Top 6 Shaft Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Empower Manufacturing – Custom Shaft Solutions
Domain: empowermfg.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
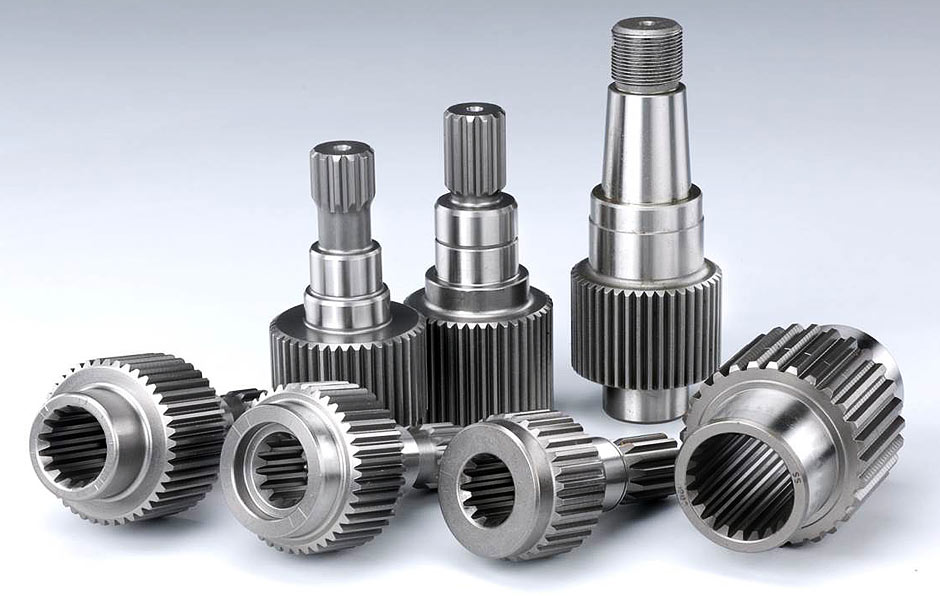
Introduction: Empower Manufacturing specializes in custom shaft manufacturing with over 40 years of experience. They offer precision-crafted shafts made to specifications, with capabilities including: achieving TIR of .001″, ground diameters up to 0.0001″ tolerance, diameters up to 24″, turned lengths up to 120″, and OD grinding up to 168″ long. They provide tailored solutions using state-of-the-art technology,…
2. Western Machine – Shaft Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: westernmachine.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Shaft Manufacturing Services for Heavy Industry, providing comprehensive solutions including dimensional inspection, non-destructive testing, shaft design with strength calculations, metallurgical analysis, reverse engineering, CNC turning and machining, custom tooling, shaft liners manufacturing, hydrostatic and spark testing, quality control, project management, and transportation services. Capa…
3. Mitsubishi – Tensei 1k Orange
Domain: shaftshack.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: ShaftShack.com offers a variety of golf shafts for demo and purchase, including driver shafts, 3-wood shafts, and hybrid shafts from brands such as Aldila, Graphite Design, Fujikura, Mitsubishi, Oban, Project X, and Veylix. Featured demo products include: 1. MITSUBISHI Tensei 1k Orange: Low-Launch Low-Spin Demo Driver Golf Shaft for $20.00 2. Graphite Design Tour AD VF: Low-Launch & Low-Spin Demo …
4. Riten Industries – Workholding Solutions
Domain: riten.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Riten Industries offers a comprehensive range of workholding products for shaft manufacturing, including standard and custom solutions. Key products include mechanical and hydraulically compensating face drivers, CNC heavy duty live centers, spline rolling live centers, special knife drivers, expanding mandrels, external clamping systems, and standard or special tailstock centers. Riten’s live cen…
5. True Temper – Key Golf Shafts
Domain: truetempersports.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: True Temper Golf Shafts – Key Products: 1. Dynamic Gold – Trusted by professionals, available in various models including Dynamic Gold MID. 2. Project X – Bold designs for tour-level performance. 3. Elevate AMT – Innovative design for improved performance. 4. Vector – Retired models available. 5. Cypher – Graphite iron and wedge shafts. 6. SteelFiber – Combines steel and graphite for performance. …
6. GolfWorks – Key Product
Domain: golfworks.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Key product details include a variety of golf club shafts from brands such as True Temper, UST Mamiya, KBS, Mitsubishi, Project X, Aldila, Fujikura, Maltby, Graphite Design, Accra, Nippon, Aerotech, Grafalloy, KINETIXX, Graftech, and FST. The shafts are available in materials like graphite (209 options) and steel (131 options). They cater to different club types including driver/wood (113), fairwa…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shaft manufacturer
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality shafts that meet specific operational requirements can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers. The intricate nature of shaft manufacturing—encompassing diverse applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy—demands a thorough understanding of various factors, including material selection, design specifications, and supplier capabilities. This guide serves as an essential resource, providing insights into the different types of shafts, their applications, and the nuances of the manufacturing process.
