Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type iii anodizing
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing, sourcing reliable Type III anodizing services presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. As industries increasingly prioritize durability and performance, understanding the nuances of hardcoat anodizing—known for its exceptional wear and corrosion resistance—becomes essential. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various types of anodizing, their specific applications across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Navigating the global market for Type III anodizing requires a strategic approach, particularly for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers will benefit from insights on supplier accreditation, cost structures, and compliance with international standards, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Furthermore, this guide highlights best practices for maximizing product performance and longevity through effective anodizing processes.
By leveraging the information provided herein, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ultimately leading to improved product quality and operational efficiency. Whether you are looking to understand the technical specifications of hardcoat anodizing or seeking to establish robust supplier relationships, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence.
Understanding type iii anodizing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Hardcoat | High voltage process, thick oxide layer (up to 0.0030″) | Aerospace, automotive, military applications | Pros: Excellent wear resistance; Cons: Higher cost due to complex processing. |
| Low Voltage Hardcoat | Uses AC overlay with DC, lower resistance, more uniform | Medical devices, precision instruments | Pros: Enhanced coating uniformity; Cons: May require specific equipment. |
| Sealed Hardcoat | Coating sealed for corrosion resistance | Marine, chemical processing industries | Pros: Improved corrosion resistance; Cons: Sealing can add to processing time. |
| Dyed Hardcoat | Incorporates dyes for aesthetic and identification purposes | Consumer goods, sporting equipment | Pros: Custom colors for branding; Cons: Limited color options beyond black. |
| Unsealed Hardcoat | Coating left unsealed for maximum performance | High-friction applications, industrial tooling | Pros: Superior lubrication retention; Cons: Increased susceptibility to corrosion. |
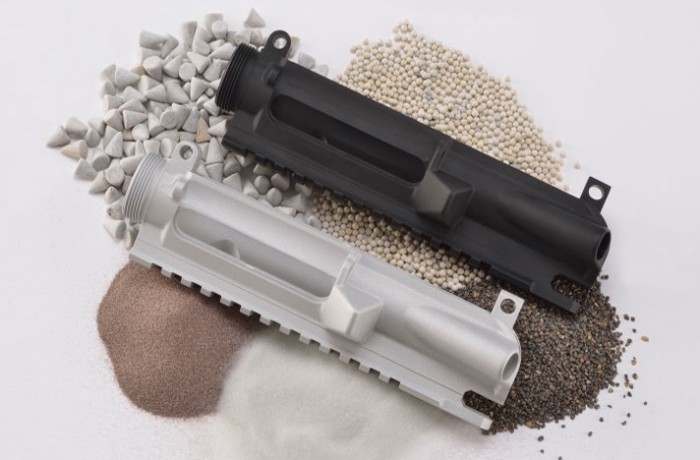
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Hardcoat Anodizing?
Conventional hardcoat anodizing is characterized by a high-voltage process that significantly increases the thickness of the oxide layer, ranging from 0.0005 to 0.0030 inches. This method is well-suited for applications in industries such as aerospace and military, where durability and resistance to wear and corrosion are paramount. Buyers should consider the complexity and cost associated with this process, as it often requires specialized equipment and expertise.
How Does Low Voltage Hardcoat Differ from Conventional Methods?
Low voltage hardcoat anodizing employs a combination of AC and DC currents to create a more uniform oxide layer with enhanced performance properties. This method is particularly advantageous for medical devices and precision instruments, where a consistent coating is essential. B2B buyers should evaluate the need for specific processing equipment and the potential benefits of improved coating uniformity when considering this option.
Why Choose Sealed Hardcoat Anodizing?
Sealed hardcoat anodizing involves applying a sealing process to enhance corrosion resistance. This type is ideal for applications in marine and chemical processing industries, where exposure to harsh environments is common. Buyers should weigh the benefits of improved corrosion resistance against the potential increase in processing time and costs associated with sealing methods.
What Are the Benefits of Dyed Hardcoat Anodizing?
Dyed hardcoat anodizing allows for the incorporation of colors, providing aesthetic appeal and identification for consumer products and sporting equipment. While black is the most common dye used, other colors may be available upon request. B2B buyers should consider the branding opportunities this provides, as well as the limitations in color variety when making their selection.
When Should You Consider Unsealed Hardcoat Anodizing?
