Top 9 Lathe Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Monarch Lathes – Manual Metal Cutting Equipment
Domain: monarchlathe.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Monarch Lathes specializes in high quality manual metal cutting equipment since 1909. Their product offerings include manual lathes, vertical machining centers, horizontal machining centers, gantry machines, horizontal boring mills, portable drills, and radial drills. They also provide rebuild and remanufacturing services to restore existing lathes to original accuracy, efficient field service sup…
2. Summit Machine Tool – American-Made Metal Lathes
Domain: summitmt.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: American-Made Lathes by Summit Machine Tool include a variety of models such as: 14” Metal Lathe, 16″ L Metal Lathe, 16″ Metal Lathes, 18″ & 20″ Metal Lathes, 22″ Metal Lathes, 20″, 24″, 28″ Metal Lathes, 30″ Swing Metal Lathes, Big Lathes (26″, 30″, and 33″), Big Hole Engine Lathes, Big Swing Geared Head and Variable Speed Metal Lathes, 42″ Hollow Spindle Oil Country Metal Lathes, Euro Hollow Spi…
3. Lathe Manufacturers – Overview and Applications
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: 45 Lathe Manufacturers in 2025, Overview of lathes and their applications, Top-ranked lathe companies: 1. WEILER Werkzeugmaschinen GmbH, 2. Laguna Tools, 3. KAAST Machine Tools, Inc., Types of lathes: Lathe Turrets, Wood Turning Lathes, Bench Lathes, Small CNC Lathes, CNC Mini Lathes, NC Lathes, Pitch Changers, CNC Lathes, Engine Lathes, General Purpose Lathes, Lathe components: Spindle Head, Bed,…
4. Tormach – 15L Slant-PRO Lathe
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“lathes”: [{“model”: “15L Slant-PRO Lathe”, “starting_price”: “$25,806”, “features”: [“standard conversational control”, “rigid tapping”, “configurable tooling and work holding”, “modular build”, “gang tooling”, “automatic collet closer”, “bar puller”], “spindle_power”: “3 hp (2.224 kW)”, “spindle_speed_ranges”: {“low”: “180 to 2,500 RPM”, “high”: “250 to 3,500 RPM”}, “through_spindle_bore”: “1.5…
5. Clausing – CT Precision Tool Room Lathes
Domain: clausing-industrial.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Clausing offers a wide range of high-quality manual and CNC lathes for the metalworking industry, with swings from 6 inches to over 100 inches. Key products include: 1. Clausing CT Precision Tool Room Lathes: 6” swing by 18” between centers, infinitely variable spindle speeds, designed for precision machining and finishing. 2. Clausing C-Series Lathes: Variable speed and geared head options, sizes…
6. Woodturners Catalog – Wood Lathes
Domain: woodturnerscatalog.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Woodturners Catalog – Wood Lathes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Grizzly – Metal Lathes
Domain: grizzly.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: This company, Grizzly – Metal Lathes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. TSINFA – CNC Lathes & Milling Machines
Domain: tsinfa.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Top 27 CNC Lathe Manufacturers in the World: 1. TSINFA – Founded in 2005, leading CNC lathe manufacturer in China, offers CNC milling machines, CNC turning machines, CNC pipe threading lathes, universal milling machines, turret milling machines, hydraulic presses, and manual lathes. 2. Okuma – Established in 1898, leading CNC machine factory in Japan, known for diverse CNC machines in various indu…
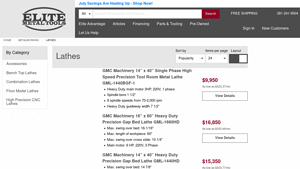
9. GMC Machinery – 14” x 40” High Speed Precision Metal Lathe
Domain: elitemetaltools.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: GMC Machinery 14” x 40” Single Phase High Speed Precision Tool Room Metal Lathe GML-1440BGF-1: Heavy Duty main motor 3HP, 220V, 1 phase, Spindle bore 1 1/2”, 8 spindle speeds from 70-2,000 rpm, Heavy Duty guideway width 7 1/2″, Price: $9,950, Financing: As low as $323.37/mo. GMC Machinery 16” x 60” Heavy Duty Precision Gap Bed Lathe GML-1660HD: Max. swing over bed: 16-1/16″, Max. length of workpie…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lathe manufacturers
In the complex landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality lathe manufacturers poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the diverse range of lathe types and applications available, from manual to CNC machines, making informed purchasing decisions can feel daunting. This guide is designed to navigate you through this intricate market, providing insights into various lathe types, their applications, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Nigeria and Brazil, will find valuable information on evaluating manufacturers based on quality, cost, and service capabilities. We delve into the importance of understanding regional compliance and standards, which can significantly impact procurement strategies. Furthermore, this guide highlights the critical aspects of cost management, ensuring that you achieve the best value for your investment while maintaining high production standards.