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe will find value in our comprehensive exploration of supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and quality assurance standards. By examining case studies and industry best practices, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability. Whether you’re navigating the complexities of custom shaft specifications or seeking reliable suppliers with global shipping capabilities, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to streamline your sourcing strategy and secure the best solutions for your business needs.
Understanding shaft manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Shaft Manufacturer | Tailored designs, CNC machining, reverse engineering | Aerospace, Automotive, Oil & Gas | Pros: Precision engineering, tailored solutions. Cons: Longer lead times, potentially higher costs. |
| Forged Shaft Manufacturer | Utilizes forging techniques for strength and durability | Heavy Machinery, Mining, Marine | Pros: Superior strength, high durability. Cons: Limited design flexibility, higher material costs. |
| Graphite Shaft Manufacturer | Lightweight, flexible designs for specific applications | Golf, Sports Equipment | Pros: Enhanced performance, improved feel. Cons: More expensive materials, limited strength compared to metals. |
| Standard Shaft Manufacturer | Mass-produced shafts adhering to industry standards | Manufacturing, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Cost-effective, quick delivery. Cons: Less customization, potential quality variability. |
| Composite Shaft Manufacturer | Made from composite materials for specific performance needs | Aerospace, Automotive, Marine | Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant. Cons: Can be more expensive, requires specialized knowledge for handling. |
What Are the Characteristics of Custom Shaft Manufacturers?
Custom shaft manufacturers focus on creating tailored solutions to meet specific client requirements. They often employ advanced CNC machining and reverse engineering techniques, ensuring high precision and quality. Ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas, these manufacturers can deliver shafts designed for unique operational conditions. B2B buyers should consider lead times and costs, as custom solutions may take longer and be more expensive than standard options.
How Do Forged Shaft Manufacturers Stand Out?
Forged shaft manufacturers utilize advanced forging techniques to produce shafts that are exceptionally strong and durable. This manufacturing method is particularly beneficial for applications in heavy machinery, mining, and marine environments, where shafts are subjected to high stress and loads. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced strength against the potential for limited design flexibility and higher material costs.
What Are the Advantages of Graphite Shaft Manufacturers?
Graphite shaft manufacturers specialize in producing lightweight and flexible shafts, primarily for sports equipment such as golf clubs. The use of graphite allows for enhanced performance, offering improved feel and energy transfer during use. While these shafts are often favored for their performance benefits, B2B buyers must consider the higher material costs and the fact that graphite may not provide the same strength as metal alternatives.
Why Choose Standard Shaft Manufacturers?
Standard shaft manufacturers provide mass-produced shafts that adhere to established industry standards, making them a cost-effective option for many businesses. They are suitable for applications in manufacturing and industrial equipment, where quick delivery and lower prices are essential. However, buyers should be aware that the lack of customization may lead to quality variability and may not meet specific operational needs.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Shaft Manufacturers?
