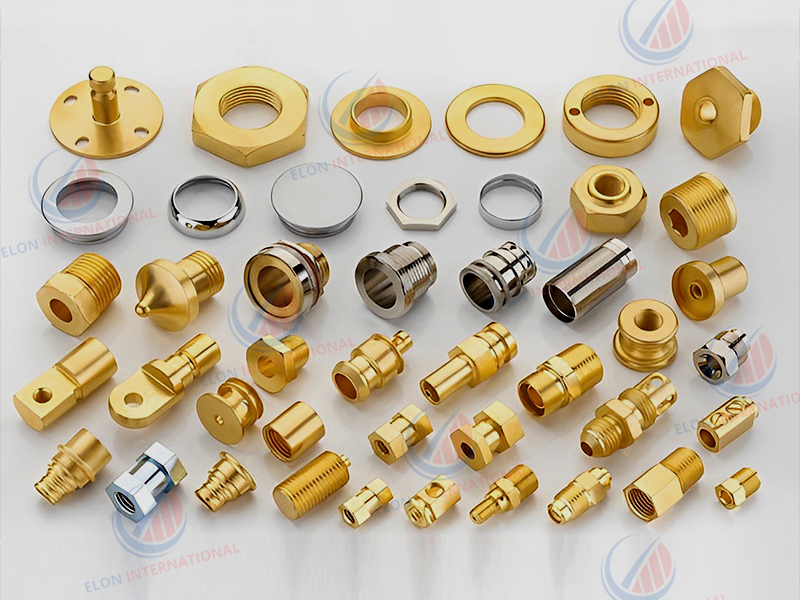
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for turned brass components
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality turned brass components poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. The intricacies of global supply chains, coupled with varying standards and quality expectations, can make the procurement process daunting. This guide is designed to navigate these complexities by providing a comprehensive overview of turned brass components, including their types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Understanding the diverse applications of turned brass components—from industrial machinery to precision medical devices—will equip buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions. Additionally, the guide delves into essential aspects such as cost considerations, quality assurance, and logistical challenges that can affect sourcing strategies. By leveraging the information presented, B2B buyers can confidently select suppliers that meet their specific needs while ensuring the reliability and performance of their components.
Whether you are a procurement specialist or a business owner, this guide serves as a valuable resource, empowering you to streamline your sourcing processes and enhance your operational efficiency in the global market for turned brass components.
Understanding turned brass components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Machining Brass | High lead content for improved machinability | Automotive, electrical components | Pros: Excellent machinability, cost-effective. Cons: Environmental concerns due to lead content. |
| Eco-Brass | Lead-free, sustainable alternative | Plumbing, medical devices | Pros: Environmentally friendly, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Potentially higher cost compared to traditional brass. |
| Brass Fittings | Various shapes for joining pipes and tubes | HVAC, plumbing | Pros: Versatile applications, durable. Cons: Size limitations may require custom orders. |
| Precision Turned Parts | High precision with tight tolerances | Aerospace, defense, medical | Pros: Exceptional accuracy, suitable for critical applications. Cons: Higher production costs due to complexity. |
| Decorative Brass Parts | Aesthetic finishes and designs | Lighting, furniture, art | Pros: Enhances visual appeal, customizable. Cons: May require additional finishing processes. |
What are the Characteristics of Free Machining Brass?
Free machining brass, characterized by its high lead content, is designed for easy cutting and shaping. This alloy is particularly suitable for high-volume production where speed and efficiency are paramount, making it a preferred choice in the automotive and electrical sectors. When considering procurement, buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced machining time against the environmental implications of lead content, which may affect regulatory compliance and sustainability goals.
How Does Eco-Brass Compare to Traditional Brass?
Eco-brass is a lead-free alternative that maintains many of the desirable properties of traditional brass, such as corrosion resistance and machinability. This alloy is increasingly favored in applications where health and environmental standards are a priority, such as plumbing and medical devices. B2B buyers should consider the slightly higher costs associated with Eco-brass, but also recognize the long-term benefits of compliance with stringent regulations and potential market advantages in eco-conscious sectors.
Why are Brass Fittings Essential in Various Industries?
Brass fittings are crucial components in HVAC and plumbing systems, providing reliable connections for pipes and tubes. Their durability and resistance to corrosion make them ideal for high-pressure applications. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements for size and shape, as some applications may necessitate custom fittings, which can impact lead times and costs.
