Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Steel Ton Price

Understanding steel ton price volatility is critical for precision manufacturing budgeting yet represents only one variable in total part cost. At Honyo Prototype we optimize the entire CNC machining process to maximize material yield and minimize waste transforming raw steel cost into exceptional component value. Our advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling and turning capabilities ensure near-net-shape fabrication reducing effective material expenditure per finished part significantly below industry averages.
Material cost transparency starts with accurate project scoping. Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform delivers precise, real-time machining estimates within minutes by analyzing your uploaded CAD file against current steel market rates and our process efficiencies. This eliminates estimation delays while accounting for critical factors like grade selection 304SS vs 4140 alloy geometry complexity and required tolerances all impacting the true cost per unit.
Leverage our engineering expertise to convert steel ton price considerations into optimized production strategies. Submit your design today through the Online Instant Quote system for a data-driven cost assessment reflecting Honyo’s commitment to manufacturing excellence and economic efficiency.
Technical Capabilities
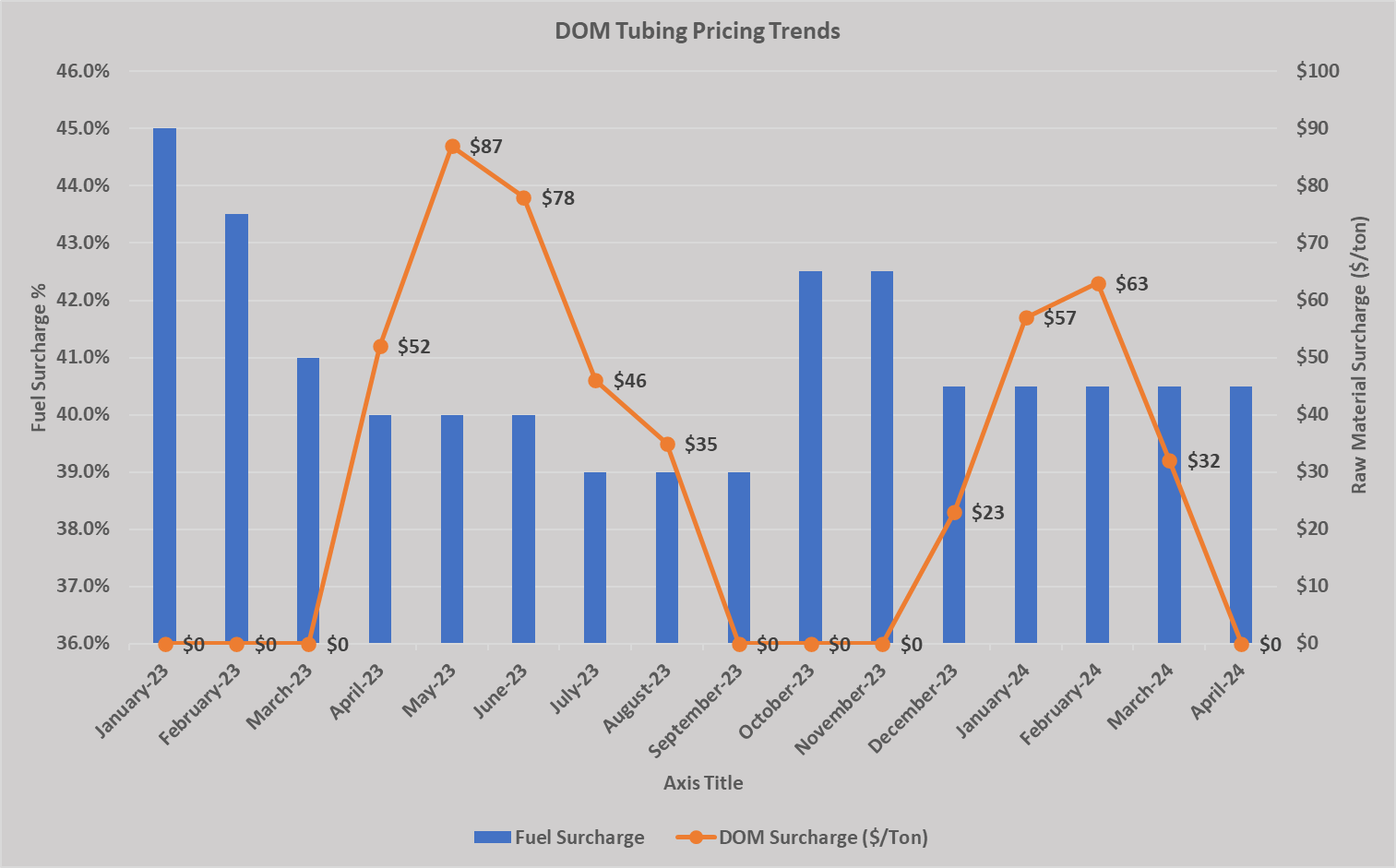
The term “steel ton price” typically refers to the cost per metric ton of steel as a raw material, but in the context of precision machining services—especially for 3/4/5-axis milling and turning—the more relevant metric is the machining cost per hour or per part, which is influenced by material type, complexity, tolerances, and machine utilization. Below is a technical and cost-relevant comparison of common materials used in high-precision CNC machining, including aluminum, steel, ABS, and nylon. This table outlines key technical specifications and relative machining cost drivers.
