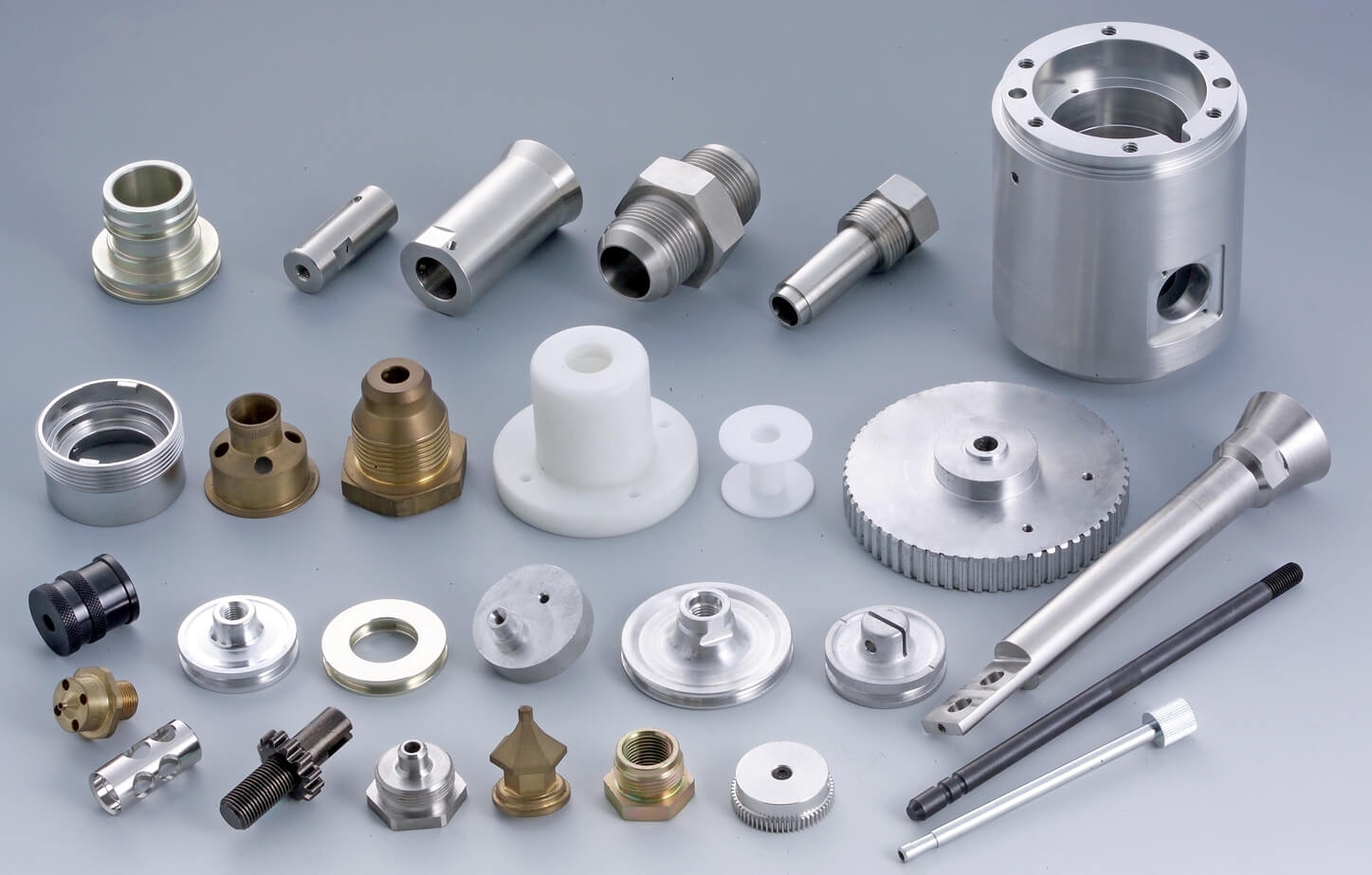
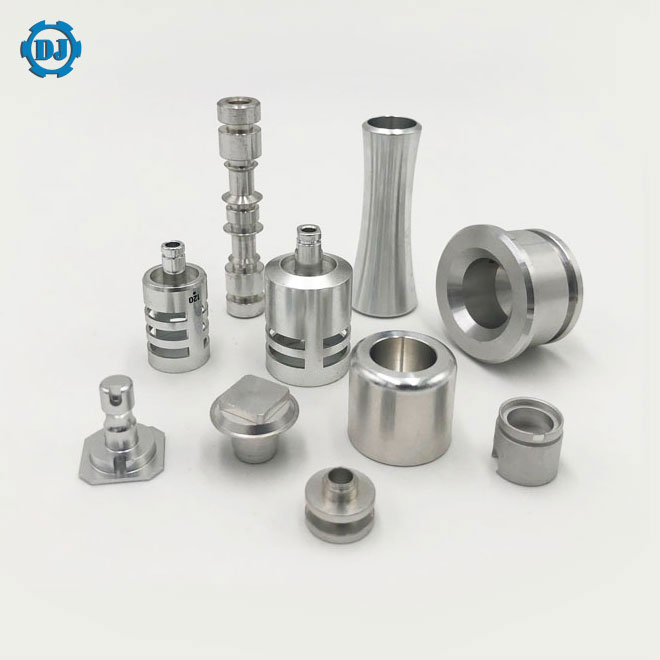
Top 9 Cnc Turned Parts Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Freeway Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: freewaycorp.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components and CNC turned parts manufacturing in the USA. Capabilities include: Automatic screw machines (over 30 machines capable of machining up to 2 5/8” round and 2 5/16” hex materials), CNC turning centers (handling up to 2 7/8” bar stock and chucking up to 7” blanks). Secondary operations include broaching (OD, ID, surface), thread and spline rolling, centerless grinding, ta…
2. Abbott Interfast – CNC Turning Services
Domain: aicfast.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Services & Turned Parts offered by Abbott Interfast include the production of complex parts using advanced CNC machining technology. The CNC turning process involves holding material in a chuck and rotating it at high speed while a cutting tool shapes the workpiece. Key benefits of CNC turning include increased production speed, enhanced efficiency, improved accuracy, consistent unifor…
3. Protolabs – CNC Turning Service
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Service provides quality custom turned parts for rapid prototyping and end-use production with lead times as fast as 1 day. The service utilizes a CNC lathe with live tooling, enabling the machining of features such as axial and radial holes, flats, grooves, and slots. CNC turning is suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts, particularly those with cylindrical features.
4. Parts Badger – CNC Turning Services
Domain: parts-badger.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning services for custom parts; capable of machining cylindrical parts using X, Y, and A movement lathes; maximum stock diameter of 7 inches and length of 32 inches; material options include Aluminum, Brass, Magnesium, Nickel, Steel, Thermoset plastics, Titanium, and Zinc; benefits include lower costs, no waiting time, and smaller batch sizes (less than 500 pieces); features CNC Machining, …
5. Screw Machine Products – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: screw-machine-products.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Precision turned parts are machined with extremely tight tolerances using CNC turning, which is computer numerical controlled. This process allows for high-precision, repeatable results in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics. CNC turning produces intricate, dimensionally accurate turned parts and components with exceptional surface finishes. It is ideal for m…