What Makes Precision Turned Parts Ideal for Critical Applications?
Precision turned parts are manufactured to meet stringent tolerances, making them essential in industries like aerospace, defense, and medical. These components often require advanced machining techniques to achieve the necessary accuracy. B2B buyers should be prepared for higher production costs due to the complexity of these parts, but the investment is justified by the critical nature of their applications where failure is not an option.
How Can Decorative Brass Parts Enhance Product Appeal?
Decorative brass parts are utilized in lighting, furniture, and art applications, offering aesthetic value alongside functionality. These components can be customized with various finishes to meet design specifications. Buyers should consider the additional finishing processes required for these parts, as they may influence lead times and overall costs, but the visual appeal they provide can significantly enhance product marketability.
Key Industrial Applications of turned brass components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of turned brass components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, fittings, and connectors | Enhanced durability and corrosion resistance | Ensure compliance with international automotive standards and specifications. |
| Plumbing | Valves, faucets, and pipe fittings | Reliable performance and longevity in harsh conditions | Look for suppliers with ISO certifications and experience in plumbing applications. |
| Electronics | Connectors and terminals | High conductivity and thermal stability | Select manufacturers with advanced CNC capabilities for precise tolerances. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and transmission parts | Biocompatibility and precision engineering | Verify that suppliers adhere to medical device regulations and quality standards. |
| Construction | Fasteners and decorative elements | Aesthetic appeal combined with strength | Consider local sourcing options to reduce lead times and shipping costs. |
How Are Turned Brass Components Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, turned brass components are essential for manufacturing various engine parts, fittings, and connectors. Their high corrosion resistance and durability make them ideal for use in environments exposed to extreme temperatures and chemicals. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing from manufacturers who comply with international automotive standards is crucial. This ensures that the components meet the rigorous quality and safety requirements necessary for automotive applications.
What Role Do Turned Brass Components Play in Plumbing Applications?
Turned brass components are widely used in plumbing for producing valves, faucets, and pipe fittings. Their excellent resistance to corrosion and wear ensures reliable performance even in harsh water conditions. For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, it is vital to partner with suppliers who have ISO certifications, as these indicate adherence to quality management systems. Additionally, understanding local plumbing codes can help in selecting the right components for specific applications.
Why Are Turned Brass Components Important in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, turned brass components like connectors and terminals are utilized due to their superior electrical conductivity and thermal stability. These properties are essential for ensuring efficient performance and reliability in electronic devices. Buyers from regions such as Europe and the Middle East should prioritize manufacturers with advanced CNC capabilities to achieve the precise tolerances required for high-performance electronic applications. This can significantly affect the overall functionality and lifespan of the electronic products.
How Are Turned Brass Components Used in Medical Devices?
Turned brass components are critical in the medical industry, where they are used in surgical instruments and transmission parts. The biocompatibility of brass, coupled with its precision engineering capabilities, makes it a preferred choice for medical applications. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with medical device regulations and quality standards, as this ensures that the components are safe for use in healthcare settings. This is particularly crucial for markets in regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory environments can vary.
What Benefits Do Turned Brass Components Offer in Construction?
In the construction industry, turned brass components are often used for fasteners and decorative elements. Their aesthetic appeal, combined with strength and durability, makes them suitable for both functional and decorative applications. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing locally can help reduce lead times and shipping costs, making it an efficient choice. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of construction projects can guide the selection of the right brass components to ensure project success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘turned brass components’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Material Specification for Brass Components
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with specifying the right grade of brass for their applications, which can lead to costly production delays or component failures. For instance, a manufacturer in the automotive sector may require brass components that can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. If they mistakenly opt for a brass alloy with too high a zinc content, the parts may not perform adequately under stress, causing premature wear or even catastrophic failures.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the properties of various brass grades and their suitability for specific applications. Conduct thorough research on the zinc content and other alloying elements, such as lead or aluminum, to ensure they meet performance requirements. Collaborate with suppliers who offer technical support and material data sheets. This partnership can help clarify which brass grade aligns best with the application’s demands, thus minimizing risk and ensuring the reliability of the components.
Scenario 2: Difficulties in Achieving Consistent Quality in Production
The Problem: Inconsistent quality of turned brass components can lead to significant challenges, including increased scrap rates and rework costs. A buyer sourcing parts for the medical industry, where precision is paramount, may find that variations in machining tolerances result in components that do not fit as intended, jeopardizing product safety and compliance with industry regulations.
