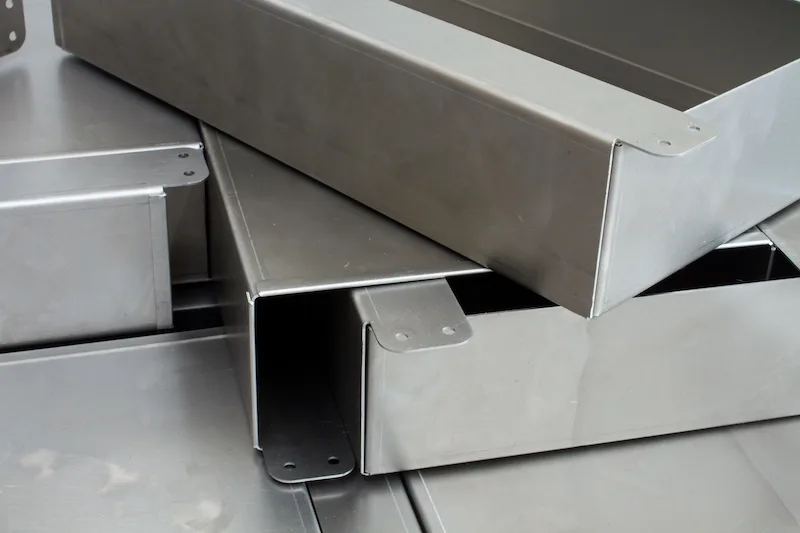
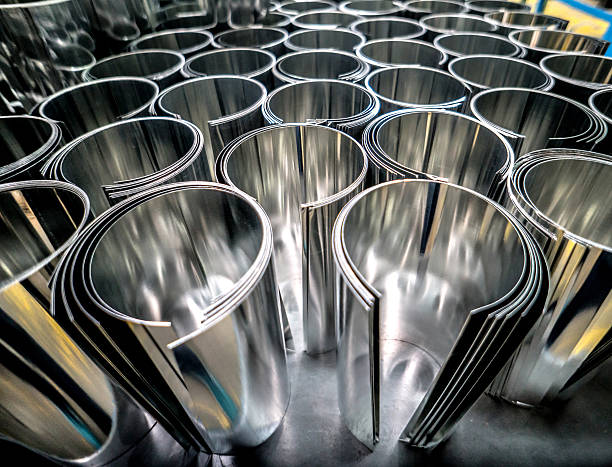
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing high-quality stainless steel sheet metal fabrication can be daunting. International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, often grapple with identifying reliable suppliers while ensuring they receive durable and cost-effective materials that meet specific project requirements. This comprehensive guide is designed to equip B2B decision-makers with the insights needed to navigate the complexities of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication.
We’ll delve into various aspects, from the different grades of stainless steel and their unique properties to applications spanning diverse industries like aerospace, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. Furthermore, we’ll outline crucial factors in vetting suppliers, such as certifications and past performance, to ensure that you partner with reputable entities.
Our discussions will also cover cost considerations, allowing you to assess potential expenses against projected budgets, while offering tips to leverage bulk negotiations effectively. By empowering you with actionable knowledge, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enabling your business to thrive in a competitive landscape. Whether you’re located in Germany or Brazil, understanding the dynamics of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication will position you for success in achieving your project goals.
Understanding stainless steel sheet metal fabrication Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, good formability | Food processing equipment, structural applications | Pros: Versatile, easily weldable; Cons: Moderate cost compared to lower grades. |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Added molybdenum enhances corrosion resistance | Chemical processing, marine environments | Pros: Superior corrosion resistance; Cons: Higher cost and less availability. |
| 301 Stainless Steel | Lower cost with reduced chromium and nickel content | Structural components, appliance enclosures | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited corrosion resistance compared to 304 and 316. |
| Custom Fabrication | Tailored designs to exact specifications and sizes | Aerospace, automotive, architectural applications | Pros: High precision; Cons: Longer lead times for customized orders. |
| Surface Finishing Types | Options vary from standard, powder coating to anodizing | Enhances aesthetic and functional properties | Pros: Improves durability; Cons: Additional costs and extended production time. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 304 Stainless Steel in Sheet Metal Fabrication?
304 stainless steel is among the most commonly used grades in sheet metal fabrication due to its versatile properties. This austenitic alloy boasts excellent corrosion resistance and is easily formed, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in the food processing industry and structural uses. B2B buyers should note its balance of performance and cost, as it typically provides good value for demanding environments. However, it may not be the best option for severely corrosive settings.