Unsealed hardcoat anodizing is designed for applications requiring maximum performance without the added layer of sealing. This type is particularly beneficial in high-friction environments, such as industrial tooling, where lubrication retention is critical. Buyers must be cautious, however, as this option may lead to increased susceptibility to corrosion without the protective sealing.
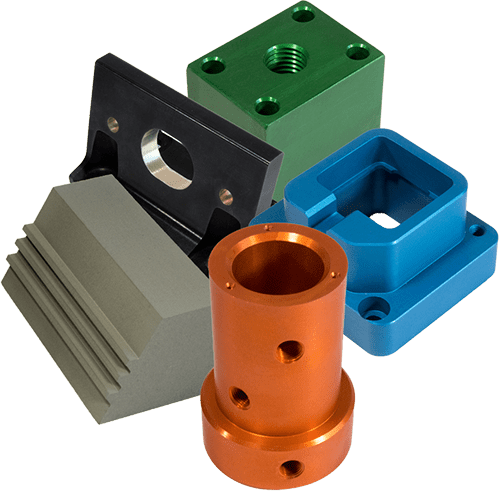
Key Industrial Applications of type iii anodizing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of type iii anodizing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Component coatings for aircraft parts | Enhances wear and corrosion resistance, ensuring safety and longevity of parts. | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications. |
| Medical Devices | Instrument coatings | Provides non-contaminating, easily sterilizable surfaces for surgical tools. | Need for stringent cleanliness and biocompatibility standards. |
| Automotive | Engine components | Improves durability and performance, reducing maintenance costs. | Material compatibility and performance under high temperatures. |
| Military | Equipment and weaponry | Increases operational lifespan and reliability in harsh environments. | Compliance with military specifications like MIL-A-8625. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Enhances thermal management and electrical insulation properties. | Importance of dielectric strength and thermal conductivity. |
How is Type III Anodizing Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, Type III anodizing is commonly applied to critical components such as landing gear and engine parts. This process significantly enhances the wear and corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys, which are often subjected to extreme conditions. By increasing the thickness of the oxide layer, manufacturers ensure that components can withstand harsh environmental factors, thus improving safety and extending service life. Buyers in this industry must prioritize suppliers who adhere to specific aerospace standards and certifications to ensure reliability and compliance.
What Role Does Type III Anodizing Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Type III anodizing is crucial in the production of medical devices, particularly surgical instruments. The anodized surfaces are non-contaminating and can be easily sterilized, making them ideal for use in healthcare settings. This coating not only provides a robust barrier against corrosion but also enhances the longevity and performance of the instruments. International buyers should focus on suppliers that meet stringent biocompatibility and cleanliness standards to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Why is Type III Anodizing Important for Automotive Parts?
In the automotive industry, Type III anodizing is applied to engine components and other parts that require high durability and resistance to wear. The anodized layer improves the performance and lifespan of these components, ultimately reducing maintenance costs for manufacturers. Buyers should consider the compatibility of the anodized surfaces with various automotive fluids and operating temperatures, ensuring that the coatings perform optimally under demanding conditions.
How Does Type III Anodizing Benefit Military Equipment?
Military applications leverage Type III anodizing for equipment and weaponry, where reliability and durability are paramount. The anodized coatings increase resistance to wear and corrosion, essential for equipment exposed to extreme environments. Compliance with military specifications such as MIL-A-8625 is critical for sourcing decisions, as it ensures that the products can withstand the rigors of military operations while maintaining operational integrity.
