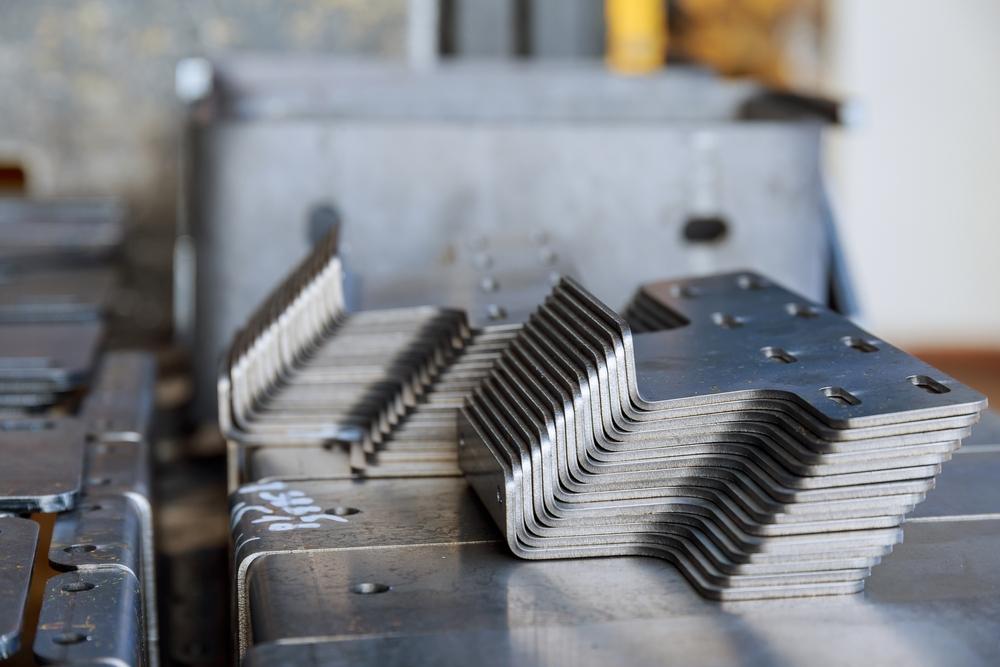
Top 7 Press Brake Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cincinnati Incorporated – XFORM Press
Domain: e-ci.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Cincinnati Incorporated offers a wide range of press brakes including CNC hydraulic, electric, and hybrid models. These machines are designed for precision metal fabrication and are available in tonnages from 40 to 2,000 tons, with single and tandem configurations. Key models include the XFORM Press Brake, Xi for precision sheet metal bending, Goform for compact electric bending solutions, and lar…
2. Press Brake – Key Product Details
Domain: pressbrakebuyersguide.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Press Brake Buyer’s Guide provides information on various press brake models and technologies. Key product details include:
1. **Press Brake Models**: Over 700 models available for comparison, including brands like ACCURL, ADIRA, ALIKO, Bystronic Group, CINCINNATI, LVD, TRUMPF, and more.
2. **Technologies**: Advanced technologies such as BendVision, RapidBend, SmartLink, FlexSpeed, AutoSense, an…
3. Pacific Press – Hydraulic Press Machines
Domain: pacific-press.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Pacific Press manufactures a variety of hydraulic press machines including C-Frame presses, Straight Side & Column presses, and Horizontal presses. Their offerings include robust models like the Press Former and economical options like the Eco-Former series. They provide high-quality American-made press brakes with standard features for precision bending and crafting. Pacific also offers automatio…
4. Bystronic – Precision Press Brakes
Domain: bystronic.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Bystronic press brakes are designed for precision bending of sheet metal. They feature advanced technology for high efficiency and flexibility in production. Key attributes include: high bending accuracy, user-friendly interface, and the ability to handle various materials and thicknesses. The press brakes are equipped with innovative safety features and can be integrated into automated production…
5. ACCURL – 4 Axis CNC Hydraulic Press Brake
Domain: accurl.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: ACCURL 4 Axis CNC Hydraulic Press Brake, 400 ton x 4000 mm, DELEM DA58T CNC Press Brake Machine, manufactured in China.
