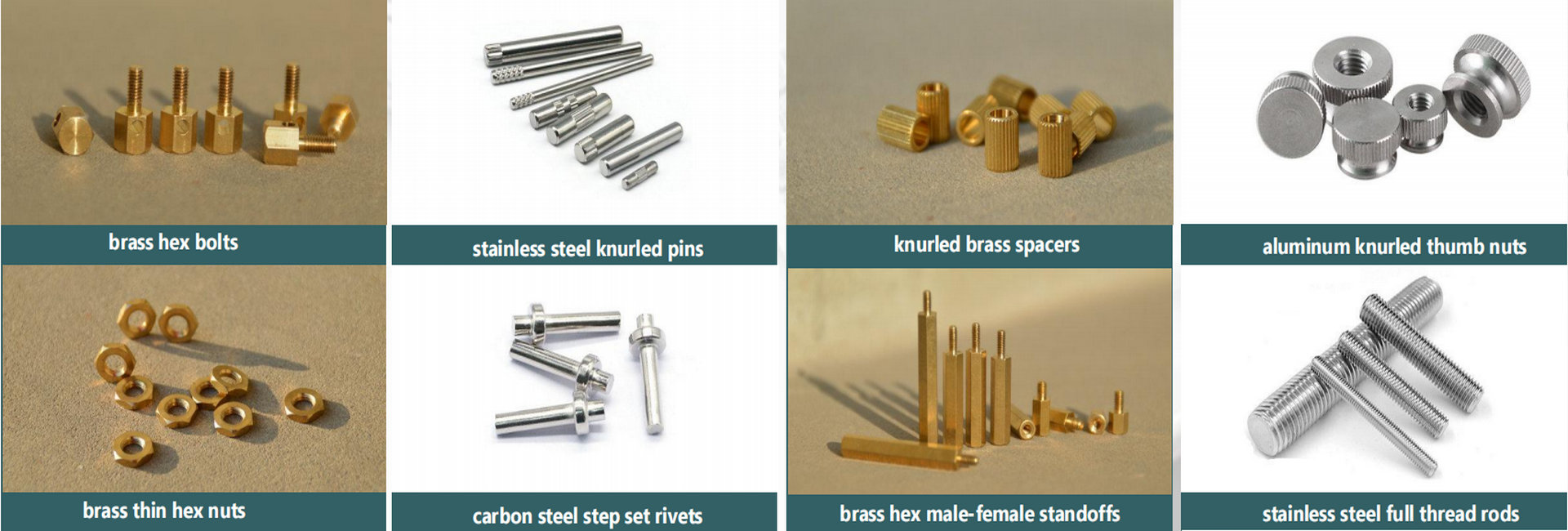
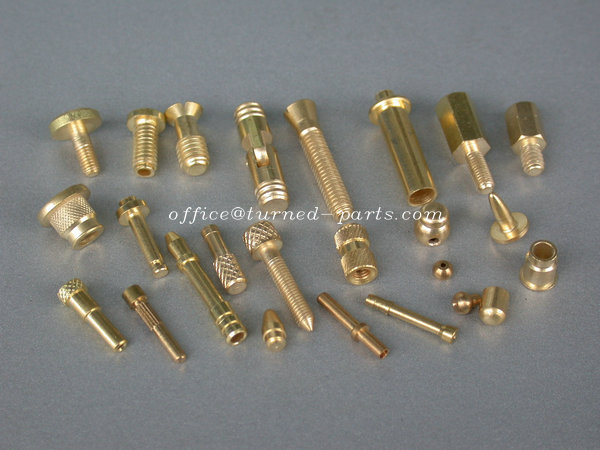
Top 10 Turned Parts Manufacturer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Freeway Corp – Precision Turned Components
Domain: freewaycorp.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision turned components and CNC turned parts manufacturing in the USA. Capabilities include over 30 automatic screw machines and multiple CNC turning centers, machining up to 2 5/8″ round and 2 5/16″ hex materials, and handling up to 2 7/8″ bar stock and 7″ blanks. Secondary operations include broaching, thread and spline rolling, centerless grinding, tapping, burnishing, reaming, milling, dri…
2. Sabner – Precision Turned Parts
Domain: sabner.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Turned parts are precision machined components formed by a manufacturing process called turning, characterized by their cylindrical shape. They are widely used in various industries, including electronics, hydraulics, pneumatics, and medical applications. The manufacturing process utilizes modern CNC turning centers for large parts and automatic lathes for smaller, complex components. Key material…
3. Abbott Interfast – CNC Turning Services
Domain: aicfast.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Turning Services & Turned Parts offered by Abbott Interfast include the production of complex parts using advanced CNC machining technology. The CNC turning process involves holding material in a chuck and rotating it at high speed while a cutting tool shapes the workpiece. Key benefits include increased production speed, enhanced efficiency, improved accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. Material…
4. AEB Torneria – High-Precision CNC Turning Services
Domain: aebtorneria.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: AEB Torneria is a manufacturer of high-precision turned parts located in the USA and Europe. They specialize in CNC turning services for complex or high-run products and offer an online quoting tool for small and simple supplies. Key materials processed include steel, aluminum, nickel-silver, bronze, brass, and copper. The company operates two production plants, one in Italy and one in Poland, emp…
5. Turned Parts – Precision Machined Products
Domain: turned-parts.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Turned parts – Screw machined products from China manufacturer. Key products include: Custom Parts, Precision Turned Parts, Threaded Turned Parts, Knurled Turned Parts, Hex Turned Parts, CNC Turning Parts, Screw Machine Parts, Finished Parts, Galvanized Parts, Anodizing Parts, Plating Parts, Special Fasteners (Pins, Nuts, Bolts, Studs, Screws, Washers). Materials used: Brass, Aluminum, Stainless S…
6. Solutions Manufacturing – Precision CNC Turning Services
Domain: solutionsmfg.net
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Precision CNC Turning Services offered by Solutions Manufacturing, Inc. include a variety of turned components for multiple industries. Key features include:
– High Precision CNC Turning Processes: Contour Turning, Form Turning, Taper Turning, Straight Turning, Boring, Drilling, Facing, Grooving, Knurling, Parting/Cutting, Secondary Grinding, Threading (External and Internal).
– Maximum part spec…
7. Currie Warner – Brass Turned Parts & Fasteners
Domain: curriewarner.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Brass Turned Parts Manufacturer, Brass Fasteners, Compression Fittings, Locking Nuts, Screws & Bolts, Brass Connectors, Couplers, Push Fit Brass Fittings, Component Housings, Glands, Valves (Shut-Off Valves, Ball Valves, Control Valves, Drain Valves), Adaptors (Male Adaptors, Female Adaptors), DN Series Fittings, NPS Fittings, Multi-Spindle Turning, Repetition Turned Parts, Screw Machine Products,…
8. Zetwerk – Precision Turned Parts Manufacturing
