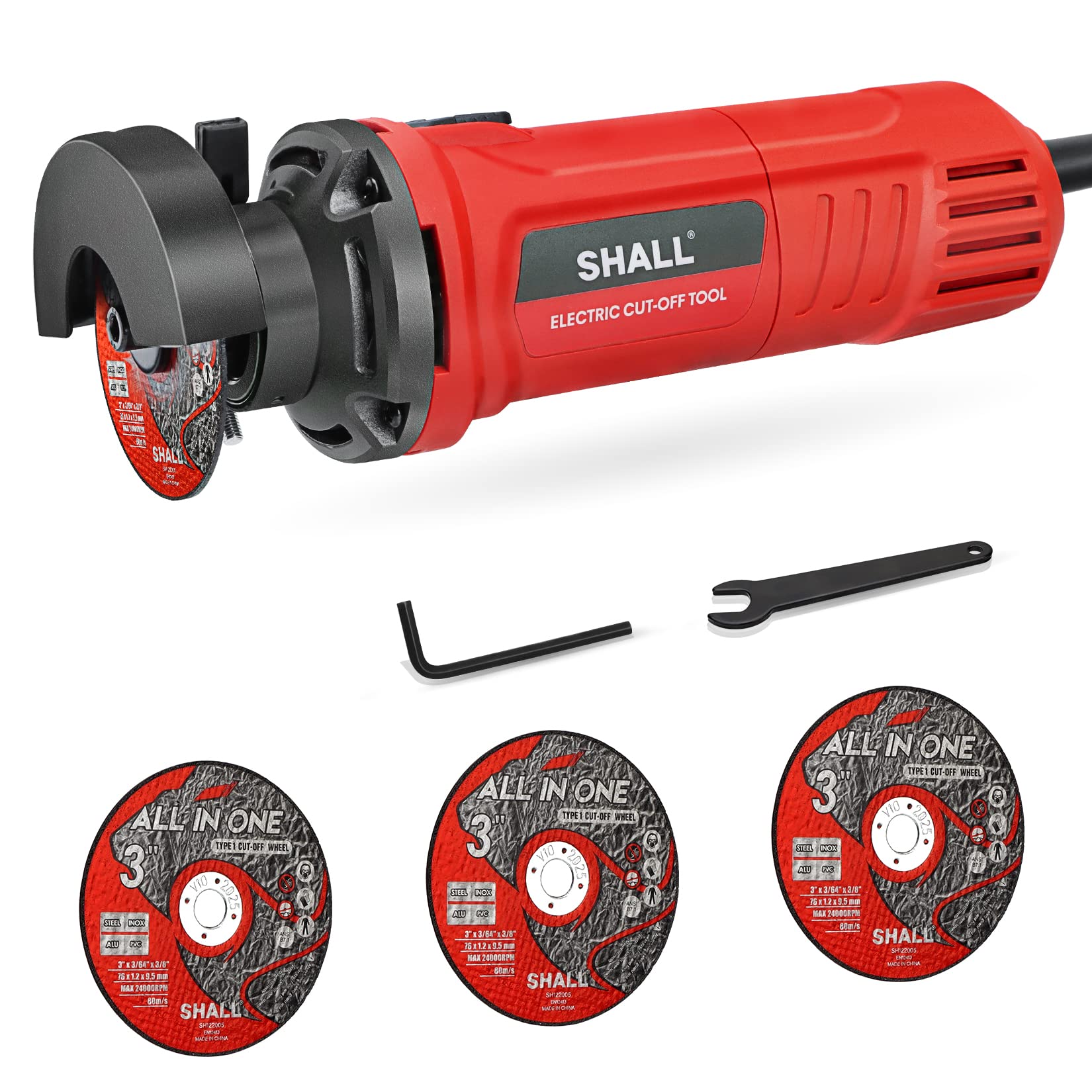
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tool to cut through metal
Navigating the complexities of sourcing tools to cut through metal can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With an increasing demand for precision and efficiency in metal fabrication, understanding the variety of cutting tools available—ranging from hand tools like snips and hacksaws to advanced power tools such as angle grinders and reciprocating saws—is essential. Each tool serves specific applications and materials, making it crucial to select the right one for your needs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of metal cutting tools, their applications, and the key factors to consider when making purchasing decisions. From evaluating supplier credibility and understanding cost implications to recognizing the specific requirements of your projects, this resource equips international B2B buyers with actionable insights. By addressing critical questions about tool performance, compatibility with different metals, and long-term value, this guide empowers you to make informed choices that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Whether you are based in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or elsewhere, navigating the global market for metal cutting tools requires a strategic approach. By leveraging the information in this guide, you can streamline your sourcing process and foster successful partnerships with suppliers that meet your business needs.