6. Innovative Metal Designs – Custom CNC Turning Services
Domain: innovativemetals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Innovative Metal Designs (IMD) provides custom CNC turning services, producing precision turned parts and components since 1982. They cater to a wide range of industries, offering quantities from one to thousands. IMD utilizes advanced CNC equipment, including Haas and Takisawa CNC lathes and mills, capable of producing parts as large as 12″ with tolerances of ± 0.001″ or better. Their CNC turning…
7. Solutions Manufacturing – Precision CNC Turning Services
Domain: solutionsmfg.net
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Precision CNC Turning Services offered by Solutions Manufacturing, Inc. include high precision CNC turning processes such as contour turning, form turning, taper turning, straight turning, boring, drilling, facing, grooving, knurling, parting/cutting, secondary grinding, and threading (external and internal). The services utilize CNC lathes for creating cylindrical-shaped parts, with a maximum dia…
8. MAPCO – CNC Turning Solutions
Domain: mapcomfg.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning at MAPCO Manufacturing includes industry-leading technology for precision parts manufacturing. Key capabilities include: 24 CNC Turning Centers, turning capacity of 1/8″ to 24″ in diameter and 192″ in length, bar feed to 2-5/8″, simultaneous main and sub-spindle production, live tooling for milling and turning, hard turning of pre-hardened steels, CNC Swiss turning for rigidity and acc…
9. Wh Bagshaw – Precision CNC Turning Services
Domain: whbagshaw.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Services: Custom-built, precision Swiss-style CNC turned parts and components. 150+ years in business, 100,000 sq. ft. facility, 500,000+ precision-machined parts per month, 1,000+ satisfied customers. CNC turning is a subtractive machining process involving a rotating metal bar or rod and a cutting tool. Ideal for rapid tooling and prototyping. Materials include aluminum, brass, carbo…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc turned parts manufacturer
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing CNC turned parts manufacturers can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the increasing demand for precision-engineered components, businesses face the challenge of finding suppliers that not only meet stringent quality standards but also offer cost-effective solutions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring various types of CNC turned parts, their applications across industries, and best practices for vetting suppliers.
