Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tool to remove broken screw
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing and construction, the ability to efficiently remove broken screws can significantly impact operational efficiency. Sourcing effective tools to remove broken screws is a critical challenge faced by businesses across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and machinery. This guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers, offering a comprehensive overview of the types of screw removal tools available, their specific applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting and cost assessment.
Navigating the global market can be complex, especially for buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into the latest technologies and methodologies for broken screw extraction, ensuring that they make informed purchasing decisions. From understanding the differences between spiral screw extractors and drill bit kits to evaluating the cost-effectiveness of various suppliers, this resource aims to demystify the sourcing process.
Furthermore, the guide emphasizes the importance of selecting the right tools to minimize downtime and enhance productivity in operations. By leveraging this information, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement processes, reduce operational disruptions, and ultimately improve their bottom line. Whether you’re a procurement officer or a project manager, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge needed to successfully navigate the global market for screw removal tools.
Understanding tool to remove broken screw Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spiral Screw Extractor | Features spiral flutes for gripping broken screws | Construction, Automotive, Manufacturing | Pros: Effective for various screw sizes; easy to use. Cons: Requires precise drilling; may not work on severely damaged screws. |
| EZ Out Extractor | Designed with a reverse spiral for enhanced grip | Repair Shops, Machinery Maintenance | Pros: High grip strength; can extract deeply embedded screws. Cons: Limited to specific screw sizes; may require multiple sizes for various applications. |
| Screw Removal Pliers | Locking mechanism for a secure grip | Woodworking, Metalworking, DIY Projects | Pros: Versatile; no need for drilling; quick removal. Cons: May damage surrounding material if not used carefully. |
| Drill Bit Extractor | Combines drilling and extraction in one tool | Heavy Machinery, Industrial Repair | Pros: Dual functionality; efficient for stubborn screws. Cons: Can be more expensive; requires skilled operation. |
| Tapping Tool | Creates new threads in broken screw holes | Metal Fabrication, Engineering | Pros: Ideal for reusing damaged threads; cost-effective. Cons: Not suitable for all screw types; requires precise alignment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Spiral Screw Extractors?
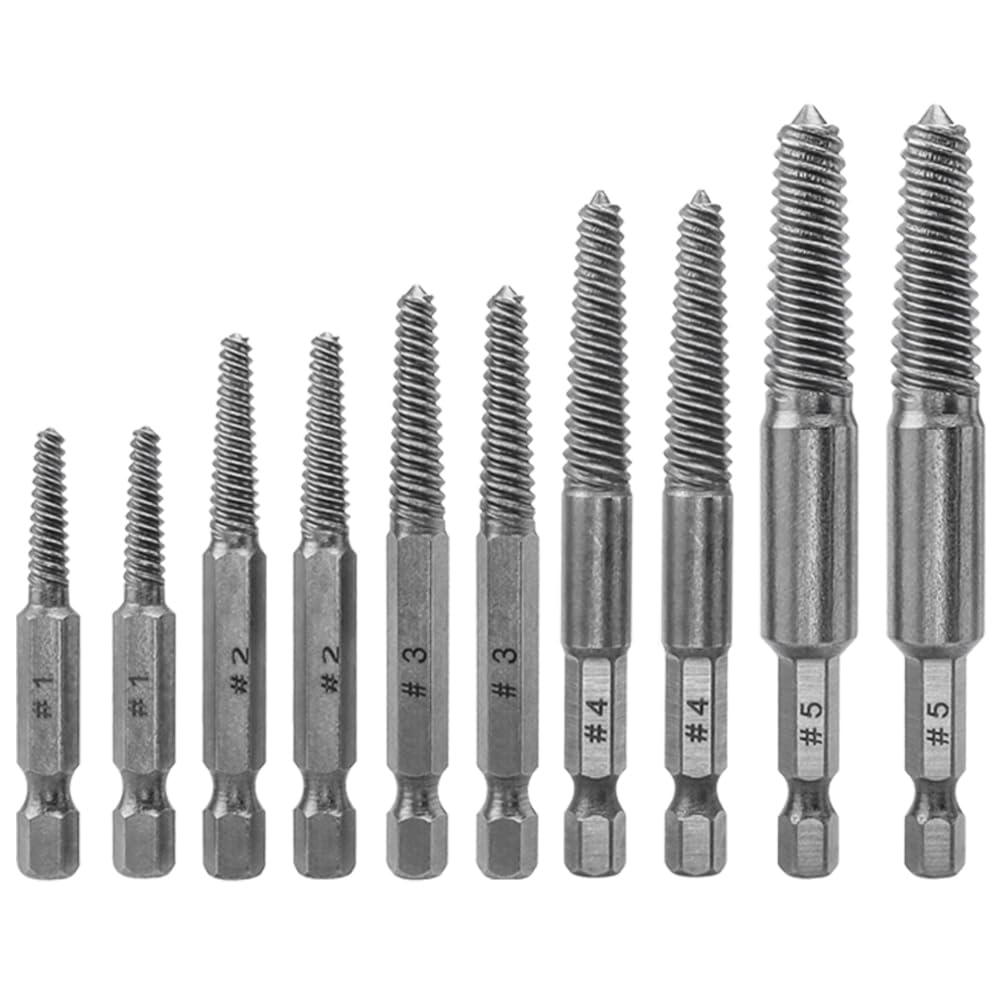
Spiral screw extractors are designed with a tapered, spiral flute that grips the broken screw as it is turned counterclockwise. These tools are particularly effective for screws that have broken off with a portion still protruding from the surface. They are commonly used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries. When purchasing, buyers should consider the range of sizes included in the set, as well as the material quality, which can affect durability and effectiveness.
How Do EZ Out Extractors Work in B2B Applications?
