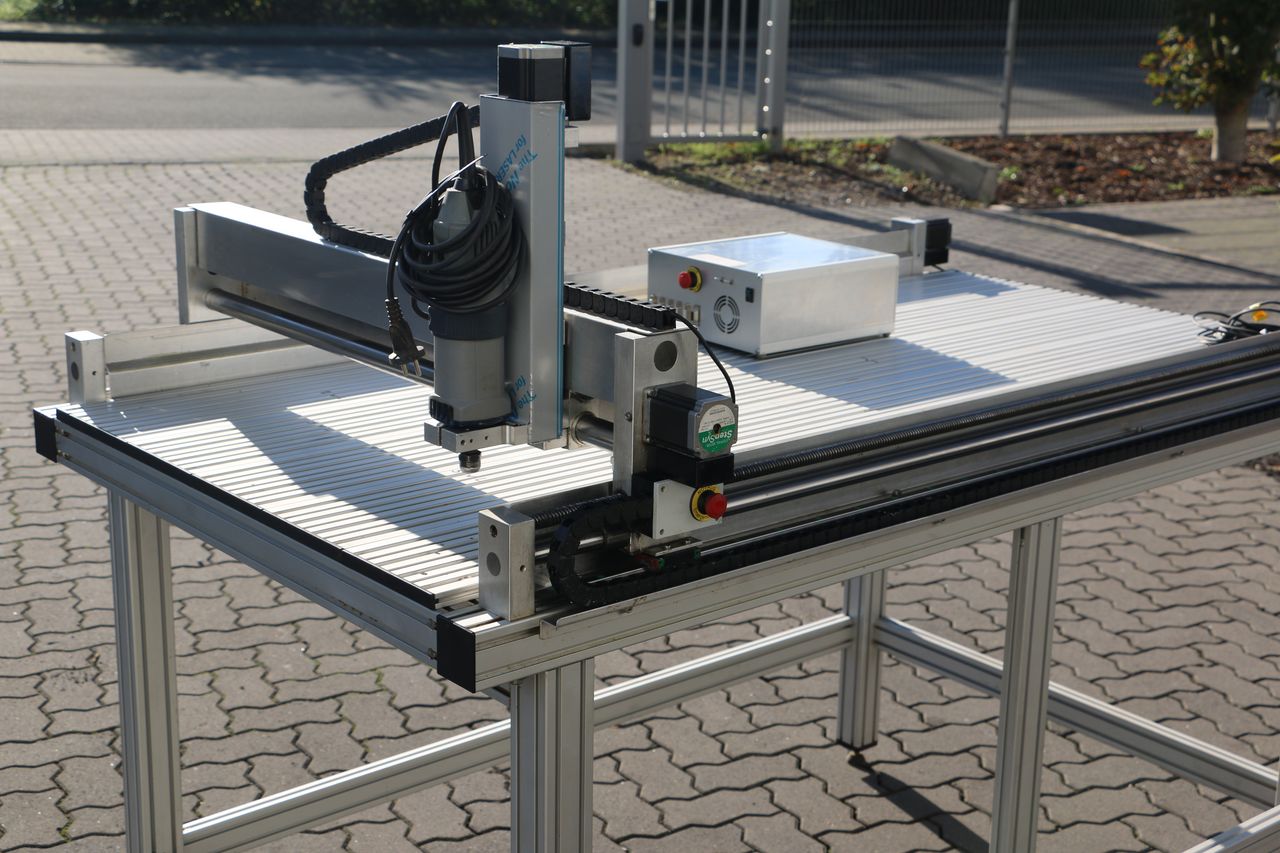
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for used cnc routers for woodworking
The global market for used CNC routers for woodworking presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. Sourcing high-quality equipment that meets specific production needs can be daunting, especially with the diverse range of models and technologies available. This guide aims to simplify the purchasing process by offering comprehensive insights into the types of CNC routers, their applications, and crucial factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Buyers will explore the various categories of CNC routers, from entry-level models suitable for small workshops to advanced machines designed for large-scale operations. We will delve into applications across different woodworking sectors, highlighting how these machines can enhance productivity and precision in manufacturing. Additionally, the guide will address cost considerations, helping buyers understand pricing trends and the potential for cost savings when purchasing used equipment.
With a focus on empowering B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Germany—this guide serves as a valuable resource. It equips decision-makers with the knowledge they need to make informed purchasing choices, ensuring they select the right CNC router to drive their business forward. By the end, buyers will feel confident navigating the complexities of the used CNC router market, ultimately leading to better investments and enhanced operational efficiency.
