Top 8 Ball Mill Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
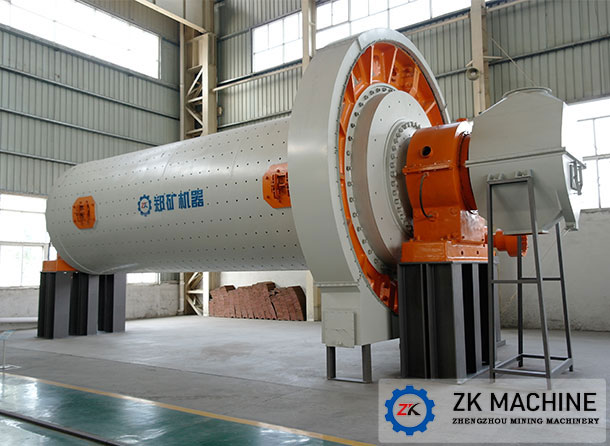
1. Economy Ball Mill – Custom Ball Mills
Domain: economyballmill.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Economy Ball Mill, a division of JSB Industrial Solutions, Inc., manufactures diverse ball mills for various applications. They have over 50 years of experience as an OEM. Key features include:
– Tapered roller bearings mounted on machine-turned trunnions for long life and smooth operation.
– Fabricated steel mill stands for necessary discharge clearance.
– Powered by high start torque motors w…
2. NETZSCH – Taurus Ball Mill
Domain: grinding.netzsch.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Taurus – Ball Mill by NETZSCH is designed for fine and ultrafine grinding of various materials. Key features include: advanced technology for micronizing, a robust rotating steel drum with liners providing kinetic energy to grinding media, and the ability to use hard wear-resistant materials such as high manganese/chromium steel, ceramic, or silex for lining and grinding media. The mill offers sev…
3. Retsch – Laboratory Ball Mills
Domain: retsch.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Retsch offers a wide selection of laboratory ball mills suitable for various applications. Key product details include: 1. **Types of Ball Mills**: – Mixer Mills: Sample volumes up to 6 x 20 ml, final fineness of 0.1 µm, cell disruption via bead beating, grinding by impact and friction. – Planetary Ball Mills: Sample volumes up to 4 x 220 ml, final fineness of 0.1 µm, high energy input due to extr…
4. FLS – Ball Mills & HPGR Solutions
Domain: fls.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Ball Mills – efficient grinding; Industry-leading mineral processing equipment; High Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR) are the most efficient comminution product for milling.
5. Paulo Abbe – Steel Ball Mills
Domain: pauloabbe.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Steel Ball Mills are designed for high efficiency, providing a narrow particle distribution and repeatable results. They operate at low temperatures, making them suitable for heat-sensitive products. The mills are sealed for chemical containment and offer predictable scale-up from small to large sizes. Key materials include abrasion-resistant steel, stainless steel, polyurethane, or rubber lining….
6. Ball Mills Supplier – Comprehensive Mill Solutions
Domain: ballmillssupplier.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Ball Mill Types: raw mill, coal ball mill, ore ball mill, small ball mill, wet ball mill, ceramic ball mill, overflow ball mill, vertical ball mill, rod mill, automatic/semi-automatic mill. Applications: cement manufacturing, mining, metallurgy, building materials, chemical industry, electric power, non-metallic mineral powder making, marble processing, heavy calcium processing, coal powder prepar…
7. MSE Supplies – High Energy Planetary Ball Mills