The Solution: To ensure consistency, buyers should establish clear quality standards and tolerances before placing orders. Engage with manufacturers that utilize advanced CNC machining technology and maintain ISO certifications, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Request sample parts to evaluate their adherence to specifications before committing to larger production runs. Implementing a robust quality assurance process, including regular audits and feedback loops with the supplier, will enhance the overall reliability of the components supplied.
Scenario 3: Supply Chain Disruptions Affecting Timeliness
The Problem: Timely delivery of turned brass components is crucial for maintaining production schedules. B2B buyers, especially those in regions such as Africa or South America, may encounter delays due to local supply chain disruptions, such as transportation issues or unforeseen demand spikes. Such delays can lead to halted production lines and lost revenue, straining business relationships and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To counteract potential supply chain disruptions, buyers should diversify their supplier base. Establishing relationships with multiple manufacturers across different regions can provide backup options in case of delays. Additionally, consider working with suppliers that offer just-in-time (JIT) delivery systems, which can help align component delivery with production schedules more closely. Implementing advanced inventory management software can also help track stock levels and predict future needs, allowing for proactive ordering and reducing the likelihood of shortages.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for turned brass components
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Turned Brass Components?
When selecting materials for turned brass components, understanding the properties of various brass alloys is crucial. Brass is primarily an alloy of copper and zinc, but variations exist depending on the specific application requirements. Below, we analyze four common brass materials used in the manufacturing of turned components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
1. Free Machining Brass (360 Brass)
Key Properties: Free machining brass, particularly 360 brass, is known for its excellent machinability due to the presence of lead. It typically offers good strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of 360 brass is its ease of machining, which leads to lower manufacturing costs and faster production times. However, the inclusion of lead raises environmental and health concerns, especially in regions with strict regulations on lead content.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly effective for components that require intricate shapes and tight tolerances, such as fittings and fasteners. However, its lead content may limit its use in applications involving potable water or food contact.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should be aware of regulations regarding lead content, such as the EU’s RoHS directive. It is essential to ensure compliance with local standards and preferences.
2. Lead-Free Brass (Eco-Brass)
Key Properties: Lead-free brass, often referred to as Eco-Brass, is formulated without lead, making it a safer alternative. It maintains good machinability and corrosion resistance, with a composition that typically includes copper, zinc, and other elements like tin or manganese.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of lead-free brass is its compliance with health and safety regulations, making it suitable for a broader range of applications, including those involving drinking water. However, it may be slightly more expensive and less machinable compared to traditional leaded brass.
Impact on Application: Eco-Brass is ideal for applications that require high corrosion resistance, such as plumbing fixtures and medical devices. Its lack of lead makes it compatible with health-conscious applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe, will find lead-free brass aligns with compliance requirements. Understanding local standards for material safety is crucial.
3. Naval Brass (C46400)
Key Properties: Naval brass, known as C46400, contains a higher percentage of zinc and small amounts of tin, which enhances its strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of naval brass is its exceptional resistance to corrosion in saltwater, making it ideal for marine applications. However, its higher cost and increased manufacturing complexity can be drawbacks for some applications.
Impact on Application: Naval brass is commonly used in shipbuilding and marine hardware due to its durability against harsh conditions. Its specific properties make it unsuitable for applications that do not require high corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in coastal regions or those involved in marine industries should prioritize naval brass for its performance. Compliance with maritime standards and specifications is critical.
4. Yellow Brass (C36000)
Key Properties: Yellow brass, or C36000, is a common alloy that offers a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and good machinability. It typically contains around 30% zinc.
Pros & Cons: This material is versatile and widely used in various applications, including decorative items and fittings. However, it may not perform as well in highly corrosive environments compared to other brass types.
Impact on Application: Yellow brass is suitable for a range of applications, from hardware to decorative components. Its moderate corrosion resistance makes it less ideal for applications exposed to harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions their products will face. Understanding local preferences for material types can aid in selecting the right brass alloy.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Turned Brass Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for turned brass components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free Machining Brass (360 Brass) | Fittings, fasteners, intricate components | Excellent machinability | Lead content raises health concerns | Medium |
| Lead-Free Brass (Eco-Brass) | Plumbing fixtures, medical devices | Compliance with health regulations | Higher cost, slightly less machinable | High |
| Naval Brass (C46400) | Marine hardware, shipbuilding | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Yellow Brass (C36000) | Decorative items, general hardware | Versatile and widely used | Moderate corrosion resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for turned brass components
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Turned Brass Components?
