Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stl vs stp
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, understanding the nuances between STL and STP file formats is paramount for B2B buyers looking to optimize their design-to-production processes. With the increasing demand for precision in product development, the challenge lies in selecting the appropriate file type that aligns with specific manufacturing needs. This guide aims to demystify the intricacies of STL and STP formats, offering insights into their applications, advantages, and limitations.
We will delve into various aspects including the types of files, their specific applications in 3D printing versus CNC machining, supplier vetting strategies, and cost considerations. By equipping international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Vietnam—with a comprehensive understanding of these file formats, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the global market for STL and STP does not have to be daunting. With the right knowledge, you can ensure that your product designs are communicated effectively to manufacturers, ultimately leading to higher quality outputs and reduced production costs. Whether you’re a seasoned buyer or new to the manufacturing sector, our insights will help you confidently choose the right file type to meet your unique business requirements.
Understanding stl vs stp Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| .STL | Triangular mesh geometry, primarily for 3D printing | Rapid prototyping, 3D printing | Pros: Simple, widely supported, storage-efficient. Cons: Limited data (no assembly or manufacturing details). |
| .STP | Comprehensive 3D model data, supports complex geometries | CNC machining, injection molding, product design | Pros: Detailed information, better for collaboration, editable. Cons: Larger file sizes, more complex to manage. |
| .OBJ | Similar to STL but includes color and texture data | 3D printing, visual rendering | Pros: Supports detailed textures, versatile. Cons: Requires separate files for color/texture, can complicate workflow. |
| .IGS | Detailed data similar to STP, larger file size | CAD data exchange, complex assemblies | Pros: High accuracy, good for collaboration. Cons: Larger files can be cumbersome to share. |
| Hybrid Formats | Combination of STL and STP features | Advanced manufacturing processes | Pros: Flexibility in design and production. Cons: May require specialized software for compatibility. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of .STL Files for B2B Buyers?
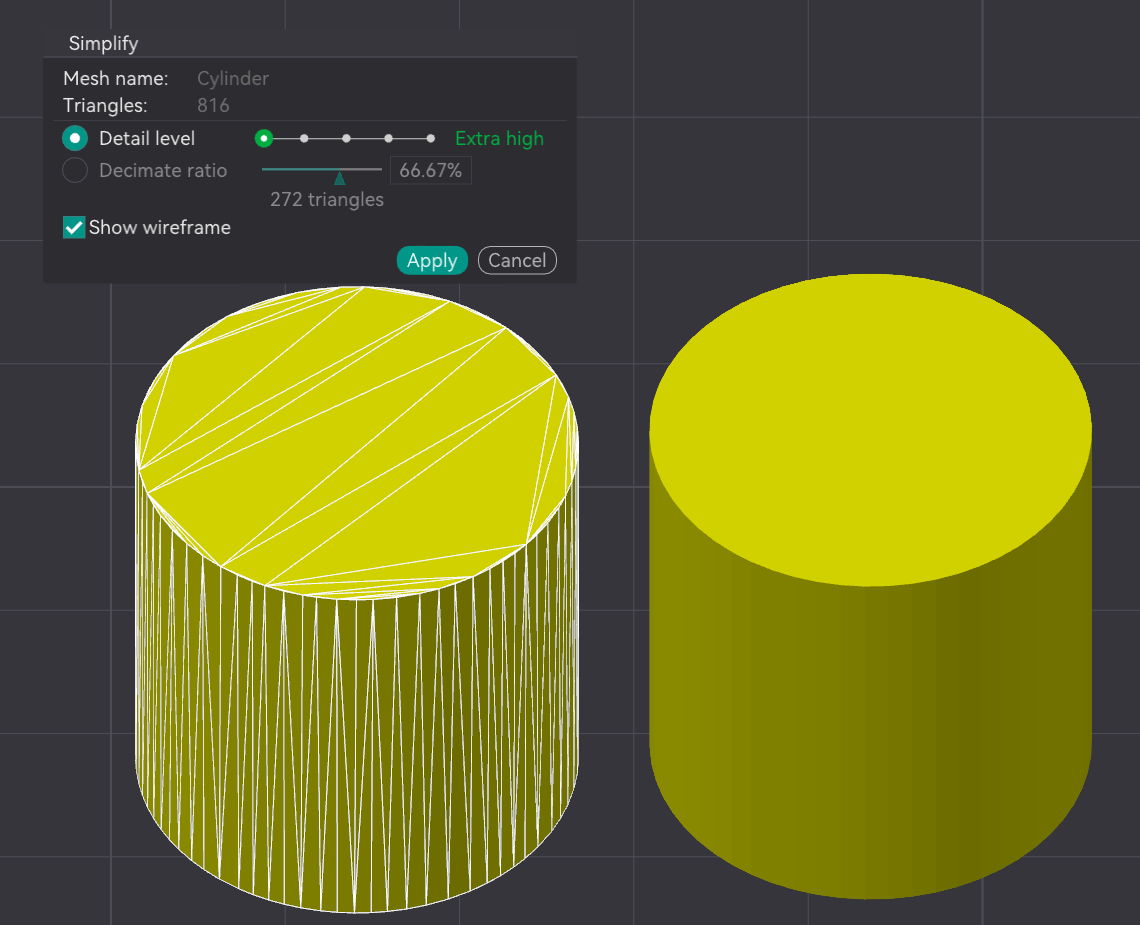
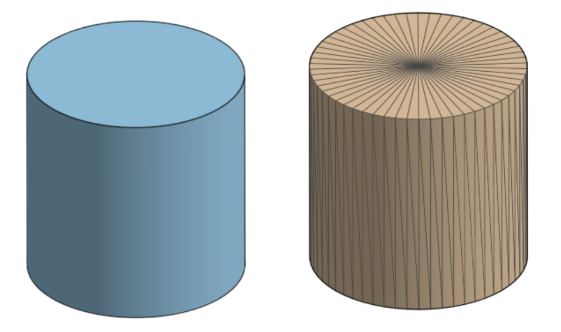
.STL files are characterized by their triangular mesh geometry, which simplifies the representation of 3D objects. This format is predominantly used in rapid prototyping and 3D printing, making it ideal for businesses looking to create quick models or prototypes. However, it lacks detailed information about the assembly and manufacturing processes, which may limit its effectiveness for complex projects. Buyers should consider the simplicity and broad compatibility of .STL files against their need for detailed design data.
Why Are .STP Files Essential for Complex Manufacturing?
.STP files provide a comprehensive representation of 3D models, including geometry, assembly structure, and product manufacturing information. This format is particularly useful for CNC machining and injection molding, where intricate details are necessary for accurate production. The ability to edit and repair these files enhances their utility in collaborative environments. Buyers in need of precision and detail in their manufacturing processes should prioritize .STP files, despite their larger size and complexity.
How Do .OBJ Files Enhance Visual Representation in Manufacturing?