Understanding used cnc routers for woodworking Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis CNC Routers | Simple design, capable of moving along X, Y, and Z axes. | Furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, signage. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to operate. Cons: Limited in complexity of cuts. |
| 4-Axis CNC Routers | Adds rotation around one axis, allowing for more complex shapes. | Custom woodworking, intricate designs. | Pros: Increased versatility. Cons: Higher cost and complexity. |
| 5-Axis CNC Routers | Can move along five axes, allowing for multi-dimensional cuts. | Aerospace components, artistic sculptures. | Pros: Exceptional precision and complexity. Cons: Requires skilled operators and maintenance. |
| Laser-Cutting CNC Routers | Uses lasers for cutting, engraving, or marking materials. | Decorative items, signage, prototypes. | Pros: Clean cuts, minimal waste. Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Hybrid CNC Routers | Combines CNC routing with laser cutting capabilities. | Versatile applications across industries. | Pros: Multifunctional, adaptable. Cons: Higher investment cost. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 3-Axis CNC Routers?
3-Axis CNC routers are the most basic and commonly used type of CNC router in woodworking. They operate by moving a cutting tool along three axes: X (horizontal), Y (vertical), and Z (depth). These machines are ideal for straightforward tasks such as cutting, engraving, and shaping wood. They are particularly suitable for businesses focused on furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and signage, where cost-effectiveness and ease of use are paramount. Buyers should consider the machine’s speed and accuracy, as well as any additional features like dust collection systems.
How Do 4-Axis CNC Routers Enhance Woodworking Capabilities?
4-Axis CNC routers add a rotational axis to the standard three axes, allowing for more intricate designs and complex shapes. This capability is crucial for businesses that require custom woodworking solutions, such as intricate carvings or detailed moldings. The additional axis enables the router to work on cylindrical objects or create multi-dimensional cuts. While these machines offer increased versatility, they also come with a higher price tag and require a more skilled operator to maximize their potential.
What Are the Advantages of 5-Axis CNC Routers?
5-Axis CNC routers represent the pinnacle of CNC routing technology, capable of moving along five axes simultaneously. This allows for unparalleled precision and the ability to create complex shapes and designs, making them ideal for high-end applications such as aerospace components or artistic sculptures. Businesses that require intricate designs and tight tolerances will find these machines invaluable. However, the complexity of operation and maintenance, along with the significant investment cost, are key considerations for potential buyers.
In What Scenarios Are Laser-Cutting CNC Routers Most Effective?
Laser-cutting CNC routers utilize laser technology to cut, engrave, or mark materials, offering a clean and precise finish. They are particularly effective for decorative items, signage, and prototypes where detail is crucial. The minimal waste produced during the cutting process is a significant advantage for businesses looking to optimize material usage. However, these routers are limited to specific materials, such as wood, acrylic, and certain metals, which buyers should consider based on their production needs.
Why Consider Hybrid CNC Routers for Diverse Applications?
Hybrid CNC routers combine traditional routing capabilities with laser cutting features, making them versatile tools for various industries. They can handle a wide range of materials and applications, from woodworking to metal fabrication. This multifunctionality allows businesses to adapt to changing market demands without needing multiple machines. However, the initial investment cost is typically higher, which may be a barrier for smaller businesses. Buyers should evaluate their specific production needs and potential return on investment when considering hybrid options.
Key Industrial Applications of used cnc routers for woodworking
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of used cnc routers for woodworking | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Precision cutting and shaping of wooden components | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced material waste | Assess machine’s capability for large workpieces and speed |
| Cabinetry Production | Custom cabinetry design and construction | Ability to produce bespoke designs with consistent quality | Look for routers with software compatibility for design tools |
| Architectural Woodwork | Intricate carvings and detailed patterns | High-quality finishes and artistic enhancements | Ensure precision and versatility in tooling options |
| Signage and Display | Production of custom signs and promotional displays | Increased brand visibility and personalized customer engagement | Evaluate the machine’s ability to handle various materials |
| Musical Instrument Making | Crafting of wooden bodies and components for instruments | Superior craftsmanship and sound quality | Consider routers that accommodate specific wood types |
How Are Used CNC Routers Beneficial for Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, used CNC routers are essential for precision cutting and shaping of wooden components. They allow manufacturers to create complex designs with high accuracy, minimizing material waste and maximizing production efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to scale operations while maintaining quality. Buyers should consider the machine’s capabilities for handling large workpieces and its operational speed to ensure it meets production demands.
Why Are Used CNC Routers Important for Cabinetry Production?
Used CNC routers play a crucial role in cabinetry production by enabling the creation of custom cabinetry designs tailored to client specifications. They facilitate intricate cuts and joints that are difficult to achieve manually, ensuring consistent quality across all pieces. For international buyers, it is essential to look for routers that are compatible with design software commonly used in the industry, as this will streamline the design-to-production process.
What Advantages Do Used CNC Routers Offer for Architectural Woodwork?
