Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steel price per kg
In the ever-evolving landscape of global commerce, one of the most pressing challenges faced by international B2B buyers is effectively navigating the complexities of steel price per kg. The volatility of steel prices, influenced by factors such as raw material costs, geopolitical dynamics, and demand fluctuations, can significantly impact procurement strategies. This guide aims to equip buyers from diverse regions—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, specifically Saudi Arabia and Germany—with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into various types of steel, their applications across different industries, and the critical importance of supplier vetting. By understanding the nuances of pricing structures and market trends, businesses can better anticipate fluctuations and secure competitive rates. Additionally, we will explore cost factors beyond just the price per kg, including logistics, quality certifications, and market forecasts.
Empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide serves as a vital tool in optimizing procurement processes. By leveraging the strategies outlined here, businesses can not only reduce costs but also enhance their operational efficiencies and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets. Navigate the steel marketplace with confidence and clarity, ensuring that your purchasing decisions align with both current market realities and future trends.
Understanding steel price per kg Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Rolled Steel | Produced at high temperatures; has a rough surface finish | Construction, automotive, machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Less precise dimensions, lower strength compared to cold rolled. |
| Cold Rolled Steel | Manufactured at room temperature; smooth finish | Appliances, furniture, automotive | Pros: Higher strength, better surface finish; Cons: Higher cost, less ductility. |
| Galvanized Steel | Coated with zinc for corrosion resistance | Construction, HVAC, automotive | Pros: Corrosion-resistant, extended lifespan; Cons: Higher price, potential for coating damage. |
| Stainless Steel | Alloyed with chromium for enhanced corrosion resistance | Food processing, medical devices | Pros: High durability, aesthetic appeal; Cons: Expensive, requires specialized fabrication. |
| Rebar (Reinforcing Bar) | Steel bars used for reinforcing concrete | Construction, civil engineering | Pros: Increases concrete strength, widely available; Cons: Weight can increase shipping costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hot Rolled Steel?
Hot rolled steel is produced by rolling steel at high temperatures, typically above 1,700°F. This process allows for easier shaping and forming, making it an ideal choice for large structural components such as beams and plates used in construction and manufacturing. While it is cost-effective and versatile, buyers should consider its rough surface finish and less precise dimensions, which may not meet stringent specifications.
How Does Cold Rolled Steel Differ from Hot Rolled Steel?
Cold rolled steel is processed at room temperature, resulting in a smoother surface and tighter tolerances. This type of steel is often used in applications requiring higher strength and a better finish, such as appliances and furniture. While it offers superior mechanical properties, the cost is typically higher than hot rolled steel, and it may be less ductile, making it less suitable for applications requiring extensive forming.
What Advantages Does Galvanized Steel Offer for B2B Buyers?
Galvanized steel is coated with zinc to protect against corrosion, making it particularly valuable in outdoor and harsh environments. Common applications include construction, HVAC systems, and automotive parts. While its corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of products, buyers should be aware of the potential for damage to the zinc coating during handling and installation, as well as the higher initial cost compared to non-galvanized options.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Specialized Applications?
Stainless steel is an alloy that contains chromium, which provides exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. It is widely used in food processing, medical devices, and architectural applications due to its aesthetic appeal and ability to withstand harsh environments. However, its higher cost and the need for specialized fabrication techniques can be a consideration for buyers, particularly in budget-sensitive projects.
How Is Rebar Essential in Construction Projects?
Rebar, or reinforcing bar, is a crucial component in construction, used to enhance the tensile strength of concrete. It is widely available and comes in various sizes and grades, making it suitable for a range of civil engineering applications. While rebar is cost-effective, its weight can lead to increased shipping costs, which buyers must factor into their project budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of steel price per kg
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steel price per kg | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Procurement of rebar for structural integrity | Ensures safety and durability of structures | Quality certifications, regional availability, and price volatility |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of steel components for vehicles | Enhances vehicle performance and safety | Compliance with international standards, sourcing timelines, and bulk pricing |
| Energy | Steel for pipelines and infrastructure in oil & gas | Facilitates efficient energy transport | Material grades, resistance to corrosion, and local supply chain reliability |
| Manufacturing | Use of steel in machinery and equipment production | Improves operational efficiency and product lifespan | Precision in specifications, lead times, and cost predictability |
| Shipbuilding | Steel hulls and structural components for ships | Increases vessel durability and performance | Weight specifications, compliance with maritime regulations, and sourcing logistics |
How Is Steel Price Per Kg Utilized in the Construction Sector?
In the construction industry, the price of steel per kg is critical for budgeting and project planning, particularly for rebar used in reinforced concrete. Buyers must navigate fluctuating prices influenced by raw material costs and market demand. The procurement of high-quality steel ensures the structural integrity and longevity of buildings, which is paramount for safety. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should consider local sourcing options to mitigate transportation costs and delays.
What Role Does Steel Price Per Kg Play in the Automotive Industry?