.OBJ files are similar to .STL files but offer the added advantage of storing color, texture, and material information. This makes them particularly suitable for projects that require detailed visual representations, such as product design and marketing materials. However, the need for separate files for texture data can complicate workflows. Businesses focusing on aesthetics alongside functionality may find .OBJ files beneficial, but they should also weigh the additional complexity against their specific needs.
What Advantages Do .IGS Files Offer for CAD Data Exchange?
.IGS files, like .STP files, contain detailed information about CAD models, making them ideal for complex assemblies and data exchange. They offer high accuracy, which is crucial for collaborative projects involving multiple stakeholders. However, the larger file sizes can pose challenges in sharing and storage. For B2B buyers engaged in intricate design and manufacturing processes, .IGS files can facilitate effective communication and collaboration, provided they have the infrastructure to handle larger data sizes.
How Can Hybrid Formats Benefit Advanced Manufacturing Processes?
Hybrid formats that combine features of both .STL and .STP files offer flexibility for advanced manufacturing processes. They can accommodate various design requirements and production methods, making them attractive for businesses that operate in diverse sectors. However, the necessity for specialized software to ensure compatibility can be a drawback. Buyers should assess their manufacturing capabilities and software infrastructure when considering hybrid formats, as they may offer the best of both worlds in terms of design and production efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of stl vs stp
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of STL vs STP | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Rapid prototyping of components using STL files | Accelerates design iterations, reducing time to market | Ensure compatibility with specific 3D printing technologies |
| Automotive | Detailed component design and analysis with STP files | Enhances collaboration and precision in manufacturing | Verify CAD software compatibility and file integrity |
| Consumer Electronics | 3D printing prototypes with STL for testing | Facilitates user feedback and product refinement | Assess material quality for prototypes and production needs |
| Medical Devices | STP files for complex geometries in device manufacturing | Improves accuracy and regulatory compliance | Focus on precision and material certifications |
| Industrial Equipment | Use of STL for rapid tooling and STP for production | Reduces costs and lead times in manufacturing | Consider supplier capabilities for both rapid prototyping and production |
How is STL Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, STL files are crucial for rapid prototyping of components such as brackets, housings, and fixtures. This format allows engineers to quickly iterate designs, enabling faster testing and validation processes. By utilizing STL files, aerospace companies can significantly reduce time to market for new innovations while ensuring that prototypes meet stringent safety and performance standards. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust 3D printing capabilities and expertise in aerospace-grade materials to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Why is STP Important for Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive sector relies heavily on STP files for detailed component design and analysis. These files facilitate the exchange of complex geometries and assembly structures among different CAD systems, enhancing collaboration between designers and manufacturers. By using STP files, automotive companies can improve precision in their manufacturing processes, thereby minimizing errors and production costs. B2B buyers in this sector should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to handle intricate designs and maintain interoperability between various CAD platforms.