By delving into essential factors such as material selection, production capabilities, and cost considerations, this guide equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. From automotive to telecommunications, the applications for CNC turned parts are vast, highlighting the importance of partnering with a manufacturer that understands the specific needs of your industry.
Moreover, we will address common concerns, such as ensuring quality control and managing lead times, enabling buyers to navigate the complexities of global sourcing confidently. Whether you are a buyer in Saudi Arabia seeking reliable suppliers or a company in Germany looking to expand your production capabilities, this guide will empower you with the knowledge to optimize your procurement strategy for CNC turned parts.
Understanding cnc turned parts manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Lathes | High precision, ability to handle complex geometries | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical Devices | Pros: High accuracy, scalability. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Multi-Spindle Screw Machines | Simultaneous machining of multiple parts, high production rates | Mass production, Consumer Electronics | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes. Cons: Limited flexibility for custom parts. |
| Swiss-Type CNC Machines | Ideal for small, complex parts; high-speed precision machining | Watchmaking, Electronics, Medical Equipment | Pros: Exceptional precision, minimal waste. Cons: More complex setup. |
| CNC Turning Centers | Versatile machining capabilities, suitable for various materials | Fluid Power, Agriculture, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Adaptability to different materials. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Precision Machining Services | Custom solutions with tight tolerances and secondary operations | Defense, Marine, Telecommunications | Pros: Tailored solutions, high quality. Cons: Potentially longer lead times. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Lathes?
CNC lathes are characterized by their ability to produce high-precision components, making them suitable for industries like automotive and aerospace. They excel in creating complex geometries and can handle a variety of materials. When considering CNC lathes, buyers should evaluate the manufacturer’s experience, the range of materials processed, and the machine’s capabilities regarding intricate designs.
How Do Multi-Spindle Screw Machines Benefit Mass Production?
Multi-spindle screw machines are designed for high-volume production, allowing simultaneous machining of multiple parts. This efficiency makes them ideal for consumer electronics and other mass-produced items. Buyers should consider their production volume and the machine’s adaptability to different part sizes when selecting a supplier, as this can significantly impact cost-effectiveness.
Why Choose Swiss-Type CNC Machines for Small Parts?
Swiss-type CNC machines specialize in machining small, complex components with high-speed precision. This makes them particularly valuable in industries like watchmaking and electronics, where detail is paramount. Buyers should assess the machine’s setup complexity and the manufacturer’s ability to produce small batches efficiently, as this can influence production timelines and costs.
What Advantages Do CNC Turning Centers Offer?
CNC turning centers provide versatile machining capabilities, accommodating various materials and part designs. They are commonly used in fluid power and agricultural applications. Buyers must consider the adaptability of the turning center to their specific requirements and the expertise of the machining staff to ensure high-quality outputs.
What Should Buyers Know About Precision Machining Services?
Precision machining services focus on delivering custom solutions with tight tolerances and the option for secondary operations, making them suitable for industries like defense and telecommunications. Buyers should weigh the importance of tailored solutions against potential lead times, as custom manufacturing can sometimes extend delivery schedules.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc turned parts manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Turned Parts Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision components for engine assemblies | Enhanced performance and durability of vehicles | Certification of materials and adherence to automotive standards |
| Aerospace | Components for aircraft engines and systems | Safety and reliability in critical applications | Compliance with stringent aerospace regulations and testing |
| Medical Devices | Custom components for surgical instruments | Improved patient outcomes and device reliability | ISO certification and biocompatibility of materials |
| Industrial Equipment | Parts for hydraulic systems and machinery | Increased efficiency and reduced downtime | Material traceability and adherence to industry standards |
| Telecommunications | Connectors and housings for communication devices | Enhanced signal integrity and device longevity | Precision tolerances and compatibility with existing systems |
How Are CNC Turned Parts Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, CNC turned parts are essential for manufacturing precision components that contribute to engine assemblies, transmission systems, and other critical systems. These parts, such as bushings, shafts, and fittings, require high accuracy to ensure optimal performance and longevity. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, must prioritize suppliers who adhere to strict automotive standards, ensuring that materials are certified and that production processes comply with industry regulations.
What Role Do CNC Turned Parts Play in Aerospace Applications?
CNC turned parts are vital in the aerospace industry, where components must meet rigorous safety and performance standards. These parts are used in aircraft engines, landing gear, and avionics systems, necessitating high precision and reliability. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to partner with manufacturers who understand aerospace compliance requirements and can provide documentation proving adherence to safety and quality standards.
