Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type iii anodize
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing Type III anodize can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for durable, corrosion-resistant, and high-performance aluminum components, understanding the nuances of Type III anodizing is crucial. This guide aims to equip decision-makers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in countries like Brazil and Nigeria—with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
We delve into the intricacies of Type III anodize, exploring its various applications across industries, from aerospace to medical devices, and the critical factors influencing supplier selection. Buyers will benefit from insights on material specifications, compliance with international standards, and the cost implications of hardcoat anodizing. Additionally, we provide strategies for evaluating potential suppliers, ensuring that they meet both quality and service expectations.
By the end of this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to navigate the global market for Type III anodize with confidence, enabling them to procure high-quality anodized aluminum products that meet their specific operational needs while optimizing costs. Understanding these dynamics will not only facilitate better procurement practices but also strengthen partnerships with suppliers, ultimately contributing to enhanced operational efficiency and product performance.
Understanding type iii anodize Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Hardcoat Anodize | Achieves thickness of 0.0005” to 0.0030”, utilizes high voltage (up to 100V) process. | Aerospace, automotive, military components | Pros: Excellent wear and corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited color options. |
| Low Voltage Hardcoat Anodize | Employs AC overlay on DC for a more uniform coating, lower electrical resistance. | Medical devices, precision instruments | Pros: Improved coating uniformity and performance. Cons: More complex process. |
| Sealed Hardcoat Anodize | Coated with hydrothermal or precipitating seals for enhanced corrosion resistance. | Food processing equipment, chemical handling | Pros: Enhanced corrosion protection. Cons: Sealing can add costs. |
| Dyed Hardcoat Anodize | Allows for colored finishes, typically black, enhancing aesthetic appeal. | Consumer goods, decorative applications | Pros: Attractive appearance. Cons: Limited color palette beyond black. |
| Specialty Hardcoat Anodize | Custom formulations for specific alloys or applications, such as enhanced lubrication. | Specialized machinery, high-performance parts | Pros: Tailored solutions for unique needs. Cons: Potentially higher costs and lead times. |
What are the characteristics of Conventional Hardcoat Anodize?
Conventional Hardcoat Anodize is recognized for its robust thickness ranging from 0.0005” to 0.0030”, achieved through a high voltage process. This variation is particularly suited for industries like aerospace and military, where components require superior wear and corrosion resistance. Buyers should consider the limited color options, as this type is primarily used for functional rather than decorative purposes. Understanding the specific alloy being anodized is crucial, as it affects both performance and appearance.
How does Low Voltage Hardcoat Anodize enhance performance?
Low Voltage Hardcoat Anodize utilizes a unique AC overlay on DC process, resulting in a more uniform coating with improved performance characteristics. This method is particularly advantageous for medical devices and precision instruments, where uniformity and cleanliness are paramount. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced coating properties against the complexity of the process, which may lead to longer lead times and higher costs.
Why choose Sealed Hardcoat Anodize for corrosion resistance?
Sealed Hardcoat Anodize incorporates hydrothermal or precipitating seals that significantly enhance corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for food processing equipment and chemical handling applications. While this sealing process adds an extra layer of protection, it may also increase overall costs. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between enhanced durability and budget constraints, particularly for industries with stringent hygiene standards.
What are the advantages of Dyed Hardcoat Anodize?
Dyed Hardcoat Anodize allows for colored finishes, predominantly black, which enhances the aesthetic appeal of aluminum components. This option is popular in consumer goods and decorative applications where visual impact is essential. However, buyers should note that the color palette is limited, and achieving colors other than black may require additional sampling and testing. Understanding the aesthetic requirements of the final product will guide purchasing decisions effectively.
When should Specialty Hardcoat Anodize be considered?
Specialty Hardcoat Anodize offers tailored formulations for specific alloys and applications, including those requiring enhanced lubrication properties. This type is ideal for specialized machinery and high-performance parts, where unique requirements must be met. Buyers should consider the potential for higher costs and longer lead times associated with custom solutions, but also recognize the value of having a coating that meets precise operational needs.