Domain: msesupplies.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: MSE PRO 0.2L (4 x 50 ml) Vertical High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Glove Box – Price: $3,791.95; MSE PRO 0.4L (4 x 100ml or 4 x 50 ml) Bench Top Mini High Energy Vertical Planetary Ball Mill – Price: $3,755.95; MSE PRO 0.4L (4 x 100ml or 4 x 50 ml) Touchscreen High Energy Planetary Ball Mill – Price: $4,408.95; MSE PRO 0.4L High Energy Vertical Cryogenic Planetary Ball Mill with 15L Liquid Nitr…
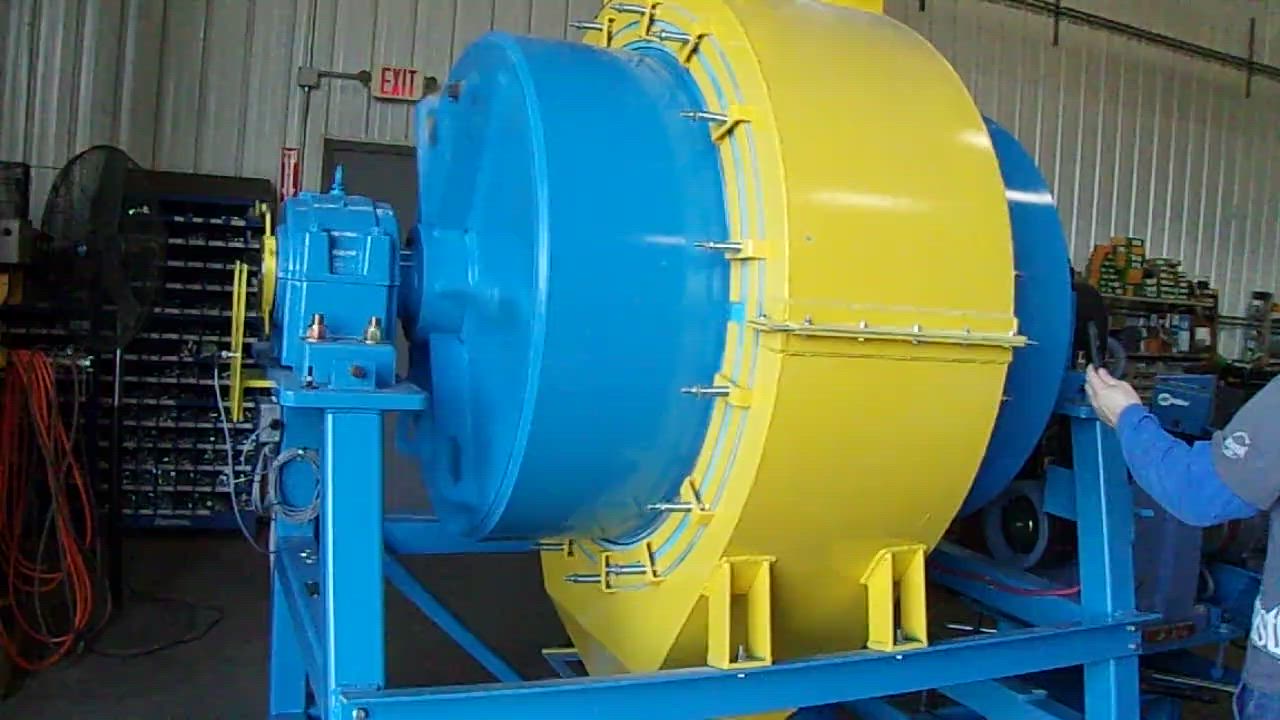
8. A.M. King – Ball Mills
Domain: inventory.amking.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Buy New and Used Ball Mills For Your Mining Operation | A.M. King specializes in supplying high-quality used and unused ball mills designed for optimal size reduction in mineral processing applications. Ball mills are critical components in grinding circuits, engineered to grind materials into fine powder, delivering consistent reduction across various ore types and conditions. Inventory includes …
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ball mill manufacturer
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right ball mill manufacturer is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to advanced ceramics, selecting a supplier that meets specific operational needs can seem daunting. This guide is designed to empower buyers by providing a comprehensive overview of the global ball mill market, detailing various types of mills, their applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
Understanding the nuances of ball mill specifications, such as capacity, material compatibility, and maintenance requirements, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we delve into cost factors, enabling buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—to optimize their procurement strategies.
By offering insights into the latest technologies, performance metrics, and supplier reputations, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the ball mill market confidently. Whether you are enhancing production efficiency or expanding your processing capabilities, making informed choices in selecting a ball mill manufacturer can significantly impact your operational success.
Understanding ball mill manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Ball Mill | Simple design, versatile, available in various sizes | Mining, construction, pharmaceuticals, ceramics | Pros: Cost-effective, easy maintenance. Cons: Limited fineness control. |
| Stainless Steel Ball Mill | Corrosion-resistant, ideal for sensitive materials | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics | Pros: Enhanced durability, reduced contamination risk. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Planetary Ball Mill | High-energy impact, suitable for nanoscale grinding | Material science, nanotechnology, research labs | Pros: Precise particle size control, versatile applications. Cons: More complex operation. |
| Taurus Ball Mill | Advanced grinding technology with customizable configurations | Fine and ultra-fine processing, chemicals, minerals | Pros: High efficiency, low maintenance. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Batch Ball Mill | Designed for small-scale production, easy to operate | Specialty chemicals, pilot projects, research | Pros: Flexible production, quick setup. Cons: Limited capacity compared to continuous mills. |
What are the Characteristics of a Standard Ball Mill?