How Does 316 Stainless Steel Differentiate Itself in Fabrication Applications?
316 stainless steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments, due to its molybdenum content. This makes it particularly valuable in marine applications and chemical processing, where components are exposed to harsh conditions. For B2B buyers, the performance benefits are clear, but the higher material cost may justify an initial investment for projects needing durability and longevity. Availability can sometimes be limited compared to more common grades.
What Makes 301 Stainless Steel Suitable for Specific Projects?
301 stainless steel is a cost-effective alternative with slightly lower corrosion resistance. It finds its primary use in less demanding structural applications, such as in appliances or train components. Buyers seeking budget-friendly options will appreciate this material, though they must also consider the performance trade-offs regarding corrosion exposure. This grade can be ideal for projects where aesthetics and longevity are less critical.
Why Opt for Custom Fabrication of Stainless Steel Sheet Metal?
Custom stainless steel sheet metal fabrication allows B2B buyers to obtain parts tailored precisely to project specifications, whether for aerospace or architecture. Precision engineering offers improved fit and functionality. While custom orders typically come with longer lead times and may incur higher costs, the benefits of specificity often outweigh these drawbacks for high-stakes applications, ensuring optimal performance.
What Are the Benefits of Different Surface Finishing Types in Stainless Steel Fabrication?
Surface finishing options, including standard finishes and powder coating, enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of stainless steel components. These finishes can improve corrosion resistance and wear performance, essential for high-use products. However, buyers should factor in additional costs and potentially longer lead times associated with specific finishing processes. Understanding these options will allow companies to make informed decisions on how to enhance their products’ longevity and performance.
Key Industrial Applications of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Fabrication of food storage tanks and processing equipment | Ensures hygiene and compliance with food safety regulations | Material certification, surface finish options, and customization capabilities |
| Marine and Offshore | Manufacturing of marine equipment and components | High corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Grade selection (e.g., 316 stainless steel), welding capabilities, and lead times |
| Chemical Processing | Construction of chemical storage tanks and piping systems | Durability and resistance to aggressive chemicals | Compliance with industry standards, material certifications, and design flexibility |
| Aerospace | Production of structural components and brackets | Lightweight yet strong materials that enhance performance | Precision machining capabilities, weight specifications, and regulatory compliance |
| Automotive | Development of exhaust systems and chassis parts | Improved performance and longevity of components | Customization options, material grades, and finishing processes |
How is Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, stainless steel sheet metal fabrication is crucial for creating equipment such as storage tanks, conveyor systems, and processing machines. The inherent properties of stainless steel, including its corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning, address hygiene concerns and comply with food safety regulations. International buyers, especially from regions with stringent food safety standards, should prioritize suppliers who can provide certified materials and specialized surface finishes to ensure compliance.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Fabrication Play in Marine and Offshore Applications?
Marine and offshore industries rely heavily on stainless steel sheet metal fabrication for components like hulls, piping, and equipment exposed to saltwater. The material’s high corrosion resistance is essential for maintaining structural integrity in harsh marine environments. Buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers that specialize in marine-grade stainless steel, such as 316, and inquire about welding processes and turnaround times to meet project deadlines effectively.
How is Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Critical in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, stainless steel sheet metal fabrication is used to create storage tanks, piping, and containment systems that can withstand aggressive chemicals. The durability and resistance to corrosion offered by stainless steel are paramount for safety and efficiency. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers who can provide materials certified for chemical compatibility and offer customized designs tailored to specific processing requirements.
Why is Stainless Steel Fabrication Important in Aerospace?
The aerospace sector utilizes stainless steel sheet metal fabrication for manufacturing lightweight yet robust structural components and brackets. These parts must endure extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity. International buyers should seek out manufacturers with expertise in aerospace standards and certifications, as well as capabilities for precision machining to ensure that components meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
How is Stainless Steel Fabrication Applied in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, stainless steel sheet metal fabrication is essential for producing exhaust systems, chassis components, and decorative elements. The use of stainless steel enhances the durability and longevity of these parts, reducing maintenance costs over time. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who offer customization options and a variety of material grades to meet specific performance and aesthetic requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stainless steel sheet metal fabrication’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Long Lead Times for Custom Parts Delivery
The Problem: One of the most significant pain points for B2B buyers in the stainless steel sheet metal fabrication industry is the long lead times associated with custom parts. Buyers often face urgent project deadlines, and delays in the fabrication process can lead to missed deadlines, increased costs, and dissatisfied clients. This challenge is exacerbated when sourcing from suppliers with inefficient production schedules or lack of transparency regarding order status.