What Advantages Does Type III Anodizing Offer in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, Type III anodizing is utilized for heat sinks and enclosures, enhancing thermal management and providing electrical insulation. This process improves the thermal conductivity of components while ensuring they remain electrically insulated, which is essential for device performance. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can guarantee the dielectric strength and thermal properties required for their specific electronic applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type iii anodizing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Meeting Tight Tolerances for Anodized Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when specifying Type III anodizing for components that require tight dimensional tolerances. Anodizing inherently alters the dimensions of the base material, as the process converts a portion of the aluminum into an aluminum oxide coating. For instance, if a part requires a coating thickness of 0.002 inches, it may lead to a dimensional change of 0.001 inches on each surface. This can result in parts that are out of specification, leading to costly delays and rework.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should ensure that exact specifications regarding tolerances are included in their ordering documents. It is crucial to engage in detailed communication with the anodizing supplier to clarify expected dimensions after anodizing. Consider conducting a pre-production trial to evaluate the impact of the anodizing process on your specific parts. This approach allows for adjustments in the design or the anodizing process to ensure that the final product meets the required tolerances without compromising quality.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Surface Quality Leading to Product Rejection
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers involves inconsistent surface quality post-anodizing. Variability in the anodizing process can lead to defects such as uneven coatings, discoloration, or even surface contamination. Such inconsistencies can cause products to be rejected during quality control checks, resulting in delays, increased costs, and a damaged reputation with customers.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize working with anodizing suppliers that have robust quality control measures in place. Before placing large orders, request sample parts and conduct thorough inspections to assess surface quality. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the supplier’s process controls, including the equipment used and the specific techniques for cleaning and preparing the aluminum. Establishing a clear quality assurance agreement with the supplier can help ensure that the anodizing process adheres to the required standards, minimizing the risk of rejection.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Seal for Enhanced Performance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with choosing the appropriate sealing method for their Type III anodized components. The sealing process significantly affects the performance characteristics of the anodized layer, such as corrosion resistance and wear properties. Without the right seal, parts may not perform as expected in their intended applications, leading to premature failure or increased maintenance costs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements before selecting a sealing method. For instance, if high corrosion resistance is critical, hydrothermal sealing may be preferred, while PTFE sealing is ideal for applications requiring enhanced lubrication properties. Engaging in discussions with the anodizing provider about the specific needs of your components can facilitate a better understanding of which sealing method will yield the best results. Additionally, consider requesting performance data or case studies from the supplier to better assess the effectiveness of different sealing options in real-world applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type iii anodizing
What Are the Key Materials for Type III Anodizing?
Type III anodizing, also known as hardcoat anodizing, is a specialized process that enhances the properties of aluminum alloys, making them suitable for demanding applications. Below, we analyze several common materials used in Type III anodizing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
Which Aluminum Alloys Are Most Commonly Used for Type III Anodizing?
6061 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 6061 aluminum alloy is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, medium to high strength, and good machinability. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and has a yield strength of approximately 275 MPa.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is versatile and cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it may not be as strong as other alloys like 7075, limiting its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: 6061 is compatible with various media, including water and oil, but may not perform well in highly acidic or alkaline environments.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions such as Europe and South America should ensure compliance with EN and ASTM standards, as 6061 is widely recognized and used.
7075 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: Known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, 7075 aluminum alloy can handle temperatures up to 120°C and has a yield strength of around 570 MPa. It also exhibits good fatigue resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of 7075 is its strength, making it ideal for aerospace and military applications. However, it is more expensive and less corrosion-resistant than 6061, which may limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: This alloy is particularly suitable for applications requiring high strength and low weight, such as aircraft components, but may require additional protective coatings in corrosive environments.
International Considerations: Buyers must consider compliance with military and aerospace standards, particularly in North America and Europe, where specifications like MIL-A-8625 are critical.
2024 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 2024 aluminum alloy is known for its high strength and excellent fatigue resistance, with a yield strength of about 480 MPa. It performs well up to temperatures of 150°C.
Pros & Cons: While it offers superior strength, 2024 is less corrosion-resistant than other alloys, necessitating protective coatings. Its higher cost may also be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: This alloy is widely used in aerospace applications, but its limited corrosion resistance makes it less suitable for marine or chemical environments.
International Considerations: Compliance with aerospace standards is essential, particularly for buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where strict regulations govern material selection.
5005 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: The 5005 alloy is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good anodizing response, with a yield strength of around 210 MPa. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: Its good aesthetic finish and corrosion resistance make it suitable for architectural applications. However, it is less strong than 6061 and 7075, which may limit its use in structural applications.
Impact on Application: This alloy is ideal for decorative and architectural elements, but its lower strength may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards, particularly in Europe, where architectural guidelines may dictate specific material requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Type III Anodizing
| Material | Typical Use Case for type iii anodizing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | General engineering and structural components | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower strength than 7075 | Low |
| 7075 Aluminum | Aerospace and military applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and lower corrosion resistance | High |
| 2024 Aluminum | Aerospace structures | Excellent fatigue resistance | Poor corrosion resistance | High |
| 5005 Aluminum | Architectural applications | Good corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to 6061 | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various aluminum alloys used in Type III anodizing. Understanding these factors can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type iii anodizing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Type III Anodizing?