The manufacturing process for turned brass components involves several critical stages that ensure precision, quality, and efficiency. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions when sourcing these components.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Brass Sourced and Prepared for Machining?
The initial step in manufacturing turned brass components is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Brass is primarily an alloy of copper and zinc, and its properties can be tailored by adjusting the zinc content and adding other elements such as lead or tin.
The material is typically sourced in the form of brass rods or bars. These are inspected for quality, ensuring they meet the required specifications before they are processed. Commonly, grades like C360 (free machining brass) are favored for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. Before machining begins, the raw materials are cut to appropriate lengths and may undergo processes such as deburring to remove any sharp edges.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in the Machining of Brass Components?
The forming stage primarily involves CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning and milling. CNC turning is particularly suited for creating rotational components and involves the use of a lathe to remove material from the workpiece. This allows for the production of precise diameters, threads, and complex shapes.
Other machining processes, such as milling, drilling, and boring, may also be employed depending on the component’s design. Manufacturers often utilize Swiss-style lathes for high-precision applications, allowing for intricate features to be machined with tight tolerances.
3. Assembly: How Are Turned Brass Components Assembled for Final Products?
While many turned brass components are used as standalone parts, some may require assembly with other components. The assembly process can include fitting parts together, soldering, or applying adhesives, depending on the design requirements.
In industries such as plumbing and medical devices, it is essential to ensure that the assembly process maintains the integrity and functionality of the components. This often involves a combination of manual labor and automated systems to ensure efficiency while adhering to strict quality standards.
4. Finishing: What Are the Common Finishing Techniques for Brass Components?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of turned brass components. Common techniques include polishing, plating, and coating. Polishing improves the surface finish, providing a bright, attractive appearance, while plating can enhance corrosion resistance or conductivity.
After finishing, components are often subjected to further inspection to ensure they meet the required standards. This is a crucial step, as the finishing process can sometimes reveal imperfections that were not apparent during earlier stages.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Turned Brass Components?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for turned brass components, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
1. What International Standards Are Relevant for Turned Brass Component Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001:2015. This standard focuses on consistent quality and customer satisfaction and is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may apply. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, while API (American Petroleum Institute) certification may be required for components used in the oil and gas sector. These certifications demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure product quality. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to verify adherence to specifications before shipment.
Each of these checkpoints plays a critical role in maintaining high-quality output and minimizing waste.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Turned Brass Components?
Manufacturers utilize various testing methods to ensure the quality and reliability of turned brass components. Common methods include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools such as calipers and micrometers to measure component dimensions against specifications.
- Material Testing: Techniques like hardness testing and tensile testing to assess the mechanical properties of the brass alloy.
- Surface Finish Evaluation: Assessing the smoothness and appearance of the component surface, often using profilometers.
These testing methods help confirm that the components will perform reliably in their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Assurance Processes of Suppliers?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse international markets, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is essential. Here are several strategies to ensure due diligence:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Buyers should consider conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers. During these audits, it’s crucial to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall compliance with international standards. Key areas to review include:
- Production Capabilities: Assessing machinery and technology used in manufacturing.
- Quality Control Protocols: Understanding the QC processes in place and how they align with international standards.
- Documentation: Reviewing quality reports, certifications, and previous audit findings.
2. Requesting Quality Reports and Certifications: How to Approach Suppliers?
Buyers should actively request quality reports and certifications from suppliers. These documents provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality assurance. Key documents to request include:
- ISO Certification: Confirmation of compliance with ISO 9001 or other relevant standards.
- Test Reports: Documentation of testing conducted on samples or batches of products.
- Inspection Reports: Records of inspections conducted at various stages of production.
3. Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: What Are the Benefits?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance practices. These services can conduct thorough inspections and testing, ensuring that the products meet the required standards before shipment.
This approach is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the capacity for on-site inspections and wish to mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for turned brass components is crucial for international B2B buyers. By gaining insights into material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing techniques, as well as robust QC practices, buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. Leveraging these insights will enhance buyer confidence and contribute to successful partnerships in the global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘turned brass components’
Introduction
Sourcing turned brass components requires careful consideration to ensure quality, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with specific industry standards. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can streamline your procurement process and secure components that meet your technical and operational needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements for your turned brass components, including dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. This step is critical as it directly impacts the performance and compatibility of the components in your applications. Be specific about any industry standards or certifications that may apply.
