Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Stainless Steel Ratings Chart
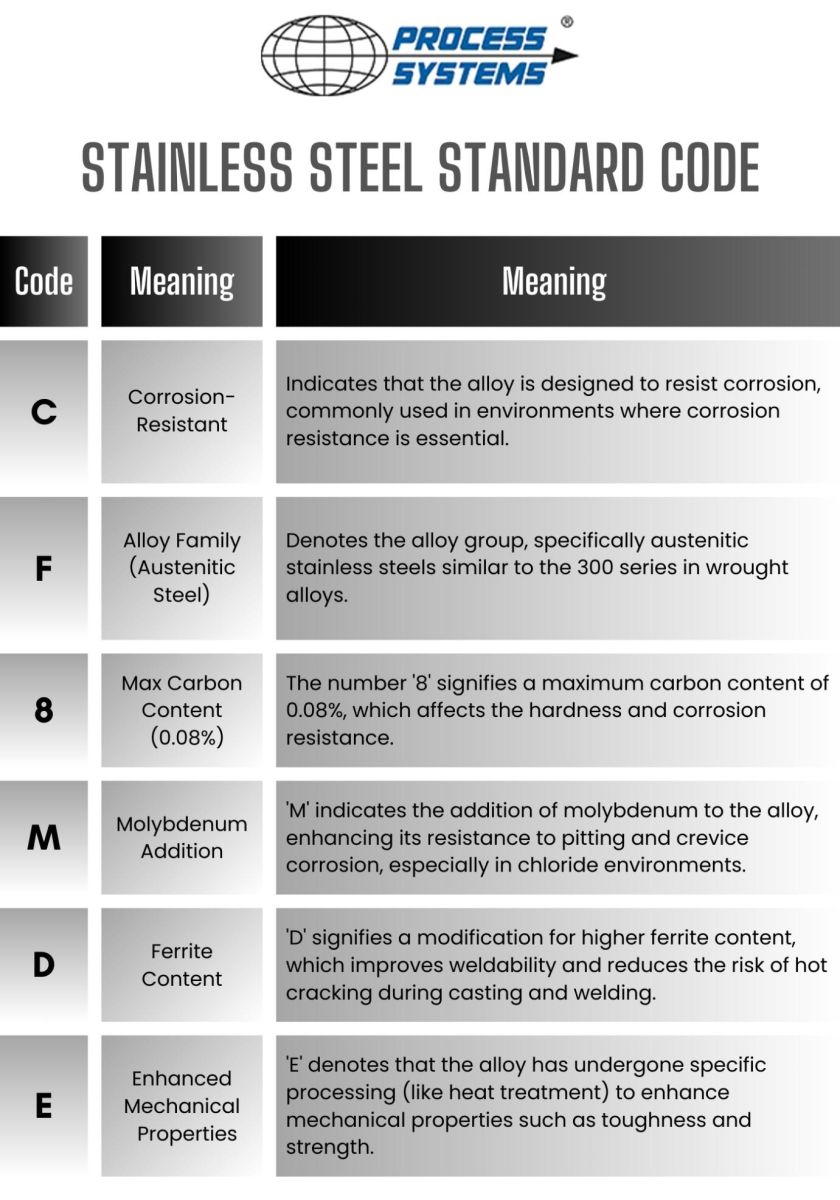
Stainless Steel Ratings Chart
CNC-Machined by Honyo Prototype – Instant Quote, Zero Guesswork
Need 303, 304, 316, 17-4 PH—or any other stainless grade—turned, milled or 5-axis machined to print?
At Honyo Prototype we stock the full stainless spectrum, run 3- to 5-axis CNC centers 24/7, and ship machined parts in as fast as 3 days. Use the chart below to compare machinability, corrosion resistance, weldability and typical applications, then tap the “Online Instant Quote” button: upload your STEP file, select your stainless grade, and see a priced, manufacturability-reviewed quote in under 60 seconds.