Key Industrial Applications of type iii anodize
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of type iii anodize | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components and structural parts | Enhanced wear and corrosion resistance, weight reduction | Compliance with aerospace standards, precise tolerances |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility, improved sterilization, durability | Certifications for medical use, specific alloy requirements |
| Automotive | Engine components and transmission parts | Increased lifespan, reduced maintenance costs | Compatibility with high-performance standards, supplier reliability |
| Defense and Military | Weapon systems and tactical equipment | Improved durability, resistance to harsh environments | Adherence to military specifications, rapid delivery capabilities |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and housings for electronic devices | Improved thermal management, electrical insulation | Customization options, precise dimensional tolerances |
How is Type III Anodize Applied in Aerospace Components?
In the aerospace industry, Type III anodize is crucial for aircraft components and structural parts, where it enhances wear and corrosion resistance while reducing weight. The anodized layer provides a dense, protective coating that withstands extreme environmental conditions, extending the lifespan of critical components. Buyers in this sector must ensure compliance with stringent aerospace standards, such as MIL-A-8625, and require precise tolerances to maintain safety and performance. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should look for suppliers experienced in aerospace applications to guarantee quality and reliability.
What Role Does Type III Anodize Play in Medical Devices?
Type III anodize is extensively utilized in the medical device sector for surgical instruments and implants, where biocompatibility and sterilization are paramount. The anodized surface is non-contaminating, ensuring that it can withstand repeated sterilization processes without degrading. Buyers in this industry must prioritize suppliers that hold relevant certifications for medical applications and can meet specific alloy requirements for optimal performance. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face varying regulatory landscapes in their regions.
Why is Type III Anodize Important for Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, Type III anodize is applied to engine components and transmission parts to increase their lifespan and reduce maintenance costs. The hard anodized layer provides superior wear resistance, which is essential for high-performance vehicles that operate under extreme conditions. Buyers should consider the compatibility of anodized parts with high-performance standards and the reliability of suppliers to ensure timely delivery and consistent quality. This is especially relevant for automotive manufacturers in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, where performance and cost-efficiency are critical.
How is Type III Anodize Utilized in Defense and Military Equipment?
Type III anodize is vital in the defense and military sectors for enhancing the durability of weapon systems and tactical equipment. The anodized coating provides resistance to harsh environments, ensuring that equipment remains functional in extreme conditions. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to military specifications and can offer rapid delivery capabilities, especially during times of urgency. This is crucial for international buyers in regions with active defense contracts, where timely sourcing of materials can impact operational readiness.
What Benefits Does Type III Anodize Offer in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, Type III anodize is used for heat sinks and housings of electronic devices, improving thermal management while providing electrical insulation. The anodized layer helps dissipate heat efficiently, enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic components. Buyers in this sector should look for suppliers that offer customization options to meet specific design requirements, as well as precise dimensional tolerances to fit within tight assembly specifications. This is particularly important for international buyers who are increasingly focused on innovation and performance in their electronic products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type iii anodize’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Achieving Consistent Coating Thickness
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with ensuring that Type III anodizing provides a consistent coating thickness across different batches of components. Variations in thickness can lead to performance issues, such as inadequate wear resistance or corrosion protection, which are critical in industries like aerospace and medical devices. This inconsistency may arise from factors like alloy variations, incorrect processing parameters, or poor part handling during anodization.
The Solution: To overcome the challenge of inconsistent coating thickness, it’s essential to establish precise specifications before initiating the anodizing process. Buyers should communicate their exact requirements, including the desired thickness range, to their anodizing supplier. Utilizing advanced process controls and quality assurance measures, such as in-process monitoring and thickness measurements, can help maintain uniformity. Additionally, it’s beneficial to select a reputable anodizing partner that employs consistent methodologies, such as using calibrated equipment and adhering to industry standards like MIL-A-8625. Regular audits of the anodizing facility can also ensure compliance with specified thickness tolerances.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Limitations of Type III Anodizing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unaware of the specific limitations and performance characteristics of Type III anodizing, leading to misguided expectations. For instance, while Type III anodizing offers enhanced abrasion and corrosion resistance, it may not be suitable for all applications, especially those requiring intricate colors or certain aesthetic properties. Misunderstanding these limitations can result in product failures, increased costs, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is crucial for buyers to educate themselves about the properties and limitations of Type III anodizing. This involves consulting technical datasheets and engaging in discussions with anodizing experts who can clarify the best applications for this coating. Buyers should consider conducting small-scale trials with different alloys to evaluate performance before committing to large orders. Additionally, specifying the application environment and desired aesthetic outcomes during the initial discussions with the anodizing provider can help ensure that the selected anodizing process aligns with the project requirements.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Proper Sealing for Enhanced Performance
The Problem: A frequent concern among B2B buyers is the effectiveness of sealing methods used after Type III anodizing. Without proper sealing, the anodized layer may become porous, leading to reduced corrosion resistance and lower durability, particularly in harsh environments. Buyers may find themselves in situations where the performance of their components does not meet the necessary industry standards, resulting in product recalls or warranty claims.
