Top 9 Brass Parts Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eMachineShop – Custom Brass Parts
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom Brass Parts offered by eMachineShop include precision machining services with over 15 years of experience. Key features include:
– Free CAD software for design or the option to upload CAD files for quotes.
– Free shipping within the USA.
– No minimum order quantity.
– 100% quality guarantee.
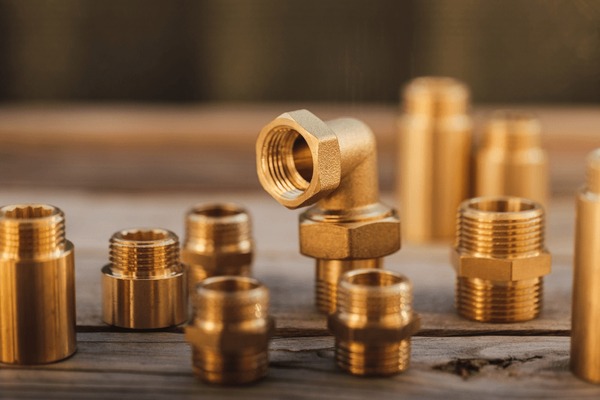
– Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its attractive gold appearance, non-magnetic propertie…
2. Abbott Interfast – Brass Screw Machined Parts
Domain: aicfast.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Brass Screw Machined Parts & Components offered by Abbott Interfast include standard and custom sizes, machined from round, hex, and square rod. Commonly produced with Free Cutting Brass, benefits include cost-effectiveness, recyclability, ease of machining, and corrosion resistance. Applications span various industries such as Electrical, Fluid Control, Medical, Musical Instruments, and Firearms….
3. Cox Manufacturing – Precision Brass Machined Parts
Domain: coxmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Cox Manufacturing specializes in precision brass screw machining and offers a variety of brass machined parts, including screw machined pins and retractable pins. The company has been producing precision turned brass components since the late 1950s and can manufacture up to 1.7 million precision components weekly. Key advantages of brass screw machined parts include durability, cost-efficiency, hi…
4. DW Products – Brass CNC Machining
Domain: dwproducts.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Brass CNC Parts Machining at DW Products includes manufacturing capabilities for various industries such as plumbing, automotive, and filtration. Key features of brass include exceptional workability, superior corrosion resistance, high conductivity, and the ability to withstand variable temperatures. Benefits of custom machined brass parts include cost savings over denser metals, antibacterial pr…
5. Wieland Chase – Brass and Eco Brass Solutions
Domain: wieland-chase.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Standard Alloys: C36000 – Brass Rod, C37700 – Brass Rod, C34500 – Brass Rod, C35000 – Brass Rod, C35300 – Brass Rod, Low Lead Brass Rod Alloy: C37000 – Brass Rod, C36300 – Brass Rod, C27450 – Brass Rod; Ecoline Solutions: ECO BRASS® C69300 – ECO BRASS® Rod, EZ-MELT Granular Ingot, ECO BRONZE® C69300 – ECO BRONZE® Rod, EZ-MELT Granular Ingot, ECO FORGE® C69850 – ECO FORGE® Rod, EZ-MELT Granular Ing…
6. Anderson Fittings – Precision Brass Components
Domain: andersonfittings.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Anderson Fittings manufactures precision brass components for various markets including plumbing (commercial and residential), gas and compressed gas, fire suppression, heavy trucking, HVAC/refrigeration, appliances, and beverage & food. Key product features include:
– PEX fittings conforming to ASTM F1807 and CSA B137.5 standards, NSF 14 and 61 listed, made from ECO-Brass® and lead-free brass fo…
7. Currie Warner – Brass Fasteners & Fittings
Domain: curriewarner.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Brass Turned Parts Manufacturer; Products: Brass Fasteners, Compression Fittings, Locking Nuts, Screws & Bolts, Brass Connectors, Couplers, Push Fit Brass Fittings, Component Housings, Glands, Valves (Shut-Off Valves, Ball Valves, Control Valves, Drain Valves), Adaptors (Male Adaptors, Female Adaptors), DN Series Fittings, NPS Fittings; Capabilities: Multi-Spindle Turning, Repetition Turned Parts,…
8. Asian Fasteners – Brass Fasteners & Custom Components
Domain: asianfasteners.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Brass Parts and Products, Brass Fasteners, Brass CNC Turned Parts, Custom Brass Components, Brass Cable Glands, Brass Wire Connectors, Brass Electrical Terminals, Brass Electrical Plug Pins, Hardware fittings, Machine parts, Screws, bolts, and nuts, Brass connectors, Pipes, Customized brass parts, Brass Moduling Inserts, Brass Pipe Fittings, PPR Connection Inserts, Special Turned Components.