Understanding tool to cut through metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Snips | Hand-operated, available in straight and curved designs | Sheet metal fabrication | Pros: Inexpensive, good for tight areas. Cons: Jagged edges, limited to thin materials. |
| Hacksaw | Manual saw with replaceable blades for various metals | General metal cutting | Pros: Versatile, easy blade replacement. Cons: Time-consuming, only straight cuts. |
| Angle Grinder | Power tool with interchangeable discs for cutting and grinding | Heavy-duty fabrication and repair | Pros: Highly versatile, compact. Cons: Not ideal for fine details, generates heat. |
| Reciprocating Saw | Electric saw with aggressive cutting action | Demolition and rough cutting | Pros: Cuts through various materials quickly. Cons: Rough and imprecise, can damage surrounding materials. |
| Circular Saw | Power tool with specialized blades for metal cutting | Fabrication of tubes and bar stock | Pros: Clean cuts for bar stock, readily available. Cons: Limited to certain materials, blades can break easily. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Metal Snips for B2B buyers?
Metal snips are hand tools specifically designed for cutting sheet metal. They come in different styles, including straight, left, and right-cutting snips, allowing for versatility in making both straight and curved cuts. B2B buyers in industries such as HVAC, automotive, and general metal fabrication often prefer metal snips for smaller projects due to their low cost and ability to handle thin materials like aluminum and copper. However, buyers should consider that snips may leave jagged edges and are not suitable for thicker stock, requiring additional finishing work.
How do Hacksaws serve B2B metal cutting needs?
Hacksaws are widely recognized for their affordability and versatility, making them a staple in many metalworking shops. Equipped with a replaceable blade, they can efficiently cut through various metals, including pipes and sheet materials. B2B buyers often choose hacksaws for their reliability in general metal cutting applications. However, the time-consuming nature of hacksaws and their limitation to straight cuts may prompt buyers to seek alternative tools for larger projects or when precision is critical.
Why are Angle Grinders essential for heavy-duty fabrication?
Angle grinders are indispensable tools in metalworking due to their versatility and power. They can accommodate various discs for cutting, grinding, and polishing, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as welding and metal repair. B2B buyers in construction and manufacturing appreciate angle grinders for their ability to work on a range of materials quickly. However, the heat generated during cutting can affect the finish of the workpiece, and they may not be ideal for intricate detail work, so buyers should consider their specific needs when choosing this tool.
What role does the Reciprocating Saw play in demolition and rough cutting?
The reciprocating saw is known for its aggressive cutting action, making it a favorite among contractors and demolition experts. This power tool is capable of cutting through various materials quickly, which is advantageous for projects requiring speed. B2B buyers engaged in demolition or rough cutting appreciate its power and ability to tackle a wide range of materials. However, its lack of precision can lead to damage in delicate areas, so it is best suited for demolition tasks rather than detailed metalwork.
How does a Circular Saw contribute to metal fabrication?
Circular saws are commonly used in metal fabrication for their ability to make clean cuts in bar stock and tubes when outfitted with the right blade. They are particularly useful in environments where speed and efficiency are paramount. B2B buyers in manufacturing and construction often choose circular saws for their reliability and ease of use. However, their effectiveness can be limited when cutting sheet goods, and the potential for blade breakage is a consideration that buyers should keep in mind when selecting this tool for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of tool to cut through metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tool to cut through metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Fabrication of metal components for machinery | Increased efficiency in production and reduced material waste | Quality of tools, availability of replacement parts |
| Construction | Cutting steel beams and reinforcements for structures | Enhanced structural integrity and safety | Tool durability, compliance with local regulations |
| Automotive | Precision cutting of metal for vehicle parts | Improved performance and reduced manufacturing costs | Precision and versatility of cutting tools |
| Metal Recycling | Processing scrap metal into reusable forms | Cost savings through material recovery | Tool adaptability for various metal types |
| Aerospace | Cutting and shaping metal for aircraft components | High precision and reduced weight in critical components | Certification and quality standards for aerospace tools |
How is ‘tool to cut through metal’ utilized in the manufacturing sector?
In the manufacturing sector, tools to cut through metal are essential for fabricating components used in machinery and equipment. These tools enable manufacturers to efficiently produce parts with precision, minimizing waste and ensuring that finished products meet rigorous quality standards. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality cutting tools can lead to significant cost savings and improved production timelines. Factors such as tool durability, the availability of local suppliers, and after-sales support are critical when selecting equipment for manufacturing needs.
What are the applications of metal cutting tools in construction?
In construction, metal cutting tools are vital for processing steel beams and reinforcements, which are crucial for structural integrity. These tools allow contractors to make precise cuts, ensuring that materials fit together seamlessly, which enhances safety and durability. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe need to consider local building codes and regulations when sourcing these tools, as compliance can affect project timelines and costs. Additionally, the durability and efficiency of the tools are paramount to withstand the demanding environments of construction sites.
How do automotive industries benefit from metal cutting tools?