The Solution: To enhance the performance of Type III anodized parts, buyers must prioritize the sealing process. They should specify the sealing method based on the intended use of the components. For example, hydrothermal sealing is often recommended for maximum corrosion resistance, while PTFE sealing can improve lubrication properties. It’s advisable to work closely with the anodizing provider to select the appropriate sealing technique that complements the anodized coating’s properties. Additionally, buyers should request documentation confirming the sealing process and any related certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards. This proactive approach can significantly improve the longevity and performance of anodized products in demanding applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type iii anodize
What Are the Key Materials Used for Type III Anodizing?
Type III anodizing, also known as hard anodizing, is a specialized process that enhances the properties of aluminum alloys, making them suitable for a variety of demanding applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in conjunction with Type III anodizing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. 6061 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: 6061 aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, and weldability. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and maintains its strength under moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons: This alloy is highly durable and versatile, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including structural components and marine environments. However, it can be more expensive than other alloys and may require additional machining, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: 6061 aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and mild chemicals, making it ideal for industrial applications. However, its performance may degrade in highly acidic or alkaline environments.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM B580) and consider the availability of this alloy in their markets.
2. 7075 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: 7075 aluminum is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and is often used in aerospace applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of 7075 is its strength, making it suitable for high-stress applications. However, it is less corrosion-resistant than 6061 and may require additional coatings or treatments, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: This alloy is ideal for applications in aerospace and military sectors where strength is critical. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can limit its use in environments with high humidity or salt exposure.
International Considerations: Compliance with military and aerospace standards (e.g., MIL-A-8625) is crucial for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations apply.
3. 2024 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: 2024 aluminum offers excellent fatigue resistance and is often used in aircraft structures. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and has moderate corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: Its high strength makes it suitable for aerospace applications, but it is less durable in corrosive environments compared to other alloys. This can lead to higher maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: 2024 is particularly effective in structural applications where weight savings are essential. However, its limitations in corrosion resistance may necessitate additional protective measures.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of specific certifications required for aerospace applications, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where compliance with standards like ASTM and JIS is critical.
4. 5005 Aluminum Alloy
Key Properties: 5005 aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) and is often used in architectural applications.
Pros & Cons: The alloy’s superior corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor applications, but it is not as strong as 6061 or 7075, which may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: 5005 is well-suited for applications where appearance is important, such as architectural facades. However, its lower strength may not meet the requirements for structural components.
International Considerations: Buyers in South America and Africa should consider local availability and compliance with architectural standards, ensuring that the alloy meets aesthetic and performance requirements.
Summary Table of Materials for Type III Anodizing
| Material | Typical Use Case for type iii anodize | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | Structural components, marine parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, increased manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| 7075 Aluminum | Aerospace, military applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Less corrosion resistant | High |
| 2024 Aluminum | Aircraft structures | Excellent fatigue resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance | High |
| 5005 Aluminum | Architectural applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to other alloys | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used for Type III anodizing, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type iii anodize
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Type III Anodize?
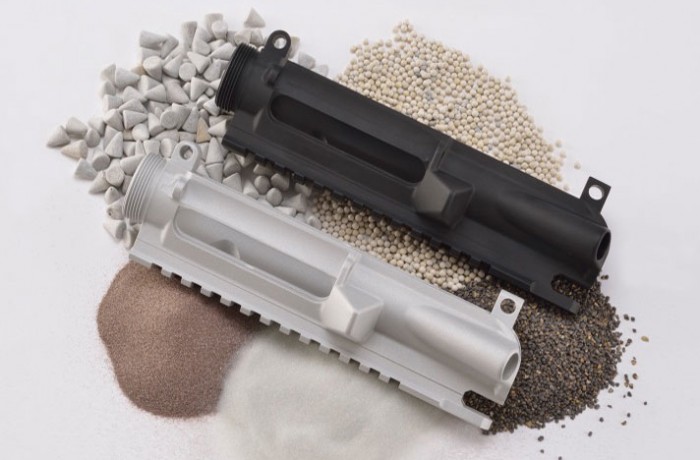
The manufacturing process for Type III anodize, also known as hardcoat anodizing, consists of several critical stages that ensure the aluminum components achieve the desired properties of increased hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main stages involved:
Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Prepped for Anodizing?
