Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Thickness Tolerance For Sheet Metal
Precision Sheet Metal Thickness Tolerance: A Critical Factor in Manufacturing Success
Achieving exact sheet metal thickness tolerance is non-negotiable in precision fabrication, directly impacting part functionality, structural integrity, and assembly compatibility. Deviations beyond specified tolerances can trigger cascading failures—from compromised weld integrity and misaligned components to accelerated wear in dynamic applications. At Honyo Prototype, we recognize that consistent thickness control begins with rigorous material certification, advanced process calibration, and real-time metrology, ensuring every bend, cut, and form adheres to ISO 2768 and customer-defined standards.
Our Sheet Metal Fabrication services integrate laser cutting, CNC punching, and precision press braking with closed-loop quality systems to maintain tolerances as tight as ±0.05 mm for critical applications. We account for material behavior across aluminum, stainless steel, and specialty alloys, adjusting for springback and stress distribution to deliver parts that meet dimensional intent on the first iteration. This disciplined approach eliminates costly rework and accelerates time-to-assembly for prototyping and low-volume production.
Leverage Honyo’s engineering expertise without procurement delays. Our Online Instant Quote platform provides real-time manufacturability feedback and pricing within minutes, incorporating thickness tolerance requirements into feasibility analysis. Upload your design to validate specifications against our capabilities and receive a production-ready quote—streamlining your path from concept to certified component.
Technical Capabilities
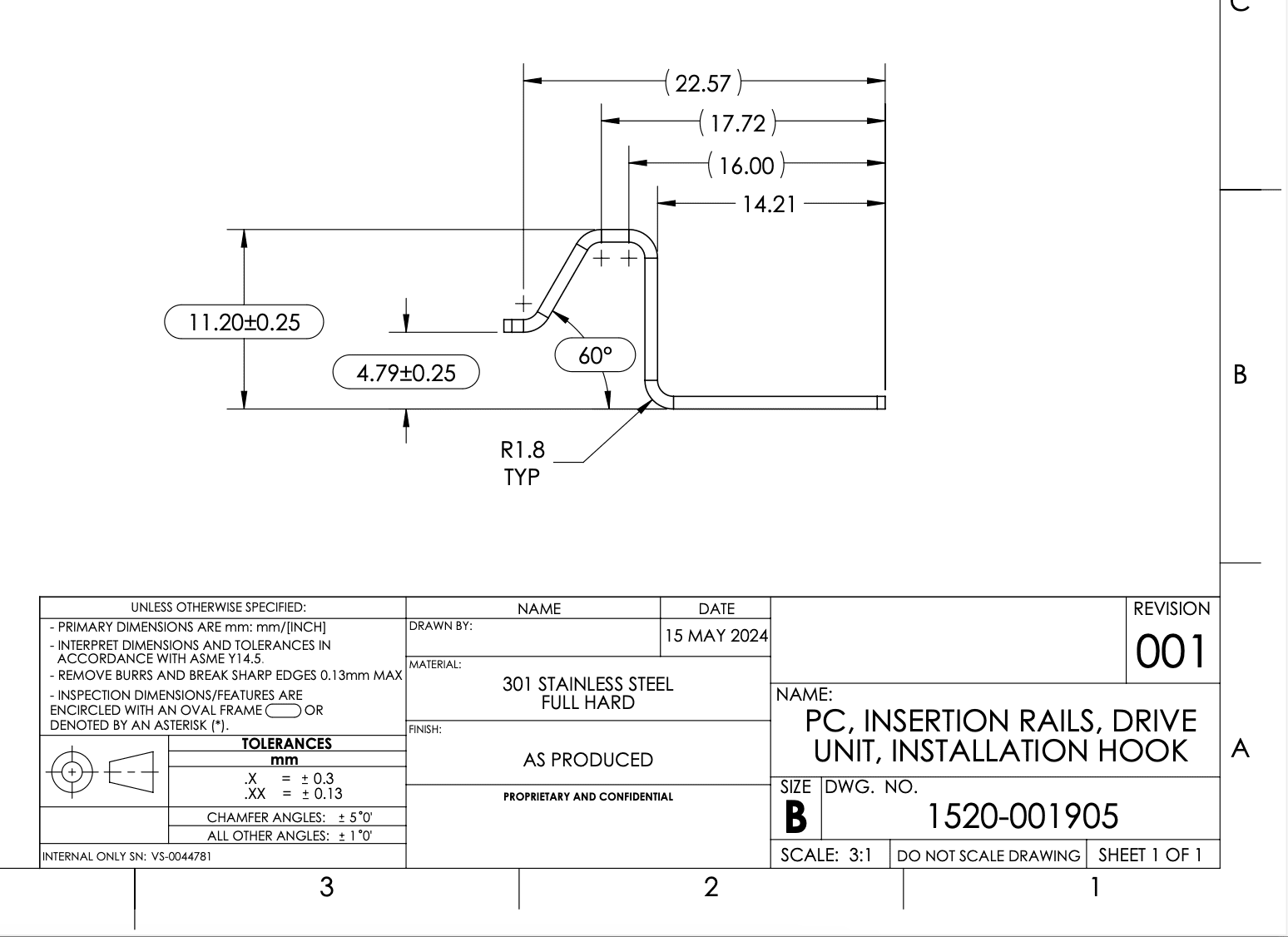
Thickness Tolerance for Sheet Metal – Technical Specifications
The thickness tolerance for sheet metal refers to the permissible deviation in the nominal thickness of raw sheet material used in manufacturing processes such as laser cutting, bending, and welding. These tolerances are critical for ensuring dimensional accuracy, fit-up during welding, proper clearance in bending, and compatibility with laser cutting parameters. Tolerances vary depending on material type, manufacturing standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO), and material form (rolled sheet or plate).
