Top 10 Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DenaliWeld – JET EZ & JET MOPA
Domain: denaliweld.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
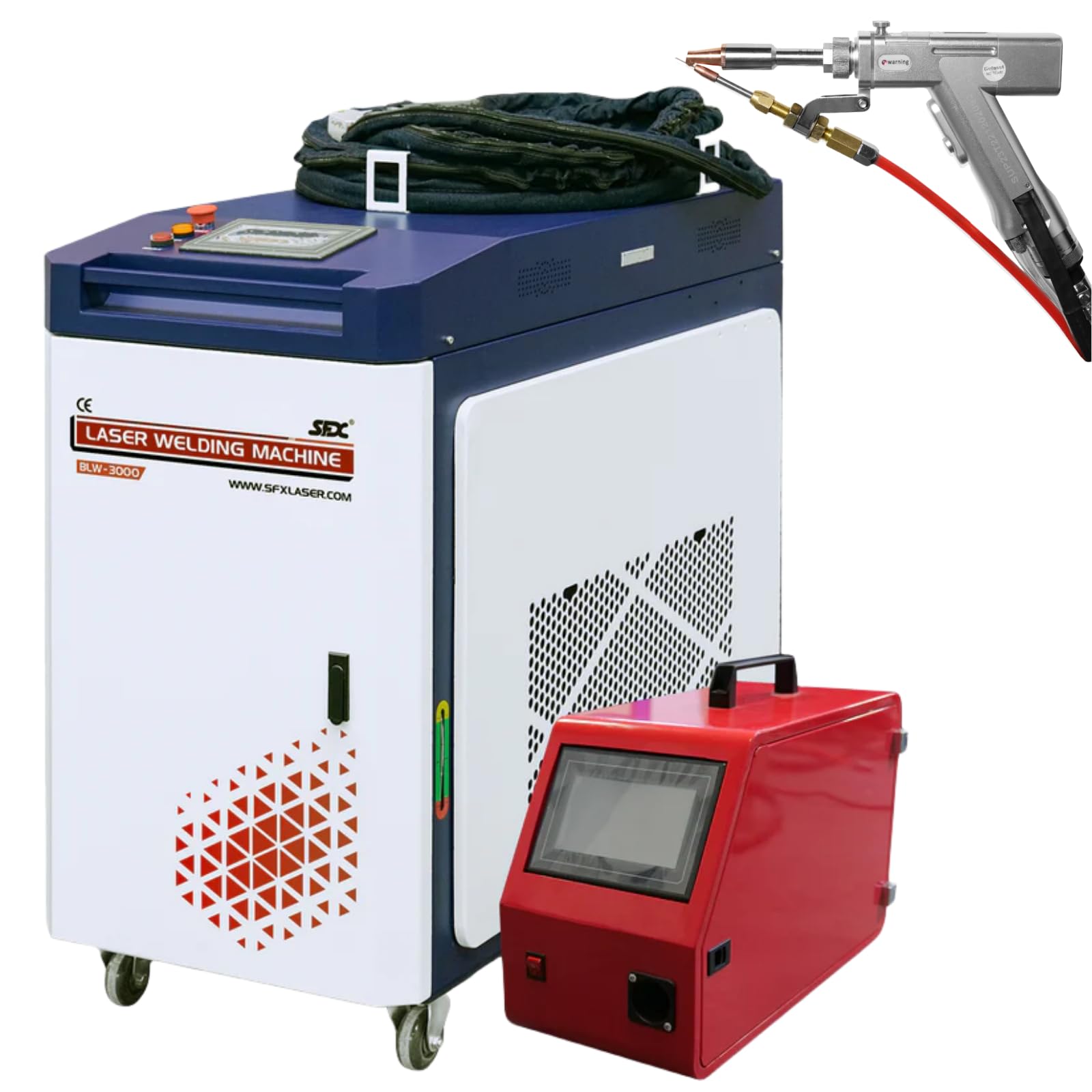
Introduction: DenaliWeld offers a range of laser welding products including: 1. JET EZ: A portable laser welder weighing 48.5 lbs, featuring dual welding/seam cleaning capabilities and a patented CUAL laser for precision on thin metals. 2. JET MOPA: A laser cleaning system that provides non-abrasive, eco-friendly solutions for removing rust, paint, and contaminants from metal surfaces, enhancing surface prepara…
2. Pioneer Machine Sales – Fiber Laser Welders
Domain: pioneermachinesales.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
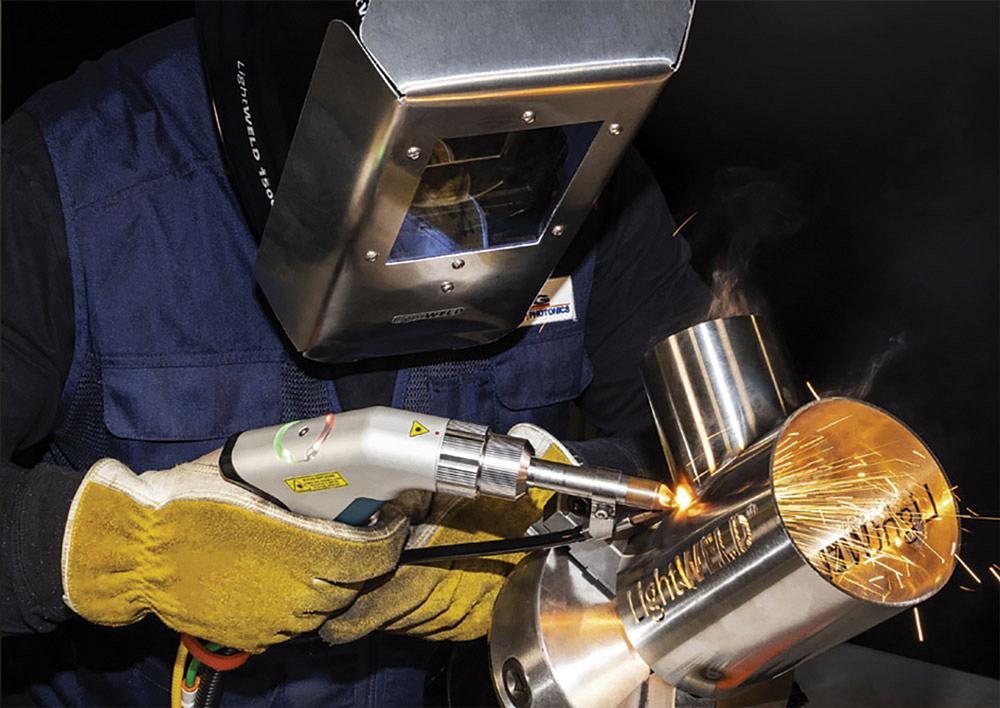
Introduction: New Fiber Laser Welders for sale by Pioneer Machine Sales Inc. include IPG LightWELD models. The LightWELD XR can weld stainless steel up to 6.35 mm thick, while the LightWELD 1500 can weld up to 4 mm thick. Both models can weld galvanized steel with the same thickness limits as stainless steel. For aluminum, the LightWELD XR can handle 3 & 5 Series aluminum up to 6.35 mm thick, while the LightWEL…
3. AMADA WELD TECH – Turn-Key Laser Welding Systems
Domain: amadaweldtech.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: AMADA WELD TECH specializes in engineering turn-key semi-automated systems for laser welding, providing the fastest path from application concept to full production. Successful laser manufacturing processes depend on effective system integration, where motion, laser, software, and tooling work together to support the desired process flow. The company offers various laser welding technologies inclu…
4. TRUMPF – Laser Welding Systems
Domain: trumpf.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Laser welding systems from TRUMPF offer versatile solutions for joining metals, plastics, and other materials with precision and minimal distortion. Key features include:
– Ability to create fine weld points (1 mm diameter) and deep penetration seams (meters long).
– Compatibility with high melting temperature and high heat conductivity materials.
– Minimal melt and short controllable melting time…
5. Alpha Laser – Industrial Laser Welding Systems