The manufacturing process for Type III anodizing, also known as hardcoat anodizing, involves several critical stages to ensure that aluminum components meet stringent performance and quality requirements. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Type III Anodizing?
Material preparation is the first step in the anodizing process. It typically involves cleaning and deoxidizing the aluminum substrate to remove any contaminants such as oils, dirt, and oxidation layers. This is often achieved through chemical cleaning agents or mechanical methods like abrasive blasting. Ensuring a clean surface is crucial, as it directly impacts the adhesion and quality of the anodized coating.
Following the initial cleaning, the aluminum components undergo a thorough inspection to verify that they meet the specifications required for anodizing. Any defects found during this stage could result in product failure later in the process, making it essential to adhere to strict quality control measures.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming and Assembly Stages?
Once the material is prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the aluminum components to their final specifications through machining, extrusion, or other manufacturing processes. Precision is critical here, as the dimensions of the part will be affected by the anodizing layer, which penetrates and builds upon the surface.
After forming, components may go through an assembly process if they are part of a larger system. This could involve fitting multiple parts together and ensuring that they function correctly as a unit. The assembly stage must also comply with quality standards to guarantee the integrity and performance of the final product.
What Are the Finishing Steps in Type III Anodizing?
The finishing stage encompasses the actual anodizing process. In Type III anodizing, the aluminum part is submerged in a sulfuric acid electrolyte solution, cooled to near-freezing temperatures. A high voltage (up to 100 volts) is applied, leading to the formation of a thick aluminum oxide layer. This layer significantly enhances wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Post-anodizing, the coating can be sealed using hydrothermal or precipitation methods, depending on the intended application. Sealing is crucial for maximizing corrosion resistance and enhancing lubrication properties, particularly if the parts will be used in environments where they are exposed to harsh conditions.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Type III Anodizing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the Type III anodizing process, especially for B2B buyers who require high-quality standards. Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with industry-specific standards, such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications, is also critical.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves the inspection of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards prevents defects later in the process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the anodizing process parameters, such as voltage, temperature, and time. This ensures that the anodizing layer meets thickness and quality specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After anodizing, the finished components are subjected to a comprehensive inspection. This includes visual checks for defects, measurements of coating thickness, and adhesion tests to confirm that the anodized layer meets required standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Type III Anodizing Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods for Type III anodized components include:
-
Coating Thickness Measurement: Using micrometers or ultrasonic thickness gauges to ensure that the anodized layer meets the specified thickness.
-
Adhesion Testing: Conducting tests such as tape tests or scratch tests to evaluate the adhesion of the anodized coating to the substrate.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Employing salt spray tests or immersion tests to determine how well the anodized layer can withstand corrosive environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial to ensure product reliability. Here are several strategies to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess quality control processes, equipment, and adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports, including inspection results and compliance certificates, provides transparency into the supplier’s quality management practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes and adherence to standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certifications is vital. Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in North America might focus on compliance with ASTM standards. It is essential for buyers to communicate their specific quality requirements clearly and ensure that suppliers can meet these standards.
Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing, environmental considerations, and labor practices can impact supply chain decisions. B2B buyers should be proactive in researching and confirming that their suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for Type III anodizing are comprehensive and critical for ensuring product performance and reliability. By understanding the key stages of production, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and verifying supplier practices, international B2B buyers can secure high-quality anodized aluminum components that meet their specific needs. Adopting these practices not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers in the anodizing industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type iii anodizing’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing Type III anodizing services requires a strategic approach to ensure quality and reliability. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, enabling you to make informed decisions that align with your technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for successful procurement of Type III anodizing. Consider factors such as coating thickness, alloy type, and specific performance requirements like corrosion and abrasion resistance. Detailed specifications ensure suppliers understand your needs, reducing the risk of errors and miscommunication.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Begin your search by identifying suppliers with a strong reputation in the anodizing industry. Look for companies that specialize in Type III anodizing and have experience with your specific applications. Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to gather a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify that your shortlisted suppliers hold relevant certifications. Look for compliance with military standards such as MIL-A-8625, as well as ISO certifications that demonstrate quality management practices. Certifications not only signify a commitment to quality but also enhance trust in the supplier’s capabilities.