-
Cleaning and Deoxidizing: The initial step involves thoroughly cleaning the aluminum substrate to remove any contaminants, oils, or residues. This is typically achieved using alkaline cleaning solutions or solvents. Following this, a deoxidizing process is performed using a mild acid solution to prepare the surface for anodizing. This step is crucial as it ensures a uniform oxide layer during the anodizing process.
-
Surface Inspection: After cleaning, visual and tactile inspections are conducted to check for surface defects. Any imperfections can affect the anodizing quality and the final product’s performance. This step may involve using non-destructive testing methods to assess surface quality.
Anodizing: What Techniques Are Used in Type III Anodizing?
-
Electrolytic Process: The actual anodizing process involves immersing the cleaned aluminum part in a cooled sulfuric acid electrolyte bath. A high voltage (up to 100 volts) is applied, which causes the aluminum to oxidize and form a thick, dense oxide layer. The current density typically ranges from 24-36 amps per square foot, ensuring a consistent coating thickness.
-
Control of Process Parameters: Throughout the anodizing process, parameters such as temperature, voltage, and current are carefully monitored and adjusted. Maintaining these parameters within specified limits is essential for achieving the desired coating thickness and characteristics.
-
Sealing: Post-anodizing, the aluminum parts may undergo sealing to enhance corrosion resistance. This can be done through hydrothermal sealing or chemical sealing methods, depending on the application requirements. Sealing also affects the final appearance and performance of the anodized surface.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Type III Anodizing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the Type III anodizing process, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications and standards. Here are the key QC aspects relevant to international B2B buyers:
Which International Standards Govern Type III Anodizing?
-
ISO 9001 Certification: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Manufacturers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high-quality processes and consistent product delivery.
-
Military and Industry-Specific Standards: Many anodizing processes adhere to military specifications such as MIL-A-8625 for Type III anodizing. Compliance with these standards is crucial for industries like aerospace, defense, and medical devices, where stringent quality and performance criteria are mandated.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Before the anodizing process begins, raw materials (aluminum alloys) undergo IQC to ensure they meet specified chemical and mechanical properties. This step often includes material certification and traceability checks.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the anodizing process, continuous monitoring occurs to ensure that process parameters remain within acceptable ranges. Regular sampling and testing of the anodized coatings may be conducted to assess thickness, hardness, and uniformity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the anodizing and sealing processes, the finished parts undergo FQC, which includes visual inspections and testing for adhesion, corrosion resistance, and other mechanical properties. This stage may also involve dimensional checks to ensure that the anodized layer meets the required tolerances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their anodizing suppliers:
-
Audits and Certifications: Requesting audits or certifications can provide insights into a supplier’s quality management practices. Buyers should look for certifications like ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific standards relevant to their application.
-
Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed QC reports that outline testing results, including coating thickness, adhesion tests, and corrosion resistance assessments. These reports serve as documentation of compliance with specified standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can perform audits and testing to verify that the supplier adheres to both international and industry-specific quality standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when sourcing anodized products:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the regulatory landscape in the supplier’s country is essential. Different regions may have varying standards for quality control, which can affect product compliance and performance.
-
Communication and Transparency: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers is vital for understanding their QC processes. Buyers should seek transparency in reporting and addressing any potential issues that arise during production.
-
Customs and Import Regulations: Buyers should be aware of the import regulations that may apply to anodized products in their respective countries. Ensuring compliance with these regulations can prevent delays and additional costs.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process and quality assurance for Type III anodizing are intricate and require meticulous attention to detail. By understanding the stages involved and the quality control measures in place, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. It is crucial to prioritize suppliers who adhere to international standards and demonstrate robust quality management practices, ensuring that the anodized products meet their specific application needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type iii anodize’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement process for Type III anodizing can be complex due to the technical specifications and quality standards involved. This checklist is designed to guide international B2B buyers through the essential steps needed to source Type III anodizing services effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that you partner with the right suppliers who meet your specific requirements for quality, performance, and compliance.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications for your anodizing project, including material types, desired thickness, and performance characteristics. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your sourcing process and helps suppliers understand your exact needs. Be specific about the aluminum alloys you are using, as different alloys may respond differently to anodizing processes.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in Type III anodizing. Look for companies with a strong reputation and experience in your industry. Consider factors such as geographical location, production capabilities, and customer reviews to narrow down your options.
