Top 7 Router Cnc Supplier Manufacturers & Suppliers List
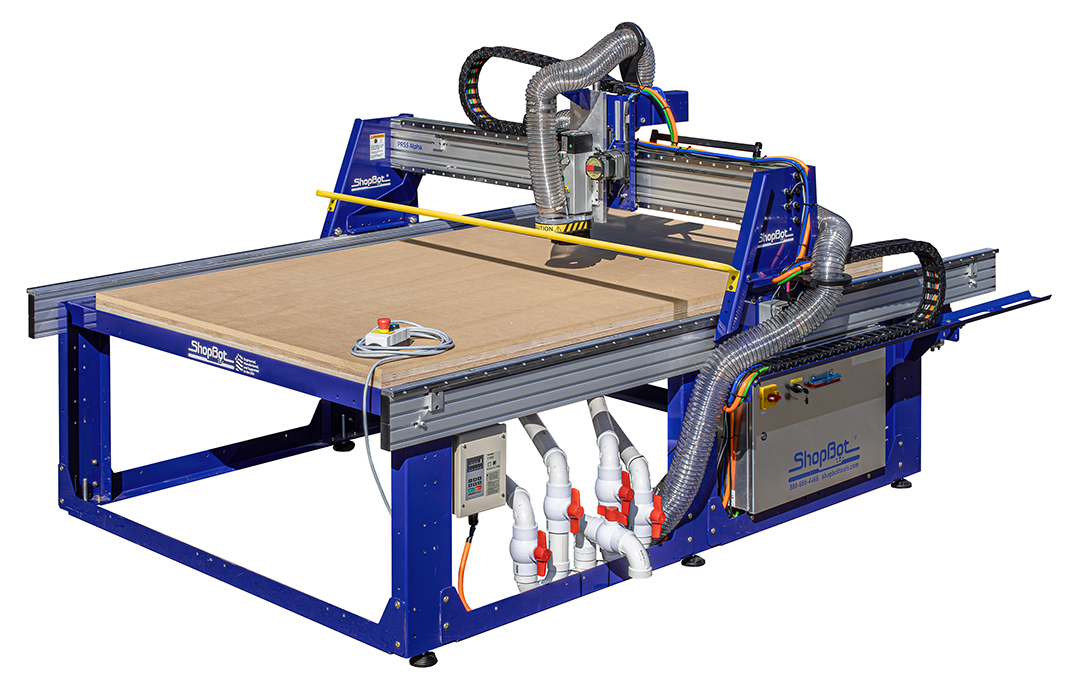
1. ShopBot Tools – PRS5 Alpha
Domain: shopbottools.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Top CNC Router Manufacturer | ShopBot Tools | Made in USA. Product Categories: Desktop Tools, Gantry Tools, Accessories, Design Software, Financing. Key Products: Desktop (24″ x 18″), Desktop MAX (36″ x 24″), Desktop MAX ATC (36″ x 24″), PRS5 Standard (96″ x 48″), PRS5 Alpha (96″ x 48″), PRS5 Alpha ATC (96″ x 48″). Features: Aluminum Deck options, MDF spoil board, Universal Vacuum Hold Down Deck o…
2. ShopSabre – IS-A and IS-M Series CNC Routers
Domain: shopsabre.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: IS-A Series CNC Router: Industrial and Commercial Use, Auto Unload, High efficiency Nested Based Sheet Processing, Starting at $99,995.00; IS-M Series CNC Router: Industrial and Commercial Use, Dedicated High Production, High Accuracy, Starting at $57,995.00; Industrial Series (IS): Industrial and Commercial Use, Starting at $40,350; IS EVA Series CNC Router: Marine/EVA Foam Applications, Starting…
3. SainSmart – Genmitsu CNC Router
Domain: sainsmart.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Genmitsu CNC Router, Affordable Beginner-Friendly | SainSmart
4. Industrial CNC – SHORT CUT 203
Domain: industrialcnc.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Industrial CNC offers a range of CNC routers designed for various applications, including sign making, cabinetry, exhibits, schools, furniture, luthiers, and woodworking. Key products include: 1. SHORT CUT 203: Small format CNC router with a 2’X3′ work area. 2. APPRENTICE 404: 4’X4′ table suitable for weekend projects. 3. ARTISAN 408: 4’X8′ CNC router for demanding production environments. 4. CRAF…
5. Techno CNC – CNC Routers & Cutters
Domain: technocnc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CNC Routers: 4×4, 4×8, 5×10 sizes; Series include: LC Series, Titan Series, Atlas Series, Venture Cabinet Nesting Series, CNC Router HD II Tabletop, Venus Series Tabletop, CNC Plasma Cutter, CO2 CNC Laser Cutter, Atlas Digital Registration Series, Venture Series, HDS Series, HDS Dual Bed Series, Goliath Series, Phoenix Series, BT1212 Tabletop Router, Venture Plus Series, Venture Nesting Production…
6. Hendrick – CNC Routers
Domain: hendrickmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Hendrick CNC Routers include a range of industrial machines designed for precise cutting of various materials such as corrugated materials, aluminum, plastic, and wood. The product lineup features: 3 Axis CNC Routers: 1. HHD Series – Powerful 3 Axis CNC Router with 24/7 uptime and up to 16 tools, designed for high-speed cutting and accuracy. 2. HSR Series – High-speed CNC router known for its dura…
7. Probotix – CNC Routers
Domain: probotix.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Probotix CNC Routers are designed for precision and versatility in various applications. They feature robust construction, high-speed performance, and user-friendly interfaces. The routers are suitable for woodworking, plastics, and metalworking, offering customizable options to meet specific project needs. Key specifications include various sizes, spindle options, and software compatibility, ensu…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for router cnc supplier
In today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right router CNC supplier can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for precision engineering and customized production, businesses must navigate a complex global market to find reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, offering insights into the diverse types of CNC routers available, their various applications across industries, and strategies for effective supplier vetting.
