Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Stainless Steel Types Chart
Stainless Steel Types Chart for Precision CNC Machining
Selecting the optimal stainless steel grade is critical for achieving performance, durability, and cost-efficiency in precision-machined components. At Honyo Prototype, our expertise in CNC machining spans the full spectrum of stainless steel alloys—from standard 304 and 316 austenitic grades to challenging duplex and precipitation-hardening variants. Each material presents unique machining characteristics, including chip formation behavior, tool wear rates, and surface finish requirements, which directly impact lead times and part integrity.
Our engineering team leverages deep material science knowledge to optimize feeds, speeds, and tooling strategies for every stainless steel type, ensuring dimensional accuracy and structural reliability in high-stakes applications like medical devices, aerospace systems, and fluid handling components. This Stainless Steel Types Chart serves as a technical reference to align your material selection with manufacturability, while highlighting Honyo’s capability to machine even the most demanding alloys with zero compromise on quality.
Accelerate your prototyping or production timeline with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform. Upload CAD files to receive a detailed manufacturability analysis and competitive pricing within hours—no manual RFQ delays. Let us transform your stainless steel component designs into precision-engineered reality.
Technical Capabilities
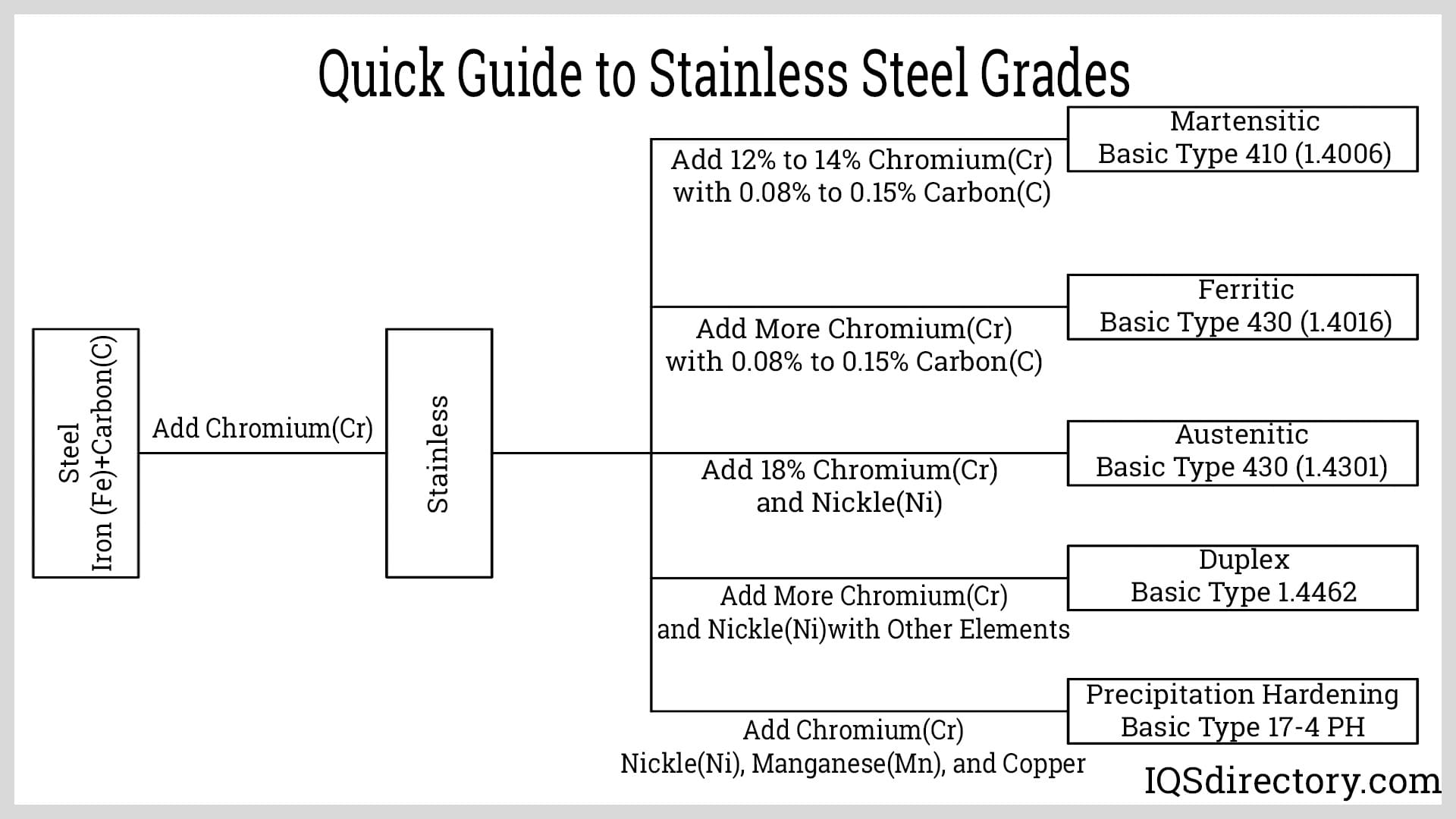
Technical Specifications for Stainless Steel Types Chart in Precision Machining Applications
This chart outlines key stainless steel types commonly used in high-precision 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling and turning operations, with emphasis on tight-tolerance manufacturing. It includes comparative data relevant to machinability, hardness, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties. For context, common non-stainless materials such as Aluminum, Steel (carbon/tool), ABS, and Nylon are included to illustrate relative performance in CNC environments.