Domain: zetwerk.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Turned parts manufacturing is a precision manufacturing process that involves rotating a workpiece and using a cutting tool to shape it, primarily utilizing lathes. It is crucial for various industries including automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. Key benefits include precision and accuracy, versatility across materials (such as brass, aluminum, and steel), and efficiency in pr…
9. M&M Turned Parts – Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain: mmturnedparts.co.uk
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: M&M Turned Parts Ltd specializes in subcontract CNC machining of precision components. They offer CNC Sliding Head turning and CNC Fixed Head turning services. The company manufactures components from 2mm dia to 65mm dia in batch sizes ranging from 200 to 100,000 components. They machine a variety of materials including steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminium, and engineering plastics. The compan…
10. HansaMatrix – Precision CNC Turned Parts
Domain: hansamatrix.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: HansaMatrix offers CNC turned parts manufacturing services with a focus on high-quality, precision components. Key features include:
– Expert CNC milling and turning for dimensional accuracy and repeatability.
– In-house assembly capabilities for mechanical and optical systems, reducing production lead times.
– Expertise in various materials including metals, technical plastics (PET, POM, PEEK)…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for turned parts manufacturer
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, sourcing high-quality turned parts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for precision components across diverse industries—from automotive to medical—understanding the intricacies of turned parts manufacturing is crucial. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of turned parts manufacturers, equipping buyers with essential insights into types of components, their applications, and the latest machining technologies.
We will explore the various materials used in production, including metals and composites, and examine how specific manufacturing techniques, such as CNC turning and automatic lathing, can impact quality and efficiency. Additionally, this guide provides a framework for vetting suppliers, ensuring that you partner with manufacturers who meet rigorous quality standards while also being responsive to your unique project needs.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—this guide offers valuable strategies for making informed purchasing decisions. By understanding the global market dynamics, material properties, and manufacturing capabilities, you can streamline your sourcing process, reduce costs, and enhance product performance. Navigate the complexities of turned parts manufacturing with confidence, and unlock the potential for innovation and growth in your operations.
Understanding turned parts manufacturer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Turned Parts | High precision, complex geometries, programmable | Automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Exceptional accuracy; Cons: Higher initial cost |
| Automatic Screw Machines | High volume production, efficient for small parts | Electronics, plumbing, HVAC | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs; Cons: Limited flexibility |
| Precision Turned Components | Tighter tolerances, specialized machining processes | Hydraulic systems, aerospace, robotics | Pros: Reliable performance; Cons: Longer lead times |
| Multi-Spindle Turning | Simultaneous machining of multiple parts, high throughput | Mass production, automotive | Pros: Increased efficiency; Cons: Setup complexity |
| Custom Machined Components | Tailored to specific requirements, versatile materials | Industrial equipment, custom machinery | Pros: Meets unique specifications; Cons: Potentially higher costs |
What Are the Characteristics of CNC Turned Parts?