Understanding the nuances of pricing, shipping, and after-sales support is crucial for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By delving into detailed evaluations of supplier capabilities and product specifications, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Moreover, it highlights the importance of assessing supplier reputation, product quality, and technological advancements, ensuring that businesses can invest confidently in their CNC machining capabilities. As you explore this resource, you will gain valuable knowledge that will streamline your sourcing process and enhance your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding router cnc supplier Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop CNC Routers | Compact size, user-friendly, lower spindle power (75W – 400W) | Prototyping, small-scale production | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use. Cons: Limited work area and power. |
| Large Format CNC Routers | Extensive work areas (up to 5′ x 10′), robust build | Furniture making, signage | Pros: High production capacity, versatile. Cons: Higher cost, requires more space. |
| Industrial CNC Routers | High spindle power (up to 10kW), advanced automation features | Aerospace, automotive, heavy industry | Pros: Exceptional precision, durability. Cons: Significant investment, complex operation. |
| Hybrid CNC Routers | Combines CNC routing with laser or plasma cutting capabilities | Metal fabrication, intricate designs | Pros: Versatile, multi-functional. Cons: Higher maintenance, initial setup complexity. |
| Custom CNC Routers | Tailored specifications, modular components | Specialized manufacturing processes | Pros: Perfect fit for unique needs, scalability. Cons: Longer lead times, potential for higher costs. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Desktop CNC Routers for B2B buyers?
Desktop CNC routers are ideal for small businesses and makers looking for an entry-level solution. Their compact size and user-friendly interfaces allow for easy operation, making them suitable for prototyping and small-scale production. With spindle power ranging from 75W to 400W, they are best used for softer materials like wood and plastics. B2B buyers should consider their project scale and material types, as these routers may not handle heavy-duty tasks effectively.
Why choose Large Format CNC Routers for high-volume production?
Large format CNC routers offer expansive work areas, often measuring up to 5′ x 10′, making them suitable for businesses involved in furniture making and signage production. Their robust construction supports high-volume output, allowing for intricate designs and the handling of large materials. While they provide excellent production capacity and versatility, the higher cost and space requirements may be a barrier for smaller operations.
How do Industrial CNC Routers meet the demands of heavy industries?
Industrial CNC routers are designed for high-performance applications in sectors such as aerospace and automotive. With spindle power reaching up to 10kW, they deliver exceptional precision and durability for complex machining tasks. Although they represent a significant investment, their advanced automation features and ability to handle demanding materials make them indispensable for businesses focused on high-quality production.
What advantages do Hybrid CNC Routers offer for specialized projects?
Hybrid CNC routers combine traditional routing capabilities with laser or plasma cutting, providing versatility for projects that require intricate designs or metal fabrication. This multi-functional capability allows businesses to streamline operations by utilizing one machine for various tasks. However, buyers should be aware of the higher maintenance needs and initial complexity in setup, which may require specialized training.