Composite shaft manufacturers create shafts from advanced composite materials, which offer unique performance characteristics such as lightweight construction and corrosion resistance. These shafts are increasingly used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries where reducing weight without sacrificing performance is critical. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the need for specialized knowledge in handling and maintenance when opting for composite solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of shaft manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Shaft Manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Wind Turbine Shafts | Enhances energy efficiency and reliability | Material strength, corrosion resistance, precision engineering |
| Marine | Propeller Shafts | Ensures optimal propulsion and stability | Customization options, weight considerations, compliance with marine standards |
| Automotive | Drive Shafts | Improves vehicle performance and longevity | Tolerance levels, balancing, heat treatment capabilities |
| Oil & Gas | Drill Shafts | Increases drilling efficiency and durability | Material selection, resistance to extreme conditions, testing protocols |
| Industrial Machinery | Conveyor Shafts | Maximizes operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Load capacity, design specifications, availability of replacement parts |
How Are Shafts Used in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, particularly in wind power, shaft manufacturers produce components that connect the turbine blades to the generator. These shafts must withstand high torque and dynamic loads, ensuring energy conversion efficiency. Buyers in this sector require materials with high tensile strength and corrosion resistance to endure harsh environmental conditions. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should consider suppliers who can provide certifications and compliance with international standards to ensure reliability and performance.
What Role Do Shafts Play in Marine Applications?
Shaft manufacturers create propeller shafts critical for marine vessels, directly influencing propulsion and maneuverability. These shafts must be lightweight yet robust enough to handle the stresses of marine environments, including saltwater corrosion. Buyers in the marine sector need to ensure that manufacturers can offer customization options and adhere to stringent marine safety standards. Sourcing from reputable manufacturers with experience in marine applications is essential for operational safety and efficiency.
Why Are Drive Shafts Important in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, drive shafts are vital components that transfer power from the engine to the wheels. Precision-engineered shafts enhance vehicle performance, reduce vibrations, and improve fuel efficiency. Automotive buyers should look for manufacturers that provide high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques, such as heat treatment and balancing. It is crucial for international buyers to verify the supplier’s ability to meet specific automotive industry standards and regulations to ensure compatibility and performance.
How Do Shafts Improve Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas sector, drill shafts are essential for the extraction process, providing the necessary strength to withstand extreme conditions. These shafts must be designed to handle high pressures and resist wear from abrasive materials. Buyers need to prioritize manufacturers who can offer robust materials and thorough testing protocols to ensure durability and reliability. International sourcing considerations include the ability to meet local regulations and the availability of support services for maintenance and replacement.
What Benefits Do Conveyor Shafts Provide in Industrial Machinery?
Shaft manufacturers supply conveyor shafts that play a crucial role in material handling across various industrial applications. These shafts must be designed to support heavy loads while ensuring smooth operation to maximize efficiency and minimize downtime. Buyers should look for manufacturers that can deliver shafts tailored to specific load capacities and design requirements. Additionally, international buyers should consider the availability of replacement parts and the manufacturer’s capability to provide ongoing support for maintenance needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘shaft manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays in Production Due to Shaft Failures
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant production delays when shafts fail unexpectedly. This often occurs in critical machinery where shafts play an essential role in transferring power and motion. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, a broken drive shaft can halt production lines, leading to costly downtime and lost revenue. Buyers may struggle to find a reliable shaft manufacturer who can quickly provide replacements or repairs while ensuring adherence to tight quality standards.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish a relationship with a shaft manufacturer known for quick turnaround times and robust support services. When sourcing shafts, it’s crucial to inquire about their manufacturing capabilities, including whether they offer emergency services for urgent repairs. Buyers should also prioritize manufacturers that conduct thorough failure analyses and quality checks, which can help identify potential weaknesses in shafts before they lead to failures. Furthermore, implementing a predictive maintenance schedule can help foresee potential shaft issues, allowing for proactive replacement and minimizing unplanned downtimes.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Customizing Shafts for Unique Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when their operations require custom shafts tailored to specific applications. Standard off-the-shelf solutions may not provide the necessary performance characteristics, leading to inefficiencies or operational failures. For example, a company in the oil and gas industry may need shafts that can withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments, which are not typically available through general suppliers.
The Solution: To effectively address customization needs, buyers should work closely with shaft manufacturers that specialize in bespoke solutions. It’s important to provide detailed specifications regarding the shaft’s required materials, dimensions, and performance criteria. Engaging in collaborative design processes with the manufacturer’s engineering team can lead to innovative solutions that meet unique operational demands. Additionally, buyers should consider manufacturers who utilize advanced technologies like CNC machining and metallurgical analysis to produce high-quality, custom shafts that ensure longevity and reliability in challenging environments.
