Top 8 Cnc Machine Tool Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
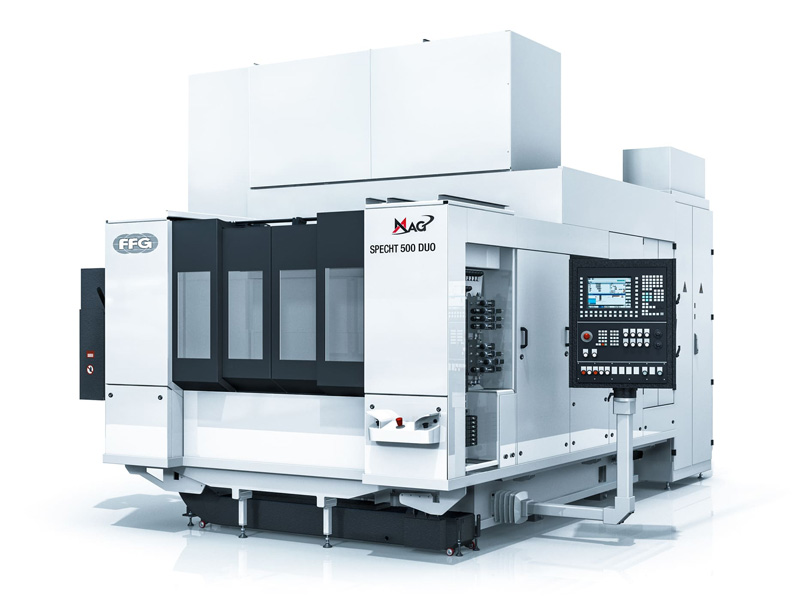
1. Mazak – Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: mazak.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 5-Axis Machining Centers, Additive Manufacturing (AM), Automation, CNC Turning Centers, Friction Stir Welding (FSW), Horizontal Machining Centers, Multi-Tasking Machines, Swiss-Style Production Turning Machines, Vertical Machining Centers.
2. Makino – CNC Machine Tools & Automation Solutions
Domain: makino.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Makino offers a range of CNC machine tools and machining centers including Horizontal 4-Axis, Horizontal 5-Axis, Vertical 3-Axis, Vertical 5-Axis, Graphite Machining Centers, Wire EDM, Sinker EDM, EDM Hole Drilling, and Grinding. They provide automation solutions such as Robot Integration, Linear Pallet Pool System (MMC2), Fixture Plate Handling System (MMC-R), and Factory Automation. Their softwa…
3. Productivity – CNC Machine Tools
Domain: productivity.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Productivity is a supplier and distributor of metalworking CNC machine tools and equipment, offering a wide range of products and services including:
– CNC Machine Tools: New and used machines, including vertical and horizontal machining centers, CNC lathes, tool room machines, rotary tables, and 5C indexers from Haas Automation.
– Tooling & Industrial Supplies: Cutting tools, coolants, abrasives…
4. Makino – CNC Machines
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Most trusted CNC machine brands mentioned include Makino, Okuma, Haas, and DMG Mori. Okuma is noted for its older lathes being durable and long-lasting, while Haas is considered good for beginners but may not withstand heavy use without maintenance. DMG Mori is recognized for its quality, being a Japanese-German company. Japanese brands are generally regarded as reliable.
