Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for spot face in machining
In the intricate world of machining, sourcing the right components can be a daunting task, particularly when it comes to understanding the nuances of spot face applications. Spot faces are crucial for ensuring that fasteners sit securely on uneven surfaces, yet many buyers struggle with identifying the appropriate specifications and suppliers. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding spot face machining by providing a comprehensive overview of its types, applications, and the key considerations for supplier vetting.
From the intricate differences between spot faces and counterbore holes to practical insights on selecting the right machining processes, this resource is designed to empower international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Germany and Vietnam. It will cover essential topics such as cost analysis, quality standards, and logistical considerations to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
By equipping buyers with the knowledge they need, this guide ensures that you can navigate the global market for spot face machining confidently, enabling you to forge lasting partnerships with reliable suppliers and streamline your procurement processes. Understanding these critical elements will not only enhance your operational efficiency but also contribute to the overall success of your projects in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Understanding spot face in machining Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Spotface | Shallow, flat-faced hole for fasteners; typically machined to a specific depth for level seating. | Used in assembling components in machinery and automotive parts. | Pros: Ensures proper fastener seating; enhances stability. Cons: Requires precise machining; potential for increased costs. |
| Counterbore Spotface | Combines characteristics of spotface and counterbore; designed to recess fastener heads while providing a flat surface. | Ideal for applications needing flush fasteners, such as in aerospace. | Pros: Reduces snagging risks; suitable for tight spaces. Cons: May require more complex machining processes. |
| Blind Spotface | Created on blind holes; ensures fasteners are securely seated without passing through the material. | Common in applications where aesthetics are important, such as consumer electronics. | Pros: Provides a clean finish; prevents fastener protrusion. Cons: Limited to specific applications; may complicate assembly. |
| Tapered Spotface | Features a conical shape; used to accommodate specific fastener types. | Useful in specialized applications such as automotive and aerospace where unique fasteners are used. | Pros: Customizable for unique fasteners; improves fit. Cons: Requires careful design considerations; may increase production time. |
| Large Diameter Spotface | Enlarged diameter for larger fasteners or unique applications; provides more surface area for stability. | Applied in heavy machinery and structural applications. | Pros: Enhances load distribution; suitable for high-stress environments. Cons: Increases material removal; can lead to higher costs. |
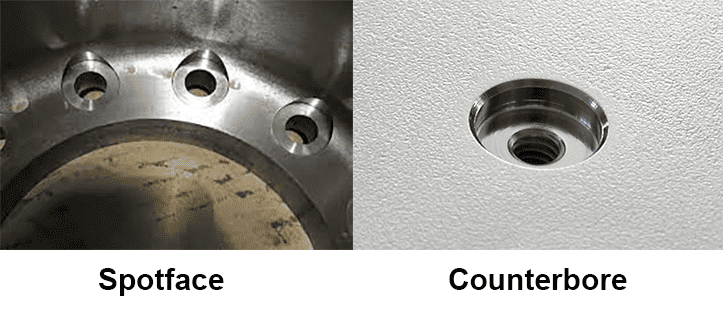
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Standard Spotface?
Standard spotfaces are shallow, flat-faced holes designed primarily for providing a level seating area for fasteners. Their depth is typically minimal, just enough to ensure that the fastener head rests securely. These are essential in applications where the surface of the component is uneven or irregular, such as in cast or fabricated parts. Buyers should consider the precision of machining, as any deviation can impact the integrity of the assembly.
How Does Counterbore Spotface Differ in Application?
Counterbore spotfaces blend the functionalities of standard spotfaces with the recessing ability of counterbores. This type allows fastener heads to sit flush with the surface, minimizing the risk of snagging and enhancing the aesthetic appeal. It is widely used in aerospace and automotive applications where safety and design are critical. Buyers should evaluate the complexity of the machining process, which can influence lead times and costs.
What are the Benefits of Blind Spotfaces in Specific Industries?
Blind spotfaces are specifically designed for holes that do not pass through the material, allowing for a clean finish without protruding fasteners. This type is particularly useful in consumer electronics and other aesthetic-sensitive applications. Buyers must consider the design implications, as the inability to access the other side of the material can complicate assembly and maintenance.
Why Choose Tapered Spotfaces for Unique Fasteners?