Scenario 3: Navigating Quality Assurance and Compliance Standards
The Problem: International buyers face the challenge of ensuring that shafts meet rigorous quality assurance and compliance standards, particularly when sourcing from different regions. Variability in manufacturing processes and standards can lead to discrepancies in product quality, potentially resulting in equipment failures and regulatory issues. This is particularly pertinent in industries like aerospace and automotive, where compliance with specific certifications is mandatory.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on potential shaft manufacturers. This includes verifying their certifications, such as ISO or AS9100, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Engaging in direct communication with manufacturers about their quality assurance processes can also provide insights into how they maintain compliance throughout the production lifecycle. Furthermore, establishing clear quality control benchmarks and requiring third-party inspections can help ensure that the shafts delivered meet all necessary specifications and compliance requirements, thereby safeguarding operational integrity and reducing risks associated with non-compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shaft manufacturer
What Are the Key Properties of Common Shaft Materials?
Selecting the appropriate material for shaft manufacturing is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in shaft manufacturing: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and composite materials.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Shaft Manufacturing?
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials for shafts due to its excellent tensile strength and durability. It typically has a high yield strength, making it suitable for high-load applications. Carbon steel shafts can also be heat-treated to enhance their mechanical properties, allowing them to withstand higher stress and fatigue levels.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively low-cost and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. Its strength and ability to be hardened through heat treatment make it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The main drawback is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. Additionally, it may require protective coatings or treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for applications where high strength is required, such as in automotive and industrial machinery. However, in humid or corrosive environments, its longevity may be compromised.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like the Middle East and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, and consider the availability of protective coatings to mitigate corrosion risks.
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel for Shafts?
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments, including marine and chemical processing. Its mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength and ductility, also make it a preferred choice for many industries.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its ability to resist corrosion, which extends the lifespan of the shaft. It also maintains its strength at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness. This can lead to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel shafts are often used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316) that comply with international standards and local regulations, especially in Europe and Africa, where quality and safety standards may vary.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Shaft Material?
Aluminum is a lightweight material that offers good corrosion resistance and is easy to machine. It is often used in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can lead to improved efficiency in applications where reducing weight is beneficial. It also has good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Cons: Aluminum generally has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum shafts are ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in drones or automotive parts. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum grades meet the necessary standards for their specific applications, particularly in industries like aerospace where compliance with international standards is critical.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Shaft Manufacturing?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are increasingly used in shaft manufacturing due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. They can be tailored for specific applications, making them versatile.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be engineered to provide specific mechanical properties, making them suitable for specialized applications. They also resist corrosion and are non-magnetic.
Cons: The main limitation of composite materials is their higher cost and complexity in manufacturing. They may also require specialized knowledge for machining and handling.
Impact on Application: Composite shafts are often used in aerospace, marine, and high-performance automotive applications where weight and strength are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite materials and the expertise required for their manufacturing and maintenance, particularly in regions where traditional materials are more common.
Summary Table of Shaft Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for shaft manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive and industrial machinery | High strength and low cost | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace and high-performance automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when sourcing shafts for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shaft manufacturer
What Are the Main Stages of Shaft Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of shafts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the exacting standards required in various industries. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The initial stage begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, typically steel or other alloys, chosen for their strength and durability. This step includes material inspection to confirm compliance with specifications. Common practices involve dimensional checks and metallurgical analysis to ensure the materials can withstand the operational stresses they will encounter in service.
What Techniques Are Used in Shaft Forming?
Forming is the next crucial stage, where the raw material is transformed into a shaft through various techniques. The predominant method utilized is CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which allows for precise shaping and cutting of the material. Other techniques include:
- Forging: This process involves shaping the material while it is heated, enhancing its strength and fatigue resistance.
- Turning and Milling: These subtractive processes shape the shaft by removing excess material to achieve the desired dimensions and tolerances.