How Are CNC Turned Parts Utilized in Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, CNC turned parts are integral to the production of surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. These components must be manufactured with extreme precision to ensure patient safety and device functionality. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on suppliers that hold ISO certifications and can guarantee the biocompatibility of materials used, as these factors significantly influence the efficacy and safety of medical devices.
What Benefits Do CNC Turned Parts Offer for Industrial Equipment?
CNC turned parts are commonly used in industrial equipment, particularly in hydraulic systems and machinery. These components enhance efficiency and reduce the likelihood of downtime, which is critical for maintaining productivity. Buyers, particularly from South America and Africa, should consider sourcing from manufacturers who provide material traceability and comply with industry standards, ensuring that the parts will perform reliably under demanding conditions.
How Are CNC Turned Parts Applied in Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications sector, CNC turned parts are used to create connectors and housings for communication devices. These components must maintain tight tolerances to ensure signal integrity and device longevity. For international buyers, especially in Europe and the Middle East, it is essential to partner with manufacturers capable of producing high-precision parts that meet specific compatibility and performance criteria, ensuring seamless integration into existing systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc turned parts manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Tighter Tolerances for Complex Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing CNC turned parts that meet stringent quality standards, especially when dealing with complex geometries. This difficulty is compounded when manufacturers lack advanced equipment or expertise, leading to inconsistencies in dimensions and performance. For industries such as aerospace or automotive, where precision is critical, any deviation can result in costly delays, rework, or even safety issues. Buyers may feel frustrated when their specifications are not met, causing project timelines to slip and budgets to overrun.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that specialize in precision CNC turning and have a proven track record in handling complex components. Look for vendors with advanced CNC lathes and multi-spindle screw machines that can maintain tight tolerances. Request detailed documentation of the manufacturer’s quality assurance processes, including certifications and previous project case studies. Engaging in early discussions about your project specifications allows for a collaborative approach, ensuring the manufacturer understands your needs and can suggest viable solutions. Consider conducting a pilot run of the part to validate performance before committing to full production.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times Affecting Production Schedules
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with long lead times from CNC turned parts manufacturers, which can severely disrupt their production schedules. When manufacturers are unable to meet delivery deadlines due to capacity constraints or inefficient processes, it creates a ripple effect that impacts the buyer’s ability to fulfill their own customer orders. This scenario is particularly detrimental for businesses in fast-paced sectors like electronics or automotive, where market demands fluctuate rapidly.
The Solution: To counteract long lead times, buyers should conduct thorough research to identify CNC manufacturers with a reputation for reliability and timely delivery. Look for companies that utilize lean manufacturing principles and have invested in scalable production capabilities. It may also be beneficial to establish a long-term partnership with a manufacturer that can better accommodate fluctuating demand through flexible production schedules. Inquire about their production planning strategies and whether they can provide real-time updates on order status. Additionally, consider local manufacturers to reduce shipping times, as proximity can enhance communication and expedite logistics.
Scenario 3: Material Sourcing Challenges for Custom Components
The Problem: Sourcing the right materials for CNC turned parts can be a daunting task, especially when buyers require custom components made from specific alloys or plastics. Inconsistent material quality can lead to subpar finished products, resulting in performance issues and additional costs for re-engineering or replacement. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the complexity of material certifications and compliance with industry standards, which can further complicate their procurement process.
The Solution: To streamline material sourcing, buyers should partner with CNC turned parts manufacturers that offer comprehensive material procurement services. Look for manufacturers who have established relationships with trusted suppliers and can provide assurance regarding material quality and compliance. When discussing your project, clearly communicate your material requirements and any relevant industry certifications needed. Manufacturers with in-house material sourcing capabilities can save you time and effort, allowing you to focus on your core business operations. Additionally, consider requesting material samples or certifications before proceeding with production to ensure they meet your specifications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Turned Parts?
When selecting materials for CNC turned parts, it’s essential to consider their properties, as these directly affect product performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Brass, and Nylon, focusing on their suitability for various applications and the implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Aluminum is prized for its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications where weight savings are critical. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, easy to machine, and provides good strength-to-weight ratios. Its excellent thermal conductivity also makes it suitable for heat dissipation applications.
Cons: While it offers good durability, aluminum can be less resistant to wear compared to harder materials. It may also require surface treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications where weight reduction is essential. However, its compatibility with certain chemicals should be assessed based on the specific media involved.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum alloys. Understanding local preferences for specific grades is also crucial, particularly in regions like Europe, where material specifications may vary.
Stainless Steel: The Versatile Workhorse
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for demanding environments. It can handle high temperatures (up to 800°C) and pressures, depending on the grade.
Pros: Its durability and aesthetic appeal make stainless steel ideal for both functional and decorative applications. It is also relatively easy to clean, which is advantageous in industries like food processing.