Tapered spotfaces feature a conical shape that accommodates specialized fasteners, making them a valuable choice in industries like automotive and aerospace. Their ability to provide a snug fit improves assembly reliability. However, buyers need to ensure that the design is tailored to the specific fastener type, as improper dimensions can lead to assembly issues.
When is a Large Diameter Spotface Necessary?
Large diameter spotfaces are employed in applications that require enhanced load distribution, such as in heavy machinery and structural components. Their increased surface area provides stability under high-stress conditions. Buyers should weigh the benefits of increased strength against the potential for higher machining costs and material waste, as larger spotfaces often require more extensive machining efforts.
Key Industrial Applications of spot face in machining
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of spot face in machining | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Creating flat surfaces for fasteners on irregularly shaped components | Enhanced safety and reliability in aircraft assembly | High precision machining capabilities and certifications |
| Automotive | Spot-facing for engine mounts and transmission components | Improved structural integrity and performance | Material compatibility and adherence to industry standards |
| Construction Equipment | Leveling surfaces for mounting brackets and fixtures | Increased durability and reduced maintenance costs | Supplier reliability and ability to handle large volumes |
| Oil and Gas | Ensuring secure fastening on drilling equipment | Enhanced operational safety and equipment longevity | Compliance with international regulations and quality assurance |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Flat surfaces for component attachment in circuit boards | Improved product reliability and performance | Quick turnaround times and precision machining capabilities |
How is Spot Face in Machining Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, spot-facing is critical for ensuring that fasteners fit securely on components with uneven surfaces. For instance, when assembling aircraft structures, irregularly shaped parts may not provide a stable seating for fasteners. Spot-facing creates a flat landing area, which enhances the safety and reliability of the assembly. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with high precision machining capabilities and relevant certifications, such as AS9100, to ensure compliance with aerospace standards.
What Role Does Spot Face Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Spot-facing is extensively used in automotive manufacturing, particularly for applications like engine mounts and transmission components. By providing a flat surface for fasteners, spot-facing contributes to improved structural integrity and performance of vehicles. Buyers in this sector must consider material compatibility and adherence to automotive industry standards, ensuring that the machined parts withstand harsh operational conditions and maintain vehicle safety.
How is Spot Face in Machining Applied in Construction Equipment?
In the construction equipment sector, spot-facing is employed to create level surfaces for mounting brackets and fixtures, which are essential for equipment stability. This practice enhances durability and reduces maintenance costs by ensuring that components fit securely. For international buyers, sourcing considerations should include supplier reliability and their ability to handle large volumes, as construction projects often require consistent and timely deliveries.
Why is Spot Face Important in Oil and Gas Industries?
Spot-facing is vital in the oil and gas industry for ensuring secure fastening on drilling equipment. Given the high-stress environments in which this equipment operates, a flat surface for fasteners is crucial for operational safety and equipment longevity. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with international regulations and maintain rigorous quality assurance processes to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure.
How Does Spot Face Improve Electronics Manufacturing Processes?
In electronics manufacturing, spot-facing is used to create flat surfaces for component attachment on circuit boards. This is essential for ensuring reliable electrical connections and overall product performance. International buyers should focus on suppliers that offer quick turnaround times and precision machining capabilities, as the electronics industry is highly competitive and demands rapid production cycles without compromising on quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘spot face in machining’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Uneven Surfaces Leading to Fastener Instability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges with components that have uneven or curved surfaces, which make it difficult to secure fasteners properly. For example, when assembling a mechanical structure, uneven surfaces can lead to improper seating of screws, bolts, or washers, resulting in unstable joints. This instability can cause premature wear, misalignment, or even catastrophic failure in critical applications. The buyer may struggle with ensuring that fasteners maintain their integrity under operational stress, leading to increased costs and downtime.
