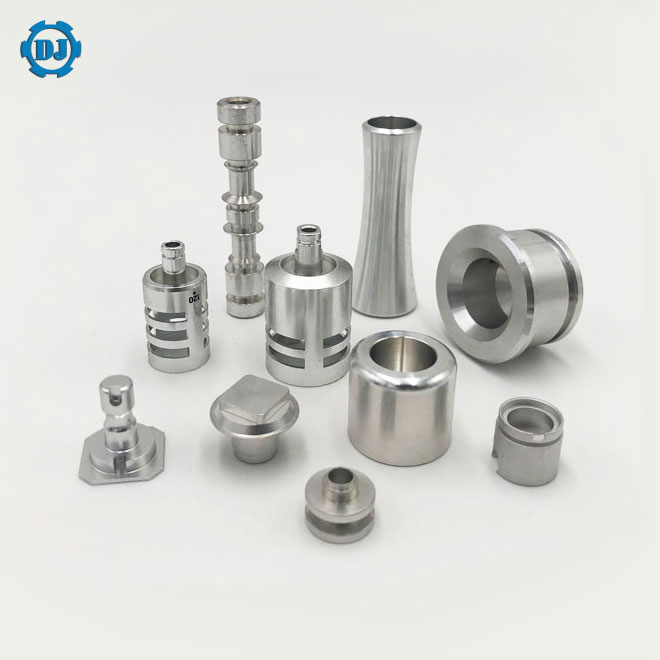
Top 8 Cnc Turned Parts Supplier Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Freeway Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: freewaycorp.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components and CNC turned parts manufacturing in the USA. High-quality precision turned parts tailored to specifications. Over 30 multiple spindle automatic screw machines and CNC single-spindle turning centers. Capable of machining up to 2 5/8” round and 2 5/16” hex materials. CNC lathes handling up to 2 7/8” bar stock and chucking up to 7” blanks. Secondary machining operations …
2. Abbott Interfast – CNC Turning Services
Domain: aicfast.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Services & Turned Parts offered by Abbott Interfast include the production of complex parts using advanced CNC machining technology. The CNC turning process involves holding material in a chuck and rotating it at high speed while a cutting tool shapes the workpiece. Key benefits include increased production speed, enhanced efficiency, improved accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. Material…
3. Rapid Axis – CNC Turned Parts
Domain: rapidaxis.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: CNC Turned Parts from Rapid Axis offer unique equipment formats and high-speed turning capabilities. They provide competitively priced, quality parts with quick lead times and no minimum quantity. Key features include:
– Consistent reliable quality and excellent pricing
– Free 1st Level Inspection on all projects
– Support for both small and large turning operations
– Finishing and second oper…
4. Protolabs – CNC Turning Service
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Service offers quality custom turned parts for rapid prototyping and end-use production with lead times as fast as 1 day. The CNC turning process utilizes a CNC lathe with live tooling, allowing for the machining of features such as axial and radial holes, flats, grooves, and slots. It is suitable for functional prototypes and end-use parts, particularly those with cylindrical features…
5. Screw Machine Products – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: screw-machine-products.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Precision turned parts are machined with extremely tight tolerances using CNC turning, which is controlled by software rather than human operators. The process involves clamping a workpiece to a spindle and using automated cutting tools to shape the part. CNC turning is preferred for high-precision, repeatable results in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics. It is use…
6. HLC – Distraction Pin
Domain: hlc-metalparts.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: {“Item Name”:”Distraction Pin”,”Material”:”SUS630 Stainless Steel”,”Surface Treatment”:”Heat treatment”,”Tolerance”:”0.001mm”,”Application”:”For medical & healthcare products”,”Dimension”:”Length 12mm/14mm/16mm”,”Craftsmanship”:”CNC Turning & CNC Milling”,”Price”:”2.33USD/PCS”,”Packing”:”PE Bag”,”Services”:”OEM & ODM available”}
7. Intrex Aerospace – CNC Turned Parts
Domain: intrexcorp.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Intrex Aerospace specializes in CNC turned parts for the aerospace, defense, and space industries. They are ISO 9001 and AS9100 certified and ITAR registered. The company utilizes IQS software for quality control and operates CMMs in a climate-controlled environment. Their machinists have over 20 years of experience, ensuring tight tolerances for components. They have lathes capable of producing p…
8. CNC24 – CNC Turned Parts
Domain: cnc24.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Order CNC turned parts online with fast service and attractive prices. Free test certificate included with every order. Upload CAD files for quotes within 48 hours. Production capabilities include:
– Workpiece diameter: 3 to 600 mm (CNC machines), 1 to 5,300 mm (CNC turning)
– Maximum length: 2000 mm (CNC machines), 0.5 to 20,000 mm
– Tolerances: up to +/- 0.05 mm
– Surface roughness: up to Ra…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc turned parts supplier
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, sourcing a reliable CNC turned parts supplier can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the demand for precision-engineered components skyrocketing across various industries, from automotive to agriculture, understanding the nuances of this sector is essential. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of procuring CNC turned parts by exploring the diverse types of components available, their myriad applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Whether you’re based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any country in Europe or South America, navigating this landscape requires a strategic approach. The comprehensive insights provided in this guide will empower you to make informed purchasing decisions, highlighting key aspects such as quality assurance, cost considerations, and the importance of supplier capabilities. By addressing potential pitfalls and offering actionable strategies, this resource serves as a roadmap for buyers seeking high-quality, precision-turned components that meet their specific needs.