In automotive manufacturing, steel components are essential for vehicle frames, engines, and safety features. The steel price per kg directly impacts production costs and, consequently, the pricing of finished vehicles. Buyers must ensure compliance with international safety standards while sourcing materials that provide optimal strength-to-weight ratios. For international B2B buyers in Europe and South America, understanding regional pricing trends can help in negotiating better deals with suppliers.
Why Is Steel Price Per Kg Important for the Energy Sector?
The energy sector relies heavily on steel for pipelines and structural components in oil and gas operations. The price per kg of steel affects the overall project budget and can influence the choice of materials based on their resistance to corrosion and pressure. Buyers must consider the specific grades of steel required for various applications, ensuring that they meet industry standards. For businesses in Africa and the Middle East, establishing reliable local supply chains is crucial for maintaining project timelines and cost efficiency.
How Does Steel Price Per Kg Influence Manufacturing Operations?
Manufacturing industries use steel in machinery and equipment, where the price per kg affects production costs and profitability. High-quality steel can enhance the efficiency and longevity of machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Buyers must focus on precision specifications and reliable lead times when sourcing steel. For B2B buyers in Europe, understanding the nuances of steel pricing can lead to better investment decisions in manufacturing processes.
What Is the Significance of Steel Price Per Kg in Shipbuilding?
In the shipbuilding industry, steel is used for constructing hulls and structural components, where the price per kg is a major factor in project budgeting. The quality and weight of steel directly influence vessel performance and durability. Buyers must ensure compliance with maritime regulations and consider sourcing logistics to minimize costs. For international buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, navigating local regulations and establishing strong supplier relationships can lead to significant cost savings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steel price per kg’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Price Volatility in Global Markets
The Problem:
B2B buyers often grapple with the unpredictable nature of steel prices per kg, particularly in a global market where geopolitical factors, trade policies, and raw material costs can fluctuate dramatically. For instance, a buyer in Saudi Arabia might lock in a price today, only to find that tariffs or supply chain disruptions have caused prices to soar by the time they need to fulfill their orders. This volatility can severely impact budgeting and project timelines, leading to financial strain and operational delays.
The Solution:
To mitigate the impact of price volatility, B2B buyers should establish a robust procurement strategy that includes real-time market monitoring and flexible purchasing agreements. Utilizing subscription services that provide up-to-date steel price indices can help buyers stay informed about market trends. Additionally, consider negotiating fixed-price contracts with suppliers for specific periods or quantities, allowing for price stability even amid market fluctuations. Diversifying suppliers and sourcing steel from multiple regions can also help secure more favorable pricing and reduce dependency on any single source.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Factors Influencing Steel Prices
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers lack a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence the price of steel per kg, which can lead to poor purchasing decisions. For example, a buyer in Germany may not realize how seasonal demand or raw material shortages can affect pricing, resulting in higher costs than anticipated. This lack of insight can hinder effective budgeting and project planning, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
The Solution:
Buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the various factors that drive steel prices, including raw material costs, demand cycles, and geopolitical events. Participating in industry webinars, subscribing to relevant publications, and networking with industry peers can provide valuable insights. Moreover, leveraging analytical tools to track historical price trends and market dynamics will allow buyers to make informed predictions about future price movements. This knowledge will enable them to time their purchases strategically and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Scenario 3: The Challenge of Sourcing Quality Steel at Competitive Prices
The Problem:
In the quest to find the best steel price per kg, buyers often face the challenge of balancing cost with quality. A buyer in South America may come across a seemingly attractive low price but discovers that the steel does not meet the necessary specifications or quality standards, leading to costly reworks or project failures. This scenario underscores the risk of prioritizing price over quality, which can have long-term repercussions.
The Solution:
To address this challenge, B2B buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process that prioritizes quality alongside pricing. Establishing clear specifications and standards for the steel required can guide sourcing decisions. Buyers should request certifications and conduct audits of potential suppliers to ensure compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider building long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a track record of providing both competitive prices and high-quality materials. This approach not only ensures the integrity of the materials used but also fosters trust and reliability in the supply chain.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steel price per kg
What are the Key Properties of Common Steel Materials?
When selecting steel for various applications, understanding the properties of different materials is crucial. Here, we analyze four common types of steel: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, and Tool Steel. Each has unique characteristics that influence its performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
Carbon Steel: What Makes It a Popular Choice?
Carbon steel is primarily composed of iron and carbon, making it one of the most widely used steel types. Its key properties include high tensile strength and good wear resistance, which make it suitable for structural applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance, which can be a drawback in humid or corrosive environments.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective option for many applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio also enhances durability.
Cons: The lack of corrosion resistance necessitates protective coatings or treatments, increasing long-term maintenance costs. Additionally, it can be brittle at higher carbon contents, affecting its performance under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for construction and manufacturing, particularly in environments where exposure to moisture is controlled. However, B2B buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider additional protective measures.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Terms of Performance?
Stainless steel contains chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance. This property makes it suitable for applications in harsh environments, including marine and chemical processing industries. Additionally, stainless steel maintains its strength at elevated temperatures.