5. Methods Machine Tools – CNC Machine Tools & Automation Solutions
Domain: methodsmachine.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Methods Machine Tools offers a range of CNC machine tools and automation solutions including Vertical CNC Machining Centers, Horizontal CNC Machining Centers, 5-Axis CNC Machining Centers, Turning Centers, Multitasking CNC Lathes, Wire EDM, Cycle-Controlled Lathes, and Multi-Pallet Machines. They distribute machines from leading brands such as Nakamura-Tome, FANUC, Yasda, Methods, OKK, KIWA, and W…
6. Hurco – CNC Machine Tools
Domain: hurco.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Hurco offers CNC machine tools equipped with exclusive technology designed to streamline the manufacturing process from print to part. Key features include: 1. CNC Control with 3D Import capability for seamless integration of solid models (.stp and .step files) directly into the machine control, along with integrated simulation of CAD/CAM tool paths. 2. Automatic creation of Transform Planes, allo…
7. DMG MORI – CNC Machines for Metalworking
Domain: us.dmgmori.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: DMG MORI offers a comprehensive range of CNC machines for various applications in metalworking, capable of machining materials such as non-ferrous metals, steel, stainless steel, high-strength alloys, plastics, composite materials, glass, and diamond. Key industries served include tool and mold making, aerospace, medical technology, and the semiconductor industry. The portfolio includes:
1. **Tur…
8. Prototool – CNC Machines
Domain: prototool.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: CNC machines are automated power tools used in industrial manufacturing for operations such as turning, milling, engraving, cutting, drilling, grinding, welding, spinning, and winding. They are controlled by computers and utilize CAD/CAM software and G code for precision machining. Common types of CNC machines include: 1. Milling machines 2. CNC lathes 3. CNC routers and engravers 4. CNC grinders …
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc machine tool manufacturer
Navigating the landscape of CNC machine tool manufacturers can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and high-quality production solutions. The complexities of sourcing the right equipment—be it lathes, milling machines, or multi-axis systems—require a strategic approach to ensure compatibility with specific industry needs and operational requirements. This guide is designed to equip buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into various types of CNC machines and their applications across multiple sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing. Additionally, we will provide detailed strategies for vetting suppliers, assessing cost implications, and understanding the technological advancements shaping the industry. With a focus on actionable insights, this guide aims to empower decision-makers by highlighting key considerations that can influence efficiency, productivity, and return on investment.
By addressing the critical aspects of sourcing CNC machine tools, this guide serves as a valuable tool for B2B buyers looking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities and navigate the global market with confidence. Whether you are in Brazil or Saudi Arabia, the insights provided here will help streamline your procurement process and ultimately drive your business success.
Understanding cnc machine tool manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Machining Centers | Typically feature a vertically oriented spindle; ideal for precision machining. | Aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors. | Pros: High precision, versatile for various materials. Cons: Limited to vertical operations. |
| Horizontal Machining Centers | Spindle is oriented horizontally, allowing for efficient chip removal. | Heavy-duty machining, large part production. | Pros: Better chip management, suitable for large parts. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| CNC Lathes | Designed for rotating workpieces, ideal for cylindrical parts. | Manufacturing of shafts, rods, and fittings. | Pros: Excellent for producing symmetrical parts. Cons: Limited in handling complex geometries. |
| Multi-Axis Machines | Capable of simultaneous movement on multiple axes for complex geometries. | Aerospace components, intricate molds, and dies. | Pros: High flexibility, reduces setup time. Cons: More complex operation and maintenance. |
| Automation Systems | Integrates CNC machines with robotics and software for streamlined production. | High-volume manufacturing and assembly lines. | Pros: Increases efficiency, reduces labor costs. Cons: Requires significant upfront investment and training. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Vertical Machining Centers?
Vertical machining centers are characterized by their vertically oriented spindle, which is ideal for precision machining tasks. They are versatile, accommodating a range of materials from metals to plastics. B2B buyers should consider their applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where precision is paramount. The main purchasing considerations include the machine’s accuracy, tooling options, and ease of operation.
How Do Horizontal Machining Centers Differ in Functionality?
Horizontal machining centers are distinguished by their horizontal spindle orientation, which enhances chip removal efficiency and is better suited for heavy-duty machining tasks. These machines excel in producing large parts, making them ideal for sectors that require robust manufacturing capabilities. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s capacity, tooling compatibility, and overall production efficiency when considering this type of equipment.
What Makes CNC Lathes a Popular Choice for Manufacturers?
CNC lathes are specifically designed for rotating workpieces, making them suitable for creating cylindrical components such as shafts and fittings. Their ability to produce highly symmetrical parts makes them a staple in manufacturing. When purchasing a CNC lathe, buyers should focus on the machine’s size, spindle speed, and tooling options to ensure it meets their production needs.
Why Consider Multi-Axis Machines for Complex Manufacturing Needs?
Multi-axis machines are capable of simultaneous movement on multiple axes, allowing for the production of complex geometries and intricate designs. They are particularly valuable in industries like aerospace and mold-making, where precision and versatility are essential. Key B2B purchasing considerations include the machine’s programming capabilities, ease of use, and the potential for reducing setup times, which can significantly enhance productivity.