The Solution: To mitigate long lead times, B2B buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who offer real-time tracking and expedited service options. When selecting a fabrication partner, inquire about their production timelines and request detailed information about their order tracking systems. Utilize online platforms that allow for instant pricing and quick turnaround times—some services promise delivery in as little as 2-4 days. Additionally, consider placing orders well in advance and maintain open communication with your supplier to ensure they understand your timeline constraints. By establishing a reliable relationship with a responsive supplier, you can significantly reduce the risk of delays impacting your projects.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Across Different Batches
The Problem: Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is inconsistent quality in stainless steel sheet metal parts, especially when ordering multiple batches over time. Variations in material properties, fabrication processes, and surface finishes can lead to discrepancies that affect the overall performance and aesthetic of the final product. This inconsistency can be particularly problematic in industries such as aerospace, food processing, and construction, where precision and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish clear specifications and quality assurance protocols with their chosen fabricator. Request samples before placing large orders and conduct thorough inspections of initial batches. Additionally, consider working with suppliers who have robust quality control measures, such as ISO certification or third-party inspections. Building a strong partnership with your fabricator enables you to communicate your expectations clearly, and in turn, they can implement standardized processes to maintain quality across all batches. Utilize advanced technologies like CNC machining and laser cutting, which offer higher precision and repeatability, further ensuring that the quality remains uniform.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the right type of stainless steel for their specific applications, leading to challenges such as corrosion resistance, weldability, and cost-efficiency. With several grades available (e.g., 304, 316, 301), each with distinct properties, making the wrong choice can result in premature failure of parts, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To overcome the material selection challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific requirements of their application and the properties of different stainless steel grades. Engage with suppliers who can provide expert guidance on material selection based on your application’s environmental conditions and performance needs. It’s also beneficial to create a decision matrix that evaluates factors such as corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and cost for each grade. For instance, if the application involves exposure to harsh chemicals or marine environments, opting for grade 316 stainless steel may be advisable due to its superior corrosion resistance. Furthermore, consider utilizing prototyping services that allow you to test various materials before committing to large-scale production, ensuring the final choice meets your performance criteria effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
What Are the Key Properties of Common Stainless Steel Alloys for Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Stainless steel sheet metal fabrication is a critical process in various industries, and the choice of material significantly impacts product performance. Below are analyses of four common stainless steel alloys used in sheet metal fabrication, emphasizing their properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel 304 Perform in Fabrication?
Stainless Steel 304 is one of the most widely used grades in sheet metal fabrication due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good formability. It contains high levels of chromium and nickel, which enhance its resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including food processing equipment and structural components.
Pros: The alloy is relatively easy to weld and fabricate, which reduces manufacturing complexity. It also offers good mechanical properties, making it durable for many applications.
Cons: While 304 is resistant to corrosion, it is not as effective in highly corrosive environments compared to other stainless steel grades, such as 316. This limitation can affect its suitability for specific applications in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Stainless Steel 304 is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and mild acids, but may not be ideal for applications involving saltwater or aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe may prefer materials that meet DIN standards, while those in South America and Africa should consider local regulations regarding food safety and environmental impact.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel 316?
Stainless Steel 316 is known for its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and chemical environments, due to the addition of molybdenum. This property makes it ideal for applications exposed to harsh chemicals, such as chemical processing equipment and marine applications.
Pros: The enhanced corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of components, reducing maintenance costs over time. It also maintains good formability and weldability.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to 304, which may impact budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, it may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: 316 is highly compatible with aggressive media, including chlorides and acids, making it suitable for a broader range of applications than 304.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 and consider the need for certifications that verify the material’s quality, especially in regulated industries.
Why Choose Stainless Steel 301 for Cost-Effective Solutions?
Stainless Steel 301 is a lower-cost alternative to 304, featuring a higher carbon content that enhances strength but reduces corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications where cost is a primary concern, such as appliance enclosures and structural components.
Pros: The lower cost makes it an attractive option for projects with budget constraints. It also offers good mechanical properties and can be easily formed.
