Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stainless passivation
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing reliable stainless passivation services poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Vietnam. Ensuring that stainless steel components are adequately passivated is crucial for preventing corrosion, enhancing product durability, and meeting stringent industry standards. However, the complexities involved—ranging from selecting the appropriate passivation method to identifying reputable suppliers—can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of stainless passivation, covering various types of passivation processes, their applications across industries, and effective strategies for vetting suppliers. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations and best practices to ensure that your procurement decisions align with your operational needs and regulatory requirements. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance product quality and reliability.
Whether you are involved in manufacturing medical devices, aerospace components, or other specialized products, understanding the nuances of stainless passivation will enable you to optimize your supply chain and mitigate risks associated with corrosion. Let’s navigate the global market for stainless passivation together, ensuring that your investments yield long-term benefits.
Understanding stainless passivation Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid Passivation | Uses nitric acid to remove surface contaminants | Aerospace, Medical Devices, Food & Beverage | Pros: Effective rust prevention; Cons: Environmental concerns, requires careful handling. |
| Nitric Acid with Sodium Dichromate | Combines nitric acid with sodium dichromate for enhanced performance | Heavy Machinery, Oil & Gas | Pros: Superior protection; Cons: Potential toxicity, more costly. |
| Citric Acid Passivation | Utilizes citric acid, a safer alternative to nitric acid | Electronics, Pharmaceutical, Automotive | Pros: Environmentally friendly, effective; Cons: May be less effective in extreme environments. |
| Electrolytic Passivation | Involves applying an electric current during passivation | High-Tech Manufacturing, Aerospace | Pros: Uniform passivation, enhanced corrosion resistance; Cons: Higher equipment costs. |
| Passivation with Organic Acids | Uses organic acids for a less aggressive treatment | Specialty Alloys, Decorative Applications | Pros: Gentle on materials, suitable for sensitive applications; Cons: Limited effectiveness on heavy contamination. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Nitric Acid Passivation?
Nitric Acid Passivation is a well-established method that leverages nitric acid to eliminate free iron and contaminants from stainless steel surfaces. This type is particularly effective in industries where stringent corrosion resistance is paramount, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Buyers should consider the environmental regulations associated with nitric acid, as well as the need for specialized handling and disposal measures.
How does Nitric Acid with Sodium Dichromate enhance performance?
This variation incorporates sodium dichromate into the nitric acid process, providing enhanced corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in heavy machinery and oil and gas applications where components face harsh operational environments. While this method offers superior protection, buyers must weigh the benefits against potential toxicity and the higher costs associated with the chemicals involved.
Why choose Citric Acid Passivation?
Citric Acid Passivation is recognized for its eco-friendliness and effectiveness in removing contaminants. It is widely used in the electronics and pharmaceutical sectors, where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are critical. Buyers should note that while citric acid is generally effective, it may not provide the same level of protection in extreme conditions compared to nitric acid options.
What benefits does Electrolytic Passivation provide?
Electrolytic Passivation employs an electric current to enhance the passivation process, resulting in a uniform protective layer on stainless steel components. This method is ideal for high-tech manufacturing and aerospace applications where precision is critical. However, buyers should consider the higher initial investment in equipment and the need for specialized expertise to manage the process effectively.
When is Passivation with Organic Acids a viable option?
Passivation with Organic Acids offers a gentler approach for treating sensitive materials, making it suitable for decorative applications and specialty alloys. This type is less aggressive than traditional methods, reducing the risk of damaging delicate surfaces. Buyers should be aware, however, that while this method is less harmful to materials, it may not be as effective on heavily contaminated surfaces.
Key Industrial Applications of stainless passivation
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stainless passivation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Passivation of surgical instruments and implants | Enhanced corrosion resistance ensures patient safety and product reliability | Compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) and traceability of materials |
| Aerospace | Passivation of aircraft components and fasteners | Improved durability under extreme conditions reduces maintenance costs | Certification of passivation processes and environmental considerations |
| Food Processing | Passivation of equipment and piping systems | Prevents contamination and maintains hygiene standards | Material certification and resistance to specific food-grade chemicals |
| Chemical Processing | Passivation of storage tanks and reactor vessels | Minimizes corrosion risk, ensuring operational efficiency | Compatibility with aggressive chemicals and adherence to safety regulations |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Passivation of wafer fabrication equipment | Reduces contamination risk, leading to higher yield rates | Precision in cleaning processes and compliance with industry standards |
How is Stainless Passivation Used in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device industry, stainless passivation is crucial for surgical instruments and implants. The process removes free iron and contaminants, creating a protective oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance. This is vital for maintaining the integrity of devices that come into contact with bodily fluids. International buyers must ensure compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO and ASTM, as well as traceability of materials to guarantee patient safety and product reliability.