Standard ball mills are characterized by their straightforward design and versatility. They are commonly used in various industries, including mining and construction, for grinding materials like ores and minerals. Buyers should consider the size and volume capacity based on their production needs. While standard mills are cost-effective and easy to maintain, they may not provide the precise fineness control that some applications require.
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Ball Mill?
Stainless steel ball mills are specifically designed to prevent contamination, making them ideal for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their corrosion-resistant properties enhance durability and extend the lifespan of the equipment. When purchasing, buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced contamination against the higher initial costs. These mills are particularly suitable for sensitive materials that require strict hygiene standards.
How Do Planetary Ball Mills Differ from Other Types?
Planetary ball mills utilize high-energy impacts, making them suitable for grinding materials at the nanoscale. They are popular in research labs and material science applications due to their ability to achieve precise particle size control. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of operation and the specific energy requirements when evaluating these mills. While they offer versatility, the operational intricacies may require additional training for staff.
What Advantages Does the Taurus Ball Mill Offer?
The Taurus ball mill features advanced grinding technology, allowing for customizable configurations tailored to specific applications. It is particularly effective for fine and ultra-fine processing of materials such as chemicals and minerals. Buyers benefit from high efficiency and low maintenance needs, making it a long-term investment. However, the initial investment can be significant, so companies should assess their budget against expected output.
When to Consider a Batch Ball Mill?
Batch ball mills are designed for small-scale production and are user-friendly, making them suitable for specialty chemicals and pilot projects. Their flexibility allows for quick setup and easy operation, catering to businesses that require a versatile solution. However, potential buyers should note that batch mills have limited capacity compared to continuous mills, which may affect production rates in larger operations.
Key Industrial Applications of ball mill manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ball mill manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Ensures uniform particle size for better bioavailability | Compliance with health regulations, material quality, and customization options |
| Mining and Minerals | Processing ores and minerals for extraction | Increases yield by optimizing particle size for extraction | Equipment durability, capacity for large volumes, and maintenance support |
| Chemicals | Producing fine chemicals and pigments | Enhances product consistency and reduces production costs | Material compatibility, safety features, and energy efficiency |
| Construction Materials | Grinding cement and other construction materials | Improves material properties for stronger, more durable products | Sourcing for specific sizes, energy consumption, and regulatory compliance |
| Food and Beverage | Milling grains and spices | Maintains flavor integrity and enhances product quality | Hygiene standards, material certifications, and process flexibility |
How Are Ball Mill Manufacturers Used in Pharmaceuticals?
In the pharmaceutical industry, ball mills are essential for grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to achieve a uniform particle size. This uniformity is critical for ensuring consistent bioavailability and efficacy in formulations. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, must prioritize sourcing equipment that meets stringent health regulations. Additionally, customization options may be necessary to accommodate specific materials or production processes.
What Role Do Ball Mills Play in Mining and Minerals?
In mining, ball mills are utilized for processing ores and minerals to optimize extraction yields. The equipment crushes and grinds materials to the desired particle size, which is crucial for maximizing recovery rates. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the durability of the equipment, as well as its capacity to handle large volumes, ensuring that it can withstand the rigors of mining operations while minimizing maintenance needs.
How Are Ball Mills Beneficial in Chemical Production?
Ball mills are widely used in the chemical industry for producing fine chemicals and pigments. The grinding process enhances product consistency and can significantly reduce production costs by improving efficiency. When sourcing ball mills, buyers should focus on material compatibility to prevent contamination, as well as safety features to protect workers and the environment. Energy efficiency is also a key consideration, particularly for businesses looking to reduce operational costs.
Why Are Ball Mills Important in Construction Materials?
In the construction materials sector, ball mills are used to grind cement and other materials, enhancing their properties for stronger and more durable products. This process is vital for maintaining quality standards in construction projects. Buyers should look for equipment that meets specific size requirements and complies with regulatory standards. Additionally, understanding energy consumption rates can help businesses optimize their production costs.
How Do Ball Mills Enhance Quality in Food and Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, ball mills are employed to mill grains and spices, ensuring that flavors remain intact and product quality is maintained. This equipment is vital for achieving the desired texture and consistency in food products. Buyers must prioritize hygiene standards and material certifications when sourcing ball mills, as these factors directly impact product safety and quality. Flexibility in processing capabilities is also essential to accommodate a diverse range of food products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ball mill manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Size and Capacity Mismatches in Ball Mill Selection
The Problem: When sourcing ball mills, B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting a machine that perfectly matches their production requirements. Many manufacturers offer various sizes and configurations, leading to confusion about which model will efficiently handle the desired throughput. For instance, a buyer in the agricultural chemical sector may overestimate the processing volume needed, resulting in the purchase of an undersized mill that cannot meet production goals, leading to delays and increased costs. Conversely, opting for a larger model may lead to wasted energy and higher maintenance costs.