6. Boschert – ElectroBend Series Press Brakes
Domain: boschertusa.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: The ElectroBend Series features servo electric press brakes that offer bending force capacities of 60, 80, and 100 tons. They are designed for higher output, accuracy, and reliability, with ram speeds that outperform competitors, resulting in some of the fastest bending cycle times on the market. The ElectroBend press brakes consume 50% less energy compared to hydraulic models and eliminate the ne…
7. Press Brakes – Accurl, Yawei, Durma, Dener, Emarksan
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Chinese press brakes mentioned include brands such as Accurl and Yawei. Turkish brands mentioned are Durma, Dener, and Emarksan. The quality of Chinese and Turkish press brakes is noted to be virtually the same, depending on the region. It is advised to consider after-sale support when purchasing, as machines may require assistance regardless of origin.
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for press brake manufacturer
In the ever-evolving landscape of metal fabrication, sourcing high-quality press brake manufacturers can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With a myriad of options ranging from CNC hydraulic to electric and hybrid models, understanding the nuances of each type is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into the various press brake technologies, applications across industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—especially in regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany—making informed purchasing decisions is essential to enhance operational efficiency and maximize ROI. We explore key features such as automation integration, dynamic thickness compensation, and advanced control systems that can significantly boost productivity and reduce scrap rates.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of market trends, this guide empowers them to navigate the global market with confidence. Whether you are looking to upgrade existing machinery or invest in new technology, understanding the capabilities and offerings of leading press brake manufacturers will ensure that your business remains competitive in today’s fast-paced industrial environment.
Understanding press brake manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Press Brakes | Utilizes hydraulic systems for bending, offers high tonnage options | Heavy manufacturing, automotive, aerospace | Pros: High power, versatile; Cons: Slower setup, higher maintenance needs. |
| Electric Press Brakes | Operates with electric drives, typically more energy-efficient and quieter | Precision metal fabrication, light manufacturing | Pros: Energy-efficient, low noise; Cons: Limited tonnage compared to hydraulic. |
| Hybrid Press Brakes | Combines hydraulic and electric technologies for flexibility | Diverse industries needing both power and precision | Pros: Best of both worlds; Cons: Potentially higher cost. |
| C-Frame Press Brakes | Compact design, suitable for smaller spaces and lighter applications | Small to medium-scale fabrication | Pros: Space-saving, economical; Cons: Limited tonnage and capabilities. |
| Tandem Press Brakes | Utilizes two or more press brakes working in unison for larger parts | Large-scale manufacturing, heavy-duty applications | Pros: Increased production capacity; Cons: More complex setup and operation. |
What are the Characteristics of Hydraulic Press Brakes?
Hydraulic press brakes are characterized by their use of hydraulic systems to generate high force, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can handle a wide range of materials and thicknesses, which is essential in industries like automotive and aerospace. When considering a hydraulic press brake, buyers should evaluate the tonnage capacity required for their operations and factor in the potential for higher maintenance costs associated with hydraulic systems.
How Do Electric Press Brakes Stand Out?
Electric press brakes leverage electric drives, which provide greater energy efficiency and quieter operation compared to hydraulic models. They are ideal for precision metal fabrication where high accuracy is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects, as electric press brakes may have limitations in tonnage compared to their hydraulic counterparts. Their operational efficiency often results in lower long-term costs, making them appealing for businesses focused on sustainability.
What Makes Hybrid Press Brakes a Versatile Choice?
Hybrid press brakes merge hydraulic and electric technologies, offering the advantages of both systems. They are particularly beneficial for companies that require flexibility in production, allowing for both high power and precision. When purchasing a hybrid press brake, businesses should assess their production needs and budget, as these machines can come at a higher initial investment but may provide better overall efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Why Choose C-Frame Press Brakes for Smaller Applications?
C-Frame press brakes are designed for lighter applications and are compact, making them suitable for smaller manufacturing spaces. They are often more economical and easier to operate, appealing to small to medium-scale fabricators. Buyers should weigh their production needs against the limited tonnage and capabilities of C-Frame models, ensuring that the chosen machine aligns with their operational goals.
How Do Tandem Press Brakes Enhance Production Capacity?
Tandem press brakes operate multiple machines simultaneously to increase production capacity for larger parts. They are particularly useful in large-scale manufacturing environments where efficiency is crucial. Companies considering tandem setups should evaluate the complexity of operation and the need for skilled operators, as the configuration can be more challenging than single-unit machines. However, the potential for higher output can significantly benefit businesses aiming to meet high demand.