Empowering you with actionable insights, this comprehensive resource equips you to make well-informed decisions that align with your operational goals. By understanding the nuances of the lathe manufacturing market, you can streamline your sourcing process and foster long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, ultimately enhancing your competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Understanding lathe manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Lathes | Operated by hand, offering simplicity and control. | Small-scale machining, repairs. | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited automation. |
| CNC Lathes | Computer-controlled for precision and repeatability. | Mass production, complex designs. | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Vertical Lathes | Workpieces are mounted vertically, suitable for large parts. | Aerospace, automotive industries. | Pros: Efficient for large components; Cons: Requires more space. |
| Horizontal Lathes | Workpieces are mounted horizontally, versatile for various tasks. | General machining, custom projects. | Pros: Versatile; Cons: May require more setup time. |
| Specialty Lathes | Designed for specific tasks (e.g., turret lathes). | High-volume production of specific parts. | Pros: Tailored for specific applications; Cons: Limited flexibility. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Manual Lathes for B2B Buyers?
Manual lathes are characterized by their straightforward operation, where the user has direct control over the machining process. These machines are particularly suitable for small-scale production and repair work, making them ideal for workshops and small manufacturers in regions like Africa and South America. When considering a manual lathe, buyers should assess their production needs, as these machines tend to be less expensive but require skilled operators to maximize efficiency.
How Do CNC Lathes Enhance Precision in Manufacturing?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes represent a significant advancement in lathe technology, offering unparalleled precision and the ability to produce complex parts with minimal human intervention. They are essential in mass production environments, particularly in automotive and aerospace sectors, where accuracy is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the return on investment, as while CNC lathes have a higher upfront cost, their efficiency and precision can lead to significant long-term savings.
In What Scenarios Are Vertical Lathes Most Effective?
Vertical lathes are designed for machining large, heavy components, with the workpiece mounted vertically. This configuration is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where large parts must be processed with high efficiency. Buyers should consider the space requirements and the type of components they need to manufacture, as vertical lathes often require more floor space and may necessitate additional handling equipment.
What Advantages Do Horizontal Lathes Offer for Versatile Applications?
Horizontal lathes are versatile machines suitable for a wide range of machining tasks, from simple turning operations to complex custom projects. They are commonly used in general machining environments, where flexibility is crucial. Buyers should evaluate their specific project requirements, as horizontal lathes typically offer a balance between versatility and ease of setup, although they may require more time to change configurations compared to specialty lathes.
How Do Specialty Lathes Cater to Specific Manufacturing Needs?
Specialty lathes, such as turret lathes, are designed for high-volume production of specific types of parts, providing tailored solutions for manufacturers. These machines excel in environments where repetitive tasks are common, allowing for increased efficiency and reduced cycle times. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in specialty lathes against their potential limitations in flexibility, as these machines are often not suitable for varied production runs.
Key Industrial Applications of lathe manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lathe manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | Ensures high accuracy and reliability for critical components | Certifications, material specifications, and lead times |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts production | Enhances production efficiency and reduces downtime | Supplier reputation, service support, and parts availability |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and piping equipment fabrication | Improves operational efficiency and safety in extreme conditions | Durability, compliance with safety standards, and service capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Supports innovation and precision in life-saving technologies | Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and customization options |
| General Manufacturing | Production of various metal and plastic components | Increases versatility and adaptability in manufacturing processes | Cost, machine versatility, and after-sales support |
How are Lathe Manufacturers Used in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, lathe manufacturers produce precision components essential for aircraft and spacecraft. These components, such as turbine blades and landing gear parts, require high accuracy and reliability due to safety regulations and performance standards. International B2B buyers must consider certifications like AS9100, ensuring that manufacturers meet aerospace quality management standards. Additionally, the sourcing of materials must comply with stringent specifications to withstand extreme conditions.