CNC turned parts are characterized by their ability to achieve high precision and intricate geometries through computer-controlled machining. This method allows for the production of complex shapes and tight tolerances, making it ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Buyers should consider the initial investment in CNC technology versus the long-term benefits of accuracy and repeatability, particularly for high-stakes applications.
How Do Automatic Screw Machines Benefit High-Volume Production?
Automatic screw machines are designed for the mass production of small, cylindrical components. They excel in efficiency and speed, making them suitable for industries like electronics and plumbing. While they offer cost advantages for large production runs, buyers should note the limitations in flexibility, as these machines are optimized for specific part designs and may not adapt easily to custom requirements.
What Makes Precision Turned Components Unique?
Precision turned components are manufactured to meet stringent tolerances and specifications, often using specialized machining processes. These components find applications in hydraulic systems, aerospace, and robotics, where reliability and performance are critical. Buyers must weigh the benefits of high precision against potentially longer lead times and the need for more advanced machinery.
Why Choose Multi-Spindle Turning for Mass Production?
Multi-spindle turning allows for the simultaneous machining of multiple parts, significantly increasing throughput. This method is particularly advantageous in mass production environments such as the automotive industry. However, while it boosts efficiency, the complexity of setup and maintenance can be a consideration for buyers looking for ease of operation.
What Are the Advantages of Custom Machined Components?
Custom machined components are tailored to meet specific requirements, offering versatility in materials and designs. This approach is essential for industries that require unique solutions, such as industrial equipment and custom machinery. While the ability to meet unique specifications is a significant advantage, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher costs and longer lead times associated with custom production.
Key Industrial Applications of turned parts manufacturer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of turned parts manufacturer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision components for engines and transmissions | Enhanced performance and reliability of vehicles | Ensure compliance with automotive standards and certifications |
| Hydraulic Systems | Custom hydraulic valves and fittings | Improved efficiency and safety in hydraulic systems | Focus on material quality and pressure tolerance specifications |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | High precision and biocompatibility for patient safety | Verify certifications for medical-grade materials and processes |
| Electronics | Connectors and housings for devices | Reliable performance in electronic applications | Assess electrical conductivity and thermal stability of materials |
| Aerospace | Components for aircraft systems | Weight reduction and increased fuel efficiency | Prioritize aerospace-grade materials and adherence to strict regulations |
How Are Turned Parts Manufacturers Used in the Automotive Industry?
Turned parts manufacturers produce precision components critical to automotive engines and transmissions. These components, such as shafts, bushings, and valves, are vital for enhancing vehicle performance and reliability. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers adhere to automotive industry standards, as these components often require rigorous testing and certification to guarantee safety and functionality.
What Role Do Turned Parts Manufacturers Play in Hydraulic Systems?
In hydraulic systems, turned parts manufacturers create custom valves and fittings designed for optimal flow and pressure control. These parts must meet high durability standards to withstand extreme conditions, ensuring system efficiency and safety. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing components that offer exceptional material quality and pressure tolerance, as these factors are crucial for preventing system failures.
Why Are Turned Parts Manufacturers Essential for Medical Devices?
Turned parts manufacturers supply precision surgical instruments and implants, which require high accuracy and biocompatibility. These components must meet stringent health regulations to ensure patient safety. Buyers in the medical sector, especially from Europe and the Middle East, should verify that their suppliers have the necessary certifications and employ quality control measures to maintain compliance with medical standards.
How Do Turned Parts Manufacturers Contribute to Electronics?
In the electronics industry, manufacturers produce connectors, housings, and other components that require reliable performance under various conditions. The precision in turned parts ensures that electronic devices function optimally, reducing the risk of failure. Buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, should assess the electrical conductivity and thermal stability of the materials used, as these characteristics significantly impact the performance of electronic applications.
What Are the Advantages of Turned Parts Manufacturers in Aerospace?