Below is a summary of typical thickness tolerances for common materials used in laser cutting, bending, and welding applications:
| Material | Form | Nominal Thickness Range (mm) | Standard Thickness Tolerance (± mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Rolled Sheet | 0.5 – 6.0 | 0.08 – 0.15 | Per ASTM B209; tighter control in 5052, 6061 alloys; affects laser cut edge quality and bend allowance |
| Steel (Mild) | Cold Rolled | 0.8 – 10.0 | 0.05 – 0.13 | Per ASTM A109; consistent thickness critical for accurate bending and weld fit-up |
| Steel (Stainless) | Cold Rolled | 0.5 – 12.0 | 0.05 – 0.15 | Per ASTM A480; tighter tolerance in precision sheets; impacts laser cutting assist gas and kerf width |
| ABS | Extruded Sheet | 1.0 – 10.0 | 0.10 – 0.30 | Not typically welded or bent like metal; used for enclosures; laser cutting requires reduced power to prevent melting |
| Nylon | Cast/Extruded Sheet | 2.0 – 25.0 | 0.20 – 0.50 | High moisture absorption; variable behavior in laser cutting; not suitable for standard metal bending or arc welding |
Laser Cutting Considerations
Consistent material thickness ensures stable focus and kerf width. Variations beyond tolerance can lead to incomplete cuts, excessive dross, or edge taper. Aluminum and steel respond well to fiber or CO₂ lasers, but ABS and nylon require controlled settings due to thermal sensitivity.
Bending Considerations
Thickness directly influences bend allowance, springback, and required tonnage. Steel and aluminum have predictable behavior under bending with tight tolerances, while ABS and nylon are rarely bent using standard press brake tooling due to lower stiffness and higher elasticity.
Welding Considerations
Uniform thickness is essential for consistent heat input and penetration, especially in butt and fillet welds. Aluminum and steel are commonly welded using MIG, TIG, or laser welding. ABS and nylon are typically joined using adhesives or mechanical fasteners rather than fusion welding.