When is it beneficial to invest in Custom CNC Routers?
Custom CNC routers are tailored to meet specific operational needs, making them ideal for specialized manufacturing processes. Their modular components allow businesses to scale and adapt their machines as production demands change. While these routers provide a perfect fit for unique requirements, buyers must consider longer lead times and potential higher costs associated with customization.
Key Industrial Applications of router cnc supplier
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of router cnc supplier | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furniture Manufacturing | Custom furniture design and prototyping | Enhances creativity, reduces lead times, and improves precision in production | Supplier’s ability to provide customizable solutions and technical support |
| Aerospace | Component fabrication for aircraft interiors | Ensures lightweight, durable, and precise parts that meet strict regulations | Compliance with industry standards and material specifications |
| Signage and Advertising | Production of custom signage and displays | Increases brand visibility and allows for unique, eye-catching designs | Availability of various materials and sizes, along with quick turnaround times |
| Automotive | Parts manufacturing for vehicle interiors | Improves the quality and customization of vehicle components, enhancing customer satisfaction | Supplier’s experience with automotive-grade materials and precision machining |
| Electronics | Enclosure and panel manufacturing | Provides high precision and customization for electronic products, improving functionality | Sourcing suppliers with expertise in handling delicate materials and intricate designs |
How is the ‘router cnc supplier’ Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture manufacturing sector, router CNC suppliers are pivotal for designing and prototyping custom furniture pieces. These machines allow for intricate designs and accurate cuts, which can significantly reduce lead times and enhance creativity in production. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider suppliers that offer customizable solutions and strong technical support to adapt to their specific needs.
What Role Do Router CNC Suppliers Play in Aerospace Component Fabrication?
Router CNC suppliers are essential in the aerospace industry for fabricating lightweight and durable components, particularly for aircraft interiors. The precision required in this sector is critical, as parts must adhere to strict regulatory standards. International buyers, especially from the Middle East and Europe, need to ensure that suppliers comply with industry regulations and can provide materials that meet aerospace specifications.
How Do Router CNC Suppliers Enhance Signage and Advertising?
In the signage and advertising industry, router CNC suppliers facilitate the production of custom signs and displays that enhance brand visibility. These routers can create unique designs that attract attention, offering a competitive edge in marketing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can provide a variety of materials and sizes, ensuring quick turnaround times to meet the fast-paced demands of this sector.
What Benefits Do Router CNC Suppliers Offer Automotive Parts Manufacturing?
Router CNC suppliers are increasingly being utilized in the automotive sector for manufacturing parts, particularly for vehicle interiors. The ability to customize components enhances customer satisfaction and improves overall quality. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, it’s crucial to select suppliers with experience in automotive-grade materials and precision machining to ensure reliability and performance.
How Do Electronics Manufacturers Benefit from Router CNC Suppliers?
In the electronics industry, router CNC suppliers are instrumental in the manufacturing of enclosures and panels that require high precision and customization. These machines allow for intricate designs that enhance the functionality of electronic products. Buyers should look for suppliers experienced in handling delicate materials, ensuring that they can meet the specific design requirements and quality standards essential for this sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘router cnc supplier’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Machine Specifications and Capabilities
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter confusion when trying to navigate the diverse range of CNC routers available on the market. Each model comes with different specifications, such as spindle power, working area size, and compatibility with materials. This can lead to uncertainty about which machine will best meet their production needs, especially in industries requiring specific performance metrics for materials like wood, metal, or composites. Misunderstanding these specifications can result in purchasing a machine that is either underpowered for the tasks at hand or unnecessarily complex and costly for simpler projects.
The Solution:
To effectively source the right CNC router, buyers should begin by clearly defining their project requirements. This includes understanding the types of materials they will be working with, the volume of production, and the complexity of the designs. Once these needs are established, buyers should engage directly with suppliers to discuss these specifications in detail. Requesting product demonstrations or visiting existing installations can provide insights into machine performance in real-world scenarios. Additionally, leveraging online resources, including user reviews and technical specifications from manufacturers’ websites, can help make informed decisions. Always prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive technical support and guidance, as this will be crucial for optimizing machine performance and ensuring it aligns with operational needs.
Scenario 2: Navigating After-Sales Support and Maintenance
The Problem:
After purchasing a CNC router, many B2B buyers realize that the support offered post-sale can be inadequate. Issues such as technical malfunctions, software updates, and routine maintenance can arise, and without proper support, these challenges can lead to extended downtimes and lost revenue. Buyers in regions with less established supplier networks may find it particularly difficult to access timely repairs and technical assistance, compounding their operational challenges.