What Role Do Lathe Manufacturers Play in Automotive Production?
Lathe manufacturers are crucial in the automotive sector, producing engine and transmission parts. The precision and speed offered by modern lathes enhance production efficiency, allowing manufacturers to meet high demand while minimizing downtime. For buyers in regions like Brazil or Nigeria, it’s vital to evaluate the supplier’s reputation for quality and the availability of service support. This ensures that any potential issues can be addressed swiftly, maintaining production continuity.
How are Lathe Manufacturers Essential in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, lathe manufacturers fabricate drilling and piping equipment that must endure harsh environments. High-quality lathes enable the production of durable components that improve operational efficiency and safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who comply with safety standards and offer robust service capabilities. This is particularly important in regions with challenging operational conditions, ensuring that equipment remains functional and safe.
Why are Lathe Manufacturers Important for Medical Devices?
Lathe manufacturers are integral to the production of custom surgical instruments and implants in the medical device industry. Precision is critical, as these tools must meet stringent regulatory standards and support innovative healthcare solutions. International buyers need to ensure that manufacturers have a solid quality assurance process and can offer customization options to meet specific medical requirements. This helps in developing advanced technologies that can save lives.
How Do Lathe Manufacturers Support General Manufacturing?
Lathe manufacturers provide versatile solutions for general manufacturing, enabling the production of various metal and plastic components. This adaptability allows manufacturers to respond to market changes and customer needs quickly. When sourcing lathes, businesses should consider costs, the versatility of the machines, and the availability of after-sales support. These factors are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring long-term productivity in diverse manufacturing processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lathe manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Quality Replacement Parts for Lathes
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing high-quality replacement parts for their lathe machines, especially when dealing with older models or machines from less prominent manufacturers. This issue can lead to extended downtimes, increased operational costs, and frustration as they sift through unreliable vendors. The lack of compatibility and quality assurance can further complicate the procurement process, leaving buyers hesitant and uncertain about their choices.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the challenges of sourcing replacement parts, buyers should first establish relationships with reputable lathe manufacturers or authorized distributors who specialize in their specific machine models. This can include utilizing manufacturers’ extensive microfiche databases or parts catalogs that detail compatibility with older machines. Buyers should also consider investing in remanufactured parts, which can offer a high-quality alternative at a lower cost. When placing orders, it’s crucial to verify part specifications and quality certifications to ensure they meet OEM standards. Additionally, joining forums or networks of lathe users can provide insights into reliable suppliers and parts recommendations, further enhancing the procurement process.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Technical Support and Maintenance Services
The Problem: International buyers often face challenges related to inadequate technical support and maintenance services from lathe manufacturers, particularly when they are located in remote regions. This lack of support can result in prolonged equipment downtimes and can significantly impact production schedules. Many manufacturers may not have a robust service network in certain regions, leading to delays in response times for repairs or maintenance.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should prioritize manufacturers with established field service teams that have a global presence. When researching potential suppliers, it’s essential to inquire about their after-sales support and service capabilities in specific regions. Buyers should look for manufacturers that provide comprehensive training resources, including online tutorials and remote troubleshooting options. Additionally, establishing a maintenance contract with the manufacturer can ensure timely service and access to trained technicians when needed. Engaging in regular preventive maintenance schedules can also mitigate downtime and enhance machine performance over time.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Complexity of Customizing Lathes for Unique Production Needs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of customizing lathes to meet specific production requirements, which can vary significantly based on industry needs. This complexity can lead to misunderstandings with manufacturers regarding specifications, resulting in machines that do not perform as expected. The risk of over-engineering or under-engineering a lathe can lead to wasted resources and unmet production goals.
The Solution: To effectively customize lathe machines, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their production processes and specific needs before initiating discussions with manufacturers. Engaging in detailed consultations with engineering teams from potential suppliers can help clarify requirements and expectations. Buyers should also request prototypes or demonstrations of customized solutions to evaluate their suitability before making a purchase. Moreover, leveraging software tools for simulation and modeling can help visualize the customization process and avoid costly mistakes. Establishing a collaborative relationship with the manufacturer throughout the design and build phases can ensure that the final product aligns perfectly with the buyer’s operational goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lathe manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Lathe Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for lathe manufacturing, it is crucial to consider properties such as strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Here, we analyze four common materials used in lathe manufacturing: Cast Iron, Steel, Aluminum, and Composite Materials.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Lathe Manufacturing?