Domain: alphalaser.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Alpha Laser offers a range of industrial laser welding systems, including:
1. **Laser Welding**: High power and capability, designed for efficient and reliable welding of various materials.
2. **Laser Cladding**: Also known as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD), enhances and restores metal surfaces with precision and quality.
3. **Laser Hardening**: Provides localized heat treatment for creating harder …
6. Coherent – Laser Welding Machines
Domain: coherent.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Laser Welding Machines from Coherent offer a range of systems from manual to fully automated options. Key features include:
– Laser Choices: Options include fiber, solid-state, diode, and USP lasers to tackle various materials.
– Increased Versatility: Single systems capable of welding, cutting, scribing, structuring, and drilling.
– Improved Workflow: Easy integration with part handling and facto…
7. Laserax – Industrial Laser Welding Machines
Domain: laserax.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Industrial Laser Welding Machines designed for welding metals like aluminum, steel, copper, and various alloys. Available in manual or automated solutions, suitable for R&D and production. Key features include:
– Built to scale up production with vision systems, robot arms, and large field of view.
– Superior weld quality compared to traditional methods (TIG, MIG, ultrasonic bonding).
– Laser w…
8. AccTek Group – Laser Welding Machines
Domain: acctekgroup.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Laser welding machines from AccTek Group deliver deep, clean seams on stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and brass. They provide fast, low-distortion joints with minimal post-processing. The machines are designed for high-speed, high-precision applications in various industries including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and metal fabrication. They support spot welding, seam weldi…
9. OmTech – Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Handheld Fiber Laser Welding Machine, high efficiency, portable design, suitable for various materials, adjustable welding speed, easy operation, low maintenance, ideal for metal welding, includes safety features, compact size, lightweight, and user-friendly interface.