Cons: The primary downside is its higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, machining stainless steel can be more complex and may require specialized tools.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is widely used in the medical, automotive, and marine industries, where corrosion resistance and strength are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 or DIN 17440 is essential. Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany should be aware of local regulations regarding material certifications.
Brass: The Corrosion-Resistant Choice
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability. It typically performs well in moderate temperature and pressure conditions.
Pros: Brass is highly ductile and provides good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electrical components. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it a preferred choice for decorative applications.
Cons: Brass can be more expensive than aluminum and may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and musical instruments, brass is ideal for applications requiring corrosion resistance and conductivity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with JIS standards for brass components. Understanding regional preferences for specific brass grades can also enhance procurement efficiency.
Nylon: The Lightweight Polymer
Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its toughness and resistance to wear and abrasion. It performs well in moderate temperature and pressure environments.
Pros: Nylon is lightweight, cost-effective, and offers excellent chemical resistance. It can be machined into complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications.
Cons: Its thermal stability is lower than metals, and it may not perform well under high-temperature conditions. Additionally, nylon can absorb moisture, which may affect its mechanical properties.
Impact on Application: Nylon is often used in applications such as gears, bearings, and bushings, where low weight and wear resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with material safety standards and specifications relevant to their industry. In regions like South America, understanding local sourcing capabilities for nylon can be beneficial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Turned Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc turned parts manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less wear resistance than steel | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical, automotive, marine applications | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Nylon | Gears, bearings, bushings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal stability | Low |
This guide provides a foundational understanding of material selection for CNC turned parts, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Turned Parts?
The manufacturing process for CNC turned parts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials used for CNC turning include various grades of stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and plastics. Suppliers should be able to source materials from approved vendors, ensuring compliance with industry standards. The material must undergo inspection upon arrival to confirm its specifications and quality. This initial quality control (IQC) is essential for preventing defects in the final product.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves placing the raw material into a CNC lathe or screw machine, where it is held in a chuck and rotated at high speeds. A cutting tool, guided by a computer program, removes material to create the desired shape. This process allows for high precision and the ability to produce complex geometries efficiently. Advanced CNC machines can execute multiple operations simultaneously, further enhancing production speed and accuracy.
3. Secondary Operations and Assembly
After the initial forming process, secondary operations may be required to enhance the functionality of the turned parts. These can include broaching, threading, drilling, and grinding. Each operation focuses on achieving tighter tolerances and improving surface finishes. If the parts require assembly, this is the stage where components are fitted together, ensuring that they meet design specifications.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves final touches to ensure the parts are ready for use. This can include processes such as deburring, cleaning, and surface treatments (e.g., anodizing or plating). Finishing not only improves aesthetics but also enhances durability and corrosion resistance, which is crucial for parts used in demanding environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into CNC Turning Processes?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the CNC turning process, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Many CNC turned parts manufacturers adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for an effective quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates that a manufacturer is committed to consistent quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, like CE marking for products sold within Europe or API certification for oil and gas components, are essential for verifying the manufacturer’s capability to meet specific regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Turning?
Quality control in CNC turning typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular checks are performed to monitor the machining process, ensuring that dimensions and tolerances are within acceptable limits.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the parts are completed, a thorough inspection is conducted to confirm that they meet all specifications before they are shipped.
Common testing methods include dimensional inspections using calipers and gauges, non-destructive testing (NDT) for material integrity, and functional testing to ensure parts perform as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring product reliability. Here are several actionable steps:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality management practices. B2B buyers should establish a schedule for on-site inspections or request audit reports from third-party inspection firms. This practice not only helps verify compliance with standards but also fosters transparency in the supplier relationship.
Request Documentation and Reports
Buyers should ask for detailed documentation, including inspection reports, material certifications, and compliance certificates. This information provides a comprehensive view of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and helps in assessing their credibility.
Utilize Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspectors can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent agencies can conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify that the products meet agreed-upon specifications before they leave the manufacturer.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices related to quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the local regulations and norms of their suppliers.
- Logistical Challenges: International shipping can complicate quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust processes in place for handling logistics and that they maintain quality standards throughout the shipping process.
