Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Steel Classification Chart
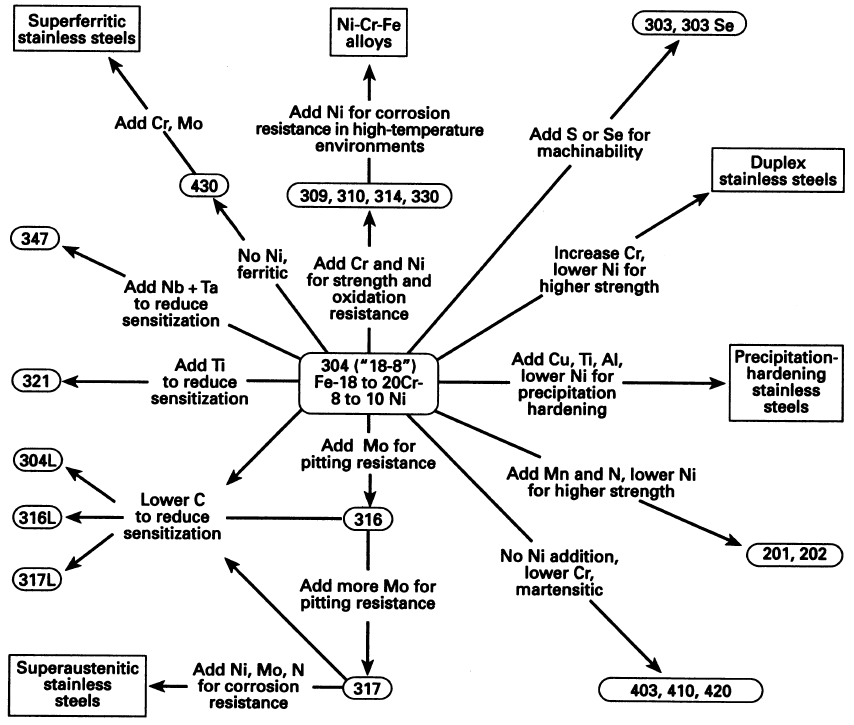
Steel Classification & Precision CNC Machining
Understanding the metallurgical characteristics of steel is fundamental to achieving optimal CNC machining outcomes, including dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and tool longevity. At Honyo Prototype, our deep expertise in material science directly informs our high-precision CNC machining capabilities, enabling us to select the ideal steel grade—whether carbon, alloy, stainless, or tool steel—for your specific application requirements. We rigorously match material properties such as hardness, machinability, and thermal stability to your design tolerances and functional demands, minimizing waste and ensuring repeatability across production runs. To streamline your prototyping or low-volume manufacturing process, leverage our Online Instant Quote system. Simply upload your CAD file to receive a detailed, transparent cost and lead time estimate within hours—accelerating your path from material specification to finished component without compromising on Honyo’s signature quality or engineering support.
Technical Capabilities
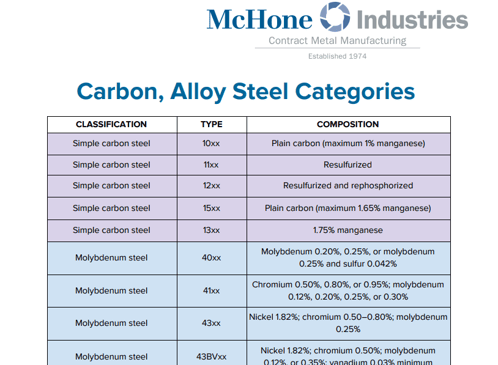
Technical specifications for a steel classification chart tailored to precision machining applications—particularly 3/4/5-axis milling, turning, and tight tolerance work—must consider material machinability, thermal stability, hardness, and dimensional consistency. While the chart primarily categorizes steels (e.g., carbon, alloy, stainless, tool steels), it is essential to compare them alongside commonly machined non-ferrous and non-metallic materials such as Aluminum, ABS, and Nylon to guide optimal material selection for high-precision components.
Below is a comparative technical specification table highlighting key attributes relevant to multi-axis milling, turning, and tight tolerance manufacturing processes.
