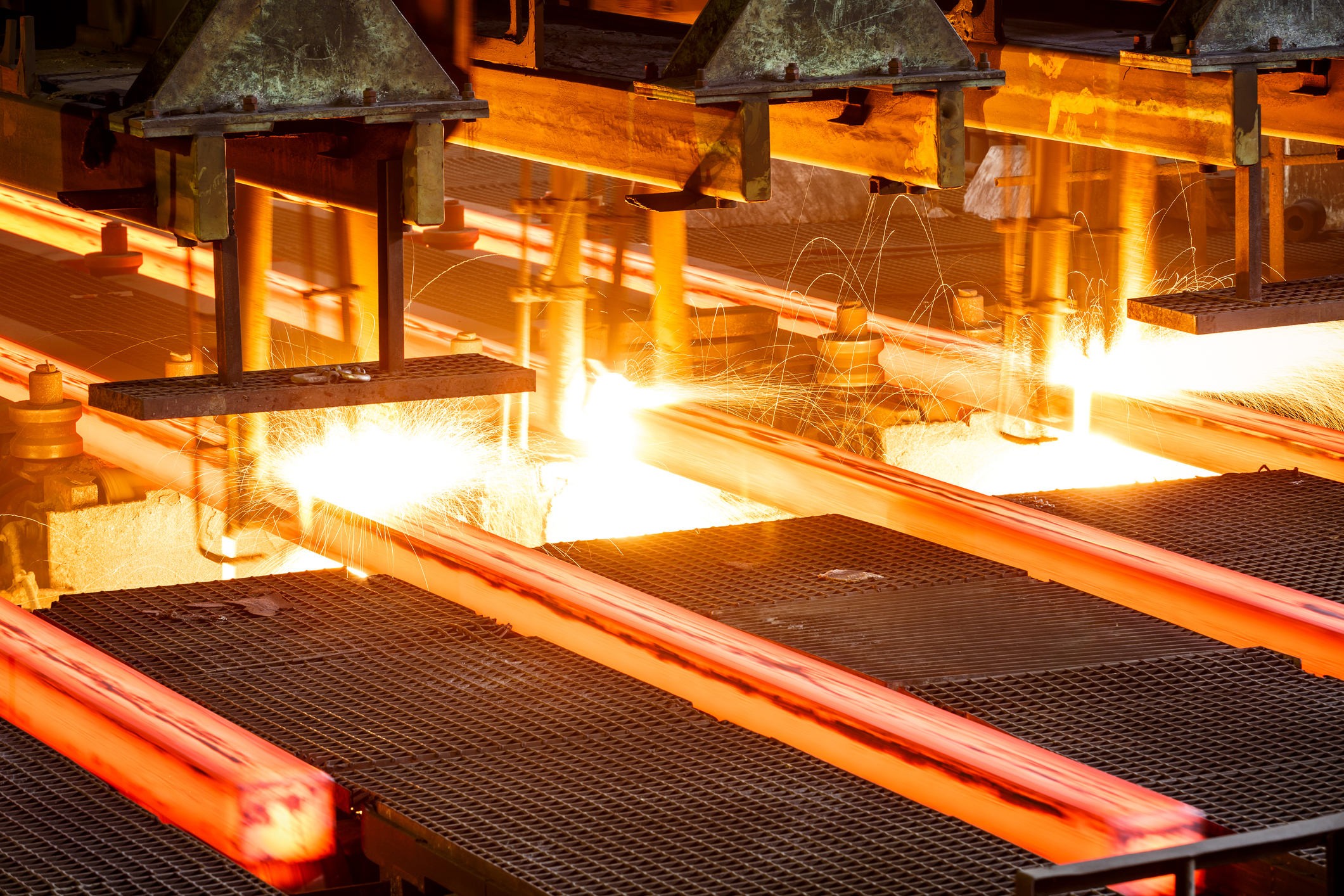
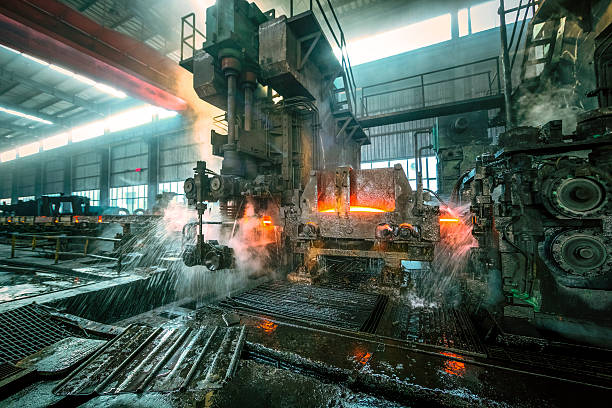
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steel machinery
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the right steel machinery presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. With the demand for high-quality, reliable equipment rising across industries in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of this market is essential. Buyers face hurdles such as navigating varying supplier capabilities, assessing production efficiency, and addressing the labor shortages that impact operations. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions in the realm of steel machinery.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the diverse types of steel machinery available, including CNC machines, beveling equipment, and automated welding systems. We will explore their applications across different sectors, from construction to manufacturing, ensuring you understand how each solution can enhance your operations. Additionally, we will provide practical advice on supplier vetting, highlighting key factors to consider when assessing potential partners. Cost considerations and financing options will also be discussed, empowering you to budget effectively for your machinery investments.
