Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Stainless Steel Alloys Chart
Stainless Steel Alloys Selection Guide: Precision Machining Expertise from Honyo Prototype
Selecting the optimal stainless steel alloy is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts component performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency in demanding applications. Factors such as corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, weldability, and thermal stability must be meticulously evaluated against project requirements. At Honyo Prototype, we recognize that material selection is only the first step; translating these specifications into high-precision, fully functional parts demands advanced manufacturing capabilities and deep metallurgical expertise.
As a leader in CNC machining for prototyping and low-volume production, Honyo Prototype specializes in processing complex stainless steel alloys—including 303, 304/L, 316/L, 17-4 PH, and 440C—with uncompromising accuracy. Our state-of-the-art CNC milling and turning centers, combined with proprietary toolpath optimization and in-process quality verification, ensure tight tolerances (±0.0002″) and superior surface finishes, even for intricate geometries. We navigate the challenges of work hardening, thermal conductivity variations, and chip control inherent to stainless steels, delivering parts that meet stringent aerospace, medical, and industrial standards.
This stainless steel alloys chart provides essential comparative data to inform your material choice. Once your specifications are defined, leverage Honyo Prototype’s Online Instant Quote platform for rapid, transparent pricing and lead time estimates. Upload your CAD file, specify your alloy and requirements, and receive a detailed quote in under 60 seconds—enabling faster iteration and time-to-market for your critical components. Partner with us to transform material science into engineered reality.
Technical Capabilities
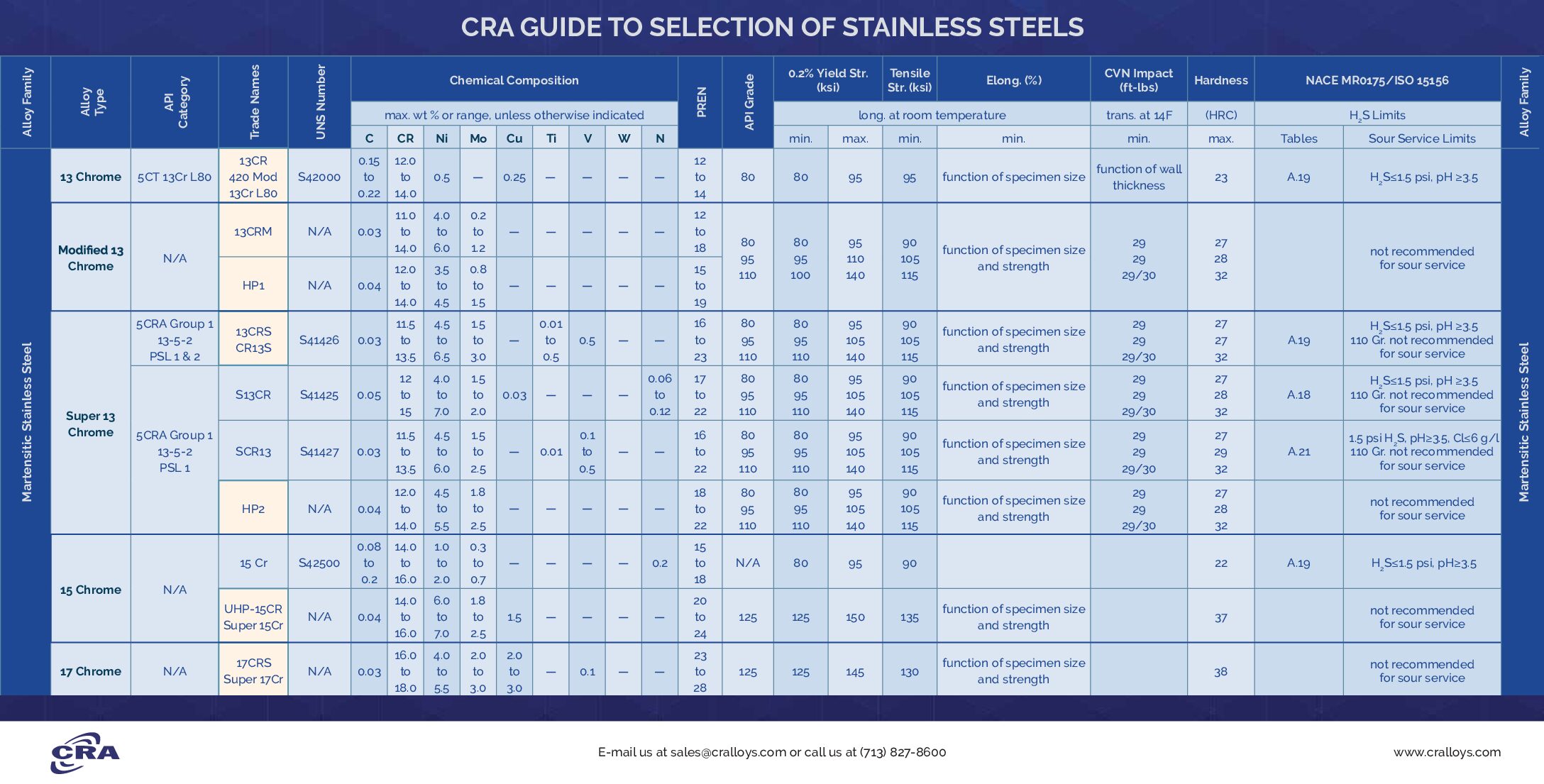
Technical specifications for machining operations involving stainless steel alloys and other common engineering materials must account for material properties, machinability, tooling requirements, and precision capabilities—especially in high-accuracy applications such as 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling and turning with tight tolerances (typically ±0.0005″ to ±0.005″ depending on feature and geometry).