In architectural woodwork, used CNC routers are indispensable for producing intricate carvings and detailed patterns that enhance the aesthetic appeal of structures. These machines provide the precision necessary to replicate complex designs, ensuring high-quality finishes. Buyers should prioritize routers with versatile tooling options and robust software capabilities to accommodate various artistic demands and project requirements.
How Do Used CNC Routers Enhance Signage and Display Production?
The signage and display industry benefits significantly from used CNC routers, which can produce custom signs and promotional displays with precision. This capability allows businesses to create personalized customer experiences and enhance brand visibility. When sourcing these machines, it is important to evaluate their ability to handle diverse materials, as signage often requires different substrates and finishes.
Why Are Used CNC Routers Essential for Musical Instrument Making?
In the realm of musical instrument making, used CNC routers are vital for crafting wooden bodies and components that contribute to superior craftsmanship and sound quality. The precision offered by these machines ensures that each piece meets the specific acoustic requirements essential for instrument performance. Buyers should consider routers that can accommodate various wood types and thicknesses to cater to diverse instrument designs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘used cnc routers for woodworking’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Precision in Used CNC Routers
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that the used CNC routers they purchase deliver the precision required for woodworking projects. Variability in machine conditions, wear and tear, or improper calibration can lead to discrepancies in cutting accuracy, which may result in wasted materials and increased production costs. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where access to high-quality machinery maintenance services may be limited, this issue is particularly pressing.
The Solution:
To mitigate precision issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing routers from reputable suppliers who provide detailed inspection reports and maintenance history. Before finalizing a purchase, request a demonstration of the machine’s capabilities, focusing on its accuracy in cutting various materials. Additionally, investing in post-purchase calibration services can ensure that the CNC router operates at optimal levels. Buyers should also consider implementing a routine maintenance schedule that includes regular calibration checks and adjustments, which can be crucial for sustaining precision over time.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Complexity of Software Compatibility
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of software compatibility. Many used CNC routers come with proprietary or outdated software that may not integrate seamlessly with modern design applications, creating friction in the workflow. This can hinder productivity, especially for businesses that rely on advanced design tools to create intricate wood designs. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where technology integration is essential, may find themselves particularly affected by this issue.
The Solution:
To address software compatibility concerns, buyers should inquire about the software that accompanies the used CNC router and its compatibility with their existing systems. Conduct thorough research on the available software updates or alternatives that can be installed on the machine. Collaborating with tech-savvy suppliers who can provide software upgrade options is beneficial. Furthermore, training staff on new software tools and ensuring they are familiar with the CNC router’s operational capabilities can enhance overall productivity and reduce downtime.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Supply Chain and Spare Parts Availability Issues
The Problem:
B2B buyers of used CNC routers frequently encounter difficulties related to the availability of spare parts. As machines age, sourcing specific components can become a logistical nightmare, leading to prolonged downtimes and lost revenue. This issue is particularly pronounced in regions like South America and Africa, where access to reliable suppliers for CNC router parts may be limited, impacting the sustainability of operations.
The Solution:
To overcome spare parts availability issues, buyers should choose CNC routers from manufacturers known for their robust distribution networks and readily available parts. Before purchasing, conduct a thorough analysis of the manufacturer’s reputation regarding parts availability and customer support. Establishing relationships with local or regional distributors can also create a buffer against potential supply chain disruptions. Additionally, consider maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts that are prone to wear, which can significantly reduce downtime and ensure that the woodworking operation remains efficient and productive. Regularly engaging with suppliers to stay informed about part availability can also help anticipate and mitigate future challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for used cnc routers for woodworking
What Are the Key Materials for Used CNC Routers in Woodworking?
When selecting used CNC routers for woodworking, understanding the materials that will be processed is crucial. Each material presents unique properties that can significantly influence the performance of the CNC router and the quality of the finished product. Below, we analyze four common materials used in woodworking applications.
How Does Wood Perform as a Material for CNC Routers?
Wood is the most common material processed by CNC routers in woodworking. Its properties vary widely based on the species and treatment. Generally, wood has a moderate density and good machinability, making it suitable for intricate designs.
Pros: Wood is relatively inexpensive and widely available. It offers aesthetic appeal and can be easily finished or treated. The machining process is generally straightforward, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: Wood can be prone to warping, splitting, and cracking, particularly if not properly dried or treated. It also requires careful handling to avoid damage during processing.
Impact on Application: Wood compatibility is high, but the type of wood can affect the router settings, such as feed rate and spindle speed. Hardwoods may require slower speeds compared to softwoods.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding wood treatment (e.g., pest control) is essential. Standards such as ASTM D198 for structural wood products may be relevant.
What Are the Benefits of Using MDF in CNC Routing?
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is a popular engineered wood product made from wood fibers, wax, and resin. Its uniform density and smooth surface make it an excellent choice for CNC routing.