- Considerations:
- What are the exact measurements required?
- Are there specific tolerances needed for functionality?
2. Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in turned brass components. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in your industry and positive reviews from previous clients. This foundational step helps ensure that you partner with a reliable source capable of meeting your specifications.
- Resources to Explore:
- Online directories and industry-specific forums
- Trade shows and exhibitions related to manufacturing and machining
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 or relevant industry-specific standards. Certifications indicate that a supplier adheres to quality management systems and best practices, which is essential for ensuring the quality of the components you will receive.
- Key Certifications to Look For:
- ISO 9001:2015 for quality management
- Industry-specific certifications for your application (e.g., medical, aerospace)
4. Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a large order, request samples or prototypes of the turned brass components. This allows you to assess the quality, craftsmanship, and adherence to your specifications. Testing samples can also prevent costly mistakes that may arise from ordering components that do not meet your needs.
- Testing Considerations:
- How do the samples perform in real-world applications?
- Are there any visible defects or quality issues?
5. Discuss Lead Times and Minimum Order Quantities
Engage in discussions with suppliers about lead times for production and minimum order quantities. Understanding these factors is vital for planning your inventory and ensuring that you can meet your production schedules without interruptions.
- Important Questions:
- What is the typical lead time for your orders?
- Are there flexible options for smaller orders or urgent requests?
6. Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Evaluate the pricing structures of your shortlisted suppliers and compare them against your budget. Look for transparency in pricing, including any potential hidden costs. Additionally, clarify payment terms to ensure they align with your financial practices.
- Considerations:
- Are there discounts for bulk orders?
- What payment methods are accepted?
7. Establish a Communication Plan
Once you select a supplier, establish a clear communication plan to facilitate ongoing collaboration. Regular communication ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations, timelines, and any potential issues that may arise during the manufacturing process.
- Communication Channels:
- Email updates on production status
- Scheduled check-ins or meetings for project milestones
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for turned brass components, ensuring that you select a supplier that meets your technical requirements and business objectives effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for turned brass components Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Turned Brass Components?
When sourcing turned brass components, understanding the cost structure is critical for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of brass itself varies based on the alloy composition (e.g., 360 Brass is commonly used for its machinability). Fluctuations in the prices of copper and zinc, the primary elements of brass, can significantly impact overall material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for machining brass components, and labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location. Countries with a higher cost of living may incur higher labor expenses, affecting the final price of components.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses fixed and variable costs associated with production facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient operations can reduce overhead costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery is substantial. Custom tooling for specific components can add to the upfront costs, but it is crucial for achieving precision and efficiency in production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that components meet the required specifications necessitates quality control measures, which may include inspections and testing. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity and volume of the order.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the method of shipping. International buyers should consider duties, taxes, and potential tariffs when calculating logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market conditions and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Turned Brass Components?
Several factors influence the pricing of turned brass components, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, which is advantageous for B2B buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: The more specific the requirements (e.g., dimensions, tolerances, finishes), the higher the costs may be. Customization may require additional tooling or specialized labor, impacting pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality brass or certified materials (e.g., lead-free options) typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of using premium materials against the costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technologies may charge more but offer superior quality and shorter lead times.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) determines the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Different terms can affect the total landed cost, so it’s vital to understand these implications.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing turned brass components:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus not only on the initial purchase price but also on long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential failures. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower TCO.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet minimum order quantities (MOQs) and negotiate volume discounts. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can also lead to better pricing.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate specifications and requirements to suppliers. This transparency can lead to better quotations and minimize the chances of misunderstandings that could result in costly rework.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with several suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify competitive pricing. However, ensure that quality remains consistent across potential suppliers.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keep abreast of market trends and fluctuations in raw material prices. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations and help buyers time their purchases effectively.
Conclusion: What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Turned Brass Components?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be mindful of the unique challenges they may face. Import duties, local regulations, and varying standards can all impact the overall cost and feasibility of sourcing turned brass components. As prices can fluctuate, buyers should maintain flexibility and be prepared to adapt their sourcing strategies as market conditions change.