Below is a comparative technical reference table highlighting key material characteristics relevant to precision CNC machining processes at Honyo Prototype. This includes stainless steel alloys commonly used in demanding environments, as well as Aluminum, Carbon Steel, ABS, and Nylon, which are frequently machined alongside stainless grades.
| Material | Typical Grades | Hardness (HB) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Machinability Rating (%) | Recommended Tooling | Max Achievable Tolerance (± in) | Coolant Required | Notes on 3/4/5-Axis Machining |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 303, 304, 316, 17-4 PH, 416, 440C | 150–330 | 500–1300 | 40–70 | Carbide, TiAlN-coated end mills | 0.0005–0.002 | Yes | High work hardening; rigid setups required; 5-axis ideal for complex geometries |
| Aluminum | 6061-T6, 7075-T6, 2024-T4 | 95–150 | 310–570 | 90–100 | Carbide, polished uncoated or ZrN-coated | 0.0005–0.001 | Yes (flood) | Excellent for high-speed 5-axis milling; low cutting forces; tight tolerances easily maintained |
| Carbon Steel | 1018, 1045, 4140, A36 | 120–250 | 400–900 | 60–75 | Carbide, CBN (for hard turning) | 0.0005–0.002 | Yes | Generates significant heat; stable fixturing critical for tight tolerance turning |
| ABS | Commercial Grade, High-Impact | 80–100 (Shore D) | 35–50 | 95 | Sharp HSS or carbide, high rake angles | 0.002–0.005 | No (air blast recommended) | Low melting point; prone to chatter; best for prototypes and non-structural parts |
| Nylon (PA6, PA66) | Unfilled, Glass-Filled | 70–90 (Shore D) | 60–90 (unfilled) | 80 (unfilled), 50 (GF) | Sharp carbide, positive rake tools | 0.002–0.005 | No | Low friction but elastic; requires sharp tools and slow feed to avoid deflection |
Key Process Considerations:
For 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining, material selection directly impacts tool life, surface finish, and dimensional consistency. Stainless steel alloys require slower speeds and rigid setups due to work hardening and high strength, while aluminum allows for aggressive high-speed machining with excellent surface finishes. Plastics like ABS and Nylon demand specialized cutting strategies to avoid melting or deformation.
Tight tolerance work across all materials benefits from in-process probing, thermal stability, and high-precision spindles (≤1µm runout). 5-axis machining reduces setup count and improves accuracy on complex stainless steel components such as aerospace fittings or medical implants.
At Honyo Prototype, we optimize feeds, speeds, stepovers, and toolpaths based on material-specific data to ensure first-time-right production within specified GD&T and surface roughness requirements (Ra 16–63 µin typical, down to Ra 8 µin with finishing passes).
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype Stainless Steel Alloy Component Manufacturing Process
Honyo Prototype employs a rigorously defined workflow for stainless steel alloy component manufacturing, ensuring material integrity, dimensional accuracy, and compliance with industry standards. The process begins with CAD Upload, where clients submit 3D models with explicit material specifications (e.g., ASTM/ASME grades like 304, 316, 17-4PH). Critical alloy parameters—such as carbon content, chromium-nickel-molybdenum ratios, and heat treatment requirements—are validated against the CAD file. Inaccurate or incomplete material declarations trigger immediate client consultation to prevent downstream non-conformance.
The AI Quote phase utilizes our proprietary algorithm to cross-reference the specified stainless steel alloy against manufacturability databases. This system evaluates factors including machinability coefficients (e.g., AISI 303’s sulfur content vs. 304’s weldability), thermal expansion rates, and corrosion resistance profiles. Real-time cost modeling accounts for alloy-specific challenges, such as the abrasive nature of duplex stainless steels or the work-hardening tendencies of austenitic grades, generating a technically validated quotation within 2 hours.
DFM (Design for Manufacturability) Analysis is conducted by senior metallurgical engineers. For stainless steel alloys, this phase scrutinizes:
Thermal distortion risks during welding or heat treatment
Tool wear implications based on alloy hardness (e.g., 440C vs. 316L)
Surface finish requirements relative to passivation needs
Weld joint design compatibility with sensitization thresholds
Non-compliant geometries—such as thin walls in high-carbon martensitic grades—are flagged with actionable redesign recommendations, ensuring the component meets ASTM A240 or equivalent standards.
Production executes under ISO 9001-certified protocols with alloy-specific controls:
Material traceability via mill test reports (MTRs) for every heat number
In-process verification of interpass temperatures for weldments
CNC machining with rigid toolpath strategies to mitigate galling in austenitic alloys
Post-machining passivation per ASTM A967 using nitric or citric acid baths
All critical dimensions undergo first-article inspection with CMM verification against GD&T callouts, with statistical process control monitoring for high-volume runs.
Delivery includes comprehensive documentation:
Certified material test reports (CMTRs) with chemical composition and mechanical properties
NDT records (e.g., dye penetrant for welds in 316L pressure vessels)
Dimensional inspection reports with ASME Y14.5 compliance
Passivation validation certificates
Components are packaged with humidity indicators and alloy-specific handling labels to prevent cross-contamination during transit. This end-to-end traceability ensures stainless steel parts meet sector-specific requirements for medical, aerospace, or chemical processing applications.
Start Your Project
For detailed technical specifications on our stainless steel alloys, refer to the comprehensive stainless steel alloys chart available upon request. To obtain a copy or for custom material recommendations, contact Susan Leo directly at [email protected]. Honyo Prototype operates a precision manufacturing facility in Shenzhen, ensuring fast turnaround and strict quality control for all alloy-based prototyping and production orders.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.