How Does STL Enhance Prototyping in Consumer Electronics?
In consumer electronics, STL files play a pivotal role in 3D printing prototypes for new devices. This application allows companies to quickly gather user feedback and make necessary adjustments before mass production. Using STL files can streamline the development process, ensuring that products meet consumer expectations and market demands. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who offer high-quality printing services and materials tailored for electronic applications, ensuring prototypes are both functional and reliable.
What Advantages Do STP Files Offer in Medical Device Manufacturing?
STP files are essential in the medical device industry, where complex geometries and precise specifications are paramount. These files provide comprehensive data on product and manufacturing information, aiding in the design of intricate medical components that must meet regulatory standards. The use of STP files enhances accuracy in manufacturing, which is critical for patient safety. International buyers should focus on manufacturers with experience in medical device compliance and certifications to ensure quality and reliability.
How is STL and STP Used in Industrial Equipment Production?
In the industrial equipment sector, STL files are often utilized for rapid tooling and prototypes, while STP files are employed for the final production of components. This combination allows companies to reduce costs and lead times significantly, as prototypes can be tested and refined before full-scale production. Buyers should assess suppliers on their capabilities in both rapid prototyping and traditional manufacturing methods, ensuring they can meet diverse production needs efficiently.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stl vs stp’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over File Format Selection
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter confusion when deciding between STL and STP file formats for their projects. This is particularly challenging for companies in diverse regions such as Africa and South America, where knowledge of CAD software and file types may be limited. Buyers often mistakenly assume that STL files are suitable for all types of manufacturing processes, leading to significant delays and increased costs when their designs do not meet the specific requirements of CNC machining or injection molding.
The Solution:
To alleviate this confusion, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research and collaborate with their manufacturing partners to understand the specific requirements of their projects. Begin by analyzing the intended manufacturing process: if the goal is 3D printing or rapid prototyping, then STL files are appropriate. However, for more complex tasks such as CNC machining or injection molding, STP files should be utilized due to their ability to convey detailed geometrical and assembly information. Buyers should create a checklist of their project requirements and consult with CAD specialists or manufacturers to clarify the best file format for their needs. This proactive approach not only saves time and resources but also enhances the quality of the final product.
Scenario 2: Miscommunication with Manufacturers
The Problem:
A common pain point for B2B buyers is miscommunication with manufacturers regarding file formats. When buyers send the wrong file type, such as STL instead of STP, manufacturers may struggle to interpret the design intent fully. This often leads to errors in production, product delays, and increased costs—issues that can severely affect a buyer’s timeline and budget, especially in competitive markets.
The Solution:
To ensure clear communication with manufacturers, buyers should establish a protocol for file sharing that includes specifications for the required file format. This can involve drafting a document outlining the project’s complexity, the intended manufacturing process, and the preferred file type. Additionally, buyers should engage in preliminary discussions with manufacturers to confirm that they understand the design’s requirements. Utilizing project management tools that facilitate real-time collaboration and feedback can also help streamline this communication process. By prioritizing clarity and collaboration, buyers can mitigate misunderstandings and foster stronger partnerships with their manufacturers.
Scenario 3: Quality Control Issues Due to Inaccurate Files
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face quality control issues stemming from the use of inaccurate or poorly exported CAD files. This is particularly prevalent when files are converted from STL to STP or vice versa without proper validation. Such inaccuracies can result in defective products that do not meet the intended design specifications, leading to costly reworks and loss of trust from clients.
The Solution:
To address quality control concerns, buyers should implement a robust review process for all CAD files before they are sent for manufacturing. This includes using software tools that can validate the geometry and integrity of STL and STP files, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications for the intended manufacturing process. It is also beneficial to establish a feedback loop with manufacturers, where initial prototypes are tested and assessed against the original design. By proactively identifying potential issues in the design phase, buyers can significantly enhance the quality of their products and reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes during production. Regular training sessions on file formats and CAD software for team members can further bolster overall quality assurance efforts.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stl vs stp
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in STL and STP Applications?
When selecting materials for STL and STP file applications, it is essential to consider the specific properties of each material, as they directly impact product performance, manufacturing complexity, and end-use suitability. Below is an analysis of four common materials: ABS, PLA, Nylon, and Polycarbonate.
How Do ABS and PLA Compare for 3D Printing and Prototyping?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a popular choice for 3D printing with STL files due to its strength and durability. It has a high-temperature resistance, making it suitable for applications that may experience heat. However, ABS can be prone to warping during the cooling process, which may complicate manufacturing.