Pros: The durability and aesthetic appeal of stainless steel make it a preferred choice for architectural applications. Its resistance to rust and staining reduces maintenance costs over time.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel compared to carbon steel can be a barrier for budget-conscious projects. Furthermore, its manufacturing process is more complex, which can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is essential for applications requiring hygiene, such as food processing and medical equipment. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, often prefer stainless steel due to stringent quality standards.
What Advantages Does Alloy Steel Offer?
Alloy steel is made by adding elements such as nickel, chromium, or molybdenum to carbon steel to enhance its properties. This type of steel is known for its strength and toughness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Alloy steel exhibits superior mechanical properties, including improved hardness and wear resistance. Its versatility allows for use in various industries, from automotive to construction.
Cons: The cost of alloy steel can be higher due to the additional alloying elements. Moreover, its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is often used in high-stress applications, such as gears and shafts. B2B buyers should consider the specific alloy composition to ensure compatibility with their intended application, especially in regions like the Middle East where heavy machinery is prevalent.
Why is Tool Steel Essential for Precision Applications?
Tool steel is designed for making tools and dies, characterized by high hardness and wear resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and maintain its shape under stress, making it ideal for cutting, shaping, and forming materials.
Pros: Tool steel’s hardness and durability make it suitable for precision applications, ensuring long tool life and reduced downtime.
Cons: Tool steel is generally more expensive and can be more challenging to machine compared to other steel types. Its brittleness can also lead to cracking if not handled properly.
Impact on Application: Tool steel is essential in manufacturing industries where precision and durability are paramount. Buyers from Europe and South America should ensure compliance with international standards to maintain quality.
Summary Table of Steel Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for steel price per kg | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural applications in construction | Cost-effective and durable | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy-duty machinery and automotive | Superior strength and toughness | Higher cost and complex production | Medium |
| Tool Steel | Precision tools and dies | High hardness and wear resistance | Expensive and challenging to machine | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common steel materials, their properties, and considerations for international B2B buyers. By understanding these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steel price per kg
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Steel?
The manufacturing of steel is a complex process that involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding their procurement strategies.
-
Material Preparation
The first step in steel manufacturing is the preparation of raw materials, primarily iron ore, coal, and limestone. The iron ore is typically processed in a blast furnace, where it is combined with coke (a form of carbon) to remove impurities and produce molten iron. Limestone is added to act as a flux, helping to bind with impurities to form slag, which is later removed. This stage is crucial as the quality of raw materials directly affects the quality of the finished steel. -
Forming
Once the molten iron is obtained, it undergoes various forming processes to create different steel products. Common techniques include:
– Casting: Molten steel is poured into molds to create semi-finished products like slabs, blooms, or billets.
– Rolling: These semi-finished products are then rolled into finished shapes, such as sheets, plates, or bars, using hot or cold rolling techniques. Hot rolling is typically performed above the recrystallization temperature, while cold rolling occurs at room temperature, resulting in improved surface finish and dimensional accuracy. -
Assembly
For specific applications, steel components may require assembly. This could involve welding, bolting, or riveting different steel parts together to create structures or machinery. The assembly process must be closely monitored to ensure that joint integrity meets the required standards. -
Finishing
The final stage involves various finishing processes, including:
– Surface Treatment: Techniques such as galvanizing, painting, or coating are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
– Heat Treatment: Processes like annealing or quenching may be employed to achieve desired mechanical properties, including hardness and ductility.
How is Quality Assurance Ensured in Steel Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in steel manufacturing, as it ensures that the final product meets the required specifications and standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA process is essential for mitigating risks associated with procurement.
-
What International Standards Apply to Steel Quality Assurance?
Key international standards relevant to steel manufacturing include:
– ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including steel manufacturing. It ensures that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
– CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet specific safety, health, and environmental protection standards to qualify for CE marking. This is particularly important for construction-grade steel.
– API Standards: For steel used in the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards to ensure the quality and safety of steel products. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to monitor quality:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs during manufacturing to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes rigorous testing and inspection before shipment to confirm it meets all specifications. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Steel Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of steel, including:
– Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to assess the mechanical properties of the steel.
– Chemical Analysis: Spectrometry and other methods are used to analyze the composition of steel, ensuring it meets required chemical specifications.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, and radiographic testing are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the material.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of steel suppliers is critical to ensuring product reliability.
-
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Buyers should look for suppliers who maintain ISO certifications and other relevant quality standards. Audits can help assess the effectiveness of a supplier’s quality management system and their adherence to international standards. -
Reviewing Quality Control Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that document the results of various tests conducted on the steel products. These reports should include information on mechanical properties, chemical composition, and any certifications obtained. B2B buyers should ensure that these reports are transparent and readily available. -
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can perform inspections at different stages of the manufacturing process, from raw material sourcing to final product testing, ensuring compliance with specified standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential for B2B buyers in different regions. Buyers should consider:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific standards and regulations that affect steel quality. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while Middle Eastern buyers might focus on API standards for oil and gas applications.