Disclaimer: The information provided is indicative, and prices may vary based on specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing turned brass components With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Turned Brass Components for B2B Buyers
In the realm of manufacturing, choosing the right material or method is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. Turned brass components are a popular choice due to their excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. However, several alternative materials and manufacturing methods can also meet similar needs. This analysis will compare turned brass components with two viable alternatives: turned aluminum components and plastic machined components.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Turned Brass Components | Turned Aluminum Components | Plastic Machined Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, corrosion-resistant, excellent electrical conductivity | Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Good for low-stress applications, lightweight, flexible |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on the alloy and machining complexity | Generally lower than brass, but varies based on alloy and finish | Low cost, especially for high-volume production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled machining, longer lead times | Easier to machine, shorter lead times | Quick to produce, especially in injection molding |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but may require periodic cleaning | Low maintenance, but susceptible to scratches | Low maintenance, but can degrade under UV exposure |
| Best Use Case | High-performance applications (e.g., aerospace, plumbing, electrical) | Applications requiring weight savings (e.g., automotive, aerospace) | Cost-sensitive applications (e.g., consumer products, packaging) |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Turned Aluminum Components
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative to brass that offers good machinability and corrosion resistance. While its strength-to-weight ratio is superior, aluminum may not provide the same level of electrical conductivity as brass. It is particularly advantageous in industries where weight reduction is essential, such as aerospace and automotive. However, aluminum components may require protective coatings to enhance durability and maintain appearance, which can add to the overall cost and complexity.
Plastic Machined Components
Plastic components are an attractive alternative for applications where cost is a primary concern. They are lightweight and can be easily machined or molded into intricate shapes. Plastic components are also resistant to corrosion and can be engineered to meet specific performance needs. However, they may not be suitable for high-stress applications or environments where temperature fluctuations occur, as they can deform or degrade over time. Additionally, UV exposure can lead to deterioration, making them less ideal for outdoor applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between turned brass components and alternative materials or methods, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific application requirements. Factors such as performance, cost, lead time, and maintenance should guide the decision-making process. For high-performance needs, brass remains a strong contender, whereas aluminum and plastic alternatives may offer more economical solutions for less demanding applications. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option will empower buyers to make informed choices that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for turned brass components
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Turned Brass Components?
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific formulation of brass, which typically consists of copper and zinc. The most commonly used grade in machining is 360 brass (free machining brass), which contains lead to enhance machinability. Understanding the grade is crucial for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts the component’s strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance in various applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufacturing processes. Precision in tolerance is essential for components that need to fit together perfectly, such as in machinery or plumbing applications. Buyers should specify their tolerance requirements clearly, as tighter tolerances often lead to higher production costs but are necessary for high-performance applications.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of the machined component’s surface. Common finishes for brass parts include polished, anodized, or matte. The surface finish can affect not only the aesthetic appeal but also the performance and longevity of the component. A smooth finish is crucial for parts that experience friction or are exposed to corrosive environments.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Brass is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against moisture and various chemicals. The specific corrosion resistance can vary based on the alloy composition, making it vital for buyers to select the right grade for their application, especially in industries like plumbing and marine where exposure to harsh conditions is common.
5. Ductility and Malleability
Ductility refers to the material’s ability to deform under tensile stress, while malleability is its ability to deform under compressive stress. Brass components are highly ductile and malleable, allowing them to be shaped and formed without cracking. This property is particularly important for applications requiring intricate designs or those that undergo significant mechanical stress.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Turned Brass Component Transactions?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are used in another company’s final product. In the brass component industry, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess quality standards and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to produce or sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Smaller companies or those testing new products may find high MOQs challenging, so it’s essential to discuss flexibility with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that solicits pricing and terms from suppliers for specific quantities of products. This term is vital for B2B transactions as it helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and evaluate multiple suppliers based on their responses, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby minimizing disputes.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and production schedules. Buyers should factor in lead times when sourcing components to ensure they meet project deadlines.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing turned brass components, ensuring they meet both quality and operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the turned brass components Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Turned Brass Components Sector?
The global market for turned brass components is experiencing a significant transformation driven by various factors. A surge in demand for precision-engineered products across industries such as automotive, medical, and electronics is a primary driver. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality, custom solutions. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, including automation and advanced CNC machining, is revolutionizing manufacturing processes, enabling quicker turnaround times and enhanced precision.