- Key Considerations:
- Supplier’s experience with specific alloys.
- Industry certifications and compliance with international standards.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, ensure that potential suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as MIL-A-8625 Type III, to guarantee compliance with industry standards. Certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability, which is essential for high-stakes applications like aerospace or medical devices.
- What to Check:
- ISO certifications.
- Specific anodizing process certifications.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Results
Ask suppliers for samples of their anodized products and any test results that validate their performance claims. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the quality of the anodizing finish and how it meets your specifications, such as wear resistance and corrosion protection.
- Important Tests:
- Abrasion resistance tests.
- Corrosion resistance evaluations.
Step 5: Evaluate Production Capabilities
Assess the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your volume requirements and deadlines. Inquire about their lead times, capacity for large orders, and flexibility in production schedules. Understanding these factors is vital to avoid delays in your supply chain.
Step 6: Review Cost Structures and Terms
Discuss pricing structures and payment terms with shortlisted suppliers. Ensure that you understand what is included in the price—such as surface preparation, masking, sealing options, and any additional services. Comparing costs alongside quality will help you make a more informed decision.
- What to Consider:
- Hidden costs, like shipping or additional treatments.
- Payment terms that align with your financial processes.
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Set up clear communication channels with your chosen supplier. Effective communication is essential for addressing any issues that may arise during production. Establish regular check-ins and updates to ensure that your project stays on track and any potential problems are resolved swiftly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for Type III anodizing, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their technical and quality requirements effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type iii anodize Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Type III Anodize Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure for Type III anodize is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The main material is aluminum, along with specific electrolytes like sulfuric acid, which are crucial for the anodizing process. The quality and type of aluminum alloy used can significantly influence costs, as higher-grade alloys may come at a premium.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary to operate anodizing equipment and ensure quality control. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region, with higher costs typically in Europe compared to regions like Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operational practices can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized equipment, such as anodizing tanks and power supplies, can be substantial. However, these costs are often amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure compliance with industry standards such as MIL-A-8625. This includes testing for coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance, all of which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international transactions, can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and customs duties. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, service quality, and relationship with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Type III Anodize Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of Type III anodize services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also dictate pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized finishes or specific thickness requirements can raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of aluminum alloy and the presence of quality certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can impact pricing. Higher quality materials typically command higher prices.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of reliability and quality may charge premium prices. Conversely, newer or less reputable suppliers may offer lower prices but could pose risks in quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can help buyers manage logistics costs more effectively. For example, FOB (Free on Board) pricing can affect who bears shipping costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of Type III Anodize?
For B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better pricing based on volume commitments or long-term contracts. Building a solid relationship can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial pricing to consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs associated with inferior coatings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and local market conditions that may affect pricing. Understanding these factors can help avoid surprises in overall costs.
-
Supplier Research: Vet suppliers thoroughly, considering their certifications, past performance, and customer reviews. A reputable supplier may be worth a higher price due to reliability and quality assurance.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides insights into the cost structure and pricing factors of Type III anodize sourcing, prices can vary significantly based on specific circumstances, including market conditions, geographical location, and supplier relationships. Always seek updated quotes and perform due diligence when engaging suppliers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type iii anodize With Other Solutions
When evaluating surface treatment options for aluminum components, it’s essential to consider alternatives to Type III anodize. Each method can offer unique benefits and drawbacks depending on specific application requirements, performance standards, and cost considerations. Here, we will compare Type III anodize with two viable alternatives: hard chrome plating and PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating.
| Comparison Aspect | Type III Anodize | Hard Chrome Plating | PVD Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High wear and corrosion resistance, excellent dielectric properties | Excellent wear resistance, moderate corrosion resistance | High hardness, excellent wear and corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on volume and specifications | Generally high due to labor and material costs | Variable, often lower than hard chrome but can vary widely |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and process control | Labor-intensive and requires skilled operators | Requires vacuum equipment and expertise in coating |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable and long-lasting | Moderate; can wear over time and require re-coating | Low; durable, but surface finish may degrade under harsh conditions |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, military, medical devices requiring high durability | Heavy machinery, automotive components needing wear resistance | Electronics, decorative applications, and components requiring high aesthetics |
What are the pros and cons of hard chrome plating compared to Type III anodize?