Tolerances should be verified at procurement and during incoming inspection to ensure process repeatability and final part conformance.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype Sheet Metal Thickness Tolerance Management Process
Honyo Prototype implements a rigorously controlled workflow for sheet metal thickness tolerance management, ensuring dimensional accuracy from design intent to final delivery. Our process integrates material science, manufacturing capabilities, and quality validation at each stage to meet ISO 2768-mK and customer-specific tolerance requirements. Below is the technical execution for thickness tolerance control within our standardized workflow:
CAD Upload
Upon receiving the customer’s CAD model, our engineering team performs an initial material specification audit. Critical parameters verified include nominal thickness, material grade (e.g., SS304, 5052-H32), and geometric features influencing thickness stability (e.g., flange length, bend radii). Discrepancies between specified thickness and material standards (e.g., ASTM A480 for stainless steel) trigger immediate clarification requests. The system cross-references thickness against Honyo’s validated material database to prevent non-compliant submissions.
AI-Powered Quoting
Our AI quoting engine evaluates thickness tolerance feasibility against 120+ process constraints. The algorithm assesses:
Material thickness vs. minimum/maximum capabilities of laser cutting (0.5–25mm), CNC punching (0.8–6.0mm), and bending (up to 12mm)
Tolerance class alignment with ISO 2768 (e.g., mK for medium precision: ±0.2mm for 1–3mm thickness)
Yield strength impact on springback (e.g., 6061-T6 aluminum requires tighter bend compensation vs. mild steel)
The quote explicitly states achievable thickness tolerances and flags designs exceeding ±0.1mm tolerance for features below 1mm thickness where material variability dominates.
DFM Analysis
During engineering-led DFM, thickness tolerance is validated through:
Finite element analysis (FEA) of bending operations to predict thickness deformation at critical radii
Tooling simulation for coining operations where thickness reduction (0.5–3%) is modeled
Material grain direction impact assessment on edge tearing for tolerances ≤±0.05mm
We provide actionable recommendations such as:
Increasing bend radius to 1.5× material thickness to maintain ±0.1mm thickness consistency
Specifying ASTM A666 annealed stainless steel instead of hardened grades for tight tolerance zones
Production Execution
Thickness tolerance adherence is enforced via:
Incoming material certification with mill test reports verifying thickness within ASTM tolerances
In-process verification using calibrated ultrasonic thickness gauges (resolution 0.001mm) at 3 locations per 300mm²
Laser cutting kerf compensation algorithms adjusted for material thickness (e.g., 0.15mm kerf for 2mm SS304)
Press brake tooling selection based on thickness-to-V-die ratio (8:1 standard) to prevent thinning
Delivery Validation
Final thickness tolerance compliance is certified through:
First-article inspection reports (FAIR) with CMM-measured thickness at 5+ critical points
Statistical process control (SPC) data showing 30-piece sample thickness distribution (CpK ≥1.33)
Material traceability linking each part to certified heat lot numbers
Tolerance Capability Reference
| Material Thickness Range | Standard Tolerance (ISO 2768-mK) | Achievable Tight Tolerance | Process Constraint |
|————————–|——————————–|—————————-|———————|
| 0.5–1.0 mm | ±0.10 mm | ±0.05 mm | Laser cutting only; no bending |
| 1.0–3.0 mm | ±0.15 mm | ±0.08 mm | Requires coining operation |
| 3.0–6.0 mm | ±0.20 mm | ±0.12 mm | Limited to hydraulic press forming |
This closed-loop process ensures thickness tolerances are maintained within 95% of design intent for standard requirements, with specialized processes available for aerospace/medical applications demanding ±0.02mm control. All tolerance deviations beyond quoted specifications undergo 8D root cause analysis prior to shipment.
Start Your Project
For precise thickness tolerance specifications in sheet metal fabrication, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. Our manufacturing facility in Shenzhen ensures strict adherence to technical standards, delivering consistent quality for your prototyping and production needs. Reach out to discuss your project requirements and receive expert support tailored to your design specifications.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.