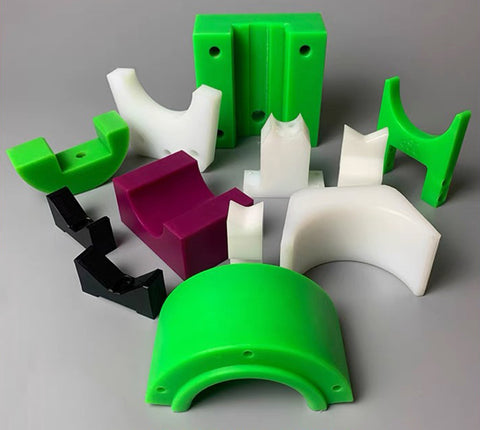
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for uhmw machining
Ultra-high molecular weight (UHMW) machining presents a unique set of challenges that can deter even the most seasoned manufacturers. With its significant thermal expansion and low melting point, sourcing reliable machining solutions for UHMW can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities of UHMW machining, covering essential topics such as types of machining processes, applications across various industries, effective supplier vetting techniques, and a breakdown of associated costs.
Navigating the global market for UHMW machining requires a nuanced understanding of the material’s properties and the specific challenges it poses during production. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by providing actionable insights that facilitate informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re in Nigeria seeking cost-effective solutions or in Germany looking for high-quality machining services, our guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to enhance your supply chain efficiency and product quality.
By addressing common obstacles and offering practical strategies, this resource positions your business to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. Join us as we explore the intricacies of UHMW machining, enabling you to make well-informed choices that can lead to operational success and sustainable growth.
Understanding uhmw machining Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Automated precision cutting and shaping of UHMW-PE | Aerospace, automotive, food processing | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Milling | Uses rotating tools to remove material from a workpiece | Custom parts, industrial machinery | Pros: Versatile and effective for complex shapes. Cons: Can generate heat, requiring cooling measures. |
| Turning | Rotational machining for cylindrical parts | Valve seats, bushings, and fittings | Pros: Ideal for symmetrical parts. Cons: Tolerance maintenance can be challenging. |
| Sawing | Straight cutting with specialized blades | Sheet material processing, packaging | Pros: Efficient for large sheets. Cons: Limited to straight cuts. |
| Grinding | Abrasive machining for fine finishes | Precision components, medical devices | Pros: Achieves tight tolerances. Cons: Slower process compared to other methods. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Machining for UHMW?
CNC machining is the most advanced method for processing UHMW-PE, offering high precision and automation. This technique is particularly suitable for producing complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive sectors. When considering CNC machining, businesses should evaluate the initial investment against the potential for high-volume production efficiency.
How Does Milling Stand Out in UHMW Machining?
Milling involves the use of rotating cutting tools to shape UHMW-PE, making it highly versatile for creating intricate designs. This method is commonly used in the production of custom parts and industrial machinery components. Buyers should be aware that while milling can yield excellent surface finishes, it may also produce significant heat, necessitating effective cooling strategies to maintain material integrity.
Why Is Turning a Preferred Method for Symmetrical Parts?
Turning is a machining process that shapes UHMW-PE into cylindrical forms, making it suitable for applications like valve seats and bushings. This technique is favored for its efficiency in creating symmetrical components. However, maintaining precise tolerances can be challenging due to the material’s properties. Buyers need to ensure that the machining environment is optimized to minimize distortion and maintain quality.
What Are the Advantages of Sawing in UHMW Processing?
Sawing is a straightforward method for cutting UHMW-PE sheets into manageable sizes. It is particularly effective for bulk material processing and packaging applications. While sawing is efficient for large sheets, its limitation lies in the inability to create complex shapes, which may require additional machining processes. Buyers should consider the trade-off between efficiency and the need for further processing.
How Does Grinding Contribute to Achieving Tight Tolerances?
Grinding is an abrasive machining technique used to achieve fine finishes and tight tolerances on UHMW-PE components. It is particularly valuable in industries requiring precision, such as medical devices. However, grinding is generally slower than other machining methods, which could impact production timelines. Buyers should weigh the need for precision against the potential for longer lead times when selecting this method.
