Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for surface roughness calculation
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, accurately calculating surface roughness is a pivotal challenge that can significantly impact product performance and durability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—understanding the nuances of surface roughness calculations is essential. This guide delves into various methodologies for assessing surface roughness, including the widely used Ra and RMS metrics, and highlights their applications across different manufacturing processes.
By exploring the intricacies of surface roughness, this comprehensive resource equips buyers with the knowledge to navigate supplier offerings, ensuring they select the right processes and finishes for their specific needs. From evaluating supplier capabilities and certifications to understanding the cost implications of different surface finishes, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. It also addresses the importance of surface roughness in enhancing product quality and longevity, ultimately helping businesses maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Whether you are sourcing components for precision engineering or looking to optimize manufacturing efficiency, this guide provides actionable insights that will facilitate successful procurement strategies. Equip yourself with the essential information needed to make strategic choices that align with your operational goals and quality standards.
Understanding surface roughness calculation Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ra (Roughness Average) | Arithmetic mean of surface height deviations; widely used and understood | CNC machining, metal finishing | Pros: Simple to calculate and understand; Cons: May not capture extreme surface variations effectively. |
| RMS (Root Mean Square) | Takes the square root of the average of the squared deviations; sensitive to outliers | Precision engineering, high-performance components | Pros: More sensitive to surface irregularities; Cons: More complex to calculate and interpret. |
| Rz (Average Maximum Height) | Average of the five highest peaks and five lowest valleys; gives a more detailed view | Automotive parts, aerospace components | Pros: Useful for quality control; Cons: Can be less intuitive than Ra for some buyers. |
| Rp and Rv (Peak and Valley Heights) | Measures the height of the highest peak and lowest valley from the mean line | Precision applications where peak and valley height is critical | Pros: Provides specific surface profile details; Cons: Requires careful measurement and may not be applicable for all surfaces. |
| Rmax (Maximum Height) | The largest single peak-to-valley height; useful for assessing worst-case scenarios | Heavy-duty machinery, construction equipment | Pros: Highlights extreme surface variations; Cons: May overlook overall surface quality. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Ra (Roughness Average)?
Ra, or Roughness Average, is a fundamental metric in surface roughness measurement, calculated as the arithmetic mean of the absolute height deviations from the mean line. This method is widely accepted in various industries, particularly in CNC machining and metal finishing, where a balance between surface smoothness and production efficiency is essential. When considering Ra, buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications, as while it is simple to understand, it may not adequately represent surfaces with significant irregularities.
How does RMS (Root Mean Square) differ in its application?
RMS offers a more nuanced approach by calculating the square root of the average of squared deviations, making it particularly sensitive to outliers. This makes RMS an ideal choice for precision engineering and applications where surface integrity is critical, such as high-performance components in aerospace and medical devices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of increased sensitivity against the complexity of calculations, as RMS may require specialized equipment or software for accurate measurement.
What advantages does Rz (Average Maximum Height) provide in quality control?
Rz measures the average of the five highest peaks and five lowest valleys, providing a more detailed understanding of surface profile than Ra. This metric is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where surface finish can directly affect performance and safety. However, while Rz can be a powerful tool for quality control, buyers need to consider that it may not be as straightforward as Ra, necessitating a deeper understanding of surface finish specifications.
In what scenarios are Rp and Rv measurements critical?
Rp and Rv focus on the heights of the highest peak and lowest valley, respectively, from the mean line. These measurements are crucial in precision applications where the specific characteristics of surface peaks and valleys can influence functionality, such as in sealing surfaces or sliding components. Buyers should assess whether such detailed profiling is necessary for their products, as these measurements can require more meticulous testing and analysis.
Why might Rmax (Maximum Height) be significant for heavy-duty applications?
Rmax highlights the largest single deviation between peaks and valleys, which is particularly useful in heavy-duty machinery and construction equipment, where extreme surface variations can impact performance and durability. While this metric can provide insights into worst-case scenarios, buyers should be cautious, as it may not reflect the overall quality of the surface finish, leading to potential misinterpretations of the product’s suitability.
Key Industrial Applications of surface roughness calculation
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Surface Roughness Calculation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft and spacecraft | Enhances safety and performance through better fit and reduced friction | Compliance with stringent aerospace standards; advanced testing capabilities |
| Automotive | Engine components and transmission parts | Increases efficiency and longevity of components, reducing maintenance costs | Material compatibility and supply chain reliability; ISO certifications |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Improves biocompatibility and reduces infection risk through smoother surfaces | Regulatory compliance (FDA, CE marking); specialized manufacturing processes |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline and valve manufacturing | Reduces wear and tear, enhancing operational efficiency and safety | Resistance to corrosion and wear; adherence to industry standards like API |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and circuit boards | Improves thermal management and electrical conductivity, leading to better performance | Precision in manufacturing processes; sourcing of high-quality materials |
How is Surface Roughness Calculation Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, surface roughness calculation is crucial for ensuring that precision components fit together seamlessly, which is vital for safety and performance. Components such as turbine blades and landing gear require specific roughness levels to minimize friction and wear. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent aerospace standards, including AS9100, and possess advanced testing capabilities to validate surface finishes.