Step 4: Request Technical Documentation
Engage with potential suppliers by requesting comprehensive technical documentation. This should include details about their anodizing process, equipment used, and any proprietary techniques that enhance performance. Reviewing technical documentation helps you assess their expertise and ensures they can meet your specific requirements.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Evaluate the production capabilities of each supplier to ensure they can handle your volume requirements and delivery timelines. Inquire about their capacity for scaling production, as well as their lead times for different order sizes. Understanding their operational efficiency is essential for maintaining your supply chain.
Step 6: Review Quality Control Processes
Quality control is paramount in anodizing processes. Investigate the quality assurance measures implemented by suppliers, such as inspection protocols and testing methods for coating thickness and adhesion. A robust quality control system minimizes the risk of defects and ensures consistent product performance.
Step 7: Obtain and Compare Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotes from the selected suppliers. Compare pricing structures, terms of service, and any additional fees that may apply. It’s essential to evaluate not just the cost but also the value offered, including customer support, warranty terms, and flexibility in meeting your needs.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for Type III anodizing, ensuring you select a reliable supplier that meets your technical and business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type iii anodizing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Type III Anodizing?
Understanding the cost structure of Type III anodizing is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary material used is aluminum, which may vary in cost depending on the alloy. Additionally, the electrolytes used in the anodizing process, typically sulfuric acid, also contribute to material costs. The quality of these materials can significantly impact the final price.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required to operate the anodizing equipment and ensure quality control. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and the complexity of the anodizing process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs of utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. High-voltage systems used for Type III anodizing require significant energy, which can raise overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially if custom fixtures are needed for specialized parts. Investment in high-quality tooling can lead to better precision and lower long-term costs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the anodized parts meet specific standards (like MIL-A-8625) necessitates rigorous quality control processes. Testing for thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are particularly relevant for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs fees must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the complexity of the order.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Type III Anodizing Costs?
Various factors can influence the pricing of Type III anodizing, making it essential for buyers to understand these elements to negotiate effectively.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Generally, larger orders can reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs to determine the optimal order size.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements such as specific coating thickness, color, or additional treatments can increase costs. Standardized orders typically yield better pricing.
-
Materials: The choice of aluminum alloy significantly impacts cost. Specialty alloys may incur higher prices, while common alloys might be more economical.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications (e.g., aerospace or medical-grade) can lead to increased costs. Buyers should evaluate their quality requirements carefully to avoid over-specifying.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and capabilities can influence pricing. Suppliers with advanced technology and experience may charge more but offer superior quality and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can affect pricing. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties can help buyers make informed decisions.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
International B2B buyers should employ strategic approaches to enhance cost-efficiency and maximize value.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Engaging with several suppliers to obtain quotes can provide leverage in negotiations. This approach allows buyers to compare pricing structures and services.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the initial price but also the long-term costs associated with quality, reliability, and maintenance. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher expenses down the line.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and preferential treatment on future orders.
-
Focus on Clear Specifications: Clearly defined requirements can reduce misunderstandings and minimize costly revisions or delays in production.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances come into play.
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate variations can affect the final costs. Buyers should be mindful of the currency in which they transact.
-
Import Tariffs and Duties: Understanding applicable tariffs and duties can prevent unexpected costs when importing anodized parts.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding materials and processes. Ensuring compliance can avoid costly penalties or project delays.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for Type III anodizing is subject to change based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers should always seek updated quotes and conduct thorough due diligence when sourcing to ensure they receive the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type iii anodizing With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Type III Anodizing
When considering surface treatment solutions for aluminum components, Type III anodizing, also known as hardcoat anodizing, is widely recognized for its durability and performance. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or budget constraints. This analysis compares Type III anodizing with two viable alternatives: Electroless Nickel Plating and Ceramic Coating. Understanding these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Type III Anodizing | Electroless Nickel Plating | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High wear & corrosion resistance; improves surface hardness | Excellent corrosion resistance; moderate wear resistance | Superior heat resistance; moderate wear resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and controlled conditions | Easier application; does not require electrical current | Requires precise application; often needs curing |
| Maintenance | Low; durable and long-lasting | Moderate; may require reapplication | Low; very durable and resistant |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, military, medical applications | Automotive, electronics, marine applications | High-temperature environments, decorative applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electroless Nickel Plating: What Are Its Strengths and Weaknesses?