Key Industrial Applications of uhmw machining
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of UHMW Machining | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Conveyor Systems and Components | Enhanced durability and reduced friction lead to lower maintenance costs. | Ensure compliance with food safety standards and certifications. |
| Mining and Minerals | Wear Plates and Liners | High abrasion resistance minimizes wear and extends equipment life. | Evaluate the impact of local environmental conditions on material selection. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Custom Gaskets and Seals | Chemical resistance ensures product integrity and safety. | Consider sourcing from suppliers with stringent quality control processes. |
| Construction | Chute Liners and Material Handling Systems | Reduces material flow friction, improving efficiency and safety. | Assess compatibility with existing systems and ease of installation. |
| Automotive | Bushings and Bearings | Low friction properties enhance performance and reduce energy consumption. | Look for precision machining capabilities to meet tight tolerances. |
In the food processing sector, UHMW machining is commonly utilized for components in conveyor systems. The material’s low friction coefficient and excellent wear resistance translate to reduced maintenance and longer operational life. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers who meet food safety standards and can provide documentation to ensure compliance with local regulations.
In mining and minerals, UHMW is often machined into wear plates and liners that experience heavy abrasion. These components significantly reduce wear on equipment, leading to lower replacement costs and increased uptime. Buyers in this sector must consider environmental factors, as different grades of UHMW may perform better under specific conditions, such as high dust or moisture environments.
The pharmaceutical industry benefits from UHMW machining through custom gaskets and seals that require high chemical resistance. These components are crucial for maintaining product integrity and ensuring safety during production. Buyers should seek suppliers with rigorous quality control processes to avoid contamination and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
In the construction sector, UHMW is used for chute liners and material handling systems. The material’s ability to reduce friction enhances the efficiency of material flow, which is vital for safety and productivity on job sites. Buyers need to evaluate the compatibility of UHMW components with existing systems and consider the ease of installation to minimize downtime.
Finally, in the automotive industry, UHMW is machined into bushings and bearings where low friction is critical for performance. This can lead to reduced energy consumption and improved vehicle efficiency. Buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers capable of precision machining to meet the tight tolerances required in automotive applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘uhmw machining’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Maintaining Tolerances During Machining
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when machining UHMW, particularly in maintaining tight tolerances. The material’s high expansion rate—up to 12 times greater than steel—means that even minor temperature fluctuations can lead to dimensional inaccuracies. Buyers may find that the components produced do not meet their specifications, leading to rework, increased costs, and project delays. This issue is particularly acute for manufacturers producing precision parts, such as valve seats, where even small deviations can render a product unusable.
The Solution:
To effectively maintain tolerances while machining UHMW, it is essential to implement precise temperature control and cooling techniques. Using high-speed steel tools with sharp edges can significantly reduce heat generation during the cutting process. It is advisable to utilize climb milling instead of conventional milling to minimize friction and heat buildup. Additionally, adopting a peck drilling method allows for better chip removal and cooling, further enhancing dimensional accuracy. Implementing a vacuum cooling system can also help manage temperature and prevent dimensional variations due to thermal expansion. Lastly, regular inspection of components during the machining process will enable manufacturers to detect and address issues before they escalate into larger problems.
Scenario 2: Managing Moisture Absorption in UHMW Parts
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the moisture absorption characteristics of UHMW, which can alter the material’s dimensions and properties over time. This issue becomes particularly problematic in humid environments or when parts are stored improperly before installation. Buyers may discover that parts produced from UHMW have swollen or distorted, leading to failures in applications where precise fits are critical, such as in conveyor systems or machinery components.
The Solution:
To mitigate moisture absorption issues, buyers should prioritize proper material storage and handling practices. It is crucial to store UHMW sheets and parts in a climate-controlled environment to minimize exposure to humidity. Additionally, manufacturers should consider sourcing UHMW with low moisture absorption rates or applying moisture-resistant coatings to parts. Implementing a drying process before machining can also help reduce the initial moisture content, leading to more stable dimensions post-processing. For applications exposed to moisture, buyers may also explore alternative materials or composite solutions that offer similar performance without the downsides of moisture sensitivity.