EZ Out extractors feature a reverse spiral design that enhances their gripping ability, making them suitable for extracting screws that are deeply embedded or stripped. They are widely used in repair shops and machinery maintenance, where precision is essential. Buyers should evaluate the extractor’s size range and compatibility with different screw types, as well as the tool’s overall build quality for longevity in demanding environments.
Why Choose Screw Removal Pliers for Quick Fixes?
Screw removal pliers utilize a locking mechanism that provides a strong grip on broken screws, allowing for quick extraction without the need for drilling. They are ideal for woodworking, metalworking, and various DIY projects, making them a versatile choice for many professionals. Buyers should look for pliers with adjustable jaws and comfortable grips, ensuring ease of use over extended periods.
What Are the Benefits of Using Drill Bit Extractors?
Drill bit extractors combine the functionalities of drilling and screw extraction, making them particularly useful for stubborn screws that resist traditional methods. They find application in heavy machinery and industrial repair settings where efficiency is paramount. Buyers should consider the extractor’s design, ease of use, and whether it can accommodate different screw sizes, as well as the cost-effectiveness of purchasing a multi-size kit.
How Do Tapping Tools Aid in Screw Removal?
Tapping tools are designed to create new threads in holes left by broken screws, allowing for the reuse of damaged threads. They are especially beneficial in metal fabrication and engineering, where precision is critical. When purchasing tapping tools, buyers should assess the compatibility with various screw sizes and the tool’s ability to maintain alignment during use, as improper alignment can lead to further complications.
Key Industrial Applications of tool to remove broken screw
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Tool to Remove Broken Screw | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Repairing engine components and assemblies | Reduces downtime, enhances repair efficiency | Quality, durability, compatibility with various fasteners |
| Construction | Fixing structural elements in buildings | Ensures structural integrity, saves costs | Material compatibility, range of sizes, ease of use |
| Manufacturing | Maintenance of machinery and assembly lines | Minimizes production interruptions | Versatility, availability of replacement parts |
| Aerospace | Repairing aircraft components and systems | Ensures safety and compliance with regulations | Certification standards, precision, reliability |
| Electronics | Repairing electronic devices and circuit boards | Protects sensitive components, enhances serviceability | Precision engineering, compatibility with small components |
How is a Tool to Remove Broken Screws Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, a tool to remove broken screws is essential for repairing engine components and assemblies. Mechanics frequently encounter broken or stripped screws during routine maintenance or repair tasks. Utilizing an extractor tool allows for the efficient removal of these problematic fasteners, reducing vehicle downtime and enhancing overall repair efficiency. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality extractors that can withstand the rigorous demands of automotive repairs is crucial to ensure durability and reliability.
What Role Does the Tool Play in Construction Applications?