The Solution: To address this issue, incorporating spot face holes into the design of components is essential. Spot facing provides a flat, stable surface for fasteners, ensuring they seat correctly and securely. B2B buyers should work closely with their engineering teams to specify the correct dimensions for the spot face holes, taking into account the diameter and depth necessary to eliminate any curvature or roughness. Additionally, sourcing spot-facing cutters designed for CNC machines can enhance precision in creating these surfaces. Ensuring that the spot face is adequately sized to accommodate the fastener type will lead to better assembly outcomes and improve the longevity of the mechanical structure.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality in Machining Processes
The Problem: A common issue for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from different regions, is inconsistent machining quality. Spot face operations may not be performed uniformly, leading to variances in the flatness and depth of the spot faces. This inconsistency can cause difficulties in fastening components properly, resulting in parts that do not meet specifications or require rework, which can lead to delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should establish stringent quality control measures for their machining processes. This includes defining clear specifications for spot face dimensions and tolerances in the engineering drawings and ensuring that suppliers are equipped with calibrated tools and machinery. Buyers can also implement a robust supplier evaluation process, focusing on those with a proven track record in precision machining. Regular audits and inspections of the machining processes can further ensure compliance with quality standards. By investing in reliable suppliers and maintaining oversight, buyers can significantly reduce the risk of inconsistencies in spot face machining.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Tooling
The Problem: Many buyers encounter challenges when it comes to selecting the appropriate tooling for spot facing operations. The choice of the right cutter, drill, or tap can be daunting, especially with various options available in the market. Incorrect tooling can lead to poor machining outcomes, such as inadequate flatness or damage to the workpiece, which ultimately affects the assembly and performance of the final product.
The Solution: To overcome this tooling challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize thorough research and collaboration with tooling suppliers who specialize in machining applications. It’s crucial to understand the specific requirements of the spot face operation, including the material of the workpiece and the desired finish. Buyers should consult with their machining teams to determine the best type of cutter for the job—whether a spot-facing cutter or a milling tool—and specify the appropriate tap types for threading. Additionally, investing in training for machinists on best practices for tooling selection and usage can enhance overall machining efficiency. By fostering strong relationships with trusted suppliers and providing adequate training, buyers can streamline their machining processes and achieve optimal results.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for spot face in machining
What Are the Key Materials for Spot Face in Machining?
When selecting materials for spot facing in machining, it is essential to consider properties that impact product performance, manufacturing complexity, and application suitability. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in this process, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Steel Alloys
Key Properties:
Steel alloys, particularly those like 4140 and 1018, offer excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and good wear resistance. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
Steel alloys are durable and cost-effective, with a relatively straightforward manufacturing process. However, they can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated, which may limit their use in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
Steel alloys are compatible with various media, including oils and gases, but may not perform well in corrosive environments without additional treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Europe and Germany, quality certifications may be necessary.
2. Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, are lightweight and exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. They have a lower density compared to steel, which can be advantageous in applications where weight is a concern.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of aluminum is its resistance to corrosion and ease of machining. However, it has lower tensile strength than steel, which may not make it suitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than some steel options.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and various chemicals, making it versatile for many applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of specific aluminum grades and their corresponding standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe, to ensure compliance.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. It maintains strength and durability in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its ability to resist corrosion and staining, making it ideal for applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for applications involving exposure to corrosive media, such as saltwater or acidic solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should consider local availability and sourcing options.
4. Plastics (e.g., PEEK, Nylon)
Key Properties:
Engineering plastics like PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) and Nylon offer excellent chemical resistance, low friction, and lightweight characteristics. They can operate effectively under moderate temperature and pressure conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Plastics are often less expensive than metals and provide good insulation properties. However, they may not withstand high loads or temperatures as well as metals, limiting their application scope.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are suitable for applications where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic complies with relevant industry standards, such as ISO or ASTM, especially in regions like Europe and South America, where regulations may be stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Spot Face in Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for spot face in machining | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Alloys | Structural components, automotive parts | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum Alloys | Aerospace, automotive, lightweight parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength than steel | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Plastics (PEEK, Nylon) | Lightweight components, insulation | Low weight and good chemical resistance | Limited load-bearing capacity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on application needs and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for spot face in machining
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Spot Face in Machining?
The manufacturing process for spot facing involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
What are the Main Stages of Spot Face Manufacturing?