Scenario 3: Chip Control and Surface Finish Challenges
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently encounter difficulties with chip control and achieving a high-quality surface finish when machining UHMW. The material tends to produce long, stringy chips that can wrap around tools and affect the machining process, leading to a poor surface finish and increased wear on cutting tools. This not only impacts the aesthetics of the final product but can also compromise functionality in critical applications.
The Solution:
To improve chip control and surface finish, buyers should employ tools specifically designed for machining UHMW, such as those with positive rake angles and a high-speed steel composition. These tools help break the chips more effectively, preventing them from wrapping around the tool. Additionally, utilizing a high feed rate during machining can ensure that chips are ejected quickly and reduce the likelihood of buildup around the cutting area. Implementing a robust coolant system, such as vacuum air blowing, can further enhance chip evacuation and maintain a cooler cutting environment, leading to better surface finishes. Regular maintenance of tools and machinery will also ensure that cutting edges remain sharp, promoting optimal performance and prolonging tool life.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for uhmw machining
What Are the Key Properties of Materials Used in UHMW Machining?
When selecting materials for UHMW machining, it is essential to consider their unique properties that affect performance. Here are four common materials used in this context:
-
Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW-PE)
– Key Properties: UHMW-PE exhibits exceptional toughness, low friction, and high abrasion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and has a high resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
– Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of UHMW-PE is its durability and low wear rate, which translates into longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. However, its machining can be challenging due to its high thermal expansion and low melting point, requiring specialized tools and techniques.
– Impact on Application: UHMW-PE is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and various chemicals. This versatility makes it ideal for applications in food processing, mining, and material handling.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM D4020 and DIN 16961, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations may apply. -
Polypropylene (PP)
– Key Properties: Polypropylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance and low density. It can operate effectively in temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) and has a moderate tensile strength.
– Pros & Cons: The low cost and ease of machining make polypropylene a popular choice for various applications. However, it has lower impact resistance compared to UHMW-PE, which may limit its use in high-stress environments.
– Impact on Application: Polypropylene is suitable for applications involving corrosive chemicals, making it ideal for the chemical processing industry. However, its lower durability may necessitate more frequent replacements.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM D4101 and JIS K 6735, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary. -
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
– Key Properties: PVC is a versatile plastic with good chemical resistance and a temperature range of up to 60°C (140°F). It is rigid and has moderate tensile strength.
– Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to source, making it a common choice for various applications. However, its rigidity can be a limitation in applications requiring flexibility and impact resistance.
– Impact on Application: PVC is widely used in construction, plumbing, and electrical applications due to its durability and resistance to environmental factors. However, it may not perform well under high-stress conditions.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D1784 and DIN 16892 is crucial, particularly in Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent. -
Acetal (POM)
– Key Properties: Acetal is known for its high strength, stiffness, and low friction properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) and has excellent dimensional stability.
– Pros & Cons: The high mechanical strength and wear resistance of acetal make it suitable for precision parts. However, it is generally more expensive than other materials, which could impact overall project costs.
– Impact on Application: Acetal is ideal for applications requiring high precision and low friction, such as gears and bearings. Its compatibility with various lubricants enhances its performance in mechanical applications.
– Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D618 and ISO 9001, particularly in regions with strict quality control measures, such as Germany.
Summary Table of Material Selection for UHMW Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for uhmw machining | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UHMW-PE | Food processing, mining, material handling | Exceptional durability and low wear rate | Difficult to machine, high thermal expansion | Medium |
| Polypropylene | Chemical processing | Low cost and ease of machining | Lower impact resistance | Low |
| PVC | Construction, plumbing, electrical | Cost-effective and widely available | Rigid, limited flexibility | Low |
| Acetal | Precision parts like gears and bearings | High strength and low friction | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials commonly used in UHMW machining, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials will aid in making informed decisions that align with specific application requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for uhmw machining
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for UHMW Machining?
Manufacturing Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) components involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage requires specific techniques and considerations due to the unique properties of UHMW.
How Is Material Prepared for UHMW Machining?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. UHMW typically comes in sheets, rods, or custom shapes. Before machining, it is essential to ensure that the material is free from moisture, as UHMW can absorb water, which may lead to dimensional inaccuracies during machining.