| Material Type | Typical Hardness (HRC) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Machinability Rating (%) | Thermal Expansion (µm/m·°C) | Common Applications in Precision Machining | Notes for 3/4/5-Axis Milling & Turning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel (e.g., 1018) | 10–15 HRC | 440–540 | 70% | 12.0 | Fixtures, housings, non-critical parts | Good for roughing; limited for tight tolerances due to lower rigidity and stability |
| Alloy Steel (e.g., 4140) | 25–32 HRC | 655–965 | 60% | 12.3 | Shafts, gears, high-strength components | Pre-hardened versions ideal for tight tolerance parts; stress-relieved for stability |
| Stainless Steel (e.g., 304) | 20–25 HRC | 505–700 | 45% | 17.3 | Medical, aerospace, food-grade parts | Work-hardens rapidly; requires sharp tools and rigid setups for precision |
| Tool Steel (e.g., A2, D2) | 58–62 HRC | 1,800–2,200 | 25–30% | 10.5 | Molds, dies, high-wear tooling | Typically machined pre-hardened; post-heat treat grinding preferred for tight tolerances |
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6) | 30–35 HB (~15 HRC) | 310 | 90% | 23.6 | Aerospace, enclosures, prototypes | Excellent for high-speed 5-axis milling; easy to hold ±0.0005″ with proper fixturing |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | 80–100 Shore D | 40–50 | 85% | 80–100 | Prototypes, jigs, non-structural parts | Low melting point; requires coolants and light cuts; suitable for tight tolerances in stable environments |
| Nylon (e.g., PA6) | 70–80 Shore D | 70–85 | 75% | 80–120 | Insulators, bushings, low-friction parts | Prone to moisture absorption and creep; must be acclimated and machined dry for dimensional accuracy |
Notes on Tight Tolerance Machining:
Materials like 4140 steel and 6061-T6 aluminum are preferred for tolerances within ±0.001″ to ±0.0002″, especially when stress-relieved or T6 heat treated.
Stainless steels require rigid setups and specialized tooling (e.g., high-feed mills, CBN or carbide inserts) to minimize deflection and work hardening.
Non-metallics such as ABS and Nylon are suitable for non-load-bearing precision parts but require environmental controls due to hygroscopic and thermal expansion behavior.
In 5-axis milling, aluminum dominates due to high material removal rates and excellent surface finish capability.
For turning operations, free-machining steels (e.g., 12L14) offer superior finish and tool life, though they are less common in tight tolerance structural applications.
This technical comparison supports informed material selection in high-precision CNC environments at Honyo Prototype, ensuring optimal balance between machinability, accuracy, and final part performance.
From CAD to Part: The Process
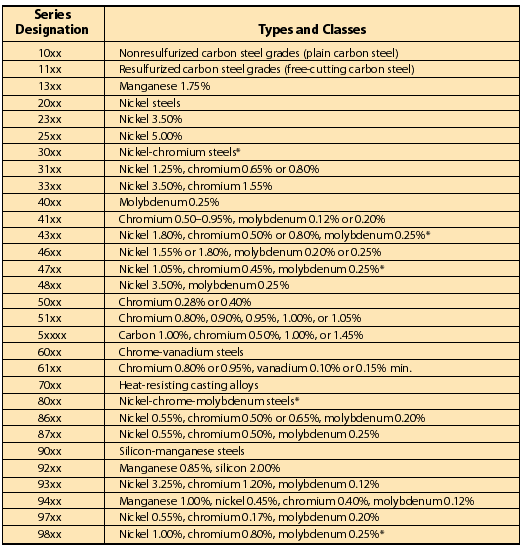
Honyo Prototype does not produce or deliver steel classification charts as physical products. Steel classification charts are industry reference documents (e.g., ASTM, ISO, SAE standards) that define material properties, compositions, and applications. Our manufacturing process applies exclusively to physical prototypes and end-use parts. If your query refers to how steel material specifications are integrated into our prototyping workflow for a physical component, here is our standardized process:
CAD Upload and Material Specification
Customers upload CAD files with explicit material callouts (e.g., “AISI 304 Stainless Steel” or “EN 1.4301”). Our system validates whether the specified steel grade aligns with standard industry classifications. If no material is specified, our engineering team requests clarification before proceeding. Honyo does not generate classification charts but relies on certified material databases during quoting and production.
AI-Powered Quoting
Our AI quotation engine cross-references the CAD-specified steel grade against real-time material availability, machinability data, and cost databases. It flags inconsistencies (e.g., “SAE 1020” vs. “ASTM A36” for structural applications) and provides cost implications for alternative grades. The quote includes material certification requirements (e.g., mill test reports per EN 10204 3.1).
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Analysis
Our engineering team conducts a rigorous DFM review focused on steel-specific factors:
Verifying weldability, hardenability, and thermal distortion risks for the selected grade
Confirming compliance with dimensional tolerances for the steel’s mechanical properties
Recommending substitutions if the specified grade is non-standard, obsolete, or unsuitable for the geometry (e.g., suggesting 4140 over 1045 for high-stress components)
Material certifications and traceability documentation requirements are finalized during this phase.