Cast iron is widely used in lathe beds and frames due to its excellent damping properties, which help absorb vibrations during machining. Key properties include high compressive strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, cast iron is brittle, which can lead to cracking under severe impact.
Pros: Cast iron is relatively inexpensive and offers excellent stability and vibration damping. It is also easy to machine and has a long service life.
Cons: Its brittleness can be a limitation in high-impact applications, and it may require additional surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance.
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local standards such as ASTM or JIS is essential. Cast iron is generally accepted globally, but variations in composition might affect performance.
What Advantages Does Steel Offer in Lathe Manufacturing?
Steel, particularly high-carbon and alloy steels, is favored for components that require high tensile strength and toughness. Key properties include excellent hardness and wear resistance, particularly when heat-treated. Steel can withstand higher temperatures and pressures compared to cast iron.
Pros: Steel provides superior strength and durability, making it suitable for high-performance applications. It can also be easily welded and machined.
Cons: The cost of high-quality steel can be significantly higher than cast iron, and manufacturing complexity increases with the need for heat treatment and surface finishing.
International buyers should consider the availability of specific steel grades and their compliance with local standards. For instance, European buyers may prefer materials that meet DIN standards, while those in the Middle East might focus on ASTM specifications.
Why Is Aluminum Used in Some Lathe Applications?
Aluminum is increasingly popular for lightweight applications and components that require high corrosion resistance. Key properties include low density, good thermal conductivity, and ease of machining. However, aluminum is generally less strong than steel and cast iron.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, making it ideal for portable lathes and applications where weight is a concern. Its natural resistance to corrosion reduces maintenance needs.
Cons: The lower strength of aluminum limits its use in heavy-duty applications, and its cost can be higher than that of cast iron.
For international buyers, especially in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, aluminum’s corrosion resistance can be a significant advantage. Compliance with standards such as ASTM can guide material selection.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Lathe Manufacturing?
Composite materials, often a combination of polymers and fibers, are gaining traction in specialized lathe applications. Key properties include lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent vibration damping. However, composites can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Pros: Composites offer unique benefits, such as reduced weight and enhanced vibration absorption, making them suitable for precision lathes.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex, and composites may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
International buyers should be aware of the specific certifications required for composite materials, as these can vary significantly by region. Understanding local preferences and standards is essential for successful procurement.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lathe Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for lathe manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Lathe beds and frames | Excellent vibration damping | Brittle, prone to cracking | Low |
| Steel | High-performance components | Superior strength and durability | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and portable applications | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Precision lathes | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex manufacturing process | High |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for lathe manufacturers, focusing on key properties, advantages, and considerations for international buyers. Understanding these factors can significantly impact procurement decisions and overall manufacturing success.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lathe manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Lathes?
The manufacturing process of lathes involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality in the final product. Each stage is designed to transform raw materials into fully functional machines, adhering to strict industry standards.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Manufacturers typically use high-grade steel and cast iron due to their durability and machinability. The raw materials undergo rigorous inspections to check for defects. This often involves ultrasonic testing to detect internal flaws that could compromise the lathe’s structural integrity.
Once the materials are approved, they are cut to size and shape using saws or plasma cutting machines. This step is crucial as it lays the groundwork for precise forming in subsequent stages.
Forming Techniques: How Are Lathes Shaped and Assembled?
The forming stage is where the raw materials are transformed into components. Various techniques are employed, including casting, forging, and machining.
-
Casting: In this method, molten metal is poured into molds to create complex shapes, such as the bed of the lathe. This technique is often used for large components due to its ability to produce intricate designs.
-
Forging: This involves shaping metal through compressive forces, enhancing its strength. Components like the headstock and tailstock may be forged to provide added durability.
-
Machining: After forming, components are machined using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines for precision. This includes turning, milling, and grinding processes that ensure the components meet tight tolerances.
Assembly: How Are Lathes Put Together?
Following the forming process, the individual components are assembled. This stage requires skilled technicians who ensure that each part fits perfectly. Key assembly processes include:
-
Alignment: Components such as the spindle and tailstock must be aligned to maintain accuracy during operation. This often involves precision measuring tools to check alignments.