To prepare the material:
- Moisture Control: Store UHMW in a climate-controlled environment to minimize moisture absorption. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face varying climate conditions.
- Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection for any defects or inconsistencies in the material, as these can affect the final product’s quality.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of UHMW Machining?
Forming UHMW components requires precise machining techniques due to the material’s tendency to expand with heat and its low melting point of 270°C.
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is the preferred method for UHMW. It allows for high precision and repeatability, essential for maintaining tight tolerances.
- Cutting Techniques: When cutting UHMW, techniques such as climb milling are recommended to reduce chatter and improve surface finish. Sharp tools are critical, as dull tools can lead to poor tolerances and surface defects.
- Drilling and Sawing: For drilling, using twist drills with larger flute areas can help remove chips and reduce heat buildup. For sawing, blades with a 0° tooth rake can minimize friction and enhance cutting efficiency.
How Is Assembly Conducted in UHMW Machining?
Assembly processes for UHMW components may vary based on the application but generally involve:
- Joining Techniques: UHMW can be joined using adhesives or mechanical fastening. The choice of joining method should consider the end-use environment, as UHMW’s chemical resistance is a significant advantage in many applications.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: It is crucial to ensure that all components fit together properly to avoid stress and potential failure during operation.
What Finishing Techniques Are Common in UHMW Machining?
Finishing processes are vital to achieve the desired surface quality and tolerances. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Grinding: This technique is used to refine surface finishes, especially for components requiring high tolerances.
- Deburring: Removing burrs is essential to prevent wear and tear in applications. Techniques like manual or automated deburring ensure smooth edges and reduce friction.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for UHMW Machining?
Quality assurance is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of UHMW machined components. International standards like ISO 9001 provide a framework for maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International and Industry-Specific Standards Should Be Considered?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is recognized globally. Compliance ensures that suppliers have consistent processes in place.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products marketed in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For components used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints During UHMW Machining?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help identify and mitigate potential issues early.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the machining process helps detect deviations in real-time. This may involve measuring dimensions and surface finishes at various stages.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that the finished products meet all specifications and standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
International B2B buyers should establish robust methods to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can include reviewing their quality management systems and production capabilities.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s quality control processes and product integrity.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in UHMW Machining?
Testing methods for UHMW components vary based on their application but generally include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and micrometers to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and wear characteristics.
- Surface Finish Testing: Measuring roughness using profilometers to ensure that surface finishes meet application requirements.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific quality control nuances:
- Regional Standards Variability: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect product compliance. Familiarizing oneself with local requirements is essential.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and collaborations with suppliers.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Recognizing the impact of logistics on quality assurance, especially concerning shipping and handling, can help mitigate risks associated with material damage or degradation.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing UHMW machined components. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also enhances the potential for successful long-term partnerships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘uhmw machining’
To assist B2B buyers interested in procuring UHMW machining services, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. UHMW (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) machining requires specific expertise and technology due to its unique properties. Adhering to this checklist will help you identify and collaborate with the right suppliers for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for successful UHMW machining. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and intended applications of the machined parts. Precise specifications help suppliers understand your requirements and reduce the likelihood of costly revisions later.
- Consider the environment: Identify whether the parts will be used in wet or dry conditions, as this may affect material choices and machining techniques.
- Specify tolerances: Clearly outline acceptable tolerances to avoid issues during production and ensure functionality in the intended application.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to create a list of potential suppliers experienced in UHMW machining. Look for companies that have a proven track record in handling similar projects.
- Evaluate supplier capabilities: Assess their machinery, technology, and workforce expertise. Ensure they have experience with UHMW specifically, as it requires different handling compared to metals.
- Check industry reputation: Read customer reviews and testimonials to gauge their reliability and quality standards.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before engaging a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards. This ensures that they adhere to quality management practices.
- Look for relevant certifications: ISO 9001 and other quality certifications demonstrate a commitment to maintaining quality in production processes.
- Compliance with regulations: Ensure suppliers comply with regional and international regulations, especially if your parts will be used in critical applications like food processing or medical devices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the machined parts. This step is crucial to assess the supplier’s capabilities and the quality of their output.