The Solution:
Before finalizing a purchase, it is critical for buyers to evaluate the after-sales support provided by router CNC suppliers. This includes assessing the availability of technical support, warranty terms, and the ease of obtaining replacement parts. Buyers should ask suppliers about their response times for service calls and whether they offer on-site support or remote troubleshooting options. It is also beneficial to seek out suppliers that provide comprehensive training on machine operation and maintenance, as this can empower staff to handle minor issues independently. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier who prioritizes customer service will ensure that any future challenges can be addressed quickly, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
Scenario 3: Balancing Cost and Quality in CNC Router Purchases
The Problem:
In an increasingly competitive market, B2B buyers often struggle to balance the cost of CNC routers with the quality they require for their operations. Many suppliers offer low-cost machines that may seem attractive, but these products can compromise on durability and performance, leading to higher long-term costs due to repairs or replacements. Buyers may feel pressured to make a quick purchase based on budget constraints, risking their investment in equipment that does not meet their production standards.
The Solution:
Buyers should approach the purchasing process with a long-term perspective, focusing on total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This involves evaluating the durability, precision, and efficiency of CNC routers offered by suppliers. Engaging with multiple suppliers to compare not just prices, but also warranty conditions, maintenance requirements, and customer service reputation, is essential. Additionally, consider investing in higher-quality machines that might have a higher upfront cost but offer greater reliability and lower operational costs over time. Look for suppliers that offer financing options or leasing arrangements, which can alleviate immediate budget concerns while still securing high-quality equipment. Ultimately, investing time in thorough research and supplier evaluation will lead to more sustainable purchasing decisions that align with business goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for router cnc supplier
What Are the Key Materials Used in CNC Router Applications?
When selecting materials for CNC routers, understanding the properties and implications of each option is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials: wood, aluminum, plastics, and composites, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
How Does Wood Perform as a Material for CNC Routers?
Wood is a traditional material used in CNC machining, known for its versatility and aesthetic appeal. Key properties include its ease of machining and natural insulation. It is generally lightweight and can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Wood is relatively inexpensive, widely available, and offers excellent aesthetic qualities for finished products. It is easy to work with and can be shaped into intricate designs.
Cons: However, wood is susceptible to warping, moisture absorption, and pest damage. Its durability can be less than that of metals or composites, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Wood is ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items but may not be suitable for structural components in high-load scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding wood sourcing and treatment, especially in regions like Europe, where compliance with sustainability standards is critical.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for CNC Router Applications?
Aluminum is increasingly popular in CNC machining due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. It has excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand higher temperatures compared to wood.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, recyclable, and offers a clean finish, making it suitable for both functional and aesthetic applications. Its machinability allows for tight tolerances and intricate designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to wood. Additionally, machining aluminum can lead to tool wear, requiring specialized equipment and maintenance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries, where strength and weight are critical factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential, particularly for industries with stringent safety and quality requirements.
How Do Plastics Compare in CNC Router Applications?
Plastics, including acrylic, PVC, and polycarbonate, are widely used in CNC machining for their versatility and ease of use. They exhibit good chemical resistance and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and available in various colors and finishes. They are easy to machine and can be used for both functional and decorative purposes.
Cons: However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress, leading to deformation.
Impact on Application: They are commonly used for signage, prototypes, and consumer goods where weight and flexibility are more critical than strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use, especially in regions with strict waste management policies.
What Role Do Composites Play in CNC Router Applications?
Composites, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, combine materials to enhance performance characteristics. They are known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to environmental factors.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, durable, and can be tailored for specific applications, making them ideal for high-performance industries.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing and higher costs can be significant barriers to entry for some businesses. Additionally, machining composites requires specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries, where performance and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards and certifications required for composite materials, which can vary significantly by region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Routers
| Material | Typical Use Case for router cnc supplier | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Furniture, cabinetry | Cost-effective, easy to machine | Susceptible to warping and pests | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight, durable | Higher cost, tool wear | High |
| Plastics | Signage, prototypes | Versatile, lightweight | Less durable under stress | Medium |
| Composites | Aerospace, high-performance products | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in CNC router applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for router cnc supplier
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for CNC Router Suppliers?