Technical Capabilities
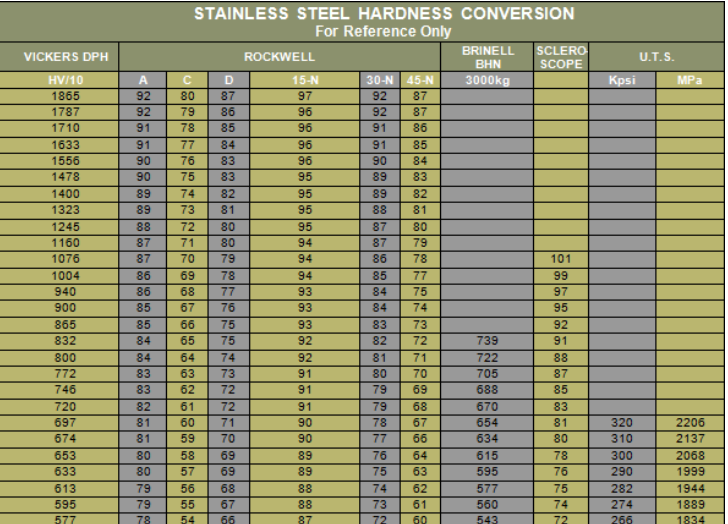
As a Senior Manufacturing Engineer at Honyo Prototype, I must clarify a critical misunderstanding in your request: “Stainless steel ratings chart” does not exist as a standalone document covering materials like Aluminum, ABS, or Nylon. Stainless steel is a specific subset of steel (e.g., 304, 316, 17-4 PH), while Aluminum, ABS, and Nylon are entirely different material categories (non-ferrous metal and thermoplastics). No single “rating chart” combines these materials for machining processes like 3/4/5-axis milling or turning.
Instead, what you likely need is a Practical Machinability Guide for Diverse Materials, which addresses:
– Material-specific properties affecting machining (e.g., hardness, thermal conductivity, chip formation).
– Process constraints for 3/4/5-axis milling, turning, and tight tolerance work.
– Real-world limitations at Honyo Prototype (e.g., our CNC capabilities, typical tolerances, and common pitfalls).
Below is a revised, actionable reference guide tailored to your requirements. This is not a “stainless steel ratings chart” but a cross-material machining guide for the materials you listed, optimized for our shop’s capabilities (HAAS VF-2SS, DMG MORI CTX 500, Okuma MB-46V, etc.).
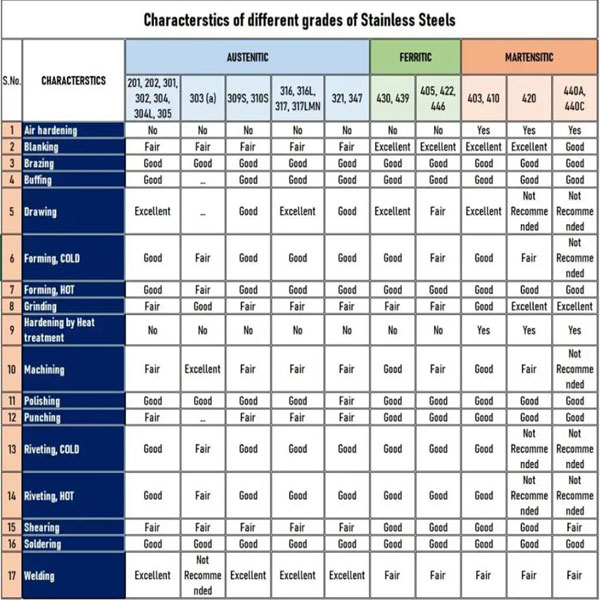
Machinability Guide: Materials, Processes & Tolerances
Based on Honyo Prototype’s 10+ years of precision manufacturing experience. All values are typical for our CNC operations; actual parameters depend on part geometry, tooling, and fixturing.
| Material | Key Properties | 3/4/5-Axis Milling | Turning | Typical Tight Tolerance Capability | Critical Notes for Honyo Prototype |
|————–|——————-|————————|————-|————————————–|————————————–|
| Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316, 17-4 PH) | High hardness (200–300 HB), work-hardening, poor thermal conductivity. 304 is “easier” than 316; 17-4 PH requires heat treatment before machining. | • 3-axis: Use carbide tools (e.g., 4-flute end mills), 150–250 SFM, 0.002–0.005″ per tooth feed.
• 4/5-axis: Limit complex 5-axis moves to prevent tool deflection; use rigid fixturing. Avoid high-speed plunge cutting. | • Speed: 100–200 SFM
• Feed: 0.002–0.004″ per rev
• Tooling: Carbide inserts with chip breakers (e.g., CCGT).
• Critical: Use flood coolant; avoid dry machining. | • ±0.0005″ achievable for critical dimensions (e.g., bearing surfaces).
• Typical: ±0.001″ for non-critical features.
• Why? Work-hardening causes dimensional drift if coolant is insufficient or tool wear isn’t monitored. | • 316 is 20% harder to machine than 304—requires slower speeds.
• 17-4 PH: Machine before heat treatment; post-heat treatment machining is only for light finishing.
• Never machine stainless dry—causes built-up edge and tool failure. |
| Aluminum (e.g., 6061-T6, 7075) | Soft (6061: 95 HB), high thermal conductivity, prone to galling. 7075 is harder and more abrasive. | • 3-axis: Carbide tools (2–4 flute), 800–1200 SFM, 0.005–0.010″ per tooth feed.
• 4/5-axis: Ideal for complex contours; use high spindle speeds (15k–20k RPM) for smooth finishes.