- Evaluate quality: Inspect the samples for dimensional accuracy and surface finish. This will give you insights into how well the supplier can meet your specifications.
- Test fit and function: If possible, test the samples in your application to ensure compatibility and performance.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capacity
Engage in discussions with your shortlisted suppliers about lead times and their production capacity. Understanding these factors will help you plan your project timelines effectively.
- Confirm production timelines: Ask for detailed timelines for both sample and full production runs to avoid delays.
- Assess scalability: Ensure the supplier can scale production if your order volume increases in the future.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is essential for the successful execution of your project. Set up clear communication channels with your chosen supplier from the outset.
- Designate points of contact: Identify key personnel on both sides who will be responsible for project management and communication.
- Regular updates: Agree on the frequency of progress updates to ensure you are informed throughout the machining process.
Step 7: Finalize Terms and Conditions
Before proceeding with the order, finalize the terms and conditions of the contract. This includes pricing, payment terms, and warranty details.
- Negotiate pricing: Ensure that the pricing reflects the complexity of the machining process and the quality of materials used.
- Understand warranty and support: Clarify the warranty terms for the machined parts and any support offered for defects or issues post-delivery.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of procuring UHMW machining services and ensure they partner with the right suppliers for their needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for uhmw machining Sourcing
When engaging in sourcing for UHMW machining, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for international B2B buyers. This material, known for its excellent abrasion resistance and low coefficient of friction, presents unique challenges and cost factors that can significantly influence overall pricing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in UHMW Machining?
-
Materials: The price of UHMW-PE itself can vary based on market conditions, supplier relationships, and the specific grades chosen. High-quality UHMW is essential for achieving desired performance characteristics, but it often comes at a premium.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for precise machining of UHMW due to its unique properties. Labor costs will vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards and the availability of skilled machinists familiar with UHMW processing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative costs. Overhead can significantly impact the pricing of machined parts, especially in regions with higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: Machining UHMW requires specialized tooling to prevent melting and ensure precision. This can involve significant upfront investment, which is often amortized over the production volume, influencing the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures is vital due to the dimensional challenges associated with UHMW. The costs associated with testing, inspection, and certification can add to the overall pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs play a crucial role, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms can affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market positioning and the level of service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect UHMW Machining Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also yield better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized parts or those with tight tolerances may require more complex machining processes, which can drive up costs. It’s essential to balance customization needs with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The specific grade of UHMW and any necessary certifications (e.g., FDA compliance for food-grade applications) can affect pricing. Suppliers may charge more for materials that meet stringent quality standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and the availability of specialized machining capabilities can influence pricing. Building a strong relationship with suppliers may lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for managing logistics costs. Different Incoterms can shift responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, affecting the total cost.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers to Optimize Costs?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term contracts to negotiate better prices. Building a relationship with suppliers can also facilitate favorable terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also costs related to maintenance, durability, and potential failures. A higher upfront cost may result in lower TCO if the material performs better over time.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Understand local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade regulations that may impact pricing in different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Get Multiple Quotes: Always seek quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing. This practice also allows for better comparison of quality and services offered.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for UHMW machining can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable to obtain tailored quotes from suppliers to understand the specific pricing for your requirements. This ensures that you account for all variables and arrive at a comprehensive understanding of the costs involved.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing uhmw machining With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Machining Solutions
When evaluating manufacturing processes, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to ensure the best fit for specific applications. In the context of machining, particularly with Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW), there are several viable alternatives that can meet similar performance objectives. This analysis compares UHMW machining with two other approaches: traditional metal machining and advanced composite machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Uhmw Machining | Traditional Metal Machining | Advanced Composite Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent abrasion resistance, low friction | High strength, excellent durability | Lightweight, tailored properties |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower for materials but higher tooling costs | Higher material costs, but potential savings on weight |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires specialized tools and techniques | Established processes; widely understood | Requires specific training and technology |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal wear on tools | Moderate; tool wear and replacement needed | Low; depends on resin type |
| Best Use Case | High-wear environments; food processing | Structural applications; automotive | Aerospace; custom applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Metal Machining
Traditional metal machining involves the processing of metals such as steel, aluminum, and brass using well-established methods like milling, turning, and drilling. The primary advantage of this method is its familiarity and the availability of skilled labor. Additionally, metals often provide superior structural integrity and durability for applications requiring high strength.