9. Liberty Brass – Custom Precision Parts
Domain: libertybrass.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Custom Made Products by Liberty Brass include a wide range of high precision custom parts made from various materials such as aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and plastics. These custom parts account for about 70% of the company’s total sales. Liberty Brass offers manufacturing services for small and large quantities, from 5 pieces to 5 million, and can work from samples, blueprints, or ideas pro…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for brass parts manufacturer
Navigating the complexities of sourcing high-quality brass parts can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the increasing demand for durable, cost-effective brass components across industries—ranging from automotive to electronics—buyers must be equipped with the right knowledge to make informed decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the brass parts manufacturing landscape, covering essential topics such as types of brass alloys, machining techniques, applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
By exploring the diverse applications of brass parts, including fittings, gears, and valves, buyers will gain insights into selecting the most suitable materials for their specific needs. Additionally, this guide provides practical advice on assessing suppliers, understanding cost structures, and identifying quality assurance measures. Armed with this knowledge, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring they partner with reliable manufacturers who can meet their production demands and quality standards.
In a world where supply chain reliability is paramount, this guide serves as a critical resource for international buyers, particularly those in regions like Nigeria and Brazil. By empowering decision-makers with actionable insights, we aim to enhance the procurement process for brass parts, ultimately fostering successful partnerships in the global marketplace.
Understanding brass parts manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Brass Parts | Tailored designs, low minimum order quantities | Automotive, Electronics, Medical | Pros: Flexibility in design; Cons: Potentially higher costs for low volume. |
| Precision Machined Brass | High accuracy, tight tolerances, various machining methods | Aerospace, Defense, Medical | Pros: Exceptional quality; Cons: Longer lead times due to complexity. |
| Screw Machined Brass Parts | High volume production, cost-effective, easy to machine | Plumbing, Electrical, Consumer Goods | Pros: Efficient production; Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Forged Brass Components | High strength and durability, suitable for heavy-duty use | Industrial Equipment, Automotive | Pros: Superior strength; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Brass Alloy Manufacturers | Variety of brass alloys available for specific needs | General Manufacturing, Decorative Items | Pros: Tailored material properties; Cons: Complexity in selection process. |
What Are Custom Brass Parts and Their B2B Relevance?
Custom brass parts manufacturers specialize in creating tailored components based on specific client requirements. These manufacturers often utilize advanced CAD software, allowing buyers to design parts that meet precise specifications. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for industries like automotive and medical, where unique components are essential. However, while customization offers significant advantages, it can lead to higher costs, especially for low-volume orders, which buyers should consider when budgeting.
How Do Precision Machined Brass Parts Stand Out?
Precision machined brass parts are characterized by their high accuracy and the ability to maintain tight tolerances. Utilizing various machining methods such as CNC milling and turning, these components are often used in critical applications within aerospace and defense industries. The exceptional quality of these parts ensures reliability in demanding environments, but buyers should be prepared for potentially longer lead times due to the intricate manufacturing processes involved.
What Benefits Do Screw Machined Brass Parts Offer?
Screw machined brass parts are manufactured using specialized machinery designed for high-volume production. This method is particularly advantageous for industries such as plumbing and electrical, where cost-effective and durable components are required. While these parts are easy to machine and can be produced at scale, buyers may find that the options for customization are limited compared to other manufacturing types, which could affect their specific application needs.
Why Choose Forged Brass Components for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Forged brass components are known for their superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications in industrial equipment and automotive sectors. The forging process enhances the material properties, resulting in parts that can withstand significant stress. While the strength of forged brass is a major advantage, buyers should be aware that this manufacturing method typically requires a higher initial investment, which may not be suitable for all budgets.
How Do Brass Alloy Manufacturers Cater to Diverse Needs?