Polylactic Acid (PLA), on the other hand, is biodegradable and easier to print than ABS, making it a preferred material for rapid prototyping. While PLA is less durable than ABS, it offers excellent dimensional accuracy and is less prone to warping. However, its lower heat resistance limits its application in high-temperature environments.
What Are the Advantages of Using Nylon and Polycarbonate in STP Applications?
Nylon is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts. It has good chemical resistance and can withstand high temperatures, but it can absorb moisture, which may affect its mechanical properties over time.
Polycarbonate is another robust material, renowned for its impact resistance and clarity. It is suitable for applications requiring high strength and transparency, such as protective covers. However, polycarbonate can be more expensive and may require specialized processing techniques, which could increase manufacturing complexity.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Selecting Materials?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Additionally, understanding the availability of materials in their region and the associated costs is crucial. For instance, while ABS and PLA may be widely available, specialized materials like Nylon and Polycarbonate may require sourcing from specific suppliers, impacting lead times and costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for STL vs STP
| Material | Typical Use Case for stl vs stp | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 3D printing prototypes | High durability and temperature resistance | Prone to warping during cooling | Medium |
| PLA | Rapid prototyping | Easy to print and biodegradable | Lower durability and heat resistance | Low |
| Nylon | Functional prototypes and end-use parts | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility | Moisture absorption can affect properties over time | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Protective covers and high-strength parts | High impact resistance and clarity | Higher cost and requires specialized processing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for STL and STP applications, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stl vs stp
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for STL and STP Files?
When it comes to manufacturing using STL and STP files, understanding the specific processes involved is crucial for B2B buyers. Each file type serves distinct purposes and requires tailored manufacturing techniques.
How Do Material Preparation and Forming Differ for STL and STP?
Material Preparation:
For STL files, which are predominantly used in 3D printing, the material preparation phase involves selecting suitable materials like PLA, ABS, or resin, depending on the 3D printing technology employed (FDM, SLA, etc.). The STL file must be optimized to reduce print time and material waste, ensuring the model is ready for the printer.
In contrast, STP files are utilized in more complex manufacturing processes such as CNC machining or injection molding. Here, the material preparation involves sourcing raw materials like metals, plastics, or composites, which must meet specific industry standards. For instance, when using STP files for injection molding, the material must be pre-processed, often requiring granulation or drying, to ensure optimal flow and mold filling.
Forming Techniques:
STL files typically lead to additive manufacturing processes, where layers of material are deposited to create the final product. Techniques such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) or stereolithography (SLA) are commonly used. These methods allow for intricate designs but may face limitations in terms of material strength and finish quality.
For STP files, forming techniques include subtractive manufacturing processes like CNC machining and injection molding. CNC machining allows for high precision and can produce parts with complex geometries. Injection molding, on the other hand, is ideal for high-volume production, offering excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
What Are the Key Assembly and Finishing Stages in Manufacturing STL and STP Files?
Assembly:
While STL files may not require assembly in many cases, they can be part of larger assemblies in 3D-printed products. In such cases, components printed separately must be accurately aligned and connected, often using adhesives or mechanical fasteners.
For STP files, assembly is a critical phase, especially in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where multiple components are integrated into a final product. This may involve welding, bolting, or using specialized adhesives. The assembly process must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure functionality and safety.
Finishing Techniques:
Finishing techniques for STL files often involve post-processing methods such as sanding, painting, or coating to enhance surface finish and aesthetics. These techniques can improve the mechanical properties of the printed part and prepare it for end-use.
Conversely, STP files lead to parts that often require less finishing due to the precision of CNC machining or injection molding. However, surface treatments such as anodizing, plating, or polishing may still be applied to meet specific performance criteria or aesthetic standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in STL and STP Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that products manufactured from STL and STP files meet required standards and specifications.
What International Standards and Industry-Specific Regulations Should B2B Buyers Consider?
For both STL and STP manufacturing, international standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental. This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for oil and gas sectors) are crucial for compliance and market acceptance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential in maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing lifecycle. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection phase evaluates the raw materials and components before production begins. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards is vital for avoiding defects later in the process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections help detect issues in real-time. For STL files, this may involve monitoring print parameters, while for STP files, it could include measuring tolerances and dimensions during machining.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, the final product undergoes thorough testing to verify that it meets all specifications. This includes dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC processes is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting production facilities, and assessing their adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s processes and outcomes. These reports should include data on defect rates, inspection results, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers or those looking to ensure compliance with international standards.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers must navigate various QC and certification nuances when sourcing products. For example, different countries may have varying regulatory requirements, affecting product certifications and testing protocols. Buyers should be aware of these differences and ensure that their suppliers comply with the necessary standards.