10. Kirin Laser – Hand-held Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Domain: kirinlaser.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Hand-held Fiber Laser Welding Machine: Price: USD$2,700 – USD$4,600; Features: Compact size for easy transport, ideal for outdoor use. 4-in-1 Economy Laser Welding Machine: Price: USD$1,575 – USD$4,285; Features: 4-in-1 function with integrated water cooling, compact size. 4-in-1 S&A Hand-held Laser Marking Machine: Price: USD$1,850 – USD$4,630; Features: Includes S&A water chiller, compact design…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laser welding machine manufacturers
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, sourcing reliable laser welding machine manufacturers presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The precision and efficiency required in modern production processes necessitate an informed approach to selecting the right equipment. This comprehensive guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the global market for laser welding machines, covering essential aspects such as types of machines, applications across various industries, and effective supplier vetting strategies.
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Vietnam and Nigeria, will find invaluable insights tailored to their unique needs. The guide will delve into cost considerations, highlighting how to assess the return on investment for different laser welding technologies. Furthermore, it will provide a framework for evaluating suppliers based on certifications, service capabilities, and technological advancements.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the laser welding market, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and drive competitive advantage. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or medical device sectors, the right laser welding machine can significantly elevate your production capabilities, making this guide an essential resource for your sourcing journey.
Understanding laser welding machine manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser Welders | High reliability, low maintenance, and automation-ready | Automotive, aerospace, electronics | Pros: High precision, low operational costs. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Handheld Laser Welders | Portable, easy to use, suitable for various materials | Construction, repair services, custom fabrication | Pros: Flexibility and portability. Cons: Limited power for heavy-duty applications. |
| Robotic Laser Welders | Seamless integration with robotics, automated processes | Mass production, automotive assembly | Pros: Consistent quality, high throughput. Cons: Requires significant setup and programming time. |
| MOPA Laser Welders | Adjustable pulse duration for precision on thin materials | Medical devices, electronics, jewelry | Pros: Excellent for delicate applications. Cons: May require skilled operators for optimal results. |
| Laser Cleaning Systems | Eco-friendly, non-abrasive cleaning solutions | Surface preparation in manufacturing | Pros: Reduces contamination risk, enhances efficiency. Cons: Not suitable for all material types. |
What Are Fiber Laser Welders and Their B2B Applications?
Fiber laser welders are known for their reliability and low maintenance requirements, making them ideal for industries that prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These machines are highly automated, allowing for seamless integration into existing production lines. They are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors, where precision is critical. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the specific material thickness capabilities when selecting a fiber laser welder, as this can impact long-term operational costs.
How Do Handheld Laser Welders Benefit B2B Buyers?
Handheld laser welders offer the advantage of portability and ease of use, making them suitable for a variety of applications, including construction and repair services. Their versatility allows for welding on-site, which can significantly reduce downtime and transportation costs. However, while they are great for lighter tasks, buyers should note that their power limitations may not meet the demands of heavy-duty industrial applications. Understanding the specific welding tasks at hand is crucial for making an informed purchase.
What Are Robotic Laser Welders and Their Advantages?
Robotic laser welders are designed for high-volume production environments, integrating seamlessly with robotic systems to deliver consistent, high-quality welds. These machines excel in mass production, particularly in automotive assembly lines, where speed and precision are paramount. While they provide significant advantages in terms of output and quality, the setup and programming can be complex, requiring skilled personnel. Buyers need to weigh the benefits of automation against the initial investment and training costs.
Why Choose MOPA Laser Welders for Delicate Applications?
MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) laser welders are characterized by their adjustable pulse duration, making them particularly effective for welding thin materials in delicate applications such as medical devices and jewelry. The ability to fine-tune the laser parameters allows for greater control over the welding process, ensuring high-quality results. However, these machines may require skilled operators to optimize performance, which is an important consideration for businesses looking to invest in MOPA technology.
How Do Laser Cleaning Systems Enhance Manufacturing Processes?
Laser cleaning systems provide eco-friendly, non-abrasive solutions for surface preparation in various manufacturing processes. By effectively removing contaminants without damaging the underlying material, these systems enhance the efficiency of subsequent welding or coating processes. However, they may not be suitable for all material types, so buyers should evaluate their specific cleaning needs and the compatibility of the system with their existing workflows. The investment in laser cleaning technology can lead to improved product quality and reduced operational risks.
Key Industrial Applications of laser welding machine manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of laser welding machine manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Welding of body panels, frames, and exhaust systems | Enhances production speed and precision, improving vehicle safety and efficiency. | Ensure compatibility with various materials and thicknesses, and look for automation-ready features. |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of aircraft components like engine blades | Delivers high-strength welds with minimal thermal distortion, crucial for safety and performance. | Focus on machines that can handle exotic alloys and meet stringent industry standards. |
| Medical Devices | Joining biocompatible materials for devices | Provides sterile, precise welds, ensuring patient safety and compliance with regulations. | Source machines that minimize contamination and offer flexibility for small component welding. |
| Electronics | Welding of delicate components such as circuit boards | Facilitates high-speed production while maintaining quality, supporting miniaturization trends. | Look for models that provide high precision and repeatability, essential for mass production. |
| Shipbuilding | Welding of hulls and watertight compartments | Improves structural integrity and production efficiency, ensuring durability in marine environments. | Consider machines that offer low thermal deformation and high precision for complex geometries. |
How Are Laser Welding Machines Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, laser welding machines are employed for critical applications such as welding body panels, frames, and exhaust systems. These machines deliver precise, high-speed welds, which not only enhance production efficiency but also improve vehicle safety and fuel efficiency. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing machines that can handle various materials and thicknesses is essential. Additionally, automation-ready features can significantly reduce labor costs and increase output.