Emerging trends indicate a growing preference for digital sourcing platforms that streamline procurement processes, allowing buyers to evaluate multiple suppliers efficiently. Additionally, the emphasis on just-in-time manufacturing is compelling suppliers to adopt lean inventory practices, thereby reducing lead times and costs. As international trade dynamics evolve, regional trade agreements are facilitating smoother cross-border transactions, particularly for buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, where local manufacturing capabilities are still developing.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Turned Brass Components Industry?
Sustainability has become a critical focus for B2B buyers in the turned brass components sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in metal machining, has prompted businesses to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. Ethical sourcing is increasingly important, as companies are held accountable for their supply chain decisions. Buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers that offer transparency regarding their sourcing practices and environmental impact.
The adoption of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, is gaining traction among suppliers. This certification assures buyers that the manufacturer follows systematic approaches to minimize environmental damage. Additionally, the use of lead-free or Eco-Brass alternatives is becoming more prevalent, meeting regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for safer, more sustainable materials. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainable practices, international buyers can enhance their brand reputation while contributing to a greener future.
How Has the Turned Brass Components Sector Evolved Over Time?
The history of turned brass components dates back centuries, with the material itself being prized for its durability and aesthetic appeal. Initially used in decorative applications, brass gained popularity in industrial settings due to its excellent machinability and resistance to corrosion. The advent of CNC machining in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater precision and efficiency in production.
Over the years, advancements in technology have led to the development of various brass alloys, enhancing performance characteristics tailored to specific applications. Today, the industry is characterized by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern manufacturing techniques, catering to a diverse range of sectors, including aerospace, plumbing, and electronics. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on innovation and sustainability remains paramount, ensuring that turned brass components meet the demands of modern applications while minimizing environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of turned brass components
-
How do I ensure the quality of turned brass components from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting potential suppliers thoroughly. Request samples of their turned brass components to assess craftsmanship and adherence to your specifications. Investigate their certifications (such as ISO 9001) and inquire about their quality assurance processes. Regularly communicate your requirements and expectations, and consider conducting factory audits if possible. Utilizing third-party inspection services can further guarantee that the components meet your standards before shipment. -
What is the best brass alloy for my specific application?
The choice of brass alloy depends on the application requirements. For high machinability, 360 brass is commonly preferred, while Eco-Brass (lead-free) is ideal for applications requiring safety and environmental compliance. If corrosion resistance is critical, consider alloys with higher zinc content or specialized formulations with additional elements like tin or aluminum. Consult with your supplier to evaluate the best alloy based on factors like strength, conductivity, and application conditions. -
What customization options are available for turned brass components?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options, including size, shape, surface finish, and threading specifications. Discuss your exact requirements with the supplier to determine their capabilities. They may use CNC machining technology to achieve precise dimensions and complex geometries. Additionally, inquire about any secondary processes such as plating or coating that may enhance the component’s performance or appearance. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for turned brass components?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and are often influenced by the complexity of the component and production costs. For standard components, MOQs might range from 100 to 1,000 pieces, while custom parts may have higher MOQs. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and negotiate with suppliers to find a balance that meets your project requirements while keeping costs manageable. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing turned brass components internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60) for established customers. It’s crucial to discuss payment options early in negotiations and consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit, to protect your financial interests. -
How can I track the logistics of my turned brass component orders?
Most suppliers will provide tracking information once your order has shipped. It’s advisable to establish clear communication regarding shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and any potential delays. Many suppliers utilize logistics partners that offer online tracking tools, allowing you to monitor the shipment’s progress in real-time. Additionally, ensure that you understand the customs regulations and duties involved in importing goods to your country to avoid unexpected delays. -
What are the most common applications for turned brass components in various industries?