Furthermore, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication about quality expectations. Establishing clear guidelines and expectations upfront can mitigate misunderstandings and enhance collaboration between buyers and suppliers.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for STL and STP files is essential for B2B buyers seeking to ensure product quality and compliance. By being aware of the specific manufacturing techniques, QC checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers globally.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stl vs stp’
When sourcing CAD files for manufacturing, particularly for STL and STP formats, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international B2B buyers make informed decisions about which file type to procure based on their specific manufacturing needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clarify your project’s technical requirements. Identify whether your project involves 3D printing, CNC machining, or injection molding, as each application necessitates different file formats. For example, STL files are optimal for rapid prototyping, while STP files are better suited for complex manufacturing processes that require detailed product data.
Step 2: Research File Format Capabilities
Understanding the capabilities of STL and STP formats is crucial. STL files represent 3D objects using a mesh of triangles, making them ideal for simple geometries and 3D printing. In contrast, STP files offer a comprehensive representation that includes assembly structures and manufacturing information, which is vital for detailed design and production. Assess which format aligns with your project’s complexity and manufacturing requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers who can provide the necessary CAD files. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients in your industry. Pay attention to their experience with the specific file formats you require, as well as their ability to support your project’s technical needs.
- Tip: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region, as they may better understand local manufacturing standards and practices.
Step 4: Request Samples of CAD Files
Ask suppliers for sample CAD files in both STL and STP formats. This will allow you to assess the quality and accuracy of their work. Evaluate how well the files adhere to your technical specifications and whether they meet the necessary criteria for your intended manufacturing processes.
- Tip: Check for compatibility with your existing CAD software to avoid integration issues later on.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the suppliers you consider comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This is particularly important for sectors like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where precision and safety are paramount. Verify certifications such as ISO or similar quality management systems that reflect their adherence to best practices.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your suppliers throughout the procurement process. Clear communication is essential for addressing any questions or concerns about the CAD files, revisions, and timelines. Establishing a collaborative relationship can lead to better outcomes and fewer misunderstandings.
- Tip: Consider using project management tools that facilitate real-time updates and feedback.
Step 7: Plan for Iterative Feedback and Revisions
Anticipate the need for revisions and feedback on the CAD files. It is common for initial designs to require adjustments based on manufacturing capabilities or changes in project specifications. Ensure that your supplier is willing to accommodate revisions and that you have a clear process in place for providing feedback.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for STL and STP files, ensuring that they select the appropriate format for their manufacturing needs while fostering productive relationships with their suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stl vs stp Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for STL vs STP Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure for STL and STP sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of file type influences material selection. STL files are commonly used for 3D printing, which can utilize various plastics, resins, and metals, depending on the application. In contrast, STP files support more complex manufacturing processes like CNC machining and injection molding, often requiring higher-grade materials that can withstand rigorous processes.
-
Labor: The complexity of the design impacts labor costs. STL files may require less skilled labor for simple 3D printing tasks, while STP files necessitate skilled technicians for detailed machining and assembly processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs include machinery maintenance and operational expenses. STL file production typically has lower overhead due to faster setup times. In contrast, STP file production, which involves more extensive machinery and longer setup periods, incurs higher overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs vary significantly between the two file types. STL files often require minimal tooling, while STP files necessitate specialized tools for precision machining, leading to increased initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): QC processes must align with the chosen file format. STL files may have a straightforward QC process, while STP files require stringent checks to ensure the integrity of complex geometries, potentially increasing costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can also differ. STL files, often smaller and lighter, may incur lower logistics costs compared to heavier and bulkier STP files, which may require specialized handling.
-
Margin: Profit margins can vary based on the complexity and scale of the project. Manufacturers may charge higher margins for STP files due to the advanced capabilities and quality assurance measures involved.
How Do Price Influencers Affect STL vs STP Sourcing?
Several factors influence pricing for STL and STP sourcing. Understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes typically reduce unit costs. Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk orders, particularly for STL files, which are less complex.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom designs can significantly affect costs. STL files are easier to modify, whereas STP files may require more extensive re-engineering, impacting pricing.
-
Materials: Material choice plays a crucial role in pricing. High-performance materials for STP files can dramatically increase costs compared to standard materials used for STL files.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications like ISO can elevate costs. STP files, which demand higher precision, often necessitate certified manufacturing processes, influencing overall pricing.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and capabilities can impact prices. Suppliers in regions with higher labor costs may charge more for STP file production.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating STL vs STP Prices?
Navigating the complexities of STL vs STP sourcing requires strategic negotiation and a keen understanding of total cost factors.