The automotive industry relies heavily on metal cutting tools for the precision cutting of parts used in vehicle assembly. These tools help manufacturers create components that optimize vehicle performance while reducing overall manufacturing costs. For B2B buyers in regions like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, investing in versatile and precise cutting tools can result in significant operational efficiencies. It is essential to evaluate the compatibility of tools with various materials and the availability of specialized blades to meet the industry’s unique requirements.
In what ways do metal cutting tools facilitate metal recycling?
Metal recycling industries utilize cutting tools to process scrap metal into reusable forms, allowing for efficient recovery of valuable materials. By cutting down larger pieces into manageable sizes, recyclers can maximize their operational efficiency and reduce transportation costs. Buyers in this sector, especially in emerging markets, should focus on the adaptability of cutting tools to handle different metal types and grades. Reliable sourcing of durable tools that can withstand heavy usage is crucial for maintaining profitability in recycling operations.
How critical are metal cutting tools in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace sector, precision is paramount, and tools to cut through metal play a crucial role in shaping components that must meet stringent performance standards. These tools enable manufacturers to create lightweight yet strong parts essential for aircraft performance and safety. For B2B buyers in this field, especially in Europe, ensuring that cutting tools meet aerospace certification standards is vital. Additionally, the ability to source high-quality, specialized tools that provide consistency and precision can significantly impact overall manufacturing success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tool to cut through metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Tool for Different Metals
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the appropriate cutting tool for varying types of metal, such as aluminum, steel, or copper. Each type of metal has distinct properties that require specific tools to ensure efficient cutting and minimize waste. For example, using a tool designed for softer metals on harder materials can lead to tool damage, reduced productivity, and increased costs due to material wastage. Buyers may also feel overwhelmed by the variety of options available in the market, making it challenging to make informed decisions.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of the metals they frequently work with and their specific cutting requirements. Create a matrix that outlines the types of metals and the recommended tools for each. For instance, angle grinders work well for rough cuts in steel, while metal snips are ideal for thin sheets of aluminum. Additionally, buyers should engage with suppliers who provide detailed specifications and recommendations based on the metal type. Utilizing product demos or trial periods can also help buyers evaluate the effectiveness of tools before making a significant investment.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Precision Leading to Poor Quality Cuts
The Problem: In many manufacturing and fabrication environments, precision is paramount. B2B buyers often experience frustration when their cutting tools fail to deliver the accuracy required for intricate designs, leading to poorly finished products. This can result in costly rework, delays in production schedules, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers. The challenge is exacerbated when tools are used improperly or are mismatched with the tasks at hand.
The Solution: To enhance precision in metal cutting, buyers should invest in high-quality tools that are specifically designed for the required applications. For intricate cuts, consider using a CNC plasma cutter or a laser cutting machine, which can offer unparalleled precision and repeatability. Additionally, training employees on the proper use of these tools can significantly improve cutting accuracy. Implementing a quality control process where cuts are inspected before moving to the next production stage can also help catch issues early, reducing the need for rework.
Scenario 3: Safety Concerns and Operational Risks During Metal Cutting
The Problem: Safety is a critical concern in any industrial environment, especially when dealing with heavy machinery and sharp cutting tools. B2B buyers often worry about the potential hazards associated with metal cutting, including accidental injuries, equipment malfunction, or fire risks due to sparks generated during the cutting process. These concerns can lead to increased insurance costs and a decline in employee morale if workers feel unsafe.
The Solution: To mitigate safety risks, buyers should prioritize the selection of tools that come equipped with safety features, such as blade guards and automatic shut-off mechanisms. Conducting regular training sessions on proper tool handling and safety protocols is essential to create a culture of safety within the workplace. Implementing strict maintenance schedules for tools can also prevent malfunctions and prolong tool life. Furthermore, ensuring that work areas are well-ventilated and equipped with fire extinguishers can help in managing risks associated with sparks and heat generated during cutting operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tool to cut through metal
What Are the Key Materials Used for Tools to Cut Through Metal?
When selecting tools to cut through metal, understanding the properties and applications of various materials is crucial for B2B buyers. The choice of material can significantly affect the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of cutting tools. Below are analyses of four common materials used in metal cutting tools, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
How Does High Carbon Steel Perform in Metal Cutting Tools?
High carbon steel is a popular choice for cutting tools due to its hardness and ability to maintain a sharp edge. It typically has a carbon content ranging from 0.6% to 1.4%, which enhances its strength and wear resistance. However, high carbon steel is more susceptible to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or maintenance.
Pros: High carbon steel tools are relatively inexpensive and can be produced with high precision, making them suitable for various applications, including cutting sheet metal and pipes. They are also easy to sharpen.
Cons: The primary limitation is their susceptibility to rust, which can affect longevity if not properly maintained. Additionally, they may not perform well under high temperatures, as they can lose hardness.
