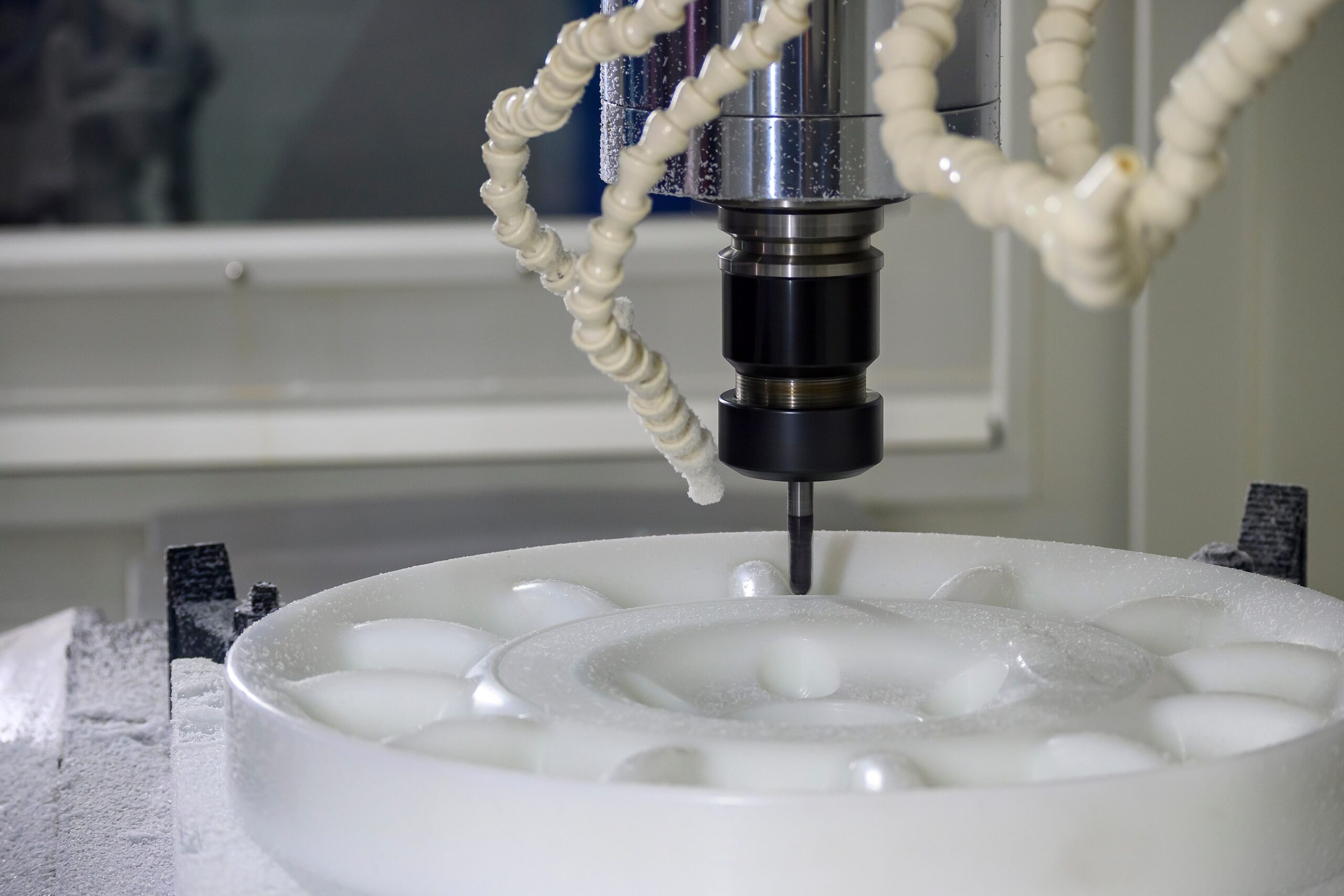
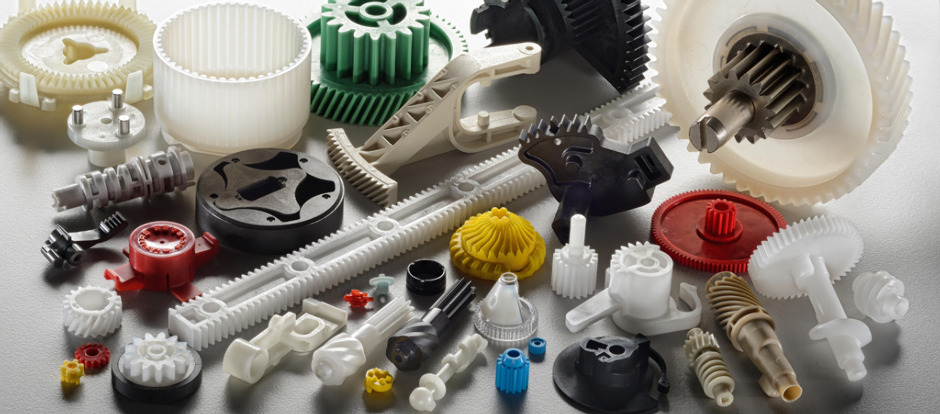
Top 9 Plastic Machining Services Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Plastic Machining Inc. – CNC Plastic Machining
Domain: plasticmachininginc.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Plastic Machining Inc. specializes in CNC plastic machining and offers a wide range of materials and services. Key materials include:
1. Engineering Plastics:
– Acetal
– Delrin®
– Nylatron®
– Nylon
– UHMW
– Turcite®
– Rulon®
2. High-Performance Plastics:
– PEEK
– PPS
– Polyimide
– Vespel®
– Ultem®
– Torlon®
– Polyamide-imide
3. Fluoropo…
2. Protolabs – Plastic CNC Machining Service
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Plastic CNC Machining Service offers cost-efficient machined plastic prototypes and production parts. Key features include:
– Fast turnaround: Parts can be produced in as fast as 1 day.