What Advantages Do Automation Systems Offer in CNC Manufacturing?
Automation systems integrate CNC machines with robotics and advanced software to create streamlined production workflows. These systems are particularly beneficial for high-volume manufacturing environments, where efficiency and consistency are crucial. Buyers should assess the initial investment, potential ROI, and the need for operator training when considering automation solutions, as they can drastically reduce labor costs and improve production rates.
Key Industrial Applications of cnc machine tool manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of CNC Machine Tool Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision Machining of Aircraft Components | Enhanced accuracy and reduced material waste | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Production of Engine Components | Increased efficiency and faster production times | Supplier reliability and ability to handle high volumes |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of Surgical Instruments | High precision and quality assurance | Regulatory compliance and material specifications |
| Electronics | PCB Manufacturing and Enclosure Machining | Improved production speed and lower costs | Advanced technology and support for automation |
| Oil & Gas | Machining of Valve Components | Durability and performance in harsh conditions | Material quality and certifications for safety standards |
How is CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing Utilized in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, CNC machines are crucial for the precision machining of components such as turbine blades, fuselage parts, and landing gear. These components require tight tolerances and high reliability due to the critical nature of their application. CNC machine tool manufacturers provide solutions that minimize material waste while ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace standards. International buyers, particularly from regions with emerging aerospace industries, need to consider suppliers with proven certifications and a track record of meeting rigorous quality controls.
What Role Does CNC Machinery Play in the Automotive Sector?
CNC machining is integral to the automotive industry, where it is used to produce various engine components, transmission parts, and chassis elements. The ability to achieve high efficiency and precision in production processes leads to faster turnaround times and reduced costs. For buyers in regions like South America and Africa, it is essential to source machines that offer reliability and scalability, ensuring they can meet increasing production demands while maintaining quality standards.
How Are CNC Machines Applied in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical sector, CNC machines are utilized for the fabrication of surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic devices. The high level of precision required in these applications ensures patient safety and device efficacy. Manufacturers must adhere to strict regulatory compliance, which necessitates sourcing CNC machines that meet specific medical device standards. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee quality assurance processes and material traceability.
How Is CNC Technology Transforming Electronics Manufacturing?
CNC machining plays a vital role in the electronics industry, particularly in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and enclosures. These applications demand high-speed production and precision to minimize errors and optimize performance. International buyers need to focus on sourcing advanced CNC machines that support automation to enhance production capabilities. Additionally, understanding the technological advancements offered by manufacturers can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements.
What Are the Key Benefits of CNC Machining in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, CNC machines are essential for machining valve components, pumps, and fittings that must withstand extreme conditions. The durability and performance of these components are critical, making precision machining a necessity. Buyers from regions with substantial oil reserves, such as the Middle East, should consider sourcing CNC machines that offer robust construction and high tolerances. It is also crucial to assess the supplier’s ability to provide materials that comply with safety and performance standards specific to this industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cnc machine tool manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Initial Investment Concerns in CNC Machine Tool Acquisition
The Problem: For many international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, the initial investment in CNC machine tools can be daunting. Companies often face budget constraints, and the high cost of advanced machinery can lead to hesitation in making a purchase. Furthermore, the fear of not getting a return on investment (ROI) due to potential operational inefficiencies or the high cost of maintenance can deter buyers from committing to a purchase. This uncertainty is compounded by the lack of access to financing options and local support for service and parts.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, buyers should engage in thorough market research to identify manufacturers that offer competitive pricing along with flexible financing options. Many CNC machine tool manufacturers now provide leasing or financing plans, which can help spread the cost over time and reduce upfront financial burden. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in used or refurbished machines from reputable manufacturers, which can significantly lower costs without sacrificing quality. Lastly, establishing a partnership with a local distributor can provide access to service and maintenance support, ensuring that machines remain operational and efficient, ultimately enhancing ROI.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Reliable Technical Support and Training
The Problem: Once a CNC machine is purchased, the next significant challenge is ensuring that staff are adequately trained to operate the equipment. Many manufacturers do not provide sufficient training resources, leading to underutilization of the machines and operational inefficiencies. This issue is especially prevalent in developing regions where access to skilled labor is limited. As a result, companies may struggle to maximize the capabilities of their CNC tools, leading to reduced productivity and increased frustration.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer comprehensive training programs as part of their sales package. This could include on-site training, online resources, and ongoing technical support. Engaging with manufacturers that have a strong reputation for customer service can lead to better training outcomes. Furthermore, buyers can consider forming alliances with local vocational schools or training centers to develop tailored training programs that meet their specific operational needs. Investing in a skilled workforce will ensure that the CNC machines are used effectively, ultimately improving production quality and efficiency.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Machine Maintenance and Downtime Management
The Problem: CNC machines are complex systems that require regular maintenance to function optimally. For many B2B buyers, particularly in regions with less robust supply chains, sourcing spare parts and technical support can be a significant headache. Unexpected downtime due to machine failure can lead to substantial losses, affecting production schedules and client relationships. The fear of prolonged downtimes can be a major deterrent for companies looking to implement CNC technology.