Impact on Application: High carbon steel is best suited for cutting softer metals like aluminum and copper. It may struggle with harder materials, leading to quicker wear.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity can be high, proper storage and maintenance practices are essential to prevent rust.
What Advantages Does Carbide Offer for Metal Cutting Tools?
Carbide, particularly tungsten carbide, is another widely used material in metal cutting tools. Known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, carbide can withstand high temperatures and is less prone to deformation under stress.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbide tools is their durability and ability to maintain sharpness over extended periods. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications, including cutting hard metals like stainless steel and high-carbon steel.
Cons: Carbide tools are generally more expensive than high carbon steel options and can be more brittle, making them susceptible to chipping if not handled properly.
Impact on Application: Carbide is particularly effective for cutting tough materials and is often used in industrial settings where precision and longevity are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the cost-benefit ratio, especially in developing regions where budget constraints may exist. Compliance with international standards is crucial, as is ensuring that suppliers provide adequate support and warranty services.
Why Is HSS (High-Speed Steel) a Popular Choice for Cutting Tools?
High-speed steel (HSS) is an alloy that contains elements like molybdenum and tungsten, which enhance its hardness and heat resistance. HSS tools can maintain their cutting edges at high temperatures, making them suitable for various metal cutting applications.
Pros: HSS tools are versatile and can cut through a wide range of materials, including both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. They are less expensive than carbide tools and can be resharpened multiple times.
Cons: While HSS tools are durable, they do not match the longevity of carbide tools. They can also lose hardness at extremely high temperatures, which may limit their effectiveness in certain applications.
Impact on Application: HSS is often used in manufacturing environments for drilling and milling, making it suitable for producing intricate designs in metal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local manufacturing standards. In regions with varying levels of technological advancement, ensuring that HSS tools are readily available and supported by local suppliers is essential.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Cutting Tool Design?
Aluminum is sometimes used in the construction of cutting tools, particularly in lightweight applications. While not as common as other materials, aluminum tools can be beneficial for specific tasks where weight reduction is a priority.
Pros: Aluminum tools are lightweight, making them easier to handle and reducing operator fatigue. They are also resistant to corrosion, which can enhance their lifespan in humid environments.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is that aluminum lacks the hardness and strength of steel, making it unsuitable for heavy-duty cutting tasks. It is primarily effective for softer materials.
Impact on Application: Aluminum tools are often used in applications requiring precision and minimal weight, such as in aerospace or automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific applications where aluminum tools excel and ensure compliance with relevant standards. In regions like the Middle East, where temperature variations can be extreme, the performance of aluminum tools may be affected.
Summary of Material Selection for Metal Cutting Tools
| Material | Typical Use Case for tool to cut through metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Carbon Steel | Cutting sheet metal and pipes | Inexpensive and easy to sharpen | Susceptible to rust | Low |
| Carbide | Heavy-duty cutting of hard metals | Exceptional durability | More expensive and brittle | High |
| High-Speed Steel | Drilling and milling in manufacturing | Versatile and resharpenable | Less durable than carbide | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications in precision tasks | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lacks hardness for heavy-duty tasks | Medium |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions when selecting cutting tools for metal applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tool to cut through metal
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Metal Cutting Tools?
The manufacturing of metal cutting tools is a multifaceted process that involves several crucial stages, each with its own techniques and considerations. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing tools.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Cutting Tools?
Material preparation is the initial step in the manufacturing process. This involves selecting high-quality raw materials, typically high-carbon steel or high-speed steel, which are essential for durability and performance. The materials undergo various treatments to improve their properties, such as heat treatment for hardness and toughness.
Once the material is selected, it is cut into manageable sizes using precision saws or lasers. This ensures that the material is uniform and suitable for the subsequent forming processes. Quality checks at this stage are critical, as the integrity of the raw material directly affects the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing Metal Cutting Tools?
Forming is the next step, where the prepared materials are shaped into the desired tool profiles. Various techniques are employed in this stage, including forging, casting, and machining.
-
Forging: This process involves shaping the metal by applying compressive forces. It enhances the mechanical properties of the material, making it denser and more resilient.
-
Casting: In this method, molten metal is poured into molds to create specific shapes. This technique is often used for more complex designs that would be difficult to achieve through forging.
-
Machining: After initial shaping, machining processes like milling, grinding, and turning are employed to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology is commonly used to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
Each of these techniques requires specialized machinery and skilled operators to maintain the highest standards of quality.
How Are Metal Cutting Tools Assembled and Finished?
After forming, the tools undergo assembly, particularly for those that consist of multiple parts. This may include attaching handles, blades, or any other components. Assembly can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity of the tool.