What Role Do Laser Welders Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
The aerospace industry relies on laser welding for fabricating components that require high strength and minimal thermal distortion, such as engine blades and turbine discs. Laser welders provide the necessary precision to meet stringent safety and performance standards. Buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, should prioritize machines capable of working with exotic alloys and ensuring high-quality welds. Compliance with industry certifications is also a critical factor in the purchasing decision.
Why Are Laser Welding Machines Essential for Medical Device Production?
Laser welding machines are vital in the medical device industry for creating sterile, precise welds in biocompatible materials. These machines ensure consistent quality in small components, which is crucial for patient safety and regulatory compliance. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should focus on sourcing machines that minimize contamination risks and offer flexibility for various applications. This ensures that production meets the high standards required in the medical field.
How Do Laser Welders Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, laser welding machines are used for joining delicate components, such as circuit boards and sensors. The technology allows for high-speed production without thermal damage, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of sensitive components. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should seek models that provide high precision and repeatability to support mass production and miniaturization trends in electronics.
What Are the Benefits of Laser Welding in Shipbuilding?
Laser welding is extensively utilized in shipbuilding for welding hulls and watertight compartments. This technology enhances structural integrity and production efficiency, ensuring durability in challenging marine environments. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America, sourcing machines that offer low thermal deformation and high precision is crucial. Such capabilities enable the handling of complex geometries, which are often required in modern ship design.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laser welding machine manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Equipment Compatibility Challenges
The Problem: One of the significant hurdles B2B buyers face when purchasing laser welding machines is ensuring compatibility with existing systems and processes. Many manufacturers operate with a variety of materials and thicknesses, requiring specific machine capabilities. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by technical specifications, leading to potential mismatches that can cause production delays, increased costs, or even damage to materials.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their current production environment before engaging with laser welding machine manufacturers. Start by cataloging the materials and thicknesses commonly used in your operations. Use this data to create a detailed specification document that outlines the required capabilities of the new laser welding machine, including power levels, cooling methods, and automation features. Engage directly with manufacturers to discuss these specifications and request demonstrations or trials of the equipment. This proactive approach ensures that the selected machine not only meets current needs but also allows for future scalability.
Scenario 2: Addressing High Maintenance and Downtime Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience frustration with the maintenance and operational costs associated with laser welding machines. Unexpected breakdowns and prolonged downtime can severely impact production schedules, leading to lost revenue and strained client relationships. Buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers that can offer efficient maintenance services and support.
The Solution: To tackle maintenance challenges, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that provide comprehensive service agreements, including regular maintenance checks and rapid response times for repairs. When evaluating potential suppliers, inquire about their track record for machine reliability and the availability of spare parts. Consider manufacturers with a global presence and local service teams, as this ensures quicker support. Additionally, investing in training for staff on proper machine operation can significantly reduce the risk of operator-induced issues, contributing to overall machine longevity and reliability.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Limited Technical Support and Training
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of adequate technical support and training when integrating new laser welding technology. Many companies find that once the equipment is purchased, they are left to navigate its complexities without sufficient guidance. This can lead to underutilization of the equipment, poor welding quality, and frustration among operators.
The Solution: To enhance the onboarding process and ensure effective use of new laser welding machines, buyers should actively seek manufacturers that offer robust training programs as part of their sales package. Before finalizing a purchase, discuss the training options available, including on-site training, online tutorials, and ongoing support. Establish a partnership with the manufacturer where periodic training sessions are scheduled, allowing for updates on new technologies and techniques. Additionally, consider creating a feedback loop with the manufacturer to address any operational challenges that arise post-installation. This collaborative approach not only improves the skill level of the workforce but also maximizes the investment in laser welding technology.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laser welding machine manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Laser Welding?
When selecting materials for laser welding, manufacturers must consider several key properties that influence product performance. The most commonly used materials include stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium. Each material exhibits unique characteristics that affect its suitability for various applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Laser Welding Applications?
Stainless steel is a popular choice due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding environments. The material is often used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
Pros: Stainless steel offers durability and longevity, which can lead to lower life-cycle costs. Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications, from structural components to intricate designs.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel can be higher than other materials, and its manufacturing complexity may require specialized equipment and techniques for optimal results.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various media makes it ideal for applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as food processing and medical equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the selected stainless steel grades meet local regulations and application requirements.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Laser Welding?
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and is highly malleable, making it a favorable option for many applications, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Pros: Aluminum’s low weight can enhance fuel efficiency in vehicles and aircraft. Its ability to be easily shaped and welded allows for innovative designs.
Cons: While aluminum is easier to work with, it can be more expensive than steel, and its lower melting point may require careful handling to prevent warping during welding.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace components and automotive frames. Its compatibility with various coatings can also enhance performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades that comply with local standards. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect material performance, selecting the right alloy is essential.