What Role Does Passivation Play in Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace components, including fasteners and structural parts, undergo stainless passivation to improve durability against harsh environmental conditions. The passivation process enhances the natural resistance of stainless steel to corrosion, which is essential for maintaining performance and safety in flight. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who can certify their passivation processes and demonstrate environmental compliance, as these factors significantly impact long-term maintenance costs and operational efficiency.
Why is Stainless Passivation Important in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, stainless passivation is applied to equipment and piping systems to prevent contamination and ensure hygiene. The process creates a non-reactive surface that minimizes the risk of rust and microbial growth, which is critical for food safety. Buyers should consider the certification of materials and their resistance to specific food-grade chemicals when sourcing passivated equipment, as these factors directly influence product quality and compliance with health regulations.
How Does Passivation Benefit Chemical Processing Facilities?
For chemical processing, stainless passivation is essential for storage tanks and reactor vessels that are exposed to aggressive chemicals. The passivation process enhances the lifespan of these components by minimizing corrosion, which can lead to costly downtime and safety hazards. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that are compatible with the chemicals they handle and ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with corrosion.
What is the Impact of Passivation in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
In semiconductor manufacturing, stainless passivation is utilized for equipment involved in wafer fabrication. This process is critical for reducing contamination risks, as even minor impurities can significantly impact yield rates. Buyers in this sector should prioritize precision in cleaning processes and ensure that suppliers comply with industry standards to maintain the high-quality requirements essential for successful semiconductor production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stainless passivation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding the Purpose of Passivation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers mistakenly view stainless passivation as an optional step in the machining process rather than a crucial one. This misunderstanding can lead to significant issues such as premature corrosion, product failure, and increased maintenance costs. Buyers in sectors like aerospace or medical device manufacturing, where reliability is paramount, may find that skipping this process or executing it incorrectly results in costly rework or even product recalls.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should educate themselves and their teams about the critical role of passivation in enhancing corrosion resistance. This can be achieved by conducting training sessions or workshops with experts in the field. Additionally, buyers should ensure that their suppliers are well-versed in the latest standards and practices for stainless passivation, such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700. Implementing a robust quality assurance process that includes passivation as a mandatory step will not only extend the life of the products but also enhance overall operational efficiency. Buyers should also request detailed documentation of the passivation process from their suppliers to ensure compliance and understanding.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality from Service Providers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges related to the inconsistency of passivation services. Different providers may use various chemicals and processes, leading to variable outcomes in corrosion resistance. This inconsistency can result in parts that do not meet stringent industry standards, causing frustration and delays in production timelines. For companies operating in sectors such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, where contamination risks are high, this inconsistency poses a significant threat to product safety and compliance.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should develop a clear set of criteria for selecting passivation service providers. This includes verifying certifications, reviewing past performance, and seeking references from other clients in similar industries. Establishing long-term partnerships with a reliable provider can also enhance quality consistency. Buyers should consider implementing a standardized evaluation process that includes regular audits of the passivation service provider’s facilities and procedures. Additionally, requesting samples of passivated parts for testing prior to large orders can help ensure that the quality meets their specific requirements.
Scenario 3: Environmental and Safety Compliance Challenges
The Problem: As environmental regulations become stricter, B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the chemicals used in the passivation process. Traditional methods, particularly those using nitric acid, pose safety risks and environmental hazards. Buyers in regions with stringent environmental laws, such as Europe, may face penalties or operational disruptions if they fail to comply with these regulations. This concern can create a dilemma when trying to balance effective passivation with compliance and safety.
The Solution: To address these compliance challenges, buyers should explore alternative passivation methods that use safer, more environmentally friendly chemicals, such as citric acid. This approach not only meets regulatory requirements but also reduces potential safety hazards for employees. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to understand the chemical composition of the passivation solutions used and ensure that they align with local and international safety standards. Additionally, engaging with regulatory bodies for guidance and keeping abreast of changes in legislation can help buyers stay compliant. Implementing a robust training program for employees on the safe handling of chemicals during the passivation process can further enhance workplace safety and compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stainless passivation
What Are the Common Materials Used for Stainless Passivation?
When considering stainless passivation, several materials are commonly utilized in the process, each with unique properties and implications for performance, cost, and application. Below is an analysis of four prevalent materials: Nitric Acid, Citric Acid, Sodium Dichromate, and Specialty Passivating Solutions.