Turned parts manufacturers play a crucial role in the aerospace sector by producing lightweight components for aircraft systems. These parts contribute to weight reduction and increased fuel efficiency, vital for modern aviation. International buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, must prioritize suppliers who utilize aerospace-grade materials and adhere to strict industry regulations to ensure safety and performance in flight applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘turned parts manufacturer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality Across Production Batches
The Problem: One of the most pressing issues for B2B buyers in industries that rely on precision turned components is the inconsistency in quality across different production batches. When a manufacturer cannot guarantee that each batch of turned parts meets the specified tolerances, it can lead to costly downtime, increased waste, and significant disruptions in the supply chain. This inconsistency can stem from variations in machinery calibration, operator skill levels, or material quality, which can be especially problematic for buyers sourcing from multiple suppliers or those requiring high precision for critical applications.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish clear quality assurance protocols with their chosen turned parts manufacturer. This begins with specifying exact tolerances, material properties, and production methods in the initial contract. Furthermore, buyers should request documentation of the manufacturer’s quality control processes, including inspection reports and certifications. Implementing regular audits and on-site visits can also provide insight into the manufacturer’s operational practices. Additionally, leveraging manufacturers that utilize advanced CNC technology and automated processes can significantly enhance the uniformity of parts produced, leading to higher overall quality and reliability.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Custom Turned Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when sourcing custom turned parts that meet unique specifications. Standard parts may not fit specific machinery or applications, forcing companies to look for custom solutions. However, finding a manufacturer capable of delivering bespoke components within tight timelines can be daunting, particularly for buyers in regions with limited supplier options or those dealing with stringent regulatory requirements.
The Solution: To overcome this sourcing hurdle, buyers should engage in thorough market research to identify manufacturers with a proven track record in custom turned parts production. It is beneficial to prioritize suppliers that showcase a robust portfolio of similar projects and have the necessary certifications to comply with industry standards. Establishing a collaborative relationship with the manufacturer early on is crucial; this includes sharing detailed designs, functional requirements, and timelines. Utilizing rapid prototyping and iterative feedback loops can also accelerate the development process. Finally, leveraging technology such as CAD software for precise design specifications can enhance communication and ensure that the final product aligns closely with expectations.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Lead Times and Delivery Schedules
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, unexpected delays in lead times and delivery schedules can severely impact production timelines and project milestones. These delays may arise from various factors, including unexpected machine downtime, material shortages, or logistical issues. Such disruptions can lead to increased operational costs and missed opportunities, particularly in competitive industries where time-to-market is critical.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with lead time variability, buyers should adopt a proactive approach in their supply chain management. This includes establishing clear communication channels with the turned parts manufacturer to monitor production progress and address potential issues before they escalate. Buyers should also consider implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, which can reduce the need for large stockpiles of components and help in aligning production schedules more closely with actual demand. Additionally, forming strategic partnerships with multiple manufacturers can provide contingency options in the event of delays, ensuring that production remains uninterrupted. Finally, setting up a comprehensive logistics plan that accounts for potential shipping delays can further enhance reliability in delivery schedules.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Turned Parts Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for turned parts, it’s crucial to consider their properties that directly affect product performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and titanium. Each material has unique characteristics that can impact the suitability for various applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding environments, such as automotive and aerospace applications. Its non-reactive nature is particularly beneficial in food and medical industries.
Pros: Stainless steel offers high durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of components. Its aesthetic appeal and ease of cleaning make it ideal for applications requiring hygiene.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other metals, which can affect budget-conscious projects. Additionally, machining stainless steel can be more complex due to its hardness, potentially increasing manufacturing time.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and chemicals, making it versatile for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 or DIN 1.4301 is crucial. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide certifications to meet regional regulations, especially in sectors like food and healthcare.
What Advantages Does Brass Offer for Turned Parts?
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and good electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in applications that require corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, such as plumbing fittings and electrical components.
Pros: Brass is relatively easy to machine, which can lead to lower manufacturing costs. Its attractive finish makes it suitable for decorative applications.
Cons: While brass offers good corrosion resistance, it is not as robust as stainless steel under extreme conditions. Its susceptibility to dezincification in certain environments can limit its use.
Impact on Application: Brass is ideal for electrical applications due to its conductivity and is often used in environments where low friction is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B36 and JIS H3250 when sourcing brass components. Understanding local preferences for brass grades can also influence procurement decisions.
Why Choose Aluminum for Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is widely used in industries that prioritize weight reduction, such as aerospace and automotive.
Pros: The low density of aluminum makes it an excellent choice for applications where weight is a critical factor. Its good machinability and ability to form complex shapes add to its appeal.
Cons: Aluminum has lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive than other materials like steel and brass, depending on the alloy.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and fuels, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B211 and ISO 209, particularly when sourcing aluminum from different regions.
What Role Does Titanium Play in Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is often used in high-performance applications, including aerospace, medical implants, and marine environments.
Pros: Titanium’s strength and lightweight nature make it ideal for applications where performance is critical. Its biocompatibility is essential for medical applications, ensuring safety in implants.
Cons: The primary limitation is its high cost and difficulty in machining, which can lead to longer production times and increased costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion in harsh environments, making it suitable for applications in chemical processing and marine industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM F136 and ISO 5832 standards is crucial for titanium components, especially in medical applications. Understanding the regional market’s standards and preferences can aid in sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Turned Parts Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for turned parts manufacturer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Automotive, aerospace, medical equipment | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex machining | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical components | Excellent machinability and conductivity | Susceptible to dezincification | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants, marine applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and difficult to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Turned Parts?