Brass alloy manufacturers provide a range of brass types, each with unique properties tailored for specific applications. These manufacturers can offer alloys that enhance corrosion resistance, machinability, or aesthetic appeal, catering to industries from general manufacturing to decorative items. While the variety allows for greater customization, the complexity of selecting the right alloy can be a challenge for buyers, necessitating a clear understanding of their application requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of brass parts manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of brass parts manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision machined components for aircraft systems | Enhanced durability and reliability in critical systems | Need for strict adherence to aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Brass fittings and connectors for fuel and fluid systems | Improved sealing and reduced leakage in high-pressure environments | Importance of high-volume production and quick turnaround times |
| Electronics | Brass components for electronic connectors and housings | Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance | Requirement for precision machining to meet electronic specifications |
| Plumbing | Brass valves and fittings for water supply systems | Longevity and resistance to corrosion in harsh environments | Focus on compliance with international plumbing standards and certifications |
| Medical | Brass parts for medical devices and instruments | Biocompatibility and durability in medical applications | Need for stringent quality control and regulatory compliance |
How Are Brass Parts Manufacturers Used in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, brass parts manufacturers produce precision machined components essential for aircraft systems, such as valves and connectors. These components must meet rigorous safety standards and durability requirements due to their critical role in flight operations. International buyers should prioritize manufacturers with aerospace certifications and a proven track record in quality control, ensuring that the parts can withstand high-stress environments and comply with international aviation regulations.
What Role Do Brass Parts Manufacturers Play in the Automotive Sector?
Brass fittings and connectors are vital in automotive applications, particularly within fuel and fluid systems. These components enhance sealing capabilities, reducing the risk of leaks in high-pressure environments. For international buyers, sourcing from manufacturers that can provide high-volume production and quick turnaround times is crucial, as the automotive industry often operates on tight schedules. Additionally, understanding regional compliance and environmental regulations can influence sourcing decisions.
How Are Brass Parts Utilized in the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics industry, brass components are widely used for connectors and housings due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. These properties ensure reliable performance in various electronic devices. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seek manufacturers that specialize in precision machining to meet specific electronic specifications. Attention to detail in the manufacturing process can prevent failures in electronic applications, making quality assurance a top priority.
Why Are Brass Parts Important in Plumbing Applications?
Brass valves and fittings are standard in plumbing systems, offering longevity and resistance to corrosion, which are essential in water supply applications. Manufacturers must adhere to international plumbing standards to ensure that their products are safe and effective. For international buyers, understanding the local plumbing regulations and certifications is vital when sourcing brass components. This knowledge helps ensure compliance and reduces the risk of costly installation issues.
How Do Brass Parts Manufacturers Contribute to the Medical Sector?
In the medical field, brass parts are used in various devices and instruments, where biocompatibility and durability are paramount. Manufacturers must follow stringent quality control measures and comply with health regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness. International buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers that can demonstrate adherence to medical standards and provide documentation to verify the quality of their brass components, as this is critical for successful medical applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘brass parts manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays in Brass Parts Delivery Impacting Production Schedules
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges with delivery timelines when sourcing brass parts from manufacturers. Unforeseen delays in shipping or production can disrupt production schedules, leading to increased costs and potential project overruns. For instance, a company in the automotive sector might need specific brass components for assembly, and any delay could halt their production line, affecting their ability to meet customer demand.
The Solution: To mitigate delivery issues, B2B buyers should establish clear communication channels with their brass parts manufacturers. Before placing an order, inquire about the manufacturer’s lead times and shipping methods. Buyers can also ask for regular updates throughout the production process. Implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory strategy can further help; this approach allows buyers to order components based on actual production needs, thus minimizing the risk of overstocking and reducing the impact of delays. Additionally, consider building a relationship with multiple suppliers to create a backup plan in case one source faces delays, ensuring uninterrupted production.
Scenario 2: Quality Control Issues Leading to Component Failures
The Problem: Quality control is a crucial concern for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing brass components that must meet strict industry standards. A manufacturer may provide parts that fail to meet specified tolerances or quality benchmarks, resulting in component failures that can lead to costly recalls, repairs, and damage to the buyer’s reputation. For example, in the medical device industry, a faulty brass fitting can compromise the integrity of the entire device, putting patient safety at risk.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize working with brass parts manufacturers that have robust quality assurance processes in place. Before finalizing a partnership, request detailed documentation of their quality control measures, including certifications (such as ISO 9001) and inspection protocols. It’s also beneficial to conduct onsite audits or request samples for testing prior to placing large orders. Establishing a clear set of quality expectations and performance metrics in the contract can provide a framework for accountability. Regularly reviewing quality performance with the manufacturer can help identify and rectify potential issues before they escalate.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Brass Parts to Meet Unique Specifications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers require custom brass parts tailored to specific applications or technical specifications. However, they often encounter challenges in communicating their needs effectively to manufacturers, leading to misunderstandings and unsatisfactory results. For instance, a company in the oil and gas sector may need a specific type of brass valve that can withstand high pressure, but if the manufacturer misinterprets the requirements, the delivered parts may not function properly.