How Does Nitric Acid Perform in Stainless Passivation?
Nitric acid is one of the most traditional and widely used materials for stainless steel passivation. It effectively removes free iron and other contaminants from the surface of stainless steel, enhancing the formation of a protective chromium oxide layer.
Key Properties: Nitric acid is highly effective in creating a robust passivation layer, especially for 300-series stainless steels. It operates effectively at ambient temperatures and can be used in both immersion and spray applications.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of nitric acid include its strong efficacy in removing contaminants and its ability to create a durable passivation layer. However, it has environmental concerns due to its corrosive nature and can lead to hazardous waste if not managed properly. Additionally, the process may require more stringent safety protocols.
Impact on Application: Nitric acid is particularly effective in industries where stringent corrosion resistance is required, such as aerospace and medical devices. However, its aggressive nature may not be suitable for all stainless steel grades, particularly those with lower chromium content.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations is crucial, especially in regions like Europe, where stringent standards (e.g., REACH) apply. Buyers should also consider the availability of nitric acid and its handling requirements in their local markets.
What About Citric Acid for Passivation?
Citric acid has gained popularity as a safer and more environmentally friendly alternative to nitric acid for stainless steel passivation. It effectively cleans and passivates the surface, forming a protective oxide layer.
Key Properties: Citric acid is less aggressive than nitric acid and can be used at lower concentrations, making it safer for operators and the environment. It is effective at room temperature and can be used in various applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of citric acid is its lower environmental impact and reduced health risks. However, it may not be as effective on heavily contaminated surfaces compared to nitric acid, requiring more thorough cleaning prior to application.
Impact on Application: Citric acid is widely used in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where safety and compliance with health regulations are paramount. Its effectiveness in removing contaminants makes it suitable for applications where hygiene is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Citric acid is generally more accepted in various regions due to its eco-friendliness. Buyers should ensure that the citric acid used meets local compliance standards, which may vary across regions like Africa and South America.
How Does Sodium Dichromate Compare?
Sodium dichromate is another chemical used for passivation, often in combination with nitric acid. It enhances the passivation process by providing additional corrosion resistance.
Key Properties: Sodium dichromate is known for its ability to create a thick, protective layer on stainless steel surfaces, enhancing corrosion resistance significantly.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its effectiveness in providing superior corrosion resistance. However, sodium dichromate is highly toxic and poses significant environmental and health risks, leading to strict regulations surrounding its use.
Impact on Application: This material is often used in industries where high corrosion resistance is essential, such as oil and gas. However, its toxicity can limit its application in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of the legal restrictions and compliance requirements associated with sodium dichromate, particularly in Europe, where its use is heavily regulated.
What Are Specialty Passivating Solutions?
Specialty passivating solutions are formulated to meet specific requirements of various industries. These solutions often incorporate a blend of acids and inhibitors tailored for particular stainless steel grades.
Key Properties: These solutions can be customized to enhance the passivation process for specific applications, offering flexibility in performance.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of specialty solutions is their tailored approach, which can optimize corrosion resistance for specific environments. However, they may come at a higher cost and require specialized handling and application techniques.
Impact on Application: Specialty solutions are ideal for niche applications in industries like aerospace and medical, where specific performance criteria must be met.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of specialty solutions with their existing processes and ensure compliance with local standards and regulations.
Summary Table of Common Materials for Stainless Passivation
| Material | Typical Use Case for Stainless Passivation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid | Aerospace, Medical Devices | Strong efficacy in removing contaminants | Environmental hazards and safety concerns | Medium |
| Citric Acid | Food Processing, Pharmaceuticals | Eco-friendly and safer for operators | Less effective on heavily contaminated surfaces | Low |
| Sodium Dichromate | Oil and Gas | Superior corrosion resistance | Highly toxic and heavily regulated | High |
| Specialty Solutions | Aerospace, Medical | Tailored for specific applications | Higher cost and specialized handling required | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stainless passivation
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Stainless Passivation?
Stainless passivation involves a multi-step manufacturing process designed to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel components. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who need to ensure product quality and longevity in demanding environments.
How Is Material Prepared for Passivation?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This stage involves cleaning the stainless steel components to remove contaminants that can interfere with the passivation process. Effective cleaning methods include:
- Ultrasonic Cleaning: Utilizing high-frequency sound waves to create cavitation bubbles in a cleaning solution, this method effectively removes dirt, grease, and machining residues.
- Aqueous Cleaning: Hot water and detergent solutions can also be employed, especially for larger components. This method is effective but may require additional drying steps to prevent water spots.