How Does Copper Compare in Laser Welding?
Copper is known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and thermal properties, making it ideal for electrical applications and heat exchangers.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity allows for efficient energy transfer, making it a preferred choice for electrical components. Its durability also ensures a long lifespan.
Cons: The high thermal conductivity can pose challenges during welding, requiring precise control to avoid overheating. Additionally, copper can be more expensive than other metals.
Impact on Application: Copper is widely used in electrical and plumbing applications where conductivity is paramount. Its resistance to corrosion adds to its appeal in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the copper grades used comply with international standards. In regions like Africa, where electrical infrastructure is developing, understanding local specifications is vital.
What Makes Titanium a Unique Choice for Laser Welding?
Titanium is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for specialized applications in aerospace and medical industries.
Pros: Titanium’s strength allows for lightweight designs without compromising durability, which is crucial in aerospace applications. Its biocompatibility makes it ideal for medical implants.
Cons: Titanium is one of the more expensive materials, and its welding can be complex, requiring specialized techniques to avoid contamination.
Impact on Application: Titanium is often used in high-performance applications where strength and weight savings are critical. Its resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for marine and chemical processing environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with stringent international standards is essential, especially in the aerospace and medical sectors. Buyers should also consider the availability of titanium in their local markets.
Summary of Material Selection for Laser Welding
| Material | Typical Use Case for laser welding machine manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace, lightweight structures | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | More expensive, lower melting point | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical components, heat exchangers | Exceptional electrical conductivity | Requires precise welding control | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex welding requirements | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic selection of materials for laser welding, offering actionable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can significantly influence purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laser welding machine manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Laser Welding Machines?
The manufacturing of laser welding machines involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure they select a reliable manufacturer.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of materials. This typically involves sourcing high-quality components such as laser sources, optics, and structural materials. Manufacturers often rely on certified suppliers to provide materials that meet international standards. For instance, steel and aluminum components must undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they can withstand high temperatures and pressures during operation.
2. Forming and Machining
Once the materials are ready, they undergo forming processes such as cutting, bending, and machining. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are frequently employed to ensure precise dimensions and tolerances. This stage is critical, as any inaccuracies can lead to significant performance issues in the final product. Techniques such as laser cutting and waterjet cutting may also be utilized for intricate designs.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves integrating various components, including the laser source, cooling systems, and control electronics. Skilled technicians and engineers meticulously fit and test each part to ensure compatibility and functionality. This step often incorporates modular designs to facilitate upgrades and maintenance, allowing manufacturers to offer customizable solutions to clients.
4. Finishing
After assembly, laser welding machines undergo finishing processes that may include painting, coating, and surface treatment. These treatments not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the machines but also improve their resistance to corrosion and wear. Quality assurance checks at this stage confirm that all components meet the specified standards for durability and performance.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements. For international B2B buyers, understanding these standards can significantly impact their purchasing decisions.
International Standards
One of the most recognized quality management standards is ISO 9001. This standard focuses on consistent quality and customer satisfaction, requiring manufacturers to implement comprehensive quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has undergone rigorous assessments and has established processes for continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, laser welding machine manufacturers often seek certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for those targeting the oil and gas sectors. These certifications demonstrate compliance with safety and performance regulations specific to various industries.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each stage meets established standards. This systematic approach helps identify defects early, minimizing costly rework and enhancing overall product reliability.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
At the beginning of the manufacturing process, Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks the quality of raw materials and components. This involves inspecting materials for defects and verifying that they meet required specifications. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned to suppliers.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors various stages, such as machining and assembly. Technicians perform regular inspections and tests, utilizing measurement tools and techniques like laser alignment to ensure that components are assembled correctly and function as intended. This proactive approach helps catch issues before they escalate.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Once the machines are assembled, Final Quality Control (FQC) is conducted. This stage includes comprehensive testing of the laser welding machine’s performance, safety features, and compliance with regulatory standards. Manufacturers often simulate operational conditions to validate that the machine operates effectively under various scenarios.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Quality in Laser Welding Machines?
To ensure that laser welding machines meet industry standards, manufacturers employ various testing methods throughout the production process. Understanding these methods can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of a supplier.
Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates the machine’s ability to perform laser welding tasks under specified conditions. This includes testing the laser’s power output, beam quality, and welding speed. Manufacturers often conduct tests on different materials and thicknesses to demonstrate the machine’s versatility.
Safety Testing
Safety testing is critical for compliance with international standards. This includes evaluating electrical safety, thermal safety, and ensuring that all moving parts are adequately shielded to prevent operator injury. Manufacturers must document these tests to provide proof of compliance to potential buyers.
Durability and Longevity Testing
Durability testing assesses how well the machine withstands prolonged use. This may involve simulating extended operational hours to identify potential failures or wear points. Manufacturers often provide data on expected lifespans and maintenance requirements based on these tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is essential to ensure they receive high-quality products. Here are several effective strategies:
Conducting Audits
B2B buyers can request to conduct audits of manufacturing facilities. This allows them to assess the quality control measures in place and verify compliance with international standards. Audits can also include reviewing documentation related to quality processes and past performance.