The Solution: To manage these maintenance challenges effectively, buyers should choose CNC machine manufacturers that provide robust after-sales support and a reliable supply of spare parts. It’s advisable to inquire about the availability of local service centers and the average response time for repairs and maintenance. Additionally, establishing a preventive maintenance schedule can help mitigate the risks of unexpected downtime. Buyers should also consider investing in condition monitoring technologies that provide real-time data on machine performance, allowing for proactive maintenance before issues escalate. By fostering a strong relationship with the manufacturer and ensuring a steady supply of parts, companies can minimize downtime and maintain production efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc machine tool manufacturer
When selecting materials for CNC machine tool manufacturing, it is essential to consider various factors that can significantly influence product performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the industry, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in CNC machine tools due to its excellent mechanical properties. It offers high tensile strength, durability, and good machinability. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a drawback unless treated or alloyed.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and versatility, allowing for various machining processes. However, the cost of high-quality steel can be significant, and its weight may complicate handling and transportation.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, making it ideal for diverse industrial applications. However, its corrosion resistance must be considered when used in environments with moisture or chemicals.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM or JIS) and consider the availability of specific steel grades.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for CNC Machine Tools?
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor. It has good thermal and electrical conductivity, which can be advantageous in specific machining processes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can enhance the efficiency of CNC machines. However, it is generally less durable than steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, but its lower strength limits its use in high-stress environments.
International Considerations: For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with aluminum standards (like EN or ISO) is crucial, as is understanding the local market for aluminum alloys.
What Role Does Titanium Play in CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications, such as aerospace and medical devices. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is biocompatible, which is essential in medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of titanium is its durability and ability to perform under extreme conditions. However, it is one of the more expensive materials and can be challenging to machine due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly suited for applications involving harsh environments or where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace.
International Considerations: Buyers must consider compliance with international standards for titanium (such as ASTM) and the availability of specific titanium grades in their region.
Why is Composite Material Gaining Popularity in CNC Machine Tools?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of fibers and resins, are becoming increasingly popular in CNC manufacturing due to their lightweight and high strength. They offer excellent resistance to corrosion and fatigue, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their customizable properties, allowing for specific performance characteristics. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture than traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in applications requiring lightweight components that can withstand environmental stressors.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the different standards governing composite materials and ensure that their suppliers can meet these requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc machine tool manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machining components | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machine parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Composite | Lightweight, high-performance components | Customizable properties | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium to High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for CNC machine tool manufacturing, highlighting critical considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed decisions that align with specific operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc machine tool manufacturer
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for CNC Machine Tool Manufacturers?
The manufacturing processes of CNC machine tools encompass several stages that ensure precision, efficiency, and reliability. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers seeking high-quality machinery.
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
-
Material Preparation:
The first stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, typically metals like aluminum, steel, or titanium. These materials are often sourced from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards. The materials undergo processes such as cutting, sawing, or shearing to achieve the desired dimensions before moving to the next stage. -
Forming:
Forming techniques include machining operations like milling, turning, and drilling. Advanced CNC machines utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed specifications, allowing for precise and repeatable results. This stage may also involve the use of specialized tooling and fixtures to enhance accuracy. -
Assembly:
Once individual components are machined, they are assembled into complete systems. This stage requires skilled labor and often involves the use of jigs and fixtures to ensure parts fit together correctly. Assembly lines are typically organized to optimize workflow and reduce production time. -
Finishing:
The finishing stage includes processes like grinding, polishing, and coating. These techniques enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the machine tools. For example, surface treatments can improve corrosion resistance and durability, which are critical for long-term performance.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for CNC machine tools, ensuring that products meet both regulatory and customer standards.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for CNC Machine Tool Quality?