- Chemical Cleaning: Specific solvents or alkaline solutions can be used to dissolve stubborn contaminants.
The aim is to achieve a surface that is free from oils, dirt, and iron particles that can act as initiation sites for corrosion.
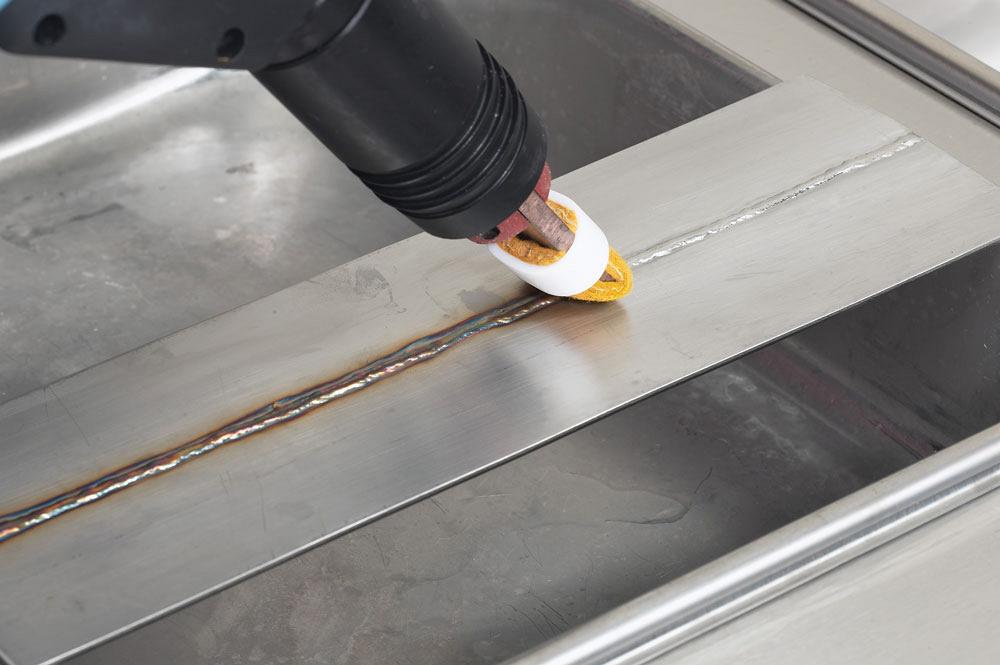
What Techniques Are Used in the Passivation Process?
After the surface is adequately cleaned, the passivation process itself can begin. The most common techniques employed include:
- Acid Passivation: Stainless steel is immersed in a bath of nitric acid or citric acid. This step removes free iron and other contaminants from the surface, allowing for the formation of a thicker, more protective chromium oxide layer.
- Electropolishing: This is an electrochemical process that polishes the surface of the stainless steel by removing a thin layer of material. This not only enhances the finish but also promotes better passivation by removing embedded contaminants.
Once the passivation treatment is complete, components are typically rinsed with deionized water to remove residual acid before being dried.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Passivation?
Quality assurance is vital throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the passivation is effective and meets international standards. Here are the primary quality assurance measures employed:
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Stainless Passivation?
Several international standards govern the passivation process. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines quality management systems that ensure consistency in quality across products and services. Manufacturers should have ISO 9001 certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- ASTM A967: This specification provides the requirements for passivation treatments for stainless steel, detailing acceptable methods and practices.
- AMS 2700: Similar to ASTM A967, this specification outlines the passivation process for aerospace applications, ensuring that components meet stringent industry standards.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
The quality control process typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies that raw materials meet specified standards before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that the components are being cleaned and passivated as required.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the passivation process, a final inspection is performed to verify the integrity of the passivated layer and ensure that no contaminants remain.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Verify Passivation Quality?
To ensure the effectiveness of the passivation process, several testing methods can be employed:
- Water Break Test: A simple visual inspection where deionized water is applied to the surface. If the water beads up, it indicates a poorly passivated surface.
- Copper Sulfate Test: This test involves applying a copper sulfate solution to the stainless steel surface. If copper deposits appear, it indicates the presence of free iron.