Key Industrial Applications of press brake manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of press brake manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Bending components for vehicle frames and panels | Improved accuracy and reduced scrap rates | Compatibility with various materials and tonnage capacity |
| Construction | Forming structural steel beams and reinforcements | Enhanced structural integrity and project durability | Customization options for specific project requirements |
| Aerospace | Precision bending of aircraft parts and components | High precision and compliance with safety regulations | Certifications and standards compliance for aerospace parts |
| HVAC Industry | Fabrication of ductwork and ventilation systems | Efficient production processes and reduced lead times | Flexibility in handling different material thicknesses |
| Electronics | Bending enclosures for electronic devices | Cost-effective production and improved product design | Integration capabilities with automation systems |
How Are Press Brakes Utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, press brakes play a crucial role in bending components for vehicle frames and panels. These machines provide the precision necessary for creating intricate shapes required in modern vehicle designs. By using advanced CNC technology, manufacturers can significantly reduce scrap rates and enhance overall production efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing press brakes that can handle diverse materials, as well as those that offer varying tonnage capacities to accommodate different automotive applications.
What Are the Applications of Press Brakes in Construction?
In construction, press brakes are essential for forming structural steel beams and reinforcements. They enable the fabrication of components that are critical for ensuring the structural integrity of buildings and infrastructure. The use of high-quality press brakes results in durable and reliable constructions. When sourcing equipment for this industry, businesses should look for machines that can be customized to meet specific project requirements, ensuring they can handle the unique demands of each construction job.
How Do Press Brakes Benefit the Aerospace Industry?
The aerospace industry relies on precision bending for aircraft parts and components, where safety and accuracy are paramount. Press brakes equipped with advanced monitoring systems can ensure that bends meet stringent safety regulations. This capability is vital for maintaining compliance and ensuring the reliability of aircraft structures. Buyers from this sector must focus on sourcing press brakes that meet specific certifications and standards to guarantee the quality and safety of aerospace components.
What Role Do Press Brakes Play in the HVAC Industry?
In the HVAC industry, press brakes are used to fabricate ductwork and ventilation systems. These machines allow for efficient production processes, enabling manufacturers to meet tight deadlines while maintaining high quality. With the capability to handle various material thicknesses, press brakes ensure that components fit perfectly in installations. Buyers should consider sourcing machines that offer flexibility in operation and can efficiently manage different types of materials to optimize their production capabilities.
How Are Press Brakes Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
For the electronics industry, press brakes are instrumental in bending enclosures for electronic devices. This application necessitates a balance of cost-effectiveness and precise design to meet market demands. By utilizing advanced bending technology, manufacturers can streamline production and reduce lead times. When sourcing press brakes for electronics, businesses should evaluate the integration capabilities with automation systems to enhance their production efficiency and adapt to evolving manufacturing processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘press brake manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Production Due to Setup Time Delays
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the metal fabrication industry face significant challenges with long setup times when using press brakes. This inefficiency can lead to reduced productivity, increased labor costs, and ultimately, a negative impact on profitability. For instance, a manufacturer may find that changing the tooling or adjusting the machine settings for different jobs can take hours, resulting in downtime that could have been spent on actual production. This is particularly problematic for companies that require high flexibility and quick turnaround times to meet customer demands.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, buyers should invest in press brakes equipped with advanced automation features such as quick-change tooling systems and digital control interfaces. These innovations allow for rapid adjustments and setup, significantly reducing the time required between jobs. Additionally, integrating a real-time monitoring system can provide insights into the setup process, helping operators to streamline workflows. Buyers should also consider partnering with manufacturers that offer comprehensive training programs, ensuring that operators are proficient in using the equipment to its fullest potential, thereby minimizing setup times and maximizing productivity.
Scenario 2: Quality Control Issues Leading to High Scrap Rates
The Problem: Inconsistent product quality is a major concern for B2B buyers who rely on press brakes for precision bending. Variability in the bending process can lead to defective parts, resulting in high scrap rates and increased costs. For example, a company may experience significant waste when bends do not meet specifications, forcing them to discard or rework materials. This not only affects profit margins but can also jeopardize customer satisfaction and long-term relationships.