– Material options: A variety of thermoplastic materials are available, including ABS, Acetal, CPVC, Delrin, HDPE, LDPE, Nylon, PEEK, PEI, PET, PMMA, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene, PPSU, PS, PSU, and PVC.
– Material…
3. Hubs – Custom Plastic CNC Machining
Domain: hubs.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Plastic CNC machining service offering custom plastic parts for various applications. Ideal for prototypes and end-use parts. Key materials include POM (Delrin/Acetal), Nylon, ABS, PEEK, PTFE (Teflon), Polycarbonate, Polyethylene, PVC, PMMA (Acrylic), PET, Polypropylene, G-10, and FR4. Features high stiffness, excellent mechanical properties, impact resistance, thermal and chemical resistance, and…
4. Curbell Plastics – Custom Fabrication & Machining Services
Domain: curbellplastics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Curbell Plastics offers fabrication and machining services for plastic parts, including custom cutting and CNC machining. They maintain an extensive inventory of plastic materials such as sheets, rods, tubes, film, tapes, and adhesives from qualified manufacturers. Specialized services include inventory programs, troubleshooting, traceability, and process efficiencies. They provide material select…
5. Röchling – CNC Machined Plastic Parts
Domain: roechling.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Machined plastic parts – Röchling US offers high-quality CNC machined components made of plastic for various industries. Key features include:
– Over 220 CNC milling machines, 150 CNC lathes, and 15 automatic profiling machines.
– Capable of producing complex geometries with tight tolerances and high surface quality.
– Custom machined parts tailored to specific industry requirements.
– Support…
6. Emco Plastics – Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain: emcoplastics.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision CNC Machining Services, CNC Machining, CNC Routing, Custom Fabrication, Plastic Welding, Edge Finishing, Forming & Polishing, Drape & Oven Forming, Vacuum Forming, Sealing & Gaskets, Injection Molding. Industries Served: Aerospace, Alternative Energy, Automotive, Building & Construction, Chemical Processing, Electrical, Fluid Handling, Food & Beverage, Heavy Equipment, Marine, Medical Gr…
7. Precision Fluorocarbon – Plastic Machining Services
Domain: pfi-plastics.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Plastics Machining Services offered by Precision Fluorocarbon Inc. include extensive plastic machining with experienced staff and in-house equipment. Services encompass design consulting, manufacturing, and machining of plastic. Equipment includes CNC milling centers, CNC lathes, standard milling machines, and lathes. The machine shop has precision lathe turning and milling capabilities for variou…
8. Plastic Systems – Precision Machining Services
Domain: plasticsystems.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Plastic Systems, Inc. offers precision machining services including CNC milling, turning, and fabrication. They provide in-house tooling and CAD modeling for cost-effective, high-quality manufacturing. Their advanced CNC mills and custom tooling capabilities allow them to machine products of any complexity, from simple designs to intricate components. They integrate machining during the forming pr…
9. Ensinger – Plastic Machining Services
Domain: ensingerplastics.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Ensinger offers plastic machining services that include a wide range of materials such as ABS, Cast Nylon, Extruded Nylon, LCP, PA, PAI, PBT, PC, PCT-G, PE, PEEK, PEI, PEKK, PES, PET, Polyimide, PK, PMP, POM, PP, PPA, PPE, PPS, PPSU, PSU, PTFE, PVDF, and Modified Plastics. The services encompass various industries including Aerospace, Biopharma, Building, Electronics, Food, Glass, Hydrogen, Mechan…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic machining services
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable plastic machining services poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the quest for precision-engineered plastic components can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of procuring plastic machining services, covering a broad spectrum of essential topics such as types of machining processes, material options, industry applications, supplier vetting techniques, and cost considerations.
By providing a comprehensive overview, this resource empowers decision-makers to make informed choices tailored to their unique operational needs. From understanding the nuances of CNC milling and turning to selecting the right thermoplastic materials, buyers will find actionable insights that enhance their procurement strategies. Our focus on key regions, including emerging markets like Vietnam and established industries in Germany, ensures that readers can navigate diverse market dynamics effectively.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a roadmap, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge and tools necessary to engage with suppliers confidently, optimize their production processes, and achieve cost efficiencies. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategy and discover how strategic partnerships in the plastic machining sector can drive innovation and growth for your business.