-
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material selection and preparation. Common materials used for spot facing include metals such as aluminum, steel, and titanium. These materials must be cut into appropriate sizes and shapes, often employing techniques like shearing or sawing. Surface treatments, such as cleaning or coating, may also be applied to enhance material properties and ensure better machining outcomes. -
Forming
The forming stage involves creating the initial hole, typically done using drilling or milling techniques. A pilot hole is drilled first, followed by the spot facing operation, which uses a specialized cutter to create a shallow, flat-faced hole. This is critical for ensuring that fasteners can sit evenly on the surface. CNC machines are commonly employed in this stage for their precision and efficiency, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and tight tolerances. -
Assembly
In many cases, spot-faced components are part of a larger assembly. This stage involves integrating the spot-faced parts with other components, such as fasteners or mating surfaces. Proper alignment and fit are crucial to ensure the integrity of the final assembly. This may involve further adjustments or machining to meet specific tolerances. -
Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the surface quality and dimensions of the spot face. Techniques such as grinding or polishing may be employed to achieve the desired finish. This step is essential for ensuring that the component meets aesthetic and functional requirements, particularly in industries where visual appearance is as important as performance.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Spot Face Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for spot faces. Implementing robust QA measures helps ensure that components meet international standards and customer specifications.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with various international and industry-specific quality standards that govern manufacturing processes. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable to organizations of all sizes. It helps ensure consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For components used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical for ensuring quality and safety.
What are the QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are essential in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. Any defects or non-conformities are addressed before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the production quality. This may include measuring dimensions, surface finishes, and ensuring that machining parameters are adhered to.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, finished products are thoroughly inspected and tested against specifications. This can include dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and functional testing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Spot Face Components?
Several testing methods are commonly employed to ensure the quality and functionality of spot face components:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify that the dimensions of the spot face meet design specifications.
- Surface Roughness Testing: This involves measuring the surface finish to ensure it meets the required smoothness for proper fastener seating.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that the spot face performs as intended within the assembly, which may involve stress testing or load testing in certain applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following practices:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of supplier facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and adherence to international standards. This can help buyers assess the reliability and capabilities of their suppliers.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports offer transparency and can be used to validate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing can impact supplier relationships. Open communication is crucial to bridge any gaps.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are aware of and comply with local regulations and standards.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality control can be affected by logistics and transportation methods. Ensuring that products are handled correctly throughout the supply chain is essential for maintaining quality.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for spot face components, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘spot face in machining’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring spot face machining services or components. Spot facing is crucial for ensuring flat and precise surfaces on uneven materials, which is essential in various engineering applications. By following this checklist, buyers can streamline their procurement process and ensure they select the right suppliers who meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for effective communication with potential suppliers. Define the diameter, depth, and surface finish required for the spot face, as these parameters will influence the machining process and the choice of tooling. Include details about the material type and any industry standards that must be adhered to.
- Considerations:
- What is the maximum allowable deviation from flatness?
- Are there specific tolerances that must be met?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers specializing in spot face machining. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and evaluate their capabilities. Supplier experience can significantly impact the quality and reliability of your components.
- Key Actions:
- Review online directories and industry forums.
- Check for customer reviews and testimonials.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a decision, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. Quality management standards, such as ISO 9001, indicate that a supplier adheres to best practices in manufacturing. This can assure you of their commitment to quality and consistency.
- What to Look For:
- Certifications specific to machining and engineering.
- Compliance with international standards relevant to your region.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes for the spot face machining services. Ensure each quote includes a breakdown of costs, lead times, and any additional services offered. Comparing these elements will help you make an informed decision.
- Considerations:
- Are there bulk discounts or long-term partnership incentives?
- What are the estimated delivery times for your components?
Step 5: Conduct a Supplier Capability Assessment
Assess the capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. This may include visiting their facilities or requesting detailed information about their equipment and technologies used for spot facing.
- Key Factors:
- What type of machinery do they use for spot facing?
- Are they equipped to handle the materials specified in your requirements?
Step 6: Review Quality Control Processes
Understanding a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure consistent product quality. Inquire about their inspection methods, testing protocols, and how they handle defects or non-conformance.
- Important Questions:
- What quality assurance measures are in place?
- How do they document and report quality issues?
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Finally, set clear communication protocols with your chosen supplier. Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that your requirements are met throughout the manufacturing process.
- Best Practices:
- Designate a point of contact for all project-related communications.
- Schedule regular updates or check-ins to monitor progress.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for spot face machining, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their technical and quality requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for spot face in machining Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Spot Face Machining?