However, metal machining can be cost-prohibitive due to the expense of raw materials and tooling, which often requires regular replacement. The machining process can also generate significant heat, which may necessitate additional cooling measures. For applications that do not require the low friction or chemical resistance offered by UHMW, traditional metal machining remains a strong alternative.
Advanced Composite Machining
Advanced composite machining involves working with materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass composites. These materials are renowned for their lightweight properties and high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for applications in industries like aerospace and automotive. The ability to tailor properties through the layering of materials also allows for customized performance characteristics.
The main drawback of composite machining is the cost of raw materials and the complexity of the machining process. Specialized tools and training are often required to handle composites effectively. While the maintenance of composite parts is generally low, the initial investment and technical challenges can be prohibitive for some manufacturers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Machining Solution
Selecting the right machining solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget, and desired performance characteristics. For B2B buyers, understanding the unique benefits and limitations of UHMW machining compared to traditional metal and advanced composite machining is crucial. If the primary need is for high wear resistance and low friction in challenging environments, UHMW may be the best choice. Conversely, if strength and cost-efficiency are prioritized, traditional metal machining might be more suitable. Finally, for lightweight and customizable applications, advanced composites offer a competitive edge. Ultimately, buyers should align their choice with the operational demands and long-term goals of their projects.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for uhmw machining
What Are the Key Technical Properties of UHMW Machining?
1. Material Grade
UHMW (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) comes in various grades, each tailored for specific applications. The most common grades are UHMW-PE 1000 and UHMW-PE 3000, with the former being the standard for most machining processes. Selecting the correct grade is crucial as it impacts factors like wear resistance, chemical stability, and overall performance in demanding environments. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific application requirements can significantly influence the longevity and reliability of the final product.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In UHMW machining, maintaining tight tolerances is essential due to the material’s tendency to expand and contract significantly under temperature changes—up to 12 times more than steel. For industries such as automotive or aerospace, where precision is non-negotiable, specifying the right tolerances ensures that components fit seamlessly, reducing the risk of malfunction or failure.
3. Coefficient of Friction (COF)
The coefficient of friction is a measure of how much resistance a material offers when sliding against another surface. UHMW has a low COF, comparable to Teflon, which makes it ideal for applications requiring low friction, such as conveyor systems or sliding components. For B2B buyers, understanding COF can lead to better material choices for applications that demand reduced wear and energy consumption.
4. Chemical Resistance
UHMW is known for its exceptional chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. The ability to withstand harsh chemicals without degrading ensures longer service life and lower replacement costs. Buyers should evaluate the chemical exposure of their applications to select the appropriate material grade, ensuring compliance and safety standards.
5. Impact Resistance
This property refers to the material’s ability to withstand sudden forces or shocks without breaking. UHMW excels in this area, providing durability in high-impact environments, such as in mining or heavy machinery applications. Understanding impact resistance is vital for B2B buyers in industries where equipment failure can lead to costly downtime and safety risks.
What Are Common Trade Terms in UHMW Machining?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of UHMW machining, OEMs often require custom components made from UHMW for specialized applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate their supply chains effectively.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For UHMW machining, MOQs can significantly affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies or startups. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to manage inventory and cash flow efficiently.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to invite them to submit price proposals for a specific quantity of goods or services. In UHMW machining, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and capabilities from different suppliers, ensuring they select the best option for their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with UHMW products.
5. Tolerance Stack-Up
This term refers to the cumulative effect of individual part tolerances on the overall assembly. In UHMW machining, managing tolerance stack-up is critical to ensure that components fit together correctly. Buyers need to understand this concept to avoid costly rework or assembly issues.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right materials and processes for their specific applications in UHMW machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the uhmw machining Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in UHMW Machining?
The global UHMW machining market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials across various industries. Key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and food processing are increasingly adopting UHMW polyethylene due to its superior abrasion resistance, low friction coefficient, and chemical stability. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing UHMW machining services is essential.