Understanding plastic machining services Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling | Uses rotating cutting tools to shape materials | Aerospace, Medical Devices, Electronics | Pros: High precision, complex geometries. Cons: Potentially higher costs for low-volume runs. |
| CNC Turning | Material rotates while a cutting tool shapes it | Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Excellent for cylindrical parts. Cons: Limited to rotational geometries. |
| Plastic Laser Cutting | Uses focused laser beams for precise cuts | Signage, Custom Components | Pros: Clean edges, no tool wear. Cons: Slower than traditional methods for thick materials. |
| Injection Molding | Melts plastic and injects it into molds | Mass production of plastic parts | Pros: High efficiency for large volumes. Cons: High initial tooling costs. |
| 3D Plastic Printing | Layer-by-layer additive manufacturing | Prototyping, Custom Parts | Pros: Flexible design changes, low waste. Cons: Slower production speed for large batches. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Milling in Plastic Machining?
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that employs rotating cutting tools to shape plastic materials into intricate designs. This method is particularly suited for producing complex geometries and high-precision components, making it ideal for industries such as aerospace and medical devices. When considering CNC milling, buyers should evaluate the complexity of their designs and the associated costs, especially for low-volume production, where pricing can be less favorable.
How Does CNC Turning Differ from Other Plastic Machining Methods?
CNC turning involves rotating the plastic material against a stationary cutting tool, allowing for the creation of cylindrical shapes with tight tolerances. This technique is widely used in automotive and industrial applications where precision is critical. Buyers should consider the specific geometrical requirements of their parts, as CNC turning is limited to rotational shapes, which may not fit all design needs.
What Advantages Does Plastic Laser Cutting Offer for B2B Buyers?
Plastic laser cutting utilizes focused laser beams to cut through materials with high precision, resulting in clean edges and minimal material wastage. This method is especially beneficial for creating signage and custom components where aesthetic finish and detail are paramount. However, buyers should note that while laser cutting provides excellent precision, it can be slower for thicker materials compared to traditional cutting methods.
Why Is Injection Molding a Popular Choice for Mass Production?
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process that melts plastic and injects it into molds to create parts. This method is favored for mass production due to its ability to produce high volumes of consistent and complex parts. While the initial tooling costs can be significant, the long-term cost savings and efficiency make it attractive for businesses looking to scale their production. Buyers should assess their production volumes and budget constraints when considering this option.
How Does 3D Plastic Printing Transform Prototyping and Custom Part Production?
3D plastic printing, or additive manufacturing, constructs parts layer by layer, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization. This method is particularly advantageous for projects requiring frequent design iterations or low-volume production runs. While 3D printing minimizes waste and enables flexible design changes, buyers should be aware of its slower production speeds compared to traditional methods, especially for larger batches.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic machining services
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Plastic Machining Services | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Custom components for aircraft interiors | Lightweight, durable parts that enhance safety and performance | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | High precision and biocompatibility for patient safety | Regulatory compliance and material traceability |
| Electronics | Enclosures and housings for electronic devices | Enhanced protection and functionality of sensitive components | Material selection for electrical insulation and durability |
| Automotive | Interior and exterior components | Improved aesthetics and reduced weight for better fuel efficiency | Customization options and rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Oil and Gas | Seals and fittings for pipelines | Chemical resistance and durability under extreme conditions | Material properties and certifications for harsh environments |
How Are Plastic Machining Services Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, plastic machining services are essential for producing custom components, such as interior fittings and lightweight structural parts. These components must meet stringent safety and performance standards while reducing overall weight. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers comply with aerospace regulations, including ISO certifications, to guarantee product reliability and safety.
What Role Do Plastic Machining Services Play in Medical Devices?
Plastic machining is crucial in the medical industry for creating precision surgical instruments and implants. The biocompatibility of materials used is paramount, as these devices come into direct contact with patients. For B2B buyers from Africa and South America, it is essential to source from manufacturers that adhere to strict regulatory standards, such as FDA and ISO certifications, ensuring that the products meet safety and quality requirements.
How Are Plastic Machining Services Applied in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, plastic machining services are utilized to manufacture enclosures and housings that protect sensitive electronic components. These machined parts must provide excellent electrical insulation while being durable enough to withstand environmental challenges. Buyers in Europe and Asia should focus on suppliers who can offer advanced materials and manufacturing capabilities to ensure the longevity and functionality of their electronic devices.
Why Are Plastic Machining Services Important for the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry leverages plastic machining for both interior and exterior components, including dashboards and body panels. The use of lightweight, aesthetically pleasing materials contributes to fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. B2B buyers, especially in South America and Africa, should consider suppliers that offer customization options and rapid prototyping services to meet the evolving demands of automotive design and manufacturing.