Equipped with this knowledge, you’ll be better positioned to engage with suppliers effectively, ensuring that your procurement processes not only meet industry standards but also align with your business objectives. Let’s delve deeper into the world of CNC turned parts and uncover how to streamline your sourcing strategy for optimal results.
Understanding cnc turned parts supplier Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision CNC Turned Parts | High accuracy, tight tolerances, custom designs | Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Exceptional quality; tailored solutions. Cons: Higher cost; longer lead times. |
| High-Volume CNC Turned Parts | Automated processes, scalability, fast production | Mass production industries, Consumer Goods | Pros: Cost-effective; quick turnaround. Cons: Less flexibility in customization. |
| Prototype CNC Turned Parts | Short runs, rapid prototyping, iterative design | R&D, Product Development | Pros: Quick validation; low initial investment. Cons: Limited production scale; potential for higher per-unit costs. |
| Custom CNC Turned Parts | Tailored to specific client needs, various materials | Specialty applications, niche markets | Pros: Meets unique specifications; material versatility. Cons: Potentially higher costs; longer lead times. |
| Secondary Operations CNC Parts | Additional machining processes (e.g., threading, milling) | Complex assemblies, High-precision applications | Pros: Enhanced functionality; comprehensive solutions. Cons: Increased complexity; may require more time. |
What Are Precision CNC Turned Parts and Their Key Characteristics?
Precision CNC turned parts are manufactured with exceptional accuracy and tight tolerances, making them ideal for critical applications in industries such as automotive and aerospace. These components are produced using advanced CNC turning technology, which allows for the creation of custom designs tailored to specific requirements. Buyers should consider the supplier’s expertise in precision machining and their ability to meet exact specifications, as well as the potential for longer lead times and higher costs associated with high-quality production.
How Do High-Volume CNC Turned Parts Benefit Mass Production Industries?
High-volume CNC turned parts are characterized by automated processes that enable scalability and fast production rates. These components are commonly used in mass production industries, such as consumer goods and automotive manufacturing. Buyers benefit from cost-effective solutions and quick turnaround times; however, they may face limitations in customization options. When selecting a supplier, it’s crucial to evaluate their capacity for handling large orders and their efficiency in maintaining quality during high-volume runs.
Why Are Prototype CNC Turned Parts Essential for R&D?
Prototype CNC turned parts are essential for research and development as they allow for rapid prototyping and iterative design processes. These short runs enable businesses to validate concepts quickly and make necessary adjustments before full-scale production. While the initial investment is lower and the speed of production is advantageous, buyers should be aware that the per-unit cost may be higher and that these parts are not suited for large-scale manufacturing. Selecting a supplier with experience in prototyping can ensure a smooth transition from concept to production.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Custom CNC Turned Parts?
Custom CNC turned parts are specifically tailored to meet unique client needs and can be produced from a variety of materials. These parts are often used in specialty applications and niche markets where standard solutions do not suffice. Buyers should consider the supplier’s ability to accommodate specific designs and material requirements. While custom parts provide significant advantages in meeting precise specifications, they may also come with higher costs and longer lead times, making it essential to balance customization with budget and timeline constraints.