Emerging technologies in CNC machining are transforming the landscape, enabling precise and efficient fabrication of UHMW components. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who invest in advanced machining capabilities, which enhance the quality and consistency of finished products. Moreover, the rise of digital procurement platforms is streamlining the sourcing process, allowing buyers to compare suppliers easily and access a broader range of options.
As the market evolves, there is a notable shift towards customization and flexibility. B2B buyers are seeking suppliers who can provide tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements, including tight tolerances and rapid prototyping. This trend underscores the importance of collaboration between buyers and suppliers to ensure that the unique properties of UHMW are effectively leveraged in product development.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing UHMW Machining?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the decision-making process for B2B buyers in the UHMW machining sector. The environmental impact of plastic manufacturing is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly production methods.
The use of recycled UHMW materials is gaining traction, offering an eco-conscious alternative without compromising on performance. Suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, such as obtaining certifications like ISO 14001, are more likely to attract international buyers who value ethical supply chains.
Additionally, the emphasis on transparency in sourcing practices is rising. Buyers are demanding detailed information about the origins of materials and the environmental impact of their production processes. This trend is driving suppliers to adopt more comprehensive reporting practices, ultimately fostering trust and long-term partnerships in the B2B landscape.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of UHMW Machining?
The evolution of UHMW machining can be traced back to the development of Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene in the 1950s. Initially used in specialized applications, its unique properties—such as high impact strength and low friction—quickly garnered interest from diverse industries. Over the decades, advancements in machining techniques have made it feasible to work with UHMW in ways that were not possible before.
The introduction of CNC machining technologies in the late 20th century revolutionized the fabrication of UHMW components. These advancements allowed for greater precision and efficiency, enabling manufacturers to meet the increasing demands for customized UHMW products. As industries continue to evolve, the adaptability of UHMW machining is likely to play a crucial role in its ongoing relevance and application across various sectors.
In summary, navigating the UHMW machining market requires a keen understanding of current dynamics, sustainability practices, and the material’s historical context. For international B2B buyers, these insights are vital for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of uhmw machining
-
How do I solve machining tolerance issues with UHMW?
To effectively manage machining tolerance issues with UHMW, focus on controlling heat during the machining process. Utilize sharp tools with high rake angles and ensure appropriate feed rates, typically around 0.02 to 0.03 for roughing. Employ techniques such as vacuum systems to maintain stability and minimize chip buildup, which can distort dimensions. If tolerances are still problematic, consider switching from turning to milling, as milling often yields better dimensional accuracy and reduces chip flow issues. -
What is the best cutting tool material for machining UHMW?
For machining UHMW, high-speed steel (HSS) tools are generally recommended due to their sharpness and ability to handle the material’s low melting point. Tungsten carbide tools can also be effective, particularly for achieving optimal surface finishes. Ensure that the tools are specifically designed for plastic machining, as using metal-cutting tools may result in dull edges that affect tolerances and surface quality. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a UHMW machining supplier?
When selecting a UHMW machining supplier, evaluate their experience with UHMW materials and their capabilities in maintaining tight tolerances. Check their certifications and quality assurance processes to ensure they meet international standards. Additionally, assess their equipment and technology to confirm they can handle your specific machining needs. Customer reviews and case studies can provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) are typical for UHMW machining?
Minimum order quantities for UHMW machining can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Typically, MOQs may range from a few pieces for custom prototypes to larger quantities for mass production runs. It’s essential to communicate your needs directly with potential suppliers to determine their MOQ policies and discuss any flexibility they may offer for smaller orders. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in UHMW machining?
To ensure quality assurance in UHMW machining, collaborate with suppliers who implement stringent QA processes, including in-process inspections and final dimensional checks. Request documentation on material certifications and machining reports. Engaging in periodic audits and establishing clear quality standards upfront can help maintain the expected quality throughout the production process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing UHMW machining services?
Payment terms for UHMW machining services can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include net 30 or net 60 terms, where payment is due within 30 or 60 days post-invoice. Some suppliers may require a deposit before starting production, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that are mutually beneficial and ensure they align with your cash flow requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing UHMW machining internationally?