- Language Barriers: Communication can sometimes hinder quality assurance efforts. Establishing clear channels for communication and documentation can mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that specifications are met.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting CNC turned parts manufacturers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc turned parts manufacturer’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure CNC turned parts from manufacturers. By following these steps, you will streamline the sourcing process and ensure that you select a reliable partner capable of meeting your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it is essential to outline your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finishes that are critical for your application. A clear specification not only helps manufacturers understand your needs but also facilitates accurate quotes and production timelines.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential CNC turned parts manufacturers. Look for companies with a strong online presence, positive reviews, and relevant industry experience. Utilize platforms like industry directories, trade shows, and referrals to compile a list of qualified suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of each potential supplier. Inquire about their machinery, technologies, and production processes to ensure they can meet your volume and complexity requirements. Pay attention to their ability to handle specific materials and secondary processes, as these can significantly impact the quality and functionality of your parts.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the manufacturers hold relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Compliance with material standards and regulations is crucial, especially for industries like automotive and aerospace, where safety is paramount.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a bulk order, request samples or prototypes of your parts. This step allows you to evaluate the quality, precision, and finish of the components produced by the manufacturer. It also gives you the opportunity to test the parts in real-world applications, ensuring they meet your performance criteria.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing from different suppliers, but don’t make decisions based solely on cost. Consider the total value offered, including quality, lead times, and customer support. Also, review payment terms and conditions to ensure they align with your budget and cash flow expectations.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support
Effective communication is vital for a successful supplier relationship. Ensure that the manufacturer has a responsive customer service team and clear channels for communication. Discuss expectations regarding updates on production status, delivery timelines, and post-delivery support to avoid potential issues.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions while sourcing CNC turned parts, ultimately leading to successful partnerships and high-quality outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc turned parts manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of CNC turned parts manufacturing is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary components influencing the total cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Common materials for CNC turned parts include aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and various plastics. Specialty materials, like high-grade alloys, can drive costs higher due to their scarcity and processing requirements.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for operating CNC machines and ensuring quality production. Labor costs can vary based on the region, experience level of the workforce, and the complexity of the parts being produced.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These costs are usually distributed across all products manufactured, impacting the per-part cost.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for tooling can be significant, especially for custom parts. Tooling includes the costs of jigs, fixtures, and cutting tools necessary for precision machining. These costs are amortized over the production run, making them a critical factor in pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specified tolerances requires rigorous testing and inspection processes. QC costs can add up, particularly if certifications (like ISO) or detailed inspections are required.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, including customs duties and insurance, are crucial for international buyers. These can fluctuate based on shipping routes, weight, and volume, impacting the final landed cost of parts.
-
Margin: Manufacturers will typically include a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. This can vary widely based on market demand, competition, and the manufacturer’s reputation for quality.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of CNC Turned Parts?
Several factors can influence pricing and should be considered by buyers when sourcing CNC turned parts:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher production volumes generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, so understanding the MOQ can aid in cost negotiation.
-
Specifications and Customization: Parts with complex designs or specific tolerances can incur additional costs. Customization may require special tooling or longer production times, impacting overall pricing.
-
Material Selection: The choice of material directly affects the cost. High-performance materials or those requiring special processing will increase base costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that need to meet strict industry standards or require specific certifications will typically be more expensive. Buyers should assess the necessary certifications for their applications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technology may command higher prices but often provide better quality and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the total cost of ownership. Understanding these terms can help avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating CNC Turned Parts Pricing?
International B2B buyers can leverage several strategies to ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing CNC turned parts:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may be flexible, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider logistics, potential delays, quality issues, and the costs associated with rework or defects. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if not managed properly.
-
Research Market Rates: Understanding the current market rates for specific materials and machining services can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge can help identify fair pricing and avoid overpaying.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often yield benefits, including priority service and flexibility in order management.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first quote. Obtaining multiple quotes allows for comparison and can reveal pricing discrepancies or unique offerings that may benefit your project.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances in Different Regions: Variations in labor costs, material availability, and currency fluctuations can affect pricing across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these nuances can enhance negotiation strategies.
Disclaimer
The pricing analysis provided here is indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers for the most accurate and competitive pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc turned parts manufacturer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to CNC Turned Parts Manufacturing
In the realm of precision manufacturing, CNC turned parts have established themselves as a go-to solution for producing complex, high-accuracy components. However, there are alternative methods that can also meet various manufacturing needs. Understanding these alternatives can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their unique requirements, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Turned Parts Manufacturer | 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing) | Traditional Machining (Manual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed | Moderate precision, varies by technology | Variable precision, often lower than CNC |
| Cost | Competitive for volume orders | High initial costs, low for small batches | Labor-intensive, can be costly for low volume |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment | Requires design software and printers | Needs skilled labor, longer setup times |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Minimal maintenance, but printer-dependent | Requires skilled maintenance, can be time-consuming |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, intricate parts | Prototyping, custom designs, low-volume runs | Simple parts, low-tech applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3D printing has gained traction as a viable alternative to CNC turning, particularly for creating prototypes and custom parts. This method allows for complex geometries that may be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional machining. Its key advantage lies in the ability to produce low volumes economically, making it ideal for startups or companies testing new designs. However, the speed and precision can vary significantly based on the technology used (e.g., FDM, SLA), and it may not be suitable for high-volume production where consistency and durability are paramount.