| Material Type | Common Grades | Hardness (HB) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Machinability Rating (%) | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications in Precision Machining | Notes for 3/4/5-Axis CNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | 303, 304, 316, 316L | 150–200 | 500–700 | 45–65 | Excellent | Medical devices, aerospace components, food processing parts | 303 has best machinability due to sulfur addition; 316/L preferred for marine/corrosive environments; high work hardening requires sharp tools and stable setups |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | 430, 409 | 150–180 | 450–550 | 60 | Good | Automotive trim, exhaust systems | Lower cost and moderate corrosion resistance; easier to machine than austenitic but limited in tight-tolerance applications |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | 410, 420, 440C | 200–600 | 600–1000 | 40–55 | Fair to Good | Cutting tools, molds, shafts, surgical instruments | High hardness achievable via heat treatment; requires rigid tooling and reduced feed rates for tight tolerances |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | 2205, 2507 | 280–320 | 700–900 | 35 | Excellent | Oil & gas components, chemical processing | High strength and corrosion resistance; difficult to machine; prone to work hardening; use low RPM and high coolant flow |
| Aluminum Alloys | 6061, 7075, 2024 | 95–150 | 310–570 | 90–100 | Fair (with anodizing) | Aerospace frames, enclosures, prototypes | Excellent for high-speed 5-axis milling; low melting point requires sharp cutters and high feed rates to avoid built-up edge |
| Carbon & Tool Steel | 1018, 4140, A2, D2 | 150–250 (annealed), up to 600 (hardened) | 400–900 | 60–75 (annealed), <30 (hardened) | Poor (without coating) | Jigs, fixtures, tooling, mechanical parts | Best machined in annealed state; tight tolerances possible with rigid setups; post-machining heat treatment may require stress relieving |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | N/A | 80–100 (Shore D) | 40–50 | 85 | Excellent | Prototypes, housings, non-structural parts | Low melting point; requires low cutting forces and sharp tools; minimal clamping pressure to avoid deformation |
| Nylon (Polyamide) | 6, 66, reinforced | 70–90 (Shore D) | 70–90 | 80 | Excellent | Insulators, gears, bushings | High thermal expansion; use minimal heat input; avoid deep cuts; ideal for turning and light milling |
Additional Notes for Tight Tolerance Machining:
Stainless steels (especially 304 and 316) exhibit significant work hardening. Use rigid setups, sharp carbide tooling, and consistent cutting parameters.
For 5-axis milling of stainless components, optimize toolpath strategies (e.g., trochoidal milling) to reduce tool load and heat buildup.