- Drilling and Boring: Essential for creating grooves and holes that accommodate gears or bearings, ensuring proper fit and function.
Each technique is selected based on the shaft’s intended application and the specific requirements set forth by the client.
How Is Shaft Assembly Conducted?
Once the shaft has been formed, it may require assembly with other components, such as gears or bearings. This stage often involves precise fitting and alignment to ensure optimal performance. The assembly process may also include the installation of protective coatings, which can enhance the shaft’s resistance to corrosion and wear, thus prolonging its service life.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Shafts?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process, aimed at enhancing the shaft’s performance and appearance. This may involve:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as heat treatment, hardening, or coating applications are performed to improve the shaft’s mechanical properties.
- Grinding and Polishing: These processes ensure that the surface finish meets the required specifications, which can be critical in reducing friction and wear during operation.
What Quality Control Measures Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality assurance is integral to the shaft manufacturing process, ensuring that every product adheres to international standards. The implementation of a robust quality control (QC) system involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of incoming materials, ensuring they meet specified standards before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure adherence to specifications and tolerances. This includes dimensional checks and process validations.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the shafts are finished, a thorough inspection is performed to confirm that all specifications and quality standards have been met before the products are shipped.
What International Standards and Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the relevant quality standards and certifications is vital. Key international standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that the manufacturer has a quality management system in place, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For shafts used in the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products meet the necessary safety and reliability requirements.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers possess these certifications, as they reflect a commitment to quality and adherence to industry norms.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can be done by the buyer or through third-party auditing firms.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed reports of their quality control processes, including results from inspections and tests performed at various stages of manufacturing.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance practices and product reliability.
What Are the Common Testing Methods in Shaft Manufacturing?
In addition to the aforementioned QC checkpoints, various testing methods are employed to ensure that the shafts meet required performance criteria:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection are used to identify internal defects without damaging the product.
- Hydrostatic Testing: This is particularly relevant for shafts used in high-pressure applications, ensuring that they can withstand operational pressures without failure.
- Dimensional Inspection: Precision measuring tools are used to verify that the final product meets specified dimensions and tolerances.
What Unique Quality Control Considerations Exist for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly in diverse regions, there are unique considerations regarding quality control:
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Buyers should be aware that quality standards may vary significantly between regions, which can impact product performance and reliability.
- Logistics and Communication Challenges: Effective communication regarding quality expectations and standards is crucial, especially when dealing with suppliers in different time zones or languages.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that the products meet the legal and regulatory requirements of their home countries, which may differ from those of the supplier.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in shaft production, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘shaft manufacturer’
Introduction
Sourcing a reliable shaft manufacturer is a critical step for businesses across various industries, from automotive to aerospace. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of selecting a suitable manufacturer for their shaft needs. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process is efficient and aligned with your technical and quality requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for your shafts, including dimensions, materials, and tolerances. This step is essential as it sets the foundation for your sourcing process. Be specific about the application of the shafts and any industry standards that must be met.
- Consider the operational environment (e.g., temperature, load) to select appropriate materials.
- Identify any required certifications or compliance standards relevant to your industry.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential shaft manufacturers that specialize in your required specifications. This step helps you create a shortlist of suppliers who have the necessary expertise and capabilities.
- Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to find manufacturers.
- Look for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge the manufacturer’s reputation.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. This step is crucial to ensure that the manufacturer adheres to international quality standards.
- Check for industry-specific certifications that may be required for your application.
- Inquire about their quality control processes and any third-party audits they undergo.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a final decision, request samples or prototypes to assess the quality of the shafts. This step allows you to evaluate the manufacturer’s capabilities and ensure that the products meet your specifications.
- Analyze the samples for material quality, finish, and dimensional accuracy.
- Consider conducting a performance test if applicable, to ensure the shafts meet your operational requirements.
Step 5: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Examine the manufacturer’s production capabilities and equipment. Understanding their technology and processes is vital to ensure they can meet your volume and lead time requirements.
- Inquire about their machining technologies (e.g., CNC machining, forging) and capacity.
- Assess their ability to handle custom orders and variations in design.