The Solution: To enhance quality control, buyers should look for press brake manufacturers that offer machines with built-in monitoring technologies, such as in-process angle correction systems. These systems, like LVD’s Easy-Form® technology, continuously check the bend angle in real-time and make automatic adjustments, ensuring that every part is produced to specification. Furthermore, investing in training for staff on the importance of quality checks at each stage of the bending process can foster a culture of quality within the organization. Regular maintenance of the equipment is also crucial; a well-maintained machine is less likely to produce defects, thus reducing scrap rates and associated costs.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Energy Consumption
The Problem: Energy costs can be a hidden but significant pain point for manufacturers using traditional hydraulic press brakes. Many businesses experience rising utility bills, which can severely impact operational budgets. For instance, a manufacturer using older hydraulic models may find that their machines consume excessive amounts of power, leading to inflated operating costs that erode profit margins.
The Solution: Buyers should consider investing in energy-efficient press brake models, such as electric or hybrid press brakes, which offer substantial energy savings compared to traditional hydraulic systems. For example, electric press brakes consume power only when they are in operation, reducing idle energy consumption. Additionally, manufacturers should conduct a thorough energy audit to identify inefficiencies within their existing operations and explore options for upgrading or retrofitting older machines with energy-saving technologies. By implementing these strategies, companies can significantly lower their energy bills while enhancing their sustainability practices, which is increasingly important in today’s eco-conscious market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for press brake manufacturer
When selecting materials for press brake manufacturing, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications of various materials. This analysis will focus on four common materials: Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Tool Steel. Each material has unique characteristics that impact its suitability for different applications in the press brake industry.
What are the Key Properties of Mild Steel for Press Brake Applications?
Mild steel, known for its ductility and weldability, is a popular choice in the press brake industry. It has a temperature rating up to 300°C and can withstand moderate pressure. Mild steel exhibits good corrosion resistance when properly coated, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Mild steel is cost-effective, easy to machine, and readily available, which makes it ideal for high-volume production. Its good strength-to-weight ratio allows for efficient designs.
Cons: While it is durable, mild steel is susceptible to rust without protective coatings. Additionally, it may not perform well in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Mild steel is commonly used for general-purpose applications in manufacturing and construction, where high strength and ductility are required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36. In Europe, adherence to EN standards is crucial.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for Press Brake Manufacturing?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it suitable for various demanding applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 800°C and has a high tensile strength.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to corrosion make stainless steel ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments. It also requires less maintenance compared to mild steel.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost and manufacturing complexity. Stainless steel can be more challenging to machine and form, leading to increased production costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in the food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel that comply with local regulations, such as AISI 304 or 316 in the U.S. and EN 1.4301 or 1.4401 in Europe.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Press Brake Applications?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it a favored choice for applications requiring reduced weight. It can withstand temperatures up to 500°C and is easy to form and machine.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for reduced transportation costs and easier handling. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Cons: Aluminum has a lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive than mild steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where weight reduction is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheets and plates. In Europe, EN 573-3 standards are applicable.
What Role Does Tool Steel Play in Press Brake Manufacturing?
Tool steel is specifically designed for high-performance applications, offering exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for tooling applications.
Pros: Tool steel’s durability and ability to maintain a sharp edge make it suitable for high-precision applications. It is also resistant to deformation under stress.
Cons: The primary limitation is its high cost and the complexity involved in machining. Tool steel requires specialized tools and processes, which can increase manufacturing lead times.
Impact on Application: Tool steel is often used for dies and molds in the manufacturing process, where precision and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A681 or JIS G4404 is essential for tool steel buyers, particularly in regions with strict quality regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Press Brake Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for press brake manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | General-purpose applications | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Susceptible to rust without coatings | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Tool Steel | Dies and molds for high-precision applications | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | High cost and complex machining | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for press brake manufacturers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for press brake manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Press Brakes?
The manufacturing process for press brakes typically consists of several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical to producing high-quality machines that meet the precise requirements of various industries.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing high-grade materials, such as steel and aluminum, which are essential for the structural integrity and longevity of press brakes. Suppliers often perform chemical and mechanical tests on materials to ensure they meet specific industry standards. Advanced CNC technology is used to cut and shape materials into the required components, ensuring precision from the outset.
-
Forming: Once the materials are prepared, they undergo a forming process, which involves bending, pressing, and shaping into the desired configurations. This stage often utilizes hydraulic or electric systems to apply force efficiently. The use of CNC technology in forming helps to maintain accuracy and repeatability, which is crucial for high-volume production.