Hard chrome plating is known for its exceptional wear resistance and is often used in applications requiring robust protection against abrasion. While it provides a strong barrier against wear, it generally offers moderate corrosion resistance compared to Type III anodize. The process is labor-intensive, requiring skilled operators to ensure quality, which can lead to higher costs. Additionally, hard chrome can be less environmentally friendly due to the use of hazardous materials and processes.
How does PVD coating stack up against Type III anodize?
PVD coating presents an alternative that combines aesthetics with functionality. It offers a high hardness level and excellent wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a range of applications, including electronics and decorative components. The initial investment for PVD technology can be lower compared to hard chrome, but it requires specialized vacuum equipment and expertise. PVD coatings may also degrade under extreme conditions, which can limit their use in harsher environments compared to Type III anodize.
How should B2B buyers choose the right solution for their specific needs?
In choosing between Type III anodize and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific application requirements, including performance criteria such as wear and corrosion resistance, cost constraints, and the complexity of implementation. For industries demanding high durability and electrical insulation, Type III anodize often stands out. Conversely, for applications where aesthetics and surface finish are paramount, PVD may be more appropriate. Ultimately, understanding the unique benefits and limitations of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type iii anodize
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Type III Anodize?
1. Coating Thickness
Type III anodizing typically results in a coating thickness ranging from 0.0005 to 0.0030 inches (12.7 to 76.2 micrometers). This increased thickness compared to Type I and II anodizing enhances wear and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Understanding the required thickness is crucial for ensuring that parts meet performance specifications without compromising dimensional tolerances.
2. Hardness and Abrasion Resistance
Type III anodize significantly increases the surface hardness of aluminum, often achieving a hardness rating of 60 HRC or higher. This property is essential for applications where components are subjected to friction, impact, or wear. For B2B buyers, specifying Type III anodizing can lead to longer-lasting products and reduced maintenance costs, especially in high-wear environments.
3. Dielectric Strength
The dielectric properties of Type III anodized surfaces typically exceed 1000 volts, making them excellent electrical insulators. This characteristic is particularly valuable in industries where electrical insulation is critical, such as in electronic components and medical devices. Buyers should consider the dielectric strength when selecting anodizing for applications involving electrical interfaces.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Type III anodized coatings offer superior corrosion resistance, especially when sealed. This property is vital for components exposed to harsh environments, such as marine applications or chemical processing. Specifying a sealed coating can enhance the longevity and reliability of parts, making it a key consideration for procurement professionals focused on durability.
5. Lubrication Retention
The porous structure of Type III anodize allows for improved retention of lubricants, which can enhance the performance of moving parts. This is particularly beneficial in applications like machinery and automotive components, where friction reduction is essential. Buyers should evaluate the lubrication requirements of their applications to fully leverage this property.
What Are Common Terms Used in Type III Anodizing?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can influence the sourcing and specifications of anodized components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For Type III anodized components, knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their procurement strategies and manage inventory costs effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific products or services. In the context of Type III anodizing, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs, lead times, and technical specifications across multiple vendors, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaging in global sourcing of anodized parts, as it clarifies shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or property. For Type III anodized components, understanding tolerance levels is vital to ensure that finished products meet precise engineering requirements, particularly in industries that demand high standards of quality and performance.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology related to Type III anodizing, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their sourcing strategies align with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type iii anodize Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Type III Anodize Procurement?
The global market for Type III anodize is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for high-performance materials in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. The need for enhanced durability, wear resistance, and corrosion protection is pushing manufacturers towards adopting hardcoat anodizing processes. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are becoming increasingly savvy, looking for suppliers who can provide customized solutions that meet specific application requirements.
Emerging technologies, such as low-voltage anodizing processes, are gaining traction as they offer improved performance characteristics and reduced energy consumption. This shift not only enhances coating uniformity but also aligns with the sustainability goals of many companies. Moreover, the rise of Industry 4.0 is transforming sourcing strategies, with digital platforms facilitating easier access to suppliers and enabling better supply chain transparency. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to optimize procurement processes, ensuring they secure the best quality at competitive prices.
As the market evolves, buyers must stay attuned to geopolitical dynamics and regulatory changes that could impact sourcing decisions. For instance, trade agreements and tariffs can affect pricing and availability, making it crucial for international buyers to maintain a diversified supplier base.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Type III Anodize Supply Chains?