Pros: MDF is cost-effective and provides a smooth finish, making it ideal for painting and veneering. It is also less prone to warping compared to solid wood.
Cons: MDF is heavier than solid wood and can be more challenging to handle. It is also less durable in humid environments, as moisture can cause it to swell.
Impact on Application: MDF is compatible with various woodworking applications, including furniture and cabinetry. However, it may require specialized tooling due to its density.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of formaldehyde emissions from MDF, which may require compliance with standards like CARB in North America or E1 in Europe.
Why Choose Plywood for CNC Router Applications?
Plywood, made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together, is another favored material in woodworking. It combines the natural look of wood with enhanced stability.
Pros: Plywood is strong and resistant to warping, making it suitable for structural applications. It is lighter than solid wood and offers good machinability.
Cons: The quality of plywood can vary based on the number of layers and the type of adhesive used. Lower-quality plywood may splinter during cutting.
Impact on Application: Plywood is versatile and can be used for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative applications. The type of veneer can affect the finish quality.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international plywood standards, such as EN 636 in Europe, is crucial. Buyers should also consider the sourcing of materials to ensure sustainability.
What Role Does Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) Play in CNC Routing?
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) is an engineered wood product made from layers of wood veneer bonded together. It is designed for structural applications and is increasingly used in CNC routing.
Pros: LVL is incredibly strong and stable, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. It is also less susceptible to warping and splitting compared to traditional wood.
Cons: LVL can be more expensive than solid wood or plywood. Additionally, the machining process may require specific tooling to accommodate its density.
Impact on Application: LVL is primarily used in structural applications but can also be processed for decorative elements. Its strength allows for thinner profiles in designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant structural standards such as ASTM D198. Understanding local building codes is also essential for structural applications.
Summary Table of Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for used cnc routers for woodworking | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture, cabinetry, decorative elements | Aesthetic appeal and easy finishing | Prone to warping and cracking | Low |
| MDF | Cabinetry, furniture, decorative panels | Smooth finish, cost-effective | Heavy and moisture-sensitive | Low |
| Plywood | Structural applications, furniture | Strong and stable | Quality can vary; may splinter | Medium |
| LVL | Load-bearing structures, decorative elements | Very strong and stable | Higher cost, requires specific tooling | High |
By understanding these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting used CNC routers for woodworking applications, ensuring they meet both performance and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for used cnc routers for woodworking
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Used CNC Routers for Woodworking?
The manufacturing of used CNC routers for woodworking involves several critical stages that ensure the machinery meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The initial stage of manufacturing CNC routers involves selecting high-quality raw materials, primarily aluminum, steel, and various plastics. These materials are chosen for their durability and ability to withstand the stresses involved in cutting and routing operations.
Once selected, materials undergo processes like cutting, milling, and laser cutting to create parts that meet precise specifications. This stage is crucial as any defects in material quality can lead to performance issues in the final product.
How Are CNC Routers Formed?
The forming stage is where the raw materials are shaped into components. This typically involves advanced techniques such as CNC machining, welding, and bending.
CNC machining is particularly important as it allows for the creation of intricate parts with high accuracy. For instance, the frame of the CNC router is often machined to ensure it can handle the vibrations and forces generated during operation.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Assembly involves putting together the various components that make up the CNC router. This includes the frame, motors, electronics, and control systems.
A significant focus during this stage is on aligning components precisely. Misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased wear on parts. Quality assurance checks are often integrated into this stage to catch any potential issues before the machine moves to the finishing phase.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Used?
Finishing involves applying protective coatings, painting, and final inspections. This step not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the router but also protects it from corrosion and wear.
Common finishing techniques include powder coating and anodizing, which provide a durable surface that can withstand the rigors of woodworking environments.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Router Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of CNC routers, particularly in international markets where standards can vary widely.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For manufacturers, adhering to international quality standards such as ISO 9001 is essential. This standard focuses on establishing a quality management system that ensures consistent production quality.
Additionally, specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) signify compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Buyers from regions like Europe, the Middle East, and South America should prioritize suppliers who hold these certifications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) in CNC router manufacturing involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards can significantly reduce defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are performed to ensure that the production process adheres to quality standards. This may include measuring tolerances and inspecting welds.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that the router functions correctly and meets performance specifications. This may include testing cutting accuracy and operational speed.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in CNC Router Quality Control?
To ensure the highest quality, manufacturers use several testing methods, including:
-
Functional Testing: Evaluating the machine’s operational performance, including speed, precision, and responsiveness.
-
Durability Testing: Subjecting the router to extended use under various conditions to assess its reliability and longevity.
-
Safety Testing: Ensuring that the machine meets safety regulations to protect operators and users.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to conduct thorough due diligence when evaluating suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request detailed audit reports from potential suppliers. These reports should outline the supplier’s adherence to international quality standards and internal processes.