How Do Plastic Machining Services Benefit the Oil and Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, plastic machining services are used to produce seals and fittings that require exceptional chemical resistance and durability under extreme conditions. These components are critical in preventing leaks and ensuring operational safety. Buyers from the Middle East, a region rich in oil and gas resources, must prioritize sourcing materials with proven performance in harsh environments, along with suppliers that hold relevant industry certifications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic machining services’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection Challenges in Plastic Machining
The Problem: One of the most common challenges B2B buyers face when sourcing plastic machining services is selecting the right material for their specific application. With a plethora of options like ABS, Nylon, PEEK, and Polycarbonate, buyers often struggle to determine which material will meet their performance requirements, especially in industries like aerospace, medical, or electronics where specifications can be stringent. This confusion can lead to costly errors, delays in production, and potential failures in the final product, which ultimately impact the bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material selection, B2B buyers should engage in thorough consultations with their machining service providers. Request detailed data sheets that outline mechanical properties, thermal resistance, and chemical compatibility of each material. Additionally, buyers should provide comprehensive information about their application, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards. A collaborative approach allows suppliers to recommend the most suitable materials, potentially utilizing advanced software tools for simulation and analysis to predict performance outcomes. Conducting a material test or pilot run can also help in confirming the material’s suitability before full-scale production, mitigating the risks associated with incorrect material choices.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Control and Compliance in Production
The Problem: In industries such as automotive or medical, compliance with industry standards and rigorous quality control measures is paramount. Buyers often encounter difficulties in ensuring that the plastic machined components meet required specifications and tolerances. A lack of standardized processes in the supplier’s operations can lead to inconsistencies, jeopardizing product quality and compliance, which can result in costly recalls or legal issues.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control concerns, buyers should prioritize working with ISO-certified machining service providers who implement robust quality management systems. Request transparency in the supplier’s quality assurance processes, including documentation of inspections and tests performed on the machined components. Buyers can also specify the use of advanced inspection technologies, such as laser scanning or coordinate measuring machines (CMM), to ensure precise dimensional accuracy. Establishing a clear quality assurance agreement that outlines the required standards and penalties for non-compliance can further protect buyers and foster accountability in the supplier relationship.
Scenario 3: Managing Lead Times and Production Delays
The Problem: Timely delivery is critical for B2B buyers, particularly when they are dependent on plastic machined parts for larger projects. However, many buyers experience frustration due to extended lead times and production delays caused by factors such as equipment breakdowns, material shortages, or inefficient machining processes. These delays can disrupt project timelines, increase costs, and damage customer relationships.
The Solution: To effectively manage lead times, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting a plastic machining service provider. Look for companies with a proven track record of on-time delivery and strong project management practices. Establishing clear communication channels with the supplier can facilitate real-time updates on production status and any potential delays. Additionally, consider implementing a contingency plan that includes sourcing alternative suppliers or maintaining a buffer stock of critical components to ensure that production schedules remain intact. By fostering a proactive partnership with suppliers, buyers can better anticipate challenges and minimize disruptions to their operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic machining services
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Plastic Machining?
When selecting materials for plastic machining services, understanding the specific properties of each material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Below, we analyze four commonly used materials in plastic machining: Acetal, Nylon, Polycarbonate, and PEEK. Each material is evaluated based on its properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Acetal: A Versatile Engineering Plastic
Acetal, also known as POM (Polyoxymethylene), is renowned for its high strength and stiffness, making it suitable for precision parts in various industries. Key properties include excellent dimensional stability, low moisture absorption, and good wear resistance. Acetal is particularly effective in applications requiring high mechanical strength and low friction.
Pros: Acetal is easy to machine and offers a good balance of cost and performance. Its resistance to deformation under load makes it ideal for gears, bearings, and other mechanical components.
Cons: While it has good chemical resistance, it is not suitable for use with strong acids or bases. Its relatively high cost compared to other plastics may also be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Acetal is compatible with a range of media, including fuels and oils, making it a preferred choice in automotive and aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential. Buyers from regions with stringent regulations, like Europe, should ensure that the material meets necessary certifications.
Nylon: The Tough Performer
Nylon, particularly Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/6, is known for its exceptional toughness and wear resistance. Key properties include high tensile strength and the ability to operate in a wide temperature range.
Pros: Its excellent mechanical properties make Nylon suitable for applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. It also has good chemical resistance to many solvents.
Cons: Nylon can absorb moisture, which may affect its dimensional stability over time. Additionally, its processing can be more complex due to the need for precise temperature control during machining.
Impact on Application: Nylon is often used in applications involving friction and wear, such as bushings and gears, where its self-lubricating properties are advantageous.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of Nylon available and their compliance with local standards. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable suppliers with quality certifications is crucial.
Polycarbonate: The Impact-Resistant Choice
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its transparency and high impact strength. Key properties include excellent toughness and resistance to UV radiation.
Pros: Its clarity and strength make Polycarbonate ideal for applications such as safety goggles, machine guards, and transparent enclosures.
Cons: It is more expensive than other plastics and can be prone to scratching. Additionally, Polycarbonate can be sensitive to certain chemicals, which may limit its use in some environments.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate’s ability to withstand high impact makes it suitable for safety applications, while its transparency is beneficial in visual applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety and performance standards is critical, particularly in industries like automotive and electronics. Buyers should verify that materials meet local regulations, especially in Europe where standards can be stringent.