-
Customs and Import Regulations: Buyers must be aware of the customs and import regulations in their respective countries, which may require specific certifications or documentation for steel imports.
-
Cultural and Market Differences: Understanding local market dynamics and cultural expectations can also influence procurement strategies. Buyers should engage with local experts or consultants who can provide insights into the regional steel market.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing steel, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steel price per kg’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring steel at competitive prices per kilogram. Understanding market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and product specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist provides a structured approach to ensure you cover all necessary aspects of sourcing steel efficiently.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the specific types of steel you require, including grades, dimensions, and coatings. Knowing your technical specifications helps in identifying suitable suppliers and ensures that the material meets your project requirements. Consider factors such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and compliance with relevant industry standards.
Step 2: Research Current Steel Prices
Stay updated on the latest market prices for steel per kilogram through reliable sources like industry reports and market analysis platforms. This knowledge will allow you to set a realistic budget and negotiate effectively with suppliers. Look for historical data trends to anticipate potential price fluctuations and make informed timing decisions regarding your purchases.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications and quality standards. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients within your industry. Evaluate their production capacity, delivery timelines, and customer service responsiveness to gauge their reliability and suitability for your needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Check for relevant certifications that confirm the quality and safety of the steel products offered by your suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and any industry-specific standards applicable to your project. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with material quality and compliance.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Reports
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the steel and any accompanying test reports. Evaluating physical samples allows you to assess the material’s quality firsthand. Ensure that the test reports include information on mechanical properties, chemical composition, and compliance with international standards, providing you with confidence in your procurement decision.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery terms, and payment conditions. Be transparent about your budget constraints and explore options such as bulk discounts or long-term contracts to enhance cost-effectiveness. Ensure that all agreed terms are documented to avoid any future misunderstandings.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
After successfully completing your purchase, consider establishing a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. Regular communication can foster trust and lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive product offerings in the future. Cultivating these relationships can provide a competitive edge in the fluctuating steel market.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for steel, ensuring they achieve quality and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing strategies.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steel price per kg Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Steel Pricing Per Kg?
Understanding the cost structure of steel pricing per kg is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base cost of raw materials, primarily iron ore and scrap steel, significantly influences the price of finished steel. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can lead to variations in steel costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for workers involved in the production process. These costs can vary based on the location of the manufacturing facility and the skill level of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to plant operations, utilities, and maintenance. Overhead costs are often fixed, but they can impact pricing based on production volume.
-
Tooling: The cost of machinery and equipment used in the steel manufacturing process also contributes to overall pricing. Investments in advanced technology can enhance production efficiency but may raise initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that steel meets specific industry standards requires rigorous quality control processes. The costs associated with testing and certification can influence the final price.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering steel from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location are crucial. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and freight charges can significantly affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers and suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market conditions and the competitive landscape.
What Factors Influence Steel Prices for B2B Buyers?
Several factors impact steel pricing, making it crucial for international buyers to consider these aspects when sourcing steel:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower prices per kg due to economies of scale. Establishing Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) with suppliers can provide cost benefits.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized steel products or specific grades can command higher prices. Understanding the required specifications can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Steel that meets international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, SGS) may incur higher costs. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and timely delivery may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can influence total costs. Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining responsibility for freight charges, insurance, and customs duties.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Steel Prices?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost efficiency when negotiating steel prices:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding current market trends and historical pricing data can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge enables them to identify reasonable pricing ranges.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It allows buyers to compare quotes and terms, fostering competitive pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the overall cost implications of sourcing decisions, including transportation, storage, and potential wastage. A lower upfront price may not always result in the best overall value.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time. Suppliers may offer loyalty discounts or preferential treatment to repeat customers.
How Can International Buyers Navigate Pricing Nuances?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding pricing nuances is crucial:
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying negotiation styles. Adapting to local customs can facilitate smoother discussions and foster goodwill.
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact the final cost of steel. Buyers should consider hedging strategies or negotiating prices in stable currencies to mitigate risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Import duties, tariffs, and local regulations can affect the landed cost of steel. Buyers must be informed about these factors to make accurate financial projections.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Steel prices can be volatile and subject to rapid changes. Buyers should consult current market data and engage with suppliers for the most accurate and relevant pricing information.
By understanding these cost components, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing process and achieve better financial outcomes in their steel procurement.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steel price per kg With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternative Solutions to Steel
In the competitive landscape of construction and manufacturing, the choice of materials can significantly influence project outcomes. While steel has long been a staple due to its strength and versatility, alternative solutions are emerging that may offer distinct advantages in specific applications. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and budget constraints.