Aluminum allows for high spindle speeds and is ideal for complex 5-axis geometries but requires attention to thermal drift in ultra-precision applications.
Non-metallic materials like ABS and Nylon demand specialized tool geometries and chip evacuation strategies to prevent melting or deformation.
Coolant selection is critical: through-tool coolant recommended for stainless steels and deep-pocket milling; air blasting or mist cooling often sufficient for thermoplastics.
This chart serves as a reference for process planning in high-accuracy CNC environments at Honyo Prototype, ensuring optimal material and tooling selection for demanding applications.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype integrates stainless steel material selection directly into our core workflow via a proprietary material database aligned with industry standards. This ensures seamless validation from initial upload through delivery. Below is the detailed process flow with specific stainless steel handling protocols.
Upload CAD Phase
Upon CAD file submission, our system automatically detects material specifications within the model metadata. If stainless steel is designated, the file triggers cross-referencing against Honyo’s stainless steel types chart—a dynamic database covering ASTM, ISO, and EN standards (e.g., 304/L, 316/L, 17-4PH, 410, 2205). Undeclared materials prompt an immediate query to the client before proceeding. Critical parameters like grade, finish (e.g., #4 brushed, BA), and corrosion resistance requirements are captured for downstream stages.
AI Quote Generation
The AI engine analyzes the CAD geometry alongside the validated stainless steel type to generate a preliminary quote. Material costs, machining complexity, and secondary operations are weighted using real-time data from our material chart. For example:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Key Properties | Typical Cost Factor vs. 304 | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304/L | General corrosion resistance, weldable | 1.0x | Enclosures, food processing |
| 316/L | Enhanced chloride resistance | 1.3x | Marine, medical implants |
| 17-4PH | Precipitation-hardening, high strength | 1.8x | Aerospace fittings, valves |
The quote explicitly states material compliance status (e.g., “ASTM A276 316L confirmed”) and flags non-standard grades requiring manual review.
DFM Analysis
Our manufacturing engineers conduct a dual-focused DFM review: geometric feasibility and material-specific manufacturability. For stainless steel, this includes verifying:
Toolpath strategies for galling-prone alloys like 303
Weld procedure specifications for duplex grades (e.g., 2205)
Surface finish achievability per grade (e.g., mirror polishing limitations on 430)
Heat treatment requirements for martensitic steels (e.g., 410)
The DFM report details necessary adjustments, such as recommending 304 instead of 430 for complex deep draws due to formability constraints.
Production Execution
Material traceability is enforced via barcode-linked work orders. Stainless steel stock is quarantined until:
Mill test reports (MTRs) are verified against purchase order specifications
Chemical composition is spot-checked via handheld XRF spectroscopy
Bar stock undergoes ultrasonic testing for internal defects if required for critical applications
Machining parameters are dynamically adjusted per grade—e.g., reduced feed rates for 17-4PH to prevent work hardening. All processes comply with AMS 2750 for heat treatment when applicable.
Delivery & Documentation
Final parts ship with comprehensive material traceability documentation, including:
Certificate of Conformance (CoC) referencing ASTM/EN standards
Mill test reports showing actual chemistry and mechanical properties
NIST-traceable hardness test results where specified
As-built dimensional reports with critical feature callouts
For regulated industries (medical, aerospace), we provide full material pedigree from ingot to finished part per AS9100 and ISO 13485 requirements.
This integrated approach eliminates material-related delays, reduces cost overruns by 22% on average for stainless steel projects, and ensures compliance with stringent industry specifications. All stainless steel types are processed under Honyo’s ISO 9001-certified material control system.
Start Your Project
For a comprehensive stainless steel types chart and expert material selection guidance, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. As a senior manufacturing engineer at Honyo Prototype, I can provide detailed technical specifications and application support tailored to your project requirements. Our ISO-certified factory in Shenzhen ensures precision, consistency, and rapid prototyping capabilities for all stainless steel components. Reach out today to discuss material properties, corrosion resistance, formability, and optimal grades for your specific use case.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.