CNC machine tool manufacturers typically adhere to several international standards, with ISO 9001 being the most recognized. This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (for Europe) and API (for the oil and gas sector) may be required depending on the application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This initial checkpoint focuses on the inspection of raw materials and components as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide documentation proving that materials meet specified standards. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to monitor processes and ensure they are within acceptable parameters. This may involve measuring critical dimensions and verifying machine settings. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
At the end of the manufacturing process, a thorough inspection is performed on the finished products. This includes functional testing, performance evaluations, and compliance checks against technical specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in CNC Machine Tool Quality Assurance?
Testing methods vary widely depending on the type of machine tool and its intended use. Common testing techniques include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing precision measuring instruments like calipers and micrometers to verify that components meet specified tolerances.
- Functional Testing: Evaluating the machine’s operational capabilities, ensuring it performs as intended under various conditions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic, magnetic particle, or dye penetrant testing are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial.
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Engage in on-site audits to assess the manufacturing environment, quality control systems, and adherence to standards. This direct evaluation can reveal insights into the supplier’s operational practices.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports, certifications, and any non-conformance reports. This transparency can help buyers gauge the reliability of the manufacturer.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Hiring independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality assurance practices. These entities often have established protocols for evaluating compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers must consider regional compliance requirements when sourcing CNC machine tools. For instance, European buyers may require CE certification, while those in the Middle East might prioritize compliance with local standards. Understanding these nuances can help buyers navigate the complexities of international procurement.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may impact communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can foster better relationships and lead to successful transactions.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of CNC machine tool manufacturers are critical factors for B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of production and the importance of quality control, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Emphasizing compliance with international standards and thorough verification practices will ensure that they procure reliable and high-performing machinery suited to their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cnc machine tool manufacturer’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure CNC machine tools from manufacturers. Given the complexity of the CNC machining industry, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you select the right supplier that meets your technical and operational needs. This checklist will help streamline your sourcing process and mitigate risks associated with procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the CNC machines you need. This includes dimensions, materials, tolerances, and the specific machining capabilities required (e.g., milling, turning, or 5-axis machining). Precise specifications will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the machines you consider align with your production goals.
- Consider your industry requirements: Different industries may have specific standards or certifications that the machinery must meet.
- Anticipate future needs: Think about scalability and whether the machine can accommodate future projects.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable CNC machine tool manufacturers. Look for companies with a strong market presence and positive customer reviews. Utilize online resources, industry forums, and trade shows to gather insights.
- Check for industry recognition: Awards or certifications can indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
- Assess their product range: Ensure the manufacturer offers a variety of machines that could suit your current and future needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step is vital to understanding the supplier’s production capabilities and reliability.
- Analyze their technology and innovation: Suppliers that invest in advanced technology often provide better quality and efficiency.
- Look for after-sales support: Reliable manufacturers will offer robust service packages, including maintenance and training.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers you are considering have the necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Certification indicates that the supplier adheres to international quality management practices.
- Request documentation: Always ask for proof of certifications and check their validity.
- Understand compliance with local regulations: This is particularly important for international buyers to avoid future legal complications.
Step 5: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include all costs—machine pricing, shipping, installation, and any additional services. Comparing these quotes will give you a clearer picture of the overall investment required.
- Look for transparency in pricing: Ensure there are no hidden costs that could affect your budget.
- Assess the value offered: Sometimes, a higher initial price may come with better service or more advanced technology.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits
If possible, arrange site visits to the manufacturers’ facilities. Observing their production processes, quality control measures, and maintenance practices can provide invaluable insights into their operational capabilities.
- Engage with the staff: Speaking with engineers and operators can give you a sense of the company culture and customer support.
- Inspect the machinery: Ensure that their machines are well-maintained and meet your specifications firsthand.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing your purchase, carefully negotiate the terms and conditions of the contract. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, warranties, and service agreements. Clear agreements will protect your interests and clarify expectations on both sides.
