services provided by the seller, such as training and technical assistance, is essential for ensuring effective usage of the CMM.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Used CMM Market?
Navigating the used coordinate measuring machine market involves familiarity with specific trade terminology that can significantly influence purchasing decisions.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to the company that originally manufactured the CMM. When purchasing used equipment, knowing the OEM is essential, as it often indicates the machine’s quality and reliability. OEMs typically have established reputations and offer necessary parts and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of used CMMs, understanding the MOQ can help buyers plan their budgets and inventory effectively. This term is particularly relevant for businesses looking to acquire multiple machines or additional components. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers ask suppliers for pricing and terms for specific products. Issuing an RFQ for a used CMM helps buyers gather competitive offers and make informed decisions based on pricing and service terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they outline shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost distribution, ensuring clarity in cross-border purchases. -
Calibration Certificate
This document verifies that a CMM has been tested and meets specific accuracy standards. A calibration certificate is vital for buyers as it serves as proof of the machine’s performance and reliability. It can influence purchasing decisions, especially in industries where precision is critical. -
Reconditioning
This refers to the process of restoring a used CMM to a condition that meets or exceeds its original specifications. Buyers should inquire about the reconditioning process, as it can significantly affect the machine’s performance and longevity, ensuring they invest in a reliable piece of equipment.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing used coordinate measuring machines, ensuring they meet their operational requirements and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the used coordinate measuring machine Sector
What are the Current Trends Influencing the Used Coordinate Measuring Machine Market?
The used coordinate measuring machine (CMM) market is undergoing significant transformation driven by various global factors. Demand for precision measurement in manufacturing sectors, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and electronics, is on the rise. This increasing emphasis on quality assurance and compliance with international standards is pushing companies to invest in advanced metrology solutions, including used CMMs. Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of acquiring used machines—often reconditioned to meet high operational standards—makes them appealing to international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also influencing sourcing trends. Businesses are increasingly looking for CMMs that integrate with digital systems for real-time data analysis and remote monitoring. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, where industrial growth is spurred by technological adoption. Additionally, the demand for customized solutions is growing, prompting suppliers to offer machines tailored to specific operational needs.
Another notable trend is the shift towards online marketplaces and platforms that facilitate the buying and selling of used CMMs. These digital platforms enhance transparency, allowing buyers to compare specifications, prices, and service histories more easily, thus improving their purchasing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Used CMM Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the sourcing of used coordinate measuring machines. With growing awareness of environmental issues, manufacturers and buyers are increasingly focused on minimizing their carbon footprint. The reconditioning and reuse of CMMs significantly reduce waste and the environmental impact associated with producing new machines. This aligns with broader corporate sustainability goals and regulations, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who adhere to responsible sourcing protocols and demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. This includes ensuring that used machines are sourced from reputable providers who maintain strict quality control standards and provide comprehensive maintenance histories. Certifications for sustainability, such as ISO 14001, can also be advantageous, signaling a commitment to environmentally responsible practices.
Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ materials and processes is rising. Suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials in their refurbishment processes or that offer machines with energy-efficient features are likely to appeal to modern buyers who prioritize sustainability.
How Has the Used CMM Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the used coordinate measuring machine market can be traced back to the increasing complexity of manufacturing processes. Initially, CMMs were primarily utilized in high-end industries, but as technology advanced, their applications expanded into various sectors, including small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The introduction of computerized systems and software enhancements has elevated the capabilities of used CMMs, allowing them to compete effectively with new models.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a surge in the availability of refurbished machines due to advancements in reconditioning techniques and a growing awareness of the value of pre-owned equipment. This evolution has not only made CMMs more accessible to a broader range of industries but has also fostered a culture of sustainability within the manufacturing sector, emphasizing the importance of resource efficiency and waste reduction. As a result, the used CMM market continues to thrive, driven by technological advancements and an increased focus on cost-effective, sustainable solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of used coordinate measuring machine
1. How do I choose the right used coordinate measuring machine (CMM) for my needs?
Selecting the right used CMM involves assessing several key factors. First, identify the specific measurement requirements for your projects, including size, accuracy, and type of materials. Next, evaluate the machine’s age, previous usage environment, and maintenance history to ensure reliability. Ensure the machine is equipped with suitable probing systems for your applications. Finally, collaborate with a reputable supplier that provides a thorough inspection report and warranty to safeguard your investment.
2. What are the advantages of purchasing a used CMM compared to a new one?
Purchasing a used CMM offers significant cost savings while still providing high accuracy and performance. Many used machines are fully reconditioned and come with warranties, ensuring they function as effectively as new models. This option allows businesses to allocate budget resources more efficiently, potentially investing in other critical areas. Additionally, a diverse inventory of used machines often presents opportunities to acquire specific models or features that may no longer be available in new machines.
3. How can I verify the quality of a used CMM before purchasing?
To verify the quality of a used CMM, request detailed documentation from the supplier that includes maintenance records, calibration certificates, and inspection reports. A reputable supplier should also allow you to conduct a test run to assess the machine’s performance. Furthermore, inquire about any warranties or service agreements that may be included, which can provide additional assurance regarding the machine’s reliability and performance.
4. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a used CMM internationally?
Payment terms for used CMM purchases can vary significantly based on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common options include upfront payments, deposits, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms in advance and ensure they align with your budget and cash flow considerations. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, to protect both parties in the transaction.
5. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a used CMM?
When importing a used CMM, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and potential import restrictions specific to your country. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in heavy machinery can streamline the process and ensure compliance with local regulations. Additionally, factor in the need for proper packaging and handling to prevent damage during transit. Planning for installation and calibration upon arrival is also crucial to minimize downtime.
6. How can I ensure supplier reliability when sourcing used CMMs?
To ensure supplier reliability, conduct thorough research on potential vendors. Look for established companies with positive customer reviews and industry certifications. Engage in direct communication to assess their expertise and willingness to provide support. Request references from previous buyers and verify their experiences. Finally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, to view their inventory and operations firsthand.
7. What should I know about customization options for used CMMs?
Customization options for used CMMs may include upgrades to software, additional probing systems, or modifications to the machine’s hardware to better suit specific applications. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to determine what modifications are feasible. Keep in mind that while some adjustments can enhance functionality, they may also affect warranty conditions. Always request detailed documentation of any customizations made to ensure compatibility and support.
8. What quality assurance measures should I expect with a used CMM purchase?
Quality assurance measures for used CMMs should include comprehensive inspections, calibration certificates, and a warranty. A trustworthy supplier will provide a detailed report outlining the machine’s condition and any repairs or upgrades performed. Additionally, confirm that the machine has passed all operational tests to meet industry standards. Understanding the supplier’s return policy and support services is also essential to ensure you have recourse if any issues arise post-purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Used Coordinate Measuring Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CMMXYZ – Used CMM Machines for Sale
Domain: cmmxyz.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: CMMXYZ offers a diverse inventory of used CMM machines for sale, including models from various manufacturers such as Mitutoyo, Zeiss, Brown & Sharpe, Wenzel, Hexagon, and DEA. Key details include: 1. Mitutoyo Crysta Plus M574 – Size: 500mm x 700mm x 400mm, Software: MCOSMOS M1. 2. Zeiss DuraMax 555 – Size: 500mm x 500mm x 500mm, Software: Calypso 2023. 3. Brown & Sharpe Global Classic 555 – Size: …
2. Coordinate Measuring Machines – Key Brands
Domain: machinetools.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Coordinate Measuring Machines for sale listings include various models and brands. Key brands include KEYENCE (32), MITUTOYO (29), HEXAGON (28), ZEISS (27), and BROWN & SHARPE (24). The machines can be manually controlled or CNC controlled. Measurements vary by model, with X-axis ranges from 8 in & Under to 118.11 in & Up, Y-axis from 3.94 in to 78.74 in & Up, and Z-axis from 2.95 in to 48 in & Up…
3. Revelation Machinery – Used CMMs
Domain: revelationmachinery.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Used CMMs for sale from leading brands like Brown & Sharpe, Mitutoyo, and others. Types of CMM equipment include Bridge CMMs, Gantry CMMs, Portable CMMs, Horizontal Arm CMMs, Optical CMMs, 3D Scanning CMMs, and White Light CMMs. Advantages include high precision, repeatable measurements, speed, large measuring range, data collection & analysis, and non-contact measurement. CMMs are essential for q…
4. OmniTech – OMP60 RMP60 SHANK ADAPTOR MP10
Domain: omnitech-renishaw.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘OMP60 RMP60 SHANK ADAPTOR MP10’, ‘price’: ‘$460.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Hexagon Reference 700 Leitz 15.9.7 CMM’, ‘price’: ‘$98,000.00’}, {‘name’: ‘LK90C CMM 10.15.8 with Renishaw Controllers’, ‘price’: ”}, {‘name’: ‘M-2028-7456 Conduit Gland fitting 1/4″ SEALTITE FITTING (INC) – INCH’, ‘price’: ‘$14.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Renishaw A-5623-0100-RBE UCCT5 REPAIR BY EXCHANGE’, ‘price’: ‘$3,361.10’}, {‘na…
5. Renishaw – RM1000 Coordinate Measuring Machine
Domain: equipnet.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Used Coordinate Measuring Machines available for purchase. Featured listing: Renishaw RM1000 Coordinate Measuring Machine, located in North America, with a best offer price of $30,000 USD. EquipNet provides a range of used coordinate measuring machines from well-known OEMs including Hexagon Metrology GmbH and Brown and Sharpe. The company offers sourcing for tooling and change parts through a glob…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for used coordinate measuring machine
In the realm of manufacturing and quality control, the strategic sourcing of used coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) presents a compelling opportunity for international buyers. By investing in pre-owned CMMs, businesses can significantly reduce costs while still acquiring high-quality, reliable equipment. The key to successful sourcing lies in partnering with established metrology providers who ensure that these machines are fully reconditioned, calibrated, and come with a warranty—essential factors that guarantee operational efficiency.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of the used CMM market can lead to better purchasing decisions. Consideration of factors such as the machine’s previous operating environment, the age of the equipment, and the specifications of probing systems can greatly influence performance outcomes.
As the demand for precision measurement continues to grow globally, now is the ideal time to explore the diverse inventory of used CMMs available. Engage with reputable suppliers to unlock the potential of these cost-effective solutions, ensuring your operations remain competitive and efficient. The future of manufacturing is shaped by smart investments—seize the opportunity to enhance your capabilities with strategic sourcing of used CMMs.