By arming yourself with the knowledge presented in this guide, you will be better positioned to select the right machinery that meets your operational needs and drives your business forward in an evolving landscape.
Understanding steel machinery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Steel Processing Machines | Automated control, precision cutting, and shaping | Structural steel fabrication, automotive | Pros: High efficiency, reduced labor costs; Cons: High initial investment. |
| Beveling Machines | Specialized for edge preparation | Pipe and plate fabrication | Pros: Ensures accurate fits and joints; Cons: Limited to edge processing tasks. |
| Automated Welding Systems | Integrated robotic welding for mass production | Heavy machinery, construction | Pros: Increases production speed, consistent quality; Cons: Requires skilled setup and maintenance. |
| Plate Processing Machines | Capable of cutting, drilling, and milling plates | Shipbuilding, construction, and manufacturing | Pros: Versatile for various materials; Cons: Space-intensive and may require multiple setups. |
| Pipe Processing Equipment | Designed for cutting, threading, and bending pipes | Oil and gas, plumbing, construction | Pros: Streamlines pipe fabrication; Cons: Specialized machines may be costly and complex. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Steel Processing Machines?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) steel processing machines are renowned for their precision and automation capabilities. They utilize advanced software to control the cutting and shaping of steel components, making them ideal for high-volume production environments. B2B buyers should consider their operational efficiency, as these machines significantly reduce labor costs and minimize human error. However, the initial investment can be substantial, requiring careful financial planning and ROI analysis.
How Do Beveling Machines Benefit Steel Fabrication?
Beveling machines are essential for preparing the edges of plates and pipes, ensuring that they are ready for welding and assembly. These machines offer various configurations, including handheld and automated options, catering to different production needs. For businesses focused on pipe and plate fabrication, investing in beveling machines can enhance joint accuracy and improve overall assembly quality. However, buyers should be aware that these machines are primarily limited to edge preparation tasks.
What Advantages Do Automated Welding Systems Provide?
Automated welding systems leverage robotics to enhance the welding process, delivering consistent quality and increased production speeds. These systems are particularly advantageous in industries such as heavy machinery and construction, where high-volume welding is required. While they streamline operations and reduce labor costs, buyers must consider the complexity of setup and maintenance, as these systems require skilled personnel for optimal performance.
Why Are Plate Processing Machines Important in Manufacturing?
Plate processing machines are versatile tools capable of cutting, drilling, and milling various plate materials. They play a critical role in industries such as shipbuilding and construction, where precision and adaptability are paramount. Businesses should evaluate their specific processing needs when considering these machines, as they can be space-intensive and may require multiple setups for different tasks. The investment can be worthwhile for companies that need high-quality plate fabrication.
How Do Pipe Processing Equipment Streamline Operations?
Pipe processing equipment is designed specifically for the cutting, threading, and bending of pipes, making it indispensable in the oil and gas, plumbing, and construction sectors. These machines help streamline the fabrication process, ensuring that pipes are manufactured to precise specifications. While they can significantly enhance productivity, potential buyers should assess the complexity and cost of these specialized machines, as they may require a higher initial investment compared to general-purpose equipment.
Key Industrial Applications of steel machinery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steel machinery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Automated Steel Fabrication | Increases production speed and reduces labor costs | Look for machines with high automation and reliability |
| Oil & Gas | Pipe Cutting and Beveling Machines | Enhances precision and safety in pipeline construction | Consider durability and compliance with safety standards |
| Automotive Manufacturing | CNC Machining for Components | Improves accuracy and consistency in production | Prioritize advanced technology and ease of integration |
| Metal Fabrication | Plate and Beam Processing | Reduces waste and optimizes material usage | Evaluate machine versatility and service support |
| Shipbuilding | Automated Welding Systems | Increases welding speed and quality | Seek out machines that offer advanced features and reliability |
How is Steel Machinery Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, automated steel fabrication is a game changer. Steel machinery, such as CNC cutting and drilling machines, streamlines the production of structural components, significantly increasing output while minimizing labor costs. This is particularly advantageous for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where skilled labor shortages are common. Buyers should prioritize sourcing machines that offer high automation levels and robust after-sales support to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
What Role Does Steel Machinery Play in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas sector, precision is paramount. Steel machinery, specifically pipe cutting and beveling machines, ensures that pipe sections are cut and prepared with high accuracy, which is crucial for safe and efficient pipeline construction. This sector requires machinery that can withstand harsh environments, making durability a key consideration for buyers from the Middle East and Europe. Compliance with international safety standards should also be a critical factor when sourcing equipment.
How is CNC Machining Revolutionizing Automotive Manufacturing?