Comparison of Steel Price Per Kg with Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Steel Price Per Kg | Alternative 1: Aluminum | Alternative 2: Composite Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength and durability | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | High strength-to-weight ratio, customizable properties |
| Cost | Approximately $0.75-$1.50 | Generally higher, $2-$4 | Variable, often comparable to steel |
| Ease of Implementation | Well-established supply chains | Requires specialized handling | May need tailored solutions for specific applications |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance required | Low maintenance, but can dent easily | Varies by type, often low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Structural applications, heavy machinery | Aerospace, automotive, building facades | Sports equipment, specialized structural components |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its corrosion resistance and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It is particularly advantageous in industries such as aerospace and automotive where weight savings are crucial for efficiency. However, aluminum typically comes at a higher cost than steel, which can be a significant factor for budget-sensitive projects. Its ease of fabrication and low maintenance needs make it attractive, but care must be taken to avoid dents and scratches, as these can compromise structural integrity.
Alternative 2: Composite Materials
Composite materials, which can be engineered to achieve specific properties, offer a high strength-to-weight ratio and can be tailored for various applications. They are especially popular in industries like sports equipment and aerospace. While the initial costs can vary widely, composites can sometimes match or exceed the cost of steel depending on the application. Their implementation may require specialized knowledge for optimal performance, and while maintenance is generally low, it can vary based on the specific composite used. Composites are ideal for applications where customization and performance outweigh the potential cost disadvantages.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between steel and its alternatives, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific needs of their projects. Steel remains a robust choice for structural applications due to its well-established supply chains and reliability. However, alternatives like aluminum and composite materials can provide innovative solutions that may offer better performance or cost-effectiveness in niche applications. By thoroughly assessing these options, buyers can ensure they choose the most suitable material that aligns with their project goals and operational strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steel price per kg
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steel That Impact Pricing?
When evaluating steel price per kg, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that affect pricing and suitability for various applications:
-
Material Grade
Material grade defines the composition and mechanical properties of steel, which can significantly influence its price. Common grades include structural steel (e.g., S235, S355) and stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316). Higher grades often come at a premium due to their superior strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making them suitable for demanding applications. -
Yield Strength
Yield strength measures the amount of stress a steel can withstand before deforming permanently. This property is vital for structural applications, where safety and reliability are paramount. Higher yield strength often correlates with higher costs, as stronger materials can improve the longevity and performance of structures. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength indicates the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can endure before failure. This property is essential for applications where steel will be subjected to tension forces, such as cables and beams. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers choose the right steel type for specific engineering requirements. -
Thickness and Tolerance
The thickness of steel products and their manufacturing tolerances impact their usability and cost. Tighter tolerances often lead to higher prices due to the increased precision required in production. Buyers must ensure that the thickness and tolerances meet their project specifications to avoid costly rework or material failures. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of steel can affect its corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and overall performance. Common finishes include hot-rolled, cold-rolled, and galvanized. Each finish has its pricing implications, with more complex finishes generally resulting in higher costs due to additional processing steps. -
Coating and Treatments
Steel may undergo various coatings or treatments, such as galvanization or heat treatment, to enhance its properties. These treatments can significantly increase the cost but also extend the life of the material and reduce maintenance needs. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits against the initial price.
What Are Common Trade Terms That B2B Buyers Should Understand?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations. Here are several essential terms related to steel purchasing:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the steel industry, it typically indicates suppliers who provide materials to be used in the production of finished goods. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source high-quality steel tailored to specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it can affect inventory management and pricing strategies. Knowing the MOQ helps companies plan their purchasing and avoid overstocking or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific quantities and specifications of steel. This process is essential for comparing prices and ensuring that the best deal is obtained. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers as they outline who bears the cost and risk during transportation, thus influencing total landed costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. In steel procurement, understanding lead times is critical for project scheduling and ensuring timely delivery of materials. Delays can have cascading effects on project timelines and costs. -
Grade Certification
Grade certification is an assurance that the steel meets specific standards set by international or local bodies. Certifications can impact the price, as certified materials often command a premium due to their guaranteed quality and compliance with safety regulations.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and budget constraints, ultimately enhancing their procurement strategy in the competitive steel market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steel price per kg Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Steel Prices Per Kg?
The global steel market is experiencing a period of volatility influenced by several interconnected factors. One of the primary drivers is the fluctuation in raw material costs, particularly iron ore and scrap metal, which directly impact production costs. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and trade policies, such as tariffs and import quotas, can create supply chain disruptions and alter pricing structures. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective sourcing strategies.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping how steel is sourced and priced. Innovations such as blockchain for supply chain transparency, artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, and advanced analytics for price prediction are gaining traction. These technologies enable buyers to make data-driven decisions, enhancing their ability to navigate price fluctuations and secure favorable contracts. Moreover, the ongoing digital transformation in procurement processes is streamlining supplier interactions and improving price visibility, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market changes.
As the market evolves, buyers must stay informed about regional trends. For instance, in Europe, a shift towards sustainable steel production is prompting investments in electric arc furnaces, which may influence future pricing. Similarly, countries in Africa and South America are seeing increased domestic production, which could impact import dependency and pricing strategies. Understanding these regional nuances will empower B2B buyers to make more informed decisions in a competitive landscape.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping Steel Procurement?