Cons: The trade-off for cost savings is reduced corrosion resistance, which limits its use in more demanding environments.
Impact on Application: 301 is suitable for applications that do not involve exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the trade-offs in performance and ensure that the chosen material meets local standards for durability and safety.
What Makes Stainless Steel 430 a Good Choice for Decorative Applications?
Stainless Steel 430 is a ferritic stainless steel known for its good corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is often used in decorative applications, such as kitchen equipment and architectural features.
Pros: The alloy is cost-effective and offers good resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for indoor applications. Its attractive finish enhances aesthetic appeal.
Cons: Its lower corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades limits its use in outdoor or highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: 430 is ideal for applications where appearance is important, but it may not withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards and consider the material’s suitability for local climates, especially in regions with high humidity or salt exposure.
Summary Table of Stainless Steel Materials for Sheet Metal Fabrication
| Material | Typical Use Case for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 304 | Food processing equipment, structural components | Excellent corrosion resistance and formability | Less effective in highly corrosive environments | Medium |
| Stainless Steel 316 | Chemical processing, marine applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and more complex manufacturing | High |
| Stainless Steel 301 | Appliance enclosures, structural components | Cost-effective with good mechanical properties | Reduced corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel 430 | Decorative applications, kitchen equipment | Aesthetic appeal and cost-effective | Limited corrosion resistance for outdoor use | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various stainless steel alloys, enabling informed decision-making for their fabrication needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication?
The manufacturing process of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Fabrication?
Material preparation is the foundational step where stainless steel sheets are sourced and cut to size. Suppliers typically utilize advanced cutting techniques such as laser cutting, waterjet cutting, or CNC routing to achieve precise dimensions. The choice of technique may depend on the thickness of the material and the complexity of the design. Quality control begins at this stage, where incoming materials undergo inspection to verify compliance with specifications and standards.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Stainless Steel Fabrication?
Forming processes shape the prepared stainless steel sheets into the desired configurations. Common techniques include bending, punching, and stamping. Bending, often performed with press brakes, allows for the creation of complex shapes while maintaining material integrity. Punching and stamping are used for creating holes or cutouts and can enhance the structural properties of the component. Each forming technique requires skilled operators and proper machinery to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication?
The assembly stage involves joining multiple fabricated components to create the final product. Techniques such as welding, riveting, and the use of adhesives are common. Welding is particularly favored for its strength and durability, especially in applications requiring high structural integrity. Quality assurance during assembly includes visual inspections and dimensional checks to ensure parts align correctly and meet design specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Stainless Steel Components?
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and performance of stainless steel products. Common finishing techniques include deburring, polishing, and surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating. These processes not only improve aesthetics but also increase resistance to corrosion and wear. Each finishing method has its own set of quality checks, including gloss measurements and adhesion tests, to ensure the finished product meets industry standards.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Stainless Steel Fabrication?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, especially for international B2B transactions. Adhering to recognized international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications can further validate a supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified criteria.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production to catch defects early. This includes measuring dimensions and visual inspections at various stages of fabrication.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive checks on the completed product, including functional testing and compliance verification against specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Stainless Steel Fabrication?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of stainless steel components. Common methods include:
-
Mechanical Testing: Such as tensile and hardness tests to evaluate material properties.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or radiography to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
-
Surface Analysis: Testing for corrosion resistance and surface finish quality through methods like salt spray tests and gloss measurements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control measures is crucial to ensure product reliability. Buyers can take several steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality control processes and adherence to standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports, including test results and compliance certificates.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices and product reliability.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control and certification nuances. Understanding the specific regulations and standards relevant to their industry is vital. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while Middle Eastern buyers might look for compliance with local industry standards. Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can impact how quality assurance is perceived and implemented.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication are multifaceted and critical for ensuring product integrity and performance. B2B buyers must be well-informed about these processes to make educated decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that their needs for quality, reliability, and compliance are met. By prioritizing robust quality control practices and understanding the manufacturing intricacies, buyers can foster successful partnerships with suppliers in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stainless steel sheet metal fabrication’
In the competitive landscape of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, sourcing the right supplier is crucial for ensuring quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure stainless steel sheet metal components effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your project requirements, including dimensions, tolerances, and material grades. This step is critical as it directly influences the fabrication process and the final product’s performance. For stainless steel, consider factors such as corrosion resistance (e.g., opting for 304 or 316 grades), thickness, and surface finish.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in stainless steel sheet metal fabrication. Look for companies with extensive experience and positive customer reviews. Utilize online directories and industry forums to gather insights about their capabilities and reputation.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify the certifications of your shortlisted suppliers. Certifications like ISO 9001 or AS9100 indicate adherence to quality management systems, which is vital for ensuring consistent product quality. Additionally, check for industry-specific certifications relevant to your application, such as food safety standards for food processing equipment.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, request samples or prototypes to assess the quality of their work. This step allows you to evaluate the material properties and workmanship firsthand. Pay attention to details such as finish quality, dimensional accuracy, and any signs of defects.