Electroless nickel plating involves a chemical process that deposits a nickel-phosphorus alloy onto a substrate without the use of electrical current. This method offers excellent corrosion resistance and uniform thickness across complex geometries. Its ease of implementation makes it a popular choice for various industrial applications, particularly in automotive and electronics sectors.
Pros:
– Uniform coating on complex shapes.
– Good corrosion resistance and moderate wear resistance.
– Easier application compared to anodizing.
Cons:
– Not as hard or wear-resistant as Type III anodizing.
– May require reapplication in high-wear environments.
Ceramic Coating: When Is It the Best Option?
Ceramic coatings are applied as a thin layer of ceramic material, providing excellent thermal stability and wear resistance. This makes them particularly suitable for high-temperature applications, such as in aerospace and automotive industries, where heat dissipation is critical. Ceramic coatings can also enhance the aesthetic appeal of components.
Pros:
– Exceptional heat resistance and thermal insulation.
– Good for decorative finishes.
– Highly durable with low maintenance needs.
Cons:
– Generally higher cost than anodizing.
– Application requires precision and may involve curing processes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right surface treatment solution hinges on several factors, including performance requirements, cost considerations, and specific application environments. Type III anodizing excels in high-wear and corrosion-prone settings, making it ideal for aerospace and medical devices. Conversely, if uniformity and ease of application are paramount, Electroless Nickel Plating could be more suitable. For applications demanding high thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal, Ceramic Coating stands out despite its higher costs. By carefully evaluating these aspects, B2B buyers can align their choice with their operational objectives and budgetary constraints, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for their aluminum components.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type iii anodizing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Type III Anodizing?
Type III anodizing, also known as hardcoat anodizing, offers several critical technical properties that enhance the performance of aluminum components in various applications. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions.
-
Coating Thickness
Coating thickness for Type III anodizing typically ranges from 0.0005 inches to 0.0030 inches (12.7 to 76.2 micrometers). The thickness is crucial as it directly impacts the durability and performance characteristics of the anodized surface. A thicker coating enhances wear resistance and corrosion protection, making it ideal for demanding applications like aerospace and military equipment. -
Surface Hardness
The anodizing process significantly increases the surface hardness of aluminum, often exceeding 60 HRC (Rockwell Hardness Scale). This enhanced hardness is vital for components exposed to high levels of abrasion or mechanical stress. For buyers, this means reduced maintenance costs and extended product lifespans. -
Corrosion Resistance
Type III anodized surfaces exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to untreated aluminum. This property is particularly important in industries such as automotive and marine, where components are exposed to harsh environments. By opting for Type III anodizing, businesses can ensure longevity and reliability in their products. -
Dielectric Properties
The anodized layer acts as an electrical insulator, providing dielectric properties that are beneficial in electronic applications. This feature is particularly important for manufacturers of electronic components, as it helps prevent electrical shorts and enhances overall safety. -
Lubrication Retention
The porous nature of the anodized surface allows for better retention of lubricants, particularly when treated with PTFE coatings. This property is crucial for applications requiring low friction and reduced wear, such as in the manufacturing of gears and bearings. -
Dimensional Change
Anodizing results in a conversion coating, with approximately 50% of the coating thickness penetrating into the aluminum substrate. This can lead to a dimensional change that must be accounted for in the design and manufacturing processes. Buyers need to communicate specific tolerances to ensure that the final product meets their requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Type III Anodizing?
Understanding trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some common terms associated with Type III anodizing:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Type III anodizing, OEMs often require anodized components to meet specific performance standards for their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is crucial for buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost-efficiency. Buyers should inquire about MOQs when sourcing anodized components to ensure they can meet their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers. This is particularly important in the anodizing industry, as the cost can vary based on factors like coating thickness, alloy type, and production volume. Clear RFQs help suppliers provide accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving anodized products, as they dictate shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the anodizing industry, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the job and current production schedules. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as MIL-A-8625 for Type III anodizing, ensure that the anodized products meet specific quality and performance criteria. Buyers should verify that their suppliers adhere to relevant certification standards to ensure compliance and reliability in their applications.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing Type III anodized components, ultimately leading to better product performance and enhanced business relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type iii anodizing Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in Type III Anodizing
The global market for Type III anodizing, also known as hardcoat anodizing, is driven by increasing demand for durable, corrosion-resistant coatings in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. As international B2B buyers seek materials that enhance product longevity and performance, the focus on advanced anodizing techniques has intensified. Key trends include the growing adoption of high-voltage processes that produce thicker and denser oxide layers, providing superior wear resistance and dielectric properties.