- Spectroscopic Analysis: More advanced techniques, like X-ray fluorescence (XRF), can be used to analyze the composition of the surface layer, confirming the presence of chromium oxide.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to high-quality standards. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help verify their quality management practices and adherence to international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports, including results from testing methods such as the copper sulfate test or spectroscopic analysis.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing process can provide additional assurance that the passivation meets required standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. It is essential for buyers to ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations, such as CE marking in Europe.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Understanding the cultural approach to quality and manufacturing practices in different regions can help buyers set realistic expectations and foster better supplier relationships.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Engaging in transparent communication with suppliers regarding their quality control measures can help mitigate risks associated with international procurement.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for stainless passivation is critical for B2B buyers seeking to procure high-quality stainless steel components. By focusing on material preparation, effective passivation techniques, rigorous quality control measures, and supplier verification strategies, buyers can ensure that they receive reliable and durable products for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stainless passivation’
When procuring stainless passivation services, it is essential to follow a structured approach to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the complexities of sourcing stainless passivation effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the requirements for your stainless steel components, including the type of stainless steel alloy, dimensions, and intended application. Establishing these specifications will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the passivation process aligns with your performance expectations. Consider factors such as corrosion resistance levels and any industry standards you must meet.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700, which govern the passivation of stainless steel. Understanding these standards will help you evaluate whether a supplier’s processes align with your needs. Additionally, be aware of any regulatory requirements specific to your region or industry, as compliance is critical to avoiding future liabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Assess their experience with stainless passivation, particularly regarding the specific alloys and applications relevant to your needs. Don’t just rely on their website; direct communication can reveal their capacity and reliability.
- Check Certifications: Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards and quality management systems, such as ISO 9001.
- Inquire About Equipment: Ensure the supplier has the necessary equipment and technology for effective passivation, including the appropriate acid baths and cleaning systems.
Step 4: Request Samples and Trials
Ask potential suppliers for samples of their passivated products or to conduct trial runs of your components. This step allows you to assess the quality of their work firsthand and determine if it meets your specifications. Evaluate the corrosion resistance and surface finish of the samples to ensure they align with your expectations.
Step 5: Understand the Passivation Process
Engage with suppliers to gain insights into their passivation processes. Understand the chemicals used (nitric vs. citric acid), the duration of treatment, and the cleaning procedures prior to passivation. This knowledge will help you gauge the effectiveness of their methods and ensure they align with your quality requirements.
Step 6: Evaluate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, compare pricing structures while considering the value offered. Inquire about any additional costs related to shipping, handling, or post-passivation services. Also, review payment terms, lead times, and warranty policies to ensure you have a clear understanding of the financial implications.
Step 7: Confirm Post-Service Support and Maintenance
Finally, ensure the supplier offers support after the passivation process. This includes guidance on maintenance and care for the passivated components to prolong their life and performance. A supplier that provides ongoing support can be a valuable partner in maintaining the integrity of your stainless steel products.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to source stainless passivation services that meet your operational needs and ensure the longevity of your stainless steel components.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stainless passivation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Stainless Passivation Sourcing?
When sourcing stainless passivation services, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The main components include:
-
Materials: The choice of passivation agents, such as nitric or citric acid, significantly affects costs. Citric acid is often preferred for its safety and environmental benefits but may carry a premium. Additionally, the quality of stainless steel can influence the required passivation process.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the passivation process. Technicians must be trained to ensure that cleaning and passivation are performed correctly, as improper handling can lead to corrosion issues. Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of the operations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes facility costs, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Overhead can vary widely based on geographical location, with regions having higher labor costs typically also facing higher overhead expenses.
-
Tooling: Specialized equipment for cleaning and passivation can require significant investment. The type of machinery used, whether automated or manual, will impact tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with industry standards, such as ASTM A967, necessitates rigorous QC processes. This can involve additional testing and certifications, contributing to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation of parts to and from the passivation facility can add to the total cost. Incoterms play a role here, as they dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can vary greatly across international borders.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can fluctuate based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stainless Passivation Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in stainless passivation sourcing:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts where possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Unique dimensions or specific performance requirements may necessitate specialized processes or materials, raising the overall price.