Finishing is a vital step that enhances the tool’s performance and aesthetic appeal. It may involve processes such as surface grinding, polishing, and coating. Coatings, like titanium nitride, not only improve wear resistance but also reduce friction during cutting, extending the tool’s lifespan.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Important for Metal Cutting Tools?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the tools meet international standards and buyer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
For B2B buyers, understanding relevant international standards is essential. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Compliance with this standard indicates that the manufacturer has a robust quality management system in place.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be necessary, depending on the application of the metal cutting tools. These certifications ensure that the tools meet specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense, where raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are performed to monitor the quality of the process and identify any deviations from standards in real-time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the tools are manufactured, they undergo comprehensive testing to verify that they meet all quality and performance specifications before being shipped.
Common testing methods may include dimensional inspections, hardness tests, and performance testing under simulated operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensure they receive reliable products. Here are some effective strategies:
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits and Inspections?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This also allows buyers to assess the supplier’s capabilities firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and documentation can help buyers understand the QC measures in place. These reports should include information on testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These organizations can conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products, providing an unbiased evaluation of quality.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware of in Quality Control?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices may vary significantly across regions. Understanding these differences can help in establishing effective partnerships with suppliers.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations as well as international standards.
-
Supply Chain Considerations: The complexity of global supply chains can introduce risks related to quality. Buyers should consider factors such as transportation conditions, storage facilities, and handling procedures that may impact product quality.
By being proactive in understanding these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships in sourcing metal cutting tools.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tool to cut through metal’
In this guide, we aim to provide B2B buyers with a practical checklist for sourcing tools specifically designed for cutting through metal. Selecting the right metal cutting tool is essential for ensuring efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness in your operations. This checklist will help you navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial before beginning your search. Consider factors such as the types of metal you will be cutting (e.g., steel, aluminum, copper) and the thickness of the materials. This will help you determine the appropriate tool type and cutting capacity needed for your projects.
- Metal types: Different tools are suited for specific metals; ensure compatibility.
- Thickness: Know the maximum thickness the tool must handle to avoid purchasing inadequate equipment.
Step 2: Assess Your Cutting Needs
Evaluate the volume and frequency of your cutting operations. Are you looking for tools for occasional use, or do you require heavy-duty equipment for continuous operations? Understanding your cutting needs will guide you in selecting tools that can withstand the demands of your workload.
- Frequency: Regular use may justify investing in more robust, professional-grade tools.
- Cutting precision: Determine if you need tools for fine cuts or if rough cuts are acceptable.
Step 3: Research Available Tool Options
Conduct thorough research on the various types of metal cutting tools available, such as hand tools (snips, hacksaws) and power tools (angle grinders, reciprocating saws). Each tool has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the application, so understanding the options will help you make an informed decision.
- Hand tools: Ideal for smaller, detailed work but may require more effort.
- Power tools: Generally faster and more efficient for larger projects but may have a higher upfront cost.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This diligence helps ensure that the supplier has a proven track record of reliability and quality.
- Supplier reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients.
- Certifications: Verify if the supplier holds relevant industry certifications that demonstrate quality standards.
Step 5: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request samples or demonstrations of the tools you are considering. This hands-on experience can help you assess the tool’s performance, ease of use, and suitability for your specific cutting tasks.
- Performance testing: Observe how the tool handles various materials.
- Ease of use: Ensure that operators can use the tool comfortably and efficiently.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Warranty Options
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare pricing, taking into account the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs. Additionally, review warranty options, as a robust warranty can offer peace of mind regarding the tool’s longevity and reliability.
- Total cost analysis: Consider the long-term costs rather than just the initial price.
- Warranty coverage: A good warranty can protect your investment and reduce future expenses.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Integration
Once you’ve selected a supplier and tool, finalize your purchase while planning for integration into your operations. Ensure your team is trained on the proper use of the tools and that safety protocols are in place to maximize efficiency and minimize risk.
- Training programs: Implement training for operators to ensure safety and proficiency.
- Safety protocols: Establish safety measures to protect workers during cutting operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can systematically approach the sourcing of metal cutting tools, ensuring that they meet their operational needs effectively and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tool to cut through metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Metal Cutting Tools?
When sourcing metal cutting tools, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of metal used in tool manufacturing significantly affects the overall cost. High-carbon steel or specialized alloys may increase initial expenses but offer enhanced durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the skill level required for manufacturing and assembly. Skilled labor may command higher wages, but can result in superior craftsmanship and product quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can help minimize overhead costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized tools. Buyers should consider how this upfront cost impacts long-term pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures can increase costs but ensures that only high-quality products reach the market. This can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on distance, weight, and shipping methods. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. Negotiating favorable terms can help lower this margin.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Metal Cutting Tools?