The manufacturing of CNC routers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the high standards expected by B2B buyers. Understanding these processes can help international buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared in CNC Router Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Suppliers typically use high-quality metals and composite materials, which are essential for the durability and precision of CNC routers. The materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specific standards. This may involve checking for material integrity, surface imperfections, and compatibility with the intended design specifications.
Advanced software is often employed to create precise designs that dictate how materials will be cut and shaped. This stage may also involve pre-treatment processes such as coating or anodizing to enhance material properties and resistance to wear and tear.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Once materials are prepared, forming techniques come into play. The most common methods include CNC machining, laser cutting, and plasma cutting. CNC machining is particularly significant, as it allows for precise shaping and dimensioning of components.
During this stage, components like the frame, gantry, and spindle are manufactured. The use of CNC machines in this process ensures that each part meets exact specifications, which is crucial for the overall performance of the router.
How Is Assembly Conducted for CNC Routers?
Assembly is a meticulous process that requires skilled labor and attention to detail. Components are fitted together according to strict guidelines to ensure structural integrity and functionality. Some suppliers utilize automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and precision, while others might rely on skilled technicians for complex assemblies.
During this phase, various components are integrated, including the drive systems, motors, and electronic controls. Testing is often conducted at this stage to ensure that each assembly meets design specifications before moving on to the finishing phase.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in CNC Router Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves several techniques aimed at enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the CNC router. This includes surface treatments, painting, and coating to protect against corrosion and wear.
In addition, final inspections are conducted to identify any defects or imperfections. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the product not only performs well but also meets the visual standards expected by buyers.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of CNC routers. Suppliers typically adhere to international standards and industry-specific certifications to guarantee product quality.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for CNC Router Suppliers?
The ISO 9001 standard is one of the most recognized quality management systems in the world. It emphasizes a process-oriented approach to quality management, ensuring that suppliers maintain consistent quality in their products and services.
Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) are essential for suppliers targeting markets in Europe. CE certification indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements, making it a crucial factor for international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several critical checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checks are performed to monitor the quality of work-in-progress items. This helps in identifying issues early and making necessary adjustments.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the final product is shipped, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure that all specifications are met. This may include functional testing, performance evaluations, and visual inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods can vary based on the type of CNC router and its intended applications. Common methods include:
-
Functional Testing: Ensures that the CNC router operates according to design specifications.
-
Durability Testing: Assesses the machine’s ability to withstand operational stresses over time.
-
Safety Testing: Verifies that the machine complies with safety regulations to protect users.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are several methods:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Audits?
Conducting audits is an effective way for buyers to assess a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Buyers can either perform these audits themselves or hire third-party firms specializing in supplier evaluations. During an audit, buyers should focus on:
- Reviewing documentation related to quality management systems.
- Inspecting production facilities and equipment.
- Interviewing key personnel about their quality control practices.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Control Reports?
Buyers should not hesitate to ask suppliers for detailed quality control reports. These documents should outline the QA processes, results from various testing phases, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues. Regular reporting can build trust and transparency in the supplier-buyer relationship.
Why Are Third-Party Inspections Important?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly useful for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct thorough audits themselves. Third-party inspectors can evaluate compliance with international standards and verify the quality of the final products.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
International buyers must understand that quality control and certification processes may vary significantly across regions. Suppliers in different countries may adhere to various local regulations and standards, which can impact the quality and safety of the products.
For example, while ISO 9001 is widely recognized, local certifications may also be required in specific markets. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with all relevant standards to avoid potential issues post-purchase.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures that CNC router suppliers employ is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and robust quality control, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘router cnc supplier’
Introduction
Sourcing a reliable router CNC supplier is critical for businesses aiming to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the complexities of procurement. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select a supplier that meets their technical and operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of materials you plan to work with, the size of the work area needed, and the desired spindle power. Having a detailed specification will help you filter out suppliers that cannot meet your needs, saving you time and ensuring you invest in the right machinery.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential router CNC suppliers. Utilize online platforms, trade directories, and industry forums to identify reputable manufacturers. Pay attention to customer reviews and feedback to gauge the reliability and quality of the suppliers you consider.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
Assess the experience and expertise of each supplier. Look for companies with a proven track record in the CNC machining industry, particularly those who have served businesses similar to yours. A supplier’s experience can often translate into better support and more refined products, which is crucial for complex machining tasks.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. Look for ISO certifications and other relevant industry credentials. These certifications are indicators of quality assurance practices and can provide peace of mind regarding the reliability of the equipment you are purchasing.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotes from your top suppliers. These quotes should include pricing, delivery timelines, warranty terms, and after-sales support. Analyzing these details will help you make a cost-effective decision while ensuring you understand the total investment required.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by each supplier. Reliable customer support can significantly impact your operational efficiency, especially in case of machine breakdowns. Inquire about the availability of spare parts, technical support, and maintenance services to ensure you have comprehensive support post-purchase.