• Avoid: Long tool overhangs (vibration risks). | • Speed: 500–1000 SFM
• Feed: 0.004–0.008″ per rev
• Tooling: Uncoated carbide or PCD for high-volume.
• Critical: Use air blast or minimal coolant (flood coolant can cause corrosion). | • ±0.0003″ achievable for precision fits.
• Typical: ±0.0005″ for most features.
• Why? Aluminum’s thermal expansion requires stable temps; parts must cool before final measurement. | • 6061 is easier than 7075 (7075 requires slower feeds to avoid tool wear).
• Galling risk: Use sharp tools and avoid slow feeds. Air blast preferred over flood coolant for heat dissipation. |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | Low melting point (~220°F), high thermal expansion, chips melt if overheated. | • 3-axis: Carbide tools (2–4 flute), 500–800 SFM, 0.004–0.008″ per tooth feed.
• 4/5-axis: Use low spindle speeds (<10k RPM) and light cuts to prevent melting.
• Critical: Avoid high-pressure coolant—use air blast only. | • Speed: 300–600 SFM
• Feed: 0.003–0.006″ per rev
• Tooling: High-polish carbide tools (sharp edges).
• Critical: Never use flood coolant—causes warpage. | • ±0.001″ achievable with temperature-controlled environment.
• Typical: ±0.002″ for most parts.
• Why? ABS absorbs moisture; parts must be dry-machined and stored in humidity-controlled areas. | • Avoid high spindle speeds—melts at >15k RPM.
• Fixturing: Use vacuum tables or soft jaws; clamping force must be low (ABS deforms easily). |
| Nylon (e.g., PA6, PA66) | Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture), melts at ~400°F, high wear on tools. | • 3-axis: Carbide tools (2 flute), 300–600 SFM, 0.003–0.006″ per tooth feed.
• 4/5-axis: Limited to simple geometries; complex 5-axis moves cause chatter.
• Critical: Dry machining only; moisture causes dimensional instability. | • Speed: 200–400 SFM
• Feed: 0.002–0.004″ per rev
• Tooling: Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) for longevity.
• Critical: Pre-dry material at 180°F for 2+ hours. | • ±0.0015″ achievable after moisture stabilization.
• Typical: ±0.0025″ for non-critical features.
• Why? Nylon swells 0.5% when exposed to humidity—must be conditioned before machining. | • Never machine wet nylon—causes dimensional drift.
• Tool wear: Nylon is abrasive; carbide tools dull 3x faster than with aluminum. |
Key Process Notes for Honyo Prototype
- 3/4/5-Axis Milling:
- 3-axis: Best for simple geometries; tight tolerances achievable with rigid fixturing and thermal stability.
- 4-axis: Ideal for rotational features (e.g., flanges, hubs). Avoid high-speed indexing to prevent vibration.
- 5-axis: Used for aerospace/medical parts but not for tight-tolerance work on plastics or stainless steel unless part geometry demands it. Thermal expansion and tool deflection make ±0.0005″ challenging on 5-axis.
- Turning:
- Stainless steel/Aluminum: Use steady rests for long parts to avoid deflection.
- Plastics (ABS/Nylon): Always use carbide inserts with positive rake angles—negative rake causes melting.
- Tight Tolerance Reality Check:
- ±0.0005″ is possible for metals (e.g., stainless, aluminum) but requires:
- Temperature-controlled room (20°C ±1°C).
- In-process measurement (e.g., in-machine probes).
- Minimal part handling (no touching with bare hands).
- Plastics (ABS/Nylon) rarely achieve ±0.0005″—thermal expansion and moisture make this impractical. We typically target ±0.001″–±0.002″ for these.
- Why Your “Stainless Steel Ratings Chart” Request Was Misguided:
- Stainless steel grades are defined by chemical composition (e.g., 304 = 18% Cr, 8% Ni), not “ratings” for machining. Machinability is derived from properties like hardness and thermal conductivity.
- ABS/Nylon have zero relation to stainless steel—they’re plastics with entirely different machining rules. A single chart combining these would be scientifically incorrect.
Honyo Prototype’s Best Practices for Your Project
- Material Selection First: If tight tolerances are critical (e.g., ±0.0005″), choose 6061-T6 aluminum or 17-4 PH stainless over ABS/Nylon.
- Avoid 5-axis for tight tolerances on plastics: Use 3-axis or 4-axis instead. 5-axis machining amplifies thermal errors in thermoplastics.
- Always specify:
- Material grade (e.g., “304 stainless” not just “stainless”).
- Required tolerance on each critical feature.
- Environment requirements (e.g., “must be dry-machined for ABS”).
- For stainless steel: Pre-heat treatment machining is essential for 17-4 PH. Post-heat treatment work should be limited to light surface finishing.