The Solution: To overcome customization challenges, B2B buyers should invest time in developing detailed technical specifications and drawings before approaching manufacturers. Utilizing CAD software can help create precise designs that clearly convey dimensions and requirements. Additionally, engaging in a collaborative design process with the manufacturer can foster better understanding and innovation. Regular communication during the design phase, including feedback loops, can ensure that both parties are aligned. Consider requesting prototypes or small production runs to test the parts before committing to larger orders, allowing for any necessary adjustments to be made early in the process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for brass parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Properties of Common Brass Alloys for Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for brass parts manufacturing, understanding the properties and applications of various brass alloys is crucial. Here, we analyze four common brass materials: Red Brass, Cartridge Brass, Free Cutting Brass, and Low-Leaded Brass. Each material has distinct characteristics that influence its suitability for different applications.
Red Brass: What Makes It Suitable for Marine Applications?
Red Brass, known as 230 Brass (UNS C23000), is composed primarily of copper and zinc, with a higher copper content that enhances its corrosion resistance, particularly against seawater. This alloy exhibits excellent malleability, allowing it to be easily formed into complex shapes.
Pros: Its high corrosion resistance makes it ideal for marine applications, including valves and fittings. The material is also suitable for hot and cold working, making it versatile.
Cons: Red Brass can be more expensive than other brass alloys due to its copper content. Its machinability is moderate, which may lead to higher manufacturing costs in precision applications.
Impact on Application: Red Brass is particularly effective in environments exposed to moisture and salt, making it a preferred choice for marine hardware and plumbing components.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding copper content, as there may be restrictions on the use of certain alloys in plumbing.
Cartridge Brass: How Does It Perform in High-Ductility Applications?
Cartridge Brass (260 Brass, UNS C26000) is renowned for its excellent cold working properties and high ductility, which allows for severe deformations without cracking. This alloy is commonly used in applications requiring intricate designs, such as ammunition casings and electrical components.
Pros: Its high ductility and formability make it suitable for deep drawing and complex shapes. Additionally, it has good corrosion resistance, particularly in non-seawater environments.
Cons: While it is easier to machine than some other alloys, it can still present challenges in high-precision applications due to its tendency to work-harden.
Impact on Application: Cartridge Brass is widely used in industries such as automotive and electronics, where high-performance components are critical.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of ASTM standards that govern the use of brass in specific applications, ensuring compliance with quality and safety regulations.
Free Cutting Brass: What Advantages Does It Offer for High-Volume Production?
Free Cutting Brass (360 Brass, UNS C36000) is favored for its exceptional machinability, making it the standard reference for machinability ratings. This alloy is often used for high-volume production of precision components.
Pros: Its high machinability results in lower manufacturing costs and faster production times. It is also versatile, suitable for a wide range of applications, including fluid connectors and threaded inserts.
Cons: The high lead content in some variations can pose health risks during machining, necessitating stringent safety measures.
Impact on Application: Free Cutting Brass is ideal for applications requiring rapid production and high precision, making it a staple in the automotive and electronics industries.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider the implications of lead content on health and safety regulations in their respective regions, particularly in Europe where stricter regulations apply.
Low-Leaded Brass: Why Is It Preferred for Precision Machining?
Low-Leaded Brass (330 Brass, UNS C33000) is designed to provide excellent machinability while minimizing lead content. This alloy is often used in applications that require both precision and corrosion resistance.
Pros: It offers good corrosion resistance and is easier to machine than many other brass alloys, making it suitable for high-precision components like fittings and connectors.
Cons: While it has lower lead content, it may not perform as well in extreme corrosion environments compared to higher lead variants.
Impact on Application: Low-Leaded Brass is widely used in plumbing and electrical applications, where both durability and precision are essential.