The Solution: To avoid size and capacity mismatches, B2B buyers should engage in a detailed analysis of their production needs. This includes calculating the desired throughput, understanding the properties of the materials being processed, and determining the specific grinding process (wet or dry). Manufacturers often provide guidelines and charts to help buyers estimate the required volume based on these factors. It’s advisable to consult directly with the manufacturer’s technical team, who can offer tailored recommendations. Additionally, consider pilot testing smaller models to verify performance before committing to larger purchases. This proactive approach ensures that the selected ball mill aligns with operational demands, ultimately optimizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Scenario 2: Navigating Maintenance and Downtime Challenges
The Problem: A significant concern for B2B buyers is the potential for unexpected downtime due to maintenance issues with ball mills. Frequent breakdowns can disrupt production schedules, leading to substantial financial losses. For instance, a mining company in South America may experience prolonged outages due to wear and tear on grinding media or mechanical components, affecting their ability to meet contract obligations. This situation is particularly frustrating when the buyer is unaware of the maintenance requirements or the expected lifespan of critical components.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance-related challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing ball mills from manufacturers known for quality and durability. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive maintenance manuals and service support is essential. Additionally, implementing a preventative maintenance schedule can help identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Buyers should also inquire about the availability of spare parts and the manufacturer’s lead times for replacements. By establishing a partnership with the manufacturer for ongoing support, B2B buyers can reduce unplanned downtime and maintain a smooth production flow.
Scenario 3: Customization and Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when trying to integrate new ball mills into their existing production lines. This challenge is particularly pronounced in industries like pharmaceuticals or advanced materials, where specific standards and processes must be adhered to. Buyers may find that off-the-shelf solutions do not meet their unique specifications, leading to compatibility issues that can derail production timelines. For example, a buyer may require a mill that can fit into a pre-existing layout with limited space, or one that adheres to strict regulatory requirements for cleanliness and contamination control.
The Solution: To address customization and integration challenges, buyers should communicate their specific needs clearly during the procurement process. This includes providing detailed information about their existing systems, operational constraints, and material handling requirements. It’s beneficial to work with manufacturers who offer customizable solutions tailored to individual specifications, including size, material, and functionality. Engaging in early-stage discussions about integration can lead to the design of bespoke solutions that fit seamlessly into existing workflows. Furthermore, consider requesting prototypes or demonstrations to ensure compatibility before full-scale implementation. By taking these steps, buyers can successfully integrate new ball mills into their operations, enhancing productivity and compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ball mill manufacturer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Ball Mill Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for ball mill manufacturing, several key options stand out based on their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. High Manganese Steel
Key Properties: High manganese steel is known for its excellent wear resistance and toughness. It can withstand high impact and pressure, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°C and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of high manganese steel is its durability, which leads to a longer lifespan for grinding media. However, its manufacturing process can be complex and costly. While it excels in abrasive environments, it may not be the best choice for applications involving corrosive materials.
Impact on Application: High manganese steel is particularly effective for grinding hard materials, such as ores and minerals, due to its ability to maintain structural integrity under stress.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A128 and consider local sourcing options to reduce costs. Countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia have specific regulations regarding material quality that may affect procurement.
2. Ceramic Materials
Key Properties: Ceramic materials offer excellent hardness and low density, along with high resistance to wear and corrosion. They can operate effectively at elevated temperatures, typically up to 1000°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of ceramics is their ability to minimize contamination during grinding, making them ideal for sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals and food processing. However, they are brittle and can fracture under high impact, which limits their use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are suitable for fine grinding applications where purity is critical. They are particularly beneficial in industries such as cosmetics and advanced ceramics.
Considerations for International Buyers: When sourcing ceramic materials, compliance with standards like ISO 12677 is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of local suppliers to ensure timely delivery, especially in regions with logistical challenges.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it versatile for various applications. Common grades include 304 and 316, with varying levels of corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust, making it suitable for both wet and dry grinding processes. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process may involve additional steps to ensure quality.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring hygiene and minimal contamination, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU regulations) is critical when purchasing stainless steel components. Buyers should also be aware of local standards and certifications that may affect their procurement process.