In today’s market, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a critical component of steel procurement strategies. The environmental impact of steel production is significant, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Consequently, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing from mills that utilize renewable energy and employ processes that minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence. Buyers are now more focused on ensuring that their supply chains are free from human rights violations and that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (environmental management) and ISO 45001 (occupational health and safety) are becoming essential for establishing credibility and trust. Companies are also turning to ‘green’ steel products, which are produced using lower carbon footprints, as a way to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer demand for sustainable products.
By adopting sustainable and ethical sourcing practices, businesses not only contribute to environmental conservation but can also enhance their brand reputation. This is particularly important in competitive markets where consumers are becoming more conscious of the origins of the products they purchase. For B2B buyers, integrating sustainability into procurement strategies is a way to future-proof their operations and align with global sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Steel Pricing Dynamics for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of steel pricing has been marked by significant fluctuations influenced by both economic cycles and technological advancements. Historically, the steel industry has been cyclical, with prices rising during periods of high demand and construction booms and falling during recessions. The introduction of new production technologies, such as the basic oxygen process in the mid-20th century, significantly increased efficiency and affected pricing structures.
In recent decades, the globalization of the steel market has further complicated pricing dynamics. Increased competition from emerging economies, particularly in Asia, has led to price pressures in traditional markets. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and digital procurement platforms has transformed how buyers access steel price information and negotiate contracts, making the market more transparent and competitive.
Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it provides insights into potential future trends. The lessons learned from past price fluctuations can guide current procurement strategies, enabling buyers to better anticipate market changes and optimize their sourcing decisions. As the steel industry continues to evolve, staying informed about historical trends can help businesses navigate the complexities of the market with greater confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steel price per kg
-
1. How do I find the most accurate steel price per kg for my needs?
To find the most accurate steel price per kg, it’s essential to utilize reliable sources such as industry reports, market analysis from trusted platforms like MEPS International, and local suppliers. Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide a comparative view of pricing. Additionally, consider subscribing to steel price indices that offer real-time updates and historical data, which can aid in forecasting future price movements. Always verify the credibility of the data source to ensure that your purchasing decisions are based on accurate and up-to-date information. -
2. What factors influence the steel price per kg in international markets?
The steel price per kg is influenced by several factors, including raw material costs, production capacity, transportation expenses, and market demand. Global economic conditions, trade tariffs, and geopolitical events can also impact prices. For instance, tariffs on steel imports can lead to price increases in domestic markets. Additionally, seasonal demand fluctuations, particularly in construction and manufacturing sectors, can cause variations in steel pricing, making it vital for buyers to stay informed about market trends. -
3. How can I vet potential steel suppliers for quality and reliability?
To vet potential steel suppliers, start by reviewing their certifications, such as ISO 9001 or other industry-specific quality assurance standards. Request samples to assess the quality of the steel products. Additionally, check customer references and reviews to gauge their reliability and service levels. Engaging in direct communication to discuss their production processes and lead times can also reveal their operational capabilities. Finally, consider suppliers who have a transparent pricing structure and a clear return policy. -
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for purchasing steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly depending on the supplier, product type, and market dynamics. Generally, MOQs for steel products can range from a few tons to hundreds of tons. It’s essential to clarify the MOQ with potential suppliers during initial discussions. If your requirements are below the MOQ, inquire about the possibility of negotiating terms or consolidating orders with other buyers to meet the supplier’s requirements without compromising your needs. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing steel internationally?
Payment terms for international steel purchases typically include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. Terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms, ensuring clarity on payment timelines, currency, and any associated fees. Understanding the risks involved in international transactions is crucial, so consider using secure payment methods that provide buyer protection. -
6. How do logistics and shipping affect the cost of steel per kg?
Logistics and shipping play a critical role in the total cost of steel per kg. Factors such as transportation mode (sea, air, or land), distance, and fuel prices significantly impact shipping costs. Additionally, customs duties, tariffs, and import/export regulations can lead to unexpected expenses. To optimize costs, consider working with suppliers who have established logistics partnerships or those that can provide door-to-door service, ensuring a smoother procurement process and potentially lower overall costs. -
7. How can I ensure the quality of steel products during international shipping?
To ensure the quality of steel products during international shipping, request that suppliers provide detailed documentation, including material test certificates and quality assurance reports. Insist on inspections before shipping, which can be conducted by third-party quality control companies. Additionally, proper packaging and handling during transit are crucial to prevent damage. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding any quality concerns and ensure that their shipping practices align with your quality standards. -