Production Execution
Steel parts are manufactured using grade-specific parameters:
CNC machining with optimized feeds/speeds for the steel’s Brinell hardness
Heat treatment cycles validated for the exact alloy composition
In-process material verification via PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing for critical applications
All steel stock is sourced from certified mills with full traceability to heat numbers.
Delivery and Documentation
Physical parts ship with:
Dimensional inspection reports
Material certification matching the heat number to the delivered part
Process validation records (e.g., hardness test results)
No “steel classification charts” are provided, but material certifications reference the applicable industry standard (e.g., “Conforms to ASTM A516 Grade 70”).
For clarity, Honyo’s role is manufacturing parts to your material specifications—not creating reference charts. Below is a simplified comparison of common steel classifications we frequently machine:
| Standard System | Example Grade | Typical Use Case at Honyo | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI/SAE | 4140 | High-strength shafts, tooling | Requires pre-heat for welding |
| ASTM | A36 | Structural brackets, fixtures | Limited machinability vs. 1018 |
| EN (European) | 1.4301 (X5CrNi18-10) | Medical/corrosive environments | Non-magnetic properties critical |
| JIS | SS400 | Low-cost brackets, non-critical parts | Lower precision tolerance capability |
All steel material selections undergo explicit validation during DFM to ensure producibility, cost efficiency, and compliance with your functional requirements. We recommend specifying grades per international standards in your CAD files to avoid delays.
Start Your Project
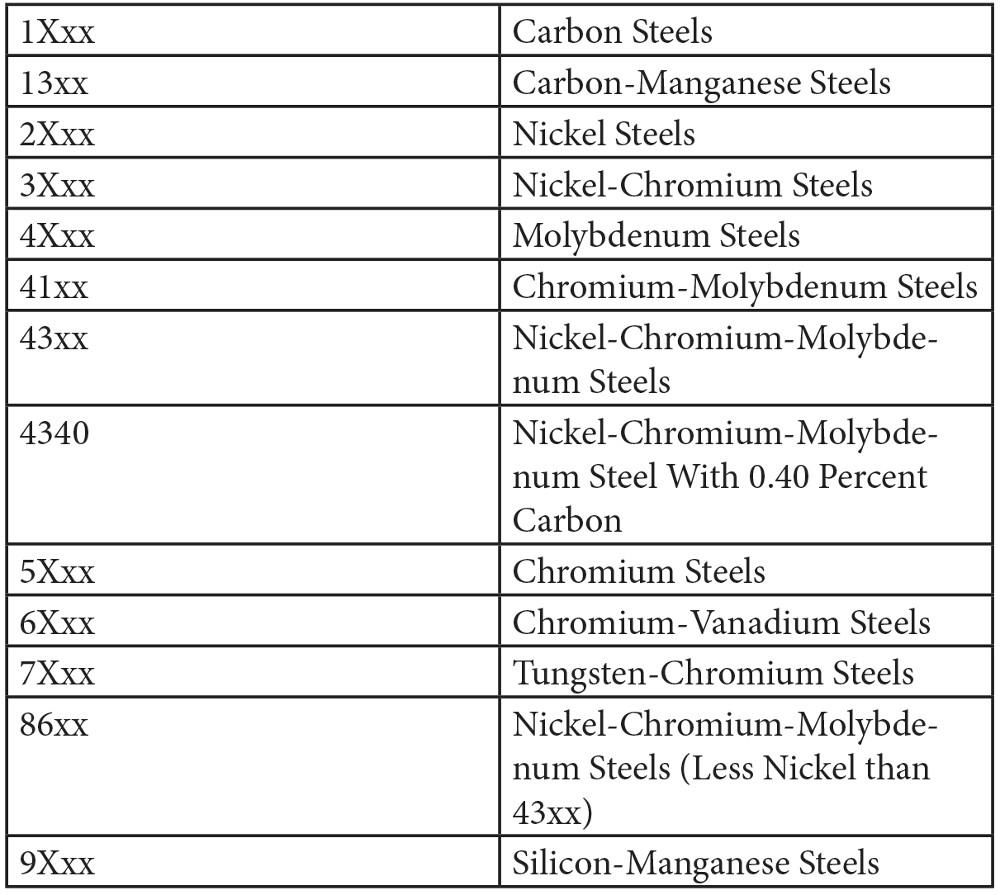
Download our comprehensive steel classification chart to streamline material selection for your next precision manufacturing project. This detailed reference guide covers mechanical properties, chemical compositions, and common applications for carbon, alloy, stainless, and tool steels.
For technical inquiries or custom material recommendations, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. As a trusted manufacturing partner with an advanced production facility in Shenzhen, Honyo Prototype ensures material traceability, strict quality control, and fast turnaround for prototyping and low-volume production.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.