PEEK: The High-Performance Thermoplastic
PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional thermal, chemical, and mechanical properties. Key properties include high tensile strength and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
Pros: PEEK is ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to harsh chemicals, making it suitable for aerospace, medical, and oil and gas industries.
Cons: The high cost of PEEK can be a barrier for some applications. Additionally, machining PEEK requires specialized equipment due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: PEEK’s ability to perform in extreme conditions makes it ideal for applications in the aerospace and medical fields, where reliability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PEEK materials comply with relevant standards such as ASTM and ISO, particularly for medical applications where biocompatibility is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic machining services | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetal | Gears, bearings, precision components | Excellent mechanical properties | Not suitable for strong acids | Medium |
| Nylon | Bushings, gears, industrial machinery | High toughness and wear resistance | Moisture absorption affects stability | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Safety goggles, machine guards, enclosures | High impact strength and clarity | Prone to scratching, chemical sensitivity | High |
| PEEK | Aerospace, medical devices, oil and gas | Exceptional thermal and chemical resistance | High cost, requires specialized machining | High |
This guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed decisions regarding material selection for plastic machining services. Understanding the properties and applications of each material will facilitate better procurement strategies and ensure product performance meets industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic machining services
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Plastic Machining Services?
The manufacturing process for plastic machining services involves several critical stages, each designed to transform raw materials into high-quality finished products. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: How Is the Right Plastic Material Selected and Processed?
The first step involves selecting the appropriate thermoplastic material based on the specific application requirements. Common materials include ABS, PEEK, Nylon, and Polycarbonate, each offering unique properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and heat deflection. Once the material is chosen, it undergoes preparation, which includes cutting it to size and ensuring it meets the required specifications for thickness and dimensions.
Additionally, advanced suppliers may use computerized systems to optimize material usage, reducing waste and costs. This preparation stage is crucial, as the quality of the input materials directly influences the final product’s performance and durability.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Plastic Components?
The forming stage encompasses various machining techniques, primarily CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which allows for high precision and repeatability. The main methods include:
- Turning: This involves rotating the plastic material while a cutting tool shapes it, ideal for cylindrical parts.
- Milling: In this technique, the material is fixed on a sliding table, and rotating cutting tools create complex shapes and features.
- Drilling: This method is used to create holes or bores in the material and can be performed on both lathes and mills.
Each technique is selected based on the design specifications, complexity of the part, and required tolerances, allowing manufacturers to produce intricate and high-precision components.
3. Assembly: How Are Components Joined Together?
Depending on the project, assembly may involve fitting together multiple machined parts. Techniques can include mechanical fastening, adhesive bonding, or welding, depending on the material and application. Precision during assembly is essential to maintain the integrity and functionality of the final product.
For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly process is crucial, especially if the components are part of larger systems or products, as it can affect both performance and quality.
4. Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Quality and Appearance of Machined Plastics?
The finishing stage may involve additional processes to enhance the surface quality and appearance of the machined parts. Techniques such as polishing, sanding, or coating can be employed to achieve the desired aesthetics and functional properties, such as increased resistance to wear or improved UV stability.
A well-executed finishing process can significantly impact the product’s marketability and performance, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical in Plastic Machining Services?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the plastic machining process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding these measures can provide confidence in supplier reliability.
Relevant International Standards: Which Certifications Should You Look For?
ISO 9001:2015 is the most recognized quality management standard, ensuring that companies consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as AS9100D for aerospace, ITAR for defense, and CE marking for European markets may also apply.
When selecting a supplier, B2B buyers should verify that the company holds the relevant certifications, indicating a commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Main Stages of QC?
Quality control (QC) typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter production. Suppliers should have rigorous inspection protocols to ensure only compliant materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections ensure that the machining processes adhere to specified tolerances and standards. This may involve real-time monitoring using advanced software and machinery.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished parts undergo thorough inspections to ensure they meet all specifications. This can include dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and functional testing.
Common Testing Methods: How Are Products Evaluated for Quality?
Testing methods can vary based on the application but commonly include:
- Tensile Testing: To assess the material’s strength and elasticity.
- Impact Testing: To evaluate the durability of the material under sudden force.
- Thermal Testing: To determine how materials perform under varying temperature conditions.
These tests provide valuable data on the performance characteristics of the finished products, allowing buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers have robust quality control systems in place. Here are several methods to verify QC practices:
Supplier Audits: What Should You Look For?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality systems firsthand. During an audit, buyers should evaluate:
- The supplier’s adherence to ISO standards and other relevant certifications.
- The effectiveness of their QC checkpoints and testing methods.
- The training and expertise of their quality assurance personnel.
Requesting QC Reports: How Can Documentation Support Your Decision?
Buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers, which should outline inspection results, testing procedures, and any corrective actions taken. This documentation provides insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to deliver consistent products.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: How Can Independent Verification Help?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent evaluators can conduct inspections and testing to verify that products meet specified standards before they are shipped. This is particularly beneficial for international transactions, where buyers may not have the ability to inspect products in person.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Differences in regulations, standards, and cultural expectations can affect supplier relationships.