Traditional Machining (Manual)
Traditional machining encompasses methods like manual lathes and milling machines. While this approach can be effective for simple components, it generally lacks the precision and efficiency of CNC turning. Manual machining requires skilled labor, which can lead to higher labor costs and longer production times. This method is best suited for low-tech applications or one-off projects where advanced technology is not required. However, its limitations in scalability and precision make it less favorable for high-demand industries needing consistent quality.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing method, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints. CNC turned parts manufacturing is ideal for high-volume production with tight tolerances, while 3D printing offers flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities. Traditional machining can serve well for simpler projects but may fall short in precision and efficiency. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Turned Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of CNC turned parts is crucial for B2B buyers looking to procure high-quality components. Here are some critical specifications that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific type of material used in manufacturing turned parts, such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, or carbon steel. Each material has unique properties that affect durability, corrosion resistance, and machinability. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring that the final product meets the performance requirements of its intended application, especially in demanding industries like automotive and aerospace.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, such as diameter or length. It is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies and perform as expected. Tight tolerances are especially important in applications where precision is critical, as even slight deviations can lead to failure or inefficiencies. Understanding tolerances helps buyers communicate their needs accurately and avoid costly errors.
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of a CNC turned part impacts its aesthetic and functional properties, including wear resistance and friction. Common surface finishes include machined, polished, and anodized. The required surface finish can vary based on the application; for instance, components used in fluid systems may require smoother finishes to reduce turbulence. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure compatibility with their operational standards.
4. Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy refers to how closely the produced parts match the specified dimensions. This property is essential for maintaining the integrity of assemblies, especially in high-precision industries. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s capabilities regarding dimensional accuracy to ensure that their components will perform reliably in their applications.
5. Production Volume
Production volume indicates the quantity of parts that can be manufactured within a specific timeframe. Understanding the scalability of a manufacturer’s operations is essential for buyers who may need both low-volume custom parts and high-volume production runs. It helps in planning inventory and managing supply chain logistics effectively.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from when an order is placed until the product is delivered. This metric is crucial for project timelines and inventory management. Buyers should assess lead times when selecting a manufacturer to ensure that they can meet their production schedules without delays.
What Are Common Terms Used in the CNC Turning Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication between buyers and manufacturers. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers looking to source components that fit into larger systems or assemblies.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers to understand, as it can affect purchasing decisions and inventory management strategies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It typically includes detailed specifications and quantities. Using RFQs can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics, shipping costs, and risk during the import/export process.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through the use of computers executing pre-programmed sequences. This technology is fundamental in CNC turning, allowing for high precision and repeatability in manufacturing processes.
6. Secondary Operations
Secondary operations are additional processes applied to a part after the primary machining is completed. These may include processes like drilling, tapping, or deburring. Knowledge of secondary operations can help buyers understand the full scope of manufacturing capabilities available to them.
By grasping these technical properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting a CNC turned parts manufacturer, ensuring that their needs are met effectively and efficiently.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc turned parts manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics in the CNC Turned Parts Manufacturing Sector?
The CNC turned parts manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by global trends in technology and supply chain management. The increasing demand for precision-engineered components across diverse industries—such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics—highlights the importance of CNC turning in producing high-quality parts with tight tolerances. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany, seek reliable suppliers, understanding these market dynamics becomes crucial.
One of the current trends is the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, which enhance automation and data exchange in manufacturing. This shift is leading to improved efficiency and reduced lead times, allowing manufacturers to respond swiftly to changing market demands. Moreover, advancements in CNC technology, such as multi-spindle machines and high-speed lathes, enable manufacturers to increase production rates and maintain consistency in quality.
Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on customization. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that align with specific project requirements, thus fostering stronger partnerships. The rise of digital platforms is also facilitating better communication and collaboration between manufacturers and buyers, streamlining the sourcing process.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Decisions in CNC Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions for CNC turned parts manufacturers. Environmental concerns are prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices and materials. The impact of manufacturing processes on the environment is under scrutiny, leading to a demand for transparency in sourcing and production methods.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important, as businesses recognize their responsibility to minimize environmental footprints. This includes selecting materials that are sustainably sourced and manufactured with minimal waste. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of recycled materials can serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient technologies and processes to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For international buyers, particularly from regions where environmental regulations are stringent, aligning with manufacturers who embrace sustainability can enhance their own compliance and brand reputation. As sustainability becomes a key differentiator, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship.
