Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Stainless Steel Machining Properties

Precision Stainless Steel Machining: Overcoming Material Challenges with Honyo Prototype
Stainless steel remains a cornerstone material for demanding applications across aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors due to its exceptional corrosion resistance, strength, and biocompatibility. However, its inherent properties—such as work hardening, low thermal conductivity, and high abrasiveness—pose significant challenges in CNC machining. These characteristics can lead to accelerated tool wear, dimensional inaccuracies, and compromised surface finishes if not addressed through specialized processes and expertise. At Honyo Prototype, we leverage decades of metallurgical insight and advanced CNC capabilities to transform these challenges into opportunities for precision and reliability.
Our dedicated stainless steel machining protocols are engineered to mitigate material-specific risks. We deploy optimized toolpath strategies, rigid fixturing, and coolant-rich environments to manage heat generation and prevent work hardening. Precision-controlled spindle speeds and feed rates ensure consistent chip evacuation, while our premium carbide tooling maintains edge integrity across complex geometries. This systematic approach guarantees tight tolerances (±0.0002″ achievable), superior surface finishes (Ra 0.8 µm standard), and structural integrity—critical for components operating in high-stress or sterile environments.
Below outlines key machining parameters we tailor for common stainless steel grades:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Typical Machining Challenge | Honyo’s Mitigation Strategy | Max Tolerance Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 / 304L | Severe work hardening | High-pressure coolant, interrupted cut strategies | ±0.0005″ |
| 316 / 316L | Galling and built-up edge | Sub-micron coated tools, optimized chip breakers | ±0.0003″ |
| 17-4 PH | Hardness variability post-heat treat | In-process metrology, stress-relieved stock | ±0.0002″ |
| 440C | Extreme abrasiveness | CBN tooling, reduced depth of cut | ±0.0004″ |
Honyo Prototype’s ISO 9001-certified facility combines 5-axis milling, Swiss turning, and multi-tasking centers with real-time process monitoring to deliver stainless steel components that meet exacting functional and regulatory standards. Whether prototyping or low-volume production, our engineering team collaborates with clients to select optimal grades, define critical features, and validate first-article inspections—ensuring seamless transition from design to deployment.
Accelerate your timeline with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your 3D model to receive a detailed manufacturability analysis and competitive pricing within hours, backed by our commitment to precision-engineered stainless steel solutions.
Technical Capabilities

Stainless Steel Machining Properties – Technical Specifications for CNC Machining (3/4/5-Axis Milling, Turning, Tight Tolerance Applications)
When machining stainless steel—particularly in precision environments involving 3, 4, and 5-axis milling and turning—several material properties directly influence tool selection, cutting parameters, surface finish, and achievable tolerances. Below is a comparative analysis of stainless steel against other commonly machined materials such as aluminum, carbon steel, ABS, and nylon, focusing on CNC machining performance and suitability for tight tolerance parts.
| Material | Machinability Rating | Typical Cutting Speed (SFM) – Milling | Typical Feed Rate (IPR) – Turning | Tool Wear Resistance | Surface Finish (Ra, μin) | Tight Tolerance Capability (±) | Recommended Coolant Use | Key Challenges in Precision Machining |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | Low to Moderate (40–45% relative to 1212 steel) | 100–250 | 0.005–0.015 | High | 16–32 | ±0.0005″ (12.7 μm) achievable with proper setup | Required (flood or high-pressure) | Work hardening, built-up edge, high cutting forces, thermal conductivity |
| Aluminum (6061/7075) | High (Machinability ~170–200%) | 800–2000 | 0.008–0.020 | Low | 8–16 | ±0.0002″ (5 μm) easily maintained | Recommended (for chip evacuation and cooling) | Chatter in thin walls, burring, soft adhesion to tools |
| Carbon Steel (1018/1045) | Moderate (Machinability ~60–70%) | 250–400 | 0.010–0.020 | Moderate | 16–32 | ±0.0005″ (12.7 μm) with rigid setup | Required | Built-up edge, consistent tool wear, moderate thermal load |
| ABS (Thermoplastic) | High (soft material) | 500–1000 | 0.005–0.015 | Very Low | 32–64 | ±0.005″ (127 μm) typical; limited by thermal expansion | Not required; air blast preferred | Melting, deformation under heat, poor dimensional stability |
| Nylon (PA6/PA66) | Moderate to High | 400–800 | 0.005–0.012 | Low | 32–64 | ±0.005″ (127 μm); moisture absorption affects precision | Not required; air cooling | Swelling due to moisture, low stiffness, elastic recovery |
Notes on Stainless Steel for Tight Tolerance Machining:
Stainless steel—especially austenitic grades like 304 and 316—presents unique challenges in high-precision CNC applications. Its low thermal conductivity leads to concentrated heat at the cutting edge, increasing tool wear. The tendency to work-harden requires consistent feed rates and avoidance of interrupted cuts. For 4 and 5-axis milling, where tool engagement varies dynamically, specialized carbide or ceramic tooling with PVD/TiAlN coatings is recommended.