Buyers should be aware of:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that suppliers understand and comply with the regulations in the buyer’s country, which may differ significantly from their own.
- Cultural Differences: Navigating communication styles and expectations can be challenging. Building strong relationships and clear lines of communication can mitigate misunderstandings.
- Logistics and Shipping: Quality control doesn’t end with manufacturing. Ensuring that products are packaged, shipped, and received without damage is vital. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s logistics practices to prevent issues.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in plastic machining services, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic machining services’
Introduction
Sourcing plastic machining services can be a complex process, particularly for international B2B buyers. This guide outlines essential steps to ensure you select the right supplier that meets your technical requirements, quality standards, and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for your project, including dimensions, tolerances, and material types. Having precise requirements will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your needs. Consider factors such as:
– Material Properties: Understand the properties of different plastics (e.g., tensile strength, heat resistance) to choose the right one for your application.
– Production Volume: Specify whether you need prototypes or large-scale production runs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in plastic machining. Look for companies with a solid reputation and relevant experience in your industry. Use resources such as:
– Industry Directories: Explore platforms like ThomasNet or Alibaba for a comprehensive list of suppliers.
– Reviews and Case Studies: Check customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their expertise and reliability.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015 or industry-specific certifications like AS9100D for aerospace applications. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality management and can significantly reduce the risk of poor-quality products. Additionally, inquire about:
– Quality Control Processes: Understand their quality assurance measures and inspection protocols.
– Traceability: Confirm that they can provide detailed reports on materials and processes used.
Step 4: Evaluate Manufacturing Capabilities
Assess the supplier’s machining capabilities to ensure they have the necessary equipment and technology. This includes:
– Machining Techniques: Look for suppliers that offer a range of services such as CNC milling, turning, and drilling.
– Material Options: Confirm that they can work with a variety of plastics suitable for your project, such as PEEK, Nylon, or Polycarbonate.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a significant commitment, ask for samples or prototypes of your parts. This step is crucial for evaluating the supplier’s machining quality and adherence to your specifications. Consider:
– Turnaround Time: Evaluate how quickly they can produce samples and the quality of those samples.
– Adjustments: Discuss the possibility of making adjustments based on your feedback.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage in discussions about pricing structures and payment terms to avoid any surprises later. Ensure that you understand:
– Cost Breakdown: Request a detailed quote that outlines costs for materials, labor, and any additional services.
– Payment Options: Clarify payment terms, such as deposits, milestones, or net payment periods.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support
Ensure that the supplier offers robust customer support and clear communication channels. Effective communication is essential for addressing any issues or changes throughout the production process. Look for:
– Dedicated Account Managers: Suppliers that assign account managers can facilitate better communication and service.
– Response Times: Assess how quickly they respond to inquiries, which can be indicative of their overall service quality.
By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process for plastic machining services and make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic machining services Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Plastic Machining Services?
Understanding the cost structure of plastic machining services is critical for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of plastic significantly impacts costs. Common thermoplastics like ABS and nylon may be more affordable compared to high-performance materials like PEEK or Ultem, which offer superior properties but come at a premium. Buyers should consider not only the base material price but also the availability and lead times associated with specialized materials.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for precision machining. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the machining process. Countries with a strong engineering workforce may command higher labor costs, but they often provide superior craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility costs. Advanced machining technologies and rigorous quality control processes can increase overhead but are necessary for maintaining high standards.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific parts, which adds to the initial setup costs. This expense can be amortized over larger production runs, making it more cost-effective for higher volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the precision and reliability of machined parts involves quality assurance processes that can add to overall costs. Certifications like ISO 9001 or AS9100D may be required for certain industries, influencing the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping finished parts can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms. This is particularly relevant for international buyers, as shipping regulations and tariffs can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Pricing in Plastic Machining?
Pricing is heavily influenced by the volume of the order and the degree of customization required. Larger orders can lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Conversely, highly customized parts may incur additional engineering and tooling expenses, impacting the overall price.
What Role Do Material Quality and Certifications Play in Cost Structure?
The quality of materials and the presence of industry certifications can significantly affect pricing. High-quality materials often come with higher costs, but they can lead to better product performance and longevity. Certifications are crucial for industries like aerospace and medical, where compliance can dictate supplier selection and pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Plastic Machining Costs?
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: When placing large orders, leverage your purchasing power to negotiate lower prices. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with a part, including maintenance and replacement, rather than just the initial purchase price. High-quality parts may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and logistics costs. Engaging with suppliers who understand local regulations can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Request Detailed Quotations: Ensure quotes are itemized, breaking down costs for materials, labor, tooling, and logistics. This transparency can aid in identifying areas where costs can be minimized.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be cognizant of various factors that may affect pricing, including:
- Incoterms: Familiarize yourself with Incoterms that define shipping responsibilities and costs. This can significantly impact the total price you pay.
- Customs Duties and Taxes: Research any applicable tariffs that may apply to your imports, as these can add to the overall expense.