Step 5: Inquire About Production Capabilities
Discuss the production capabilities of your potential suppliers, including their machinery, technology, and workforce expertise. Understanding their capacity to handle your order volume and complexity is essential for ensuring they can meet your timelines. Ask about their lead times, especially for bulk orders.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you are satisfied with the quality and capabilities of a supplier, initiate discussions on pricing and payment terms. Be transparent about your budget and expectations, and consider negotiating for bulk discounts or favorable payment terms. A clear agreement helps prevent misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish a communication plan to facilitate ongoing dialogue with your chosen supplier. Clear communication is vital for managing expectations and addressing any potential issues that may arise during production. Set regular check-ins to discuss project progress and any modifications needed along the way.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process and ensure they partner with a reliable supplier for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication. This proactive approach minimizes risks and enhances the likelihood of successful project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication?
When sourcing stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: Stainless steel is available in various grades, such as 304 and 316, each influencing the cost. The price per sheet can fluctuate based on market demand, alloy composition, and thickness. For instance, the price of 316 stainless steel, known for its superior corrosion resistance, will generally be higher than that of 304.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for processes like cutting, welding, and finishing. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region, with higher wages in developed markets like Germany compared to developing regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the facilities, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, thereby reducing the overall cost.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for tooling can be a substantial investment, especially for custom parts. This cost is often spread over the volume of production, making it more economical for larger orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final product meets industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspection, which can add to costs. Certifications like ISO or industry-specific standards can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must be factored into the total cost. International shipping can introduce additional fees, customs duties, and delays, particularly when sourcing from suppliers across continents.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on their business model and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs, unique specifications, or complex geometries can increase costs. Providing precise drawings and detailed specifications can help mitigate additional charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications for specific applications (e.g., food-grade stainless steel) can increase costs but are essential for compliance in certain industries.
-
Supplier Factors: Reliability, reputation, and the supplier’s location can impact pricing. Working with established suppliers may yield better service and quality assurance but could come at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital, as they dictate who bears the risk and cost of transportation. FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) are common terms that can affect overall pricing.
What Tips Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
To achieve cost efficiency in sourcing stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Contracts: Leverage volume commitments or long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing and terms with suppliers.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also logistics, quality assurance, and potential rework costs. A lower upfront price may result in higher TCO if quality issues arise.
-
Explore Local Sourcing: For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing responsiveness.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of how currency fluctuations and regional economic conditions can affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly assess market trends and pricing benchmarks to ensure you are getting competitive quotes. This can also help in identifying new suppliers or alternative materials that may offer cost savings.
By being informed about these cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their procurement processes and optimize their overall expenditure in stainless steel sheet metal fabrication.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stainless steel sheet metal fabrication With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Sheet Metal Fabrication Solutions
In the realm of manufacturing and industrial applications, stainless steel sheet metal fabrication is highly regarded for its excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and versatility. However, businesses may explore alternatives that align better with specific project requirements, budget constraints, or environmental considerations. Understanding these alternative solutions allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions, optimizing their manufacturing processes while meeting quality expectations.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication | Aluminum Sheet Metal Fabrication | Carbon Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High corrosion resistance; excellent formability | Lower strength under high stress; lightweight | High strength-to-weight ratio; prone to rust |
| Cost | Generally higher due to material costs | Moderate, often lower than stainless | Low-cost option, especially in bulk |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tools and expertise | Easier to machine and weld; less technical skill needed | Requires welding expertise; cut and form easily |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; scrubbing suffices for cleanliness | Requires surface treatment to prevent oxidation | High maintenance; needs coatings to resist rust |
| Best Use Case | Harsh environments (marine, chemical) | Aerospace, automotive, packaging | Structural applications, temporary fixtures |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Aluminum Sheet Metal Fabrication
Aluminum is recognized for its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a popular substitute for stainless steel, particularly in applications like aerospace and transportation. The ease of machining and cost-effectiveness are significant advantages. However, aluminum’s strength under high stress is lower than that of stainless steel, which might limit its application in demanding environments. For businesses seeking a balance between weight and durability for non-corrosive environments, aluminum provides a flexible solution.