4. Chrome Steel
Key Properties: Chrome steel is characterized by its high hardness and wear resistance, particularly when heat-treated. It typically has a good temperature rating and performs well under high-stress conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of chrome steel is its cost-effectiveness and durability, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, it may not be as corrosion-resistant as stainless steel, limiting its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Chrome steel is commonly used in the mining and mineral processing industries, where it can efficiently grind hard materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that chrome steel products meet relevant standards such as ASTM A532. Understanding local market conditions and sourcing options is vital for optimizing costs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for ball mill manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Manganese Steel | Grinding hard ores and minerals | Excellent wear resistance | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Ceramic Materials | Fine grinding in pharmaceuticals and food | Low contamination risk | Brittle and prone to fracture | High |
| Stainless Steel | Applications requiring hygiene | Corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Chrome Steel | Mining and mineral processing | Cost-effective and durable | Less corrosion-resistant | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various materials used in ball mill manufacturing, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ball mill manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Ball Mill?
The manufacturing process of ball mills is intricate and involves several key stages, each critical to producing high-quality machinery that meets diverse industrial needs.
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing a ball mill begins with material preparation. Manufacturers typically source high-grade raw materials, including various grades of steel for the mill’s body and wear-resistant materials for the liners and grinding media. Rigorous quality checks on incoming materials ensure compliance with international standards, which is crucial for maintaining the durability and efficiency of the final product.
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This stage involves several techniques such as casting, forging, or machining, depending on the design specifications of the ball mill. Advanced technologies like CNC machining are often employed to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances, which are vital for optimal performance. For instance, the use of tapered roller bearings and trunnions is common in forming processes to ensure smooth operation and longevity of the mills.
Assembly Processes
After forming, components are assembled into the final product. This stage includes integrating the drive systems, including motors and gear reducers, which are essential for the ball mill’s operation. Manufacturers often utilize standardized assembly procedures to enhance efficiency and maintain quality. During this phase, attention to detail is paramount; any misalignment can lead to operational issues, making proper assembly critical.
Finishing Touches
The final stage involves finishing processes, which may include surface treatments, painting, and polishing. These processes not only enhance the aesthetics of the ball mill but also provide additional protection against wear and corrosion. Manufacturers often conduct final inspections to ensure that all components meet the specified standards before shipping.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Ball Mill Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing process for ball mills. It ensures that the products meet both international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Ball Mill Manufacturers?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance. ISO 9001 outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with such standards is crucial for manufacturers aiming to establish credibility in the global market.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (which indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for equipment used in the oil and gas industry are vital for manufacturers targeting particular sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that all raw materials meet required specifications before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to verify that processes align with established standards. This includes monitoring dimensions, tolerances, and assembly techniques.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the ball mill is fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This may involve functional testing, where the mill is run under operational conditions to assess performance and reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Ball Mill Quality Control?
Testing methods are critical for validating the quality and performance of ball mills. Common methods include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and micrometers to verify that all components conform to specified dimensions.
-
Material Testing: Conducting tensile strength tests and hardness tests to ensure that materials used can withstand operational stresses.
-
Functional Testing: Running the ball mill to assess its performance, including grinding efficiency and noise levels, ensuring it operates within acceptable parameters.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers, particularly when sourcing from international markets. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility can provide invaluable insights into their quality management practices and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation regarding their quality assurance processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the supplier’s claims regarding quality and compliance with international standards. This is particularly important for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may differ significantly from international norms.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when sourcing ball mills. For instance, understanding the specific certifications required in their region is crucial. Buyers from Europe may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East may look for compliance with local regulations.
Additionally, cultural and logistical considerations can impact the manufacturing process and delivery times. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that quality expectations are met.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting ball mill manufacturers, ensuring they receive reliable and high-quality equipment tailored to their specific industrial needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ball mill manufacturer’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring ball mills from manufacturers. By following this checklist, you will ensure that your procurement process is thorough, efficient, and aligned with your specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to manufacturers, it’s essential to establish your technical requirements. This includes understanding the type of materials you will be processing, the desired particle size, and whether the application will involve wet or dry milling. Clearly defined specifications help streamline communication with suppliers and ensure you receive equipment tailored to your needs.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify potential ball mill manufacturers. Look for companies with a strong industry presence, proven track records, and positive customer reviews. Key factors to consider include:
– Experience: Manufacturers with years of expertise are more likely to offer reliable products.
– Diversity of Applications: Ensure the manufacturer has experience with materials similar to yours.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verification of supplier certifications is crucial for quality assurance. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. This not only assures you of the manufacturer’s commitment to quality but also enhances your credibility when integrating the equipment into your operations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. A comprehensive quote should include:
– Pricing: Ensure it covers all costs, including shipping and installation.
– Technical Specifications: Confirm that the equipment meets your defined requirements.