Requesting Quality Reports
Manufacturers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their testing methods, results, and certifications. Buyers can review these documents to gain insights into the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and their history of meeting industry standards.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. These inspectors can evaluate the production facility and conduct independent testing of the machines, offering additional assurance to buyers.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing laser welding machines. This includes understanding the specific requirements for their regions, such as CE marking for the European market or compliance with local safety standards in Africa or South America.
Regional Compliance
Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific certifications required for their markets. For instance, the Middle East may have distinct standards that differ from those in Europe, impacting how products are certified and accepted.
Language and Documentation
Language barriers can pose challenges when dealing with international suppliers. Buyers should ensure that all quality documentation, including certifications and testing reports, are available in a language they understand. This helps prevent misinterpretations and ensures clarity in compliance requirements.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural differences can influence communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should approach negotiations and supplier relationships with cultural sensitivity, fostering collaboration and mutual understanding to achieve desired outcomes.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of laser welding machine manufacturers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laser welding machine manufacturers’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure laser welding machines from manufacturers. This step-by-step approach will help ensure that you select a supplier that meets your technical requirements, operational needs, and business goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with manufacturers, clearly outline the technical specifications of the laser welding machines you need. Consider factors such as the types of materials you’ll be welding (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum, copper), the thickness of those materials, and the desired speed and precision of the welds. Having these specifications in place will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your requirements.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential laser welding machine manufacturers. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, positive customer reviews, and a proven track record of delivering quality equipment. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry publications to compile a list of candidates that fit your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify that the manufacturers hold relevant certifications, such as CE, SGS, or ISO standards. These certifications indicate compliance with international safety and quality standards, providing assurance that the equipment meets industry benchmarks. Additionally, check for any specific certifications related to your region, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Quality after-sales support is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations. Inquire about the availability of local service centers, warranty terms, and technical support options. A reliable manufacturer should offer training, maintenance services, and prompt assistance in case of equipment issues, which is particularly important for businesses in regions with less access to technical expertise.
Step 5: Request Product Demonstrations
When possible, request demonstrations of the laser welding machines you are considering. Observing the equipment in action allows you to assess its performance and suitability for your specific applications. Pay attention to aspects such as ease of use, speed of operation, and the quality of the welds produced during the demonstration.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Once you have narrowed down your choices, compare pricing structures and financing options from different manufacturers. Look for transparent pricing that includes all costs—such as shipping, installation, and training. Some manufacturers may offer leasing options or financing plans that can help ease the upfront costs, making it easier to acquire the necessary equipment without straining your budget.
Step 7: Seek Customer References and Case Studies
Finally, ask for references from other customers who have purchased similar laser welding machines. Engaging with previous clients can provide valuable insights into the manufacturer’s reliability, product performance, and customer service. Case studies can also illustrate how the equipment has been successfully implemented in similar industries, giving you confidence in your purchasing decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing laser welding machines effectively, ensuring they select a manufacturer that aligns with their operational needs and strategic objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laser welding machine manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Laser Welding Machine Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of laser welding machines is essential for B2B buyers looking to source these advanced technologies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys often constitute the bulk of material expenses. For instance, using high-grade fiber optics and laser diodes can increase initial costs but may enhance long-term performance and durability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for both assembly and maintenance. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may provide competitive pricing, but may also compromise on quality unless managed properly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the final pricing of laser welding machines.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized machine configurations. The cost of these tools can be significant, especially for unique designs or high-precision requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that machines meet industry standards and certifications (e.g., CE, SGS). Investing in QC can increase costs upfront but reduces the risk of warranty claims and enhances customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the destination. Buyers should consider freight costs, insurance, and any potential tariffs that may apply when importing equipment.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin to cover operational risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market demand and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Laser Welding Machines?
Several factors influence the pricing of laser welding machines, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can lead to bulk purchasing discounts. Ordering in larger quantities often results in lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specialized software or unique configurations, can significantly increase prices. Buyers should evaluate whether the added capabilities align with their operational needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with premium materials and certified to high standards typically command higher prices. However, investing in quality often translates to lower maintenance costs and enhanced performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the manufacturer can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium but provide peace of mind regarding after-sales support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affect the total landed cost and should be clearly outlined in contracts.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation Skills: Engaging in negotiations can lead to better pricing, especially when discussing volume purchases or long-term contracts. Building a relationship with suppliers can also yield favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term operational expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic factors that may affect pricing. Researching local competitors can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Consider Local Support: Sourcing from manufacturers with local representation can reduce logistics costs and provide easier access to service and support.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing structure for laser welding machines, actual prices may vary significantly based on specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always consult with manufacturers for precise quotations tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laser welding machine manufacturers With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers
When evaluating manufacturing processes, particularly for welding, it’s essential to consider various alternatives that can meet similar needs. While laser welding machines offer advanced capabilities, other technologies and methods may provide viable solutions depending on specific project requirements, material types, and operational constraints. This analysis compares laser welding machine manufacturers with two alternative solutions: traditional arc welding and resistance welding.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers | Traditional Arc Welding | Resistance Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and speed; minimal heat distortion | Good for thick materials; slower speed | Fast cycle times; suited for high-volume production |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs over time | Lower upfront cost; higher operational costs | Moderate cost; often economical for high volume |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled technicians; complex setup | Easier to implement; widely available | Simple setup; requires less training |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; requires specialized parts | Moderate maintenance; accessible parts | Low maintenance; minimal downtime |
| Best Use Case | Thin materials, intricate designs, and high precision | Heavy-duty applications, thicker materials | High-volume applications, such as automotive assembly |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Arc Welding?