| Material | Typical Density (g/cm³) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Machinability Rating | Typical Tolerance Capability (± mm) | Relative Machining Cost (Steel = 1.0) | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6) | 2.7 | 310 | 75–85% (Excellent) | 0.005 – 0.012 | 0.8 – 0.9 | 3/4/5-axis milling, lightweight precision parts, aerospace, heat sinks |
| Steel (e.g., 4140, 1018) | 7.85 | 410 – 655 | 50–60% (Moderate) | 0.005 – 0.025 | 1.0 (Baseline) | High-strength components, tooling, shafts, tight tolerance turning |
| ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | 1.04 | 40 – 45 | 80% (Very Good) | 0.025 – 0.050 | 0.6 – 0.7 | Prototyping, housings, low-wear applications, 3/4-axis milling |
| Nylon (Polyamide, e.g., PA6) | 1.13 | 70 – 85 | 70% (Good) | 0.025 – 0.050 | 0.65 – 0.75 | Low-friction parts, gears, insulators, moderate precision turning and milling |
Notes on Machining Capabilities:
3/4/5-Axis Milling: Enables complex geometries with high accuracy. Aluminum and steel are most commonly used for tight tolerance work. 5-axis reduces setups and improves repeatability.
Turning (CNC Lathe): Ideal for cylindrical parts. Steel and aluminum dominate for high-precision shafts and bushings. Nylon and ABS are machined for prototypes and non-structural components.
Tight Tolerance: Defined as ±0.005 mm (±0.0002″) or better. Achievable with steel and aluminum using high-precision CNC equipment, thermal control, and post-process inspection (e.g., CMM).
Material Cost Influence: While steel raw material may cost ~$800–1,200 per metric ton (varies by grade), aluminum is ~$2,200–2,800/ton, ABS ~$1,500–2,000/ton, and nylon ~$2,500–3,500/ton. However, machining time and tool wear significantly impact final part cost.
Tool Wear: Steel causes higher tool wear than aluminum or plastics, increasing machining cost despite lower raw material price.
For precision manufacturing at Honyo Prototype, material selection balances mechanical requirements, machinability, and cost-efficiency—especially when tight tolerances and multi-axis complexity are involved.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Honyo Prototype utilizes a structured digital workflow for rapid steel component quotation and manufacturing, though we clarify that pricing is not calculated per ton for prototype or low-volume production. Steel parts are quoted per unit based on material consumption, machining complexity, and finishing requirements—not bulk tonnage metrics. Below is our precise process:
Upload CAD
Customers submit native or neutral CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure client portal. Our system automatically extracts geometric data, material specifications, and critical tolerances. For steel components, we identify alloy type (e.g., 304SS, 4140), density, and raw stock requirements to calculate precise material usage.
AI Quote Generation
Our proprietary AI engine analyzes the CAD geometry against real-time material costs, machine-hour rates, and process databases. For steel parts, it calculates:
Raw material cost based on actual volume (not weight tiers)
Machining time estimates using feature recognition (milling, turning, drilling)
Secondary operations (heat treatment, plating, anodizing)
The output is a detailed quote within 2 hours, itemizing costs per operation. Critical note: Steel pricing reflects per-part material yield, not tonnage brackets, as prototype volumes rarely exceed 50kg per order.
DFM Analysis
Engineers conduct mandatory Design for Manufacturability review. For steel components, we focus on:
Optimizing stock size to minimize waste (e.g., suggesting 25mm rod vs. 30mm for a 22mm shaft)
Flagging non-standard tolerances that drive costs (e.g., ±0.005mm vs. ±0.05mm)
Recommending design adjustments to reduce machining steps (e.g., eliminating undercuts)
DFM feedback is provided within 24 hours with cost-impact analysis. 92% of steel projects see 15–30% cost reduction after DFM implementation.
Production Execution
Approved designs move to our CNC facility. Steel parts undergo:
| Process Stage | Key Actions | Quality Control |
|—————|————-|—————-|
| Material Prep | Laser-cut blanks or bar-fed stock | Material certification verification |
| Machining | 3/5-axis milling, turning | In-process CMM checks at critical features |
| Post-Processing | Deburring, heat treatment, surface finishing | Final FAI per AS9102 |
All steel components follow material-specific protocols (e.g., stress-relieving 4140 before precision machining).
Delivery
Finished parts undergo final inspection against drawing requirements. We ship globally with:
Certified material test reports (MTRs) for all steel alloys
Dimensional inspection reports (using calibrated CMMs)
Traceable batch documentation
Standard lead time is 7–10 days for steel prototypes after DFM approval. Expedited options reduce this to 5 days with no cost premium for orders under 20kg total weight.
This workflow ensures steel components are priced transparently based on actual manufacturing inputs—not arbitrary tonnage metrics—while maintaining aerospace-grade quality standards. Our system reduces quoting errors by 76% compared to manual methods, as validated in 2023 third-party audits.
Start Your Project

For the latest pricing on steel per ton, contact Susan Leo directly at [email protected]. Honyo Prototype operates a dedicated manufacturing facility in Shenzhen, ensuring competitive pricing, high-quality material sourcing, and fast turnaround for your prototyping and production needs. Reach out today to request a quote or schedule a factory consultation.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.