- Local Market Conditions: Prices can vary significantly based on local supply and demand dynamics, so it’s crucial to conduct market research.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for plastic machining services can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is essential for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers and consider all associated costs to make an informed decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic machining services With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Plastic Machining Services
In the realm of manufacturing, especially for custom components, businesses often seek the most efficient and cost-effective solutions. While plastic machining services have established themselves as a reliable method for producing high-precision plastic parts, several alternative solutions may also meet specific production needs. This analysis compares plastic machining with injection molding and 3D printing, evaluating their performance, costs, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best-use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Plastic Machining Services | Injection Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, suitable for complex designs | Excellent for high-volume production; limited to simple shapes | Versatile, allows for complex geometries but slower than machining |
| Cost | Higher initial costs for small runs, economical for larger quantities | High upfront costs; lower per-unit cost at scale | Low initial costs; can be expensive for large runs due to speed |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires advanced machinery and skilled labor | Needs specialized molds, which can take time to produce | User-friendly, suitable for rapid prototyping without extensive setup |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of CNC machines required | High maintenance of molds, but less frequent | Minimal maintenance; mainly software and printer upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Custom, low-to-medium volume parts needing precision | High-volume production of standardized parts | Rapid prototyping, custom designs, and low-volume production |
Injection Molding: What Are Its Pros and Cons?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts. The primary advantage of injection molding is its efficiency for large production runs. Once the initial mold is created, the cost per unit decreases significantly, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing. However, the initial setup cost for molds can be prohibitively expensive, especially for small production runs. Additionally, the design flexibility is somewhat limited; complex designs may require intricate molds, which can increase both time and cost.
3D Printing: How Does It Compare?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, offers a unique approach by building parts layer by layer from a digital model. This method excels in creating intricate designs and prototypes quickly, with minimal setup time. It is particularly advantageous for low-volume production and custom parts. However, 3D printing generally has a slower production speed compared to machining and injection molding, which can be a drawback for larger quantities. Furthermore, while initial costs are low, the per-unit cost can escalate for larger runs, making it less economical than injection molding in such scenarios.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the best manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific needs. If precision and customization are paramount, plastic machining services may be the optimal choice, especially for small to medium production runs. For large-scale production, injection molding becomes more cost-effective despite its higher initial investment. Meanwhile, 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping and complex designs, particularly when flexibility is required. Understanding these alternatives empowers buyers to make informed decisions that align with their production goals, budget constraints, and project timelines.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic machining services
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Plastic Machining Services?
In the realm of plastic machining, understanding critical specifications is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions. Here are several key technical properties that directly impact the performance and suitability of machined plastic components:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic used in machining, such as ABS, Nylon, or PEEK. Each grade has unique properties that dictate its performance in various applications, such as tensile strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. For instance, PEEK is renowned for its high strength and thermal resistance, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring product longevity and reliability.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in a machined part. It is a critical factor in industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Tighter tolerances often lead to higher production costs, so understanding the acceptable limits for a specific application can help buyers optimize their budgets without sacrificing quality.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish defines the texture and smoothness of a machined part’s surface. It can affect not only aesthetics but also functional performance, such as friction and wear resistance. In industries like electronics or medical devices, a high-quality surface finish can enhance the product’s performance and longevity. Buyers should specify their surface finish requirements to ensure compatibility with their intended applications.
4. Impact Strength
Impact strength measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden forces or shocks without failing. This property is particularly important for applications where parts may experience high stress or impact, such as automotive and industrial machinery. Understanding the impact strength of different materials helps buyers choose the right plastic that can endure operational demands.
5. Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
HDT is the temperature at which a material deforms under a specified load. This property is vital for applications subjected to high temperatures, such as in automotive or aerospace components. Knowing the HDT can guide buyers in selecting materials that maintain structural integrity under operational conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Plastic Machining Services?
Navigating the world of plastic machining also involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are several commonly used trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding whether a supplier operates as an OEM can help buyers assess the reliability and quality of the components they procure.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises that may not need large quantities of parts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers. It typically includes specifications for the parts needed, quantities, and delivery timelines. Issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare offers from different manufacturers and negotiate better terms.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are a series of international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, risk, and delivery timelines, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the finished product. Understanding lead times is critical for planning and inventory management, especially in industries with tight deadlines. Buyers should always inquire about lead times when discussing production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring they select the best materials and services for their specific needs in plastic machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic machining services Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Plastic Machining Services Market?
The plastic machining services sector is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, including CNC machining and additive manufacturing, is enabling companies to produce high-precision plastic components more efficiently. Additionally, the shift towards customization and rapid prototyping is reshaping sourcing strategies, as businesses seek suppliers capable of delivering tailored solutions quickly.
Emerging technologies like IoT and AI are also influencing this sector. These innovations facilitate real-time monitoring of production processes, enhancing quality control and operational efficiency. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for suppliers who can integrate these technologies into their operations to ensure competitive pricing and timely delivery.