How Do Secondary Operations Enhance CNC Turned Parts?
Secondary operations in CNC turning involve additional machining processes such as threading, milling, and surface finishing, which enhance the functionality of the final product. These operations are particularly valuable in complex assemblies and high-precision applications. Buyers looking for comprehensive solutions should evaluate suppliers who offer these additional services. Although these enhancements improve part performance, they also add complexity to the manufacturing process and may require more time to complete, so it’s vital to discuss timelines and capabilities with potential suppliers.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc turned parts supplier
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Turned Parts Supplier | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision components for engine assemblies | Enhanced performance and reliability in vehicles | Need for high tolerance, material quality, and scalability |
| Aerospace | Custom machined parts for aircraft systems | Improved safety and efficiency in flight operations | Compliance with strict industry regulations and standards |
| Oil & Gas | Components for drilling and extraction equipment | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Resistance to harsh environments and material sourcing |
| Medical Devices | Turned parts for surgical instruments | Assurance of precision and safety in medical procedures | Certification and compliance with health regulations |
| Industrial Machinery | Parts for manufacturing equipment | Enhanced machinery performance and reduced maintenance | Customization capabilities and quick turnaround times |
How Are CNC Turned Parts Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, CNC turned parts are integral to the production of precision components such as engine blocks, transmission parts, and suspension systems. These parts require tight tolerances to ensure optimal performance and safety. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, must consider suppliers that can consistently deliver high-quality materials, as well as the ability to scale production based on demand fluctuations. The right CNC turned parts can significantly enhance vehicle reliability, ultimately leading to better market competitiveness.
What Role Do CNC Turned Parts Play in Aerospace Applications?
CNC turned parts are vital in aerospace manufacturing, where they are used to create components for engines, landing gear, and structural frames. The aerospace industry demands extremely high precision and adherence to strict regulatory standards to ensure safety and performance. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers with proven certifications and a history of compliance with aerospace manufacturing standards. The use of high-quality turned parts can lead to improved aircraft efficiency and reduced risk of mechanical failure.
Why Are CNC Turned Parts Important in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, CNC turned parts are essential for the production of components used in drilling rigs, pipelines, and extraction equipment. These parts must withstand extreme conditions, including high pressures and corrosive environments. Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia must ensure their suppliers can provide materials that offer durability and performance under such demanding conditions. High-quality CNC turned parts can lead to significant cost savings through reduced downtime and increased operational efficiency.
How Are CNC Turned Parts Utilized in Medical Devices?
CNC turned parts find critical applications in the manufacturing of surgical instruments and medical devices, where precision and reliability are paramount. These components often require certifications and compliance with health regulations to ensure safety in medical applications. International buyers, particularly from Europe, need to work with suppliers who understand the stringent requirements of the medical industry. Quality CNC turned parts can greatly enhance the performance and safety of medical devices, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
What Benefits Do CNC Turned Parts Provide in Industrial Machinery?
In the realm of industrial machinery, CNC turned parts are used to manufacture components that enhance the efficiency and performance of manufacturing equipment. These parts can include gears, shafts, and housings, which require customization to meet specific operational needs. Buyers from Africa and South America should look for suppliers that offer quick turnaround times and the ability to produce low to high-volume runs. By sourcing high-quality CNC turned parts, businesses can reduce maintenance costs and improve overall machinery performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc turned parts supplier’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays in Delivery of CNC Turned Parts
The Problem: One of the most pressing issues for B2B buyers of CNC turned parts is the unpredictability of delivery schedules. Buyers often face production delays when suppliers fail to meet agreed-upon timelines, which can be particularly detrimental in industries like automotive or aerospace where just-in-time manufacturing is critical. These delays can lead to increased costs, strained relationships with customers, and disruptions in the supply chain.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of delays, buyers should prioritize establishing clear communication and setting realistic timelines during the procurement process. It is essential to conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their past performance regarding delivery times. Engaging in open discussions about lead times, production capacities, and potential bottlenecks is crucial. Additionally, consider implementing a vendor management system that allows for tracking supplier performance over time. By fostering a collaborative relationship with suppliers, you can work together to develop contingency plans and ensure that your production schedules remain on track.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of CNC Turned Parts
The Problem: Inconsistent quality can severely impact a buyer’s operations, leading to increased rejection rates and rework costs. This issue often arises when suppliers lack stringent quality control measures or do not adhere to industry standards. For businesses that rely on high-precision components, such as those in the medical or aerospace sectors, the repercussions of subpar parts can be catastrophic, affecting product safety and compliance.