Step 7: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Tour
If feasible, visit the supplier’s facility or request a virtual tour. This step allows you to see the manufacturing processes firsthand and assess the quality control measures in place. Observing the production environment can provide insights into the supplier’s capabilities and commitment to quality, helping you make a more informed decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for router CNC suppliers, ensuring they select a partner that aligns with their operational goals and technical requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for router cnc supplier Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing CNC Routers?
When evaluating the cost structure for CNC router suppliers, several components contribute to the overall pricing. These include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-quality components such as steel frames, precision spindles, and advanced electronics can elevate costs significantly. For example, routers designed for heavy-duty applications often require more robust materials, leading to higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Suppliers in regions with higher wages will naturally have increased labor costs, which can affect pricing. Automation in manufacturing can mitigate some of these costs but often requires substantial upfront investment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The need for specialized tooling can add to the cost structure, especially for custom CNC routers. Suppliers may need to invest in unique tools to meet specific client requirements, which can be reflected in the pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC processes ensure the reliability and precision of CNC routers. This can add to costs, but it is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the destination, weight, and size of the machines. International buyers should consider these logistics costs, especially when sourcing from suppliers in different continents.
-
Margin: Supplier margins also play a crucial role in pricing. Established brands with strong reputations may command higher margins, reflecting their perceived value and customer trust.
What Influences Pricing for CNC Routers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CNC routers, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether they need specialized features or if standard models suffice to save on expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Routers made from high-grade materials and those with industry certifications (e.g., ISO) may come with a higher price tag. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, history, and service capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics, which can affect overall costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating CNC Router Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and a thorough understanding of costs are vital:
-
Negotiate with Flexibility: Be open to discussing different configurations or payment terms that can lead to cost savings. Suppliers may be willing to adjust prices for bulk orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operating costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the machine is less reliable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal pricing trends, currency fluctuations, and local market conditions that may affect costs. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from various suppliers can help identify competitive pricing and better understand the market landscape.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC routers can vary widely based on specifications, configurations, and supplier factors. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accuracy in specific purchasing scenarios.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing router cnc supplier With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions in CNC Routing
When exploring the landscape of CNC routing solutions, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives that can meet their operational needs. While router CNC suppliers offer specialized machinery for cutting and carving materials, there are other technologies and methods available that can provide similar functionalities. Understanding these alternatives enables buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific use cases.
Comparison Table of Router CNC Supplier and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Router CNC Supplier | Laser Cutter | 3D Printer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for intricate cuts and designs | Excellent for detailed engraving and cutting | Best for prototyping and custom designs |
| Cost | Moderate to high (e.g., $500 – $30,000) | Moderate to high (e.g., $300 – $25,000) | Varies widely (e.g., $200 – $10,000) |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires setup and calibration | Moderate; requires knowledge of laser safety | Generally easy; plug-and-play models available |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Lower maintenance; periodic lens cleaning required | Minimal; mainly software updates and occasional part replacements |
| Best Use Case | Woodworking, metal fabrication, signage | Engraving, cutting materials like acrylic, wood, and metal | Rapid prototyping, custom models, and small batch production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Cutter
Laser cutters utilize focused light beams to cut or engrave materials with high precision. This technology excels in producing detailed designs and is particularly effective for materials like acrylic, wood, and thin metals.
Pros: Laser cutters offer high accuracy and can create complex designs quickly. They are also versatile, accommodating various materials without needing extensive adjustments.
Cons: The initial investment can be substantial, and the operational costs may increase due to energy consumption and the need for protective gear. Additionally, laser cutting is less effective for thicker materials compared to CNC routers.
3D Printer
3D printers create three-dimensional objects by layering materials such as plastics and resins. This technology is ideal for prototyping and custom designs, allowing users to develop intricate models that would be challenging to produce with traditional methods.
Pros: 3D printers can produce highly customized designs with minimal material waste. They are also increasingly affordable, with many desktop models available for small businesses.