Sustainability is becoming a central concern for B2B buyers in the Type III anodize sector. The anodizing process itself can have significant environmental impacts, particularly concerning water usage and the management of hazardous materials. As such, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly electrolytes and implementing closed-loop water systems to minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is also a key consideration. Buyers are more likely to partner with suppliers who maintain transparent supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that labor practices meet ethical standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications specific to anodizing processes can provide assurance to buyers regarding a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise. Suppliers that can offer Type III anodize coatings using environmentally friendly processes or recycled aluminum are likely to attract more business. As sustainability becomes a differentiating factor in procurement decisions, buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate their efforts in reducing environmental impact while maintaining high-quality standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Type III Anodize in B2B Markets?
Type III anodize, also known as hardcoat anodizing, has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for military applications, the process was standardized under MIL-A-8625 to enhance the durability of aluminum components exposed to harsh environments. Over the decades, its application has expanded into various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, driven by the need for materials that can withstand extreme conditions.
The technology has seen numerous advancements, particularly with the introduction of low-voltage anodizing techniques that improve coating uniformity and reduce energy consumption. As global industries continue to demand high-performance materials, Type III anodize remains a pivotal solution, adapting to meet the evolving needs of international B2B buyers. This historical perspective underscores the importance of Type III anodize as a cornerstone in materials engineering, offering insights into its future trajectory in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type iii anodize
-
How do I ensure the quality of Type III anodize coatings?
To guarantee quality in Type III anodize coatings, it’s essential to partner with suppliers who adhere to industry standards, such as MIL-A-8625 Type III. Request certifications and conduct audits to assess their compliance with these standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes, including testing methods for coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion resistance. Regular communication with the supplier about any specific requirements will also help maintain quality throughout the production process. -
What are the key specifications to consider when sourcing Type III anodize?
When sourcing Type III anodize, focus on specifications such as coating thickness, surface finish, and compatibility with your alloy. Understand the intended application to determine whether you need a sealed or unsealed coating. Additionally, consider dielectric properties if the application involves electrical components. Lastly, be aware of any regional regulations or standards that may affect your procurement process, especially in regions like Africa or South America. -
What customization options are available for Type III anodize?
Customization options for Type III anodize include variations in coating thickness, sealing methods, and surface finishes. Suppliers may offer the ability to mask specific areas to maintain electrical conductivity or precise dimensions. Discuss with your supplier any unique requirements for aesthetics or functionality, such as color matching or specific mechanical properties. Ensure that your specifications are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings during production. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Type III anodizing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Type III anodizing can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs are influenced by factors such as production capabilities, material costs, and the complexity of the anodizing process. When sourcing internationally, consider the potential for higher shipping costs with smaller orders. It’s advisable to engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to find a balance between MOQ and cost-effectiveness. -
How do payment terms work when sourcing Type III anodize internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of Type III anodize often vary by supplier and region. Common terms include upfront deposits, progress payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and procurement cycle. Additionally, explore options for secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially when dealing with new suppliers in regions like Africa or South America. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing Type III anodize?
Logistics considerations for importing Type III anodize include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier provides clear information about packaging and documentation required for customs clearance. It’s also important to understand the lead times for production and shipping, particularly when sourcing from regions with variable infrastructure. Partnering with a logistics provider familiar with international trade can help streamline this process. -
How can I vet suppliers for Type III anodize effectively?
Effective supplier vetting for Type III anodize involves a thorough evaluation of their capabilities, certifications, and customer references. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry. Request samples to assess the quality of their anodized coatings and inquire about their production processes. Visiting the supplier’s facility, if possible, or conducting virtual audits can also provide valuable insights into their operational standards. -
What are the common applications of Type III anodize in various industries?