-
Integration of Electronics: Modern lathes often include CNC systems for enhanced control. These systems are integrated during assembly, requiring thorough testing to ensure they work seamlessly with the mechanical parts.
-
Final Assembly: Once all components are integrated, the lathe is assembled into its final form, ready for the finishing process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Lathe Manufacturing?
The finishing stage is vital for both aesthetics and functionality. Common techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting are applied to protect the machine from corrosion and wear.
-
Grinding and Polishing: These processes enhance the surface finish of components, reducing friction and improving overall performance.
-
Quality Checks: Before moving to the next stage, manufacturers conduct inspections to ensure that components meet specified tolerances and surface finishes.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of lathe manufacturing, ensuring that each machine meets international standards for performance and safety. Buyers should be familiar with the following standards:
ISO 9001: What Does This Standard Entail?
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized quality management standard that focuses on consistent quality in products and services. For lathe manufacturers, compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that they have established effective quality management systems, ensuring continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Industry-Specific Standards: What Are CE and API Certifications?
In addition to ISO 9001, there are specific certifications relevant to the lathe manufacturing industry:
-
CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, the CE mark indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Specification: For manufacturers involved in the oil and gas industry, API certifications ensure that the equipment meets rigorous industry standards for safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Lathe Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that every lathe meets the required specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival. Any non-conformities are addressed before manufacturing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, random sampling and inspections are conducted to ensure that processes adhere to specified tolerances and standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing. This includes performance testing, safety assessments, and detailed inspections of the finished lathe.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of lathe manufacturers is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier reliability:
Conducting Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Visiting the manufacturing facility for an audit provides insight into the supplier’s quality control processes. Buyers should assess:
- Compliance with Standards: Check if the supplier adheres to ISO and industry-specific standards.
- Process Documentation: Review records of quality control procedures and inspections.
- Employee Training: Ensure that staff are adequately trained in quality assurance practices.
Requesting Quality Reports: What Information Should Be Included?
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that include:
- Test Results: Documentation of testing methods and outcomes for key components.
- Defect Rates: Information on any defects found during manufacturing and how they were addressed.
- Customer Feedback: Insights from previous clients regarding the performance and reliability of the lathes.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: How Can They Help?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These services can conduct thorough inspections at various stages of production, ensuring compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances that may vary by region:
- Regulatory Differences: Understanding local regulations and certifications required in the buyer’s region can prevent compliance issues.
- Cultural Expectations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service, which should be considered in supplier selection.
- Logistics Challenges: Ensure that quality standards are maintained throughout the supply chain, including during shipping and handling.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting lathe manufacturers, ultimately ensuring they receive reliable and high-quality machinery tailored to their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lathe manufacturers’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring lathe manufacturing equipment. With various manufacturers available globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to have a structured approach. This checklist outlines key steps to ensure you select a reliable supplier that meets your specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensure that the lathe you procure meets your production requirements. Consider factors such as the type of materials you will be machining, the size and complexity of the parts, and the desired precision levels. This clarity will help narrow your search to manufacturers that specialize in the specific lathes you need.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research on potential lathe manufacturers. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry, focusing on their history, customer reviews, and product offerings. Utilize platforms like industry directories, trade shows, and online reviews to gather insights about their market standing and product reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with any supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. This may include ISO certifications or specific industry-related standards. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and can assure you that the manufacturer adheres to best practices in production and safety.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations for the lathes you are interested in. Ensure the quotations include not only the price but also specifications, delivery timelines, warranty terms, and after-sales support. A comprehensive quote will provide a clearer picture of the overall value and service you can expect.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Services
After-sales support is critical for maintaining operational efficiency. Inquire about the manufacturer’s service offerings, such as installation, training, maintenance, and repair services. A supplier that provides robust support will help minimize downtime and enhance the longevity of your lathe.