How Has CNC Turning Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of CNC turning has significantly shaped the manufacturing landscape. Initially, traditional turning methods relied heavily on manual operations, limiting precision and scalability. The introduction of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology revolutionized the process, enabling automated operations that enhance accuracy and repeatability.
Over the decades, advancements in CNC machines have led to the development of multi-spindle and high-speed lathes, which cater to high-volume production needs while maintaining strict tolerances. This evolution has allowed manufacturers to meet the increasing demand for complex geometries in various applications. Today, CNC turning is integral to modern manufacturing, providing solutions that support innovation and efficiency in producing precision parts across multiple industries.
In summary, understanding the current market trends, the importance of sustainability, and the historical context of CNC turning is essential for B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing in the CNC turned parts manufacturing sector. By prioritizing technology, ethical sourcing, and innovation, businesses can position themselves strategically in a competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc turned parts manufacturer
-
How do I select the right CNC turned parts manufacturer for my business?
Selecting the right CNC turned parts manufacturer involves several critical steps. First, assess their experience and expertise in your specific industry, as familiarity with your requirements can enhance quality and efficiency. Next, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including machinery and technology, to ensure they can meet your volume and complexity needs. Additionally, consider their quality assurance processes, customer service, and ability to communicate effectively. Finally, request samples or prototypes to gauge their production quality before making a commitment. -
What are the common materials used in CNC turned parts manufacturing?
CNC turned parts can be manufactured from a wide range of materials, each suited for different applications. Common materials include aluminum, brass, stainless steel, carbon steel, and various plastics. The choice of material will depend on factors such as the part’s intended use, required strength, and environmental conditions. Discuss your specific requirements with potential manufacturers, as they can provide recommendations based on their expertise and available materials. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC turned parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC turned parts can vary significantly among manufacturers. Some may have a low MOQ for custom orders, while others might require larger quantities to justify setup and production costs. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront to ensure the manufacturer can accommodate your order size. Additionally, some manufacturers may offer flexibility in MOQs for repeat orders or long-term contracts, so it’s worth exploring these options. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in CNC turned parts?
To ensure quality assurance in CNC turned parts, look for manufacturers that adhere to recognized quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Inquire about their quality control processes, including inspections and testing protocols throughout the manufacturing process. Additionally, request documentation of certifications and compliance with industry-specific standards. Establishing clear specifications and requirements upfront will also help maintain quality throughout production. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing CNC turned parts?
Payment terms for CNC turned parts can vary by manufacturer and the nature of your order. Common terms may include upfront deposits, milestone payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms before initiating production to avoid misunderstandings. Some manufacturers may offer flexible financing options or discounts for larger orders, which can be beneficial for budgeting and cash flow management. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing CNC turned parts?
When importing CNC turned parts, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Assess the manufacturer’s experience with international shipping and their ability to handle customs documentation and tariffs. Additionally, consider the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) that best suit your needs. Planning for potential delays and ensuring clear communication with your logistics provider can help streamline the process and avoid disruptions. -
Can CNC turned parts be customized to specific designs?
Yes, CNC turned parts can be highly customized to meet specific designs and specifications. Most manufacturers offer prototyping services, allowing you to validate designs before full-scale production. Provide detailed drawings or CAD files to communicate your requirements effectively. Discuss your customization needs with potential manufacturers, as their capabilities may vary, and some may specialize in particular types of custom parts. -
What industries commonly utilize CNC turned parts, and how do I know if my application fits?
CNC turned parts are utilized across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. To determine if your application fits, consider the part’s required precision, volume, and functionality. Consult with manufacturers who can provide insights based on their experience in your industry. Sharing your project details will help them assess compatibility and suggest appropriate solutions tailored to your needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc turned parts manufacturer
As the demand for precision-engineered components continues to grow, strategic sourcing of CNC turned parts emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the importance of partnering with manufacturers who leverage advanced CNC technology to ensure high-quality, cost-effective solutions tailored to specific requirements. By selecting suppliers with proven expertise and a diverse material capability, businesses can enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to source CNC turned parts strategically can significantly impact overall operational success. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize manufacturers that offer comprehensive services, including prototyping, secondary operations, and strict quality control measures. This not only mitigates risks but also fosters innovation and responsiveness to market needs.
Looking ahead, the landscape of CNC manufacturing is poised for further advancements, driven by technological innovations and evolving industry standards. By forging strong partnerships with reliable suppliers, B2B buyers can position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities and ensure their supply chains remain resilient. Engage with a trusted CNC turned parts manufacturer today to unlock the potential of your projects and secure a competitive edge in the marketplace.