– Lead Times: Understand the production timeline to plan your project effectively.
Step 5: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Tour
If feasible, schedule a site visit to the manufacturer’s facility. Observing the production process can provide insights into their operational capabilities and quality control measures. If a visit is not possible, request a virtual tour to evaluate the manufacturing environment and equipment used.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the level of after-sales support provided by the manufacturer. This includes:
– Technical Support: Determine if they offer ongoing assistance for troubleshooting and maintenance.
– Warranty Terms: A solid warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in their product and provides you with peace of mind.
Step 7: Seek References and Customer Feedback
Before finalizing your decision, ask for references from previous customers, particularly those in your industry or region. Engaging with existing clients can provide valuable insights into the manufacturer’s reliability, product performance, and customer service. This step is vital in ensuring you choose a partner who aligns with your operational goals.
By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to make informed decisions when sourcing ball mills from manufacturers, ultimately leading to successful procurement and enhanced operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ball mill manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Ball Mills?
When sourcing ball mills, understanding the cost structure is crucial for buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as steel, liners, and grinding media significantly impacts the overall price. High-quality materials will enhance durability and performance, but they also come with a higher price tag. For instance, specialized ceramics or high-chromium steel may be required for specific applications, which can increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the final price. Skilled labor may be necessary for precise manufacturing and assembly, particularly for custom ball mills. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may result in more expensive products.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, depreciation of manufacturing equipment, and operational expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or sizes can add to the cost. The complexity of the ball mill design directly affects tooling costs, with more intricate designs requiring more investment in specialized tools.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the finished product meets industry standards. The costs associated with testing and certification can contribute significantly to the overall price.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, particularly for international buyers, can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms chosen. Understanding these costs upfront can help avoid surprises later in the procurement process.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on the manufacturer’s positioning in the market. Established brands with a strong reputation may command higher prices, reflecting their perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Ball Mill Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ball mills, making it essential for buyers to consider these elements when negotiating:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect the cost. Selecting standard materials instead of specialized ones can lead to substantial savings.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards and certifications may cost more but can be more reliable and provide better long-term value.
-
Supplier Factors: The manufacturer’s experience, reputation, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers often offer superior service and support, justifying a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers of Ball Mills?
International buyers should leverage several strategies to negotiate better pricing and terms:
-
Conduct Market Research: Familiarize yourself with the average pricing and standard terms in the industry. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to more favorable terms and pricing. Long-term partnerships often result in better support and service.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not only the upfront costs but also the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy consumption. A more expensive mill may offer lower operating costs, making it a better investment.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can help manage cash flow. Consider negotiating partial payments based on milestones or performance.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should account for currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes when assessing the final cost.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for ball mills can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to seek quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough evaluations to ensure they are receiving the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ball mill manufacturer With Other Solutions
When considering the purchase of a ball mill, it’s essential for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives that can achieve similar grinding and milling objectives. The right choice often depends on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and desired outcomes. Below is a comparative analysis of ball mill manufacturers against two alternative solutions: vertical roller mills and jet mills.
| Comparison Aspect | Ball Mill Manufacturer | Vertical Roller Mill | Jet Mill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for a wide range of materials; suitable for coarse to fine grinding. | High throughput with low energy consumption; ideal for fine grinding. | Produces ultra-fine powders with precise particle size control. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs can vary. | Higher initial cost but lower operational costs over time. | Typically higher costs due to specialized equipment and maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward setup; requires skilled personnel for operation. | More complex installation; may need extensive modifications to existing infrastructure. | Requires specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; components can be replaced easily. | Lower maintenance requirements due to fewer moving parts. | High maintenance needs; wear on components can increase costs. |
| Best Use Case | Versatile applications across multiple industries; effective for bulk material processing. | Best for materials requiring high efficiency and low energy use; suitable for cement and minerals. | Optimal for pharmaceutical and chemical applications where particle size is critical. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Vertical Roller Mills?
Vertical roller mills (VRMs) have gained popularity in recent years, particularly in the cement and mineral industries. Their primary advantage lies in their energy efficiency and ability to handle large volumes of material. VRMs utilize a grinding table and rollers to achieve high throughput with lower energy consumption compared to traditional ball mills. However, their initial investment is typically higher, and the setup can be complex, necessitating adjustments to existing facilities. Additionally, they are less versatile than ball mills, which can limit their use in varied applications.
How Do Jet Mills Compare to Ball Mills?