International Considerations: International buyers should verify compliance with local standards regarding lead content, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Summary Table of Brass Alloys
| Material | Typical Use Case for brass parts manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Brass | Marine hardware, valves, fittings | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost due to copper content | Medium |
| Cartridge Brass | Ammunition casings, electrical components | High ductility and formability | Tendency to work-harden | Medium |
| Free Cutting Brass | Precision components, fluid connectors | Exceptional machinability | Health risks due to lead content | Low |
| Low-Leaded Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Good machinability and corrosion resistance | Less effective in extreme corrosion environments | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations of various brass alloys, aiding in informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for brass parts manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Brass Parts?
Manufacturing brass parts involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each step plays a vital role in achieving the desired specifications and performance characteristics of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Brass Part Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate brass alloy based on the specific requirements of the application. Common alloys include C36000, known for its machinability, and C26000, which offers excellent cold working properties. Once the alloy is selected, the brass is acquired in the form of bars, sheets, or coils, depending on the intended machining method.
The raw material undergoes thorough inspection to ensure it meets the required chemical composition and mechanical properties. This step is crucial for ensuring that the finished parts will perform reliably in their intended applications. Additionally, suppliers often maintain certifications to verify the quality of their raw materials, which can be a significant factor for international buyers.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Brass Manufacturing?
Forming processes for brass parts can vary based on the complexity and volume of the components being produced. Key techniques include:
-
CNC Machining: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are widely used for producing intricate brass components with high precision. This method allows for complex shapes and tight tolerances, making it suitable for a range of applications, from automotive to aerospace.
-
Swiss Machining: Ideal for high-volume production, Swiss machining employs a sliding headstock to produce small, precise parts efficiently. This technique is particularly effective for components that require a high degree of accuracy and repeatability.
-
Die Casting: For larger brass components, die casting is a preferred method. It involves injecting molten brass into a mold, allowing for the mass production of complex shapes with excellent surface finish.
-
Waterjet Cutting: This method uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasives to cut through brass sheets, yielding clean edges without thermal distortion.
How Are Brass Parts Assembled and Finished?
After forming, brass parts may require assembly, especially if they are part of a larger system or product. Assembly processes can involve threading, soldering, or welding, depending on the design specifications.
Finishing is the final stage, aimed at enhancing the appearance and performance of brass parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Polishing: This process provides a smooth, reflective surface, often required for decorative applications.
- Plating: Electroplating with metals like nickel or chrome can improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Anodizing: Although more common with aluminum, anodizing can also be applied to brass to enhance surface durability.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Brass Manufacturers?
Quality assurance is paramount in the brass manufacturing process to ensure that products meet both international standards and customer specifications. Many brass parts manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard assures buyers of consistent quality in products and services.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for the oil and gas industry can be critical for certain applications. These certifications signify that the products meet the regulatory requirements necessary for specific industries, providing additional assurance to international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Brass Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, each designed to catch defects early and ensure compliance with specifications:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials upon receipt. Suppliers should conduct rigorous testing of incoming materials to confirm they meet specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC ensures that operations are performed according to established procedures. This may involve regular inspections and measurements of components to catch deviations from specifications early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished brass parts. This may include dimensional checks, functional tests, and visual inspections to ensure that the products meet all quality requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Processes?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control processes. Several strategies can help verify a supplier’s QC measures:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to observe the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in action. An audit can reveal the supplier’s commitment to quality and adherence to standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes, including metrics on defect rates, inspection results, and compliance with industry standards.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices. These services often provide certifications that can enhance buyer confidence.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality certification is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and regulatory requirements, which can affect product acceptance in local markets. For example:
-
CE Certification: In Europe, CE marking is mandatory for many products, indicating compliance with EU safety and health standards. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide appropriate documentation for CE compliance.
-
API Certification: In industries such as oil and gas, API certification can be critical. Buyers must verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications to produce components that meet API standards.
-
Local Regulations: Buyers should be aware of any local regulations that may impact the acceptance of brass parts, including environmental considerations and material safety standards.
Understanding these factors can help B2B buyers from diverse regions make informed decisions when selecting brass parts manufacturers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘brass parts manufacturer’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure brass parts from manufacturers. Given the diverse applications of brass components across industries such as automotive, electronics, and plumbing, it’s essential to approach the procurement process methodically. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select a reliable manufacturer that meets their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the first step in sourcing brass parts. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and material grades needed for your application. Providing precise specifications helps manufacturers understand your requirements, reducing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring that the final product meets your standards.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential brass parts manufacturers. Look for companies with a proven track record, industry experience, and positive customer reviews. Create a shortlist based on factors such as their production capabilities, material types, and experience in your specific sector.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify the certifications of your shortlisted suppliers. Certifications like ISO 9001 indicate adherence to quality management standards, which is crucial for consistent product quality. Additionally, check for industry-specific certifications that may apply to your application, ensuring compliance with international standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Requesting samples or prototypes is a vital step to evaluate the quality of the manufacturer’s work. This allows you to assess the brass parts’ finish, dimensions, and overall quality against your specifications. It also provides an opportunity to identify any potential issues before committing to a larger order.