What Role Does Surface Roughness Calculation Play in the Automotive Sector?
Surface roughness is a key factor in manufacturing engine components and transmission parts, where smoother surfaces lead to improved efficiency and reduced friction. This results in lower maintenance costs and longer component life. Automotive manufacturers in South America and Africa need to focus on sourcing materials that not only meet their performance requirements but also comply with industry standards such as ISO/TS 16949, ensuring consistency and reliability in their supply chain.
Why is Surface Roughness Calculation Important for Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, surface roughness calculations are essential for the production of surgical instruments and implants. A smoother surface finish enhances biocompatibility and reduces the risk of infection. Buyers from international markets, especially in Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers who comply with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and have specialized manufacturing processes to ensure high-quality finishes that meet safety and efficacy requirements.
How Does Surface Roughness Calculation Affect the Oil & Gas Industry?
For the oil and gas sector, surface roughness calculations are vital in the manufacturing of pipelines and valves, where minimizing wear can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety. A rougher surface can lead to increased friction and wear, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. Buyers in this industry must consider the corrosion resistance of materials and ensure adherence to standards such as API 5L and ISO 3183 to maintain operational integrity.
What is the Significance of Surface Roughness Calculation in Electronics?
In electronics, surface roughness impacts the performance of heat sinks and circuit boards, where smooth surfaces facilitate better thermal management and electrical conductivity. Manufacturers in regions like Europe and South America should focus on sourcing precision components that meet specific roughness criteria to ensure optimal performance. It is essential to partner with suppliers who have robust quality control processes and can provide detailed surface roughness data to support product reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘surface roughness calculation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Surface Roughness Standards Across Regions
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties when dealing with surface roughness calculations due to varying international standards. For instance, a manufacturer in Nigeria may be accustomed to ISO standards, while a partner in Saudi Arabia follows ASME guidelines. This inconsistency leads to confusion and potential quality issues, as products may not meet the required specifications when they are shipped across borders. This problem can delay projects, increase costs, and damage business relationships.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should conduct thorough research on the surface roughness standards relevant to their specific industry and region. It is advisable to create a comprehensive guide that includes the key differences between ISO, ASME, and other applicable standards. Buyers can also invest in training sessions for their teams, focusing on the importance of these standards. Additionally, establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers can ensure that everyone is aligned on the surface roughness requirements from the outset. Regular audits of the finished products can also help identify discrepancies early in the process.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Measuring Surface Roughness Accurately
The Problem: Another common pain point is the challenge of accurately measuring surface roughness during production. Many manufacturers rely on manual measurement techniques, which can be inconsistent and prone to human error. This inaccuracy can lead to subpar products, resulting in increased rework and wasted materials, which ultimately affects the bottom line.
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should consider investing in advanced measurement tools such as laser profilometers or stylus-based surface roughness testers. These devices provide precise and repeatable measurements, significantly reducing the chances of error. Furthermore, implementing a standardized procedure for surface roughness measurement can enhance consistency. Training employees on how to use these tools effectively and interpret the data will also contribute to more reliable results. Regular calibration of measurement equipment is essential to maintain accuracy over time.
Scenario 3: Balancing Cost and Desired Surface Finish Quality
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with finding the right balance between achieving desired surface roughness and managing production costs. While a smoother surface finish can enhance product performance, it often comes with increased manufacturing costs. This dilemma can lead to compromises that may affect the quality and functionality of the final product, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive where precision is critical.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should perform a cost-benefit analysis to determine the optimal surface finish that meets both quality requirements and budget constraints. Collaborating closely with suppliers to explore different finishing processes, such as mechanical polishing, electropolishing, or chemical treatments, can reveal cost-effective solutions without sacrificing quality. Additionally, engaging in early-stage design discussions can help identify the necessary surface roughness before production begins, allowing for the integration of smoother finishes without incurring excessive costs later in the process. By establishing a solid partnership with suppliers, buyers can also negotiate better rates for finishing processes that meet their specific needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for surface roughness calculation
When selecting materials for applications requiring precise surface roughness calculations, it is essential to consider various factors, including material properties, manufacturing processes, and specific application requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in industries that prioritize surface finish quality, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Surface Roughness Calculations?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas. The surface roughness of stainless steel can be finely controlled through processes like electropolishing or mechanical polishing, which enhance its aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Pros & Cons: Stainless steel’s durability and resistance to corrosion are significant advantages, ensuring longevity in demanding environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and machining can be complex due to its hardness, potentially increasing manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for industries requiring stringent hygiene standards. Its surface finish can significantly affect adhesion properties, which is crucial in applications like medical devices and food processing equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. Preferences for specific grades (e.g., 304 or 316) may vary based on local regulations and application requirements.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Surface Roughness Calculations?