-
Negotiate Early: Start discussions early to explore potential discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts. This can lead to more favorable pricing terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. Consider long-term implications, including maintenance and operational costs, particularly with STP files that may involve more complex manufacturing processes.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional price differences and currency fluctuations. Understanding local market conditions in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Request Transparency: Ask for detailed breakdowns of costs to identify potential areas for negotiation. Understanding how each cost component contributes to the total price can help in negotiating better terms.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and shifts in material costs can provide insights into potential pricing changes and opportunities for cost savings.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for STL and STP sourcing can vary widely based on numerous factors. Buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough market research to ensure competitive pricing and quality.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stl vs stp With Other Solutions
When evaluating CAD file formats for manufacturing, it’s essential to consider alternatives to STL and STP that can fulfill similar roles. Each format offers unique advantages and limitations, making the choice dependent on specific project requirements, manufacturing processes, and desired outcomes.
| Comparison Aspect | Stl Vs Stp | Alternative 1: OBJ | Alternative 2: IGS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High for 3D printing; limited in detail | Good for 3D printing with color and texture | Excellent for complex geometries and detailed data exchange |
| Cost | Generally low | Moderate, due to additional data | Higher due to file size and complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple and widely supported | More complex due to separate files for texture | Requires more knowledge to handle and edit |
| Maintenance | Minimal, easy to regenerate | Moderate, requires managing multiple files | Higher, due to larger file sizes and complexity |
| Best Use Case | Rapid prototyping and 3D printing | 3D modeling requiring color and texture | Detailed CAD modeling and manufacturing processes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using OBJ as an Alternative?
OBJ files are an excellent alternative for projects that require not only geometry but also the representation of color and texture. This format is particularly beneficial in industries like gaming and visualization where aesthetics are crucial. However, the added complexity of managing separate files for texture and color can be a downside. This makes OBJ less ideal for straightforward manufacturing processes where simplicity and speed are paramount.
How Does IGS Compare to STL and STP in Practical Applications?
IGS (IGES) files serve as another robust alternative, especially in environments where detailed product data exchange is necessary. This format excels in handling complex geometries and is widely used in CAD applications for detailed modeling and manufacturing. The downside is that IGS files tend to be larger and require more processing power, which can complicate workflows. Consequently, while IGS is powerful, it may be overkill for simpler projects that don’t require extensive detail.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right CAD File Format?
Selecting the appropriate file format—be it STL, STP, OBJ, or IGS—depends on the specific needs of the project. For rapid prototyping and 3D printing, STL is often the most efficient choice, while STP is preferable for complex manufacturing requiring detailed product data. If color and texture are essential, OBJ may be the best fit, whereas IGS is ideal for intricate designs needing comprehensive data exchange. Ultimately, B2B buyers should assess their project requirements, the manufacturing processes involved, and the level of detail needed to make an informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stl vs stp
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of STL and STP File Formats?
Understanding the technical properties of STL and STP file formats is essential for B2B buyers, especially those involved in manufacturing and product design. Here are some critical specifications that should be considered:
-
File Structure
– STL: Utilizes a triangular mesh structure to represent 3D objects. This format focuses solely on the surface geometry, making it suitable for 3D printing but limiting in terms of detailed design features.
– STP: Employs a more complex structure that encapsulates not only the geometry but also product and manufacturing information (PMI), allowing for a comprehensive representation of the design. This makes STP files ideal for applications requiring intricate details. -
Interoperability
– STL: Widely recognized across 3D printing platforms, but it lacks compatibility with various CAD software for detailed design exchanges. This can lead to potential issues when trying to integrate designs into different systems.
– STP: Designed for seamless data exchange between various CAD applications, ensuring that different systems can interpret the file accurately. This property is crucial for manufacturers who collaborate with multiple partners. -
File Size and Complexity
– STL: Generally smaller in size due to its simpler structure, making it easier to share and manage, particularly for rapid prototyping.
– STP: Typically results in larger files due to the additional information they contain. While this can make them more cumbersome to transfer, the benefits in accuracy and detail often outweigh the drawbacks, especially for complex projects. -
Detail and Accuracy
– STL: Best suited for projects that require less detail and are primarily focused on the external shape of the object, such as 3D printing prototypes.
– STP: Offers higher precision and detail, making it ideal for CNC machining and injection molding processes where tolerances are critical.
Which Industry Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand Related to STL and STP?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and streamline processes in the B2B landscape. Here are some essential terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential suppliers and ensure that they’re working with reputable partners. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage budgets and inventory effectively, particularly when dealing with specialized components like STL and STP files. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A document used to invite suppliers to submit price proposals for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and facilitate competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, particularly for international shipping, as it clarifies who bears the risk and costs at various stages of the shipping process. -
CNC Machining
Refers to computer numerical control machining, a method that uses computers to control machine tools. Understanding this term is important for buyers dealing with STP files, as they often pertain to products that will be CNC machined. -
Injection Molding
A manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting material into a mold. This term is relevant for B2B buyers considering STP files, as they are frequently used in the injection molding process for detailed and high-quality parts.