Traditional arc welding is a well-established method that utilizes an electric arc to melt and join metals. It is particularly effective for thicker materials, making it a popular choice in heavy industries such as construction and shipbuilding. One of the main advantages of arc welding is its lower initial cost, as the equipment is generally more affordable and widely available. However, it tends to have slower welding speeds compared to laser welding and may introduce more heat into the workpiece, resulting in greater distortion. This method also requires skilled technicians to operate effectively, which can be a limiting factor in some scenarios.
How Does Resistance Welding Compare in Terms of Efficiency?
Resistance welding is another alternative that is particularly efficient for high-volume production scenarios, such as in the automotive industry. This method uses heat generated by electrical resistance to join metals, allowing for fast cycle times and the ability to weld multiple layers of material simultaneously. The simplicity of the setup and operation makes it accessible for various manufacturing environments. However, resistance welding is best suited for specific applications, such as spot welding on sheet metals, and may not provide the precision required for intricate designs that laser welding offers. The cost-effectiveness of resistance welding shines in mass production, but its limitations in material types and thicknesses should be considered.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Welding Solution?
Choosing the right welding solution depends on various factors, including project requirements, material types, production volume, and budget constraints. For businesses focused on high precision and intricate designs, laser welding machines may be the most suitable choice despite the higher initial investment. On the other hand, companies that prioritize cost-effectiveness and efficiency in high-volume production might find resistance welding to be a more appropriate solution. Traditional arc welding serves well for heavy-duty applications and thicker materials, making it a versatile choice in diverse industries. Ultimately, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs and weigh the pros and cons of each option to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laser welding machine manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Laser Welding Machines?
Understanding the technical specifications of laser welding machines is crucial for B2B buyers, as these properties directly impact the performance, efficiency, and suitability of the equipment for specific applications. Here are some essential technical properties to consider:
1. Welding Speed
Welding speed is a critical specification that refers to the rate at which the laser welder can complete a weld. It is typically measured in meters per minute (m/min). Higher speeds can significantly reduce production time and costs, making this a vital metric for industries with high-volume demands, such as automotive and aerospace.
2. Maximum Material Thickness
This specification indicates the maximum thickness of materials that the laser welder can effectively process. For instance, some models can weld stainless steel up to 6.35 mm thick, while others may be limited to 4 mm. Knowing the maximum material thickness is important for manufacturers to ensure the machine meets the requirements of their specific applications.
3. Beam Quality (M² Factor)
The beam quality, often represented by the M² factor, measures the focusability and efficiency of the laser beam. A lower M² value indicates a higher quality beam, allowing for finer cuts and welds. This property is particularly relevant for industries that require precision, such as electronics and medical device manufacturing.
4. Cooling System
The cooling system of a laser welder is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and prolonging the life of the machine. Different machines may use air-cooling or water-cooling technologies. An efficient cooling system minimizes downtime due to overheating, enhancing productivity in high-demand environments.
5. Power Output (Wattage)
The power output, measured in watts, determines the laser’s ability to penetrate materials and achieve high-quality welds. Higher wattage is generally needed for welding thicker materials or for applications that require faster processing. Understanding the power requirements helps buyers select the right machine for their operational needs.
6. Automation Capability
Automation features, such as robotic integration and programmable settings, enhance the efficiency of laser welding machines. Machines that support automation can reduce labor costs and improve consistency in weld quality. For manufacturers looking to scale operations, investing in automation-ready machines is essential.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Laser Welding Machines?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B sector. Here are some common trade terms associated with laser welding machines:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser welding machines, OEMs often provide the underlying technology and components that enable various welding systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the equipment.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. For laser welding machines, MOQs can affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller manufacturers. Buyers should clarify MOQs to avoid overcommitting to inventory that may not be needed.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers from different manufacturers. An effective RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers dealing with international suppliers, as they dictate shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In laser welding machinery, understanding lead times can help businesses plan their production schedules and avoid delays.
6. Warranty and Service Agreements
Warranty and service agreements outline the support and maintenance terms provided by the manufacturer. Knowing these terms can help buyers ensure they receive adequate post-purchase support, which is crucial for minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in laser welding machines, ensuring they select equipment that aligns with their operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laser welding machine manufacturers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Laser Welding Machine Sector?