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. The surface roughness of aluminum can be effectively managed through anodizing and polishing, which not only improve aesthetics but also enhance corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces transportation costs and energy consumption. However, it is softer than steel, which may lead to lower durability in high-stress applications. Additionally, the cost of aluminum can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum surfaces can be tailored to specific applications, such as improving friction for components like gears or providing a smooth finish for aesthetic purposes in consumer products. Its compatibility with various coatings further enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the differences in aluminum grades and their corresponding surface finish standards, which may vary by region. Compliance with international quality standards is crucial, especially in aerospace and automotive applications.
What are the Benefits of Using Titanium in Surface Roughness Calculations?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making it a preferred choice in the aerospace, medical, and marine industries. The surface roughness of titanium can be finely tuned through processes like grit blasting and polishing, which can significantly affect its performance in specific applications.
Pros & Cons: Titanium’s strength and resistance to extreme environments are significant advantages, particularly in aerospace applications. However, its high cost and complex machining requirements can be limiting factors for some manufacturers.
Impact on Application: In medical applications, the surface roughness of titanium implants can influence osseointegration, affecting their success rates. In aerospace, a smoother surface can reduce drag, improving fuel efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific titanium alloys required for their applications and ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and AMS. Understanding local market conditions and sourcing options is essential for cost-effective procurement.
How Does Carbon Steel Compare in Surface Roughness Calculations?
Carbon steel is widely used due to its strength, toughness, and low cost. It is commonly found in construction, automotive, and manufacturing applications. The surface roughness of carbon steel can be controlled through various finishing processes, including grinding and polishing.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its affordability and availability. However, it is prone to corrosion and may require protective coatings, which can increase overall costs. Additionally, achieving a fine surface finish can be more challenging compared to stainless steel or aluminum.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where strength is prioritized over corrosion resistance. Its surface finish can impact friction and wear characteristics, making it essential to consider the intended use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards and regulations regarding carbon steel grades and surface finishes. Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is often necessary for construction and manufacturing applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Surface Roughness Calculation
| Material | Typical Use Case for surface roughness calculation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex machining | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Softer than steel, fluctuating cost | Med |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, manufacturing | Affordability and availability | Prone to corrosion, challenging finish | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions regarding surface roughness calculations tailored to their specific industry needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for surface roughness calculation
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Processes for Surface Roughness Calculation?
The manufacturing process for achieving desired surface roughness is critical in various industries, especially in precision engineering and component fabrication. Understanding the main stages of manufacturing—material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing—can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding their suppliers.
How Does Material Preparation Influence Surface Roughness?
Material preparation is the foundational stage that significantly influences surface roughness. This involves selecting the right material based on the application requirements, followed by processes like cutting, machining, or surface treatment. For instance, materials such as stainless steel or aluminum are often chosen for their favorable properties, including corrosion resistance and strength.
Before machining, it’s essential to ensure that the material is free from defects. Techniques such as visual inspections and non-destructive testing (NDT) can be employed to detect any irregularities. Proper material preparation not only minimizes the likelihood of defects but also sets the stage for achieving the desired surface finish.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Surface Roughness Manufacturing?
In the forming stage, various techniques are applied to shape the material into the desired form. This includes methods such as CNC machining, casting, extrusion, and injection molding. Each method has its own impact on surface roughness.
CNC machining, for example, can achieve high precision and relatively smooth finishes (Ra values as low as 0.4 µm), while casting might result in a rougher surface that may require additional finishing. Understanding the trade-offs between these techniques is crucial for B2B buyers. Selecting a forming method that aligns with the required surface roughness can help avoid costly rework and delays.
How Important Is the Assembly Process for Surface Roughness?
During the assembly process, care must be taken to maintain the integrity of the surface finishes achieved in prior stages. Any contact or friction between parts can lead to scratches or other surface imperfections. It is vital to implement appropriate handling and assembly techniques, such as using protective coverings or specialized tools, to prevent damage.
In addition, the design of the assembly process should consider how components will interact. For example, parts that require a smooth interface should be assembled in a manner that minimizes contact pressure. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly procedures a supplier uses to safeguard surface finishes.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance Surface Roughness Quality?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process where surface roughness is optimized. Techniques such as polishing, grinding, and electropolishing are commonly employed to improve surface quality.
- Polishing: This method removes superficial imperfections and can achieve a mirror-like finish.
- Grinding: Used for precision applications, it can enhance surface finish while maintaining tight tolerances.
- Electropolishing: Particularly effective for stainless steel, this electrochemical process can improve surface smoothness and reduce roughness by up to 50%.
Choosing the right finishing technique depends on the application requirements and the initial surface roughness achieved during forming. B2B buyers should consult with suppliers to determine the most effective finishing methods for their specific needs.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that the surface roughness meets industry standards and customer specifications. Adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001:2015, which focuses on quality management systems, is a critical factor for B2B buyers when assessing suppliers.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Surface Roughness?