-
Materials: The type of stainless steel and the chosen passivation method can impact pricing. Certain grades may require more intensive processing, affecting the cost.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with specific industry standards can add to costs. Suppliers with higher certifications may charge more due to the additional quality assurance measures they implement.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly impact the total cost. Buyers should be aware of their responsibilities regarding shipping and customs to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Stainless Passivation Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing based on volume or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial price. Consider potential savings from reduced maintenance and longer product lifespan due to effective passivation.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be mindful of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and shipping costs when sourcing internationally. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and collaboration.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for stainless passivation can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough research to ensure they receive competitive pricing that meets their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stainless passivation With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Stainless Passivation: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the realm of metal finishing, particularly for stainless steel, passivation is a well-regarded process that enhances corrosion resistance. However, there are several alternative methods available that also aim to protect stainless steel from environmental factors. Understanding these alternatives can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs, budget, and operational contexts.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Stainless Passivation | Alternative 1: Electropolishing | Alternative 2: Coating (Paint or Powder) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly effective in removing contaminants and enhancing corrosion resistance. | Provides a smooth, reflective surface that reduces friction and corrosion. | Varies widely; can offer good protection but may wear off or degrade over time. |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on the scale and method used (citric vs. nitric acid). | Generally higher due to specialized equipment and labor costs. | Variable; typically lower initial cost but requires ongoing maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires controlled conditions and expertise in handling acids. | Complex setup; requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. | Relatively straightforward application; can be done on-site with proper prep. |
| Maintenance | Minimal once applied; long-lasting if properly executed. | Low maintenance but may require reapplication in harsh environments. | Moderate; may require periodic touch-ups or reapplication. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-performance applications in medical, aerospace, and food processing. | Best suited for applications where smooth surfaces and low friction are critical. | Suitable for decorative purposes or environments with low to moderate exposure to corrosive elements. |
Understanding Each Alternative in Detail
Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from the surface of stainless steel, resulting in a smooth, shiny finish. This method not only enhances corrosion resistance but also improves cleanliness, making it ideal for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. However, the initial setup costs can be high due to the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel. While maintenance is minimal, the process requires careful monitoring to ensure consistent results.
Coating (Paint or Powder)
Coating stainless steel with paint or powder can offer a protective barrier against corrosion. This method is often more cost-effective than passivation or electropolishing and can be applied relatively easily. However, coatings can wear off over time, especially in harsh environments, necessitating regular maintenance and reapplication. Additionally, coatings may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as passivation, making them less suitable for high-performance applications where durability is critical.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between stainless passivation and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and the environmental conditions the stainless steel will face. For industries demanding high corrosion resistance and reliability, stainless passivation remains a top choice. Conversely, if cost is a primary concern or if the application is less demanding, alternatives like electropolishing or coatings may offer satisfactory results. Ultimately, aligning the chosen method with the operational context and performance expectations will lead to better long-term outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stainless passivation
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stainless Passivation?
Understanding the essential technical properties of stainless passivation is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure the longevity and performance of stainless steel components. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
Stainless steel is categorized into various grades, with the 300-series (e.g., 304, 316) being the most common. Each grade has different levels of corrosion resistance, strength, and ductility. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade is vital because it affects the passivation process and the final product’s performance in specific environments.
2. Passivation Layer Thickness
The passivation layer, typically around 0.0000001 inches thick, is an invisible oxide film that protects the stainless steel surface. The effectiveness of this layer is determined by the type of acid used in the passivation process and the duration of exposure. A well-formed passivation layer enhances corrosion resistance, which is critical for industries like aerospace and medical devices where failure can have severe consequences.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and properties of the passivated surface. Maintaining tight tolerances is essential in applications requiring precision, such as in the manufacturing of medical devices. Buyers must specify their tolerance requirements to ensure compatibility with their production processes and to avoid costly rework.
4. Contaminant Removal Efficiency
The efficiency of the passivation process in removing contaminants—such as free iron particles, sulfides, and machining debris—is a significant factor in achieving optimal corrosion resistance. Buyers should inquire about the cleaning procedures followed before passivation, as inadequate cleaning can lead to premature corrosion and product failure.
5. Corrosion Resistance Rating
Corrosion resistance is often measured using standardized tests such as ASTM A967. A higher rating indicates better performance in corrosive environments. B2B buyers should evaluate the corrosion resistance ratings of passivated stainless steel to ensure they meet the specific requirements of their applications.
6. Compliance with Industry Standards
Passivation processes are governed by standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700, which outline acceptable practices for stainless steel treatment. Compliance with these standards not only ensures quality but also facilitates international trade, as products meeting these standards are often more readily accepted in global markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Stainless Passivation?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiations between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the stainless passivation services they provide.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially when dealing with specialty passivated components.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. Buyers should provide detailed specifications for stainless passivation in their RFQ to ensure accurate and competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms used in international trade. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving passivated stainless steel, as they dictate who bears the risk and costs associated with transport.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving it. In industries where timing is critical, understanding the lead time for passivation services can help buyers plan their production schedules effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding stainless passivation, ensuring they select the right products for their needs while fostering successful supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stainless passivation Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Stainless Passivation Sector?