Step 5: Inquire About Production Capabilities
Understanding a manufacturer’s production capabilities is essential for ensuring they can meet your order volume and timeline. Ask about their machining processes, such as CNC milling or turning, and whether they can accommodate high-volume production or custom orders. This will help you gauge their ability to meet your current and future needs.
Step 6: Assess Quality Control Processes
Inquire about the quality control measures in place at the manufacturing facility. A reliable supplier should have rigorous testing and inspection processes to ensure each batch of brass parts meets your specifications. Look for details on their quality management system, such as in-process inspections and final product testing.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable manufacturer, negotiate the terms and conditions of the contract. Discuss pricing, payment terms, lead times, and after-sales support. Clear agreements will help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process, leading to a successful long-term partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for brass parts manufacturers, ensuring they select the right partner for their needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for brass parts manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Brass Parts Manufacturing?
When sourcing brass parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Brass alloys, such as C36000 and C35300, are the foundation of cost. Prices fluctuate based on global copper and zinc market trends, alloy compositions, and availability. Buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers who offer bulk purchasing options to mitigate material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. In countries with lower labor costs, manufacturers may offer competitive pricing. However, skilled labor is necessary for precision machining, which can drive costs up.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can reduce overhead costs, translating to better pricing for buyers. Suppliers with advanced technologies, such as CNC machining, often achieve higher efficiency.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom parts. Buyers should inquire about tooling charges, particularly for low-volume orders, as these costs can significantly impact the overall price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in QC processes ensures that parts meet specifications and reduce the risk of defects. Suppliers with robust QC systems may have higher upfront costs but can provide long-term savings by minimizing returns and rework.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight, customs duties, and insurance, can heavily influence total costs, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms is vital to avoid unexpected logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market positioning. It’s essential to evaluate the value-added services provided by suppliers to justify their margins.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Brass Parts Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in the brass parts manufacturing sector:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often result in reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their needs to avoid excess inventory.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts require more engineering and manufacturing effort, leading to higher prices. Clearly defining specifications can help streamline the process and control costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Brass parts used in critical applications (e.g., aerospace, medical) may require specific certifications, which can increase costs. Ensure suppliers can meet these standards without compromising quality.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capacity are critical. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and predict total expenses more accurately.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Brass Parts Sourcing?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, implementing cost-efficient strategies is essential:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers are often willing to adjust pricing, especially for long-term contracts or bulk orders.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Consider maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher upfront price may result in lower overall expenses if the quality is superior.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that can affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local agents can help navigate these complexities.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying your supplier base can mitigate risks and provide competitive pricing. Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for brass parts can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is recommended that buyers request quotes tailored to their specific needs and consider market conditions when assessing costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing brass parts manufacturer With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Brass Parts Manufacturing
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, B2B buyers often seek the most effective solutions for their component needs. While brass parts manufacturing offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider alternative materials and methods that may better suit specific applications or budget constraints. This analysis compares brass parts manufacturing with two viable alternatives: plastic injection molding and stainless steel machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Brass Parts Manufacturer | Plastic Injection Molding | Stainless Steel Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, corrosion resistance, excellent machinability | Good for high-volume production, limited durability compared to brass | Exceptional strength and durability, high resistance to heat and corrosion |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs, but economical for small to medium runs | Low cost per part in high volumes, high upfront tooling costs | Higher material and machining costs, but offers long-term durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and specific machinery | Requires upfront investment in molds, but simple once established | Complex setup, requires specialized equipment and skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but can corrode without proper treatment | Minimal maintenance, but can degrade with time | Low maintenance, but may require periodic polishing |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for decorative and functional components in various industries | Best suited for mass production of consumer goods | Perfect for applications requiring high strength, such as aerospace and automotive |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten plastic into a mold. This method excels in high-volume production where unit costs can be significantly lower than brass. However, the initial investment in mold design and fabrication can be substantial. While it offers excellent versatility in design, the durability of plastic parts may not match that of brass, especially in demanding applications. This makes plastic a great option for consumer products where cost efficiency is crucial, but less ideal for industrial components requiring high strength.