CNC machining has transformed the automotive manufacturing landscape by providing precise machining of various components. Steel machinery used in this sector enhances production accuracy, leading to fewer defects and reduced waste. For international B2B buyers, especially in Europe and Brazil, sourcing advanced CNC machinery that integrates seamlessly into existing production lines is essential. Additionally, machine reliability and technical support are vital to ensure consistent production quality.
Why is Steel Machinery Important in Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication relies heavily on efficient steel machinery for processes like plate and beam processing. These machines help reduce material waste and optimize production timelines, crucial for staying competitive in the market. Buyers from regions with emerging manufacturing sectors, such as Africa, should look for versatile machines that can handle various tasks while ensuring ease of maintenance. The availability of local service support can also be a significant advantage.
What Benefits Do Automated Welding Systems Offer in Shipbuilding?
Automated welding systems are integral to the shipbuilding industry, where speed and quality are critical. These machines enhance welding efficiency and consistency, reducing labor costs and improving safety. For international buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing reliable and advanced welding technology is essential to meet stringent maritime standards. Ensuring that the machinery can handle the specific materials and thicknesses used in shipbuilding will further enhance operational effectiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steel machinery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Labor Shortages in Steel Processing
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in Africa and South America, the manufacturing industry is grappling with significant labor shortages. Skilled workers are increasingly difficult to find, leading to production delays and increased operational costs. B2B buyers in the steel machinery sector often face the dilemma of needing to maintain productivity while simultaneously managing a dwindling workforce. This situation can hinder their ability to meet client demands and compromise project timelines, ultimately affecting profitability and competitiveness.
The Solution: To address labor shortages, B2B buyers should consider investing in automated steel processing machinery that integrates advanced robotics and software solutions. When sourcing equipment, it is crucial to prioritize machines that offer automation features, such as Voortman’s fabricators or Steel Machinery Group’s beveling machines, which can operate with minimal human intervention. Buyers should engage with manufacturers to explore training programs that accompany the equipment, ensuring that their current workforce can quickly adapt to new technologies. Additionally, selecting machinery with user-friendly interfaces will enhance operational efficiency and reduce the learning curve for existing staff. By adopting these advanced solutions, companies can maintain production levels, improve job satisfaction among employees, and ultimately deliver on their commitments to clients.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Control in Steel Fabrication
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers in the steel machinery market is maintaining consistent quality control during the fabrication process. Variability in product quality can lead to costly rework, customer dissatisfaction, and damage to brand reputation. Buyers often struggle with outdated machinery that lacks the precision required to meet today’s stringent industry standards, leading to increased scrap rates and wastage.
The Solution: To enhance quality control, buyers should focus on acquiring high-precision steel machinery equipped with advanced features like integrated measurement systems and automated calibration. For instance, investing in CNC steel processing machines can significantly improve fabrication accuracy, reducing the risk of defects. It is advisable to conduct thorough research into suppliers that offer machines with a proven track record in quality assurance, and to seek testimonials from existing users. Additionally, implementing a robust maintenance schedule for machinery will ensure optimal performance and longevity, further contributing to consistent product quality. Establishing a feedback loop where operators can report on the machinery’s performance will also help in continuously refining processes and ensuring that quality standards are met.
Scenario 3: Managing Production Costs Effectively
The Problem: Rising production costs are a persistent issue for B2B buyers in the steel machinery sector, particularly in regions facing economic fluctuations. Factors such as increased energy prices, raw material costs, and the need for ongoing equipment maintenance can significantly impact profitability. Buyers often find themselves under pressure to reduce costs while still delivering high-quality products, creating a challenging balancing act.
The Solution: To manage production costs effectively, buyers should explore energy-efficient machinery that minimizes operational expenses over time. Investing in machines with lower energy consumption, such as those with advanced hydraulic systems or energy recovery features, can lead to substantial savings. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles can streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency. Buyers should also consider forming partnerships with suppliers who offer flexible financing options or leasing programs, allowing them to invest in modern machinery without incurring heavy upfront costs. Regular training sessions for staff on efficient operational practices can further optimize resource use and reduce unnecessary expenses. By taking these proactive steps, companies can better control production costs while maintaining their competitive edge in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steel machinery
What Are the Key Materials Used in Steel Machinery?
When selecting materials for steel machinery, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Here, we analyze four prevalent materials used in steel machinery: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, and Tool Steel.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Steel Machinery Applications?
Carbon steel is widely used in steel machinery due to its excellent strength and versatility. It is characterized by its high tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance, which can be a significant drawback in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. Its durability and ability to withstand high pressure make it ideal for structural components.
Cons: The lack of corrosion resistance can lead to premature failure in harsh environments, necessitating protective coatings or treatments. Additionally, carbon steel may require heat treatment to achieve desired hardness levels, adding complexity to the manufacturing process.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local environmental conditions when selecting carbon steel to ensure longevity and reliability.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Steel Machinery?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring hygiene and durability. Its key properties include high tensile strength, resistance to oxidation, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, which is particularly beneficial in marine or chemical processing environments. It also requires minimal maintenance, leading to lower lifecycle costs.