Carbon Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication
Carbon steel is favored for its affordability and high strength, making it suitable for various structural applications. Its low cost makes it attractive for projects with tight budgets, especially when ordering in bulk. However, carbon steel is highly susceptible to rust and corrosion, which necessitates the application of protective finishes, such as galvanizing or painting. This added maintenance requirement can deter some users, particularly in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. For applications where structural integrity is paramount and conditions are less aggressive, carbon steel can be a viable option.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Fabrication Solution
When selecting a fabrication method, B2B buyers must evaluate their unique project requirements, including environmental factors, budget, and required performance characteristics. Stainless steel sheet metal fabrication excels in durability and corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh industrial environments. Aluminum offers a lighter and more cost-effective alternative for specific applications, while carbon steel presents an economical option, albeit with increased maintenance needs. By thoroughly assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and product specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stainless Steel in Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Understanding the essential technical properties of stainless steel is crucial for B2B buyers involved in sheet metal fabrication. The following specifications significantly impact the decision-making process regarding material selection and operational effectiveness.
1. Material Grade
Material grades, such as Stainless Steel 304 or 316, define the alloy’s composition and functional properties. Grade 304 is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and is widely used for non-critical applications, while Grade 316 offers enhanced resistance due to its molybdenum content, making it ideal for harsher environments like chemical processing and marine applications. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures the longevity and reliability of fabricated products.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. In sheet metal fabrication, achieving tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 inches) is essential for applications requiring high precision, such as aerospace parts and medical devices. Tighter tolerances can lead to improved product performance and reduced costs associated with rework or backorders.
3. Yield Strength
Yield strength indicates the maximum stress that stainless steel can withstand before deforming. For example, Stainless Steel 304 has a yield strength of around 215 MPa. Understanding yield strength is critical for B2B buyers as it influences the design and weight of components, affecting both functionality and cost-efficiency.
4. Elongation at Break
Elongation refers to the material’s ability to stretch before breaking, expressed as a percentage. This property is particularly important for applications requiring bending or forming, as higher elongation values (like the 70% for Grade 304) enable better shaping without cracking. A good elongation property is essential for ensuring the reliability of parts under stress.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Familiarizing yourself with pertinent trade terminology can streamline communication and transactions between buyers and suppliers. Below are several critical terms in the sheet metal fabrication industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers that align with their production needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and planning inventory. Suppliers may set an MOQ to ensure cost-effectiveness in production.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that requests pricing and terms for specific goods or services. B2B buyers typically use RFQs to obtain competitive quotes from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make an informed decision based on quality and cost.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is vital for minimizing risks and ensuring smooth logistics in global supply chains.
5. Fabrication Tolerance
This term refers to the acceptable range of variation in the dimensions of finished products. Different industries may have specific standard tolerances, impacting the feasibility and quality of the output. Aligning expectations regarding fabrication tolerance can prevent misunderstandings and errors in production.
Grasping these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, fostering strong supplier relationships and ultimately enhancing their competitiveness in various markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stainless steel sheet metal fabrication Sector
What are the Key Drivers and Trends Transforming the Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Market?
The global stainless steel sheet metal fabrication market is witnessing dynamic changes driven by various factors. First, the increasing demand for corrosion-resistant materials across industries—such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and food processing—has led to a sustained rise in the popularity of stainless steel. The material’s inherent characteristics, including high mechanical strength, formability, and hygiene, make it particularly attractive for international B2B buyers.
Technological advancements in fabrication processes like laser cutting, CNC machining, and rapid prototyping are reducing lead times and increasing production efficiency, which appeals to businesses that need swift turnaround on customized components. Notably, the rise of online platforms enabling instant quoting and ordering is reshaping how buyers interact with suppliers. These platforms cater specifically to smaller businesses or startups that might require lower volume orders without sacrificing quality or service speed.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America are contributing to an uptick in sourcing activity, as industrialization accelerates and local manufacturers seek competitive, high-quality stainless steel solutions. For international B2B buyers, an essential trend to watch is the shift towards multi-supplier strategies in procurement, allowing businesses to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
How Can B2B Buyers Address Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Their Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Decisions?