-
Assembly: After forming, the components are assembled into a complete press brake. This stage involves fitting together various parts, including the frame, ram, and control systems. Manufacturers may employ robotic assembly techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Each assembly line typically follows a strict protocol to ensure that all components fit together perfectly.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatments, such as painting or powder coating, to enhance durability and aesthetics. Additionally, manufacturers conduct final inspections to ensure that the machine meets all specifications before shipping. This stage may also involve calibrating the press brake to ensure optimal performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to ensuring that press brakes meet international standards and customer expectations. Manufacturers often adhere to various standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for certain applications, are crucial for compliance.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs when materials arrive at the manufacturing facility. QA teams inspect materials for defects, dimensions, and compliance with specifications. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned to the supplier, ensuring that only high-quality components enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor production. These may include regular inspections of critical dimensions and functionality tests at different stages of assembly. The use of automated monitoring systems can help detect deviations from specifications in real time, allowing for immediate corrective action.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before a press brake is shipped, a thorough final inspection is conducted. This includes testing the machine’s functionality, calibration checks, and verifying compliance with safety standards. Manufacturers often conduct load testing to ensure the machine can handle its rated tonnage without issues.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Press Brakes?
Testing methods vary widely, but several are commonly employed to ensure the quality and reliability of press brakes:
-
Load Testing: This involves applying a load to the press brake to ensure it can operate within its specified tonnage without failure. This test is crucial for identifying potential weaknesses in the structure or hydraulic systems.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measurement tools, QA teams verify that all dimensions of the machine match specified tolerances. This is essential for ensuring that the press brake will operate correctly and produce parts to specification.
-
Functional Testing: Manufacturers often conduct functional tests to ensure that all controls, safety features, and automation systems operate as intended. This testing phase is vital for identifying any operational issues before the equipment is delivered to the customer.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control?
B2B buyers seeking to verify a supplier’s quality control practices can take several proactive steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures firsthand. This is an opportunity to review documentation, observe production practices, and evaluate the overall facility.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed QA reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC, can provide insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality. These reports should include data on defect rates, corrective actions taken, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent evaluators can provide unbiased assessments of a supplier’s quality control processes and product performance.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Different regions have specific standards and regulations that manufacturers must comply with. For example, European buyers will prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may look for compliance with GSO standards.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulations in their region, which may affect the types of certifications required for press brakes. This knowledge ensures that they select suppliers who meet local compliance standards.
-
International Certifications: Buyers should look for suppliers with internationally recognized certifications, such as ISO 9001, as these indicate a commitment to quality management practices that meet global standards.
-
Cultural and Market Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may face different market dynamics and cultural considerations that influence supplier selection. Building strong relationships and open communication with suppliers can help navigate these complexities.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of press brake manufacturers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and high-quality equipment.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘press brake manufacturer’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure press brake manufacturing equipment. By following these steps, you will ensure a thorough evaluation process, leading to informed purchasing decisions that align with your business’s needs and goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your requirements for the press brake. Consider factors such as tonnage capacity, bending length, and the types of materials you will be working with.
– Why it matters: Precise specifications help narrow down your options and ensure the machine can handle your production demands.
– What to look for: Evaluate the range of models available from manufacturers to find those that meet your technical needs.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Compile a list of reputable press brake manufacturers. Utilize online directories, industry publications, and trade shows to discover potential suppliers.
– Why it matters: A well-researched list gives you a starting point for comparisons and helps you identify manufacturers known for quality and reliability.
– What to look for: Focus on suppliers with a solid track record in your target region, such as Africa or Europe, as regional support can be crucial.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Why it matters: Understanding a supplier’s capabilities and history helps mitigate risks associated with quality and service.
– What to look for: Look for testimonials and case studies that demonstrate their experience with projects similar to yours.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers you are considering have the necessary certifications, such as ISO or CE marks, which indicate compliance with international quality standards.
– Why it matters: Certifications are a mark of reliability and quality assurance, essential for long-term investment in machinery.
– What to look for: Request documentation of certifications and verify them through relevant industry bodies.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Investigate the after-sales support provided by each manufacturer, including maintenance services, spare parts availability, and training for your staff.
– Why it matters: Good after-sales support ensures minimal downtime and helps your team maximize the machine’s capabilities.
– What to look for: Evaluate the responsiveness and reputation of the supplier’s service team, and consider any training programs they offer.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, arrange for machine demonstrations or trials to see the press brake in action.
– Why it matters: Observing the machine’s performance in real-world conditions allows you to assess its efficiency and suitability for your operations.