The Solution: To address quality concerns, buyers should implement a rigorous vetting process when selecting CNC turned parts suppliers. Request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control procedures and certifications (like ISO 9001) to ensure they adhere to industry standards. Furthermore, consider requesting samples or prototypes before committing to large orders. Establishing a quality assurance agreement that outlines acceptable tolerances, testing procedures, and penalties for non-compliance can also safeguard your interests. Regular audits and performance reviews can help maintain high standards and ensure that your supplier consistently delivers parts that meet your specifications.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Customization of CNC Turned Parts
The Problem: Many buyers encounter difficulties when sourcing customized CNC turned parts that meet specific requirements. This challenge can stem from a lack of communication with suppliers regarding design specifications or insufficient technical expertise on the supplier’s part. In industries where unique designs are critical to product differentiation, these obstacles can hinder innovation and market competitiveness.
The Solution: To navigate customization challenges, buyers should invest time in clearly defining their specifications and expectations from the outset. Collaborating closely with engineers or product designers can help create comprehensive technical drawings and detailed requirements that can be shared with potential suppliers. It’s beneficial to engage suppliers early in the design process to leverage their expertise, which may lead to design optimizations that enhance manufacturability and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, consider using rapid prototyping to test designs before full production, allowing for adjustments without significant financial risk. Building a strong partnership with suppliers who are willing to work collaboratively on custom projects can foster innovation and lead to better end products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc turned parts supplier
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in CNC Turned Parts?
When selecting materials for CNC turned parts, it’s essential to consider properties that directly impact product performance. Here are four common materials used in the manufacturing of CNC turned components, along with their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and offers good mechanical properties in various environments.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is highly durable and suitable for applications in harsh conditions, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and marine. However, it can be more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized machining tools due to its toughness.
Impact on Application:
Due to its corrosion resistance, stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including chemicals and saline environments, making it suitable for fluid control applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 or DIN 1.4301. Understanding local material availability and sourcing from approved suppliers can also mitigate risks related to quality and consistency.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion. It typically has a density of 2.7 g/cm³ and can withstand temperatures up to 400°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which is crucial for applications in aerospace and automotive sectors. However, it is less durable than steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength, such as in transportation and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the various aluminum grades (e.g., 6061, 7075) and their respective properties. Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 is crucial, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
3. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass offers excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance, and low friction properties. It typically operates well in temperatures up to 300°C and is known for its acoustic properties.
Pros & Cons:
Brass is often used in plumbing and electrical applications due to its conductivity and resistance to corrosion. However, it is more expensive than some steel options and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application:
Brass is particularly effective in applications involving water and gas fittings, where its corrosion resistance and machinability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Brass components should meet standards like ASTM B16 for fittings. Buyers in regions such as South America should consider local availability and the potential for price fluctuations based on copper market trends.
4. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its high strength and hardness, with a temperature rating typically around 600°C. It can be treated to enhance its properties, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and durability, making it suitable for high-stress applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion and may require protective coatings in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is widely used in structural applications and machinery parts, where strength is a primary concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the different grades of carbon steel and their respective properties. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is essential, particularly in Europe, where regulations can be stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Turned Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc turned parts supplier | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Automotive, marine components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, consumer electronics | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical fittings | Good machinability and low friction | More expensive, not for high-pressure | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Structural applications, machinery parts | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC turned parts, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc turned parts supplier
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for CNC Turned Parts?
The manufacturing process for CNC turned parts involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. Each stage is designed to transform raw materials into finished components, ready for use in various industries.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Suppliers typically use a variety of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and plastics, depending on the application requirements. Material selection is crucial, as it impacts the performance and durability of the final product.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes inspection to ensure it meets the specified standards. This inspection may include checking for surface defects, dimensional accuracy, and compliance with international material standards. After passing inspection, the material is cut into manageable sizes, such as bars or sheets, ready for the turning process.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used in CNC Turning?
CNC turning is where the bulk of the manufacturing occurs. In this stage, the raw material is mounted on a CNC lathe, which rotates it at high speeds. A cutting tool then removes material to create the desired shape and dimensions.
Key techniques in CNC turning include:
- CNC Turning Centers: These machines handle various bar stocks and can produce parts with complex geometries, achieving tight tolerances.
- Multi-Spindle Automatic Screw Machines: These machines allow for high-volume production and efficiency by enabling multiple operations simultaneously.
- Secondary Operations: After initial turning, parts may undergo additional processes such as broaching, tapping, milling, and drilling to achieve specific features or enhance functionality.
This multi-step approach ensures that the final products meet the precise specifications required by the end-users.
Assembly and Finishing: How Are Parts Prepared for Delivery?
Once the components are formed, they may require assembly, especially if they are part of a larger system. This can involve fitting different turned parts together or integrating them with non-turned components.
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the surface quality and performance of the parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Deburring: Removing sharp edges and burrs to prevent damage during handling and use.
- Burnishing: Improving surface finish and durability.
- Plating or Coating: Applying protective layers to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
These finishing steps not only improve the quality of the parts but also ensure they are ready for immediate use in their intended applications.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for CNC Turned Parts Suppliers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing CNC turned parts, ensuring that every component meets rigorous standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the relevant quality standards is paramount. The ISO 9001 standard is widely recognized for quality management systems and is essential for suppliers aiming to provide consistently high-quality products. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Ensures products meet European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for parts used in the petroleum and natural gas industry.
These certifications provide assurance that the supplier adheres to global quality standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality control in CNC manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring manufacturing processes to detect any deviations from quality standards during production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive inspections of finished parts before shipment, ensuring they conform to specifications.
This multi-tiered approach helps identify and rectify issues early, ensuring high-quality outputs.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes. Here are some effective methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes firsthand. This is particularly important for international transactions, where trust may need to be established.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance over time. These reports should include data on defect rates, inspection results, and compliance with standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is especially valuable for buyers in regions with diverse regulatory environments, such as Africa and the Middle East.
-
Certifications and Documentation: Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications and documentation, ensuring they align with industry standards and customer specifications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing CNC turned parts from different regions. Key considerations include:
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality. Understanding these cultural nuances can aid in better communication with suppliers.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that the supplier complies with local regulations and international standards. This is particularly crucial when sourcing from regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks may differ significantly.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Reliability: Quality control extends beyond manufacturing. Buyers should assess the supplier’s logistics capabilities, ensuring timely delivery and handling of products to maintain quality during transit.
By understanding these factors, international buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that prioritize quality and reliability in their manufacturing processes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc turned parts supplier’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of CNC turned parts can be complex, especially for B2B buyers from diverse markets. This guide offers a structured checklist to help you source high-quality suppliers effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that your procurement process is streamlined and meets your specific requirements.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical needs, including dimensions, tolerances, materials, and quantities. Precise specifications help suppliers determine if they can meet your requirements and provide accurate quotes. This clarity minimizes misunderstandings and ensures that the final product aligns with your expectations.
2. Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in CNC turned parts manufacturing. Look for companies that specialize in your industry or have experience with similar applications. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn, industry forums, and trade shows to gather information and insights about potential partners.
3. Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of each supplier, focusing on their machinery, technology, and expertise. Key factors to consider include:
– Equipment: Ensure they have advanced CNC turning and secondary operations capabilities.
– Quality Control: Inquire about their quality assurance processes to verify their commitment to high standards.
4. Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a large order, ask for samples or prototypes of the CNC turned parts. This step allows you to evaluate the supplier’s craftsmanship and quality. Assess the samples for adherence to your specifications and overall performance, which can save you from costly errors later.
5. Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or equivalent, which signify a commitment to quality management. Compliance with international standards is crucial, especially for buyers in regulated industries. Ask for documentation to confirm their adherence to safety, environmental, and industry-specific regulations.
6. Check Customer References and Reviews
Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your industry or region. Engaging with these references can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, communication, and service quality. Look for consistent feedback about their performance, delivery times, and responsiveness to issues.
7. Negotiate Terms and Finalize Agreements
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms including pricing, payment schedules, lead times, and shipping arrangements. Clear agreements help prevent misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations. Be sure to discuss any potential penalties for delays or quality issues to safeguard your interests.
By following this checklist, you can systematically approach the procurement of CNC turned parts, ensuring that you partner with a supplier capable of meeting your specific needs while maintaining high standards of quality and service.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc turned parts supplier Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for CNC Turned Parts Suppliers?
When sourcing CNC turned parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials like aluminum, brass, and stainless steel have varying costs based on market demand and availability. Suppliers often provide flexibility in sourcing materials, either from their inventory or customer-supplied options.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct manufacturing labor and skilled technician wages. Advanced CNC machining requires experienced operators, which can increase costs. Additionally, the labor market conditions in the supplier’s region can affect pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operations, utilities, and maintenance of equipment. Suppliers with modern machinery may have higher initial investments, but they can benefit from increased efficiency and lower long-term operational costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary widely based on the complexity of the parts and the need for custom tools. Initial setup for specialized parts can add to the upfront costs but is often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality output is paramount, especially for precision components. QC processes, including inspections and testing, contribute to the overall cost. Suppliers that adhere to strict quality certifications may charge a premium but offer peace of mind regarding product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the shipping method chosen. International buyers should consider tariffs, duties, and other import costs that could impact the total expense.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a margin to ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market competition, demand, and the supplier’s unique value proposition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Turned Parts Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC turned parts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders generally benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that could affect pricing strategies for smaller orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts that require unique designs or tight tolerances often incur higher costs due to increased engineering time and specialized tooling.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the type of material selected can significantly affect pricing. High-performance materials or exotic alloys will typically command higher prices than standard options.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that require specific industry certifications or compliance with international standards may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against the price.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technology may charge more but can offer superior quality and faster turnaround times.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect the total cost. Different terms dictate who bears the shipping risk and costs, which can influence the final price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CNC Turned Parts?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to consider:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions to negotiate pricing and terms. Leveraging volume purchases or long-term contracts can yield favorable pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial price. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including logistics, quality, and potential rework costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of fluctuations in material costs and how they affect pricing. Currency exchange rates can also impact costs for international buyers.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes are comprehensive, covering all aspects of the cost structure. This transparency aids in comparing suppliers effectively.
-
Evaluate Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service. Trust and communication are vital in any B2B partnership.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC turned parts can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, material availability, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to request tailored quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and terms.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc turned parts supplier With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to CNC Turned Parts Suppliers
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, international B2B buyers often seek various solutions to meet their precision component needs. While CNC turned parts suppliers are a popular choice for high-quality, precise components, there are alternative methods and technologies that can also fulfill these requirements. Understanding these alternatives can help buyers make informed decisions based on their specific applications, budgets, and operational capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Turned Parts Supplier | 3D Printing | Traditional Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and tight tolerances; suitable for complex geometries | Good for prototypes; can achieve moderate precision | Excellent for high-volume production; limited in complex shapes |
| Cost | Generally higher due to precision and material costs | Lower initial costs for prototypes; higher for mass production | Cost-effective for large runs; setup costs can be significant |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor | User-friendly software; less skilled labor required | Requires skilled machinists; longer setup time |
| Maintenance | Moderate; depends on equipment | Low; minimal maintenance required | High; regular maintenance for machines needed |
| Best Use Case | Automotive, aerospace, and medical applications requiring precision | Rapid prototyping, low-volume production, and custom parts | High-volume production of standard parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a rapidly growing technology that allows for the creation of parts layer by layer. One of the primary advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional machining or CNC turning. This technology is particularly beneficial for rapid prototyping and low-volume production, as it significantly reduces the time from concept to finished product. However, while 3D printing can offer lower initial costs for prototypes, the cost can increase for mass production, and the material properties may not always meet the high standards required for critical applications.
How Does Traditional Machining Compare to CNC Turning?
Traditional machining encompasses various processes, including milling and drilling, to shape materials into desired forms. This method is often cost-effective for high-volume production runs, as it can leverage existing tooling and machinery to produce standard parts efficiently. However, traditional machining may not achieve the same level of precision as CNC turning, especially for complex shapes that require tight tolerances. Additionally, setup times can be longer, which may not be ideal for projects requiring quick turnaround times or custom parts.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Choosing the right solution for precision components involves assessing various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and production volume. CNC turned parts suppliers excel in delivering high-precision components, particularly for industries where reliability is critical. However, for projects that require rapid prototyping or lower volumes, alternatives like 3D printing may be more appropriate. Traditional machining remains a strong contender for high-volume production of standard parts. By evaluating these alternatives against specific project needs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc turned parts supplier
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Turned Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of CNC turned parts is critical for international B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and performance in their applications. Here are some key specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of material used in manufacturing CNC turned parts, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or brass. The choice of material impacts the part’s strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For industries like automotive or aerospace, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial to meet safety and regulatory standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in a part’s dimensions. It is a critical specification that ensures parts fit together correctly and function as intended. In precision engineering, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are essential for high-performance applications, while looser tolerances may suffice for less critical components. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers and ensures compatibility with their assembly processes.
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of CNC turned parts affects not only aesthetics but also functionality. A smoother finish can enhance corrosion resistance and reduce friction, which is vital in mechanical applications. Buyers should specify their required surface finish (e.g., Ra value) to ensure the final product meets performance criteria.
4. Hardness
Hardness indicates a material’s resistance to deformation and wear. It is especially relevant for components subjected to high stress or abrasive conditions. Different hardness levels can be achieved through processes such as heat treatment. B2B buyers should consider the operational environment of their parts to choose the appropriate hardness specifications.
5. Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy refers to how closely a part’s dimensions match its design specifications. High dimensional accuracy is vital for parts that must fit precisely within assemblies. This property is particularly significant in sectors like medical devices and aerospace, where even minor deviations can lead to failures or safety concerns.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Turning?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can enhance communication and decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding whether a supplier operates as an OEM can help buyers evaluate the quality and reliability of the components they source, as OEMs typically adhere to stringent standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier requires to process an order. This term is essential for B2B buyers to know, as it affects budgeting and inventory management. Understanding MOQs can help buyers negotiate better terms or find suppliers that align with their production volumes.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process by obtaining detailed offers from multiple suppliers, aiding in cost comparison and decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risks and costs at various stages of the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the finished product. This term is crucial for B2B buyers who rely on timely deliveries to meet production schedules. Understanding lead times can help buyers plan more effectively and avoid production delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable CNC turned parts suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc turned parts supplier Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in CNC Turned Parts Supply?
The global market for CNC turned parts is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision components, and the need for cost-effective manufacturing solutions. Key trends include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 practices, which enhance production efficiency and accuracy. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, the focus is on suppliers who can deliver both high-volume and custom solutions quickly and reliably. This demand is further fueled by the automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which require components that meet stringent quality standards and tight tolerances.
Moreover, the integration of digital tools in the supply chain, such as cloud-based platforms for real-time tracking and management, is becoming increasingly prominent. Buyers are leveraging these technologies to streamline procurement processes, improve supplier collaboration, and reduce lead times. Additionally, the trend towards localized sourcing is gaining traction, as businesses seek to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. This shift encourages suppliers to establish regional production facilities, thus enhancing their responsiveness to local markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the CNC Turned Parts Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the CNC turned parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste generation and resource consumption, has prompted companies to seek suppliers committed to sustainable practices. This includes using energy-efficient machinery, implementing waste reduction strategies, and opting for environmentally friendly materials.
Moreover, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers with ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signifies a commitment to effective environmental management systems. The use of recycled materials and sustainable sourcing practices not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the brand reputation of companies in competitive markets. This trend aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsibly sourced products, making it essential for suppliers to adopt transparent and ethical practices throughout their supply chains.
How Has the CNC Turned Parts Industry Evolved Over Time?
The CNC turned parts industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from manual machining to highly automated processes. Initially, turning operations relied heavily on skilled labor and traditional machinery, which limited production capabilities and precision. The introduction of CNC technology revolutionized the sector, allowing for high-speed, precise machining that could produce complex geometries with minimal human intervention.
As technology advanced, the industry saw the rise of multi-spindle machines and sophisticated software that enabled manufacturers to optimize production and reduce costs. Today, CNC turned parts are integral to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare, reflecting the ongoing demand for high-quality, reliable components. This evolution underscores the importance of continuous innovation and adaptation to meet the changing needs of international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets where demand for precision engineering is rapidly increasing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc turned parts supplier
-
How do I select the right CNC turned parts supplier for my business needs?
Choosing the right CNC turned parts supplier involves assessing their capabilities, industry experience, and production quality. Look for suppliers with advanced machinery and a proven track record in your specific industry, such as automotive or electronics. Request samples to evaluate quality and precision. Additionally, consider their customer service, lead times, and flexibility in meeting your production volumes. Establishing clear communication regarding your project requirements and timelines is essential for a successful partnership. -
What should I consider when negotiating payment terms with a CNC turned parts supplier?
When negotiating payment terms, consider factors like order size, lead time, and your relationship with the supplier. It’s common to negotiate terms such as partial upfront payments or credit terms based on your order history. Ensure that the terms are favorable while also being fair to the supplier. Additionally, clarify any penalties for late payments and the acceptable payment methods (e.g., bank transfers, credit cards). Clear payment terms help in maintaining a smooth transaction process and fostering a trustworthy business relationship. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC turned parts, and how does it affect pricing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) vary by supplier and can significantly influence pricing. Suppliers may set MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness in production and cover setup costs. Typically, larger orders lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Discuss your needs with the supplier to find a balance between MOQ requirements and budget constraints. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for new customers or prototypes, so it’s worthwhile to inquire about options that fit your project. -
How can I ensure the quality of CNC turned parts during production?
Ensuring quality during production involves selecting a supplier that adheres to strict quality assurance processes. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request detailed inspection reports and ask about their quality control measures, including in-process inspections and final product testing. Establishing a clear communication channel for updates during production can help you address any concerns promptly and ensure that the final parts meet your specifications. -
What are the advantages of custom CNC turned parts versus off-the-shelf solutions?
Custom CNC turned parts offer tailored solutions that meet specific design requirements and performance criteria, which off-the-shelf solutions may not fulfill. Customization can enhance product functionality, improve fit and compatibility with existing systems, and optimize material usage, potentially reducing waste. Although custom parts may have a higher initial cost, the long-term benefits of improved performance and efficiency often justify the investment. Discuss your needs with suppliers to explore design options and prototypes that align with your project goals. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing CNC turned parts internationally?
When sourcing CNC turned parts internationally, consider shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Work with suppliers experienced in international trade to ensure they can handle logistics efficiently. Factor in lead times for production and shipping, as delays can affect your project timeline. Additionally, confirm that the supplier has robust packaging practices to protect parts during transit. Establishing a reliable logistics plan will help you manage costs and ensure timely delivery of your components. -
How can I assess the supplier’s capability for handling large-scale production runs?
To assess a supplier’s capability for large-scale production, inquire about their machinery, workforce, and past project experiences. Visit their facility if possible to evaluate their production processes and equipment. Ask for case studies or references from similar projects to gauge their ability to meet deadlines and quality standards. Additionally, discuss their scalability options, such as the ability to ramp up production quickly if demand increases. A supplier with strong capabilities will ensure consistent delivery and quality, even at scale. -
What role does communication play in the success of a CNC turned parts procurement process?
Effective communication is crucial in the CNC turned parts procurement process. It ensures that all parties have a clear understanding of project requirements, timelines, and expectations. Establish regular check-ins and updates with your supplier to address any issues proactively. Clear communication helps prevent misunderstandings that can lead to delays or quality concerns. Moreover, it fosters a collaborative relationship, enabling both parties to adapt to changes and challenges throughout the production cycle.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc turned parts supplier
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of CNC turned parts is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chains and enhance product quality. By partnering with reputable suppliers who utilize advanced manufacturing technologies and adhere to rigorous quality standards, buyers can ensure the delivery of high-precision components tailored to their specific needs. This not only accelerates production timelines but also drives down costs and improves overall operational efficiency.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, stand to gain significantly from leveraging the expertise of established CNC turned parts suppliers. As industries evolve and demand for customized solutions increases, sourcing partners that can provide scalable production capabilities and comprehensive service offerings will become invaluable.
Looking ahead, the global market for CNC turned parts is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and a rising emphasis on quality and sustainability. Now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers who can help you navigate these changes and position your business for success. Reach out today to explore how strategic sourcing can elevate your operations and meet the demands of your industry.