Cons: The main limitation is its higher cost compared to carbon steel, which may not be justifiable for all applications. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to machine, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
International buyers must be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or JIS G4303. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures and humidity can accelerate corrosion, stainless steel is often the material of choice.
Why Choose Alloy Steel for Steel Machinery Applications?
Alloy steel is engineered to enhance specific properties, such as strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It is often used in applications that demand high performance under stress, such as gears and shafts.
Pros: The ability to tailor alloy steel to specific requirements makes it highly versatile. It can be designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Cons: The manufacturing process for alloy steel can be more complex and costly than for carbon steel, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, the specific alloying elements can affect the material’s properties, necessitating careful selection.
For international buyers, compliance with standards like ASTM A572 or DIN 17200 is crucial. Buyers in Europe and South America should consider local availability and sourcing of specific alloys to ensure timely project execution.
What Role Does Tool Steel Play in Steel Machinery Manufacturing?
Tool steel is specifically formulated for manufacturing tools and dies, characterized by its hardness and ability to retain a sharp edge. It is essential in applications that require precision and durability.
Pros: Tool steel offers exceptional wear resistance and can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for cutting and shaping materials. Its durability leads to longer tool life, reducing replacement costs.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its high cost and the complexity of heat treatment required to achieve optimal hardness. Additionally, it may be brittle if not properly processed, which can lead to failure under certain conditions.
International buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A681 or JIS G4404. In regions with stringent manufacturing regulations, such as Europe, understanding local standards is critical for successful procurement.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steel Machinery
| Material | Typical Use Case for steel machinery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, frames | Cost-effective and durable | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Alloy Steel | Gears, shafts, high-stress components | Tailored properties for specific needs | More complex and costly manufacturing process | Medium |
| Tool Steel | Cutting tools, dies | Exceptional wear resistance | High cost and brittle if improperly processed | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steel machinery
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Steel Machinery?
The manufacturing process of steel machinery involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both functional and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is Steel Processed for Machinery Production?
The first stage in manufacturing steel machinery is material preparation. High-quality steel is sourced based on specifications relevant to the intended application. This often involves cutting large steel sheets or coils into manageable sizes. Additionally, material properties such as tensile strength and hardness are verified through testing to ensure they meet the required standards. This stage may also include pre-treatments like annealing or hardening to enhance the material’s performance characteristics.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Steel Machinery Components?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This process can involve various techniques such as:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are widely used to achieve high precision in shaping steel components. This technology allows for complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it ideal for intricate parts.
- Welding: Different welding techniques, such as MIG and TIG welding, are employed to join steel parts. The choice of technique depends on the thickness and type of steel, as well as the desired strength of the joint.
- Bending and Forming: Sheet metal is often bent or formed using hydraulic presses or roll formers, which shape the steel into specified angles or curves.
These techniques are crucial in ensuring that the components not only fit together but also perform reliably under operational stresses.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Steel Machinery Manufacturing?
The assembly stage involves bringing together the formed components into a cohesive unit. This process typically includes:
- Subassembly: Smaller components are assembled into subunits before being integrated into the final product. This can streamline the overall assembly process and improve efficiency.
- Quality Checks: At this stage, initial quality checks (IQC) are performed to ensure that each component meets specifications before full assembly. This includes verifying dimensions and finishes.
- Final Assembly: The subassemblies are combined, and additional elements such as electrical systems, controls, and safety features are integrated.
Effective assembly is critical in achieving the desired functionality and performance of the machinery.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Steel Machinery?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of steel machinery. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as sandblasting, powder coating, or galvanization are used to improve corrosion resistance and surface quality. These treatments protect machinery from environmental factors, extending its lifespan.
- Painting and Coating: Aesthetic finishes can also be applied, which may include branding or protective coatings that enhance visibility and functionality.
Finishing not only improves the machinery’s appearance but also plays a significant role in its performance and longevity.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Steel Machinery Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of steel machinery manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Steel Machinery Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards that guide quality assurance in steel machinery manufacturing. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates a commitment to quality at all stages of production.
- CE Marking: Common in Europe, CE marking signifies that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for machinery exported to European markets.
- API Standards: For machinery used in the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential. These standards ensure that machinery can withstand the rigors of these industries.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility and reliability of their suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Steel Machinery Production?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks at various stages of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify their compliance with specifications. This step helps prevent defects from entering the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, operators conduct checks to monitor tolerances, dimensions, and surface finishes. This proactive approach allows for early detection of issues.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the machinery is fully assembled, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that all components function as intended and meet quality standards.
Implementing these QC checkpoints is essential for maintaining high-quality output and minimizing defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must adopt strategies to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are several methods to consider:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance protocols. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and their commitment to quality.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for quality assurance reports, including details of inspections and compliance certifications. These documents can provide transparency regarding the supplier’s quality management processes.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent bodies can evaluate the supplier’s processes and products, ensuring they meet specified standards.