Understanding these technical properties and industry terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding STL and STP file formats, ultimately leading to more efficient manufacturing processes and successful partnerships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stl vs stp Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing STL vs STP File Types?
The global landscape for STL and STP file types is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increased demand for efficiency in manufacturing processes. As industries pivot towards digital transformation, international B2B buyers—especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—are increasingly seeking compatibility and interoperability among various CAD systems. This trend is underscored by the growing reliance on cloud-based solutions that facilitate seamless collaboration across borders, making the STP format particularly appealing due to its comprehensive data exchange capabilities.
Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are also influencing sourcing strategies. These technologies enable more sophisticated simulations and optimizations, allowing manufacturers to leverage STL files for rapid prototyping while ensuring that STP files provide the detailed product data necessary for complex manufacturing processes like CNC machining and injection molding. Furthermore, the rise of additive manufacturing and 3D printing is propelling the demand for STL files, particularly among startups and innovators looking to bring prototypes to market quickly.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in STL vs STP File Types?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B sourcing strategies, compelling companies to evaluate the environmental impact of their manufacturing processes. The choice between STL and STP file formats can also reflect a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. For instance, STL files are often associated with 3D printing, which can reduce material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. On the other hand, STP files facilitate the efficient transfer of complex geometries that can lead to more optimized designs, ultimately minimizing resource consumption.
Moreover, businesses are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or adherence to green manufacturing practices. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who are conscious of their supply chain’s environmental footprint. Companies that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, as indicated through their choice of CAD file formats, can enhance their market appeal and foster stronger partnerships with like-minded organizations.
What Is the Historical Context Behind STL and STP File Formats?
The evolution of STL and STP file formats is rooted in the need for efficient communication in the manufacturing sector. Introduced in the 1980s, the STL format was primarily designed for stereolithography and rapid prototyping, allowing designers to create and test physical models quickly. Its simplicity and focus on surface geometry made it a go-to choice for 3D printing applications.
Conversely, the STP format emerged in the 1990s as part of efforts to standardize data exchange among various CAD systems. This development was crucial for industries requiring detailed product data, such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and complex geometries are paramount. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the strengths of each file type and make informed sourcing decisions aligned with their specific manufacturing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stl vs stp
-
How do I choose between STL and STP files for my project?
Choosing between STL and STP files largely depends on the manufacturing process you plan to use. STL files are ideal for 3D printing and rapid prototyping, as they efficiently represent the surface geometry of a model. In contrast, STP files are better suited for CNC machining and injection molding, as they encapsulate detailed product information, including assembly structure and manufacturing data. Understanding your project’s requirements and collaborating with your manufacturer can help streamline this decision. -
What is the best file format for 3D printing and why?
The best file format for 3D printing is typically the STL format. It is widely supported by 3D printers and slicing software, making it easy to convert into physical objects. STL files use a triangular mesh to represent a model’s surface, which is sufficient for most 3D printing applications. However, for projects requiring complex geometries or additional product information, consider using STP files, which provide a more comprehensive data set. -
How can I ensure the quality of my CAD files before sending them to manufacturers?
To ensure the quality of your CAD files, perform thorough checks for accuracy in dimensions, surface integrity, and file format compatibility. Utilize CAD software tools to validate the model and perform simulations if possible. Additionally, consider sharing preliminary versions with your manufacturer for feedback, allowing them to identify potential issues early in the process. Collaborating closely during this stage can significantly enhance the quality of the final product. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for STL and STP file manufacturing?
When vetting suppliers, consider their expertise in handling STL and STP files, as well as their experience with your specific manufacturing process. Check for certifications, previous client testimonials, and their ability to meet your project’s quality standards. Additionally, assess their communication practices and responsiveness to ensure that they can provide support throughout the design and production phases, especially if you’re sourcing from international markets. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) I should expect for STL and STP file projects?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and project scope. For 3D printing using STL files, some suppliers may accept low MOQs, especially for prototypes. However, for STP files used in CNC machining or injection molding, MOQs tend to be higher due to setup costs and production runs. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find a balance between production efficiency and your budget. -
What payment terms are typical for international B2B transactions in STL and STP file manufacturing?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely, but common practices include upfront deposits (often 30-50% of the total cost) followed by the balance upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., Net 30 or Net 60), allowing you to pay after receiving the goods. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How does logistics impact the sourcing of STL and STP file services across different regions?