The laser welding machine sector is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for precision and efficiency across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As global manufacturing continues to evolve, the shift towards automation and advanced manufacturing technologies is becoming more pronounced. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide innovative solutions that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
Emerging technologies, such as fiber lasers, are leading the charge in improving weld quality and processing speeds, making laser welding an attractive option for complex projects. The trend towards portable and user-friendly machines, such as handheld laser welders, is also gaining traction, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities in laser welding machines is enhancing operational efficiency and facilitating real-time monitoring, which is crucial for maintaining high-quality standards in production.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers?
Sustainability is becoming a focal point for laser welding machine manufacturers, as the environmental impact of production processes comes under scrutiny. Many manufacturers are prioritizing the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies to minimize their carbon footprint. Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining importance, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to responsible sourcing of raw materials.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications are becoming essential for manufacturers seeking to enhance their market appeal. These certifications not only indicate compliance with environmental standards but also reassure buyers about the sustainability of their supply chains. Furthermore, laser welding technology itself is inherently more sustainable than traditional welding methods, as it typically results in less waste and energy consumption. This alignment with sustainability trends can be a significant differentiator for manufacturers looking to capture the attention of international B2B buyers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Laser Welding Technology and Its Significance in B2B?
The evolution of laser welding technology dates back to the early 1960s when lasers were first used for industrial applications. Initially, the technology was limited in scope and primarily used in specialized sectors. However, advancements in laser technology, particularly fiber lasers, have dramatically improved their capabilities, making them a viable option for a broader range of industries.
As the technology has matured, laser welding has gained recognition for its ability to produce high-quality, precise welds with minimal thermal distortion. This precision is crucial for industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where the integrity of components is paramount. The development of portable and automated laser welding solutions has further expanded the technology’s reach, allowing manufacturers to improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs. For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context and technological advancements in laser welding can inform sourcing decisions, ensuring they partner with manufacturers who are at the forefront of innovation and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laser welding machine manufacturers
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with laser welding machines?
To address compatibility issues, first, assess the specific materials and thicknesses you intend to weld. Ensure that the chosen laser welding machine is capable of handling those materials. Manufacturers often provide detailed specifications regarding material compatibility. Additionally, consult with the supplier to verify if they offer customization options or special attachments for unique welding tasks. Regular maintenance and calibration of the equipment can also help in achieving optimal performance and preventing compatibility issues. -
What is the best laser welding machine for thin metal applications?
For thin metal applications, a portable laser welder like the DenaliWeld JET EZ is highly recommended. It features patented CUAL laser technology that ensures precision and minimizes heat distortion. This model is lightweight and designed for ease of use, making it ideal for intricate welding tasks on thin sheets. When selecting a machine, consider factors such as power output, cooling methods, and the range of materials it can handle effectively to ensure it meets your specific requirements. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting laser welding machine manufacturers?
When vetting manufacturers, consider their certifications (like CE, SGS), production capacity, and experience in the industry. Research their reputation through customer reviews and case studies to assess reliability. It’s essential to inquire about after-sales support, including training and maintenance services. Additionally, check their ability to provide customized solutions tailored to your specific needs, as well as their compliance with international quality standards. -
What customization options are typically available for laser welding machines?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options, including power settings, welding speed, and specialized attachments for various materials. Some may also provide tailored software for specific applications or integration with existing automated systems. It’s crucial to discuss your specific welding requirements with potential suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Customization can significantly enhance efficiency and quality, making it a worthwhile investment. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for laser welding machines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among manufacturers. Some may offer single units for specialized projects, while others might require bulk orders to ensure cost-effectiveness. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ and explore options for sample orders to assess machine performance. Additionally, consider potential discounts for larger orders, as well as the implications for inventory management and cash flow in your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing laser welding machines?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the manufacturer and your negotiation power. Common terms include a deposit upfront (often 30% to 50%), with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger purchases. Always ensure that the payment terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid any misunderstandings, and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing laser welding machines internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and performance data from manufacturers. It’s advisable to conduct a factory audit or engage third-party quality inspection services before shipment. Additionally, verify that the machines comply with international standards and certifications. Establish clear quality expectations in your contract, including warranty terms and support for any potential defects. Consistent communication with the supplier throughout the process can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing laser welding machines?
When importing laser welding machines, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Work closely with your supplier to understand the packaging requirements and ensure that the machines are protected during transit. It’s beneficial to partner with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial equipment to streamline the process. Additionally, plan for potential delays and ensure you have the necessary documentation for smooth customs clearance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laser welding machine manufacturers
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of laser welding machines is not just a procurement necessity but a pathway to operational excellence. By prioritizing manufacturers like DenaliWeld and Pioneer Machine Sales, businesses can access advanced technologies that enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and ensure high-quality welds across diverse materials. The integration of automation and eco-friendly solutions further positions laser welding as a sustainable choice for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should leverage the rich capabilities offered by these manufacturers to address their specific operational challenges. Engaging with suppliers who provide robust after-sales support and localized services can significantly impact overall return on investment.
Looking ahead, the demand for precision welding solutions will only grow as industries evolve. Embrace the opportunity to connect with leading laser welding machine manufacturers and explore tailored solutions that drive efficiency and innovation in your operations. The future of manufacturing is bright, and with the right partnerships, your business can lead the charge in this transformative journey.