Step 6: Evaluate Customer Support and Communication
Effective communication and customer support are essential for a successful partnership. Assess how responsive and helpful the manufacturer is during your interactions.
- Evaluate their willingness to provide technical support and guidance throughout the project.
- Ensure they have a clear process for addressing issues or concerns that may arise.
Step 7: Review Pricing and Terms
Finally, review the pricing structure and contractual terms offered by the manufacturers. Ensure that the pricing aligns with your budget while considering the quality and service level.
- Compare quotes from multiple suppliers to identify competitive pricing.
- Pay attention to payment terms, lead times, and warranty policies to avoid future complications.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and make informed decisions when selecting a shaft manufacturer that meets your needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shaft manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Shaft Manufacturing?
When sourcing shafts from manufacturers, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary components of cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly influences the cost. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialized alloys, each with varying price points. High-performance applications may require advanced materials, which can increase costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for precision manufacturing. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America often having lower wages compared to Europe and the Middle East. However, this can also affect the quality and reliability of the work.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, which is reflected in the pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is necessary for precision engineering. The initial investment in tooling can be high, but it is amortized over the volume of shafts produced. This cost becomes more favorable at higher production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the shafts meet industry standards and specifications requires rigorous QC processes. This may involve testing and inspections, which add to the overall cost but are vital for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely depending on the distance and chosen Incoterms. International buyers should consider these costs when calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the manufacturer’s reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Shaft Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing shafts, particularly for international buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts due to economies of scale. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom shafts tailored to specific applications can command higher prices due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Clear specifications can facilitate better quotes from suppliers.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials plays a significant role in pricing. High-performance or specialized materials will increase costs. Buyers should assess their needs against budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers who meet international standards (such as ISO certifications) may charge a premium. However, this investment often pays off through enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The manufacturer’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but offer better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for cost management in international trade. Different terms can affect shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Shaft Sourcing?
To maximize value when sourcing shafts, buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to compare prices and terms. Leverage volume commitments to negotiate lower rates.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the shaft’s lifespan. This approach can reveal hidden costs and inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and potential tariffs that can affect overall costs. Understanding local market conditions in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East can also provide insights into pricing strategies.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Trust and communication can foster more favorable terms.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Stay informed about industry trends and competitor pricing. Benchmarking against similar suppliers can help identify fair pricing and service expectations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The pricing outlined in this analysis is indicative and may vary based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain quotes tailored to their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing shaft manufacturer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for Shaft Manufacturing
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, selecting the right solution for shaft production is crucial. While traditional shaft manufacturers provide tailored solutions, various alternative methods and technologies can also meet specific needs. This section will compare shaft manufacturing with other viable options, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Shaft Manufacturer | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Forged Shaft Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, custom specs | Variable precision, depending on the printer | Excellent strength and durability |
| Cost | Generally higher, especially for custom designs | Can be lower for small batches, but material costs can add up | Moderate to high, depending on complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and setup | Relatively easy, but requires design software | More complex, with longer lead times |
| Maintenance | Regular quality checks needed | Minimal maintenance, but part quality can vary | Requires inspections for wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications requiring exact tolerances | Prototyping or low-volume production | Heavy-duty applications in harsh environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, offers a modern approach to producing shafts. The primary advantage of this method is its ability to create complex geometries with reduced material waste. It is particularly beneficial for prototyping or low-volume production, where traditional methods may be cost-prohibitive. However, the performance may vary depending on the printer and materials used, often falling short of the precision and strength found in traditionally manufactured shafts. Additionally, while initial costs can be lower, high-quality materials may lead to increased overall expenses.
2. Forged Shaft Solutions
Forged shafts are manufactured through a process that involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces. This method provides superior strength and durability, making forged shafts ideal for heavy-duty applications in industries such as oil and gas, aerospace, and automotive. The primary downside is that the forging process can be more complex and time-consuming compared to traditional manufacturing methods, leading to longer lead times. Furthermore, while forged shafts offer high performance, the initial setup and tooling costs can be significant, particularly for custom designs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Shaft Solution
When selecting the right solution for shaft production, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and application specifics. For high-stress and precision-demanding applications, traditional shaft manufacturing remains a robust choice. In contrast, additive manufacturing may suit businesses looking for flexibility in design and lower upfront costs for prototypes. Forged shafts present an excellent option for industries requiring exceptional strength and reliability but may come with longer lead times. Ultimately, understanding the unique needs of your application will guide you in choosing the most appropriate shaft manufacturing solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shaft manufacturer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Shafts in Manufacturing?