When sourcing UHMW machining internationally, consider shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Ensure that your supplier has experience in international shipping and can provide reliable logistics solutions. It’s advisable to work with freight forwarders familiar with the specific regulations of your importing country. Also, consider incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and risks during transportation. -
How does moisture content affect UHMW machining, and what can be done about it?
Moisture content can significantly impact the dimensional stability of UHMW during machining. To mitigate issues, control the moisture levels from the time the material arrives at your facility until it is machined. Storing UHMW in a climate-controlled environment can help prevent absorption. If machining involves parts exposed to liquids, consider using coolants that minimize moisture absorption, ensuring the material maintains its integrity throughout the process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Uhmw Machining Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – UHMW Bushing
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Material: UHMW (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene)\nOperations: \n- Facing on a mill (reduce thickness from 0.75″ to 0.653″)\n- Turning on a lathe to make a bushing\nBushing Specifications: \n- Inner Diameter (ID): 1.2495″ (press fit on a 1.25″ shaft)\n- Outer Diameter (OD): 2.25″\n- Length: 2.65″\nTooling Recommendations: \n- Use sharp uncoated tools, preferably those meant for aluminum\n-…
2. Practical Machinist – UHMWPE Ball Valve Seats
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Material: UHMWPE (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene)\nApplications: Used for producing seats for ball valves\nMachining Techniques: Turning and milling recommended, with a preference for milling for dimensional accuracy\nTooling Recommendations: Use sharp tools with positive cutting edges, large tool nose radius (minimum .032, better at .048), and high rake angles for milling tools\nCutting…
3. AIP Precision – Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Domain: aipprecision.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) is a thermoplastic known for its toughness and high impact strength, with molecular mass between 3.5 and 7.5 million amu. Key properties include:
– Resistance to Weathering: Excellent
– Tensile Strength at Break: 24 MPA
– Elongation at Break: 300%
– Thermal Expansion: 20 x 10^-4 K
– Coefficient of Friction: 0.29
– Impact Strength: No break
-…
4. Bee Plastic – UHMW-PE CNC Machining
Domain: beeplastic.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: UHMW-PE CNC machining involves the use of Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW-PE), known for its exceptional properties suitable for precision parts. The guide covers the unique characteristics of UHMW-PE, the CNC machining process, and how to procure high-quality accessories made from this versatile polymer.
5. SendCutSend – UHMW Plastic Sheets
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: UHMW (Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) is a durable, versatile, and cost-effective plastic known for its abrasion, impact, and chemical resistance. Available in two thicknesses: .375″ (9.53mm) and .500″ (12.7mm). Offered in black and white with a cutting tolerance of +/- .005″. Minimum part size for cutting is 1″ x 2″ and maximum is 30″ x 44″; custom quotes available for sizes up to 30″ x…
6. Hobby Machinist – UHMW Plastic Pulleys
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Material: Ultra High Molecular Weight (UHMW) Plastic
Applications: Suitable for making pulleys
Machining Techniques:
– Use high speed steel tooling with lots of back rake, side rake, and clearances, plus a generous nose radius.
– Cutting speed: around 500 surface feet per minute, slightly higher for finish cuts.
– Clamping: Careful clamping is necessary to avoid distorting the material.
– Drillin…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for uhmw machining
In the evolving landscape of UHMW machining, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial component for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations. Understanding the unique challenges associated with machining UHMW—such as its high thermal expansion and specific tooling requirements—can help businesses mitigate risks and enhance product quality. Key insights include the importance of using the right cutting tools, maintaining appropriate speeds and feeds, and controlling heat buildup during machining processes.
Moreover, ensuring consistent material quality and moisture control can significantly impact tolerances and dimensional accuracy. By fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers who specialize in UHMW machining, companies can secure the necessary expertise and resources to meet their operational needs.
As the demand for high-performance materials continues to grow across diverse industries, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage with strategic sourcing practices. This proactive approach not only drives efficiency but also positions businesses to capitalize on emerging market opportunities. Embrace the future of UHMW machining—partner with trusted suppliers and leverage advanced machining techniques to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.