Environmental concerns and ethical sourcing are now key considerations for international B2B buyers in the stainless steel sheet metal fabrication sector. The production and post-production processes of stainless steel can have significant environmental impacts, from energy consumption to emissions. Thus, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer sustainable practices and products.
Opting for certified “green” materials, which are produced with less environmental impact, or recycled content stainless steel can reduce the carbon footprint of fabricated products. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and programs like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming benchmarks for assessing suppliers’ environmental commitments.
Furthermore, fostering ethical supply chains—where materials are sourced responsibly and workers are treated fairly—is gaining traction. As global consumers become more environmentally conscious, B2B buyers must align with suppliers who share similar values and are transparent about their sourcing practices. This not only enhances the company’s brand reputation but also opens avenues for customers who prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
What is the Historical Context of Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
Stainless steel has been a significant material in industrial applications since the early 20th century, when its combination of strength, resistance to corrosion, and aesthetic appeal were first recognized. Originally used in cutlery and kitchenware, its application soon expanded into various industries, including aerospace and architecture.
The evolution of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication has been marked by advancements in alloy compositions and manufacturing techniques, leading to significant improvements in durability and versatility. The introduction of austenitic stainless steel grades, such as 304 and 316, brought forth materials specialized for specific applications, enhancing performance in extreme environments.
Today, the history of stainless steel fabrication contributes to its ongoing relevance in modern markets. A solid understanding of material properties allows contemporary B2B buyers to make informed choices about their sourcing strategies, integrating historical insights with current technological advancements to meet the fast-paced demands of the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
-
How do I choose the right stainless steel grade for my project?
Selecting the appropriate stainless steel grade hinges on the application’s specific requirements. For example, 304 stainless steel is highly versatile, offering excellent corrosion resistance and formability, making it ideal for general use. If your project involves exposure to harsh environments, such as chemical processing, consider 316 stainless steel, which includes molybdenum for superior corrosion resistance. Evaluating factors such as tensile strength, weldability, and industry standards can help in making an informed decision. -
What are the typical lead times for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication?
Lead times for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication can vary based on complexity and volume. Generally, standard production times range from 2 to 4 weeks. However, some suppliers offer expedited services that can reduce this timeframe significantly. It’s crucial to discuss your urgent needs with the supplier upfront to ensure they can accommodate your timeline and plan for potential delays that international shipping may introduce. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) can I expect when sourcing from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities vary widely among suppliers and can depend on the specific fabrication processes and materials required. Many suppliers cater to both small and large businesses, offering no minimum orders on certain services. However, for customized parts or larger projects, you may encounter MOQs ranging from 25 to 100 units. Always clarify MOQ with suppliers during your initial discussions to ensure alignment with your purchasing requirements. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for stainless steel fabrication?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, production capabilities, and quality control processes. Request case studies or references to understand their past performance, especially in your industry. Inquire about their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, consider their communication responsiveness and willingness to collaborate, as a strong partnership is crucial for successful project delivery. -
How can I customize my stainless steel sheet metal components?
Customization options for stainless steel components are extensive and may include cutting, bending, surface finishes, and adding hardware. Most suppliers allow you to specify dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. To streamline the process, provide comprehensive CAD files, sketches, or templates to convey your design intent clearly. Engaging with the supplier’s design team early on can also foster additional recommendations for optimizing your product. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by stainless steel fabrication suppliers?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and are often negotiated based on order size, business relationships, and geographic factors. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or upfront payments for smaller orders. It’s advisable to clarify payment options early in negotiations, especially with international suppliers where currency exchange and payment methods could introduce complexities. Ensure to discuss any potential discounts for bulk purchases to maximize cost-effectiveness. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from my fabricator?
Quality assurance is pivotal in stainless steel sheet metal fabrication. Suppliers should implement stringent QC processes, including material testing, dimensional inspections, and surface checks. Look for suppliers that offer certifications, such as certifications for welding processes and ISO 9001 compliance. Establishing a clear QA plan early in the collaboration can help align expectations and address potential issues proactively. -
How does logistics work for international orders of stainless steel sheet metal?