ISO 9001:2015 ensures consistent quality in manufacturing processes, while industry-specific standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) and CE (Conformité Européenne) certification may apply based on the application. These certifications guarantee that the products meet specific safety and quality requirements.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are compliant with these standards. This can be done through documentation review and requesting certificates of compliance during the procurement process.
What QC Checkpoints Should Be in Place?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential in the manufacturing process to ensure surface roughness specifications are met. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing ensures that any deviations from the desired surface roughness are promptly addressed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to verify they meet the specified surface roughness and other quality criteria.
These checkpoints help in identifying and rectifying issues before they escalate, thereby reducing waste and ensuring customer satisfaction.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier QC Practices?
B2B buyers should actively engage in verifying supplier QC practices to ensure that they align with their quality expectations. Here are some strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. These audits should evaluate compliance with international standards and internal QC processes.
- Review Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including surface roughness measurements and inspection records, can help buyers assess the supplier’s performance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices and surface roughness measurement accuracy.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various regulatory and quality assurance nuances. Different regions may have specific compliance requirements, and cultural differences may influence quality expectations.
Buyers should be aware of these differences and maintain open communication with suppliers to ensure clarity on quality standards. Establishing clear specifications and expectations from the outset can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that the final products meet the required surface roughness criteria.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices related to surface roughness calculation is crucial for B2B buyers. By evaluating each stage of manufacturing—from material preparation to finishing—and verifying supplier QC practices, buyers can ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements. Engaging with suppliers who adhere to international standards and implement rigorous quality control measures can lead to successful partnerships and superior product performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘surface roughness calculation’
To assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of surface roughness calculation, this practical sourcing guide provides a structured checklist. The goal is to equip you with actionable insights that ensure you procure reliable and precise surface roughness measurement solutions, tailored to your specific industry needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of any successful procurement process. Identify the required surface roughness parameters, such as Ra and RMS values, and the specific applications for which they will be used. Knowing the nuances of your project will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the products meet your standards.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Requirements
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards, such as ASME B46.1 and ISO 1302:1992, which dictate acceptable surface roughness values for different applications. Understanding these standards will guide you in assessing whether a supplier’s offerings align with your requirements. Additionally, knowing the appropriate metrics helps in avoiding discrepancies during the manufacturing process.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers within your industry or region. Ensure that the suppliers possess the necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. This step is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring that your procurement aligns with best practices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
It’s essential to evaluate the quality of the surface roughness measurements through practical trials. Request samples or conduct pilot tests to assess the precision and accuracy of the surface roughness calculations. This hands-on approach allows you to verify that the supplier’s methodology meets your specifications before full-scale production begins.
Step 5: Inquire About Measurement Techniques and Equipment
Understanding the measurement techniques used by your potential suppliers is vital. Ask about the types of equipment they utilize, such as stylus-based profilometers or non-contact optical systems, and their calibration processes. This information will provide insights into the reliability and accuracy of the surface roughness data you can expect.
Step 6: Consider Post-Processing Capabilities
Evaluate whether your supplier offers post-processing services to improve surface finish, such as polishing or bead-blasting. Knowing the additional services available can help you achieve the desired surface roughness without needing to engage multiple vendors. This can streamline your supply chain and reduce overall costs.
Step 7: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in discussions about pricing and contract terms. Ensure that you understand the full scope of costs, including any potential fees for additional services or expedited delivery. Clear communication during this stage can prevent misunderstandings and help establish a mutually beneficial partnership.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for surface roughness calculation, ensuring they select the right suppliers to meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for surface roughness calculation Sourcing
When sourcing surface roughness calculation services, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The costs involved can be broadly categorized into several components, each influencing the final pricing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Surface Roughness Calculation?
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts costs. High-quality materials that meet specific industry standards typically come at a premium. For instance, stainless steel surfaces may require advanced treatments such as electropolishing, which can enhance surface roughness but also increase material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for accurate surface roughness measurement and finishing processes. The complexity of the surface finish desired dictates labor intensity. For example, achieving ultra-fine finishes (Ra values of 0.1 µm or lower) requires highly trained technicians and potentially longer processing times, thereby increasing labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes facility costs, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Advanced machinery for measuring and finishing surfaces, such as CNC machines and surface profilometers, contribute to overhead. Facilities that maintain high standards of cleanliness and precision may also incur higher overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools may be necessary for achieving specific surface finishes. The cost of these tools, including wear and tear, must be factored into the overall pricing. Custom tooling can further escalate costs, particularly if unique specifications are required.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the surface roughness meets the required specifications. This may involve additional testing equipment and procedures, adding to the cost structure. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can also impact pricing due to compliance requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly, especially for international orders. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a role. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers navigate these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin on top of their costs to ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and supplier relationships.
What Influences Pricing for Surface Roughness Services?