In construction, the tool to remove broken screws is vital for fixing structural elements in buildings. When screws break during installation or while securing components, it can compromise the integrity of the structure. Extractors allow contractors to address these issues swiftly, ensuring that projects remain on schedule and within budget. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider tools that are robust and can handle various materials, given the diverse construction environments.
How is the Tool Beneficial in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers rely on the tool to remove broken screws for the maintenance of machinery and assembly lines. Equipment failures can lead to significant production interruptions, impacting profitability. By effectively removing broken screws, manufacturers can quickly restore machinery to operational status, minimizing downtime. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize tools that offer versatility and compatibility with a wide range of fasteners to meet diverse manufacturing needs.
Why is the Tool Critical in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, the tool to remove broken screws plays a crucial role in repairing aircraft components and systems. Given the stringent safety regulations governing this sector, it is imperative that any maintenance work is conducted with precision and reliability. Extractor tools must meet specific certification standards to ensure compliance and safety. International buyers, particularly from the Middle East and Europe, should focus on sourcing tools that are not only effective but also adhere to the highest industry standards.
How Does the Tool Aid Electronics Repair?
For the electronics industry, a tool to remove broken screws is essential for repairing electronic devices and circuit boards. These applications often involve small, delicate components where precision is paramount. An extractor tool allows technicians to safely remove damaged screws without compromising surrounding parts. Buyers in this sector should look for tools with precision engineering and compatibility with various screw sizes to facilitate effective repairs and maintenance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tool to remove broken screw’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inaccessible Broken Screws in Tight Spaces
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter situations where screws are broken in tight or hard-to-reach locations, such as machinery, automotive components, or intricate assembly structures. This can lead to significant downtime as workers struggle to access the broken screw, wasting both time and resources. The challenge is compounded when the broken screw is flush with the surface, making it difficult to grip or extract without damaging surrounding materials.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, it’s crucial to invest in a high-quality screw extractor set specifically designed for tight spaces. Look for extractors with a tapered design that can easily fit into small openings while providing a secure grip on the broken screw. Additionally, consider using a right-angle drill attachment, which allows for drilling in confined areas. Before attempting removal, ensure that the area is clean and free of debris to maximize the effectiveness of the extractor. Using penetrating oil on the screw can also help loosen it, making extraction easier. For particularly stubborn screws, heating the area with a heat gun can expand the material and allow for easier removal.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality of Screw Extractors
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges with the inconsistent quality of screw extractor tools available on the market. Poor-quality extractors can lead to stripped screw heads or breakage during use, ultimately resulting in additional repair work and increased costs. This inconsistency can create frustration and reduce productivity on the job site, especially when workers must repeatedly attempt to extract a single broken screw.
The Solution: To combat this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing screw extractor kits from reputable manufacturers known for their durability and effectiveness. Look for extractors made from high-carbon steel or other hardened materials that offer strength and longevity. It’s also beneficial to read reviews or seek recommendations from industry peers regarding the best brands. When purchasing, consider kits that include a variety of sizes and types of extractors to cover different scenarios. Additionally, training staff on the proper use of these tools can significantly reduce the risk of damage during extraction, ensuring that the tools perform as intended and last longer.
Scenario 3: Risk of Damage to Surrounding Materials
The Problem: When attempting to remove broken screws, there’s always a risk of damaging the surrounding materials, whether it’s wood, metal, or plastic. This concern is particularly pronounced in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing, where aesthetics and structural integrity are paramount. A careless extraction attempt can lead to costly repairs or replacement of components, further complicating the project timeline.
The Solution: To minimize the risk of damage during screw extraction, implement a strategic approach that includes the use of protective measures. Begin by carefully assessing the surrounding area and using masking tape or cardboard to shield adjacent surfaces from scratches or impacts. When using extractors, ensure that they are properly aligned and that you apply steady, controlled pressure. For wood surfaces, consider using a plug cutter to create a clean hole around the broken screw, allowing for easier extraction while preserving the integrity of the surrounding material. Finally, always have a plan for repairs, such as wood fillers or adhesives, on hand to address any incidental damage that may occur during the extraction process. This proactive approach will not only safeguard materials but also enhance overall project efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tool to remove broken screw
When selecting materials for tools designed to remove broken screws, it is essential to consider various properties that affect performance, durability, and overall suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of screw extractors and related tools.