Understanding the technical properties of shafts is critical for B2B buyers looking to ensure the reliability and performance of their machinery. Here are key specifications that are crucial in the shaft manufacturing process:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of material used in shaft production, which can include carbon steel, stainless steel, or specialized alloys. The choice of material significantly impacts the shaft’s strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. For industries such as automotive or oil and gas, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring operational safety and longevity.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In shaft manufacturing, tight tolerances (often in the range of micrometers) are essential for ensuring proper fit and function within machinery. Poor tolerance can lead to misalignment, increased wear, and potential failure of components, making this property vital for industries that demand precision, such as aerospace and high-speed machinery.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength indicates the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it deforms permanently. For shafts, this property is critical in applications where high loads and dynamic forces are present. Ensuring that shafts have adequate yield strength helps to prevent failures and extends the life of the equipment, reducing costs associated with downtime and repairs.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture of the shaft’s surface, which can affect friction, wear, and corrosion resistance. A smoother surface finish can lead to better performance in applications involving rotating components. Understanding the required surface finish is essential for buyers to achieve optimal efficiency and longevity in their operations.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a process used to enhance the mechanical properties of a shaft, such as hardness and strength. Different heat treatment methods, like quenching and tempering, can be applied based on the material and application requirements. B2B buyers must consider heat treatment options to ensure that the shafts can withstand operational stresses without succumbing to fatigue.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Shaft Manufacturing?
Navigating the terminology in shaft manufacturing can be challenging for non-technical decision-makers. Here are some common trade terms that are essential for effective communication and negotiation:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are sold under another company’s brand. In shaft manufacturing, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the shafts being offered.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for projects that require large volumes of shafts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate terms effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border procurement, as they dictate aspects like shipping, risk, and costs.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools through a computer. This technology is fundamental in modern shaft manufacturing, enabling precision and repeatability. Buyers should inquire about CNC capabilities to ensure that their specifications can be met accurately.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the right shafts for their applications while optimizing costs and performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the shaft manufacturer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Shaft Manufacturing Sector?
The global shaft manufacturing market is witnessing significant growth, driven by various factors including technological advancements, increased demand for precision-engineered components, and a rising focus on automation across industries. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate this evolving landscape, it’s crucial to stay abreast of emerging trends.
One key trend is the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, which enhance production efficiency and provide real-time data for better decision-making. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting CNC machining and automated processes to meet tighter tolerances and reduce lead times. Additionally, customization is becoming a standard expectation, as businesses seek tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving, with a notable shift towards collaborative partnerships between manufacturers and clients. This approach fosters transparency and innovation, ensuring that the products developed align closely with market needs. Furthermore, the demand for sustainable practices is reshaping the supplier landscape, compelling manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and processes, thereby appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Shaft Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional considerations but essential aspects of the shaft manufacturing landscape. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has become a primary concern for many businesses, leading to a demand for more responsible practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through their operations.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies are expected to conduct due diligence in sourcing raw materials, ensuring that they come from responsible suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications play a crucial role in establishing credibility and trust with buyers.
Moreover, the use of sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly coatings, is gaining traction. By opting for suppliers who embrace these practices, businesses not only reduce their environmental footprint but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market. This trend is particularly relevant for companies in regions where regulatory frameworks are evolving towards stricter environmental standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Shaft Manufacturing Relevant to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The history of shaft manufacturing can be traced back to the industrial revolution when the need for mechanical power transmission led to the development of early shaft designs. Initially, shafts were rudimentary, often crafted from wood or wrought iron. However, as technology advanced, the introduction of high-strength materials and precise machining techniques revolutionized the industry.