Several factors can influence the pricing of surface roughness calculations:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders where possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized surface finishes or specific Ra values may incur additional costs. It’s essential to clarify requirements upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can lead to increased pricing but often result in better performance and durability. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more due to their reliability and reputation. New or smaller suppliers may offer competitive pricing but could come with risks related to quality and delivery.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in Surface Roughness Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Engaging suppliers in discussions about pricing can lead to favorable terms. Understanding the cost structure allows buyers to negotiate effectively, especially when placing large orders.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with a supplier’s services. A lower initial price may lead to higher maintenance or replacement costs, while a slightly higher upfront investment might yield better durability and lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should account for currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some international shipping risks and costs.
-
Requesting Quotes: Buyers should obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers to compare costs and services. Be sure to specify all requirements to receive accurate pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for surface roughness calculation services can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes tailored to their specific needs to obtain accurate pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing surface roughness calculation With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Surface Roughness Measurement
In the realm of manufacturing and quality control, accurately assessing surface roughness is crucial for ensuring product performance and durability. While traditional surface roughness calculation methods, such as Ra and RMS, are widely used, several alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar objectives. This analysis aims to compare surface roughness calculation with other viable methods, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Surface Roughness Calculation | Optical Profilometry | Contact Profilometry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Accurate for standard surfaces | High-resolution data, 3D mapping | Effective for uneven surfaces |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High initial investment | Moderate investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple | Requires specialized training | User-friendly with some training |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular calibration needed | Minimal |
| Best Use Case | General manufacturing | High-precision applications | Industrial applications where contact is feasible |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Optical Profilometry
Optical profilometry employs light to measure surface topography, providing high-resolution 3D mapping of surfaces. This non-contact method excels in applications where precision is paramount, such as semiconductor manufacturing or advanced materials testing. The primary advantage of optical profilometry is its ability to produce detailed surface profiles without physically contacting the sample, reducing the risk of damage. However, the high initial investment and the need for specialized training to operate the equipment can be significant drawbacks, particularly for smaller manufacturers.
Contact Profilometry
Contact profilometry involves using a stylus that physically contacts the surface to measure its roughness. This method is particularly effective for measuring uneven surfaces or materials that may not be suitable for optical measurements. One of the advantages of contact profilometry is its relatively straightforward operation, making it accessible for many users. However, it can be less effective on delicate surfaces, where the contact may alter the surface profile. Additionally, while the cost is moderate, ongoing maintenance and stylus replacements can add to the overall expense.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Surface Roughness Measurement Solution