When analyzing the cost structure of spot face machining, several components contribute to the overall pricing. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials for spot-faced components include aluminum, steel, and various alloys. Prices fluctuate based on market demand and material specifications, so it’s essential to select materials that balance quality and cost-effectiveness.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled machinists and operators. Labor rates can vary widely based on location, skill level, and the complexity of the machining process. Regions with higher wage standards, such as parts of Europe, may have increased labor costs compared to lower-wage regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with running the machining facility, such as utilities, rent, and maintenance of machinery. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment for creating spot faces, such as spot-facing cutters, contribute to upfront costs. Tooling costs can be amortized over production volume, making high-volume orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that spot-faced components meet specified tolerances and surface finishes requires robust QC processes. Investments in inspection technologies and skilled personnel can add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining quality standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are significant, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can all influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. The margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the relationship between the buyer and supplier.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Spot Face Machining Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of spot face machining, particularly for international buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, which can significantly lower the overall cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specific tolerances may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (like ISO or AS9100) can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, capabilities, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but the reliability could justify the cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact the total cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Spot Face Machining Procurement?
Navigating the procurement of spot face machining requires strategic planning and negotiation skills, especially for international buyers.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly for large orders. Leverage your purchasing power to negotiate better terms and discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of total costs, including initial pricing, logistics, and any potential tariffs. This holistic view will help identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial costs, consider TCO, which includes long-term expenses such as maintenance, downtime, and replacement parts. Investing in higher-quality components may reduce TCO over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and how they can affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks associated with exchange rates.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Request formal quotes to obtain accurate pricing for your needs.
By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic procurement tips, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing spot face machining services.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing spot face in machining With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Spot Facing in Machining
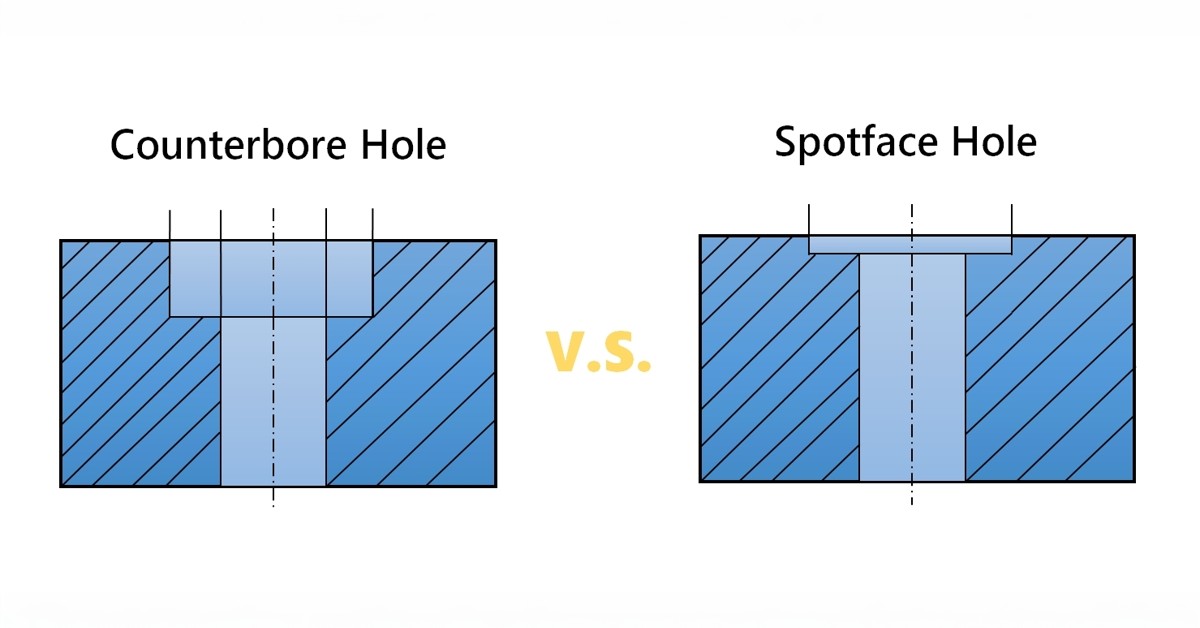
When evaluating machining processes, it’s essential to consider various options available to achieve the desired outcomes. Spot facing, while effective for creating a flat landing surface for fasteners, is not the only method available. This section compares spot facing with alternative solutions, including counterboring and milling, to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Spot Face In Machining | Counterbore | Milling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides a level surface on uneven substrates; ideal for shallow depth. | Creates a recessed area for fasteners; suitable for flush mounting. | Versatile; can create complex shapes and surfaces. |
| Cost | Generally low; requires specialized tooling but minimal setup. | Moderate; involves deeper cutting and more tool wear. | Higher; setup and tooling can be expensive, depending on complexity. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward with dedicated tools; requires precision. | Requires more precision and depth control; may need specialized tools. | Complex setup; requires skilled operators for effective use. |
| Maintenance | Low; tools used for spot facing are durable and easy to maintain. | Moderate; counterbore tools may require regular sharpening. | Higher; milling machines demand consistent maintenance and calibration. |
| Best Use Case | Uneven surfaces needing a flat area for fastener seating. | Applications where fasteners need to be flush with the surface. | Projects requiring intricate designs or profiles beyond simple holes. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Counterboring?