Step 6: Verify Customer References
Request references from previous customers, particularly those in similar industries or geographical locations. Speak directly with these references to gain insights into their experiences with the manufacturer, focusing on product performance and customer service. This firsthand feedback can significantly influence your decision-making process.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Contract
Once you have selected a manufacturer, negotiate the terms of the purchase. Ensure that all aspects, including pricing, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions, are clearly defined in the contract. A well-structured agreement protects both parties and lays the groundwork for a successful partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing lathe manufacturers, ultimately leading to successful procurement and enhanced production capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lathe manufacturers Sourcing
When evaluating the costs and pricing for sourcing lathes, international B2B buyers must consider a multifaceted approach that encompasses various cost components and pricing influencers. This analysis is crucial for organizations in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where unique market dynamics can affect procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Lathe Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure is essential for buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components in lathe manufacturing include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used, such as high-grade steel and alloys, significantly impact costs. Suppliers may offer different grades, which can influence both price and durability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for both manufacturing and assembly processes. Labor costs can vary based on location and expertise, with countries having lower wage rates potentially offering more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the production facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can add significant expenses, especially for specialized lathes. Standard tooling may be less expensive but might not meet specific needs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the lathes meet international standards. High-quality certifications can add to the cost but also provide assurance of product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and delivery costs can vary widely, especially for international shipments. These costs should be factored into the overall pricing analysis.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market positioning. Understanding the margin can help buyers gauge the reasonableness of the price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lathe Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of lathes:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often yield discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and purchasing power to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized lathes generally command higher prices due to additional engineering and production requirements. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs but are often necessary for compliance in certain industries. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better support and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding delivery terms is critical. Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, affecting total landed costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices with Lathe Manufacturers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Nigeria and Brazil, effective negotiation is vital for achieving cost-efficiency:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the equipment is less reliable.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Frequent communication and trust can yield advantages during negotiations.
-
Research Market Prices: Having benchmark pricing information helps in negotiations. Buyers should gather data on similar products and market trends to strengthen their position.
-
Be Open to Alternative Solutions: Sometimes, opting for refurbished or remanufactured lathes can provide significant savings without sacrificing quality. Evaluate all available options.
Conclusion: Why Is It Important to Stay Informed About Pricing Nuances?
The lathe manufacturing landscape is intricate, and pricing can vary significantly based on multiple factors. By understanding the cost structure and price influencers, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. It’s crucial to stay informed and adaptable in this evolving market, particularly for international buyers navigating different regulatory and economic environments. Always remember to seek clarity on pricing terms and conditions and remain vigilant about market trends to achieve the best value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lathe manufacturers With Other Solutions
Introduction: Why Consider Alternatives to Lathe Manufacturers?
When sourcing manufacturing equipment, particularly lathes, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives. While traditional lathe manufacturers offer reliable, high-quality solutions, there are other technologies and methods that can achieve similar goals, such as CNC machining and 3D printing. Understanding these alternatives helps buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and production goals.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Lathe Manufacturers | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for metal working | Very high precision, complex shapes | Moderate precision, suited for prototypes |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate to high, depending on setup | Lower for small batches, but can escalate with complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators | Requires programming knowledge | User-friendly, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Moderate, mostly software updates | Low, but depends on printer quality |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of metal parts | Complex, high-volume manufacturing | Rapid prototyping and low-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machining: Is It Right for Your Needs?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining offers advanced performance, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate designs with high precision. This technology is particularly beneficial for creating complex geometries that lathes may struggle with. However, the initial setup costs can be significant, and the technology requires operators who are skilled in programming and machine operation. CNC machines can also be more versatile, handling various materials beyond metal, making them suitable for diverse applications. Despite these advantages, the complexity and higher costs can be a barrier for small businesses or those just starting in manufacturing.
3D Printing: A Flexible and Cost-Effective Alternative?
3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology, especially for rapid prototyping and low-volume production runs. It allows manufacturers to create parts directly from digital models, reducing lead times and material waste. The technology is generally user-friendly, requiring less technical expertise than CNC machining or traditional lathes. However, while 3D printing excels in flexibility, it may not achieve the same level of precision or strength as lathes or CNC machines for metal parts. Moreover, costs can escalate rapidly with more complex designs or larger production volumes, making it less economical for some applications.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between lathe manufacturers and alternative technologies like CNC machining or 3D printing, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including production volume, material types, and the complexity of the parts being produced. For high-precision metal components in large quantities, traditional lathes or CNC machining may be the best fit. Conversely, for rapid prototyping or projects with limited runs, 3D printing could provide the necessary flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, evaluating these factors will empower buyers to choose the most suitable solution for their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lathe manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties That Lathe Manufacturers Should Know?