- Clarify warranty details: Understand what is covered and for how long to avoid future disputes.
- Discuss training and support: Ensure that the manufacturer provides adequate training for your staff on using and maintaining the equipment.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing CNC machine tools, ensuring a successful procurement process that aligns with their operational needs and goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc machine tool manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of CNC machine tool manufacturing is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys, can significantly impact the final price. High-quality materials are essential for durability and performance, but they also increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the machinery being produced. Skilled labor is necessary for precision engineering, which can lead to higher wages and training costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can be a substantial portion of total costs, especially in regions with higher operational expenses.
-
Tooling: The tooling costs involve the purchase and maintenance of cutting tools, molds, and fixtures essential for the manufacturing process. Advanced tooling can enhance production efficiency but also adds to the initial investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that machines meet industry standards and customer specifications. This involves testing and inspections, contributing to overall production costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, as well as the shipping method chosen. Incoterms will also influence responsibility for logistics costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can range from 10% to 30% depending on market conditions, competition, and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect CNC Machine Tool Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of CNC machines, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider negotiating for better pricing based on their order volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machinery tailored to specific requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) may increase costs but can also lead to better performance and reliability, reducing long-term operational costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established manufacturers may charge a premium for their expertise and service support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs, insurance, and risks.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating CNC Machine Tool Pricing?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to optimize their procurement process:
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Understand the market rates for CNC machines and the specific costs associated with various manufacturers. This knowledge will empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A more expensive machine with lower operational costs may be a better investment.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service over time. Consider establishing partnerships that benefit both parties.
-
Explore Financing Options: Many manufacturers offer financing solutions that can help mitigate upfront costs. Discuss available options with suppliers to ease budget constraints.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations that can affect the final price when importing machines from other regions.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of sourcing CNC machine tools requires a comprehensive understanding of cost structures and pricing influencers. By applying strategic negotiation techniques and focusing on total cost considerations, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always consult with multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing while maintaining quality and service standards.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cnc machine tool manufacturer With Other Solutions
When considering the best solution for precision machining, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate alternatives to traditional CNC machine tools. While CNC machine tool manufacturers provide robust solutions for various machining needs, several alternatives can also deliver quality results, often with different benefits and considerations. This analysis compares CNC machine tools with robotic automation and manual machining, highlighting their relative advantages and drawbacks.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | CNC Machine Tool Manufacturer | Robotic Automation | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed | Moderate precision; speed varies by task | Variable precision; highly skilled labor needed |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Mid-range costs; potential savings in labor | Low initial cost; high labor costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional setup | Moderate complexity; need for programming | Simple setup; requires skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Lower maintenance; less wear and tear | High maintenance; depends on operator skill |
| Best Use Case | Mass production, complex parts | Repetitive tasks, high-volume production | Custom or low-volume jobs |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotic Automation?
Robotic automation is a viable alternative to CNC machine tools, particularly in high-volume production environments. Robots can execute repetitive tasks efficiently, often at a lower operational cost once set up. They excel in applications that require consistent quality across numerous products, such as assembly or material handling. However, they may lack the precision of CNC machines for intricate machining tasks and often require programming expertise, which can add to implementation time.
How Does Manual Machining Compare to CNC Machines?
Manual machining relies on skilled labor to operate traditional lathes, mills, and other machinery. This method has a lower initial investment and is suitable for custom, low-volume jobs where flexibility is essential. However, the performance can be inconsistent depending on the operator’s skill level, leading to variability in precision and quality. Additionally, manual machining can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, which may not be ideal for high-demand production scenarios.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
For B2B buyers, the choice between CNC machine tools, robotic automation, and manual machining hinges on specific operational needs and budget considerations. CNC machines are ideal for high precision and complex parts, making them suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive. Robotic automation is beneficial for high-volume, repetitive tasks, while manual machining offers flexibility for custom jobs. By assessing factors such as production volume, required precision, and budget, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their manufacturing goals and operational strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc machine tool manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Machine Tools?