What are the Key Properties of Steel for Screw Extractors?
Steel, particularly high-carbon steel, is a popular choice for screw extractors due to its high tensile strength and durability. High-carbon steel can withstand significant torque and pressure, making it ideal for removing stubborn screws. Additionally, it can be heat-treated to enhance hardness, which is crucial for maintaining sharp cutting edges.
Pros: Steel tools are generally more affordable than alternatives, making them accessible for a wide range of buyers. They also offer excellent performance in terms of wear resistance and can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which can limit its lifespan, especially in humid or corrosive environments. Furthermore, manufacturing complexities can arise when producing intricate designs.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for use in diverse environments, from construction to automotive applications.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Tool Manufacturing?
Aluminum is another material sometimes used in the production of screw extractors, especially in lightweight applications. Its low density makes it easy to handle, and it has good corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in environments where moisture is present.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum tools reduces user fatigue during prolonged use. Additionally, aluminum is resistant to rust, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Cons: While aluminum is less expensive than high-grade steel, it does not offer the same level of strength and durability. It may bend or deform under high torque, making it less suitable for heavy-duty tasks.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable toolkits.
What Advantages Does Titanium Offer for Screw Removal Tools?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for high-end screw extractors. It can perform well in extreme temperatures and is less likely to deform under stress.
Pros: The durability and lightweight nature of titanium tools make them ideal for professional use, especially in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precision is crucial.
Cons: The primary drawback of titanium is its cost, which is significantly higher than that of steel or aluminum. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Titanium’s compatibility with various media, including high-temperature environments, makes it a preferred choice for specialized applications.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Tool Design for Removing Broken Screws?
Plastic, particularly high-performance polymers, is often used for the handles of screw extractors. These materials provide a non-slip grip, enhancing user comfort and control during operation.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and can be molded into ergonomic shapes, improving user experience. It is also resistant to corrosion and chemical damage, making it suitable for various environments.
Cons: Plastic lacks the strength of metals and may not withstand high torque, limiting its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, it can wear down faster than metal counterparts.
Impact on Application: Plastic handles improve usability and comfort, particularly in consumer-grade tools aimed at DIY enthusiasts.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Tools to Remove Broken Screws
| Material | Typical Use Case for tool to remove broken screw | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | General-purpose screw extraction | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Med |
| Titanium | High-performance applications | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Tool handles for comfort and grip | Ergonomic and non-slip | Limited strength under torque | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tool to remove broken screw
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Tool to Remove Broken Screws?
Manufacturing a tool designed to remove broken screws involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. High-quality steel is commonly used for screw extractors due to its strength and durability. The chosen material typically undergoes processes such as heat treatment to enhance its hardness and resistance to wear. This is essential, as the tool must withstand significant torque and pressure during use. Additionally, suppliers often conduct a chemical analysis to ensure that the material composition aligns with specifications.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. Common techniques include forging and machining.
- Forging involves shaping the metal under high pressure, which aligns the internal grain structure, enhancing strength.
- Machining is utilized to create precise dimensions and features, such as the spiral design of the extractor, which allows for effective gripping of the broken screw.
These processes are crucial as they define the tool’s performance characteristics.
Assembly
In the assembly stage, components are brought together to form the final product. For multi-piece extractors, such as those in a set, this may involve fitting various sizes of extractors into a single package. Quality checks during assembly ensure that parts fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing Processes
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that may include surface treatment, coating, and packaging. Surface treatments like nitriding or coating with anti-corrosive materials enhance durability and resistance to rust, which is particularly important for tools used in various environments. Proper packaging also plays a role in protecting the tools during transport and ensuring they arrive in optimal condition.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Screw Removal Tools?
Quality assurance is paramount in ensuring that tools to remove broken screws meet both customer expectations and regulatory standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on process improvement and customer satisfaction. Compliance with these standards involves implementing a quality management system that oversees all manufacturing processes, from material sourcing to final inspection.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API specifications in the oil and gas sector may apply. These certifications indicate that the tools meet specific safety and performance standards relevant to their intended applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications. This includes checking for defects and verifying material certifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, operators conduct regular checks to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that the products are being formed to the right specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the final products undergo rigorous testing. This may include dimensional checks, hardness testing, and torque resistance tests to ensure they function as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the quality and reliability of their tools. Common practices include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of materials and ensures they can withstand the forces applied during use.
-
Torque Testing: Ensures that the extractor can handle the torque required to remove a broken screw without failure.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: Assesses the tool’s ability to resist rust and degradation over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating internationally, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
Conduct Supplier Audits
Engaging in on-site audits can provide invaluable insights into the manufacturing processes and quality control practices of potential suppliers. During these audits, buyers can assess the manufacturing environment, review quality documentation, and observe testing procedures firsthand.
Review Quality Reports
Requesting quality assurance reports, including compliance certificates and inspection results, can help verify that the supplier adheres to relevant standards. These documents provide transparency into the quality control measures employed throughout the manufacturing process.
Utilize Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality of products before shipment. These services can conduct independent tests and inspections to ensure that the tools meet specified standards and performance criteria.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of in Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the following nuances:
-
Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards for product quality and safety. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers comply.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can help facilitate better communication and collaboration with suppliers, enhancing the overall quality assurance process.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Risks: Delays in shipping and customs clearance can impact the quality of products. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that proper handling and storage practices are in place throughout the supply chain.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for tools to remove broken screws, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tool to remove broken screw’
To successfully procure tools for removing broken screws, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist aimed at B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions while considering the unique needs of their operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the specifications of the tools required. This includes determining the type of screw extractors needed, such as spiral or straight extractors, based on the typical screws encountered in your projects. Consider the size range, material durability, and compatibility with existing tools in your inventory.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in screw extraction tools. Look for companies with a solid reputation in the industry, particularly those that cater to your geographical region, such as Africa, South America, or Europe. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of viable suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It’s critical to verify that suppliers adhere to international quality standards and safety regulations. Request documentation regarding certifications such as ISO, CE, or local equivalents. Compliance ensures that the tools meet safety and performance benchmarks, reducing risks associated with product failures.
Step 4: Assess Product Range and Quality
Review the product range offered by potential suppliers. A diverse selection indicates a supplier’s capability to meet various needs. Additionally, examine product quality by requesting samples or reviewing customer feedback and case studies. Pay attention to the materials used in manufacturing, as high-quality materials enhance durability and effectiveness.
Step 5: Request Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified reliable suppliers, request detailed pricing information along with payment terms. Consider not only the upfront costs but also any potential bulk purchase discounts or long-term contract options. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling, can significantly impact your budget.
Step 6: Conduct Supplier Audits or Visits
If feasible, perform audits or site visits to shortlisted suppliers. This step allows you to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and overall operational standards firsthand. Engaging directly with suppliers can also foster stronger relationships and improve negotiation outcomes.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase Agreements
After selecting the most suitable supplier, finalize the purchase agreements. Ensure that all terms regarding delivery timelines, warranties, and return policies are clearly documented. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations upfront can prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement process for tools designed to remove broken screws, ensuring they invest in high-quality products that meet their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tool to remove broken screw Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Tools to Remove Broken Screws?
When analyzing the cost structure for tools designed to remove broken screws, several components play a critical role in determining the final pricing. These components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in screw extractors and related tools significantly affect the cost. High-quality steel or carbon composites, which offer durability and resistance to wear, are often preferred. The choice of material directly impacts the tool’s longevity and performance, leading to varying price points.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. Skilled labor is typically required for precision manufacturing processes, which may drive up costs, especially in regions with higher labor rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead and, consequently, product prices.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and dies required for producing specific designs of screw extractors can be substantial. This cost is amortized over the production volume, influencing unit pricing, especially for lower-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that tools meet quality standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous testing and certification can elevate production costs, but they are essential for maintaining a good reputation and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs also contribute to the overall pricing. The geographical location of manufacturing plants and the destination markets can affect shipping costs, which is especially relevant for international buyers.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and desired profit margin. This can vary widely based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Screw Removal Tools?
Several factors influence the pricing of tools to remove broken screws, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing often leads to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer lower prices per unit for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs and negotiate accordingly.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tools tailored to specific requirements or featuring advanced technology (like ergonomic designs or specialized coatings) may command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Tools made from higher-grade materials or those that meet international quality standards (such as ISO certifications) can be more expensive. Buyers must weigh the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality products against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly influence pricing. Established brands with a history of quality may charge more, but they often provide better service and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms negotiated between buyers and sellers (like FOB, CIF, etc.) can also impact the total cost. Understanding these terms is crucial for international transactions to avoid unexpected charges.
What Are the Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
To maximize value when sourcing tools to remove broken screws, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing, especially for bulk orders. Buyers should research market rates and be prepared to discuss terms openly with suppliers.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assessing the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime, can provide a clearer picture of the overall investment. Tools that are slightly more expensive but offer greater durability may result in lower TCO over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and import duties is crucial. Engaging with local distributors may provide access to better pricing and support.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s important to note that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, exchange rates, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers should seek quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic buying tips can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing tools to remove broken screws.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tool to remove broken screw With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Broken Screw Removal
When faced with the challenge of removing a broken screw, various solutions exist beyond the standard tool specifically designed for this purpose. Understanding these alternatives can empower B2B buyers to select the most effective method tailored to their operational needs and budget constraints. This comparison will focus on the traditional tool to remove broken screws and two viable alternatives: the spiral screw extractor kit and the use of locking pliers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Tool To Remove Broken Screw | Spiral Screw Extractor Kit | Locking Pliers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate | Easy | Easy |
| Maintenance | Low | Low | Low |
| Best Use Case | General screw removal tasks | Stripped or broken screws | Quick removal of protruding screws |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Spiral Screw Extractor Kit
Spiral screw extractors are specially designed tools that grip onto the screw’s head or shaft, allowing for easy removal. They are particularly effective for screws that are stripped or partially broken. The main advantage of this method is its high performance and relatively low cost, making it accessible for many businesses. However, the ease of implementation can vary, as users must drill a precise hole into the screw, which requires some skill. Overall, a spiral screw extractor kit is best suited for situations where screws are not completely sheared off and can be gripped effectively.
Locking Pliers
Locking pliers are versatile hand tools that can be used to grip and turn broken screws, especially those that protrude above the surface. This method is easy to implement and has a low cost, making it appealing for quick fixes in various environments. However, the performance can be moderate since it heavily depends on the amount of screw shank available for gripping. Locking pliers are best for situations where the screw head has snapped off but still leaves part of the screw exposed, allowing for a straightforward extraction process.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate tool or method for removing broken screws hinges on several factors, including the specific circumstances surrounding the screw’s condition, the skill level of the operator, and budget constraints. For businesses that frequently encounter stripped screws, investing in a spiral screw extractor kit might offer a reliable long-term solution. Conversely, for less frequent repairs or smaller operations, locking pliers can provide a cost-effective and easy-to-use alternative. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and improve overall efficiency in maintenance tasks.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tool to remove broken screw
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Tool to Remove Broken Screws?
When considering tools for removing broken screws, several technical specifications are critical for ensuring efficiency and durability. Understanding these properties can assist B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a screw extractor is essential as it determines the tool’s strength and resistance to wear. Common materials include high-carbon steel and HSS (High-Speed Steel), which offer superior toughness and longevity. A higher material grade is crucial for heavy-duty applications, as it can withstand the stresses of extracting broken screws without breaking or deforming. -
Thread Design
The thread design of a screw extractor significantly impacts its grip on the broken screw. Spiral threads are commonly used, as they provide a better grip and allow for easier extraction. This design creates a biting action that helps remove screws with minimal effort. Understanding the thread design can help buyers select extractors suitable for various screw types and conditions. -
Size and Tolerance
The size and tolerance specifications of screw extractors are vital for compatibility with different screw sizes. Extractors come in various diameters and lengths, making it crucial to choose the right size to avoid damaging the surrounding material. Tolerance levels ensure that the extractor fits snugly, reducing the risk of slippage during use. -
Coating and Finish
The coating and finish of the tool can enhance its performance and lifespan. For instance, titanium or black oxide coatings can provide corrosion resistance and reduce friction. This is particularly important in humid or corrosive environments, where tools may be exposed to adverse conditions. Buyers should consider the coating based on their operational environment and frequency of use. -
Extraction Mechanism
Different extractors employ various mechanisms for removing screws. Some may use a straight extraction method, while others might feature a tapered design that increases grip as torque is applied. Understanding the extraction mechanism can help buyers select tools that best fit their specific applications, whether in automotive, construction, or manufacturing sectors.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Relevant to Tools for Removing Broken Screws?
Familiarity with trade terminology can enhance communication between buyers and suppliers, ensuring that all parties are aligned regarding expectations and requirements.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of screw extractors, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source high-quality tools that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when sourcing tools for large-scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to invite suppliers to bid on a specific product or service. When purchasing tools for broken screw removal, buyers can use RFQs to obtain competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers who engage in global trade, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. For businesses that rely on the timely acquisition of tools, understanding lead times can aid in planning and avoiding operational delays. -
Technical Data Sheet (TDS)
A TDS provides detailed information about a product’s specifications, usage, and performance. For buyers, reviewing a TDS for screw extractors can help in assessing suitability for specific applications and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing tools for removing broken screws more effectively, ultimately leading to better purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tool to remove broken screw Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Affecting the Tool to Remove Broken Screw Sector?
The market for tools to remove broken screws is witnessing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing prevalence of DIY projects and home improvement activities, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and South America, is a key driver. As consumers become more empowered and skilled, they seek reliable tools for various applications, including automotive repair and woodworking. Moreover, the surge in e-commerce has facilitated easier access to specialized tools, allowing international buyers to source high-quality screw extractors from various suppliers.
Technological advancements are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with innovations such as automated inventory management systems and AI-driven procurement platforms gaining traction. These technologies enable B2B buyers to optimize their supply chains, improve inventory turnover, and reduce lead times. Furthermore, the rise of 3D printing technologies is paving the way for custom tool manufacturing, allowing businesses to tailor solutions to specific needs, enhancing competitiveness in the market.
In regions like the Middle East, where construction and infrastructure projects are booming, there is a growing demand for robust and durable screw removal tools. Local manufacturers are increasingly focusing on producing high-quality tools that meet international standards, thus appealing to B2B buyers who prioritize reliability and efficiency. Overall, the market dynamics indicate a shift towards more specialized, high-performance tools that cater to diverse industrial applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Tool to Remove Broken Screw Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount concerns for B2B buyers in the tool to remove broken screw sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning waste and resource consumption, necessitates a careful evaluation of suppliers. Businesses are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability by implementing eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing carbon footprints.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek manufacturers who comply with international labor standards, ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions for their employees. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and SA8000 (Social Accountability) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices. By choosing suppliers with these credentials, businesses can enhance their brand reputation while contributing to sustainable development.
In addition, the incorporation of ‘green’ materials in the production of screw removal tools is gaining traction. Tools made from biodegradable or recyclable materials not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers. B2B buyers should actively seek out these options and consider the lifecycle of products when making purchasing decisions.
How Has the Tool to Remove Broken Screw Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the tool to remove broken screws can be traced back to the increasing complexity of machinery and construction techniques. Initially, simple manual extractors were used, but as materials and fastening technologies advanced, the need for more sophisticated solutions became evident. Innovations such as spiral screw extractors and high-torque drill bits have emerged, allowing for more efficient and effective removal of broken screws.
Over the years, manufacturers have focused on improving the durability and functionality of these tools. The introduction of high-strength materials and ergonomic designs has enhanced user experience, making it easier for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts to tackle screw removal tasks. Today, the market offers a wide range of options, from basic kits for home use to specialized tools designed for industrial applications, reflecting the diverse needs of international B2B buyers. This evolution underscores the importance of continual innovation in meeting the demands of an ever-changing market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tool to remove broken screw
-
How do I effectively remove a broken screw without damaging surrounding materials?
To remove a broken screw without causing damage, start by assessing the situation. If the screw head is still accessible, use locking pliers to grip and turn it counterclockwise. If the head has broken off, drill a small pilot hole in the center of the remaining screw and use a screw extractor designed for this purpose. For screws flush with the surface, carefully chisel around the area to expose the shank for better grip. Always work slowly to minimize stress on the surrounding materials. -
What is the best tool for removing broken screws in industrial applications?
For industrial applications, a high-quality screw extractor set is essential. Look for sets that include various sizes to accommodate different screw types and sizes. Additionally, consider extractor kits that come with drill bits and guides for accurate drilling, such as the RYOBI Spiral Screw Extractor Set. These kits are designed for durability and can handle the rigors of frequent use in demanding environments, ensuring efficient removal of broken screws. -
How can I ensure the quality of screw removal tools when sourcing internationally?
When sourcing screw removal tools internationally, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request product samples and certifications to ensure compliance with quality standards. Additionally, check supplier reviews and ratings from previous customers. Utilize platforms that allow for supplier verification and consider visiting manufacturing facilities if possible. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and conducting regular quality audits can further mitigate risks associated with international sourcing. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for screw removal tools from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for screw removal tools can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as 50 units, while others might require orders of 500 or more. It’s essential to clarify MOQs before entering negotiations. Many suppliers are open to negotiation, especially for first-time orders or larger contracts. Always consider your inventory needs and the potential for bulk purchasing discounts to optimize your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing screw removal tools internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s negotiation leverage. Common terms include advance payments (30-50% upfront), net 30, or net 60 days post-delivery. For larger orders, consider using letters of credit to secure your transactions. Ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement, and consider using escrow services for added security, particularly when dealing with new suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing screw removal tools?
Logistics play a critical role in the importation of screw removal tools. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), which affect delivery times and costs. Ensure you understand customs regulations in your country to avoid unexpected delays. Collaborate with freight forwarders who specialize in your product category, as they can provide valuable insights into optimal shipping routes and documentation requirements. Additionally, factor in insurance options to protect against potential loss or damage during transit. -
How can I customize screw removal tools to meet specific needs?
Customization options for screw removal tools often depend on the supplier’s capabilities. When negotiating, inquire about the possibility of custom sizes, materials, or branding options. Many manufacturers can accommodate modifications based on your specifications, such as different extractor sizes or unique packaging. Be prepared to provide detailed requirements and consider potential costs associated with customization. Establishing a strong relationship with the supplier can also facilitate future custom orders. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing screw removal tools?
Implementing robust quality assurance (QA) measures is essential when sourcing screw removal tools. Start by setting clear specifications and standards for the tools you intend to purchase. Conduct pre-shipment inspections to ensure compliance with your quality requirements. Additionally, consider establishing a quality control team to review samples and conduct on-site audits of manufacturing facilities. Maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations can help foster accountability and improve product reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Tool To Remove Broken Screw Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. ProMAXX Tool – Broken EZ Out/Extractor Removal Kits
Domain: promaxxtool.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Broken EZ Out/Extractor Removal Kits – Platinum Drill Bits
Brand: ProMAXX Tool
Part Numbers:
– PMXBEKMSTR (Master Kit)
– PMXBEK125 (Small Kit)
– PMXBEK188 (Medium Kit)
Key Features:
– Platinum tooling drill bits for superior durability and performance
– Precision-crafted to drill out stubborn broken extractors
– Saves time and energy by eliminating costly repairs or stud replacement…
2. DaiTool – Double-Sided Screw Extractors
Domain: daitool.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, DaiTool – Double-Sided Screw Extractors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. DDS Gadget – Fractured Broken Screw Removal Tool Kit
Domain: ddsgadget.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Fractured Broken Screw Removal Tool Kit
SKU: MCT-SRK-01
Price: $479.00
Shipping: Standard Shipping $15.99, FREE over $699
Components: 6 Guides for various implant systems, 2 Drills, 1 Tap, 1 Guide Handle, 1 Remover Wrench
Technique: Counter-torque and reverse screw technique
Compatibility: Must verify compatibility with implant systems before purchase
Additional Products: Replacement…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tool to remove broken screw
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of tools for removing broken screws is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime in various industries. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse offerings—from spiral screw extractor sets to specialized removal kits—enables informed decision-making. The ability to access reliable and effective tools can significantly impact project timelines and overall productivity.
Investing in high-quality screw removal tools not only ensures a smoother workflow but also enhances safety and reduces the risk of damage to materials. As the market evolves, staying attuned to innovative solutions and supplier capabilities will provide a competitive edge.
We encourage buyers to leverage strategic sourcing practices to identify and partner with reputable suppliers who can meet their specific needs. By prioritizing the procurement of efficient screw removal tools, businesses can foster resilience and adaptability in their operations. Embrace this opportunity to streamline your projects and enhance your toolkit—your efficiency depends on it.