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these verification methods is crucial for selecting reliable suppliers.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control in steel machinery. Key considerations include:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Understanding these cultural nuances can help buyers set realistic expectations and foster better communication with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and standards applicable in their markets. This may require additional documentation or certifications.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who provide transparency in their supply chain practices. This can help in assessing the quality of raw materials and components used in the manufacturing process.
By being aware of these considerations, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they receive high-quality steel machinery that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steel machinery’
Introduction
Sourcing steel machinery can be a complex process, particularly for B2B buyers operating across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide provides a structured checklist to streamline your procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline your machinery requirements. Consider factors such as production capacity, material types, and any specific processing capabilities needed. This step is vital as it sets the foundation for identifying suitable machinery that meets your operational demands.
- Key Considerations:
- Machine dimensions and weight for space planning.
- Required automation level to improve efficiency.
- Integration capabilities with existing systems.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest advancements in steel machinery. Understanding market trends helps you identify innovative solutions that can enhance productivity and reduce costs. This knowledge will empower you to ask the right questions during supplier discussions.
- Focus Areas:
- Automation technologies and software integrations.
- Emerging materials and processing techniques.
- Case studies of successful implementations in your industry.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can deliver high-quality machinery. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from existing clients in similar industries. This diligence helps mitigate risks associated with vendor reliability.
- Important Actions:
- Check for certifications and industry standards compliance.
- Review customer testimonials and case studies.
- Assess their after-sales support and service capabilities.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
After narrowing down your supplier list, request detailed quotes for the machinery that meets your specifications. Comparing quotes not only helps you understand market pricing but also reveals differences in terms of warranties, service agreements, and delivery timelines.
- What to Look For:
- Breakdown of costs, including shipping and installation.
- Warranty terms and conditions for equipment.
- Availability of spare parts and after-sales services.
Step 5: Assess Financing Options
Evaluate the financing options available for your machinery purchase. Understanding your financing alternatives can significantly impact your cash flow and investment strategy. Look for suppliers that offer flexible payment terms or leasing options that suit your budget.
- Considerations:
- Interest rates and payment schedules.
- Impact on overall project budgets.
- Potential for tax benefits or incentives.
Step 6: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Demo
If possible, arrange a site visit to the supplier’s facility or request a virtual demonstration of the machinery. This step allows you to see the equipment in action and assess its functionality and ease of use, which is critical for ensuring it meets your operational needs.
- Key Points:
- Observe the machinery’s performance and quality.
- Engage with current users to gather insights.
- Evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Terms
Once you’ve selected a supplier, carefully review the contract and ensure all terms are clear and favorable. This includes payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. A well-defined contract protects your interests and clarifies expectations for both parties.
- Contract Essentials:
- Clear definitions of deliverables and timelines.
- Terms for handling defects or delays.
- Confidentiality and compliance clauses.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complex landscape of sourcing steel machinery with confidence, ensuring that your investment aligns with your operational goals and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steel machinery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Steel Machinery Sourcing?
When sourcing steel machinery, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts pricing. High-grade steel and specialized alloys can increase costs but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing and assembly. Regions with higher labor costs may see increased machinery prices, while automation can mitigate labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower these overheads, affecting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: The cost of custom tooling can be substantial, especially for specialized machinery. The more complex the tooling requirements, the higher the initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machinery meets industry standards involves rigorous quality checks, which can add to the total expense. Suppliers with strong QC processes may charge a premium, but this often results in lower long-term maintenance costs.
-
Logistics: Transporting heavy machinery can be costly, particularly for international buyers. Consideration of shipping methods, distances, and tariffs is vital in calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand and competition. Understanding the margin expectations can provide leverage in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Steel Machinery Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of steel machinery, and being aware of these can aid in making informed purchasing decisions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Negotiating MOQs can significantly lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machinery tailored to specific needs can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials Used: The quality and type of materials can vary widely. Opting for premium materials may lead to higher upfront costs but could result in lower maintenance and replacement expenses.
-
Quality Certifications: Machinery that meets international quality standards often commands higher prices. Certifications can be indicative of reliability and performance, which are crucial in B2B transactions.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers may charge more due to their reputation and reliability. However, newer suppliers might offer competitive pricing to build their market presence.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for international transactions. They define responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and liability, which can greatly influence total pricing.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Steel Machinery Procurement?
International B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies by considering the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts or flexible payment terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. This holistic approach can reveal the most cost-effective options.
-
Research Market Prices: Stay informed about prevailing market prices and trends. Understanding the competitive landscape can provide insights during negotiations.