Additionally, buyers can inquire about the supplier’s history with quality certifications and any third-party evaluations that have been conducted.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be arranged before a purchase to verify that the supplier meets all necessary standards and requirements.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various regulatory landscapes when purchasing used CNC routers. It’s essential to understand that:
-
Regional Certifications: Different regions have unique certification requirements, which can affect the machine’s usability. For instance, a machine certified for use in Europe may need additional modifications to comply with regulations in South America or Africa.
-
Import Regulations: Buyers should also be aware of import regulations in their respective countries. This includes understanding tariffs, compliance requirements, and potential modifications needed to meet local standards.
In summary, a robust understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is crucial for B2B buyers of used CNC routers. By focusing on material quality, adherence to international standards, and thorough inspection processes, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable machinery that meets their specific woodworking needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘used cnc routers for woodworking’
Introduction
When sourcing used CNC routers for woodworking, an organized approach is essential for ensuring that you obtain a machine that meets your operational needs while also providing value for money. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps necessary to make an informed purchase, ensuring that your investment enhances your production capabilities.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by identifying the specific requirements for your woodworking projects. Consider factors such as:
– Material Types: Different routers are optimized for various materials (e.g., hardwood, softwood, composites).
– Size and Capacity: Ensure the router can handle the dimensions of your typical workpieces.
– Precision and Tolerances: High precision is crucial for intricate designs; verify the machine’s capabilities.
2. Set a Budget and Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership
Establish a clear budget that includes not just the purchase price but also:
– Maintenance Costs: Factor in the potential need for repairs and upkeep.
– Operational Costs: Consider energy consumption and any additional tools or software required.
– Training Expenses: If staff need training to operate the new equipment, include these costs in your budget.
3. Research and Compare Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of used CNC routers. Look for:
– Reputation: Check online reviews and industry forums for feedback on suppliers.
– Experience: Prefer suppliers with a proven track record in selling CNC machines specifically for woodworking.
– Inventory: Ensure they have a diverse range of models to meet your needs.
4. Inspect the Equipment Thoroughly
Before finalizing your purchase, inspect the CNC router in person or request detailed images and documentation. Focus on:
– Physical Condition: Look for signs of wear, rust, or damage that could affect performance.
– Operational History: Request maintenance records and information on previous usage.
– Upgrades and Modifications: Verify if the machine has been upgraded with newer technologies or parts.
5. Verify Supplier Certifications and Warranty
Confirm that the supplier adheres to industry standards and offers sufficient warranty coverage. Important aspects to check include:
– Certifications: Look for ISO or other relevant certifications that indicate quality assurance.
– Warranty Terms: A solid warranty can protect your investment; ensure you understand the coverage duration and conditions.
6. Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier and a specific machine, engage in negotiation to secure favorable terms. Discuss:
– Payment Options: Explore financing or leasing options if upfront costs are a concern.
– Shipping and Handling: Clarify who is responsible for transport and any associated costs.
– Return Policy: Understand the return policy in case the machine does not meet your expectations upon delivery.
7. Plan for Installation and Training
Finally, develop a plan for the installation and training of your staff on the new equipment. Consider:
– Professional Installation: It may be beneficial to have the supplier handle installation to ensure everything is set up correctly.
– Training Sessions: Schedule training for operators to maximize productivity and minimize mistakes.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure a well-informed, strategic approach to sourcing used CNC routers for woodworking, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and business success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for used cnc routers for woodworking Sourcing
When evaluating the cost structure and pricing for used CNC routers for woodworking, it is essential to understand the various components that contribute to the overall expense. This understanding aids international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational budgets and production needs.
What are the Key Cost Components in Used CNC Routers?
-
Materials: The primary materials involved in CNC routers include the metal frame, motor components, and electronic systems. The cost of these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chain dynamics, affecting the overall price of the machinery.
-
Labor: Labor costs include the wages of skilled technicians who assemble, maintain, and refurbish used CNC routers. Regions with higher labor costs may see increased pricing, while countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Suppliers with efficient operations can pass on savings to buyers, while those with higher overheads will reflect these costs in their pricing.
-
Tooling: The condition and quality of tooling that comes with the CNC router can significantly impact the price. High-quality tooling is essential for achieving precision in woodworking and may command a premium.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure that the used CNC routers meet specific performance standards. Suppliers that invest in rigorous QC may charge higher prices, but this often translates into better reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs play a critical role, especially for international buyers. The distance from the supplier, as well as the chosen shipping method, can influence the final cost significantly.
-
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s profit margin will also affect pricing. Different suppliers may adopt various pricing strategies based on their market positioning and competition.