Several factors can influence the pricing of metal cutting tools:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should assess their needs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tools tailored to specific applications may come at a premium. It’s essential to evaluate whether the benefits justify the added costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Tools made from higher-grade materials or those certified to international standards (e.g., ISO) tend to be more expensive. Buyers should weigh the importance of quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects cost calculations. This knowledge helps buyers anticipate logistics expenses and potential risks.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency in Metal Cutting Tools?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should adopt specific strategies for cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers. Leverage volume commitments or long-term partnerships to secure better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to better long-term decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect overall costs. Establishing relationships with local distributors may also reduce expenses and streamline logistics.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research to compare pricing, quality, and service levels among various suppliers. This practice can uncover hidden costs and better options.
Conclusion
Sourcing metal cutting tools requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers. By focusing on cost components, leveraging negotiation tactics, and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remain vigilant about market trends and supplier dynamics to ensure the best possible outcomes in your procurement strategy.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tool to cut through metal With Other Solutions
In the metalworking industry, selecting the right cutting solution is crucial for efficiency and quality. While a dedicated tool to cut through metal is a popular choice for many applications, it’s essential to consider alternative methods that may offer distinct advantages depending on the specific requirements of a project. This analysis will compare a traditional metal cutting tool against two viable alternatives: plasma cutting and laser cutting.
| Comparison Aspect | Tool To Cut Through Metal | Plasma Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for various metals with clean cuts for thin materials. | Excellent for thick materials; produces smooth edges. | Highly precise; ideal for intricate designs and thin sheets. |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate initial investment. | Moderate to high setup costs; operational costs vary. | High initial investment; operational costs can be significant. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to use with minimal setup required. | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex. | High precision requires training; setup can be time-consuming. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; tools are durable. | Moderate maintenance; requires regular checks and consumables. | High maintenance; requires specialized service and upkeep. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small-scale projects and repairs. | Best for heavy-duty applications and industrial environments. | Perfect for detailed work, prototyping, and high-volume production. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting is a process that utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials. The primary advantage of plasma cutting is its ability to cut through thick metals rapidly while producing a clean edge. However, it requires skilled operators due to the complexities involved in setup and operation. The initial investment can be moderate to high, and while operational costs vary, they can add up over time, especially in high-volume environments. This makes plasma cutting an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications in industrial settings, but it may not be the best fit for smaller projects.
How Does Laser Cutting Compare?
Laser cutting uses focused light beams to cut materials with exceptional precision. This method is particularly beneficial for intricate designs and thin materials, making it a favorite in applications such as signage, automotive, and aerospace manufacturing. The precision of laser cutting allows for minimal material waste and reduced need for secondary finishing processes. However, the initial investment is significantly higher than traditional metal cutting tools, and operational costs can also be considerable. Maintenance is crucial, as laser systems require specialized upkeep and regular servicing. As such, while laser cutting is ideal for high-volume production and detailed work, it may not be suitable for all budgets or project scales.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Metal Cutting Solution?
When selecting a metal cutting solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including project scale, material thickness, and budget constraints. For smaller projects or repairs, a traditional tool to cut through metal may be most effective due to its ease of use and lower costs. Conversely, for larger-scale industrial applications where speed and precision are critical, plasma or laser cutting may provide a better return on investment despite their higher costs. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing operational efficiency, budget, and the specific requirements of the task at hand.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tool to cut through metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Metal Cutting Tools?
When selecting tools for cutting metal, understanding critical technical properties can significantly enhance purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of cutting tools indicates their composition and hardness, which directly affects durability and cutting efficiency. For example, high-speed steel (HSS) is commonly used for blades due to its ability to maintain sharpness at elevated temperatures. Knowing the material grade helps buyers choose tools that can withstand specific metal types and thicknesses. -
Cutting Capacity
– This specification refers to the maximum thickness or size of the metal that a tool can effectively cut. Understanding cutting capacity is crucial for B2B buyers, as it ensures that the tool meets the demands of their specific projects. Selecting a tool with inadequate cutting capacity can lead to inefficiencies or project delays. -
Tolerances
– Tolerances define the allowable variation in dimensions during the cutting process. Tight tolerances are critical for precision applications, where even minor deviations can affect the final product’s functionality. Buyers in industries such as aerospace or automotive must prioritize tools that can maintain stringent tolerances to meet regulatory and quality standards. -
Speed Rating
– The speed rating, often expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM), indicates how fast a tool can operate safely. Different metals require different speeds for optimal cutting performance. Understanding the speed rating helps buyers match tools to their operations, minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency. -
Weight and Portability
– The weight of a cutting tool can affect its usability and the ease of handling, especially in mobile or field applications. For B2B buyers, selecting tools that balance weight with performance can enhance productivity and reduce operator fatigue. -
Power Source
– Tools can be powered manually, electrically, or pneumatically. Understanding the power source is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing operations and determining the appropriate safety measures. Buyers should evaluate their operational environment to choose the most suitable power source for their cutting tasks.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Their Importance in Metal Cutting Tools?