Counterboring is a method that creates a cylindrical hole with a flat bottom and a larger diameter above it, allowing fasteners to sit flush with the surface. Its primary advantage is that it effectively hides fastener heads, making it suitable for aesthetic applications or environments where exposed fasteners may catch or interfere with other components. However, counterboring can be more expensive due to the need for deeper cuts and additional tool wear. It also requires precise depth control, which can complicate the process compared to spot facing.
How Does Milling Compare to Spot Facing in Terms of Flexibility?
Milling is a highly versatile machining process that can produce complex geometries, including flat surfaces, contours, and intricate designs. This flexibility is its greatest strength, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, the cost of milling equipment and the need for skilled operators can make it less accessible for simpler tasks that spot facing could accomplish more efficiently. Additionally, milling may require more extensive setup and maintenance, making it less ideal for projects focused solely on creating flat surfaces for fasteners.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Machining Solution?
When selecting a machining method, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects, such as surface conditions, desired aesthetics, and budget constraints. Spot facing excels in scenarios involving uneven surfaces where fasteners must be securely seated. Counterboring is ideal for applications requiring flush fastener placement, while milling offers extensive flexibility for more intricate designs. By assessing these factors, buyers can select the most suitable machining solution that aligns with their operational needs and financial objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for spot face in machining
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Spot Face in Machining?
When engaging in spot face machining, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product. Here are several essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the material used in the machining process, such as steel, aluminum, or titanium. The choice of material affects not only the strength and durability of the component but also its machinability. For instance, higher-grade materials might be required for applications subject to extreme stress or corrosion, influencing procurement decisions and costs.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In spot face machining, maintaining strict tolerances ensures that fasteners fit securely and that components align correctly. Tight tolerances are critical in industries like aerospace and automotive, where safety and performance are paramount. Understanding tolerance specifications can prevent costly reworks or failures in the field.
3. Depth of Cut
The depth of cut in spot facing determines how much material is removed to create a flat surface for fasteners. This specification is vital, as it ensures that the fastener sits flush or slightly below the workpiece surface, preventing interference with adjacent components. Incorrect depth can lead to assembly issues, impacting operational efficiency.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture of the surface after machining, usually specified in microinches or micrometers. A smooth surface finish is essential for effective sealing and load distribution when fasteners are applied. In sectors such as medical devices or electronics, where cleanliness and precision are non-negotiable, understanding surface finish requirements can be crucial for compliance and performance.
5. Diameter of Spot Face
The diameter of the spot face must be larger than the fastener head to ensure proper seating. This specification is important to ensure a stable mounting point, especially when dealing with uneven or curved surfaces. Incorrect diameter can lead to inadequate support for the fastener, potentially resulting in component failure.