Logistics can significantly impact the efficiency and cost of sourcing STL and STP file services, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and local infrastructure can affect delivery schedules and overall project timelines. To mitigate risks, consider suppliers with established logistics capabilities and transparent shipping policies. Additionally, factor in potential delays when planning your project timeline. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from suppliers of STL and STP files?
Quality assurance measures can vary by supplier but should generally include inspections at multiple stages of production. Look for suppliers who implement standardized QA processes, including dimensional checks, material testing, and post-production reviews. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide certifications or quality documentation, which can be crucial for compliance with international standards, especially if your products will be used in regulated industries.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Stl Vs Stp Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bambu Lab – STEP vs STL File Formats
Domain: forum.bambulab.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The discussion compares STEP and STL file formats in terms of print quality for 3D printing. STEP files are noted for higher resolution and precision, as they use mathematical equations to describe shapes, while STL files are mesh-based and approximate curves with triangles. Users report that printing with STEP files results in smoother surfaces, especially for curved paths. STEP files are preferr…
2. Alibre – 3D Modeling & Printing Solutions
Domain: alibre.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: STL and STP file formats are used for 3D modeling and printing. STL files are larger (e.g., 3MB for a small part) and represent a point cloud of triangles, making them suitable for 3D printing. They can be generated by structured light scanning and are used for contour/dimensional inspection. STEP files are smaller (e.g., 100k for the same part) and provide a standard method for exchanging 3D and …
3. Bravo Fabs – 3D Printing & Prototyping Formats
Domain: bravofabs.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: STL Format: Used for 3D printing and rapid prototyping; represents surface geometry without color or texture; describes raw triangulated surfaces with a mesh of vertices and facets. STP Format: Based on the STEP standard; contains detailed geometric and parametric data; includes topology, relationships, tolerances, and materials; allows full editing and manipulation in CAD systems; supports NURBS …
4. 3Faktur – STL and STP 3D Printing Formats
Domain: 3faktur.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: STL and STP are two popular 3D printing data formats. STL (.STL) is the most commonly used format for 3D printing, representing 3D shapes using a mesh of triangles. It is easy to recognize syntax errors but does not convey textures, making it suitable only for monochromatic models. STP (.STP) is a more complex format used for exchanging product data, containing comprehensive information about tole…
5. Jaycon – 3D File Export Formats
Domain: jaycon.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: 3D File Export Formats: STL, OBJ, IGES, STEP. STL: Dominant in 3D printing, stores objects as triangular faces, suitable for 3D printers. OBJ: Developed for animations, supports polygonal faces, better representation of geometry, includes color and texture data. IGES: Encodes curves and surfaces, maintains high accuracy, stores units in file header. STEP: Developed for Model-Based Definition, enco…
6. GrabCAD – STL and STP File Formats in 3D Modeling
Domain: grabcad.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the use of STL and STP file formats in 3D modeling and rapid prototyping. STL files are commonly used for 3D printing, while STP (or STEP) files are used for sharing designs between different CAD software. Users express challenges in converting STL files to STP due to the complexity of the process, particularly when using software like PTC Creo Direct Elements, which…
7. All3D Labs – Understanding 3D File Formats
Domain: all3dlabs.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: The article discusses the differences between three common 3D file formats: STEP, STL, and 3MF.
1. **STEP File**:
– Stands for Standard for the Exchange of Product Data (.stp).
– Contains mathematical data for curves and finer details, allowing for accurate design.
– Requires conversion to a triangulated format for 3D printing.
– Example file size: 49kb.
2. **STL File**:
– S…
8. Simplify3D – Premium 3D Printing Software
Domain: forum.simplify3d.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Simplify3D is a premium 3D printing software preferred by innovators, engineers, and professional users worldwide. Users are requesting the ability to import .stp or .STEP files directly into the slicer for better accuracy and results compared to .stl files. However, there are concerns about the complexity of parsing CAD files and the potential issues with bad meshes. Other slicers like GrabCAD Pr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stl vs stp
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, understanding the nuances between STL and STP file formats is essential for international B2B buyers. STL files are predominantly suited for 3D printing and rapid prototyping, offering simplicity and compatibility. In contrast, STP files excel in conveying detailed product data, making them ideal for complex manufacturing processes such as CNC machining and injection molding. By selecting the appropriate file type, businesses can ensure a smoother transition from design to production, enhancing product quality and reducing costs.
Strategic sourcing is not just about choosing the right materials or suppliers; it also involves making informed decisions about the tools and technologies used in production. By leveraging the strengths of both STL and STP formats, companies can optimize their manufacturing workflows, resulting in higher efficiency and better end products.
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of technological advancements will be vital. Embrace the future of manufacturing by investing in the right CAD file formats today, and position your business for success in an increasingly interconnected world. Reach out to industry experts to refine your sourcing strategies and elevate your manufacturing capabilities.