Another noteworthy trend is the globalization of supply chains. Buyers are now sourcing from a broader range of suppliers, often seeking partnerships in emerging markets where costs are lower. This shift requires buyers to navigate complex logistics and compliance issues, highlighting the importance of establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who understand local regulations and can ensure product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Plastic Machining?
As environmental concerns continue to mount, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in B2B sourcing decisions. The plastic machining sector is not exempt from this trend, with buyers increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and ensuring energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses seek to align with suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and contribute positively to their local communities. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are increasingly sought after by buyers looking to validate their suppliers’ commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Additionally, the availability of bio-based and biodegradable plastic materials is gaining traction. By opting for these alternatives, companies can reduce their environmental footprint and appeal to eco-conscious consumers. B2B buyers should actively inquire about the sustainability credentials of their suppliers and consider integrating these materials into their product offerings.
How Has the Plastic Machining Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the plastic machining industry has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, plastic machining was a niche area, primarily focused on basic machining processes. However, the introduction of CNC technology revolutionized the sector, allowing for greater precision and the ability to create complex geometries.
Over the years, the industry has expanded to include a wide range of thermoplastic materials, each tailored for specific applications. As industries have evolved, so too has the demand for faster production times and more customized solutions. Today, plastic machining services are critical in sectors ranging from medical devices to automotive components, highlighting the industry’s adaptability to meet diverse client needs. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards innovation and efficiency, positioning the plastic machining sector as a vital player in global manufacturing.
In summary, understanding these market dynamics and sourcing trends is essential for international B2B buyers navigating the plastic machining services landscape. By aligning with innovative, sustainable, and ethical suppliers, companies can enhance their competitive edge and ensure long-term success in an increasingly complex marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic machining services
-
1. How do I choose the right plastic material for my machining project?
Selecting the appropriate plastic material is crucial for the success of your project. Consider the mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and impact resistance, as well as environmental factors like temperature and chemical exposure. For applications requiring high strength and thermal stability, materials like PEEK or Nylon 6/6 are excellent choices. If cost is a primary concern, ABS or HDPE may suffice for less demanding applications. Always consult with your supplier for recommendations tailored to your specific needs and application requirements. -
2. What are the common machining methods used in plastic machining services?
The primary machining methods for plastics include CNC milling, turning, and drilling. CNC milling is ideal for creating complex shapes and fine details, while turning is used for cylindrical components. Drilling is versatile and allows for precise hole creation in various materials. Each method has its advantages depending on the design specifications and material properties, so it’s essential to discuss your project requirements with your machining service provider to choose the most efficient method. -
3. What is the typical lead time for plastic machining services?
Lead times can vary based on the complexity of the project, material availability, and the machining service provider’s current workload. Generally, for standard projects, you can expect a lead time of 2 to 4 weeks. However, for more complex or custom parts, it may take longer. It’s advisable to communicate your project timelines clearly with your supplier and confirm their capabilities to meet your deadlines. -
4. How can I ensure quality assurance in my plastic machining order?
To ensure quality assurance, look for suppliers that adhere to recognized quality management systems such as ISO 9001:2015. Request detailed inspection reports and certifications for the materials used. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer traceability for their products, ensuring that every step of the manufacturing process is documented. Regular communication and updates throughout the production process can also help maintain quality standards. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic machining services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may accommodate low-volume orders, especially for prototypes, while others may require a minimum quantity for cost-effectiveness. Typically, MOQs can range from a few pieces for prototypes to hundreds for production runs. It’s essential to clarify these details during your initial discussions with the supplier to ensure alignment with your project needs. -
6. What payment terms are typically offered by plastic machining service providers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms depending on your business relationship and order size. Always discuss and agree on payment terms before commencing work to avoid any misunderstandings. -
7. How do I vet potential suppliers for plastic machining services?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in your specific industry and their capabilities in handling the required materials and complexities. Request case studies or references from previous clients to assess their reliability and quality. Additionally, check for certifications such as ISO compliance, which can indicate a commitment to quality. Engaging in a trial project can also help you evaluate their performance before committing to a larger order. -
8. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plastic machining services internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure that your supplier can provide clear documentation for customs clearance. Also, factor in potential delays caused by international shipping and customs processing. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the process, and discussing shipping options with your supplier can lead to cost-effective solutions. Always confirm the supplier’s ability to support your distribution needs in your target market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic machining services
In the rapidly evolving landscape of plastic machining services, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse range of materials—ranging from ABS to PEEK—and the specific machining capabilities available, businesses can tailor their sourcing strategies to meet unique operational demands. This not only fosters cost efficiencies but also enhances product quality and innovation.
Leveraging advanced technologies and precision machining techniques, suppliers are equipped to handle complex specifications and provide timely delivery, which is vital for maintaining competitive advantage in global markets. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to innovate, the demand for high-performance plastic components is set to rise.
Looking ahead, businesses should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer comprehensive support—from material selection to prototyping and design assistance. This proactive approach will not only optimize procurement processes but also drive long-term success. International buyers are encouraged to explore these opportunities and engage with leading manufacturers to ensure they remain at the forefront of the plastic machining sector.