-
Evaluate Supply Chain Logistics: Assess logistics costs and lead times. Choosing suppliers closer to your operation can reduce shipping costs and delays.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions, labor costs, and material availability. Understanding these nuances can aid in making strategic purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for steel machinery can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The information provided here is indicative and should be supplemented with direct quotes from suppliers for accurate budgeting. Always perform due diligence when sourcing machinery to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steel machinery With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Steel Machinery
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, steel machinery plays a pivotal role in the production and processing of steel products. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may better suit their operational needs, budget constraints, or specific applications. This analysis compares steel machinery with two viable alternatives: laser cutting systems and manual fabrication methods. Each of these options has distinct characteristics that can influence a buyer’s decision.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Steel Machinery | Laser Cutting Systems | Manual Fabrication Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput and precision | Exceptional precision and detail | Variable performance; reliant on skill |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate to high initial cost | Low initial cost; labor-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires trained operators | Generally user-friendly; training needed | Simple tools; no special training required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Low maintenance; consumables needed | Minimal maintenance; tool upkeep necessary |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale, high-volume production | Detailed, custom work or prototyping | Small-scale projects or repairs |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Laser Cutting Systems?
Laser cutting systems are known for their precision and versatility. These systems can cut through various materials, including steel, with minimal waste and high accuracy. The primary advantage is the ability to produce intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional methods. Additionally, the operational costs can be lower over time due to reduced material waste and labor costs. However, the initial investment can be significant, and ongoing costs for consumables like laser tubes must be considered. Moreover, while they are generally user-friendly, operators still require training to ensure safe and efficient operation.
How Do Manual Fabrication Methods Compare?
Manual fabrication methods involve using basic tools and skilled labor to shape and assemble steel components. One of the main benefits of this approach is the low initial investment, making it accessible for small businesses or startups. Additionally, these methods allow for flexibility in production, enabling custom projects and quick modifications. However, the performance is highly dependent on the skill level of the workers, leading to variable quality and efficiency. Furthermore, this method can become labor-intensive, making it less viable for large-scale production or when dealing with high-demand projects.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right solution for steel processing, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs, including production volume, budget, and the complexity of the projects they undertake. Steel machinery is ideal for high-volume production where precision and efficiency are critical. In contrast, laser cutting systems offer flexibility for detailed work and prototyping, while manual fabrication methods may be suitable for smaller operations or custom jobs. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steel machinery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steel Machinery?
Understanding the critical specifications of steel machinery is essential for B2B buyers, especially in regions with growing industrial demands like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some crucial technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of steel based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include structural steel (e.g., S235, S355) and high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA). The choice of material grade affects the machinery’s strength, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Selecting the appropriate grade is vital for ensuring the machinery can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions, enhancing longevity and reducing maintenance costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a component. In steel machinery, tolerances are crucial for ensuring components fit together correctly and function efficiently. Tight tolerances can lead to higher manufacturing costs but are often necessary for precision applications, such as in CNC machining. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess whether a machine will meet their operational requirements and quality standards.
3. Production Capacity
Production capacity refers to the maximum output that a machine can achieve within a specific timeframe. This metric is critical for businesses looking to scale operations or meet fluctuating demand. Buyers should evaluate whether the machinery can handle their required volumes without compromising quality. Understanding this property helps companies plan their production schedules and optimize resource allocation.
4. Automation Level
The level of automation in steel machinery determines how much manual intervention is required during operation. Highly automated machines can significantly reduce labor costs and increase efficiency, particularly in regions facing labor shortages. When assessing machinery, buyers should consider the degree of automation as it directly impacts operational efficiency and workforce management.
5. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is increasingly important in the steel industry due to rising energy costs and environmental concerns. Machines that consume less energy while maintaining performance levels can lead to substantial cost savings over time. Evaluating energy efficiency not only aids in budgeting but also aligns with sustainability initiatives, which are becoming critical for businesses globally.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Steel Machinery Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in the steel machinery market. Here are some commonly used trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the steel machinery industry, OEMs provide the machinery and components that meet specific industry standards. Understanding the role of OEMs helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure quality in their machinery sourcing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In steel machinery, MOQs can impact purchasing decisions, particularly for smaller businesses or those testing new products. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their orders efficiently and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process in which a buyer solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It is a critical step for B2B buyers to ensure they receive competitive pricing and understand the available options. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process and foster better supplier relationships.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in cross-border transactions, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the machinery. In the steel industry, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and meeting project deadlines. Buyers should factor in lead times when assessing suppliers to avoid production delays and maintain operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and build successful partnerships in the steel machinery market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steel machinery Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Steel Machinery Sector?
The steel machinery sector is currently experiencing significant transformation driven by global economic recovery, technological advancements, and evolving customer needs. Key market drivers include increasing demand for high-quality steel products in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As countries invest in infrastructure and industrial development, the demand for efficient and automated steel processing equipment is surging.
Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0, artificial intelligence, and robotics are reshaping sourcing trends in the steel machinery market. Buyers are increasingly seeking machinery that integrates advanced software for enhanced automation, which not only increases productivity but also addresses the global labor shortage issue. For instance, companies are looking for solutions that offer real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and seamless supply chain integration. Moreover, the trend towards customization is gaining momentum, as buyers demand machinery tailored to specific production processes, which can improve operational efficiency and reduce waste.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the growing competition from local manufacturers in these regions. As local players enhance their capabilities, it becomes essential for international suppliers to demonstrate superior quality, reliability, and after-sales support to maintain a competitive edge. The ability to offer comprehensive solutions, from equipment procurement to ongoing service and maintenance, will be crucial in winning contracts and establishing long-term partnerships.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Steel Machinery Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions within the steel machinery sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, businesses are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprint and environmental impact. This shift has prompted B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are now a vital consideration for international buyers. Companies are expected to provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly and without adverse social impacts. This includes certifications for eco-friendly materials and adherence to international labor standards. For instance, buyers are increasingly seeking steel machinery that utilizes recycled materials or minimizes energy consumption during production, which not only aligns with environmental goals but also often results in cost savings over time.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are gaining traction in the industry. Buyers should actively seek suppliers who can provide these certifications, as they indicate a robust commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. This focus on sustainability not only helps companies mitigate risks but also enhances their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of Steel Machinery Development and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of steel machinery can be traced back to the industrial revolution, where advancements in technology transformed steel production and processing. Early machinery was primarily manual, leading to high labor costs and inefficiencies. However, the introduction of mechanization and later, automation, revolutionized the sector, allowing for higher productivity and consistency in quality.
In recent decades, technological innovations such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining and automated welding have further enhanced the capabilities of steel machinery. These developments are particularly relevant today as businesses face challenges such as labor shortages and the need for greater efficiency. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the trajectory of technology in the steel machinery sector and informs their sourcing decisions as they seek to invest in equipment that not only meets current demands but is also future-proofed against ongoing industry changes.
As the steel machinery sector continues to adapt to market dynamics and sourcing trends, international buyers must stay informed and agile, leveraging technological advancements while prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices in their procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steel machinery
-
How do I choose the right steel machinery for my production needs?
Selecting the right steel machinery involves assessing your specific production requirements, including the types of steel processing (e.g., cutting, welding, bending) you need to perform. Consider factors such as the scale of your operations, the complexity of the tasks, and the level of automation required. It’s also beneficial to review case studies or testimonials from similar businesses to understand the effectiveness of different machinery. Additionally, consulting with manufacturers or industry experts can provide insights tailored to your unique circumstances. -
What is the best type of steel machinery for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, automated CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often the best choice. These machines offer precision, speed, and consistency, significantly reducing manual labor and the potential for human error. Look for machinery that integrates advanced software for process optimization and can handle various types of steel materials. It’s also wise to evaluate the machine’s ability to work seamlessly with other equipment to ensure a smooth workflow and maximize productivity. -
How can I ensure the quality of steel machinery before purchasing?
To ensure quality, start by researching reputable manufacturers with a track record of reliability and customer satisfaction. Request samples or live demonstrations of the machinery to assess its performance firsthand. Additionally, verify certifications and compliance with international quality standards, as these indicate adherence to best practices. Engaging with current users of the machinery through forums or testimonials can also provide valuable insights into the machinery’s long-term reliability and support. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing steel machinery internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Typically, international transactions might involve a deposit (often 30-50%) before production, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods, such as letters of credit or wire transfers, and to ensure that they are secure and mutually agreeable. Understanding the currency exchange implications and potential tariffs or duties associated with international purchases is also essential for budgeting. -
What should I consider regarding lead times and logistics when sourcing steel machinery?
Lead times for steel machinery can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the equipment and the manufacturer’s location. When planning your procurement, factor in not just production time but also shipping duration, customs clearance, and local delivery logistics. Collaborating with experienced freight forwarders familiar with heavy machinery can streamline this process. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your supplier about any potential delays can help manage expectations. -
How can I customize steel machinery to fit my specific needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor machinery according to your operational requirements. This may include modifications in size, additional features, or specialized software integration. When discussing customization, clearly outline your needs and ensure that the supplier has the capability and expertise to deliver. It’s also prudent to request a detailed proposal that includes timelines, costs, and any implications for maintenance or support. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steel machinery purchases?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among manufacturers, particularly for customized machinery. While some suppliers may allow single-unit purchases, others might require larger quantities to justify production costs. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during negotiations and explore options for bulk purchases if you’re considering future expansions. Some manufacturers may also offer leasing or rental agreements, which can be a flexible alternative for smaller operations. -
What are the best practices for vetting steel machinery suppliers?