Emerging technologies such as low-voltage anodizing are gaining traction, offering a more uniform coating and improved performance characteristics. Additionally, the integration of automation in the anodizing process is streamlining production, allowing for better quality control and reduced lead times. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly interested in these innovations as they strive to enhance product offerings while optimizing supply chains.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and trade dynamics are influencing sourcing strategies. Companies are increasingly looking to diversify their suppliers to mitigate risks associated with regional disruptions. This has led to a greater emphasis on establishing robust relationships with manufacturers who can provide consistent quality and adhere to international standards, such as MIL-A-8625, which governs Type III anodizing processes.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Type III Anodizing Materials?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the Type III anodizing sector. The environmental impact of anodizing processes, particularly in terms of waste management and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly electrolytes and implementing waste recycling programs.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide transparency about their sourcing practices and demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to gain a competitive edge.
Investing in ‘green’ materials and processes not only meets regulatory demands but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe, where stringent environmental policies are in place. As a result, sourcing Type III anodizing services that adhere to sustainability standards is not just a trend; it is becoming a fundamental aspect of procurement strategies.
What is the Evolution of Type III Anodizing in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of Type III anodizing can be traced back to its origins in military applications, where durability and corrosion resistance were paramount. Over the decades, advancements in technology and processing methods have expanded its use beyond military specifications to commercial applications, particularly in industries requiring high-performance materials.
Initially, Type III anodizing was limited to specific aluminum alloys, but modern techniques have broadened its applicability. The introduction of high-voltage anodizing processes has enhanced the thickness and uniformity of coatings, making them suitable for a wider range of applications, from medical devices to aerospace components.
As the market continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on quality assurance and adherence to international standards. This evolution reflects a shift in buyer expectations, where the demand for high-quality, reliable anodized products drives innovation and enhances competitiveness in the global market. B2B buyers are now more informed and discerning, seeking suppliers who can not only meet their technical requirements but also align with their values regarding sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type iii anodizing
-
How do I choose the right supplier for Type III anodizing?
When selecting a supplier for Type III anodizing, consider their experience and specialization in anodizing processes. Look for certifications such as MIL-A-8625 Type III, as these indicate adherence to industry standards. Evaluate their production capabilities, lead times, and the range of alloys they work with. Additionally, request samples of their work to assess quality and consistency. Establish clear communication regarding your requirements and ensure they can accommodate any specific needs you may have. -
What are the typical lead times for Type III anodizing services?
Lead times for Type III anodizing can vary based on the supplier’s capacity, the complexity of your order, and the volume of parts. Generally, standard lead times range from 2 to 4 weeks for smaller orders. However, larger volumes or specialized finishes may require longer processing times. It’s crucial to communicate your deadlines upfront and inquire about expedited options if necessary to ensure your project stays on schedule. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Type III anodizing?
Minimum order quantities for Type III anodizing differ among suppliers. Some may accept small batch orders, while others might have an MOQ of several hundred units to optimize production efficiency. When sourcing suppliers, clarify their MOQ policies early on and evaluate whether they can accommodate your specific needs. This understanding can help you avoid unexpected costs and ensure your procurement aligns with your project scale. -
Can Type III anodizing be customized for specific applications?
Yes, Type III anodizing can be customized to meet specific application requirements. This includes varying the thickness of the anodic coating, choosing sealing methods, and even altering the surface finish. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to explore customization options, such as color and texture, to ensure the final product meets your performance and aesthetic standards. Collaborating closely with the supplier will facilitate a tailored solution that fits your application perfectly. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Type III anodizing?
Payment terms for Type III anodizing services can vary widely between suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established clients. It’s essential to negotiate terms that work for both parties and ensure clarity regarding payment schedules, especially for international transactions where currency exchange and transfer fees may apply. -
How is quality assurance managed in Type III anodizing processes?