Jet mills are particularly effective for producing ultra-fine powders and controlling particle size distribution. They operate by using high-velocity jets of air or steam to accelerate particles, resulting in fine grinding without the need for additional grinding media. This method is advantageous for applications in pharmaceuticals and chemicals where contamination from grinding media must be avoided. However, jet mills can be expensive to purchase and maintain, and their operational complexity requires skilled personnel for effective management.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Milling Solution for Your Business?
Selecting the appropriate milling solution involves evaluating specific business needs, material characteristics, and operational goals. Ball mills offer versatility and a proven track record across diverse industries, making them a solid choice for many applications. However, for processes that demand high efficiency and fine particle control, vertical roller mills or jet mills may provide superior performance despite their higher costs and complexity. Ultimately, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their requirements and consult with manufacturers to ensure they choose the most effective milling solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ball mill manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ball Mills?
Understanding the essential technical properties of ball mills is crucial for international B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact operational efficiency, product quality, and overall manufacturing costs. Here are some of the most critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the ball mill, including the grinding media and drum liner, is vital for durability and performance. Common materials include high manganese/chromium steel for its wear resistance, ceramic for its non-reactivity, and silex for specific applications. Choosing the right material can prevent premature wear and reduce maintenance costs, ensuring a long service life.
2. Size and Capacity
Ball mills are available in various sizes, typically defined by their diameter and length. The capacity, often measured in gallons or liters, reflects the volume of material that can be processed in a single batch. For buyers, understanding the required size and capacity is essential to ensure that the ball mill meets production demands without over- or under-utilizing resources.
3. Motor Power and Type
The motor power of a ball mill determines its grinding efficiency and operational speed. High start torque motors are commonly used to facilitate quick starts and stops. It’s important for buyers to consider the motor specifications that align with their production needs and the type of materials being processed, as this affects energy consumption and overall performance.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the permissible limits of variation in the dimensions of the ball mill components. High precision in tolerances ensures that the grinding media interacts optimally with the material, leading to efficient size reduction. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers that can guarantee tight tolerances to enhance product consistency and quality.
5. Maintenance Requirements
The design of the ball mill should facilitate easy maintenance, including access to grinding media and liner replacements. Buyers should inquire about the maintenance schedules and the expected lifespan of components to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
6. Filling Ratio
The filling ratio indicates the proportion of the mill’s volume occupied by the grinding media and product. For dry milling, a typical filling ratio might be around 25%, while wet milling may vary between 25% and 65%. Understanding the appropriate filling ratio is crucial for optimizing the milling process and achieving desired particle size reduction.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Ball Mill Manufacturing Industry?
In the B2B landscape, familiarizing oneself with industry jargon can streamline communication and enhance negotiations. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of ball mills, this term is important when considering partnerships or sourcing equipment, as it signifies the manufacturer’s capability to produce custom solutions tailored to specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage their inventory and budget effectively. It can influence purchasing decisions, particularly for smaller companies or those with limited production runs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers. This term is critical for buyers to communicate their specifications and requirements clearly, ensuring that they receive accurate and competitive pricing for ball mills.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for international transactions, as they affect the total cost of ownership and the logistics of delivery.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules effectively and manage expectations regarding project timelines.
6. Custom Solutions
This term refers to tailored products or services designed to meet specific customer needs. For ball mills, custom solutions may include modifications in size, material, or operational features, which can significantly enhance performance based on unique operational requirements.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing ball mills, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ball mill manufacturer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Ball Mill Manufacturing Sector?
The ball mill manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, increasing global demand for efficient grinding solutions, and shifting market dynamics. As industries such as mining, construction, and pharmaceuticals expand, the need for high-performance machinery has surged. This demand is particularly pronounced in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where infrastructure development and industrialization are accelerating. International B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on suppliers that offer customizable solutions, which are tailored to specific industry needs, such as the processing of abrasives, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals.
In addition, advancements in digital technology are shaping the sourcing landscape. Automation and IoT (Internet of Things) integration are becoming prevalent, enabling manufacturers to optimize operational efficiency, monitor equipment performance, and reduce downtime. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces allows buyers to access a broader range of suppliers, facilitating competitive pricing and enhanced supplier collaboration. Buyers are also prioritizing manufacturers that demonstrate strong technical support and after-sales service, ensuring their machinery can maintain peak performance over time.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing Strategies for Ball Mill Manufacturers?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the sourcing strategies of international B2B buyers in the ball mill manufacturing sector. Environmental concerns are prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices, which not only mitigate ecological impact but also resonate with increasingly eco-conscious consumers. Manufacturers are now focusing on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste during production processes, which can significantly lower operational costs.