Stainless Steel Machining
Stainless steel machining involves shaping and finishing stainless steel components through various machining techniques. This alternative provides exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and heat, making it suitable for critical applications in industries such as aerospace and automotive. However, the costs associated with stainless steel are generally higher than those for brass, both in terms of raw materials and machining processes. Additionally, the complexity of machining stainless steel may require more specialized equipment and skilled labor, which could affect lead times and overall production flexibility.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best manufacturing solution, B2B buyers must assess their specific requirements, including performance, cost, and intended application. Brass parts manufacturing offers a balanced approach with high durability and moderate costs, making it ideal for a variety of industries. However, for projects emphasizing mass production, plastic injection molding may prove more economical. Conversely, if the application demands superior strength and resistance to extreme conditions, stainless steel machining is the preferable choice. Ultimately, understanding the unique characteristics of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for brass parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Brass Parts Manufacturing?
When considering brass parts for manufacturing, understanding the critical specifications is vital for ensuring quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential technical properties that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and properties of the brass alloy used. Common grades include C26000 (Cartridge Brass) and C36000 (Free Cutting Brass). Each grade has distinct characteristics such as corrosion resistance, machinability, and strength. Selecting the right grade affects the durability and performance of the end product, making it crucial for buyers to match the material to their application needs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. It is critical in precision machining where parts must fit together accurately. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are essential for components in high-performance applications like aerospace or medical devices. Understanding tolerances helps buyers ensure that their components will function properly and meet industry standards. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and appearance of a part’s surface after manufacturing. Various finishes, such as polishing or anodizing, can enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. The right surface finish can improve the part’s functionality, especially in applications where friction and wear are concerns. Buyers must specify their surface finish requirements to achieve the desired performance. -
Machinability Rating
Machinability rating is a measure of how easily a material can be machined. Brass typically has a high machinability rating, making it a preferred choice for complex parts and high-volume production. Understanding machinability helps buyers anticipate manufacturing costs and lead times, as easier-to-machine materials can lead to faster production and lower expenses. -
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance indicates how well a material can withstand environmental factors that lead to degradation. Brass alloys, particularly those with higher zinc content, exhibit good corrosion resistance, making them ideal for plumbing and marine applications. Buyers should consider the operating environment of their parts to select a brass alloy that will maintain integrity over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Brass Parts Manufacturing?
Navigating the terminology used in brass manufacturing can significantly impact purchasing decisions. Here are some key trade terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In brass parts manufacturing, understanding OEM relationships is essential for ensuring that components meet the specific requirements of the original design. Buyers often work directly with OEMs to procure high-quality parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their orders effectively and avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Submitting an RFQ is a common practice in B2B transactions and helps ensure that buyers receive competitive pricing and clear terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers to clarify shipping costs and responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In brass manufacturing, lead times can vary based on factors such as order complexity and supplier capabilities. Knowing lead times helps buyers manage their production schedules and minimize downtime.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing brass parts, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the brass parts manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Shaping the Brass Parts Manufacturing Sector?
The brass parts manufacturing sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving buyer preferences. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe engage with suppliers, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial. Key drivers include the rising demand for customized solutions, facilitated by advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC machining and waterjet cutting, which allow for high precision and rapid prototyping. Furthermore, the shift towards automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is enhancing efficiency and reducing lead times, making it easier for buyers to source quality brass components quickly.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of digital platforms that streamline the sourcing process. Tools such as CAD software enable buyers to design and order custom parts with ease, while online quoting systems improve cost transparency and competitiveness. Additionally, the focus on supply chain resilience has intensified, as companies seek reliable partners who can adapt to market fluctuations and demand variability. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions facing infrastructural challenges, where dependable sourcing can significantly impact operational continuity.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Brass Parts Sourcing Decisions?
In today’s market, sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount considerations for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of brass manufacturing, which includes energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a shift towards greener practices. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable operations, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient processes. This trend is not just about compliance; it also enhances brand reputation and aligns with consumer expectations for environmentally responsible practices.