The manufacturing process for turned parts involves several critical stages that ensure high precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate suppliers effectively.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. The choice of raw material is pivotal and typically includes metals such as stainless steel, brass, and titanium. The selected material is cut into appropriate lengths, often in bar stock form, to fit the specifications of the parts being produced. This preparation stage also includes inspection of the raw materials to ensure they meet predetermined quality standards. Buyers should inquire about the source and quality certifications of these materials, as this is crucial for the overall integrity of the final product.
2. Forming Techniques: How Are Turned Parts Shaped?
Forming is where the raw material is transformed into the desired shape through various machining techniques. The primary methods used in the production of turned parts include:
-
CNC Turning: This computer-controlled process allows for precise shaping of cylindrical components. CNC turning centers are capable of handling complex geometries and tight tolerances, making them ideal for high-precision applications.
-
Automatic Screw Machining: For smaller and simpler parts, automatic lathes can be used. These machines operate efficiently, producing high volumes of components with consistent quality.
-
Secondary Operations: After the initial turning process, secondary operations such as broaching, tapping, milling, and deburring are often performed to enhance the functionality and precision of the parts. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that offer comprehensive machining solutions, as this can reduce lead times and improve overall project efficiency.
3. Assembly of Turned Components
While many turned parts are sold as standalone components, some may require assembly with other parts. This stage involves fitting and joining various components, which may include using fasteners or welding. Quality assurance during assembly is vital to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. Buyers should ask about the assembly capabilities of their suppliers, especially for complex components requiring precise alignment.
4. Finishing Processes: What Enhancements Are Applied?
Finishing processes are essential for achieving the desired surface quality and enhancing the durability of turned parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Grinding: To achieve ultra-smooth finishes and tight tolerances.
- Burnishing: For improved surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Coating or Plating: Often applied to enhance corrosion resistance or aesthetic qualities. Buyers should verify if the finishing processes align with their specific industry requirements.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Expect from Turned Parts Manufacturers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing turned parts. For international buyers, understanding the QA practices of potential suppliers can be a decisive factor in choosing a partner.
1. What International Standards Should Be Considered?
Most reputable turned parts manufacturers adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system and emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Buyers should request documentation proving compliance with such standards.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be necessary depending on the application. For example, components used in the oil and gas sector might require API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications, while parts for the European market may need CE marking. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should clarify these requirements upfront to avoid compliance issues.
2. How Are QC Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control is typically structured around several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor tolerances and overall quality. This may include visual inspections and measurements using precision tools.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a final inspection is conducted to verify that the finished parts meet all specifications and quality standards. This is crucial for preventing defects from reaching the customer.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific QC protocols their suppliers follow to ensure thorough checks are in place at each stage.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized?
Manufacturers utilize various testing methods to ensure the quality and performance of turned parts. Common techniques include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and micrometers to verify that parts meet specified dimensions.
-
Material Testing: Techniques like hardness testing or tensile testing to ensure that materials used meet required specifications.
-
Functional Testing: Depending on the application, testing components under actual operating conditions may be necessary to confirm performance.
Buyers should ask for test reports or certifications that demonstrate compliance with these testing methods.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is critical for B2B buyers. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Conduct Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards. Buyers should consider conducting on-site audits or leveraging third-party audit services to gain an unbiased view of supplier capabilities.
2. Request Documentation and Reports
Suppliers should be willing to provide quality control documentation, including inspection reports, test results, and certifications. This transparency can help build trust and ensure that the supplier is committed to maintaining high standards.
3. Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services
For added assurance, buyers can employ third-party inspection services to evaluate the quality of components before shipment. This can be especially important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight of the manufacturing process.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers need to navigate various challenges related to quality control. Factors such as language barriers, cultural differences, and varying standards can complicate the procurement process. Here are some considerations:
-
Cultural Understanding: Familiarize yourself with the cultural practices of suppliers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This understanding can help facilitate smoother communication and collaboration.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are aware of and comply with both local and international regulations relevant to your industry. This includes understanding import/export restrictions and compliance with regional standards.
-
Partnerships with Local Agents: Engaging local representatives or agents can help bridge gaps in communication and ensure a better understanding of the local market and supplier capabilities.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting turned parts manufacturers, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their quality and performance expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘turned parts manufacturer’
When sourcing precision turned parts, it is essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach to ensure they select the right manufacturer. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps needed to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. This includes detailed dimensions, tolerances, material requirements, and any special features necessary for your application. Precise specifications help manufacturers assess their ability to meet your needs and minimize misunderstandings during production.
- Considerations:
- What materials (e.g., stainless steel, brass, titanium) are best suited for your application?