Cons: However, 3D printing is generally slower than CNC routing for large-scale production. The range of materials is often limited compared to CNC routers, particularly for heavy-duty applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right CNC Solution
Selecting the right CNC solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and production volume. For businesses focused on high-precision cutting and fabrication, a router CNC supplier might be the best fit. In contrast, those requiring intricate designs on softer materials may benefit more from a laser cutter. For companies prioritizing rapid prototyping and customization, 3D printing could be the optimal choice. By evaluating these alternatives against their operational needs, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their production capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for router cnc supplier
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Routers for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical specifications of CNC routers is essential for B2B buyers, especially when selecting machines that best fit their operational needs. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Spindle Power
Spindle power, measured in watts (W), indicates the router’s capability to handle various materials. Higher spindle power allows for more efficient cutting and engraving, particularly in harder materials like metal and dense wood. For B2B buyers, selecting the right spindle power is crucial to ensure the router can perform the intended tasks without underperformance or damage. -
Work Area Size
The work area defines the maximum dimensions of the material that can be processed. Common sizes range from compact desktop models (e.g., 300mm x 300mm) to large format routers (e.g., 5′ x 10′). Choosing the correct work area is vital for businesses that need to maximize their production capacity while minimizing waste. -
Material Compatibility
CNC routers are designed to work with various materials, including wood, plastic, and metals. Understanding the material compatibility helps buyers select machines that meet their specific production requirements, ensuring versatility and efficiency in operations. -
Precision and Tolerance
Precision refers to the accuracy of the machine’s movement, often measured in micrometers (μm). Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. High precision and tight tolerances are critical for industries that require intricate designs and consistent quality, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing. -
Drive System
The drive system influences the machine’s speed, accuracy, and overall performance. Common types include stepper motors and servo motors. Buyers should consider the drive system’s capabilities to ensure it aligns with their production goals, especially for high-speed or high-precision applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the CNC Router Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM relationship helps buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure they receive quality products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQs is important for budget management and inventory planning, especially for businesses looking to scale their operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare costs and terms, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery timelines, which are crucial for smooth operations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing customer expectations. -
After-Sales Support
This term encompasses the services provided after the purchase, such as technical support, warranty, and maintenance. Reliable after-sales support is vital for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of CNC routers, making it an important consideration for buyers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the router cnc supplier Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Router CNC Supplier Sector?
The global CNC router market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes across various industries. Key trends include the rise of compact and affordable models catering to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America. These regions are seeing a surge in local craftsmanship and manufacturing initiatives, creating a demand for versatile and cost-effective CNC routers that can handle diverse materials, from wood to metals and plastics.
Additionally, technological advancements such as integrated software solutions and IoT connectivity are transforming CNC routers into smart machines capable of real-time monitoring and analytics. This shift is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making are becoming essential for competitive advantage. As businesses increasingly prioritize customization and rapid prototyping, suppliers that offer modular and scalable solutions are likely to gain traction.
Another notable trend is the growing focus on after-sales support and training services, which are critical for buyers new to CNC technology. Suppliers that provide comprehensive training, maintenance packages, and technical support can differentiate themselves in this competitive landscape, ensuring a smoother transition for buyers looking to integrate CNC routers into their operations.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Being Integrated into the CNC Router Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. The router CNC supplier sector is increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using sustainable materials and minimizing waste during manufacturing. Buyers are actively seeking suppliers that can demonstrate their commitment to reducing environmental impact through certifications and transparent sourcing practices.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence, as businesses recognize the importance of responsible supply chains. This includes ensuring fair labor practices and sourcing raw materials from suppliers that adhere to ethical standards. For instance, certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for wood products and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential benchmarks for buyers assessing supplier credentials.
Moreover, the demand for “green” materials is rising. Buyers are interested in CNC routers that can work with recycled or sustainably sourced materials, aligning with broader corporate sustainability goals. Suppliers that can offer solutions in this space not only enhance their appeal to environmentally conscious buyers but also position themselves as leaders in the transition toward sustainable manufacturing practices.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Routers and Their Impact on Current Sourcing Trends?
The evolution of CNC routers dates back to the 1950s when the first computer-controlled machines were introduced. Initially, these machines were large and expensive, limiting their use to well-established manufacturing companies. Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to the development of more compact, affordable, and user-friendly CNC routers, making them accessible to a broader audience, including SMEs and individual entrepreneurs.