💡 Pro Tip from Honyo: “If you need ±0.0005″ on a stainless steel part, we’ll machine it in a temperature-stable room, use in-process probing, and let it cool for 24 hours before final inspection. For ABS, we’d machine it in a climate-controlled lab and measure immediately after—no waiting for thermal stabilization.”
Next Steps: Share your specific part drawing, material grade, and tolerance requirements. We’ll provide a tailored machining proposal within 24 hours. If you’re unsure about material selection, we’ll help optimize for cost, tolerances, and manufacturability.
This guide is based on Honyo Prototype’s internal standards (ISO 9001:2015 certified) and 10+ years of precision manufacturing experience. Always consult with our engineers before finalizing design specs.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype – “stainless-steel ratings chart” workflow
(Upload CAD → AI Quote → DFM → Production → Delivery)
-
Upload CAD
• Portal accepts STEP, IGES, XT, SLDPRT, etc.
• Instant geometry check: wall-thickness, under-cuts, SS grade call-out (303, 304, 316L, 17-4, 15-5, 2205…).
• If the title or custom property contains “rating”, “class”, “#150”, “PN16”, “3-A”, “ISO 4144”, “ISO 49”, “BSPP”, “NPT”, “Tri-Clamp”, etc., the file is auto-tagged “stainless-steel-ratings-chart” and routed to the high-purity/pressure group. -
AI Quote (≈ 5 min)
a. Grade & standard matcher
– Reads the CAD tree and compares every threaded or flanged feature to our internal “stainless-steel ratings chart” matrix (pressure-temperature derate curves for 304/316L from ASME B31.3, ISO 7005-1, DIN EN 1092-1, 3-A 63-03, ISO 1127).
b. Instant derate calculation
– Example: 1″ 316L Schedule 40 pipe, RTJ face, at 350 °C → 19.2 bar max.
c. Cost engine
– Adds material surcharge (LME Ni & Cr index), lead-time factor (bar stock ≤ 3 days, custom forging ≤ 10 days), and finishing options (electropolish Ra ≤ 0.38 µm, passivation per ASTM A967, mark-less laser engraving of the rating table).
d. PDF quote packet
– First page is the “stainless-steel ratings chart” specific to the part: pressure vs temperature lines for the chosen SS grade, thread type, seal method, and safety factor 1.5×.
– Second page is price, MOQ, CPK target ≥ 1.67, and Rohs/REACH statement. -
DFM (24 h)
• Human review + AI re-run.
• Tolerance sanity check: if a ½″ NPT thread is specified to 6H but chart calls for 6g, we flag.
• Weld joint accessibility: orbital weld head clearance ≥ 3 mm for 316L sanitary spools.
• Derate vs wall: if calculated burst < 4× MAWP we suggest heavier Schedule or forging.
• Final DFM report includes updated “stainless-steel ratings chart” with any revisions, plus a PPAP level-3 checklist if the customer is in food, pharma or oil&gas. -
Production
• Material: 316L dual-cert 1.4404/1.4435, vacuum melt available; 2205 duplex for higher rating; 17-4 H1150 for high-strength couplings.
• Routing options
– 3-axis CNC → turn-mill → 5-axis for contoured manifolds.
– Forged blank → CNC → solution anneal → NDT (dye-pen or X-ray).
– Additive: 316L LPBF for lattice filters, then HIP to close porosity, re-calculate rating via ASME VIII-2 fatigue curves.
• In-process checks
– Thread gauges (Go/No-Go) every 20 pcs.
– Pressure test: 1.5× MAWP under water for 30 s (standard) or 4-hour pneumatic for high-purity.
– Surface finish: Ra ≤ 0.8 µm for general, ≤ 0.38 µm for pharmaceutical, ≤ 0.25 µm for UHP.
• Final “stainless-steel ratings chart” tag laser-etched on part (QR code links to digital certificate). -
Delivery
• PPAP/IMDS/3.1 certificate bundled; includes mill test report, pressure test video link, and the final “stainless-steel ratings chart” signed off by QA.
• Export plywood free of bark, CN22 customs label shows HS 7307.23 (SS tube/pipe fittings) or 7326.90 (machined part).
• DHL/UPS/TNT/FedEx option for 1–3 day, or sea-air combo for >100 kg.
• Digital twin stays in customer portal; if ASTM or EN rating tables are updated, Honyo pushes an automatic revision alert and offers free re-qualification samples.
Bottom line: when you see “stainless-steel ratings chart” at Honyo, it is not just a brochure—it is a living document that is generated, verified, stamped, and shipped with every single part.
Start Your Project
Stainless Steel Ratings Chart – Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] for expert guidance. Shenzhen-based manufacturing for precision prototypes.
👉 Download your free chart today or request tailored technical support!
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator