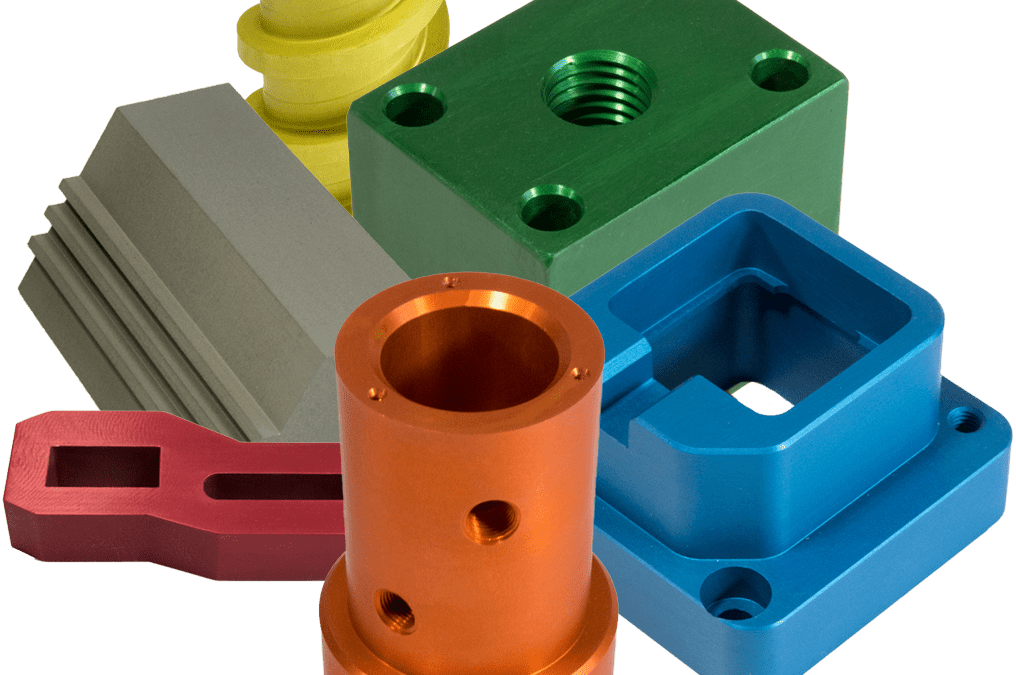
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type ii anodizing
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing Type II anodizing services can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. As industries increasingly demand durable, aesthetically pleasing, and corrosion-resistant aluminum components, understanding the intricacies of anodizing processes becomes crucial. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Type II anodizing, including its various applications across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, alongside insights into the differences between anodizing types.
We delve into the essential aspects of supplier vetting, helping buyers identify reliable partners in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany. By exploring cost factors, quality standards, and the latest innovations in anodizing technology, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you’re looking to enhance product durability or improve aesthetic appeal, understanding the specifications and benefits of Type II anodizing will position your business for success. Equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring that your procurement strategy aligns with your operational goals and industry standards.
Understanding type ii anodizing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Type II | Sulfuric acid anodizing; thickness: 0.0001” to 0.0005” | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile color options. Cons: Less abrasion-resistant than Type III. |
| Decorative Type II | Enhanced aesthetic appeal with a wide range of dye options | Consumer Products, Cosmetics, Electronics | Pros: Customizable colors, visually appealing. Cons: May require additional protective coatings. |
| Hardcoat Type II | Denser coating; improved wear resistance compared to standard | Military Equipment, Firearms | Pros: Enhanced durability, longer lifespan. Cons: Higher cost, limited color options. |
| Biocompatible Type II | Designed for medical applications; meets strict hygiene standards | Medical Devices, Surgical Instruments | Pros: Safe for human contact, corrosion-resistant. Cons: Potentially higher production costs. |
| High-Temperature Type II | Resistant to thermal shock; suitable for extreme environments | Aerospace, Electronics, Marine | Pros: Withstands harsh conditions, versatile. Cons: Complex processing requirements. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Type II Anodizing?
Standard Type II anodizing is characterized by its use of sulfuric acid to create a protective oxide layer on aluminum, typically ranging from 0.0001” to 0.0005” in thickness. This method enhances corrosion resistance and provides a base for various dyeing options, making it suitable for industries such as aerospace and automotive. Buyers should consider the balance between cost-effectiveness and the desired durability, as this type is less abrasion-resistant compared to harder anodizing options.
How Does Decorative Type II Anodizing Enhance Aesthetics?
Decorative Type II anodizing is specifically tailored for applications where visual appeal is paramount. It allows for a broad spectrum of dye options, enabling customization for consumer products, cosmetics, and electronics. While it offers significant aesthetic advantages, buyers must weigh the need for additional protective coatings to ensure longevity, especially in environments where wear and tear are prevalent.
What Makes Hardcoat Type II Anodizing Unique?
Hardcoat Type II anodizing provides a thicker and denser oxide layer, enhancing wear resistance and durability, making it ideal for military equipment and firearms. This type is particularly valued for its robustness in extreme conditions. However, buyers should be prepared for a higher cost and potentially limited color options, which may affect design flexibility.
Why Choose Biocompatible Type II Anodizing for Medical Applications?
Biocompatible Type II anodizing is designed to meet stringent hygiene and safety standards required in the medical field. This variation is essential for medical devices and surgical instruments, providing corrosion resistance and ensuring safety for human contact. Buyers should be mindful of the potentially higher production costs associated with this specialized anodizing process.
What Are the Benefits of High-Temperature Type II Anodizing?
High-Temperature Type II anodizing is engineered to withstand significant thermal shock, making it suitable for applications in aerospace, electronics, and marine environments. Its ability to endure harsh conditions adds versatility for various industries. However, buyers must consider the complexity of processing and the associated costs, which may impact overall project budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of type ii anodizing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Type II Anodizing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Protective coatings for aircraft components | Enhanced corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance costs | Compliance with industry standards, reliable supply chain |
| Automotive | Anodized aluminum parts for vehicle interiors and exteriors | Improved durability and aesthetic appeal, increasing resale value | Color options, compatibility with existing manufacturing processes |
| Medical Devices | Anodized surfaces on surgical instruments | Biocompatibility and ease of cleaning, ensuring patient safety | Certification requirements, precision in anodizing thickness |
| Semiconductor | Anodizing for semiconductor manufacturing equipment | Corrosion resistance and high purity, crucial for performance | Material specifications, environmental considerations |
| Consumer Goods | Decorative finishes for cosmetic packaging | Visually appealing products that enhance marketability | Custom color options, consistency in finish quality |
How is Type II Anodizing Applied in Aerospace, and What Benefits Does it Offer?
In the aerospace industry, Type II anodizing is utilized to protect aircraft components from environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. This anodizing process enhances the corrosion resistance of aluminum parts, significantly extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance needs. For international buyers, especially from regions with harsh climates, sourcing anodized components that meet military specifications (MIL-A-8625) is crucial to ensure compliance and performance in demanding applications.
What Role Does Type II Anodizing Play in the Automotive Sector?
Type II anodizing is commonly applied to various aluminum parts in the automotive industry, particularly for vehicle interiors and exteriors. This process not only improves the durability of components but also allows for a wide range of aesthetic options through dyeing, which can enhance the vehicle’s appeal and potentially increase resale value. Buyers should consider the availability of custom colors and the anodizing provider’s ability to integrate with existing manufacturing processes to ensure seamless production.
Why is Type II Anodizing Essential for Medical Devices?
In the medical field, Type II anodizing is applied to surgical instruments to provide a biocompatible and corrosion-resistant surface. This anodizing process ensures that instruments can be easily cleaned and maintained, promoting patient safety. International buyers in this sector must pay close attention to certification requirements and the precision of anodizing thickness to meet stringent health regulations and standards.
How Does Type II Anodizing Benefit Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Type II anodizing is vital in the semiconductor industry, where it is used on various manufacturing equipment to enhance corrosion resistance and maintain high purity levels. The anodized surfaces help ensure that equipment operates efficiently, which is critical for semiconductor processing. Buyers should focus on material specifications and environmental considerations when sourcing these components to ensure they meet the industry’s rigorous demands.
What Advantages Does Type II Anodizing Provide for Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods sector, Type II anodizing is often employed for decorative finishes on cosmetic packaging, such as perfume bottles and jewelry. This anodizing process not only enhances the visual appeal of products but also provides a corrosion-resistant finish that can withstand daily use. Buyers should prioritize sourcing options that offer custom color capabilities and maintain consistent finish quality to meet branding and market demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type ii anodizing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Anodized Products
The Problem: A common challenge for B2B buyers is receiving anodized aluminum parts with inconsistent quality. Variations in thickness, color, or surface finish can lead to discrepancies in product performance and aesthetic appeal. This inconsistency often results from fluctuations in the anodizing process, including variations in bath temperature, chemical concentrations, or processing times. Such issues can lead to significant delays in production, increased costs, and potentially damaged relationships with customers who rely on uniform product standards.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality in Type II anodizing, buyers should prioritize working with reputable anodizing service providers who adhere strictly to established standards such as MIL-A-8625. It’s essential to conduct a thorough vetting process by asking for certifications, reviewing past work, and requesting samples to evaluate their consistency. Additionally, establishing clear specifications regarding thickness, color, and finish before the anodizing process begins can mitigate risks. Regular audits and quality control checks throughout the production cycle will also help maintain standards, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications.
Scenario 2: Limited Color Options for Custom Anodizing
The Problem: Many buyers encounter frustration when they find that the anodizing service they are using offers a limited palette of colors for their Type II anodizing projects. This is particularly problematic for industries like automotive and consumer goods, where color and aesthetics can significantly impact marketability. Buyers may feel constrained in their design choices, leading to a lack of differentiation in the marketplace.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, buyers should seek out anodizing suppliers who can provide custom color matching and a broader range of dye options. When reaching out to potential suppliers, ask about their capabilities in creating custom colors, including the types of dyes they use and the processes involved. It’s also beneficial to request samples of potential colors on the specific aluminum alloy you plan to use, as the dye uptake can vary by alloy type. Establishing a collaborative relationship with the anodizer can facilitate more tailored solutions, allowing for the development of unique color formulations that align with your brand identity.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers often face issues with the corrosion resistance of anodized aluminum parts when used in particularly harsh environments, such as marine or industrial settings. While Type II anodizing provides a level of corrosion protection, it may not be sufficient for applications exposed to extreme conditions, leading to premature failure of components and costly replacements.
The Solution: To enhance corrosion resistance in challenging environments, buyers should consider a multi-faceted approach. First, they can opt for Type III anodizing, which provides a thicker, more durable coating compared to Type II, offering superior protection against wear and corrosion. However, if Type II anodizing is preferred due to cost considerations or aesthetic requirements, ensure that the anodizing process includes a sealing treatment post-anodization. This sealing process can significantly improve the corrosion resistance of the anodized layer. Additionally, conducting a thorough environmental assessment to understand specific exposure conditions will allow for better material selection and processing decisions. Collaborating with experienced anodizing specialists can provide insights into the best practices for enhancing the longevity of aluminum components in corrosive environments.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type ii anodizing
What Are the Key Materials Suitable for Type II Anodizing?
When selecting materials for Type II anodizing, it’s essential to consider the properties of various aluminum alloys, as they directly impact performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze several common materials used in conjunction with Type II anodizing, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Which Aluminum Alloys Are Commonly Used for Type II Anodizing?
6061 Aluminum Alloy
6061 is one of the most widely used aluminum alloys due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. It has a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
- Key Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability.
- Pros: Durable and versatile; can be anodized to enhance aesthetics and corrosion resistance; relatively low cost.
- Cons: Moderate resistance to stress corrosion cracking; may require additional surface preparation for optimal anodizing results.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for components exposed to moderate environmental conditions; maintains structural integrity under various loads.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is paramount.
7075 Aluminum Alloy
7075 aluminum is known for its high strength and is often used in applications requiring superior mechanical properties, such as aerospace and military components.
- Key Properties: Exceptional strength and fatigue resistance; lower weight compared to steel.
- Pros: Excellent for high-stress applications; anodizing improves corrosion resistance and surface finish.
- Cons: More expensive than other aluminum alloys; can be challenging to machine and form.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for applications where weight and strength are critical, such as aircraft components.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy certification requirements in their regions, especially in Europe and North America.
5052 Aluminum Alloy
5052 aluminum is widely recognized for its excellent corrosion resistance and formability, making it a popular choice in marine and automotive industries.
- Key Properties: Good weldability, high corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.
- Pros: Excellent for marine applications; anodizing enhances aesthetic appeal and adds an extra layer of protection against saltwater.
- Cons: Lower strength compared to 6061 and 7075 alloys; may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
- Impact on Application: Best for applications where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in marine environments.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with marine standards and regulations is essential, especially for buyers in coastal regions.
2024 Aluminum Alloy
2024 aluminum is often chosen for its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for aerospace applications.
- Key Properties: High strength, good machinability, and moderate corrosion resistance.
- Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; anodizing improves corrosion resistance and surface finish.
- Cons: Prone to stress corrosion cracking; requires careful handling during fabrication.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for aerospace components that require high strength and low weight.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with aerospace standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations like Germany and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Type II Anodizing
| Material | Typical Use Case for Type II Anodizing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum Alloy | Automotive and aerospace components | Durable and versatile | Moderate resistance to stress corrosion | Medium |
| 7075 Aluminum Alloy | Aerospace and military components | Exceptional strength and fatigue resistance | Higher cost and machining challenges | High |
| 5052 Aluminum Alloy | Marine and automotive applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to others | Medium |
| 2024 Aluminum Alloy | Aerospace components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Prone to stress corrosion cracking | High |
This strategic material selection guide offers insights into the most common aluminum alloys suitable for Type II anodizing, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type ii anodizing
What Are the Main Stages of the Type II Anodizing Manufacturing Process?
Type II anodizing involves several critical manufacturing stages designed to enhance the properties of aluminum components. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they select suppliers who adhere to high-quality standards.
Material Preparation: Ensuring Cleanliness and Compatibility
The first step in the anodizing process is material preparation, which is crucial for achieving a uniform anodized layer. This involves thorough cleaning to remove any contaminants such as oils, dirt, or oxidation. Common cleaning methods include:
- Ultrasonic Cleaning: This technique uses high-frequency sound waves in a cleaning solution to remove impurities effectively.
- Acid Cleaning: A mild acid solution may be used to dissolve surface contaminants, particularly for aluminum alloys.
Following cleaning, the aluminum parts are often inspected for defects, ensuring they are free of scratches or other imperfections that could affect the anodizing outcome.
Forming: Shaping Aluminum Components
After cleaning, the aluminum parts may undergo forming processes such as machining, bending, or extrusion, depending on the final application requirements. It’s essential that these processes are executed with precision to maintain the dimensional integrity of the parts. Buyers should ensure their suppliers have robust forming capabilities that comply with international standards, as this will directly affect the quality of the anodizing layer.
Assembly: Combining Components Where Necessary
If the final product involves multiple aluminum parts, the assembly stage takes place before anodizing. This is particularly relevant for industries such as automotive or aerospace, where components must fit together precisely. Suppliers should utilize techniques such as welding or fastening that do not compromise the material integrity, as these methods can introduce weaknesses that may be exacerbated during anodizing.
Finishing: The Anodizing Process Itself
The core of Type II anodizing lies in the electrochemical process. The aluminum parts are submerged in a sulfuric acid bath, where an electrical current is passed through the solution. This process creates a controlled oxidation layer on the aluminum surface, enhancing its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Key aspects include:
- Temperature Control: The anodizing bath is maintained at approximately 70°F (21°C) to ensure optimal oxide layer formation.
- Thickness Regulation: The typical anodized coating thickness ranges from 0.0001 to 0.0005 inches, depending on specific customer requirements.
After anodizing, parts may be dyed in various colors, allowing for customization that meets aesthetic and branding needs.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance in Type II anodizing is paramount, especially for international buyers who must navigate various standards and regulations. Understanding these measures can help buyers ensure the reliability and quality of their anodized products.
What International Standards Apply to Type II Anodizing?
Type II anodizing must comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which governs quality management systems. In addition to this, buyers should consider industry-specific standards such as:
- CE Marking: Ensuring products meet EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant in the oil and gas sectors, these standards ensure that products are fit for purpose and safe.
By selecting suppliers who adhere to these standards, buyers can mitigate risks associated with product failure.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Anodizing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the anodizing process. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who implement the following QC measures:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process, ensuring they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the anodizing process helps identify any deviations that could affect the final product.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After anodizing, parts undergo a comprehensive inspection, including visual checks and measurements of coating thickness and adhesion.
These checkpoints are vital for maintaining product quality and consistency.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized in Quality Assurance?
To ensure the integrity of anodized products, several testing methods are commonly employed:
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Using tools like micrometers or eddy current gauges to verify the anodized layer’s thickness.
- Adhesion Testing: Methods such as tape tests assess how well the anodized layer adheres to the aluminum substrate.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Salt spray tests evaluate how well the anodized layer protects against corrosion.
B2B buyers should inquire about these testing methods when assessing potential suppliers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets. Here are some strategies to ensure suppliers maintain high standards:
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request:
- Quality Management System Audits: These can reveal how well suppliers comply with ISO 9001 and other relevant standards.
- Production and Inspection Reports: Detailed documentation of the manufacturing process, including QC checkpoints and test results, can demonstrate a supplier’s commitment to quality.
Are Third-Party Inspections Necessary for Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These agencies can conduct independent audits and testing, providing unbiased verification of a supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly beneficial for buyers from regions with varying standards, such as Africa and South America, where local suppliers may not always meet international expectations.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like the Middle East and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are familiar with local regulations and standards in the buyer’s region.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can influence supplier relationships and expectations regarding quality.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: International shipping can introduce risks; thus, suppliers should have robust logistics plans to ensure product integrity during transit.
By considering these factors, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for Type II anodizing. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures will empower B2B buyers to choose partners who meet their quality expectations and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type ii anodizing’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in procuring Type II anodizing services effectively. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that your procurement process is thorough, aligned with industry standards, and tailored to meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to outline your technical requirements clearly. Consider factors such as the type of aluminum alloy you are using, desired thickness of the anodic layer (typically between 0.0001” and 0.001”), and any specific color or finish requirements. Documenting these specifications will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify suppliers specializing in Type II anodizing. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry, preferably those with international experience. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before committing, verify that the suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as the military standard MIL-A-8625. These certifications ensure that the anodizing process meets specific quality and performance criteria. Additionally, inquire about their environmental compliance and waste management practices, as these are increasingly important in global markets.
Step 4: Request Samples and Case Studies
To assess the quality of the anodizing, request samples of previous work or case studies relevant to your industry. This step allows you to evaluate their anodized finishes and color options firsthand. Pay attention to the durability, aesthetics, and uniformity of the samples to determine if they meet your standards.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Understanding the lead times and production capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers is crucial. Engage in discussions about their manufacturing processes, capacity to handle your order volume, and expected turnaround times. Suppliers should be able to accommodate your timelines without compromising quality.
Step 6: Analyze Pricing Structures and Terms
Gather detailed quotes from potential suppliers and analyze their pricing structures. Look for transparency in pricing, including costs associated with setup, anodizing, and any additional services like dyeing. Compare quotes but remember that the lowest price may not always reflect the best value—consider quality and service in your assessment.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement and Monitor the Process
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that you finalize the agreement with clear terms and conditions regarding quality control, delivery schedules, and payment terms. Establish a communication plan to monitor the anodizing process and maintain quality assurance throughout production. Regular updates can help address any issues promptly and ensure a successful partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing Type II anodizing services with confidence, ensuring that their procurement process aligns with both technical requirements and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type ii anodizing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Type II Anodizing?
When sourcing Type II anodizing services, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The aluminum substrate and sulfuric acid used in the anodizing process represent significant material costs. The type and quality of aluminum, as well as the concentration of the sulfuric acid bath, can vary, influencing overall expenses.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for setup, operation, and monitoring of the anodizing process. Labor costs can differ based on the region and the complexity of the project.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the operational costs associated with running the anodizing facility, including utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of equipment. Overhead costs are generally factored into the pricing per unit.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be needed for specific parts, affecting the initial setup costs. This includes any jigs or fixtures that ensure precise anodizing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the anodized products meet industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspections. The cost of QC can vary based on the extent of testing required and the certifications sought (e.g., MIL-A-8625).
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, weight, and packaging requirements will influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of the cumulative costs. This can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s position within the industry.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Type II Anodizing Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of Type II anodizing services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger order volumes often lead to reduced unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for favorable pricing based on their anticipated order sizes.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique color requirements or thickness variations, can increase costs. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help manage expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality aluminum and certifications add to the cost but may be necessary for specific applications (e.g., aerospace, medical). Ensure that suppliers can provide the required certifications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, capabilities, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) is essential, as they dictate who bears the cost and risk during transport. This can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Type II Anodizing Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some valuable tips:
-
Negotiate for Better Pricing: Leverage your order volume and long-term potential to negotiate better prices. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for larger contracts or long-term partnerships.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial price. Evaluate factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential failure rates to determine the most cost-effective solution.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and customs duties that may affect the final cost of anodized products. This is especially important for buyers in regions with volatile currencies.
-
Request Samples and Test Quality: Before finalizing large orders, request samples to evaluate the quality of the anodized finish. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the supplier meets your specifications.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: If possible, consider sourcing from local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. This can also simplify communication and quality assurance processes.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for Type II anodizing services can vary widely based on numerous factors. The information provided is indicative and should be used as a guideline. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and quality standards tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type ii anodizing With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Type II Anodizing
When considering surface treatment options for aluminum components, it’s essential to evaluate alternatives to Type II anodizing. While Type II anodizing offers excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic versatility, other methods may provide distinct advantages depending on specific application requirements, budget constraints, and desired performance characteristics. Below, we compare Type II anodizing with two viable alternatives: Powder Coating and Type III Anodizing.
| Comparison Aspect | Type II Anodizing | Powder Coating | Type III Anodizing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good corrosion resistance; moderate wear resistance | Excellent durability; limited corrosion resistance | Superior corrosion and wear resistance |
| Cost | Economical for large runs | Variable; generally cost-effective | Higher cost due to thicker coatings |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment | Easier application process | Requires more stringent conditions |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable finish | Moderate maintenance; can chip | Low maintenance; highly durable |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, medical | Consumer products, appliances | Military, aerospace, high-stress applications |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a popular finishing method that applies a dry powder to the surface of aluminum, which is then cured under heat. This process results in a hard, protective layer that is highly resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading. One of the primary advantages of powder coating is its ability to produce a wide variety of colors and finishes, making it aesthetically appealing. However, while it excels in durability, it offers limited corrosion resistance compared to anodizing, which could be a critical factor in harsh environments. Additionally, the application process is generally easier and less costly, but it may not provide the same level of electrical insulation that anodizing does.