When vetting suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation and customer reviews. Look for suppliers who are transparent about their manufacturing processes and provide detailed specifications for their machinery. Engaging in direct communication to discuss your needs can reveal their responsiveness and willingness to support. Requesting references from past clients and verifying their compliance with international standards can further ensure that you are partnering with a reliable manufacturer.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Steel Machinery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Steel Machinery Group – SMG HPAC-3000B Double Acting Electric Hydraulic Pump
Domain: steelmachinerygroup.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”SMG HPAC-3000B Double Acting Electric Hydraulic Pump”,”sku”:”SMG-HPAC-3000B”,”price”:”$2,588.50 USD”,”description”:”A powerhouse companion designed for maximum performance and durability in high-pressure tasks.”},{“name”:”SMG DCS-14 Dust Collector System, Single Phase – 240V”,”sku”:”SMG-1400-DES”,”price”:”$877.10 USD”,”description”:”Designed for optimal performance with durab…
2. Ficep – Endeavour 1003DD
Domain: ssslmachinery.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Key Products: 1. Endeavour 1003DD – Type: Drill Line, Manufacturer: Ficep, Condition: As Is / Where Is, Stock #: I1733, Price: $250,000 2. BDL-1250/9A – Type: Drill Line, Manufacturer: Peddinghaus, Condition: As Is / Where Is, Stock #: Consignment, Price: $20,000 3. Advantage – Type: Drill Line, Manufacturer: Peddinghaus, Condition: Remanufactured, Stock #: I-1784, Price: $423,200 4. SBA Compact+ …
3. Moog – Advanced Motion Control Solutions
Domain: moog.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Moog provides advanced motion control solutions for steel and iron production machinery, focusing on enhancing efficiency and productivity. Their products are designed to withstand harsh environments and deliver precise control in applications such as rolling mills, furnaces, and casting machines. Key offerings include servo valves, actuators, and control systems that improve operational performan…
4. GMB Heavy Industries – Steel Mill Equipment
Domain: gmbindustries.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GMB Heavy Industries offers a wide range of steel mill equipment and products designed to meet the needs of the steelmaking industry. Key products include: 1. Long Product Cooling Bed – Supports hot-rolled steel from the hot mill to cool products. 2. Aligning Rolls – Ensures proper alignment during processing. 3. Grid Castings for Steel Mills – Used in various applications within steel mills. 4. E…
5. American Steel – Metal Processing Machinery
Domain: americansteel.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: American Steel Products Company specializes in buying and selling metal processing machinery. Key products include: Blanking Lines, Cut-To-Length Lines, Edging Lines, Embossing, Rolling Mills (Hot and Cold), Levelers, Pickle Lines, Presses, Press Feed Lines, Slitting Lines, Pipe Straightener, Tube & Pipe Mills, and Used/Reconditioned Equipment. Specific product details include: Edging Lines with t…
6. Steltech – Steel Mill Machinery
Domain: steltech.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Steel mill machinery includes various types of equipment essential for steel production: 1. Blast Furnaces: Used to obtain raw iron by melting iron ore and coke with hot air and oxygen. 2. Basic Oxygen Furnaces (BOF): Converts raw steel from iron ore or scrap metal by injecting oxygen to reduce carbon content. 3. Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): Produces steel from scrap metal using an electric arc, a…
7. Ocean Machinery – Structural Steel Fabrication Solutions
Domain: oceanmachinery.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Ocean Machinery offers a range of structural steel fabrication machinery, including: 1. Ocean Structural Solutions – Provides exceptional accuracy of hole placement, fully automatic measuring, layout, and drilling cycle. 2. Avenger CNC Single Spindle Drill Line – Drills, mills, marks, scribes, threads, counter-sinks, and counter-bores; processes profiles up to 48″ in height with an 8 position tool…
8. Peddinghaus – Drill Lines & Plate Processors
Domain: peddinghaus.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Drill Lines: PeddiSubX-1120, Peddi XDM-630, Advantage-2, BDL-1250/9D; Plate Processors: HSFDB-C (Max Plate Thickness: 4″), HSFDB-B (Max Plate Thickness: 3″), FPB-1800 (Max Plate Thickness: 1-1/4″); Angle Lines: Anglemaster-663 (Angle Capacity: 6.3″ x 6.3″ x 3/4″), Anglemaster-HD (Angle Capacity: 8″ x 8″ x 1″), Anglemaster-643 (Angle Capacity: 6″ x 6″ x 5/8″); Thermal Cutting: PeddiBot-1250 (Plasma…
9. Cumic – Carbon & Special Steel Solutions
Domain: cumic.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Types of Carbon & Special Steel For Sale: Carbon Steel (Flat, Long, Pipes & Tubes, Coils, Sheets, Sections, Rods, Hot Rolled, Cold Rolled, Coated), Special Steel (Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel, Square Bar, Round Bar, Flat Bar, Hexagon Bar, Hot Forged Bar, Hot Rolled Bar, Cold Drawn Bar, Peeled Bar). Applications in machinery and engineering include components like pin, piston, track shoe, track rol…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steel machinery
In the dynamic landscape of steel machinery, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical driver for operational efficiency and competitive advantage. By prioritizing high-quality, automated solutions, international B2B buyers can significantly enhance their production capabilities while addressing labor shortages and rising operational costs. The testimonials from industry leaders highlight the transformative power of investing in advanced machinery that integrates seamlessly with existing workflows, resulting in improved productivity and reduced lead times.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Shape Your Future in Steel Machinery?
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing steel machinery, consider the long-term benefits of building relationships with reputable suppliers who offer not just products but comprehensive solutions tailored to your specific needs. Leveraging innovations in robotics, software integration, and automation can propel your business to new heights, ensuring you remain competitive in an evolving market.
Looking ahead, the steel machinery sector is poised for growth, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategy and align it with the latest technological advancements. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operational efficiency and position your business for success by making informed decisions in your sourcing endeavors.