As the technology has advanced, so has the demand for precision and versatility. The introduction of desktop models and customizable CNC routers has empowered small businesses and hobbyists to engage in production activities that were previously the domain of larger enterprises. This democratization of technology is reshaping sourcing trends, as international buyers now seek suppliers that offer not just machines but also support systems that facilitate the integration of CNC technology into diverse business models.
In summary, understanding these historical shifts is crucial for B2B buyers as they navigate the current landscape, ensuring they align their sourcing strategies with the evolving capabilities and market expectations in the router CNC sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of router cnc supplier
-
How do I choose the right CNC router supplier for my business needs?
Choosing the right CNC router supplier involves assessing several key factors. Start by evaluating the supplier’s reputation and experience in the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and testimonials that demonstrate their reliability. Consider the range of products offered—ensure they provide machines that meet your specific requirements in terms of size, power, and capabilities. Also, inquire about their support services, including installation, training, and technical assistance. Finally, compare pricing and payment terms to ensure they align with your budget and cash flow needs. -
What types of CNC routers are best for various applications?
The best CNC router type depends on your specific applications. For woodworking, a standard desktop CNC router with a spindle power of 75W to 300W may suffice. If you require precision for metalworking or larger projects, opt for industrial-grade routers with higher spindle power (700W and above) and larger work areas. For specialized tasks like engraving or intricate designs, consider models with advanced features like dual Z-axis and ball screw drive systems. Assess your project requirements carefully to select the most suitable router. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC routers?
The MOQ for CNC routers varies by supplier and the specific models you are interested in. Many suppliers may offer options for single units, especially for standard models, while customized machines may have higher MOQs due to the bespoke nature of production. When sourcing, always clarify the MOQ with potential suppliers to understand their policies and see if they can accommodate your needs, especially for smaller or emerging businesses that may not require large quantities. -
How can I verify the credibility of a CNC router supplier?
To verify the credibility of a CNC router supplier, conduct thorough research. Check their business registration and certifications, such as ISO standards, which reflect quality assurance processes. Look for industry affiliations and membership in relevant trade organizations. Additionally, seek references from previous clients and request case studies showcasing their work. Consider visiting their facility if possible, or arrange a virtual tour to see their operations firsthand. Online reviews and feedback from industry forums can also provide insights into their reputation. -
What should I consider regarding payment terms when sourcing CNC routers?
When discussing payment terms, consider factors such as the total cost, deposit requirements, and acceptable payment methods. Most suppliers may require a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Ensure you understand the implications of these terms, especially in relation to your cash flow. Additionally, inquire if they offer financing options, extended payment plans, or discounts for early payments, which can be beneficial for managing your budget. -
What is the typical lead time for CNC router orders?
Lead times for CNC router orders can vary significantly based on factors such as the complexity of the machine, customization options, and the supplier’s production capacity. Generally, standard models may have lead times ranging from 2 to 6 weeks, while customized machines could take longer, often between 6 to 12 weeks. Always confirm the estimated delivery timeline with your supplier before placing an order to ensure it aligns with your project schedule and operational needs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my CNC router?
To ensure quality assurance for your CNC router, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes. Ask if they conduct pre-shipment inspections and if they provide a warranty or guarantee on their products. Request documentation related to testing and certification of the machines to ensure they meet industry standards. It’s also beneficial to establish a clear communication channel for reporting issues or concerns post-purchase, ensuring that any problems can be addressed promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC routers?
When importing CNC routers, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Choose a reliable shipping partner experienced in handling machinery to avoid damage during transit. Familiarize yourself with your country’s import regulations and ensure all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, is in order. Additionally, factor in delivery timelines and costs for installation, as these can significantly impact your project’s launch and overall budget.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for router cnc supplier
In summary, strategic sourcing for CNC routers is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and competitive advantage. By focusing on suppliers that offer a diverse range of products—from affordable entry-level machines to high-performance models—buyers can meet specific project needs while maximizing their budget. The ability to customize machines and access robust support services, such as lifetime technical assistance, further enhances the value proposition of sourcing from reputable suppliers.
As global markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable and innovative CNC solutions will only grow. B2B buyers should prioritize establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who demonstrate not only technical expertise but also a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, now is the time to assess your sourcing strategies, embrace technological advancements, and invest in CNC routers that align with your business goals. Take action today to secure partnerships that will empower your operations and drive growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.