– What to look for: Pay attention to the ease of use, the precision of bends, and the overall build quality during the demonstration.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Finally, analyze the pricing of different models, but also consider the total cost of ownership, including energy consumption, maintenance, and potential downtime.
– Why it matters: The lowest initial price may not be the best value if long-term costs are high.
– What to look for: Request detailed quotes that include all potential costs to make an informed comparison between suppliers.
By following this structured checklist, you will be better equipped to select a press brake manufacturer that meets your operational requirements and supports your business’s growth.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for press brake manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Press Brake Manufacturing?
When sourcing press brakes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. High-grade steel and advanced components for hydraulic systems can raise costs but also enhance durability and performance. Buyers should inquire about material specifications to ensure they align with their operational needs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs might produce machines with more advanced technology, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead, which can be a point of negotiation for buyers.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often a hidden expense. Custom tooling for specific applications can increase initial costs but may lead to better performance and reduced cycle times in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): A rigorous QC process ensures that the machinery meets industry standards and customer specifications. While this adds to the upfront cost, it can reduce maintenance and operational issues, providing long-term savings.
-
Logistics: The costs associated with transporting the machines, including shipping and handling, can vary widely. International buyers should consider local tariffs and customs duties, which can significantly impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin based on their production costs and market demand. Understanding the margin can provide insight into the flexibility for negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Press Brake Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of press brakes, making it essential for buyers to consider these elements:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Manufacturers may offer reduced pricing for larger orders, allowing buyers to negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to get accurate quotes and avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The type of materials used and the presence of quality certifications can impact price. Machines built with higher-quality materials or those certified by reputable standards may command higher prices but offer better longevity and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their machines often come with robust support services and warranties.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the final price, including who bears the risk and costs during shipping.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
To maximize value when sourcing press brakes, international buyers should employ several strategies:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the average pricing in the market can empower buyers during negotiations. Tools like industry reports and competitor analysis can provide valuable insights.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Highlighting TCO can justify a higher upfront cost if long-term savings are evident.
-
Negotiate Terms: Discuss payment terms and delivery schedules. Flexible payment options can ease cash flow concerns, making it easier to close deals.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often result in preferential treatment and discounts.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary significantly across regions due to economic conditions, tariffs, and local demand. Understanding these nuances helps buyers make informed decisions.
Conclusion
While sourcing press brakes, being aware of the cost components, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies can lead to significant savings and better machine performance. Buyers should approach negotiations with a comprehensive understanding of their needs and the market landscape to achieve optimal results.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing press brake manufacturer With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Press Brake Manufacturing
In the landscape of metal fabrication, selecting the right equipment is critical for achieving precision and efficiency. While traditional press brake manufacturers offer robust solutions for bending metal, various alternatives exist that can also fulfill similar objectives. Understanding these alternatives enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Comparison of Press Brake Manufacturer with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Press Brake Manufacturer | Hydraulic Shearing Machines | CNC Laser Cutting Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and versatility for complex bends | Excellent for straight cuts but limited in bending | Exceptional precision for intricate designs; not limited to bending |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, but long-term ROI through efficiency | Generally lower upfront costs, but may require additional equipment for bending | Higher costs associated with technology and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators for optimal use | Easier to operate for basic cuts, less training needed | Steeper learning curve; requires skilled technicians for programming |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts can be expensive | Lower maintenance; simpler mechanics | High maintenance costs; sensitive components |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for diverse applications requiring various bend angles and materials | Best for high-volume production of flat parts | Suitable for complex designs needing high precision and flexibility |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hydraulic Shearing Machines
Hydraulic shearing machines excel in cutting flat sheets of metal and are often less expensive than traditional press brakes. They are particularly effective for high-volume production where straight cuts are required. However, their limitations in bending capabilities mean that additional equipment may be necessary for projects that require shaping metal, leading to potential increased costs and space requirements.