Logistics for international orders involves coordinating shipping methods, customs requirements, and delivery timelines. Most suppliers can assist with logistics by offering shipping options that balance time and cost. During negotiations, inquire about who handles customs and tariffs to ensure you are aware of potential extra charges. Establish an understanding of delivery schedules and tracking systems, which help manage your project timeline efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SendCutSend – Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: SendCutSend offers custom sheet metal fabrication services including laser cutting, CNC routing, waterjet cutting, anodizing, bending & forming, countersinking, dimple forming, hardware insertion, plating, powder coating, tapping, tumbling, and deburring. The company caters to both high and low quantity orders with no minimum required. They provide instant pricing through file uploads in STEP, DXF…
2. Cut2Size Metals – Custom Metal Fabrication
Domain: cut2sizemetals.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Cut2Size Metals offers custom metal fabrication services and a wide variety of metal products including: Aluminum (sheets, plates, diamond plates, expanded metal, pipes, tubing, bars, channels, angles), Stainless Steel (sheets, plates, expanded metal, pipes, tubing, threaded rods, bars, flat bars), Brass (sheets, plates, bars), and Copper (sheets, plates, bars). They provide custom cutting to any …
3. Great Lakes Stainless – Stainless Steel Fabrication Solutions
Domain: greatlakesstainless.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Great Lakes Stainless specializes in stainless steel fabrication, focusing on unique challenges associated with stainless steel sheet metal design and manufacturing. Key capabilities include:
– Material handling with specialized equipment to prevent scratches and damage.
– Use of a 4KW fiber laser for precise cutting, utilizing 3,000 gallons of liquid Nitrogen for clean cutting.
– A specialized tw…
4. SSFab – Stainless Steel Tanks & Pans
Domain: ssfab.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Rectangular Tanks & Batch Cans: Made from 18 gauge Type 304 & Type 316 material with optional drains; used in medical, pharmaceutical, restaurant supply, food processing industries.
Stainless Steel Pans & Tapered Trays: Made from 22 gauge Type 316 material; used in pharmaceutical industry with custom sizes available.
Stainless Steel Utility Carts & Mobile Machine Stands: Made fro…
5. RapidDirect – Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: rapiddirect.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Fabrication Service: Precision stainless steel sheet metal fabrication for durable, corrosion-resistant parts. Quick lead times (< 5 days) and cost-effective solutions. Available stainless steel grades: SUS303, SUS304, SUS316. Wall Thickness: 0.2 mm, Tolerances: ISO2768-C, Max Part Size: 200 x 80 x 100 cm. Surface finishing options include: Machined, Sand Blasting, Tumb…
6. Proto Labs – Stainless Steel for Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel for Sheet Metal Fabrication offers two types of stainless steel: 304 and 316. 304 stainless steel is available in two surface finishes – 2B (low shine, cost-effective) and #4 (brushed aesthetic). It is suitable for indoor applications but may corrode in high-chloride or high-heat environments. 316 stainless steel, which includes molybdenum, is better for marine environments and che…
7. Zetwerk – Stainless Steel Fabrication
Domain: zetwerk.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Stainless steel fabrication techniques include cutting, bending, forming, welding, and finishing techniques. Key cutting methods are shearing, plasma cutting, laser cutting, and waterjet cutting. Bending techniques include press brake bending, roll bending, hydraulic press forming, and spinning. Welding techniques consist of TIG welding, MIG welding, resistance spot welding, and submerged arc weld…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stainless steel sheet metal fabrication
In the ever-evolving landscape of stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for achieving operational excellence and competitive advantage. By leveraging a diverse range of materials such as 304 and 316 stainless steel, buyers can ensure optimal selection for their specific applications, whether in industrial, food processing, or chemical sectors. Understanding key properties and pricing dynamics allows businesses to make informed decisions that enhance profitability and product quality.
Moreover, the integration of advanced technologies—like instant pricing tools and expedited services—enables quicker turnaround times and streamlined supply chain management. For international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with reputable suppliers fosters reliability and can lead to significant cost reductions.
As we look to the future, fostering partnerships with leading fabrication services will not only facilitate timely deliveries but also provide access to innovative manufacturing capabilities. Engaging proactively in this strategic sourcing process empowers businesses to navigate market uncertainties while enhancing their production capabilities. Now is the time to embrace the opportunities in stainless steel sheet metal fabrication—partner wisely and invest in your supply chain success.