Ethical sourcing and supply chain transparency are also gaining prominence. Buyers are looking for suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and possess certifications, such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates commitment to environmental management. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as recyclable metals and biodegradable components—is becoming a competitive advantage. By prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable practices, buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements, ultimately contributing to a circular economy.
How Has the Ball Mill Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The ball mill manufacturing sector has evolved considerably over the decades, transitioning from basic mechanical designs to sophisticated, high-tech solutions. Initially, ball mills were predominantly used in mining for the purpose of ore grinding. However, with advancements in materials science and engineering, the applications have expanded into various industries, including pharmaceuticals, construction, and advanced ceramics.
Technological innovations, such as the introduction of variable frequency drives and automation, have enhanced the operational efficiency and flexibility of ball mills. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions that cater to specific industry requirements, enabling buyers to optimize their processes effectively. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards customization and efficiency in the manufacturing sector, driven by the need for competitive advantage in a global marketplace.
In summary, the ball mill manufacturing sector is marked by dynamic market trends, a growing emphasis on sustainability, and a rich history of innovation that continues to shape its future. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed and leverage these insights to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ball mill manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right ball mill for my specific application?
Choosing the right ball mill depends on several factors, including the material to be processed, desired particle size, and production capacity. Start by assessing the physical and chemical properties of your material. Consider whether you need a wet or dry milling process, as this will influence the design and configuration of the mill. Additionally, consult with manufacturers about customization options that can optimize performance for your specific needs. Engaging with a supplier that offers a variety of models and configurations can help ensure you find the best fit for your application. -
What is the best ball mill for fine grinding applications?
For fine grinding applications, high-performance ball mills like those from NETZSCH or Retsch are often recommended. Models such as the Taurus ball mill are designed to achieve particle sizes down to d98 < 2 μm, making them suitable for ultrafine grinding. When selecting a mill, consider its grinding media options and the specific materials you will process, as these factors significantly affect performance and efficiency. Consulting with suppliers can help you identify the best model that meets your fineness requirements. -
What are the typical lead times for ball mill manufacturing and delivery?
Lead times for ball mill manufacturing can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the design and the manufacturer’s current production capacity. Generally, you can expect lead times to range from a few weeks to several months. To ensure timely delivery, it’s advisable to discuss your project timeline with potential suppliers upfront. Additionally, consider factors such as customs clearance and logistics if you’re sourcing internationally, as these can impact delivery schedules. -
What customization options are available for ball mills?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for ball mills, including size, material, and features tailored to specific processing needs. Common customizations include the type of grinding media, lining materials (ceramic, steel, etc.), and configurations for wet or dry milling processes. You can also request specific features like discharge mechanisms or additional safety features. Engaging directly with suppliers during the design phase can help you achieve optimal performance for your unique applications. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for ball mills?
Minimum order quantities for ball mills can vary by manufacturer and depend on the model and customization level. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit orders, especially for standard models, while others may have higher MOQs for specialized or custom designs. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their policies and find a manufacturer that aligns with your purchasing capabilities and project requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a ball mill?
Payment terms for ball mill purchases can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the size of the order. Common arrangements include deposits (ranging from 20% to 50%) upfront, with the balance due upon completion or before shipping. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms, including currency and methods accepted, during negotiations to ensure mutual understanding and avoid potential issues. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in my ball mill purchase?
To ensure quality assurance in your ball mill purchase, engage with manufacturers who adhere to recognized quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request documentation of their quality control processes and inquire about testing procedures, including performance trials and inspections before shipment. Additionally, consider asking for references or case studies from previous clients to gauge the manufacturer’s reliability and the performance of their equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing ball mills internationally?
When sourcing ball mills internationally, logistics considerations are crucial. Assess the shipping methods available, including air or sea freight, and understand the associated costs and transit times. Be aware of customs regulations and import duties that may apply in your country. Collaborate with your supplier to ensure that all necessary documentation is in order and that packaging is suitable for international transport to prevent damage during shipping.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ball mill manufacturer
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for ball mill manufacturers is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking quality, reliability, and performance. By understanding the diverse applications of ball mills—from pharmaceuticals to advanced ceramics—buyers can better align their sourcing decisions with their specific industry needs. The emphasis on tailored solutions, advanced technology, and low maintenance costs further underscores the importance of collaborating with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and customization.
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient and durable milling solutions is set to rise. Buyers are encouraged to leverage this momentum by establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers who offer comprehensive support and expertise.
Investing in high-quality ball mills not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives long-term profitability. Now is the time to act—connect with leading ball mill manufacturers to explore how their solutions can elevate your production capabilities and meet your unique processing requirements.