The stainless passivation market is experiencing notable growth driven by the increasing demand for corrosion-resistant materials across various industries, including aerospace, medical devices, and automotive. As global supply chains adapt to regional market demands, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are keenly interested in sourcing high-quality passivation services. Key trends include a shift towards automated passivation processes, which enhance efficiency and consistency while reducing human error. Additionally, the adoption of citric acid-based passivation methods is gaining traction due to their lower environmental impact compared to traditional nitric acid methods.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced surface analysis techniques, are enabling manufacturers to better understand and optimize the passivation process. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring of the passivation layer’s effectiveness, ensuring that the final product meets stringent quality standards. Furthermore, as industries evolve, the demand for specialty stainless steels and tailored passivation solutions is increasing. B2B buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who offer customization options to cater to specific application needs.
In terms of market dynamics, competition is intensifying among suppliers, prompting a focus on value-added services such as technical support and customized formulations. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide comprehensive solutions that include surface preparation, passivation, and post-treatment analysis. This holistic approach not only enhances product reliability but also fosters long-term partnerships that can adapt to changing market conditions.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Stainless Passivation Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the sourcing decisions of international B2B buyers, particularly as environmental regulations tighten and consumers demand more eco-friendly products. The environmental impact of traditional passivation processes, particularly those using nitric acid, has led to a shift towards more sustainable practices. Suppliers that offer citric acid passivation not only meet performance requirements but also align with the growing emphasis on reducing chemical waste and improving safety standards.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This includes responsible sourcing of raw materials, minimizing energy consumption during the passivation process, and ensuring waste is properly managed. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
B2B buyers should also consider suppliers that utilize “green” materials and processes. These may include recyclable packaging, eco-friendly chemicals, and energy-efficient machinery. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, businesses can enhance their own corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and stakeholders.
What Is the Historical Context of Stainless Passivation and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The concept of passivation can be traced back to the mid-1800s, when chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein first discovered the protective properties of a passive layer formed on metals exposed to nitric acid. This foundational work laid the groundwork for the widespread adoption of passivation as a critical post-fabrication process in the 20th century. Initially, nitric acid was the primary agent used for passivation; however, growing environmental concerns led to the development of citric acid as a safer alternative.
Understanding the historical context of stainless passivation is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the evolution of industry standards and the continuous improvement of techniques. Knowledge of historical practices can inform purchasing decisions, enabling buyers to choose suppliers who not only adhere to current standards such as ASTM A967 and AMS 2700 but also demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability in their processes. As the industry evolves, staying informed about these developments will be key to ensuring quality and reliability in stainless steel applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stainless passivation
-
How do I ensure proper passivation of stainless steel components?
To ensure proper passivation, start with a thorough cleaning process to remove any contaminants such as grease, dirt, and machining debris. Following the cleaning, immerse the stainless steel components in an appropriate acid bath, either nitric or citric acid, to remove free iron and enhance the protective chromium oxide layer. Ensure that the passivation process adheres to industry standards like ASTM A967 or AMS 2700, which outline the specific requirements for effective passivation. It’s also advisable to work with experienced suppliers who can provide detailed process documentation. -
What is the most effective method for passivating stainless steel?
The most effective method for passivating stainless steel typically involves a two-step process: cleaning followed by immersion in an acid solution. While nitric acid is commonly used, citric acid has gained popularity due to its environmental benefits. The choice between these methods can depend on the specific application and material grade. Always consult with your supplier to determine the best method for your particular needs, especially if you require compliance with stringent industry regulations. -
What are the key benefits of stainless steel passivation for my products?
Stainless steel passivation offers several key benefits, including enhanced corrosion resistance, extended product lifespan, and improved reliability in demanding environments. By removing free iron and other contaminants from the surface, passivation helps prevent rust and surface degradation, making it crucial for industries like medical devices and aerospace. This treatment also reduces maintenance needs and can contribute to overall cost savings by minimizing the risk of premature failure. -
How can I vet suppliers for stainless steel passivation services?
When vetting suppliers for stainless steel passivation services, consider several factors: their experience in the industry, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and compliance with relevant standards like ASTM A967. Request references and case studies to evaluate their past performance and customer satisfaction. Additionally, assess their facility capabilities, quality control processes, and ability to handle your specific material types and quantities to ensure they can meet your needs effectively. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for passivation services?
Minimum order quantities for stainless steel passivation services can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the service. Some suppliers may accommodate small orders, especially for custom or specialized projects, while others might have higher MOQs to justify the processing costs. It is advisable to discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers upfront to understand their policies and determine if they can accommodate your needs within your desired volume. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing passivation services internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of passivation services can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include advance payment, net 30 or 60 days after delivery, or a letter of credit. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, etc.) and any additional fees related to currency conversion or international transactions. Establishing clear payment terms in the contract can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in the passivation process?