8. What are the implications of fluctuating steel prices for long-term contracts?
Fluctuating steel prices can pose significant risks for long-term contracts, affecting budgeting and project costs. Buyers should consider including clauses in contracts that account for price adjustments tied to market indices. Establishing fixed pricing for a portion of the contract while allowing for variable pricing on the remainder can help mitigate risks. Regularly reviewing market conditions and maintaining open communication with suppliers can also ensure that both parties remain aligned and can adjust terms as necessary to manage cost fluctuations effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
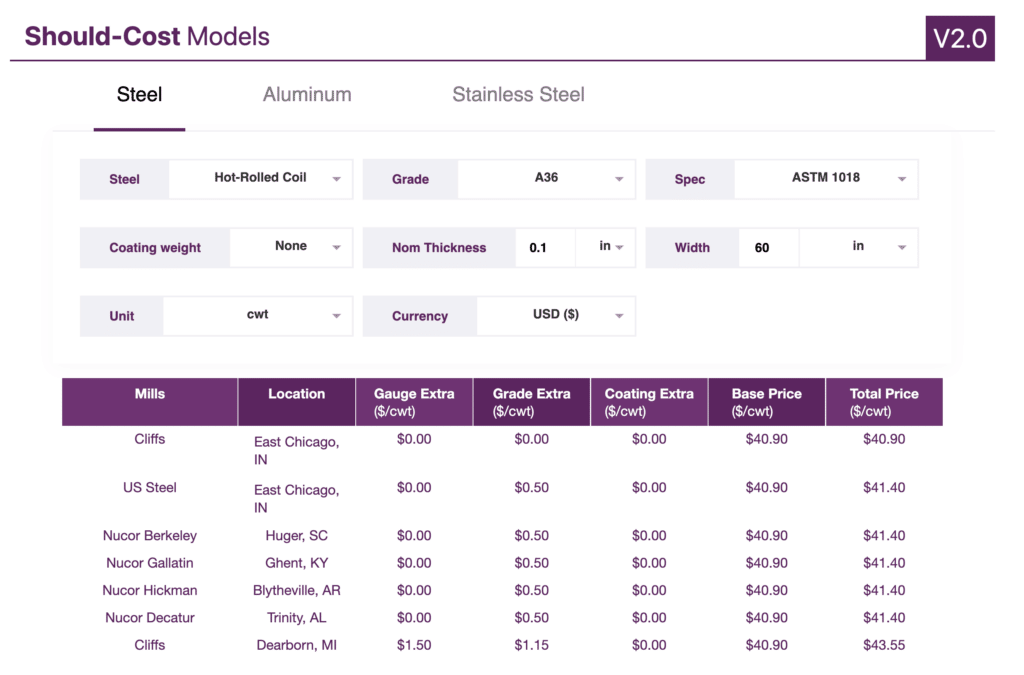
Top 8 Steel Price Per Kg Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Trading Economics – Steel Futures
Domain: tradingeconomics.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Steel futures in China rose to CNY 3,090 per tonne in July, with expectations of government-mandated capacity cuts. Major producer Baosteel expects national output to fall by 50 million tonnes this year. The construction PMI rose to a three-month high in June. Steel’s price fell to 3,071 CNY/T on July 15, 2025, down 0.45% from the previous day, but rose 4.00% over the past month. Steel is expected…
2. MEPS International – North America Steel Prices
Domain: mepsinternational.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: North America Steel Prices data includes the following products: Hot Rolled Coil, Hot Rolled Plate, Cold Rolled Coil, Hot Dipped Galvanised Coil, Electro Zinc Coated Coil, Wire Rod, Sections & Beams, Rebar, and Merchant Bar. Prices are provided in various units: Tonnes (T), Kilograms (KG), Pounds (LB), and Short Tons (SHT). The data is updated monthly and includes 3 years of historical data. Subsc…
3. Focus Economics – Steel Prices
Domain: focus-economics.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Steel (USA) prices averaged USD 874 per metric ton in June, down 1.0% from May. On 30 June, the commodity traded at USD 880 per metric ton, up 4.8% from 30 May. Prices increased in early June after Trump raised tariffs on U.S. steel imports from 25% to 50%, but the rise was short-lived due to elevated U.S. steel inventories, downbeat demand, and lower import requirements compared to other metals l…
4. Business AnalytIQ – Medium Steel Price Index
Domain: businessanalytiq.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Medium Steel Price Index provides pricing information for medium steel across various regions as of July 2025. Prices are as follows: North America: US$1/KG (unchanged), Europe: US$0.85/KG (unchanged), Africa: US$0.57/KG (-1.7% down), Northeast Asia: US$0.43/KG (-2.3% down), Southeast Asia: US$0.61/KG (-1.6% down), South America: US$0.99/KG (unchanged), India: US$0.73/KG (-1.4% down). The index is…
5. ARS Group – CRS 550D Steel Bars
Domain: arsgroup.in
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Product Types: ARS 550D, ARS CRS 550D; Sizes Available: 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, 16mm, 20mm, 25mm, 32mm; Pricing: CRS 550D – Rs. 72,000 /MT (Inclusive of all Taxes & Transportation charges); Key Features: Optimized for weather conditions, certified by international boards like SGS, adheres to IS 1786 – 2008 standard certification; Benefits of TMT Calculator: Transparency of price, ease of budgeting, accur…
6. Rungta Steel – TMT Bars
Domain: tatanexarc.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Rungta Steel offers a range of steel products including TMT Bars, Mild Steel (MS) Bars, MS Pipes, Wire Rods, and Structural Steel.