Buyers should actively seek suppliers with recognized green certifications or those who utilize eco-friendly materials in their production processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By engaging with manufacturers who prioritize ethical supply chains, buyers can mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations and enhance their own sustainability profiles in the marketplace. This approach is particularly significant for international buyers in emerging markets, where the demand for sustainable products is rapidly growing.
What Is the Historical Context of Brass Parts Manufacturing?
The brass parts manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the centuries, transitioning from artisanal craftsmanship to highly automated production. Historically, brass was favored for its aesthetic appeal and mechanical properties, making it a popular choice for various applications ranging from decorative items to functional components in machinery and plumbing. The introduction of precision machining technologies in the late 20th century revolutionized the sector, allowing for mass production while maintaining high quality standards.
Today, the industry is characterized by advanced manufacturing techniques and a global supply chain that enables access to a diverse range of brass alloys. This evolution has not only increased the availability of custom brass parts but has also positioned the industry to meet the complex demands of various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. As buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the historical context helps inform their sourcing strategies and decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of brass parts manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right brass parts manufacturer for my needs?
When selecting a brass parts manufacturer, consider factors such as industry experience, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Look for manufacturers that offer customization options and have a proven track record of delivering high-quality products. Evaluate their communication practices, responsiveness, and ability to meet your specific requirements. Additionally, check for certifications that ensure compliance with international standards, which is crucial for quality assurance in global trade. -
What are the advantages of sourcing brass parts internationally?
Sourcing brass parts internationally can provide access to a wider range of suppliers, competitive pricing, and advanced manufacturing technologies. Manufacturers in different regions may offer unique brass alloys and machining capabilities that meet specific project needs. International suppliers can also help diversify your supply chain, reducing dependency on local sources and potentially lowering costs. However, it’s essential to navigate trade regulations and tariffs that may apply to your imports. -
What should I know about Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) when sourcing brass parts?
Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) vary by manufacturer and can significantly impact your purchasing strategy. Some suppliers may have low or no MOQ, making them ideal for small businesses or prototype projects. Conversely, others may require larger quantities to justify production runs. Always clarify MOQ with potential suppliers upfront and consider your own production needs and budget when making decisions. -
How can I customize brass parts to meet my specifications?
Customization of brass parts often involves specifying dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. Most manufacturers provide CAD software for designing parts or allow you to upload your own designs. Communicate your requirements clearly, including any specific alloy types or machining processes you prefer. Engaging in a collaborative design process with the manufacturer can also lead to cost-effective solutions and enhanced product performance. -
What payment terms are typically offered by brass parts manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary widely among manufacturers, but common options include upfront payments, net 30, or net 60 terms. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or flexible financing options for larger orders. Always negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure that they are clearly outlined in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality control in my brass parts orders?
To ensure quality control, choose a manufacturer that adheres to strict quality assurance protocols, such as ISO certifications. Request detailed information about their inspection processes, including the use of advanced measurement technologies and testing methods. Conducting periodic audits or requesting sample parts before committing to larger orders can also help validate the manufacturer’s capabilities and quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing brass parts?
When importing brass parts, consider shipping options, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Choose a reliable logistics partner that understands international trade complexities and can manage import duties and taxes. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs clearance and plan your orders accordingly to avoid production disruptions. -
How do I vet potential brass parts suppliers effectively?
Effective supplier vetting involves researching their reputation, customer reviews, and industry experience. Request references from previous clients and assess their financial stability. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, quality certifications, and compliance with international standards. Conducting site visits or virtual tours can also provide insights into their operations and commitment to quality, ensuring that you partner with a trustworthy manufacturer.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for brass parts manufacturer
In navigating the dynamic landscape of brass parts manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for B2B buyers seeking quality, cost-efficiency, and reliability. Key takeaways highlight the importance of selecting suppliers that offer not only precision machining capabilities but also a diverse range of brass alloys tailored to specific applications. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance, timely delivery, and adaptability to fluctuating demand, ensuring that their supply chain remains robust and responsive.
As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality brass components is likely to grow. This presents an opportunity for B2B buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to enhance their competitive edge. By fostering partnerships with reputable manufacturers and utilizing innovative machining technologies, businesses can streamline their operations and reduce production costs.
Looking ahead, now is the time for international buyers to engage actively with brass parts manufacturers. Explore potential collaborations, request quotes, and stay informed about the latest advancements in brass machining. Your proactive approach to sourcing can significantly impact your operational success in the competitive global marketplace.