When evaluating lathes for manufacturing purposes, several critical specifications are essential for ensuring optimal performance and meeting production goals. Here are some vital technical properties:
-
Material Grade: The type of materials used in the construction of a lathe significantly affects its durability and performance. Common materials include cast iron, which provides stability and vibration dampening, and high-strength steel for added rigidity. Selecting the right material grade is crucial for manufacturers aiming for longevity and reliability in their equipment.
-
Tolerance: This specification refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of machined parts. Tolerances are critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. In a B2B context, understanding tolerance levels can help buyers determine whether a lathe can produce parts that meet their precise specifications, affecting product quality and operational efficiency.
-
Spindle Speed: Measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), spindle speed is a key indicator of a lathe’s capability to handle different materials and types of operations. Higher spindle speeds allow for faster machining, which is essential for meeting production deadlines. However, the appropriate spindle speed must be matched with the material being machined to avoid damage or inaccuracies.
-
Horsepower: This measurement indicates the power output of the lathe’s motor. Higher horsepower typically allows for more robust machining capabilities, enabling the lathe to handle tougher materials and more complex operations. For B2B buyers, understanding horsepower is vital for assessing whether a lathe can meet their production requirements without overloading the machine.
-
Bed Length: The bed length of a lathe determines the maximum length of the workpiece it can accommodate. This specification is crucial for manufacturers that deal with larger components, as it influences both the machine’s versatility and the types of projects that can be undertaken.
Which Trade Terms Are Essential for Lathe Manufacturers to Understand?
Navigating the world of lathe manufacturing also involves familiarizing oneself with specific trade terms that can impact purchasing decisions. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the lathe industry, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can assure buyers of the quality and compatibility of the machines and parts they are purchasing.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For lathe manufacturers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when sourcing replacement parts or materials from suppliers.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of lathe manufacturing, submitting an RFQ can help businesses compare pricing and terms across different suppliers, facilitating more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for buyers involved in cross-border transactions, as they clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Lead Time: This term indicates the amount of time it takes for an order to be fulfilled. For lathe manufacturers, understanding lead times is vital for planning production schedules and ensuring that machinery is available when needed to meet customer demands.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing lathes and associated equipment, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lathe manufacturers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Lathe Manufacturers Sector?
The lathe manufacturing sector is currently experiencing a transformation driven by several global trends. One of the foremost drivers is the increasing demand for precision and automation across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where industrial growth is accelerating. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is influencing lathe manufacturers to incorporate advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and machine learning into their operations. These innovations facilitate real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which are crucial for enhancing productivity and minimizing downtime.
International B2B buyers are also seeking suppliers that offer comprehensive solutions, including machine rebuilding and remanufacturing services. Companies like Monarch Lathes exemplify this trend, providing not just machinery but also ongoing support and access to high-quality spare parts. The focus on total cost of ownership (TCO) is becoming increasingly significant, with buyers prioritizing suppliers that can demonstrate long-term value through quality and service.
Another notable trend is the globalization of supply chains. As businesses expand their operations internationally, they are looking for reliable manufacturers who can meet their specific needs while ensuring timely delivery. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, where local manufacturing capabilities may still be developing. Therefore, establishing partnerships with reputable lathe manufacturers can provide buyers with a competitive edge in their respective markets.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Lathe Manufacturers Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical focus for lathe manufacturers, driven by growing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures. Companies are increasingly assessing their environmental impact and striving to implement greener practices throughout their supply chains. For B2B buyers, selecting manufacturers that prioritize sustainability can be a key differentiator. This includes sourcing materials from ethical suppliers and utilizing energy-efficient production processes.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to the European Union’s REACH regulation for chemical safety are becoming important criteria for buyers. Manufacturers that obtain these certifications not only demonstrate compliance but also commitment to reducing their ecological footprint. This commitment can enhance brand reputation and lead to increased customer loyalty.
Additionally, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as businesses recognize the importance of transparency in their supply chains. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the practices of their suppliers, looking for evidence of fair labor practices and responsible sourcing. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like the Middle East, where the push for ethical standards is gaining momentum. Manufacturers that align with these values are more likely to attract international buyers who prioritize corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Lathe Manufacturing?
The lathe, one of the oldest machine tools, has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations. However, its evolution into a modern precision tool began during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries. Early lathes were primarily used for woodworking, but innovations such as steam-powered engines and improved control systems allowed for the machining of metal, significantly enhancing their capabilities.