CNC Laser Cutting Systems
CNC laser cutting systems offer unparalleled precision and versatility in metal fabrication, allowing for intricate designs and cuts that traditional press brakes cannot achieve. They are particularly useful in industries requiring complex shapes and details, such as aerospace and automotive. However, the high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be prohibitive for smaller operations. Additionally, the learning curve for programming and operation is steeper, necessitating skilled labor.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between a press brake manufacturer and alternative solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the types of projects they typically undertake. If your work primarily involves complex bending operations, investing in a reliable press brake may be the best option despite the higher costs. Conversely, if your needs lean towards high-volume, flat sheet production or intricate cutting, hydraulic shearing machines or CNC laser systems may offer more cost-effective and efficient solutions. Ultimately, evaluating the performance, cost, and suitability of each option is crucial for optimizing productivity and achieving long-term success in metal fabrication.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for press brake manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Press Brakes That B2B Buyers Should Consider?
When evaluating press brakes, several technical specifications play a crucial role in determining the machine’s performance and suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Tonnage Capacity
Tonnage refers to the maximum force the press brake can exert, measured in tons. Common capacities range from 40 tons for smaller applications to over 2,000 tons for heavy-duty operations. Understanding the required tonnage is vital for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts the thickness and type of materials that can be bent effectively. -
Bending Length
This specification indicates the maximum length of the sheet metal that can be processed in a single operation. Bending lengths typically vary from 2 meters to over 4 meters. Selecting the appropriate bending length ensures that the machine can accommodate the specific dimensions of the materials being used, which is crucial for operational efficiency. -
Accuracy and Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In the context of press brakes, it refers to the precision of the bend angles and dimensions. High accuracy is essential for industries requiring tight tolerances, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where even minor deviations can lead to significant issues in assembly and performance. -
Back Gauge System
This feature helps in positioning the material accurately before bending. Advanced back gauge systems, often CNC-controlled, enhance repeatability and reduce setup time. For B2B buyers, a reliable back gauge system can significantly boost productivity and minimize waste, making it a critical factor in the purchasing decision. -
Drive System Type
Press brakes can be hydraulic, mechanical, or electric. Each type has its advantages: hydraulic systems offer high force and flexibility, electric systems provide energy efficiency and lower operating costs, and mechanical systems are known for speed and precision. Understanding these differences helps buyers choose the most suitable machine for their specific production needs. -
Material Compatibility
The type of materials that can be processed by a press brake is another important consideration. Different machines are designed to handle various material grades, including aluminum, steel, and stainless steel. B2B buyers should assess their material requirements to ensure they select a machine capable of handling their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Press Brake Industry That Buyers Should Know?
Navigating the press brake market involves familiarity with certain industry jargon. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure they are purchasing high-quality machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest order size a supplier is willing to accept. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who may be looking to procure multiple machines or components. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory planning. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings during the purchasing process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for production planning, especially for businesses that rely on timely delivery to meet customer demands. -
Aftermarket Support
This term encompasses services provided after the initial sale, such as maintenance, repair, and training. Buyers should consider the level of aftermarket support offered by manufacturers to ensure they can maintain and optimize their press brake investment over time.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting press brakes, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and productivity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the press brake manufacturer Sector
What Are the Key Drivers of Change in the Press Brake Manufacturing Market?
The global press brake manufacturing market is witnessing significant transformation driven by several key factors. A surge in demand for precision metal fabrication across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, is propelling growth. As manufacturers strive for enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs, there is a growing emphasis on advanced technologies such as CNC automation, real-time monitoring systems, and AI integration. These technologies not only optimize the bending process but also improve overall efficiency and accuracy, which are critical for meeting the stringent quality requirements of international markets.
Moreover, the shift towards sustainability is becoming increasingly influential. B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that implement environmentally friendly practices and offer energy-efficient machines. This trend is particularly prominent in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent, and in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where there is a rising awareness of sustainable practices. Additionally, the market is seeing a diversification of sourcing strategies, with many buyers opting for localized suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. This shift not only enhances supply chain resilience but also fosters stronger relationships with regional manufacturers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Press Brake Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are gaining traction in the press brake manufacturing sector, driven by increasing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted many companies to adopt greener practices. For instance, manufacturers are now integrating energy-efficient designs and materials that reduce the carbon footprint of their machines. This not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers.
Furthermore, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the sourcing practices of their suppliers, favoring those who demonstrate a commitment to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for manufacturers aiming to establish credibility and trust with their international clients. By prioritizing these aspects, press brake manufacturers can enhance their brand reputation and create a competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Press Brake Manufacturing and Its Evolution?
The evolution of press brake manufacturing can be traced back to the early 19th century, when simple mechanical devices were first introduced for metal bending. The introduction of hydraulic technology in the mid-20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater force application and versatility in bending operations. As industries advanced, so did the need for precision and automation, leading to the development of CNC-controlled press brakes in the 1980s.