- Are there specific industry standards or certifications required for your parts?
Step 2: Identify Potential Suppliers
Research and compile a list of potential turned parts manufacturers. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and those that specialize in the types of components you require. Evaluating their experience can provide insights into their capability to handle your order efficiently.
- Resources:
- Industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms can be valuable for identifying suppliers.
- Check for client testimonials and case studies relevant to your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed information about their manufacturing processes, machinery, and technology used. A capable supplier should have advanced CNC machinery and automatic screw machines to ensure high accuracy and efficiency.
- What to Look For:
- Can they handle both high-volume and custom orders?
- Do they offer secondary operations such as deburring, threading, or finishing?
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry-related certifications. These certifications indicate that the manufacturer adheres to quality management systems and meets international standards, which is vital for reliability.
- Why This Matters:
- Certification can be an assurance of quality and consistency in production.
- It may also help in meeting compliance requirements for certain industries.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a large order, request samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality of the turned parts. This step allows you to assess the manufacturer’s capabilities and ensure that the components meet your specifications.
- Key Points:
- Review the dimensions, tolerances, and finish of the samples.
- Provide feedback and check how responsive the supplier is to adjustments.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capacity
Understanding the lead times and production capacity of potential suppliers is crucial for planning your supply chain. Discuss how quickly they can fulfill orders and their ability to scale production based on your demands.
- Considerations:
- Are they equipped to handle rush orders if needed?
- What is their typical turnaround time for both prototypes and bulk orders?
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Ensure that the supplier has a dedicated point of contact for your account who can address any questions or issues promptly. Clear communication helps to build a strong partnership and facilitates smoother operations.
- Why It’s Important:
- A reliable communication channel can help resolve issues quickly and effectively.
- It fosters a collaborative relationship, allowing for better alignment on project goals.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for turned parts manufacturers, ensuring they select a partner that aligns with their technical requirements and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for turned parts manufacturer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Turned Parts Manufacturing?
When sourcing turned parts, understanding the cost structure is critical for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. Common materials like stainless steel, brass, and titanium have different price points, with titanium generally being more expensive due to its unique properties. It’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of your project to select the most cost-effective material that meets performance standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the manufacturing process and the skill level required. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s crucial to ensure that quality and precision are not compromised.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with running machinery, utilities, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes and modern machinery can help reduce overhead costs, which can be a significant factor in pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom parts. However, these costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making it important to consider volume when assessing tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet stringent quality standards incurs additional costs. Comprehensive QC processes, including testing and certification, are vital, particularly for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on the location of the manufacturer and the buyer. Understanding Incoterms can help clarify who is responsible for costs at various stages of the shipping process.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on their operational efficiency, market conditions, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Turned Parts?
Several factors influence pricing in the turned parts market:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Discussing volume discounts with suppliers can provide significant cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts or those requiring tighter tolerances generally cost more. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Material Selection: As previously mentioned, the choice of material greatly impacts pricing. Opting for standard materials may reduce costs, while specialized materials may enhance performance but at a higher price.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific certifications (e.g., ISO, AS9100) may incur higher costs due to the additional quality assurance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capabilities, and geographic location can all influence pricing. Engaging with multiple suppliers and obtaining quotes can provide a clearer picture of the market rate.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can significantly impact the total landed cost of parts.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Turned Parts Sourcing?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing turned parts, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, MOQ, and payment terms. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price and consider the total cost of ownership, including logistics, quality control, and potential rework costs due to defects. This holistic view can help in selecting the most cost-effective option.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, being aware of local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and import tariffs is essential. These factors can affect overall costs and should be factored into budget planning.
-
Use Technology for Sourcing: Leverage technology platforms for sourcing to compare prices, quality, and capabilities across multiple suppliers. This can help identify the best value options.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate quality and ensure they meet your specifications. This can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
By carefully considering these components and strategies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing turned parts and achieve better cost outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing turned parts manufacturer With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Turned Parts Manufacturing
In the competitive landscape of precision component production, buyers often seek alternatives to traditional turned parts manufacturing. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses optimize their manufacturing processes, reduce costs, and enhance product performance. Below, we compare turned parts manufacturing with two viable alternatives: 3D printing and injection molding.