To achieve tight tolerances (±0.0005” or better), stable machine platforms, high-precision tool holding (e.g., hydraulic or shrink-fit), and adaptive CNC strategies (high-speed machining, trochoidal toolpaths) are essential. In turning operations, rigid setups and constant surface speed (CSS) control help maintain dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
While aluminum and plastics like ABS and nylon are easier to machine, they lack the strength, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance of stainless steel—making stainless the preferred choice for demanding industrial, medical, and aerospace components where precision and durability are critical.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype Stainless Steel Machining Process Overview
Honyo Prototype employs a rigorously defined workflow optimized for the unique challenges of stainless steel machining, including work hardening, thermal conductivity limitations, and galling susceptibility inherent in grades like 304 and 316. This process ensures dimensional accuracy, surface integrity, and corrosion resistance preservation from design through delivery.
CAD Upload and Material Specification Validation
Upon receiving the customer’s CAD file, our engineering team validates critical parameters specific to stainless steel. We confirm the exact alloy grade (e.g., 304, 316, 17-4 PH), required surface finishes, and corrosion resistance standards. Geometric features prone to work hardening—such as thin walls, deep pockets, or sharp internal corners—are flagged for immediate DFM review. Material certification requirements and passivation specifications are cross-referenced against the design intent to prevent downstream non-conformities.
AI-Powered Quoting with Stainless Steel-Specific Cost Modeling
Our proprietary AI quoting engine analyzes the CAD geometry while applying material-specific machining algorithms for stainless steel. It dynamically calculates toolpath complexity, anticipated tool wear rates due to abrasion and adhesion, and extended cycle times required for lower surface speeds and feeds. The model factors in coolant requirements, specialized tooling needs (e.g., carbide grades with PVD coatings), and in-process inspections to mitigate risks like thermal distortion. This generates a technically accurate cost and lead time projection reflective of stainless steel’s machining realities, not generic material assumptions.
DFM Analysis Focused on Stainless Steel Machinability Constraints
The DFM phase is where Honyo’s stainless steel expertise is most critically applied. Engineers conduct a granular review addressing:
Work Hardening Mitigation: Recommending optimized tool engagement angles, minimum depth of cut thresholds, and avoidance of dwell times to prevent strain-induced hardening.
Thermal Management: Proposing adjusted feeds/speeds, high-pressure coolant strategies, and chip evacuation enhancements to counteract low thermal conductivity.
Galling Prevention: Suggesting geometric modifications (e.g., reduced contact areas, chamfered edges) and surface finish specifications to minimize adhesion during cutting.
Fixture Strategy: Designing low-distortion workholding to counteract thermal expansion during machining.
Customer collaboration is mandatory at this stage to resolve conflicts between design intent and stainless steel’s physical limitations.
Precision Production with Stainless-Optimized Parameters
Machining executes under strict protocols proven for stainless alloys:
CNC programs utilize reduced surface speeds (50-70% of carbon steel) with aggressive chip-thinning feeds to maintain productivity while controlling heat.
Dedicated tooling libraries with polished flutes, negative rake geometries, and TiAlN/TiCN coatings are deployed to resist built-up edge and crater wear.