How Does Type III Anodizing Compare to Type II Anodizing?
Type III anodizing, often referred to as hard coat anodizing, is a more robust alternative that delivers a thicker and denser oxide layer than Type II. This method is ideal for applications that demand superior abrasion resistance and durability, such as military and aerospace components. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of Type III anodizing also makes it suitable for parts exposed to extreme conditions. However, the cost of Type III anodizing is typically higher, and the process is more complex, requiring stricter control over temperature and bath chemistry. This option is best suited for industries where performance and longevity outweigh budget considerations.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate surface treatment for aluminum components, B2B buyers should consider several factors: the specific application, environmental conditions, aesthetic requirements, and budget. Type II anodizing is an excellent choice for those looking for a cost-effective solution with good corrosion resistance and design flexibility. In contrast, powder coating may be ideal for projects where aesthetics are paramount, while Type III anodizing is recommended for high-performance applications that require maximum durability and resistance to wear. By carefully assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type ii anodizing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Type II Anodizing?
Understanding the technical properties of Type II anodizing is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The aluminum alloys commonly used for Type II anodizing include 6061 and 7075, with 6061 being the most versatile. The choice of material grade influences the anodizing process’s effectiveness and the final product’s performance. Selecting the appropriate alloy ensures optimal corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, vital for applications where durability is paramount.
2. Anodic Coating Thickness
Type II anodizing typically results in a coating thickness ranging from 0.0001 inches to 0.0005 inches (2.5 to 12.7 microns). This specification is crucial because it directly affects the corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and wear properties of the finished product. Buyers should consider the required thickness based on the environmental conditions the aluminum will face.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Type II anodizing enhances the aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various applications exposed to moisture and chemicals. The anodic layer provides a barrier against environmental degradation, prolonging the lifespan of components. In sectors such as automotive and aerospace, this property is essential to ensure safety and reliability.
4. Dielectric Strength
The anodic coating formed during Type II anodizing provides excellent electrical insulation, with a dielectric strength of approximately 800 volts per 0.001 inches of thickness. This characteristic makes it ideal for applications in electronics and electrical systems, where preventing conductivity is critical.
5. Coloring Options
Type II anodizing allows for a wide range of color options through dyeing processes. This aesthetic flexibility is particularly beneficial in industries where visual appeal is crucial, such as consumer products and automotive components. The ability to customize colors can enhance branding and marketability.
6. Environmental Impact
Anodizing is a relatively eco-friendly process compared to other metal finishing techniques. It generates minimal waste and utilizes water-based dyes, making it an attractive choice for companies aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. This aspect can be a significant selling point for businesses committed to sustainability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Type II Anodizing?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to Type II anodizing:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is essential for buyers looking to source components that meet specific performance and quality standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers should be aware of MOQs, as they can affect inventory management and overall costs, especially for smaller projects or startups.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. A well-prepared RFQ helps ensure that buyers receive accurate and comparable pricing, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for international transactions, as they clarify cost allocation and risk management.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries where timing is critical.
6. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the final surface quality of a product, which can influence aesthetics and functionality. In Type II anodizing, the surface finish can impact corrosion resistance and the ability to accept dyes, making it a key consideration for buyers.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding Type II anodizing, ensuring they select the right solutions for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type ii anodizing Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Type II Anodizing?
The type II anodizing sector is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance product durability and aesthetics, type II anodizing presents a compelling solution. The process is noted for its cost-effectiveness, versatility in color customization, and superior corrosion resistance, making it particularly appealing for manufacturers aiming to improve product longevity while managing costs.
Emerging technologies such as automation and advanced coating techniques are transforming the anodizing landscape. Suppliers are increasingly adopting digital platforms for order processing and tracking, enhancing transparency and efficiency in the supply chain. Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles allows for real-time monitoring of anodizing processes, ensuring consistent quality and reduced waste. These innovations provide buyers with a competitive edge, enabling them to respond swiftly to market demands.
In addition to technological advancements, global sourcing trends are leaning towards localized suppliers to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical uncertainties and supply chain disruptions. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers that can demonstrate agility and reliability, particularly in regions with burgeoning manufacturing sectors.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Type II Anodizing?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the type II anodizing sector, as environmental concerns shape purchasing decisions. The anodizing process itself is more environmentally friendly compared to other metal finishing techniques, primarily due to its minimal waste generation and the ability to recycle aluminum. However, buyers must also consider the environmental impact of their supply chains.
Ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, with businesses seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and relevant local green certifications can signal a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers from Europe, particularly in Germany and Scandinavia, are particularly focused on these certifications, often requiring them as part of their procurement process.
Furthermore, the demand for “green” materials, such as non-toxic dyes and eco-friendly chemical treatments, is on the rise. Buyers who prioritize sustainability not only enhance their brand reputation but also align with consumer expectations for environmentally responsible products. This shift towards sustainable practices is not just a trend but a fundamental transformation in how businesses approach sourcing in the anodizing sector.
What Has Been the Evolution of Type II Anodizing in the B2B Landscape?
Type II anodizing has evolved significantly since its inception, with origins dating back to the mid-20th century when it was primarily developed for military applications. The process, governed by military specifications like Mil-A-8625, was initially adopted to enhance the durability of aerospace components. Over time, as industries expanded and diversified, the applications of type II anodizing broadened to include automotive parts, consumer electronics, and medical devices.
The evolution has been marked by technological advancements that have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of the anodizing process. Modern innovations, including automated anodizing lines and improved dyeing techniques, have enhanced the aesthetic options available to manufacturers, allowing for a wide range of colors and finishes. This adaptability has made type II anodizing a preferred choice for businesses looking to combine functionality with visual appeal, solidifying its place in the global B2B market.
As the sector continues to adapt to changing market dynamics and buyer preferences, type II anodizing stands out as a vital process for businesses aiming to meet the demands of modern manufacturing while maintaining sustainability and ethical sourcing standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type ii anodizing
-
How do I choose the right anodizing supplier for Type II anodizing?
Selecting the right supplier involves several key steps. First, ensure they have experience and specialization in Type II anodizing, particularly in your industry sector. Look for certifications such as MIL-A-8625 to verify compliance with quality standards. Request samples of their work to assess the quality of anodizing, including color consistency and thickness. Additionally, consider their capability to handle international shipping, lead times, and customer service responsiveness. Engaging in discussions about your specific requirements can also help gauge their expertise and reliability. -
What are the typical lead times for Type II anodizing services?
Lead times for Type II anodizing can vary based on the supplier and the complexity of your order. Generally, for standard orders, you can expect a turnaround time of 1 to 3 weeks. However, for custom colors or larger quantities, it may take longer. It is advisable to communicate your project timeline upfront and confirm the supplier’s capacity to meet your deadlines. Always factor in additional time for logistics, especially when dealing with international shipments, to avoid any delays in your supply chain. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for Type II anodizing?
Minimum order quantities for Type II anodizing can differ significantly among suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as 50 pieces, while others might require orders of 100 or more. It is essential to inquire about MOQs during your initial discussions to ensure they align with your project needs. If your requirement is below their MOQ, ask if they offer flexibility or if you can combine orders with other customers. This can help you manage costs while still accessing the services you need. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Type II anodizing?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days after invoicing. Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders or custom services. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing your order to avoid any misunderstandings later. Additionally, consider discussing options for early payment discounts or financing arrangements, which can enhance cash flow management for your business. -
Can Type II anodizing be customized for specific colors or finishes?
Yes, Type II anodizing can be customized to achieve a wide range of colors and finishes. Suppliers often have a selection of standard colors available and can also create custom dyes based on your specifications. However, it’s important to note that not all aluminum alloys take dye equally, so it’s advisable to discuss your color preferences with the supplier upfront. They can provide guidance on the best options for achieving your desired aesthetic while maintaining the quality and durability of the anodized surface. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for Type II anodizing?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing Type II anodizing. Reputable suppliers should have stringent quality control processes, including pre-anodizing inspections, adherence to industry standards, and post-anodizing testing for thickness and color consistency. Request documentation of their QA processes, including any certifications they hold. Some suppliers may also offer third-party inspection services to further validate the quality of their anodized products. Ensuring these measures are in place can help mitigate risks associated with product performance and durability. -
What industries commonly use Type II anodizing, and why?
Type II anodizing is widely used across various industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, aesthetic enhancement, and electrical insulation properties. Common applications include aerospace components, automotive parts, medical equipment, and consumer goods such as cosmetics packaging. Its versatility allows manufacturers to improve the longevity of their products while meeting specific design requirements. When sourcing anodized components, understanding the typical applications can help you assess whether Type II anodizing is suitable for your specific industry needs. -
How does international shipping affect the sourcing of Type II anodizing?