When selecting the appropriate method for measuring surface roughness, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including the nature of the materials involved, the required precision, and budget constraints. While traditional surface roughness calculations offer a reliable and cost-effective approach for many applications, alternatives like optical and contact profilometry provide unique advantages in precision and versatility. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the operational requirements and the specific applications within the manufacturing process. By evaluating the performance, cost, and ease of implementation of each option, buyers can make a well-informed decision that aligns with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for surface roughness calculation
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Surface Roughness Calculation?
Understanding the essential technical properties involved in surface roughness calculation is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in manufacturing and engineering sectors. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Roughness Average (Ra)
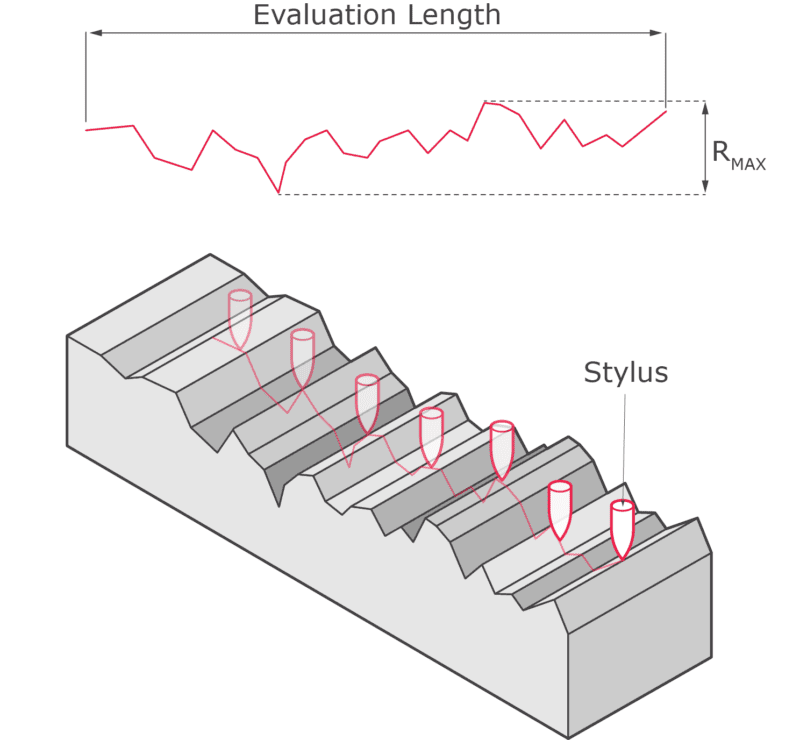
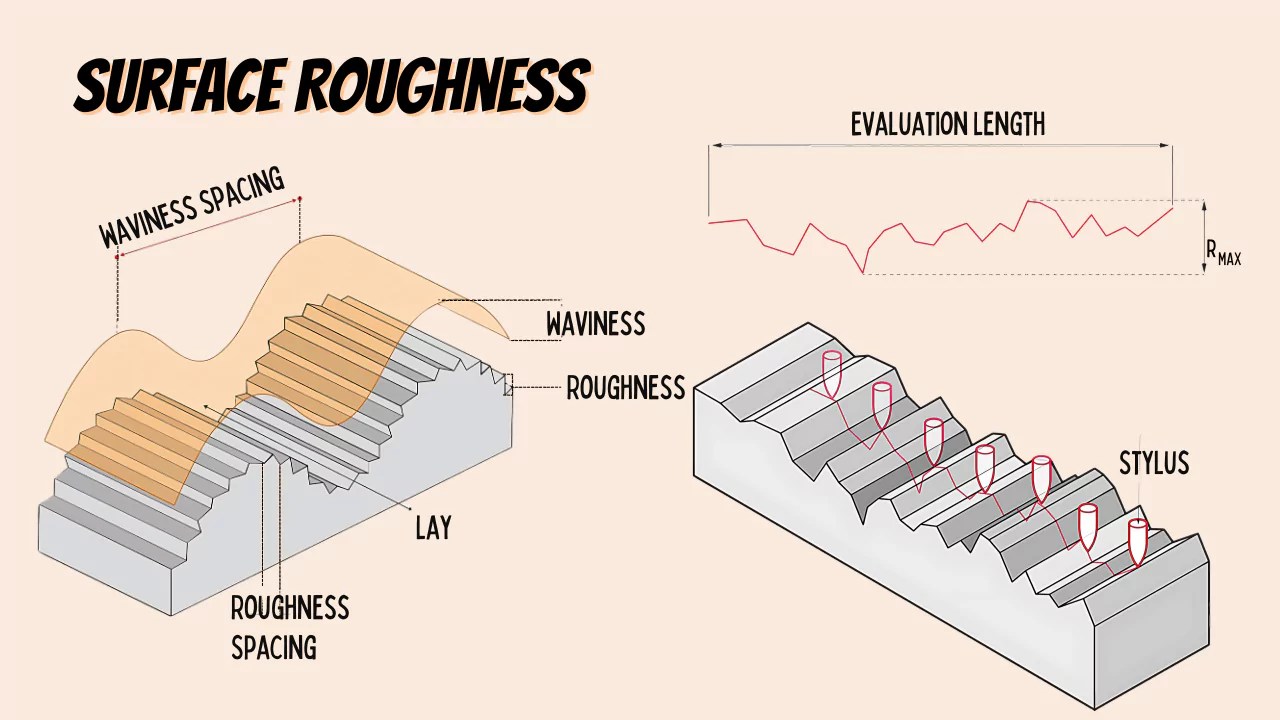
Ra is the most commonly used parameter to quantify surface roughness. It is calculated as the arithmetic mean of the absolute values of the surface height deviations from the mean line over a specified evaluation length. For B2B buyers, knowing the Ra value is vital as it directly affects the functionality and performance of machined parts. A lower Ra value typically indicates a smoother surface, which is essential for components that require precise fitting or reduced friction.
2. Root Mean Square (RMS)
RMS provides a more comprehensive view of surface roughness by calculating the root mean square of the height deviations. It is particularly sensitive to large surface irregularities, making it a valuable metric when assessing parts that will undergo significant mechanical stress. For international buyers, understanding RMS can inform decisions on durability and longevity in varying operational environments.
3. Material Grade
The material grade of a component influences its surface roughness characteristics. Different materials respond uniquely to machining processes, which can lead to variations in the resultant surface finish. For buyers, specifying the appropriate material grade ensures that the desired surface roughness aligns with the performance requirements of the application, whether in automotive, aerospace, or industrial machinery.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance defines the acceptable limits of surface roughness and dimensional accuracy. Tight tolerances may necessitate advanced machining techniques and additional finishing processes, impacting cost and lead time. Buyers must communicate their tolerance requirements clearly to suppliers to avoid discrepancies that could affect product performance or compliance with industry standards.
5. Evaluation Length
The evaluation length is the distance over which the surface roughness is measured. This parameter can significantly affect the calculated roughness values; a longer evaluation length may yield a more accurate representation of the overall surface texture. B2B buyers should be aware of how evaluation lengths can impact surface roughness specifications, especially when comparing different suppliers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Surface Roughness?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that the surface roughness of components meets the standards required for compatibility and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, being aware of the MOQ can influence purchasing decisions, especially when considering budget constraints and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Including surface roughness specifications in an RFQ allows buyers to receive accurate pricing and lead time estimates based on their requirements.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and insurance. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions, particularly in international trade, to avoid misunderstandings related to delivery and liability.