| Comparison Aspect | Turned Parts Manufacturer | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and tight tolerances; ideal for complex geometries | Good for prototyping; limited in material strength for final products | Excellent for high-volume production with consistent quality |
| Cost | Moderate setup costs; cost-effective for medium to large runs | High per-unit costs; economical for low volumes or prototypes | High initial investment; lower cost per unit in mass production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and advanced machinery | Simple setup with CAD software; easy for rapid prototyping | Complex mold design and setup; longer lead times |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of CNC machines required | Minimal maintenance; dependent on software updates | High maintenance for molds; wear and tear can affect quality |
| Best Use Case | High-precision components in automotive and aerospace | Rapid prototyping and low-volume custom parts | High-volume production of standardized components |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has gained traction for its ability to produce complex designs directly from digital models. This method is particularly advantageous for rapid prototyping and small-batch production, allowing for quick iterations and design changes. However, the material options are often limited, and while it excels in flexibility and speed, the mechanical properties of printed parts may not match those of traditionally turned components. Therefore, 3D printing is best suited for applications where design complexity and speed outweigh the need for high strength and durability.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process used primarily for producing large volumes of identical parts. It involves injecting molten material into a pre-designed mold, resulting in consistent and high-quality components. The primary advantages of injection molding include its cost-effectiveness in mass production and the ability to use a wide range of materials, including plastics and metals. However, the initial setup costs for mold creation can be significant, and the process lacks flexibility for design changes once the mold is made. Injection molding is ideal for companies that have a steady demand for high quantities of standardized parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting between turned parts manufacturing and its alternatives, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including production volume, budget, and the specific performance requirements of their components. For high-precision applications with moderate production needs, turned parts manufacturing may be the most suitable option. Conversely, businesses focused on rapid prototyping might find 3D printing more advantageous. Lastly, for companies aiming for mass production of uniform components, injection molding presents a compelling case. Ultimately, the decision should align with the strategic goals of the business and the specific demands of the target market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for turned parts manufacturer
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Turned Parts Manufacturing?
When considering the procurement of turned parts, understanding critical technical specifications is essential for ensuring that components meet operational demands. Here are some key properties that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the type of raw material used in manufacturing turned parts, such as stainless steel, brass, or titanium. Each material has unique properties that affect performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. For example, stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance in harsh environments, making it ideal for medical and aerospace applications. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension, ensuring that parts fit together properly during assembly. In precision turned parts, tight tolerances (often in the range of ±0.01 mm) are critical for maintaining functionality and performance. Understanding tolerance levels is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers to ensure the reliability of the final product in its application. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a turned part affects its aesthetic quality and performance characteristics, such as friction and wear resistance. Common finishes include polished, ground, or anodized surfaces. B2B buyers should specify surface finish requirements to meet industry standards and operational needs, particularly in sectors like automotive and medical devices. -
Machining Process
Different machining processes, such as CNC turning or automatic screw machining, define the efficiency and precision of production. Understanding the specific processes used can help buyers assess production capabilities and lead times. For instance, CNC turning is suitable for complex geometries, while automatic lathes excel in high-volume, small-part production. -
Production Volume
The scale of production—whether low-volume custom runs or high-volume mass production—affects pricing and lead times. Manufacturers often have different capabilities based on their equipment and processes, so it’s important for buyers to communicate their volume needs clearly to receive accurate quotes and timelines. -
Secondary Operations
Many turned parts undergo secondary operations such as drilling, tapping, or plating to enhance functionality. Understanding which secondary operations are available can help buyers ensure that their components meet all necessary specifications and requirements for their intended application.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Turned Parts Manufacturing?
In the realm of turned parts manufacturing, familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiations. Below are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are marketed by another company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality components that fit seamlessly into their existing products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it can affect inventory management and overall project costs. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs with suppliers before placing orders to ensure alignment with production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ helps suppliers provide accurate quotes, ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing and clear timelines for delivery. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations associated with the delivery of turned parts. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when coordinating production schedules and supply chain logistics. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
QA encompasses the processes and procedures that ensure products meet specified quality standards. Buyers should inquire about a manufacturer’s QA practices to ensure that components will perform reliably and meet regulatory requirements.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product performance in their respective industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the turned parts manufacturer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Turned Parts Manufacturing Sector?
The global market for turned parts manufacturing is witnessing dynamic changes, driven by technological advancements and evolving buyer demands. Key drivers include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, which enable manufacturers to improve efficiency and precision in production processes. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable suppliers, the ability to scale production while maintaining quality has become a significant factor in supplier selection.
Emerging trends indicate a growing reliance on CNC technology, which allows for the production of complex geometries and tighter tolerances. This is especially pertinent for industries such as automotive, medical, and electronics, where precision is critical. Furthermore, there is an increasing demand for customization, prompting manufacturers to offer tailored solutions that meet specific client needs. The use of advanced materials, including composites and specialized alloys, is also gaining traction, enhancing product performance in demanding applications.
Additionally, the supply chain landscape is evolving. With geopolitical uncertainties and fluctuating raw material costs, buyers are prioritizing suppliers who can offer transparency and agility in their sourcing processes. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where local manufacturing capabilities are being developed to reduce reliance on imports and mitigate risks associated with global supply chains.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Transforming Turned Parts Manufacturing?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional considerations; they are essential to modern manufacturing practices. The environmental impact of production processes, particularly in the turned parts sector, has prompted a shift towards greener operations. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing waste, optimizing energy consumption, and utilizing recyclable materials.