By the late 19th and early 20th centuries, American manufacturers began to dominate the lathe market, creating a legacy of high-quality machine tools. Companies like South Bend and LeBlond played pivotal roles in advancing lathe technology, producing machines that were not only reliable but also adaptable to various industrial needs. This historical foundation set the stage for the current landscape, where precision, automation, and sustainability are at the forefront of lathe manufacturing, reflecting the industry’s ongoing commitment to innovation and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lathe manufacturers
1. How do I choose the right lathe manufacturer for my business needs?
Selecting the right lathe manufacturer involves assessing several key factors. Start by identifying your specific requirements, such as the type of materials you will work with, production volume, and desired precision. Research manufacturers’ reputations, focusing on their experience, quality certifications, and customer reviews. Additionally, consider their after-sales support, including maintenance services and parts availability. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can help clarify their capabilities and customization options, ensuring they align with your production goals.
2. What should I know about the customization options available from lathe manufacturers?
Customization options vary significantly among lathe manufacturers. When considering a supplier, inquire about their ability to tailor machines to your specific applications. This may include modifications to size, speed, or tooling systems. Some manufacturers also offer bespoke features like automation enhancements or specialized software for improved efficiency. Understanding the customization process, including lead times and associated costs, will help you make an informed decision that meets your operational requirements.
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lathes?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lathes can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and the type of machine. Smaller manufacturers may have lower MOQs to accommodate startups or smaller businesses, while larger manufacturers might set higher MOQs for production efficiency. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront to ensure they align with your budget and production plans. If your needs fall below the MOQ, some manufacturers may offer alternatives, such as partnering with other buyers or providing leasing options.
4. How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing lathe manufacturers?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing lathe manufacturers, verify their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Request detailed information about their manufacturing processes, including inspections and testing protocols. Engaging in factory visits or third-party audits can provide further assurance of quality. Additionally, consider requesting sample products or trial runs to evaluate the machinery’s performance before committing to a larger purchase.
5. What payment terms should I expect when dealing with lathe manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among lathe manufacturers, influenced by factors such as your location, the supplier’s policies, and the size of the order. Common terms include deposits of 30-50% upfront with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger purchases. Always clarify payment terms in advance and ensure they are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings.
6. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing lathes?
When importing lathes, consider logistics aspects such as shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Identify reliable freight forwarders who specialize in heavy machinery to ensure safe transport. Understanding the import regulations specific to your country is critical, as they can affect the delivery process. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturer’s support in logistics, as some suppliers may offer assistance with documentation and customs clearance.
7. How do I vet a lathe manufacturer for reliability and performance?
Vetting a lathe manufacturer involves several steps to ensure reliability and performance. Start by researching their industry reputation through online reviews and testimonials. Look for case studies or references from similar businesses to gauge their experience with specific lathe models. Attend industry trade shows or exhibitions to see the equipment in action and speak directly with representatives. Additionally, consider seeking recommendations from industry peers to identify manufacturers known for their quality and service.
8. What are the common challenges faced when sourcing lathes internationally?
Sourcing lathes internationally can present challenges such as language barriers, cultural differences, and varying quality standards. Time zone differences can complicate communication, affecting timelines for orders and support. Additionally, understanding international shipping logistics and customs regulations is vital to avoid delays. To mitigate these challenges, work with experienced import/export professionals and establish clear lines of communication with your supplier to ensure a smooth sourcing process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lathe manufacturers
As the global manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, the importance of strategic sourcing in the lathe manufacturing sector cannot be overstated. By partnering with reputable manufacturers, businesses can access high-quality equipment that meets specific production needs while ensuring reliability and longevity. Companies like Monarch Lathes and Summit Machine Tool exemplify the value of investing in established brands known for their craftsmanship and customer support.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize sourcing strategies that emphasize not only the machinery but also the associated services, such as rebuild and remanufacturing. This holistic approach ensures that investments are protected over time, facilitating sustained operational efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced lathes and machining centers is expected to grow, driven by technological advancements and increased production capabilities. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers who demonstrate innovation and a commitment to quality. By doing so, you position your business to harness the benefits of modern manufacturing techniques while navigating the complexities of global supply chains. Engage with trusted suppliers today to elevate your manufacturing processes and remain competitive in an ever-changing market.