5. Surface Finish Grade
Surface finish grades categorize the quality of the surface finish based on defined roughness parameters. Familiarity with these grades helps buyers specify their needs effectively and ensures that suppliers understand the required surface roughness for their applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, performance, and overall satisfaction in their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the surface roughness calculation Sector
What Are the Global Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Surface Roughness Calculation?
The surface roughness calculation sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving industry standards. Global demand for precision-engineered components is on the rise, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality materials that meet stringent surface finish requirements. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing real-time monitoring and quality assurance processes, thus enabling manufacturers to optimize surface finish while reducing waste.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on customization, where buyers seek tailored solutions that align with specific performance criteria. For instance, in Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, industries are transitioning towards advanced manufacturing techniques, including CNC machining and additive manufacturing, which demand precise surface roughness metrics. Additionally, the shift towards automation in manufacturing processes facilitates faster and more accurate surface roughness calculations, ensuring that products meet desired specifications without compromising quality.
As sustainability becomes a priority, international buyers are also gravitating towards suppliers who can provide eco-friendly surface finishing processes. This trend is particularly pronounced in Europe, where regulatory frameworks are tightening around environmental impacts. Therefore, sourcing decisions are increasingly influenced by a supplier’s ability to demonstrate compliance with environmental standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in Surface Roughness Calculation?
Sustainability is reshaping the sourcing landscape in the surface roughness calculation sector. As environmental concerns rise, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that adopt sustainable practices and materials. The surface finishing processes, such as electropolishing and mechanical polishing, can have substantial environmental impacts, particularly in terms of waste generation and energy consumption. Companies are now scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure that sourcing decisions align with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
Ethical sourcing involves selecting suppliers who not only comply with environmental regulations but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications like ISO 14001. These certifications indicate that a supplier has implemented effective environmental management systems, making them more attractive to conscientious buyers. Additionally, the use of green materials—such as biodegradable lubricants and recyclable abrasives—can significantly reduce the ecological footprint associated with surface finishing processes.
International buyers are also increasingly aware of the importance of transparency in supply chains. They seek suppliers who provide detailed information about their sourcing practices and environmental impact. This trend not only helps in meeting regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty, particularly in markets where consumers are more environmentally conscious.
What Is the Historical Context of Surface Roughness Measurement in B2B?
The measurement of surface roughness has evolved significantly since its inception in manufacturing. Initially, surface finishes were assessed through tactile methods, where operators would manually gauge the texture using feeler gauges. The introduction of standardized measurement techniques in the mid-20th century, such as the Ra (Roughness Average) and RMS (Root Mean Square) parameters, revolutionized the industry by providing quantifiable metrics for surface texture.
As manufacturing technologies advanced, so did the methods for measuring surface roughness. The advent of optical and laser-based measurement tools allowed for non-contact assessments, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Today, with the integration of digital technologies, manufacturers can employ sophisticated software solutions that analyze surface profiles in real-time, ensuring that products meet rigorous quality standards.
This historical context underscores the importance of precision in surface roughness calculations, as it directly impacts product performance and longevity. Understanding these developments is crucial for B2B buyers who are navigating the complexities of sourcing in an increasingly competitive global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of surface roughness calculation
-
How do I solve discrepancies in surface roughness measurements?
Discrepancies in surface roughness measurements can arise from various factors, such as instrument calibration, measurement techniques, or environmental conditions. To resolve these issues, ensure that your measuring equipment is calibrated according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Additionally, use standardized measurement procedures, and conduct tests in a controlled environment to minimize external influences. Regular training for personnel on measurement protocols can also help maintain consistency and accuracy in results. -
What is the best surface roughness specification for precision components?
The best surface roughness specification for precision components depends on the application and performance requirements. For most applications, a surface roughness of Ra 0.8 to 1.6 µm is adequate for reducing friction and wear. However, in high-precision applications, such as aerospace or medical devices, a roughness of Ra 0.4 µm or lower may be necessary. It’s crucial to collaborate with your supplier to define the optimal surface finish based on the specific operational context and performance criteria. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a supplier for surface roughness calculations?
When selecting a supplier, consider their experience and expertise in surface roughness measurement and calculations relevant to your industry. Evaluate their quality assurance processes, certifications (such as ISO), and technological capabilities. Additionally, assess their communication responsiveness, lead times, and ability to provide customized solutions to meet your specific requirements. Request references or case studies to gauge their reliability and performance in similar projects. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect for surface roughness services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for surface roughness services can vary significantly among suppliers, influenced by their operational capabilities and the complexity of the work. Some suppliers may not have an MOQ, especially for specialized services, while others might require a minimum order to cover setup costs. It’s advisable to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to clarify their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that accommodate your production volume. -
What payment terms are typical for international B2B transactions in surface roughness calculation services?
Payment terms for international transactions often include options such as advance payment, net 30/60/90 days, or letter of credit. Many suppliers prefer partial upfront payments to secure the order, followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. It’s essential to clearly define payment terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. Always consider currency fluctuations and transaction fees that may arise in international dealings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for surface roughness calculations?