Ethical supply chains are gaining importance, especially for international B2B buyers. This involves ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly, adhering to labor laws, and minimizing environmental harm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming crucial benchmarks for buyers assessing potential suppliers.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise. Manufacturers are exploring the use of bio-based plastics and recycled metals, which not only reduce the carbon footprint but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. By prioritizing sustainability, manufacturers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing expectations of buyers who value corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of Turned Parts Manufacturing?
The evolution of turned parts manufacturing can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution when mechanized lathes began to transform the production of cylindrical components. Early methods were labor-intensive and limited in precision, but advancements in machining technology, such as the introduction of CNC lathes in the late 20th century, revolutionized the sector. These developments allowed for greater accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency, catering to the rising demands of various industries.
Today, turned parts manufacturing stands at the intersection of tradition and innovation, with a focus on precision engineering and sustainable practices. As the industry continues to evolve, manufacturers are not only adapting to technological advancements but also responding to the increasing complexity of buyer requirements on a global scale. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding both past practices and future trends for effective sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of turned parts manufacturer
-
How do I ensure quality when sourcing turned parts manufacturers?
To ensure quality, start by researching potential manufacturers’ reputations and certifications. Look for ISO 9001 or similar quality management certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Request samples or prototypes to assess their machining precision and material quality. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspections and testing methods. Establishing clear specifications and performance standards in your contract will also help maintain quality throughout the manufacturing process. -
What is the typical lead time for turned parts production?
Lead times for turned parts production can vary based on factors like complexity, volume, and the manufacturer’s capacity. Generally, standard orders may take anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks, while custom parts or larger orders could extend to 8 weeks or more. When discussing lead times, clarify your project’s urgency and any specific deadlines. A reliable manufacturer should provide you with a timeline that includes production, quality checks, and shipping, allowing you to plan accordingly. -
How can I customize my turned parts for specific applications?
Customization of turned parts is usually achieved by collaborating closely with the manufacturer. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, tolerances, and material requirements. Many manufacturers use advanced CNC technology, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries. Discuss any secondary operations needed, such as coating, threading, or finishing. A good manufacturer will guide you through the design process, suggesting modifications to optimize performance and manufacturability while meeting your unique application needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for turned parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among manufacturers, often depending on the complexity and material of the parts. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 100 units for simple components, while more complex or customized parts may require larger orders, sometimes starting at 500 or more. Discuss your needs with the manufacturer upfront to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller initial orders or pilot runs, especially if you are testing a new product. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with international turned parts manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and your relationship with them. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some manufacturers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) for established clients. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, currency, and any additional costs such as tariffs or shipping fees. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I vet a turned parts supplier for reliability and performance?
To vet a turned parts supplier, start by checking their industry experience and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients in similar industries to gauge their reliability. Additionally, assess their manufacturing capabilities and technology, ensuring they can meet your specific requirements. Conducting site visits, if feasible, can provide insight into their operations and quality controls. Finally, review their certifications and compliance with international standards to confirm their commitment to quality and performance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing turned parts internationally?
When sourcing turned parts internationally, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may affect delivery times and costs. Discuss logistics with your supplier to determine the best shipping options, whether air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Ensure that your supplier provides appropriate packaging to protect the components during transit. Additionally, familiarize yourself with your country’s import regulations to avoid delays or complications upon arrival. -
What industries typically require precision turned parts, and how can I identify potential clients?
Precision turned parts are essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics, where high precision and reliability are critical. To identify potential clients, conduct market research to understand industry demands and trends. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to network and showcase your capabilities. Online platforms like LinkedIn can also be useful for connecting with industry professionals. Tailor your marketing materials to highlight how your turned parts can solve specific challenges within these industries.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for turned parts manufacturer
As international B2B buyers increasingly seek high-quality turned parts, strategic sourcing has become paramount in ensuring competitive advantage and operational efficiency. By understanding the capabilities of manufacturers, such as precision machining, scalability, and the ability to work with diverse materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Emphasizing quality standards and technological advancements, such as CNC and automatic lathes, can significantly impact the performance and reliability of critical components across various industries.
In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for precision turned parts is poised for growth, driven by sectors ranging from automotive to medical technology. Collaborating with reputable manufacturers not only guarantees access to high-performance components but also fosters innovation through shared expertise and resources.
Looking ahead, it is essential for buyers to establish strong partnerships with turned parts manufacturers who can adapt to evolving market demands and provide tailored solutions. Engage with industry leaders today to secure a competitive edge in your supply chain and ensure your operations are equipped with the best components for future success.