In the late 20th century, the advent of CNC technology marked a significant turning point, enabling manufacturers to produce complex shapes and dimensions with high precision. This evolution has culminated in today’s sophisticated manufacturing processes that leverage automation and advanced materials science.
For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential. It highlights the continuous innovation in the sector, emphasizing the importance of partnering with manufacturers who not only have a rich legacy but are also committed to ongoing improvement and adaptation to modern challenges. This awareness allows buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers that align with their strategic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shaft manufacturer
-
How do I evaluate the quality of a shaft manufacturer?
To evaluate the quality of a shaft manufacturer, consider their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Review their manufacturing processes, including the use of advanced technologies like CNC machining and non-destructive testing. Request samples or references from past clients to assess their performance and reliability. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance protocols, including dimensional checks and metallurgical analysis, to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. -
What are the key factors to consider when customizing a shaft?
When customizing a shaft, focus on the application requirements, including load capacity, operating environment, and material selection. Discuss design specifications with the manufacturer, such as dimensions, tolerances, and surface treatments. It’s also important to consider the manufacturing processes available and whether they can accommodate your customization needs. Additionally, ask about the lead times for custom orders and any minimum order quantities (MOQs) that may apply. -
What are the typical lead times for shaft manufacturing?
Lead times for shaft manufacturing can vary significantly based on factors such as complexity, material availability, and the manufacturer’s production capacity. Generally, standard orders may take between 2 to 6 weeks, while custom shafts may require longer due to design and engineering processes. It’s advisable to communicate your project timelines clearly with potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your deadlines and discuss expedited options if necessary. -
How can I ensure compliance with international trade regulations?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, familiarize yourself with the import/export laws in your country and the country of the manufacturer. Verify that the manufacturer adheres to relevant international standards and certifications. Engage with a customs broker or trade advisor who can provide guidance on tariffs, duties, and documentation required for shipping. Additionally, ensure that the manufacturer provides all necessary compliance certificates, such as CE or RoHS, to avoid delays during customs clearance. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with a shaft manufacturer?
Payment terms can vary among shaft manufacturers, but common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50% of the total order value) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some manufacturers may offer net payment terms (e.g., Net 30 or Net 60), allowing a grace period for payment. It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms in advance, including any potential financing options, to ensure a smooth transaction process. -
What shipping options are available for international orders?
Shipping options for international orders typically include air freight, which is faster but more expensive, and ocean freight, which is cost-effective for larger shipments but takes longer. Discuss with your manufacturer the best shipping method based on your timeline and budget. Additionally, inquire about their logistics capabilities, including whether they handle customs clearance and delivery logistics to your location, as this can simplify the process for you. -
How do I assess the reliability of a shaft manufacturer?
To assess the reliability of a shaft manufacturer, research their reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and case studies. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record of delivering quality products on time. Ask for client testimonials or references, and consider their experience in your specific industry. Engaging in direct communication with the manufacturer can also provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness, which are key indicators of reliability. -
What quality assurance processes should a shaft manufacturer have in place?
A reputable shaft manufacturer should implement comprehensive quality assurance processes, including initial design reviews, in-process inspections, and final product testing. They should perform dimensional checks, non-destructive testing, and metallurgical analyses to ensure the shafts meet specified standards. Additionally, look for manufacturers that maintain detailed documentation of quality control measures and are willing to share these records with you as part of their commitment to transparency and accountability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shaft manufacturer
In the realm of shaft manufacturing, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize precision engineering and rigorous quality control, international B2B buyers can significantly enhance their operational efficiency. Key takeaways include the importance of thorough supplier evaluations, understanding the nuances of different manufacturing processes, and considering customization options to meet specific application needs.
Moreover, as industries evolve, the demand for innovative and durable shaft solutions will only increase. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to actively seek manufacturers that not only offer advanced technology but also exhibit a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Engaging in strategic sourcing not only secures high-quality products but also fosters long-term relationships that can lead to collaborative innovation and competitive advantage.
As you navigate your sourcing strategy, consider the unique challenges and opportunities within your region. Now is the time to connect with leading shaft manufacturers who can meet your specifications and drive your business forward. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your supply chain and ensure the reliability of your operations.