Type III anodize is widely used across industries such as aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and electronics due to its exceptional wear and corrosion resistance. In aerospace, it protects components from harsh environments, while in medical applications, it ensures sterility and non-contamination. Automotive manufacturers utilize it for parts that require high durability, and electronics companies value its dielectric properties. Understanding these applications can help you identify the right suppliers who specialize in your industry needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Type Iii Anodize Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Precision Coating – Hardcoat Anodizing (Type III)
Domain: precisioncoating.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Hardcoat Anodizing (Type III) is a military standard coating (MIL-A-8625 Type III) used to enhance wear and corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and thermal and dielectric properties of aluminum objects. It increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer from 2-3 nanometers to 50 micrometers (0.002 inches). The process involves a high voltage (up to 100V) and uses concentrated acid solutions…
2. Anoplate – Hardcoat Anodizing Solutions
Domain: anoplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hardcoat Anodize | MIL-A-8625 Type III | Aluminum Anodizing | Dense anodic coating of aluminum oxide | Applied using sulfuric acid cooled to nearly freezing | Voltages upwards of 100 volts | Current density of 24-36 amps per square foot | Thickness: 0.0005 to 0.0030 inches | Increased abrasion resistance (best when unsealed) | Increased wear resistance | Increased corrosion resistance (best when s…
3. Light Metals Coloring – Type II Anodizing
Domain: lightmetalscoloring.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Type II Anodizing:
– Thickness: 0.00010″ to 0.0005″
– Process: Sulfuric acid anodizing at around 70°F
– Benefits: Enhanced corrosion protection, aesthetic dyeing options, economical
– Common Applications: Aerospace (moisture and chemical protection), Automotive (longevity and aesthetics), Medical (biocompatibility), Semiconductor (corrosion resistance), Cosmetics (visually appealing finishes)….
4. Caswell Plating – Hardcoat Type III Aluminum Anodizing
Domain: caswellplating.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Caswell Plating – Hardcoat Type III Aluminum Anodizing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Pioneer Metal – Type III Anodize Finishes
Domain: pioneermetal.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Type III Anodize finishes, also known as hardcoat finishes, are exceptionally hard and durable, providing resistance to corrosion and abrasion. They are suitable for applications requiring excellent engineering characteristics, such as cookware, military devices, and electrical equipment. Pioneer Hardcoat, Type III, offers superior hardness and coating density compared to Type II Anodize. Taber ab…
6. Valence Surface Tech – Type II Anodizing
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Type II Anodizing: A cost-effective method that creates a thin oxide layer on aluminum surfaces, suitable for general-purpose applications. Thickness ranges from 0.5 to 25 microns, depending on immersion time and current. Benefits include exceptional corrosion resistance, wear protection, high electrical insulation, aesthetic appeal, and ease of cleaning. Disadvantages include lower resistance to …
7. Novation Inc – Type III Hardcoat Anodizing
Domain: novationinc.net
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Type III Hardcoat Anodizing – MIL-A-8625 Type III Class 1 & 2 Anodizing. High-performance anodizing services for CNC machine and precision sheet metal shops. Applications include Space, Medical, Military and DoD, Industrial equipment. Anodizing layers range from 0.0005 inches to 0.003 inches. Type III, Class 1 (non-dyed) and Class 2 (dyed black) options available. PTFE-impregnated hard anodized la…
8. Hubs – Type II & III Anodizing Solutions
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Type II and Type III anodizing are electrochemical processes used to enhance the oxide layer on aluminum and its alloys. Type II anodizing (sulfuric acid anodizing) improves corrosion resistance, provides aesthetic finishes in various colors, and is suitable for applications in architecture, electronics, automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, and industrial equipment. Type III anodizing (hardcoat …
9. OMW Corp – Anodizing Solutions for Aluminum Parts
Domain: omwcorp.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Anodizing is a commonly specified finish for aluminum machined parts, offering advantages such as a thin coating (.0002-.0012″ for Type II), durability, abrasion resistance, and excellent corrosion protection. It is environmentally friendly and inexpensive compared to painting and powder coating. Anodizing is a conversion coating that integrates with the aluminum substrate, preventing chipping or …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type iii anodize
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Type III Anodizing Needs?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of Type III anodizing offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This advanced anodizing process not only enhances the wear and corrosion resistance of aluminum components but also improves their thermal and dielectric properties, making them ideal for a range of applications—from medical devices to aerospace components.
By collaborating with reputable suppliers who adhere to stringent military and industry standards, buyers can ensure high-quality outcomes that meet specific performance requirements. Moreover, understanding the nuances of coating thickness, sealing options, and surface preparation can lead to better product specifications and ultimately, cost savings.
As markets continue to evolve, investing in strategic sourcing for Type III anodizing will position your business for future growth. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your product offerings and solidify your competitive edge. Reach out to established anodizing providers today to explore tailored solutions that align with your operational goals and market demands.