1. **TMT Bars**:
– High tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
– Used for reinforcement in construction.
– Prices per kg (INR):
– Fe 415: 8 mm – ₹45.50, 10 mm – ₹46.00, 12 mm – ₹46.50, 16 mm – ₹47.00, 20 mm – ₹47.50
– Fe 500: 8 mm – ₹48.50…
7. Statista – Steel Price Trends in India
Domain: statista.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Statista – Steel Price Trends in India, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
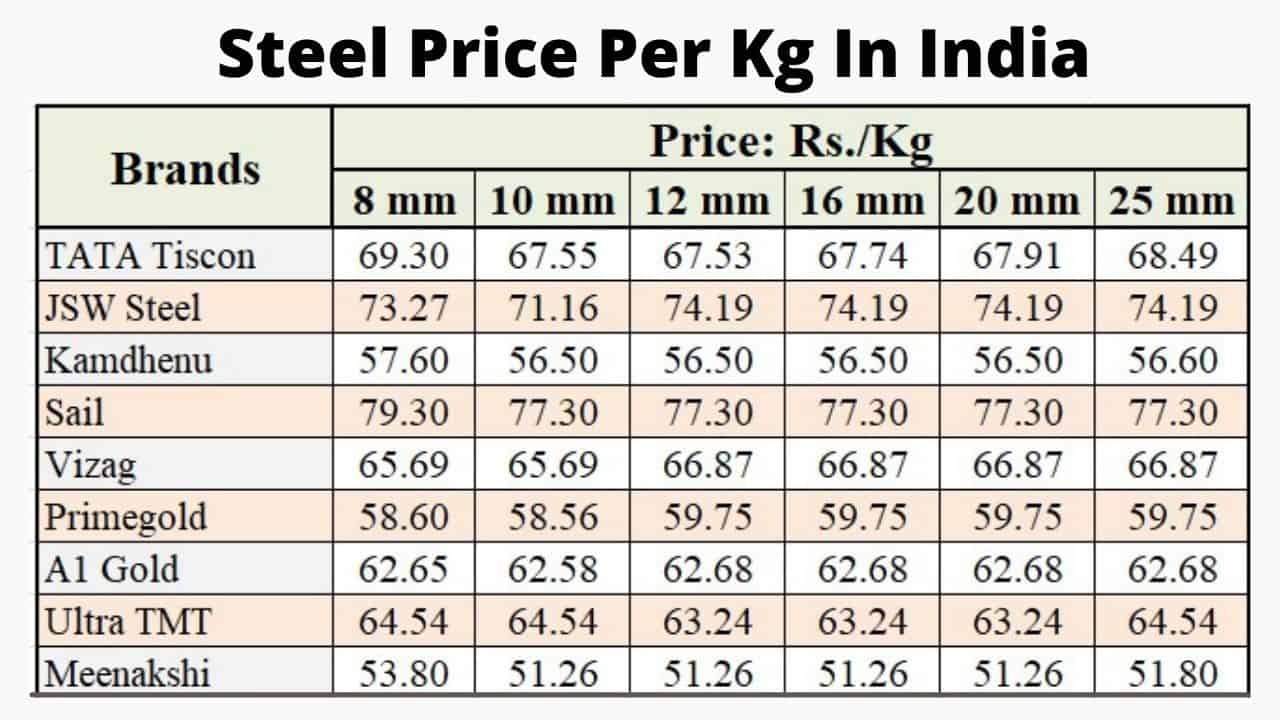
8. Tata Tiscon – TMT Steel Bars Prices
Domain: getpowerplay.in
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Steel prices in India vary by brand and size. Key brands and their prices per kg for TMT steel bars are as follows: Tata Tiscon (8mm: 388, 10mm: 591, 12mm: 835, 16mm: 1485, 20mm: 2322, 25mm: 3619), Jindal Panther (8mm: 388, 10mm: 591, 12mm: 835, 16mm: 1485, 20mm: 2321, 25mm: 3618), Birla TMT (8mm: 260, 10mm: 395, 12mm: 565, 16mm: 1006, 20mm: 1575, 25mm: 2456), JSW Steel (8mm: 391, 10mm: 594, 12mm:…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steel price per kg
As the steel market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to navigate price fluctuations effectively. Key factors influencing steel prices per kilogram include raw material costs, demand-supply dynamics, and geopolitical developments. Understanding these variables allows businesses to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring cost efficiency and budget adherence.
Investing in comprehensive market analysis and historical data is essential for anticipating price trends. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this information to optimize their procurement strategies. By aligning sourcing practices with market conditions, companies can not only secure competitive pricing but also enhance their supply chain resilience.
Looking ahead, the steel market is poised for further changes, driven by technological advancements and sustainability initiatives. To remain competitive, B2B buyers should stay proactive, continuously monitor market indicators, and explore diverse sourcing options. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategies today, ensuring your business is well-positioned to thrive in the evolving landscape of steel pricing.