What Influences the Pricing of Used CNC Routers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of used CNC routers, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often come with discounts. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or advanced specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Routers made with high-quality materials and certified for safety or performance will typically cost more. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are essential for their operations.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge higher prices due to perceived reliability and service. However, newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to capture market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can significantly affect the total cost. Buyers should understand whether costs like shipping, insurance, and duties are included in the quoted price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Engage in Negotiation: Buyers should be prepared to negotiate prices and terms. Understanding market trends and competitor pricing can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A cheaper router might incur higher long-term costs.
-
Evaluate Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can impact final costs. It may be beneficial to work with a local partner who understands these factors.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market rate and help identify reasonable pricing.
-
Inspect Before Purchase: If possible, inspect the equipment before finalizing the purchase. This can prevent costly surprises related to condition and functionality.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for used CNC routers can vary widely based on condition, specifications, and market demand. Buyers should view all pricing as indicative and subject to change based on real-time market conditions and supplier negotiations. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain the best possible deal.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing used cnc routers for woodworking With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Used CNC Routers for Woodworking
In the realm of woodworking, businesses often seek efficient and cost-effective solutions to enhance production capabilities. While used CNC routers are a popular choice for their precision and automation, several alternative technologies and methods can also achieve similar outcomes. This analysis compares used CNC routers with two viable alternatives: traditional woodworking machinery and laser cutting systems. Understanding the pros and cons of each option will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Used CNC Routers For Woodworking | Traditional Woodworking Machinery | Laser Cutting Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Varies; depends on operator skill | Excellent for detailed cuts |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; potential for savings on used models | Generally lower upfront cost; higher long-term labor costs | Higher initial investment; operational costs vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and setup | Familiar to most woodworkers; minimal training needed | Requires specialized training for operation |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts can be costly | Lower maintenance; more robust | Regular maintenance; specific consumables required |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production with complex designs | Custom, one-off projects or smaller production runs | Intricate designs and rapid prototyping |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Woodworking Machinery?
Traditional woodworking machinery, such as table saws, band saws, and planers, provides a hands-on approach to woodworking. These machines are often more affordable upfront than CNC routers and do not require extensive training for operators familiar with manual techniques. However, the performance can vary significantly based on the skill level of the operator, potentially leading to inconsistencies in product quality. While traditional machinery is ideal for bespoke projects, it may not be as efficient for high-volume production, limiting scalability.
How Do Laser Cutting Systems Compare to CNC Routers?
Laser cutting systems offer exceptional precision and are particularly effective for intricate designs, making them a strong alternative to CNC routers. They excel in producing detailed cuts and can process a variety of materials beyond wood, such as plastics and metals. However, the initial investment for laser systems tends to be higher, and they may require specialized training for operators. Additionally, while they can operate quickly, the speed may vary based on the thickness and type of material being processed, potentially affecting production time.
Conclusion: Which Solution is Right for Your Woodworking Business?
When choosing the right solution for woodworking needs, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their production requirements, budget constraints, and the skill level of their workforce. Used CNC routers provide a robust option for businesses looking to scale production with high precision. In contrast, traditional woodworking machinery may suit smaller-scale operations or custom projects where hands-on craftsmanship is valued. Laser cutting systems stand out for intricate designs but come with a higher cost and training needs. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific goals and operational context of the business to ensure optimal efficiency and return on investment.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for used cnc routers for woodworking
What Are the Essential Technical Specifications for Used CNC Routers in Woodworking?
When considering the purchase of used CNC routers for woodworking, understanding key technical specifications is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are some critical specs to evaluate:
-
Working Area Dimensions
– This specification denotes the maximum size of material that the CNC router can accommodate. Common dimensions include 48”x96” or 60”x120”. B2B buyers should assess the working area relative to their typical project sizes to ensure compatibility. A larger working area can enhance productivity by allowing for multiple pieces to be processed simultaneously. -
Spindle Power and Speed
– The spindle power, usually measured in horsepower (HP), indicates the router’s capability to cut through various materials efficiently. Spindle speed, expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM), affects the quality of cuts and the types of materials that can be processed. Higher horsepower and variable speed options allow for greater versatility in woodworking applications, making it essential for businesses to consider their specific needs. -
Accuracy and Tolerance
– Accuracy refers to how closely the CNC router can replicate a specified dimension, while tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in these measurements. Tighter tolerances are crucial in precision woodworking projects where even slight deviations can affect the final product’s quality. Businesses should prioritize routers with high accuracy ratings to maintain consistent production quality. -
Control System and Software Compatibility
– The control system dictates how the CNC router interprets design files and executes cuts. Most routers use G-code for programming, but compatibility with various CAD/CAM software is vital for operational efficiency. Ensuring that the router can integrate with existing design software minimizes downtime and enhances workflow. -
Material Compatibility
– Different routers are designed to handle specific materials, such as hardwood, softwood, or composite materials. Understanding which materials a router can efficiently process is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the machine aligns with their production capabilities and requirements. -
Maintenance and Support
– The availability of replacement parts and technical support is critical when purchasing used CNC routers. Understanding the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability and service can impact long-term operational efficiency. B2B buyers should consider machines from reputable brands known for their durability and support networks.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CNC Router Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly assist in navigating the purchasing process for used CNC routers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to the company that originally manufactures the CNC router. Understanding OEM status is important for buyers as it often correlates with the quality and reliability of the equipment, as well as the availability of parts and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ defines the smallest quantity of products a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially when purchasing multiple units or components. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers before making a decision. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery points, which can significantly affect overall costs. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
– CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools via a computer. This technology allows for precise cuts and designs, making it essential for modern woodworking operations. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and meeting customer demands.