To ensure quality assurance in surface roughness calculations, choose suppliers with robust QA processes and industry certifications, such as ISO 9001. Request detailed documentation of their measurement procedures, equipment calibration records, and inspection protocols. Additionally, consider establishing clear acceptance criteria for surface roughness in your contracts, and ask for samples or prototypes for verification before full-scale production. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international surface roughness services?
Logistics is crucial in international transactions, especially for services involving surface roughness calculations. Consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential delays that could affect your delivery timeline. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide timely updates on order status. Additionally, factor in costs related to shipping, insurance, and customs duties when budgeting for your project. -
How can I customize surface roughness services to meet my specific project needs?
Customizing surface roughness services involves clear communication of your project specifications and performance requirements to your supplier. Discuss desired roughness values, materials, and any secondary processes needed, such as polishing or coating. Many suppliers are willing to adapt their processes to achieve specific surface finishes, so don’t hesitate to ask for tailored solutions. Providing detailed drawings and examples can further assist suppliers in understanding your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Surface Roughness Calculation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Harrison EP – Electropolishing Services
Domain: harrisonep.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Electropolishing services for various materials including stainless steel, nickel, Hastelloy, and aluminum. Benefits include improved cleanability, corrosion resistance, surface finish, reduced product adhesion, and aesthetic appeal. The process can improve surface finish by up to 50%, with real-world improvements ranging from 10 to 35%. The company adheres to ASME BPE specifications and holds ISO…
2. Get It Made – Comprehensive Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: get-it-made.co.uk
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Get It Made offers a range of manufacturing services including CNC Machining (5 axis CNC machining, CNC turning, CNC milling), 3D Printing (with diverse materials and color options), Subtractive CNC, Metal Forming, Custom Aluminium Extrusion, Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication, Assembly & Welding, Moulding & Casting (Plastic Injection Moulding, Aluminium Die Casting, Metal Injection Moulding), and Add…
3. Michmet – Average Roughness Measurement Solutions
Domain: michmet.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Average roughness (Ra) is a key surface texture parameter that measures the average height deviations of a surface from its mean height. It is commonly specified in microns (µm) or micro-inches (µ-in). Ra is measured using stylus-based instruments or optical profilers, with stylus instruments ranging from handheld gauges to automated systems. Ra provides a general indication of surface texture but…
4. GD&T Basics – Surface Finish Standards
Domain: gdandtbasics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Surface finish refers to the texture of a surface, often specified in technical drawings for mechanical parts. It consists of three elements: roughness, lay, and waviness. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) has established standards for surface texture symbols (Y14.36M) and definitions/measurement methods (B41.6). Roughness is the most commonly specified aspect, measured using a p…
5. Engineers Edge – Surface Roughness Measurement
Domain: engineersedge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Surface roughness is the measure of finer surface irregularities and consists of three components: roughness, waviness, and form. Surface Roughness Average (Ra), also known as arithmetic average (AA), is the arithmetic average deviation of surface valleys and peaks, expressed in micro inches or micro meters. ISO standards refer to this as CLA (Center Line Average). The manufacturing operation’s ab…
6. Timesavers – Metal Finishing Machines
Domain: timesaversint.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Timesavers offers a range of machines for metal finishing, including deburring, edge rounding, sheet metal finishing, precision grinding, laser oxide removal, and heavy slag removal. Their machine series include the 10 series, 12 series, 12 RB series, 22 series, 22 RB series, 31 series, 32 RB series, 42 series, 62 series, 71 series, 72 series, and 81 series. They also provide industrial automation…
7. ISO Finishing – Surface Finishing Solutions
Domain: isofinishing.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: ISO Finishing specializes in surface finishing processes that refine surface deviations for optimal part performance. They offer services such as deburring, deflashing, descaling, and polishing, utilizing various media types, processing speeds, and cycle lengths to achieve precise polishing or texturizing. The company is ISO 9001:2015 certified and FFL licensed, experienced in working with all mat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for surface roughness calculation
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Surface Roughness Calculations?
In the realm of manufacturing, understanding surface roughness is paramount for ensuring product quality and performance. By strategically sourcing materials and processes that optimize surface finishes—like CNC machining, electropolishing, and mechanical polishing—businesses can achieve precise specifications that meet industry standards. This not only enhances the aesthetic and functional attributes of products but also reduces friction and wear, ultimately leading to increased durability and customer satisfaction.
Moreover, the calculated use of parameters such as Ra and RMS can inform decisions that balance cost and quality effectively. For international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging these insights can lead to significant competitive advantages.
As you move forward, consider how a refined approach to sourcing can elevate your manufacturing capabilities. Engage with suppliers who understand the intricacies of surface roughness calculations and can provide tailored solutions to meet your specific needs. Embrace innovation in your sourcing strategies to position your business for growth and success in an increasingly competitive market.