International shipping can significantly impact the sourcing of Type II anodizing, affecting lead times, costs, and logistics. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have experience handling international orders and understand customs regulations in your region. Discuss shipping options, including freight forwarding and delivery timelines, to ensure your products arrive on schedule. Additionally, consider potential tariffs or import duties that may apply, as these can influence overall costs. A well-planned shipping strategy will help streamline the procurement process and minimize delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Type Ii Anodizing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PFI Inc – Type II Aluminum Anodizing
Domain: pfiinc.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Type II Aluminum Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances aluminum’s abrasion and corrosion resistance. It adheres to military standard specification MIL-A-8625. The process involves submerging aluminum in a sulfuric acid bath, creating an aluminum oxide layer that is both on the surface and within the material, providing excellent electrical insulation properties (withstanding 800 vo…
2. Light Metals Coloring – Type II Anodizing Solutions
Domain: lightmetalscoloring.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Type II Anodizing:
– Thickness: 0.0001″ to 0.0005″
– Process: Sulfuric acid anodizing at around 70°F
– Benefits: Versatile, economical, enhanced corrosion protection, aesthetic dyeing options, suitable for automotive, aerospace, medical, semiconductor, and cosmetics industries.
Type III Anodizing:
– Thickness: 0.001″ to 0.002″
– Process: Hard coat anodizing at lower temperatures
– Benefits…
3. OMW Corp – Anodizing Solutions
Domain: omwcorp.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. It is commonly used for aluminum and other non-ferrous metals. Key specifications include thickness, color, and type of anodizing (Type I, Type II, Type III). Anodizing can enhance surface properties such as wear resistance, adhesion, and electrical insulati…
4. Precision Coating – Type II Aluminum Anodizing
Domain: precisioncoating.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Type II aluminum anodizing is used for decorative purposes, providing protection and color to aluminum parts. The coatings are thin, highly porous, and can be dyed in a wide spectrum of colors. The thickness of the anodic coatings ranges from 1.8 μm to 25 μm (0.00007″ to 0.001″). The process involves passing direct current through an electrolytic solution of diluted sulfuric acid, creating a build…
5. Valence Surface Tech – Type II Anodizing
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Type II anodizing, also known as conventional or sulfuric acid anodizing, creates a thin, durable coating on aluminum parts. The process involves submerging the aluminum in a sulfuric acid electrolyte bath and passing an electric current, resulting in a sturdy aluminum oxide coating that is harder and more resilient than the aluminum itself. The coating thickness ranges from 0.5 to 25 microns, inf…
6. Hubs – Type II and Type III Anodizing
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Type II and Type III anodizing are electrochemical processes used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on aluminum and its alloys. Type II anodizing, also known as sulfuric acid anodizing, improves corrosion resistance, provides aesthetic finishes, and is used in applications such as architecture, electronics, automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, and industrial equipment. Type II…
7. Anoplate – Anodizing Finishes
Domain: anoplate.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Anodizing Finishes: Hardcoat (Type III), Sulfuric Anodize, Chromic Acid Anodize, Boric Sulfuric Anodize (BSAA), Titanium Anodize. Anodizing process involves conversion of aluminum to aluminum oxide, resulting in both outward growth and inward penetration. For Type III anodize, the ideal ratio is 50% buildup and 50% penetration, but typically achieves 45% buildup and 55% penetration. For Type I ano…
8. Linetec – Anodic Coatings
Domain: linetec.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Class I and Class II anodic coatings are designations created by the Aluminum Association for anodized aluminum specifications. Class I coating has a mil thickness of 0.7 (18 microns) or greater and is a high-performance anodic finish used primarily for exterior building products and products that must withstand continuous outdoor exposure. Class II coating has a minimum mil thickness of 0.4 (10 m…
9. Anodize Inc – Types of Anodizing
Domain: anodizeinc.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Types of Anodizing: 1. Type II Anodizing: – Standard anodizing based on military specification MIL-A-8625. – Utilizes a sulfuric acid solution. – Coating thickness: 1.8 μm to 25 μm (0.00007″ to 0.001″). – Used in various industries including medical, aerospace, military, and defense. 2. Type III Anodizing (Hardcoat): – Currently not offered as of 2/8/2021. – Produces coatings thicker than 25 μm (0…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type ii anodizing
What Are the Key B2B Insights for Type II Anodizing?
In conclusion, Type II anodizing stands out as a cost-effective solution that enhances aluminum’s durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of Type II anodizing can lead to strategic advantages in procurement. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics benefit significantly from its versatile applications, making it essential to incorporate this anodizing process into your supply chain strategy.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Anodizing Needs?
By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can optimize their supply chain, ensuring access to high-quality anodizing services that meet specific military and industry standards, such as MIL-A-8625. This approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term partnerships with anodizing service providers who can offer tailored solutions to meet diverse market demands.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers in Anodizing?
As the global market evolves, the demand for Type II anodizing is expected to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing environmental considerations. Now is the time for businesses to assess their anodizing needs and connect with reliable partners to enhance product offerings. Take the proactive step today—explore suppliers who specialize in Type II anodizing and position your business for success in a competitive landscape.