6. Angle of Entry
The angle at which the fastener is introduced to the spot face can influence the overall strength of the joint. A 90-degree angle is standard, but variations may be necessary based on the design requirements. Understanding this property is crucial for ensuring that the assembly can withstand operational stresses without failure.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Spot Face Machining?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the machining sector. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for components that meet specific quality and compatibility standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their procurement strategies and manage inventory effectively, especially in large-scale projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific goods or services. This process is critical for establishing cost expectations and comparing supplier offers, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping, insurance, and risk management aspects, which are vital for successful cross-border operations.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools through a computer. CNC technology enhances precision and repeatability in spot face machining, making it essential for high-quality production in various industries.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time from the initiation of an order until its completion and delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and meeting project deadlines, particularly in industries where timing is critical.
By comprehending these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of spot face machining more effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the spot face in machining Sector
What are the Key Market Drivers Influencing Spot Face in Machining?
The global machining market, particularly for spot face applications, is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving industrial demands. Key factors include the increasing need for precision engineering in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where spot face holes ensure secure fastening on uneven surfaces. Additionally, the rise of automation and CNC machining technologies enhances production efficiency, allowing for high-quality spot face operations at scale. As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable machining solutions, they increasingly prioritize suppliers that can offer customized services, robust quality assurance, and rapid turnaround times.
Emerging trends such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping sourcing strategies. Companies are leveraging smart manufacturing technologies to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and enhance supply chain transparency. In this context, international B2B buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who adopt these technologies, as they are more likely to provide innovative solutions that meet specific project requirements. Additionally, the growing focus on local sourcing is compelling manufacturers to establish regional partnerships, reducing lead times and transportation costs while fostering economic development in emerging markets.
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Practices in the Spot Face Machining Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the spot face machining sector. The environmental impact of machining processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is gaining traction, with buyers increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly materials and processes. This shift is not only beneficial for the planet but can also enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Buyers should consider suppliers that utilize ‘green’ certifications and materials, such as recycled metals or eco-friendly cutting fluids, which minimize environmental impact. Furthermore, a transparent supply chain that adheres to ethical labor practices can be a significant differentiator in the global marketplace. As awareness around corporate social responsibility grows, buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East are particularly inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
What is the Historical Context Behind Spot Face Machining Practices?
The practice of spot facing has its roots in traditional machining techniques, evolving significantly over the last century. Originally employed to address the challenges of fastening components on uneven surfaces, spot face machining has become a critical operation in modern manufacturing. With the advent of CNC technology in the late 20th century, the precision and efficiency of spot face operations have dramatically improved, allowing for tighter tolerances and more complex designs.
As industries continue to advance, the role of spot face machining has expanded beyond simple applications to become integral in high-stakes sectors like aerospace and defense, where safety and reliability are paramount. This evolution reflects broader trends in manufacturing, where the demand for precision and adaptability drives the development of innovative machining solutions. Understanding this historical context enables B2B buyers to appreciate the significance of spot face machining in today’s competitive landscape and make informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of spot face in machining
-
How do I ensure the quality of spot face machining from suppliers?
To ensure quality in spot face machining, request detailed specifications and quality assurance processes from potential suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards that indicate a commitment to quality. It’s advisable to ask for samples or conduct an initial test order to evaluate the workmanship. Additionally, establish clear communication channels and regular updates during production to address any concerns promptly. A thorough vetting process, including checking references and reviewing past projects, will also help ensure you choose a reliable supplier. -
What is the best material for spot face machining applications?
The best material for spot face machining depends on the specific application and environmental conditions. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and various alloys, each offering different strengths and properties. For high-stress applications, steel or titanium may be preferred due to their durability. In contrast, aluminum is often chosen for lightweight applications. Discuss your project requirements with suppliers to identify the most suitable material that balances performance, cost, and availability for your specific needs. -
How can I customize spot face machining to meet my project requirements?
Customization in spot face machining can be achieved by specifying the dimensions, depth, and finish of the spotface according to your project needs. Provide detailed engineering drawings and specifications to your supplier to ensure they understand your requirements. Additionally, discuss any unique features or tolerances you may need. Many suppliers are equipped to handle custom orders, but it’s important to confirm their capabilities and lead times to avoid delays in production. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for spot face machining?
Minimum order quantities for spot face machining can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may have MOQs as low as 10 units, while others might require hundreds, especially for customized or specialized parts. It’s essential to communicate your needs and inquire about flexibility in MOQs, particularly if you are testing a new design or entering a new market. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate MOQs based on your specific project requirements and potential for long-term business. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing spot face machining?