When evaluating CNC machine tools, understanding essential technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a CNC machine tool affects its durability, performance, and cost. Common materials include cast iron, steel, and aluminum. For instance, machines made from high-grade steel offer superior rigidity and longevity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. B2B buyers must assess the material grade to ensure it aligns with their production needs and budget. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions during manufacturing. In CNC machining, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are often necessary for precision components, especially in industries like aerospace and medical devices. Understanding tolerance requirements is essential for buyers to guarantee product quality and compliance with industry standards. -
Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is a critical specification that influences machining efficiency and surface finish quality. Higher spindle speeds allow for faster machining operations, but they may also require more advanced tooling. Buyers should consider spindle speed in relation to the materials they will be machining to optimize productivity. -
Axis Configuration
CNC machines come in various axis configurations, such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis systems. The choice of configuration impacts the complexity of the parts that can be manufactured. For instance, 5-axis machines enable intricate shapes and reduce the need for multiple setups. Buyers should evaluate their production requirements to select the appropriate axis configuration. -
Power Rating
The power rating of a CNC machine, typically measured in horsepower (HP), determines its cutting capabilities. Higher power ratings facilitate machining harder materials and improve feed rates. When selecting a CNC machine, buyers should assess the power requirements based on the materials and processes involved in their operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in CNC Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the CNC machining sector. Here are some important terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In CNC machining, OEMs often supply essential components for machine tools. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure the quality of their machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell at one time. This term is particularly relevant for buyers looking to procure custom parts or materials. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses manage inventory effectively and negotiate better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is an essential tool for B2B buyers to obtain competitive quotes and make informed purchasing decisions. Crafting a clear RFQ can facilitate better supplier responses and streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and customs duties. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers to ensure smooth transactions and avoid unexpected costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In CNC manufacturing, lead times can vary significantly based on production schedules and material availability. Buyers must consider lead times in their planning to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through computer programming. It enables precise control of machining processes, resulting in high-quality, repeatable outputs. Understanding CNC technology is fundamental for buyers to appreciate the capabilities and advantages of modern machine tools.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of CNC machine tool manufacturing more effectively, leading to better purchasing decisions and optimized production processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cnc machine tool manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the CNC Machine Tool Manufacturer Market?
The CNC machine tool manufacturing sector is witnessing significant transformations, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and changing customer demands. A key trend is the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which integrate IoT, artificial intelligence, and data analytics to enhance machine performance and operational efficiency. This shift allows manufacturers to optimize production processes and reduce downtime, making it particularly appealing to B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where operational efficiency is crucial for competitiveness.
Emerging sourcing trends are also notable, as international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer comprehensive automation solutions and advanced machining capabilities. This demand is particularly strong in markets such as Saudi Arabia and Brazil, where industrial growth is accelerating. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement is reshaping how buyers interact with manufacturers, enabling greater transparency and faster response times.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern, with manufacturers and buyers alike focusing on environmentally friendly practices. As global markets lean towards greener solutions, CNC machine tool manufacturers are investing in sustainable technologies and materials to meet the expectations of conscientious buyers, particularly in Europe.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the CNC Machine Tool Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral concern in the CNC machine tool industry; it is a central pillar influencing sourcing decisions. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted buyers to seek out manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are increasingly stringent regarding emissions and waste management.
Ethical sourcing has emerged as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Companies are now expected to demonstrate transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and ethically. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for sustainable materials, are becoming essential criteria for procurement decisions. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers that adhere to these standards, reflecting their commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the integration of recycled materials and energy-efficient technologies in machine production is gaining traction. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East are particularly interested in solutions that not only enhance productivity but also minimize environmental footprints, aligning with global sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Machine Tool Manufacturing?
The CNC machine tool industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially driven by the need for precision and efficiency in manufacturing, the sector has undergone a technological revolution. The introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) systems in the 1960s marked a turning point, enabling automated machining processes that dramatically increased production capabilities.
As globalization took hold in the late 20th century, manufacturers began to expand their reach, establishing supply chains that spanned continents. This evolution has led to a more interconnected market, where international B2B buyers can access a diverse range of suppliers and technologies. The advent of digital technologies and the rise of e-commerce platforms in the 21st century have further transformed the landscape, facilitating seamless interactions between manufacturers and buyers across different regions.