Today, the market is characterized by a blend of traditional craftsmanship and cutting-edge technology, with manufacturers focusing on smart features such as real-time monitoring and automated adjustments. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to the increasing complexity of metal fabrication tasks and the demand for higher quality and efficiency from B2B buyers across the globe. By understanding this historical context, international buyers can better appreciate the technological advancements and innovations that continue to shape the press brake manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of press brake manufacturer
-
How do I choose the right press brake manufacturer for my needs?
Selecting the right press brake manufacturer involves assessing your specific production requirements, such as tonnage, bending length, and material types. Research potential manufacturers’ reputations, ensuring they have a proven track record in quality and reliability. Look for certifications and customer testimonials that confirm their expertise. Additionally, consider their technological offerings, such as automation and integration capabilities, which can enhance efficiency. Finally, evaluate their after-sales support, including maintenance and training services, to ensure long-term operational success. -
What are the key features to consider in a press brake?
When evaluating press brakes, focus on features that enhance precision and efficiency. Important aspects include the machine’s tonnage capacity, bending length, and whether it has CNC controls for automation. Advanced features like dynamic thickness compensation, sheet-following systems, and in-process angle monitoring can significantly improve accuracy and reduce waste. Additionally, consider the machine’s construction quality, as robust builds typically offer better longevity and reliability under high production demands. -
What customization options are typically available for press brakes?
Many manufacturers offer a range of customization options to tailor press brakes to specific applications. Common customizations include adjusting tonnage and bending lengths, integrating specialized tooling, and incorporating advanced control systems for automation. Some manufacturers also provide bespoke solutions for unique bending requirements or industry-specific needs. Discussing your requirements upfront with the manufacturer can help ensure the machine meets your operational goals without compromising on efficiency. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for press brakes?
MOQs for press brakes can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the machine. Some manufacturers may have no MOQ for standard models, while others may require a minimum order for custom configurations or specialized machines. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during initial discussions, as this can impact your budgeting and production planning. Additionally, consider the potential for bulk discounts if you plan to order multiple machines. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a press brake?
Payment terms for press brakes can vary widely among manufacturers. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or installment plans to ease the financial burden. Always review the payment terms carefully and ensure they align with your cash flow capabilities. Transparent communication about payment schedules can facilitate a smoother transaction and build a good relationship with the supplier. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my press brake purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, verify that the manufacturer adheres to recognized international standards, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation of their quality control processes and ask for details on testing procedures for the machines prior to shipment. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, as these can provide assurance of the machine’s reliability. On-site inspections or third-party assessments can also be beneficial, especially for high-value equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing a press brake?
When sourcing a press brake internationally, logistics play a crucial role. Consider the shipping methods available, as well as the associated costs and transit times. Customs regulations in your country can affect delivery times and require specific documentation, so ensure that the manufacturer can assist with customs clearance. Additionally, plan for the machine’s installation and any required training, as these factors can influence your overall project timeline and operational readiness. -
How can I vet a press brake manufacturer before making a purchase?
To effectively vet a press brake manufacturer, start by researching their industry reputation and customer reviews. Seek out case studies or testimonials from businesses similar to yours that have purchased from them. Evaluate their experience in your specific industry and their ability to provide tailored solutions. Additionally, consider visiting their facility or attending industry trade shows to witness their manufacturing processes firsthand. Establishing direct communication with their sales and technical teams can also provide valuable insights into their reliability and customer service commitment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for press brake manufacturer
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Press Brake Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking press brakes. By focusing on quality, technological advancements, and supplier reliability, companies can ensure they invest in machines that not only meet current needs but also support long-term operational efficiency. Key features such as automation capabilities, dynamic thickness compensation, and energy-efficient designs can significantly enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
Moreover, understanding the diverse offerings from manufacturers—ranging from hydraulic to electric and hybrid models—enables buyers to tailor their investments to specific production requirements. This informed approach not only mitigates risks but also leverages supplier expertise, fostering strong partnerships that can yield ongoing support and innovation.
As we look to the future, the demand for advanced, sustainable manufacturing solutions will only grow. International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should proactively engage with leading press brake manufacturers to explore the latest technologies and capabilities. Investing in the right press brake today will pave the way for operational excellence tomorrow. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your manufacturing processes and drive competitive advantage.