Familiarity with trade terms can facilitate smoother transactions and better negotiations in the B2B sector. Here are some critical terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of cutting tools, purchasing from an OEM can ensure quality and compatibility with specific machinery. Buyers often seek OEM tools to guarantee performance and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to cost savings, especially for companies that require large volumes of cutting tools. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. This is crucial for B2B transactions as it allows for competitive bidding and ensures transparency in pricing. Buyers should prepare comprehensive RFQs that detail their requirements to receive accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage logistics and shipping costs effectively, ensuring that all parties are clear on who bears responsibility for various aspects of transportation. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for a supplier to deliver goods after an order is placed. Knowing the lead time is critical for planning and scheduling in production environments. Buyers should consider lead times when placing orders to avoid delays in their operations. -
Warranty
– A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the quality and durability of a product. Understanding warranty terms can protect buyers from defects and ensure that they receive value for their investment in cutting tools.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tool to cut through metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Metal Cutting Tool Sector?
The global market for metal cutting tools is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand from various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate this landscape, they must be aware of key trends shaping their sourcing strategies. A notable trend is the rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as CNC machining and additive manufacturing, which necessitate high-precision cutting tools. These technologies not only enhance productivity but also require tools that can withstand higher levels of stress and heat, leading to an increased focus on durability and performance.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on digital transformation within the B2B sector. The adoption of e-commerce platforms and supply chain management software enables buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers, streamlining procurement processes. Blockchain technology is also emerging, providing transparency in the supply chain, which is particularly valuable for buyers looking to ensure the authenticity and quality of metal cutting tools.
In addition to technological advancements, sustainability is becoming a central theme in sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, including the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where regulatory pressures are driving companies to adopt greener practices. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions in the evolving metal cutting tool market.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing of Metal Cutting Tools?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the B2B sourcing of metal cutting tools. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This shift is not merely a trend but a necessity, as industries face increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprints and comply with stricter environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing plays a significant role in this landscape. Buyers are seeking suppliers who can guarantee responsible sourcing of raw materials, particularly metals, which often involve complex supply chains that can lead to ethical concerns. The importance of certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Steel certification, is growing. These certifications assure buyers that the tools they procure are produced with minimal environmental impact and adhere to social responsibility standards.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a rise in the availability of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals or tools designed for longevity, which reduce waste and resource consumption. As a result, B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating the sustainability credentials of their suppliers, recognizing that responsible sourcing not only aligns with corporate values but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
How Have Metal Cutting Tools Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of metal cutting tools has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demand. Historically, metal cutting began with basic hand tools, such as chisels and saws, which required considerable manual effort. As industrialization progressed in the 19th century, the introduction of powered tools revolutionized the sector, allowing for greater precision and efficiency in metalworking.
The 20th century saw the advent of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, such as high-speed steel and carbide-tipped blades, which further enhanced cutting performance. The rise of computer numerical control (CNC) technology in the late 20th century transformed the landscape, enabling automated and highly accurate cutting processes. Today, the focus is on integrating smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled tools that provide real-time data on performance and maintenance needs.
This historical trajectory highlights the ongoing innovation in the metal cutting tools sector, driven by the need for higher efficiency, precision, and sustainability, which remains paramount for B2B buyers as they navigate current market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tool to cut through metal
Frequently Asked Questions for B2B Buyers of Tools to Cut Through Metal
-
How do I choose the right metal cutting tool for my project?
Choosing the right metal cutting tool depends on several factors, including the type of metal you are working with, the thickness, and the precision required for the cut. For thinner materials, hand tools like metal snips or hacksaws may suffice, while thicker metals often necessitate power tools such as angle grinders or reciprocating saws. Additionally, consider the project’s scale; larger operations may benefit from more robust, industrial-grade tools. Always assess the tool’s specifications and user reviews to ensure it meets your specific needs. -
What are the best power tools for cutting metal?
The best power tools for cutting metal include angle grinders, reciprocating saws, and circular saws outfitted with appropriate blades. Angle grinders are incredibly versatile and can handle various metal types, making them ideal for rough cuts. Reciprocating saws excel in demolition tasks, while circular saws provide clean cuts for sheet goods when equipped with specialized blades. For intricate work, consider a jigsaw with metal cutting blades. Always select tools based on the material and cut type for optimal performance. -
What should I look for when vetting a supplier for metal cutting tools?
When vetting suppliers for metal cutting tools, prioritize their industry reputation, product range, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and adherence to international quality standards, which is crucial for reliability. Additionally, assess their responsiveness and support services, as these factors can impact your procurement experience. Request samples or product demonstrations if possible, and consider suppliers that offer customization options to meet your specific needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal cutting tools?
Minimum order quantities for metal cutting tools can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may offer low MOQs for standard tools, while others might require larger quantities for customized or specialized equipment. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations to align with your purchasing capabilities. If you are a smaller business, seek suppliers willing to accommodate your needs or consider group purchasing options with other businesses to meet MOQ requirements. -
What are the common payment terms for international B2B transactions?