By grasping these specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in used CNC routers for woodworking, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the used cnc routers for woodworking Sector
The market for used CNC routers for woodworking is experiencing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and changing buyer preferences. Globally, the woodworking industry is increasingly adopting automation to enhance production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve precision. This shift is particularly pronounced in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where manufacturers are seeking cost-effective solutions to remain competitive.
International B2B buyers are particularly interested in sourcing high-quality used CNC routers due to their affordability compared to new models. The demand for specific brands and models, such as Multicam and Laguna, is rising, influenced by their reputation for durability and performance. Furthermore, emerging technologies, such as cloud-based software for remote machine monitoring and predictive maintenance, are becoming essential. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer these technological upgrades, as they enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Another trend is the increasing importance of customization. As businesses strive to meet diverse customer demands, the ability to quickly adapt CNC routers for various applications is crucial. This flexibility not only improves production timelines but also allows manufacturers to diversify their product offerings, catering to niche markets.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence B2B Decisions in the Used CNC Router Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of purchasing decisions in the used CNC router market. With growing awareness of environmental issues, B2B buyers are now prioritizing equipment that minimizes environmental impact. This includes routers that utilize energy-efficient technologies and those made from sustainable materials.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important, as companies seek to ensure that their supply chains do not contribute to environmental degradation or exploit workers. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to ethical standards and consider certifications that signify environmentally friendly practices, such as ISO 14001 or specific ‘green’ certifications related to machinery. By choosing suppliers committed to sustainability, businesses not only enhance their corporate image but also comply with increasing regulatory pressures regarding environmental responsibility.
What Historical Context Should B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing Used CNC Routers?
The evolution of CNC technology from manual routing to computer-aided control has significantly shaped the woodworking industry. Initially, CNC routers were seen as niche tools for high-end manufacturers. However, as technology progressed and prices became more accessible, these machines entered the mainstream. The introduction of user-friendly interfaces and software has made it easier for smaller businesses to adopt CNC technology, broadening its application across various woodworking tasks. Understanding this history allows B2B buyers to appreciate the advancements in precision and efficiency that modern used CNC routers offer, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions.
In summary, the dynamics of the used CNC router market reflect broader trends in technology, sustainability, and customization. B2B buyers must navigate these trends strategically to maximize their investments and stay competitive in an evolving global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of used cnc routers for woodworking
-
1. How do I choose the right used CNC router for my woodworking business?
Selecting the appropriate used CNC router involves assessing your specific production needs, including the types of materials you’ll work with, the size of the projects, and your desired precision. Evaluate the machine’s specifications, such as its cutting area, spindle speed, and compatibility with various tooling options. Additionally, consider the brand’s reputation and the availability of spare parts and service support in your region. It’s also beneficial to request a demonstration or review any operational history to ensure the machine meets your performance expectations. -
2. What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of used CNC routers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation in the industry, which can be assessed through reviews, testimonials, and their history of servicing clients in your region. Verify their certifications and compliance with international trade standards, especially if you’re importing machinery. Request references and inquire about their after-sales support, warranty policies, and return terms. Additionally, assess their response times and willingness to provide comprehensive machine documentation, including maintenance records and technical specifications. -
3. What are the common payment terms for purchasing used CNC routers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the transaction size. Common options include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or financing arrangements. For international purchases, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to safeguard your investment. Always clarify the payment terms in the contract and ensure they are aligned with your budget and cash flow requirements, taking into account potential import duties and taxes. -
4. How can I ensure the quality of a used CNC router before purchase?
To ensure the quality of a used CNC router, request a thorough inspection report from the seller, ideally conducted by a qualified technician. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to see the machine in operation. Look for signs of wear and tear, such as rust, unusual noises, or inconsistent movements. Inquire about previous maintenance records and any upgrades made to the machine. A trial run or demonstration can also provide insights into the router’s performance and reliability. -
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for used CNC routers?
The minimum order quantity for used CNC routers typically varies by supplier. Some may offer single units, while others may require larger quantities, especially if they specialize in bulk sales or export. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with the supplier and negotiate terms that align with your production capabilities. If you’re considering multiple machines, inquire about bulk pricing discounts or package deals that can provide better value for your investment. -
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing used CNC routers?