In-process inspections verify critical dimensions after roughing and semi-finishing to account for residual stress relaxation.
All operations maintain continuous coolant flow with corrosion-inhibited emulsions, and parts undergo mandatory passivation per ASTM A967 post-machining to restore the chromium oxide layer.
Delivery with Comprehensive Stainless Steel Compliance Documentation
Final delivery includes not only the machined components but also full traceability documentation: material mill test reports, dimensional inspection certificates (including surface roughness validation per ISO 1302), and passivation process records. For critical applications, we provide microstructural analysis confirming absence of embedded iron particles or heat-affected zones. This package ensures the customer receives parts meeting both geometric specifications and the essential corrosion performance requirements of the specified stainless grade.
This integrated process eliminates common stainless steel machining failures—such as dimensional drift from thermal effects or premature corrosion initiation—by embedding material science expertise into every phase, from initial quotation through final validation.
Start Your Project
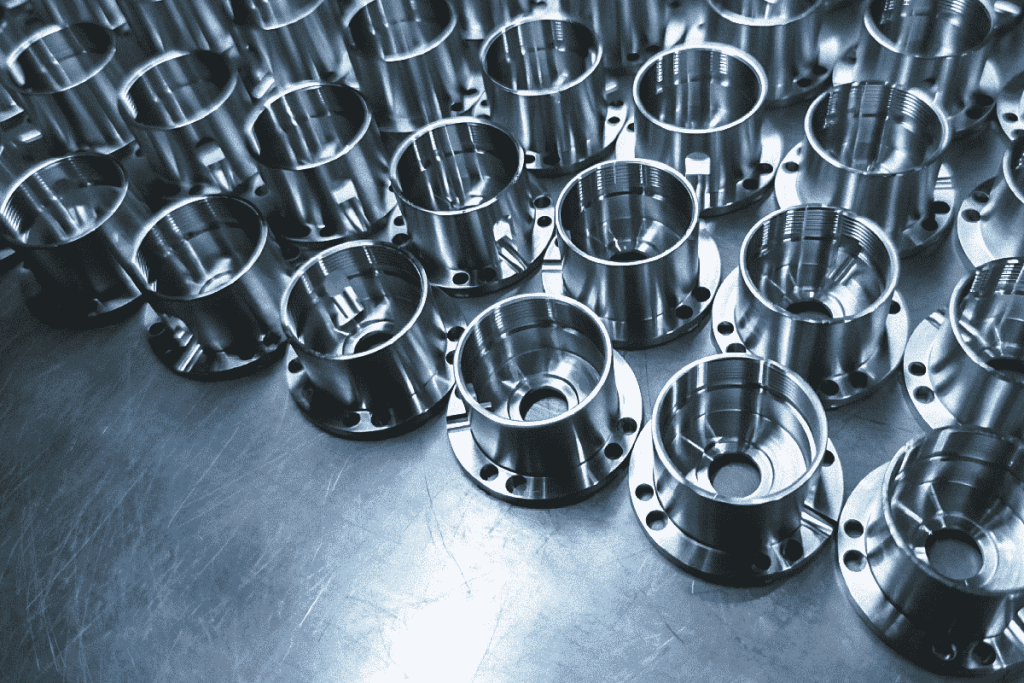
For detailed insights into stainless steel machining properties and expert support for your precision manufacturing needs, contact Susan Leo at [email protected].
Honyo Prototype operates a state-of-the-art facility in Shenzhen, leveraging advanced CNC capabilities to deliver high-precision stainless steel components with optimal surface finish, tight tolerances, and superior material integrity.
Our team specializes in machining austenitic, martensitic, and duplex stainless steel grades, applying proven strategies to manage work hardening, tool wear, and thermal deformation. Whether for prototyping or low-volume production, we ensure efficient, cost-effective results tailored to your engineering requirements.
Reach out today to discuss your project and discover how our technical expertise in stainless steel machining can enhance your product development cycle.
Contact: Susan Leo
Email: [email protected]
Factory Location: Shenzhen, China
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.