Today, the CNC machine tool sector stands at the crossroads of innovation and sustainability, with a focus on meeting the complex demands of a globalized market. This historical context underscores the importance of adaptability and forward-thinking in navigating the current dynamics of the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc machine tool manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right CNC machine tool manufacturer for my business needs?
Choosing the right CNC machine tool manufacturer involves evaluating several key factors. Start by assessing the manufacturer’s reputation and experience in your specific industry. Look for customer testimonials and case studies that demonstrate their expertise. Additionally, consider the range of products they offer, ensuring they align with your production requirements. It’s also essential to evaluate their support services, including after-sales support, training, and availability of spare parts. Finally, request quotes and compare pricing structures to find the best value for your investment. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms for international CNC machine purchases can vary significantly among manufacturers. Common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide a balance of security for both parties. For large orders, consider using escrow services to ensure funds are released only when agreed conditions are met. Always review the payment terms in the context of your cash flow needs and the supplier’s reputation for reliability and integrity. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machine tools?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC machine tools can differ widely based on the manufacturer and the type of machinery. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, while others may require larger commitments for customized or specialized machines. When sourcing, inquire directly about MOQs and express your needs; many manufacturers are willing to negotiate terms to foster long-term partnerships. Understanding the MOQ can help you plan your budget and production schedules effectively. -
How can I ensure the quality of CNC machines before purchase?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough research on potential manufacturers, including certifications such as ISO or CE. Request detailed specifications and product samples to assess their performance firsthand. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility if feasible, or seek third-party inspections and audits. It’s also beneficial to ask for references from other customers, particularly those in your industry, to gauge their satisfaction with the machinery and the manufacturer’s service. Quality assurance processes should be clearly outlined by the manufacturer. -
What customization options are typically available for CNC machines?
Customization options for CNC machines can range from software modifications to hardware upgrades. Most manufacturers offer tailored solutions to meet specific production needs, such as varying sizes, spindle types, and control systems. When discussing customization, provide detailed requirements to the manufacturer to get accurate recommendations. Additionally, inquire about lead times for customizations, as they can affect your overall project timeline. Collaborating with the manufacturer during the design phase can help ensure the machine meets your operational demands. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC machines?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the successful importation of CNC machines. First, understand the shipping methods available, including air freight or sea freight, and choose based on cost and urgency. Ensure that the manufacturer provides suitable packaging to protect the machinery during transit. Familiarize yourself with customs regulations and import duties in your country, as these can significantly affect your total cost. Finally, consider working with a logistics partner experienced in handling heavy machinery to streamline the shipping process. -
How do I vet suppliers for CNC machine tools effectively?
Vetting suppliers involves a systematic approach to ensure reliability and quality. Start by researching the supplier’s history, reputation, and customer reviews. Check for industry certifications and compliance with international standards. Conduct interviews or site visits to evaluate their manufacturing processes and capabilities. Additionally, request samples or case studies of previous work relevant to your needs. Engaging in open communication about your requirements will also help you gauge their responsiveness and commitment to customer service. -
What after-sales support should I expect from a CNC machine tool manufacturer?
After-sales support is vital for maintaining your CNC machines’ performance. Look for manufacturers that offer comprehensive service packages, including installation, training, and regular maintenance. Ensure they provide access to technical support and spare parts, which are crucial for minimizing downtime. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and conditions, as these can vary widely. A manufacturer committed to customer satisfaction will offer responsive support and resources to help you optimize your machinery’s productivity.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc machine tool manufacturer
In the rapidly evolving landscape of CNC machine tool manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a cornerstone for international B2B buyers seeking competitive advantage. As companies navigate diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing quality machinery is essential. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating suppliers based on technological innovation, reliability, and post-purchase support.
Investing in high-quality CNC machines from reputable manufacturers like Haas, Okuma, and Makino can significantly enhance productivity and operational efficiency. These brands not only offer a wide range of machine options but also provide robust customer service, ensuring that buyers can maximize their investment over time. Additionally, leveraging automation solutions can optimize workflows, reduce downtime, and ultimately drive profitability.
Looking ahead, the demand for precision machining will continue to grow, fueled by advancements in technology and the need for customized manufacturing solutions. International B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and support. This proactive approach will not only meet current production needs but also position businesses for future success in a competitive global marketplace.