Payment terms for spot face machining can differ based on supplier policies and the size of your order. Common terms include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. For larger orders or long-term relationships, suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms. Always clarify payment terms in advance and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable terms over time. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international spot face machining orders?
Logistics for international spot face machining orders typically involve coordinating production timelines, shipping methods, and customs clearance. Suppliers often handle shipping arrangements, but it’s crucial to discuss whether they provide door-to-door service or if you’ll need to manage logistics independently. Understand the delivery timelines and associated costs, including duties and tariffs, to avoid unexpected expenses. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international shipping can streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
What quality assurance practices should I look for in suppliers of spot face machining?
When sourcing spot face machining, look for suppliers with robust quality assurance practices, such as in-process inspections, final product testing, and adherence to industry standards. Inquire about their use of precision measuring tools and techniques, such as CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspections, to ensure dimensional accuracy. Additionally, ask if they have a documented quality management system that outlines their procedures for handling defects and customer feedback. This level of diligence can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar products. -
How can I evaluate potential suppliers for spot face machining?
Evaluating potential suppliers for spot face machining involves a multi-faceted approach. Start by assessing their experience and expertise in machining, particularly with spot faces. Request references and case studies to understand their capabilities and reliability. Analyze their production capacity and technology, ensuring they can meet your volume and quality requirements. Additionally, consider their communication practices and customer service responsiveness, as these factors will play a crucial role in your overall partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Spot Face In Machining Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CNC Cookbook – Spotfaces vs. Counterbores
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Spotfaces and counterbores are machining features used to create secure connections between components. Spotfaces provide a flat, accurately located surface for fasteners, while counterbores create a cylindrical recess for fastener heads. Key differences include depth, function, screw hole accommodation, and surface finish. Spotfaces are shallower and offer a smoother finish, suitable for various …
2. Erix – Spot Facing Tools
Domain: erixtool.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Erix spot facing tools are available for hole diameters ranging from 4.5 mm to 69 mm. They come with options for cylindrical and Morse taper spindles. The tools are made from high-speed steel and carbide inserts, allowing customization for different materials and machining scenarios. Spot facing is used to create a smooth, flat surface around pre-drilled holes, ensuring secure mounting of componen…
3. Rapid Axis – Back Spot Facing
Domain: rapidaxis.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Back spot facing is a machining process used to create a flat and smooth surface on the inner diameter of a hole. It involves removing material to create a uniform and level base that is perpendicular to the hole’s axis. This technique is crucial for applications such as bearing seats, flange alignment, threaded holes, and rectifying casting defects. The benefits include improved alignment, enhanc…
4. At Machining – Spotface and Counterbore Holes
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Spotface Hole: A shallow, cylindrical recess over a pilot hole that creates a smooth, flat mounting surface for fastener heads. It is also known as a shallow counterbore hole, providing accurate recess for load distribution and alignment of fasteners. Counterbore Hole: A flat, recessed mounting surface cut into a material at the entrance of a drilled hole, designed to protect the screw head. It is…
5. Reddit – Machining Techniques Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around two machining techniques: spot facing and machining flats, specifically in the context of designing a flange with tapped holes. Key considerations include ease of machining, material removal, aesthetic preferences, and the importance of consulting experienced machinists for practical insights. Spot facing may involve less material removal and can be done in a single …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for spot face in machining
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Machining Operations?
In conclusion, spot facing is a critical machining technique that ensures precision and functionality in component assembly, particularly when dealing with uneven surfaces. Understanding the distinct advantages of spot face versus counterbore holes empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions that enhance product quality and operational efficiency. By strategically sourcing components that utilize spot facing, companies can significantly reduce assembly issues and ensure a higher standard of finished products.
For international buyers, especially from emerging markets in Africa and South America, as well as established industries in the Middle East and Europe, investing in high-quality machining services can yield substantial returns. As global supply chains evolve, the demand for precision-engineered components will only grow.
To remain competitive, it is imperative to establish relationships with reliable suppliers who understand the nuances of spot facing and can deliver consistent quality. As you look to the future, consider the potential of leveraging advanced machining techniques to drive innovation in your projects. Embrace strategic sourcing today to ensure your operations are not just reactive, but proactive and primed for success.