Quality assurance in Type III anodizing involves rigorous testing and inspection protocols. Reputable suppliers adhere to industry standards and may employ certifications to validate their processes. Common QA practices include dimensional inspections, adhesion tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations. Inquire about the supplier’s QA processes and request documentation or reports from previous orders to verify their commitment to quality, ensuring that your components meet all necessary specifications. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing Type III anodizing internationally?
When sourcing Type III anodizing from international suppliers, consider logistical factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Understanding the supplier’s shipping capabilities and delivery timelines is crucial for project planning. Additionally, ensure that you are aware of import/export documentation required for your materials. Establish a reliable communication channel with your supplier to address any logistical challenges that may arise during the shipping process. -
What are the environmental regulations concerning Type III anodizing?
Environmental regulations for Type III anodizing can vary by region, particularly in Europe, Africa, and South America. Many countries have stringent laws regarding chemical use and waste disposal in the anodizing process. When selecting a supplier, inquire about their compliance with local regulations, including waste management and chemical handling practices. A supplier committed to environmental sustainability can help mitigate potential legal issues and enhance your corporate responsibility profile.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Type Iii Anodizing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Precision Coating – Hardcoat Anodizing (Type III)
Domain: precisioncoating.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Hardcoat Anodizing (Type III) is a military standard coating (MIL-A-8625 Type III) used to enhance the wear and corrosion resistance of aluminum surfaces. It increases the surface hardness and improves thermal and dielectric properties. The anodizing process thickens the natural oxide layer on aluminum from 2-3 nanometers to 50 micrometers (0.002 inches). The process involves a high voltage (up to…
2. Novation Inc – Type III Hardcoat Anodizing
Domain: novationinc.net
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Type III Hardcoat Anodizing – MIL-A-8625 Type III Class 1 & 2 Anodizing. High-performance anodizing services for CNC machine and precision sheet metal shops. Applications include aerospace, medical, military, and industrial equipment. Anodizing thickness ranges from 0.0005 inches to 0.003 inches. Offers Type III, Class 1 (non-dyed) and Class 2 (dyed black) finishes. PTFE-impregnated hard anodized …
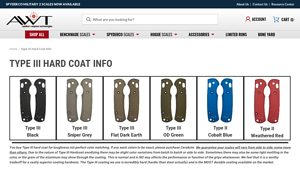
3. Applied Weapons Tech – Type III Hard Coat
Domain: appliedweaponstech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Type III Hard Coat is designed for toughness rather than perfect color matching. The product is available in various colors including Type III Black, Type III Sniper Grey, Type III Flat Dark Earth, Type III OD Green, Type II Cobalt Blue, and Type II Weathered Red. The scales are machined from 6061 aluminum and finished with Type III, Type II, or Cerakote. The Type III hard coat is known for its ha…
4. Fort Wayne Anodizing – Type III Hardcoat Anodizing
Domain: fortwayneanodizing.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Type III Hardcoat Anodizing forms a thick aluminum oxide coating (.001″ to .003″) that enhances hardness and durability. Key properties include:
– Corrosion Resistance: Passes 1000 HR 5% salt spray test
– Electrical Insulation: Equivalent to glass or porcelain
– Prevents Galvanic Reaction: Usable with steel, copper, brass, etc.
– Hardness: C60-C70 Rockwell
– High Operating Temperatures: Up to…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type iii anodizing
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers Considering Type III Anodizing?
Type III anodizing offers unparalleled benefits for industries requiring enhanced durability, wear resistance, and corrosion protection in aluminum components. Its applications span critical sectors such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive, making it essential for suppliers to ensure compliance with rigorous military and industry standards. Strategic sourcing becomes vital, allowing B2B buyers to identify reliable partners who can deliver high-quality anodizing services that meet specific operational needs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Improve Your Supply Chain for Type III Anodizing?
Investing in strategic sourcing not only secures superior anodizing services but also fosters long-term partnerships that can lead to competitive pricing and enhanced service delivery. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their technical capabilities, certification compliance, and past performance in similar projects. By building relationships with reputable anodizing vendors, businesses can mitigate risks associated with quality and lead times.
What Does the Future Hold for Type III Anodizing in Global Markets?
As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and performance, the demand for Type III anodizing is expected to grow, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about technological advancements and market trends that could influence anodizing processes. This proactive approach will empower businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape. Engage with suppliers today to explore how Type III anodizing can enhance your product offerings and drive business growth.