When importing used CNC routers, consider the logistics of transportation, including shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with customs clearance. Ensure the supplier provides adequate packaging to prevent damage during transit. Familiarize yourself with local import regulations, including any tariffs or duties that may apply. It’s also advisable to work with a freight forwarder who can assist with documentation and navigate the complexities of international shipping to ensure a smooth delivery process. -
7. Can I customize a used CNC router to fit my specific woodworking needs?
Yes, many used CNC routers can be customized to meet specific woodworking requirements. Modifications can include adding specialized tooling, upgrading the software, or enhancing the machine’s capabilities with additional features like advanced vacuum systems or automated tool changers. When discussing customization options with suppliers, clearly outline your production needs and ensure that any modifications comply with safety standards. It’s also helpful to verify whether the supplier offers support for these customizations post-purchase. -
8. What should I know about warranty and after-sales support for used CNC routers?
Warranties for used CNC routers can differ significantly between suppliers. Some may offer limited warranties covering specific components, while others might provide comprehensive support for a defined period. Always clarify the warranty terms and conditions before purchasing. After-sales support is equally important; ensure the supplier has a reliable customer service system in place for troubleshooting, spare parts availability, and technical assistance. A good after-sales relationship can enhance your operational efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the machine.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Used Cnc Routers For Woodworking Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Vevor – S4040 CNC Router Machine
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: CNC Woodworking Routers available on eBay include various types such as 3 Axis Router Machines, 4 Axis Router Machines, Mini CNC Routers, and CNC Engravers. Notable products include:
– Vevor S4040 CNC Router Machine 300W 3 Axis Wood Engraving Milling Machine priced at ILS 998.81 (New)
– Rockler Corner Radius Routing Templates priced at ILS 97.36 (New)
– RATTM Motor 1610PRO-MJ Mini Router Machin…
2. Andi – Stratos CNC Router W/ATC
Domain: exfactory.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Andi – Stratos CNC Router W/ATC, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Onsrud – Used CNC Routers
Domain: surplusrecord.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Routers For Sale | Surplus Record
Manufacturers: Onsrud (57), Multicam (25), Laguna (14), Axyz (11), Shopbot (10), Holz-Her (9), Thermwood (9), Haas (8), Weeke (8), Biesse (7), Komo (7), Dms (5), Fom (5), Precision (4), Scm (4), Baileigh (3), Cms (3), Elumatec (3), Shopsabre (3), Cnt Motion Systems (2), Fab Plus (2), Flexicam (2), Gerber (2), Gmr (2), Park Industries (2), Quintax (2), Sh…
4. Carolina Machinery Sales – CNC Routers for Sale
Domain: carolinamachinerysales.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: CNC Router for sale at Carolina Machinery Sales. Key models include: 2002 Motionmaster QE1F 6.6/12 24 130 NC CB 5-Axis CNC Router, 2015 Weeke Venture 107M CNC Router, 2018 Holz-her Dynestic 7535 CNC Router with Infeed & Outfeed, 2010 Shopbot PRS Alpha ATC CNC Router 5 X 10, 2008 MultiCam 3000 5 X 10 CNC router, 2006 Weeke Optimat BHC Venture 2.5 Point To Point CBC Router, 2020 Laguna Swift 5×10 CN…
5. BIESSE – CNC for Flexible Drilling
Domain: ferwoodgroup.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Routers and CNC Machine Centres for Wood available for sale in the USA. Key brands include BIESSE, BREMA, MASTERWOOD, HOMAG, and more. Product types include: 1. CNC for Flexible Drilling – BIESSE NEW SKIPPER 100 L (Availability: in stock) 2. CNC Machine Centers with Pod and Rail – BIESSE ROVER A 3.30 K1 (Availability: in stock) 3. Vertical CNC Machine Centres – WEEKE BHX 055 (Availability…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for used cnc routers for woodworking
In the competitive landscape of woodworking, strategic sourcing of used CNC routers presents a unique opportunity for international buyers. By leveraging the precision and efficiency of these machines, businesses can enhance their production capabilities while optimizing costs. Key factors such as machine condition, brand reputation, and post-purchase support should guide your sourcing decisions. Engaging with reputable suppliers ensures access to quality equipment that aligns with your operational needs.
Moreover, considering the diverse offerings available from various manufacturers, buyers can tailor their choices to specific project requirements. For instance, models from brands like Multicam, Laguna, and Shopsabre are known for their reliability and performance. As the demand for customized woodworking solutions continues to rise, investing in used CNC routers can significantly improve your competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the global market for used CNC routers is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for automated solutions. Now is the time to capitalize on this trend. Explore your options, connect with trusted suppliers, and make informed decisions that position your business for success in the evolving woodworking industry.