Turned brass components are widely used across many sectors. In the plumbing industry, they are common in fittings and valves. The automotive sector often employs brass for connectors and fasteners. In electronics, brass components are valued for their conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Medical devices also frequently utilize brass for precision parts that require reliability and durability. Understanding your industry’s specific needs can help in selecting the right components. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting international suppliers for turned brass components?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, manufacturing capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and review their product samples. Assess their communication responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs. It’s also vital to evaluate their lead times and logistical capabilities to ensure timely delivery. Finally, understand their warranty and return policies to safeguard your investment in case of defects or non-compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Turned Brass Components Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Brass Turning – Female Threaded Knurled Ball Finial
Domain: brassturning.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: 1/4-27 FEMALE THREADED KNURLED BOTTOM BALL FINIAL – UNFINISHED TURNED BRASS; 1/8IPS BOTTOM X 1/8IPS SIDE FEMALE THREADED 90 DEGREE STRAIGHT ARMBACK – BLACK POWDER COATED FINISH; 1/8IPS. X 1/8IPS. FEMALE THREADED UNFINISHED BRASS TURNED NECK; 1/8IPS MALE X 1/8IPS FEMALE THREADED – 5/8IN DIAMETER BALL ARMBACK – 90 DEG. UNFINISHED BRASS; 3 HOLE 1/8IPS Y-TYPE CLUSTER BODY WITH 1/4 IPS. BOTTOM – UNFINI…
2. Currie Warner – Brass Turned Parts
Domain: curriewarner.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Brass Turned Parts Manufacturer, offering a wide variety of turned parts and brass machined components including: Brass Fasteners, Brass Connectors, Brass Fittings, Valves, Adaptors. Capabilities include Multi-Spindle Turning, CNC Machining, High Volume Brass Turned Parts, and Secondary Operations. Materials used include Eco Brass, Dezincification Brass, Standard Brass, Free Machining Brass, and S…
3. Turned Brass Components – Precision Machined Solutions
Domain: turnedbrasscomponents.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Turned Brass Components, Brass Special Components, Precision Turned Components, Brass Automotive Components, Brass Electrical Components, Brass Forged Components, Brass Machined Components, Brass Pressed Components. Applications include: Brass components for Automobile, Telecommunication, Electronic Industry, Machining Parts, Pharmaceutical Industry, Aerospace Industry, Plastic Industry. Manufactu…
4. Wh Bagshaw – Custom Precision Brass Components
Domain: whbagshaw.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Custom-made precision brass components for various applications. Benefits of brass include low friction, good corrosion resistance, high malleability, non-ferromagnetic properties, excellent heat and electrical conductivity, and superior machinability. Common brass alloys include Free Machining Brass (C36000) and Naval Brass (C46400). Common CNC brass parts include valves, nozzles, bearings, and f…
5. Groov-Pin Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: groov-pin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Precision Turned Components manufactured by Groov-Pin Corp. include high-end, close-tolerance precision machined components for various industries such as Aerospace, Energy, Medical, Defense & Law Enforcement, Farming & Irrigation, Telecommunications, Die Casting, Distribution, and Automotive. Key features include:
– Surface finishes of 32 micro-inches on stainless steel.
– Parts range from 0.030″…
6. DK Comec – Precision Brass Turned Parts
Domain: eng.dkcomec.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Brass Turned Parts, Precision Brass Turned Parts, Components Brass Turned Parts, Brass Machined Parts, Brass Screw Machine Parts, Components Brass pressed parts, Diameter range: 1/8″ (3mm) to 6″ (150mm), Threads: BSP, BSPT, UNC, UNEF metric, Custom development available as per customer drawings and samples, Competitive prices, Small/tight tolerance.
7. Abbott Interfast – Brass Screw Machined Parts
Domain: aicfast.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Brass Screw Machined Parts & Components offered by Abbott Interfast include standard and custom sizes, machined from round, hex, and square rod. Commonly produced using Free Cutting Brass for its benefits. Available in inch and metric sizes. Benefits include cost-effectiveness, recyclability, ease of machining, and corrosion resistance. Applications span various industries such as Electrical, Flui…
8. Binder Precision Parts – Brass Turned Components
Domain: binder-precisionparts.ch
Introduction: Brass turned parts are produced using special tools, including turning tools, a bar feed mechanism, and pressure cooling lubrication. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, harder than copper but softer than bronze, with a lower melting point that decreases with higher zinc content. Key features include: non-magnetic, corrosion resistant, durable, flexible (bends rather than breaks), cost-effective…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for turned brass components
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing of turned brass components is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Brass, known for its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity, offers a versatile solution for various applications across industries such as aerospace, medical, and plumbing. By prioritizing suppliers that leverage advanced CNC machining technologies and adhere to strict quality standards, international buyers can ensure they receive high-quality components tailored to their specific needs.
As global markets become increasingly interconnected, the importance of sourcing from reputable manufacturers cannot be overstated. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters long-term partnerships that drive innovation and cost-effectiveness.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seize the opportunity to explore strategic sourcing options that align with their operational goals. Engaging with experienced suppliers who understand the nuances of local and international markets will be key to unlocking the full potential of turned brass components. Take action today to enhance your supply chain resilience and propel your business into a future of sustained growth and competitive advantage.