To ensure quality assurance in the passivation process, request detailed documentation from your supplier, including process specifications, material test reports, and compliance certifications. Conduct regular audits of the supplier’s facility and processes, and consider third-party inspections for critical projects. Communication is key; establish a clear line of dialogue with your supplier regarding expectations and performance metrics to ensure the passivation meets your quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for sourcing passivation services?
When sourcing passivation services internationally, consider logistics factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier is experienced in handling international shipments and can provide assistance with documentation required for customs clearance. Additionally, assess the supplier’s ability to deliver on time and whether they offer tracking services for shipments. Understanding these logistics aspects can help you better manage timelines and avoid unexpected delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Stainless Passivation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Technology – Passivation Systems
Domain: besttechnologyinc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Best Technology offers a range of passivation systems and equipment designed for stainless steel and other metals. Key product details include: 1. **Passivation Equipment**: Systems that utilize nitric acid or citric acid to remove free iron from stainless steel surfaces, enhancing corrosion resistance. 2. **Types of Passivation**: Three types based on the chemical used: Nitric acid, Nitric acid w…
2. Assda – Stainless Steel Pickling and Passivation
Domain: assda.asn.au
Introduction: Pickling and passivation are chemical treatments for stainless steel surfaces to remove contaminants and assist in forming a chromium-oxide passive film. Pickling removes high temperature scale and chromium-depleted layers using nitric (HNO3) and hydrofluoric (HF) acids, restoring corrosion resistance. Passivation involves treating the surface with acid solutions to remove free iron contaminants a…
3. CitrusPass – Stainless Steel Passivation Spray
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Citrus-based passivation spray for stainless steel; alternative methods include using 50% nitric acid or hydrogen peroxide (at least 10% concentration) combined with citric acid and a wetting agent. Avoid using any chloride in the mixture.
4. Rust Store – CitriSurf® Passivation Products
Domain: theruststore.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Stainless Passivation products include CitriSurf® formulations designed for cleaning and passivating stainless steel. Key products include: 1. CitriSurf 77 – 22 oz. Bottle: $22.99, provides convenient application, cleans and passivates stainless steel. 2. CitriSurf 77 Plus – 22 oz. Bottle: $25.99, removes rust and passivates stainless steel. 3. CitriSurf 2210 Gel – Gallon: $72.99, formulated for c…
5. Advanced Plating Technologies – Stainless Steel Passivation Services
Domain: advancedplatingtech.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Passivation of stainless steel is a process that removes free iron from the surface of stainless components and promotes the formation of a thin, dense oxide protective barrier. Advanced Plating Technologies provides passivation services to ASTM A967, AMS 2700, and QQ-P-35 specifications, using both citric and nitric acid methods. The company offers high-volume commercial stainless steel passivati…
6. Valence Surface Tech – Stainless Steel Passivation
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Passivation is a process that improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by removing free iron particles from its surface using a mild acid solution. This process involves cleaning the surface to remove contaminants, followed by treatment with an acidic solution (often nitric acid) to form a protective oxide layer that prevents further rusting. There are three types of pa…
7. CitriSurf – Passivation Products
Domain: citrisurf.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: CitriSurf® products for passivation of stainless steel include: CitriSurf® 2050, CitriSurf® 2210, CitriSurf® 2250, CitriSurf® 2310, CitriSurf® 2325, CitriSurf® 2450, CitriSurf® 2550, CitriSurf® 3050, CitriSurf® 3250, CitriSurf® 77, CitriSurf® 77 Plus, CitriSurf® 8050, CitriSurf® 8310, CitriSurf® 9002. Other products include KleerKleen™ 4000, KleerKleen™ 4002, Rust Rescue™ 100, Rust Rescue™ 200, We…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stainless passivation
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing in Stainless Passivation?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for stainless passivation is essential for businesses aiming to enhance the longevity and performance of their stainless steel components. By investing in proper passivation processes, companies can significantly reduce corrosion risks, ensuring product reliability and compliance with industry standards. This not only leads to lower maintenance costs but also minimizes the likelihood of product failures that could impact operational efficiency.
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of sourcing high-quality passivation services cannot be overstated. Understanding the nuances of passivation methods—such as nitric and citric acid treatments—can influence procurement decisions and ultimately enhance the quality of end products.
As global markets become increasingly competitive, now is the time to evaluate and refine your sourcing strategies. Engage with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance, ensuring that your stainless steel applications meet the demands of your industry. By prioritizing strategic sourcing in stainless passivation, you position your business for sustained success and resilience in the face of evolving market challenges.