Common payment terms in international B2B transactions include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders, with the balance due before shipment. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect both parties, ensuring clear timelines and conditions. Familiarize yourself with the supplier’s payment preferences and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for metal cutting tools I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance for metal cutting tools, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Consider implementing a quality control process that includes inspecting samples before full-scale production. Engage in regular communication with suppliers to address any concerns promptly. Additionally, establish a return policy or warranty conditions that allow you to return defective products, which can safeguard your investment and enhance your supply chain reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing metal cutting tools?
When sourcing metal cutting tools, logistics considerations include shipping methods, delivery times, and customs regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to ship to your location and the associated costs. Understand the potential delays that may arise from customs clearance, especially for international shipments. Establish clear communication regarding tracking and delivery schedules to ensure timely receipt of your tools. Additionally, consider warehousing options if you anticipate bulk purchases. -
Are there customization options available for metal cutting tools?
Many suppliers offer customization options for metal cutting tools to meet specific industry needs. Customization can include modifications in tool size, blade type, and handle design, tailored to particular materials or applications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and inquire about their design capabilities. Custom tools may involve higher costs and longer lead times, so it’s essential to weigh these factors against your operational needs before proceeding.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Tool To Cut Through Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Recommended Metal Cutting Tools
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Reciprocating saw (also known as Sawzall) with a rough cut metal blade, grinder with a grinding disc, and grinder with a flapper disc are recommended tools for cutting metal. Users suggest using a reciprocating saw for initial cuts and a grinder for cleanup. It’s advised to use a longer blade for better access and to cut slowly, applying oil to prevent overheating and blade wear.
2. Woodsmith – Cutting Tools
Domain: woodsmith.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hacksaws: Handheld tools with fine-toothed blades for cutting metal; require secure clamping and controlled strokes. Angle Grinders: Versatile power tools with abrasive cutting discs; require stable workpiece and safety gear. Plasma Cutters: Machines using high-velocity ionized gas for precision cutting; require protective equipment and proper settings. Circular Saws: Adaptable for metal cutting w…
3. Nibbler – Precision Metal Cutting Tool
Domain: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Nibbler: A tool that cuts slivers of metal ahead of the cut using a shearing motion, similar to a jigsaw for metal. Recommended for making precise cuts with no sparks. Can be attached to a 1/4″ impact driver or 3/8″ drill for tight and precise circles and corners. Oscillating tool: Suggested for cutting metal with precision and minimal sparks, though the user has not previously cut metal with it. …
4. Cool Tools – Metal Clay Cutting Essentials
Domain: cooltools.us
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Cool Tools – Metal Clay Cutting Essentials, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Hobby Machinist – Essential Cutting Tools
Domain: hobby-machinist.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Miter saw with a cut-off wheel, Angle grinder attached to a holder, Hacksaw with a 32 tooth blade, Band saw in vertical position, Dremel with cutoff wheel, HSS cut-off tool (.025″), Portaband saw with a 32 tooth blade.
6. Woodworking Masterclasses – Essential Cutting Tools
Domain: woodworkingmasterclasses.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: 1. Hacksaw: Suitable for thinner cuts; requires appropriate blade for material. 2. Angle Grinder: Can cut thicker materials with a cutting disk; versatile for various metal finishing. 3. Power Hacksaw/Bandsaw: For heavier cuts; requires more space and investment. 4. Circular Saw: Metal cutting blades available; special circular saws designed for metal cutting. 5. Cold Saws: Similar to power miter …
7. Grassroots Motorsports – Aviation Shears & Hacksaw
Domain: grassrootsmotorsports.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Aviation Shears: Great for cutting sheet metal (steel, aluminum, stainless); designed to trim no more than 1/4 inch; available in red (left cuts), green (right cuts), yellow (straight cuts). Hacksaw: Quick and easy for straight cuts in smaller metal pieces; must-have for fabricators. Air-Powered or Electric Die Grinder with 3-inch Cutoff Wheel: Versatile for thicker materials (up to 3/16 inch); pr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tool to cut through metal
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Metal Cutting Tool Procurement?
In summary, the strategic sourcing of metal cutting tools is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize operations, reduce costs, and ensure product quality. By understanding the diverse range of tools—from hand tools like snips and hacksaws to power tools such as angle grinders and reciprocating saws—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific project requirements. Additionally, fostering strong relationships with suppliers allows for better negotiation on prices, access to exclusive offers, and insights into the latest technological advancements.
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is vital for businesses to stay ahead of trends and invest in high-quality, reliable tools. Embracing strategic sourcing not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions your business for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
We encourage buyers to evaluate their current sourcing strategies and consider the benefits of diversifying their supplier base to meet the growing demands of their industries. Take proactive steps today to leverage strategic sourcing as a tool for growth and innovation in your metalworking operations.