Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small metal laser cutter
In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, sourcing a small metal laser cutter can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With various options available globally, including advanced technologies and diverse supplier offerings, navigating this market requires strategic insight. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the different types of small metal laser cutters, their applications across industries, and the critical factors for effective supplier vetting. By exploring cost considerations, performance specifications, and operational efficiencies, this guide equips buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically in markets like Nigeria and Germany—with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
Understanding the nuances of small metal laser cutters is essential for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The laser cutting technology’s precision and efficiency can significantly reduce operational expenses compared to outsourcing, promising a substantial return on investment. This guide not only illuminates the essential features and capabilities of small metal laser cutters but also offers insights into the latest trends and innovations within the industry. By empowering international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this resource aims to streamline the procurement process, ensuring that companies can invest wisely in equipment that meets their specific needs and operational goals.
Understanding small metal laser cutter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Fiber Laser Cutter | Enclosed design, energy-efficient, cuts up to 12mm steel | Monograms, automotive parts, jewelry | Pros: Cost-effective, safe, high precision. Cons: Limited size for larger projects. |
| Open Bed Fiber Laser Cutter | Open design for larger sheets, versatile power options | Architectural components, signage, custom parts | Pros: Flexible size, adaptable. Cons: Safety concerns with open design. |
| Hybrid CO2/Fiber Laser Cutter | Cuts both metal and non-metal, dynamic focus laser head | Advertising materials, decorative items | Pros: Multi-functional, efficient for diverse materials. Cons: May require more maintenance. |
| Handheld Fiber Laser Cutter | Portable, user-friendly, ideal for on-site cutting | Repair work, small fabrication jobs | Pros: Mobility, ease of use. Cons: Limited cutting capacity compared to fixed models. |
| Industrial Flatbed Laser Cutter | High power options (up to 20kW), robust for heavy-duty use | Large-scale production, complex designs | Pros: High throughput, can handle thick materials. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires more space. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Compact Fiber Laser Cutters?
Compact fiber laser cutters are designed for small to medium-sized operations, featuring an enclosed structure that enhances safety while minimizing environmental impact. They are capable of cutting metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum with high precision, making them ideal for applications such as jewelry making and automotive components. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate their cutting needs, space availability, and the potential return on investment, as these machines can significantly reduce outsourcing costs.
How Do Open Bed Fiber Laser Cutters Differ?
Open bed fiber laser cutters offer a flexible approach to metal cutting, accommodating larger sheets and various materials. Their design allows for easy access to the work area, making it suitable for complex cutting jobs and larger components. However, buyers must consider the trade-off between versatility and safety, as open designs expose operators to laser radiation. This type of cutter is particularly beneficial for businesses in sectors like architecture and signage, where large, intricate designs are common.
What Makes Hybrid CO2/Fiber Laser Cutters a Smart Choice?
Hybrid CO2/fiber laser cutters combine the capabilities of both laser types, allowing for cutting of both metal and non-metal materials. This versatility makes them valuable in industries such as advertising and decorative arts, where different materials may be used in a single project. While they offer flexibility, potential buyers should be aware of the increased maintenance requirements and the need for a more complex setup compared to single-type laser cutters.
Why Consider Handheld Fiber Laser Cutters?
Handheld fiber laser cutters are portable solutions ideal for on-site applications, such as repairs and small fabrications. Their user-friendly design enables quick adjustments and straightforward operation, making them an attractive option for businesses that require mobility. However, they typically have lower cutting capacities and may not be suitable for high-volume production environments. Buyers should assess their specific needs for portability versus production efficiency before investing.
What Are the Advantages of Industrial Flatbed Laser Cutters?
Industrial flatbed laser cutters are designed for high-volume production and can handle thick materials with power options reaching up to 20kW. They are robust machines capable of executing complex designs quickly and efficiently, making them suitable for large-scale manufacturing operations. However, the higher initial investment and space requirements may be a barrier for smaller businesses. Buyers should consider their production capacity, budget, and space before making a decision on this type of cutter.
Key Industrial Applications of small metal laser cutter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of small metal laser cutter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Cutting automotive panels and components | High precision and reduced waste enhance production efficiency | Power requirements, cutting thickness, and speed capabilities |
| Jewelry Manufacturing | Creating intricate jewelry designs | Ability to cut fine details with minimal kerf, enhancing product quality | Material compatibility, laser power options, and design flexibility |
| Electrical Equipment | Fabricating electrical enclosures and parts | Streamlined production processes and lower operational costs | Enclosure size, material specifications, and safety features |
| Construction | Fabricating metal structures for buildings | Improved accuracy and reduced lead times in construction projects | Cutting area dimensions, power requirements, and portability |
| Signage and Advertising | Producing custom metal signs | High-quality finishes and the ability to create complex shapes | Material types, design software compatibility, and support for bulk orders |
How is a Small Metal Laser Cutter Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, small metal laser cutters are extensively utilized for cutting automotive panels and components. These machines offer high precision, which is critical for fitting parts together seamlessly. By minimizing waste during the cutting process, manufacturers can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. Buyers in this industry should consider the power requirements and cutting thickness capabilities of the laser cutter to ensure it meets the specific needs of their production line.
What Role Does a Small Metal Laser Cutter Play in Jewelry Manufacturing?
Small metal laser cutters are revolutionizing the jewelry manufacturing industry by allowing artisans to create intricate designs with high precision. The ability to cut fine details with minimal kerf ensures that each piece of jewelry maintains its quality and value. For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing a machine that accommodates various materials and offers flexible laser power options is essential for adapting to diverse design requirements.
How Can Electrical Equipment Manufacturers Benefit from Small Metal Laser Cutters?
Electrical equipment manufacturers use small metal laser cutters to fabricate enclosures and components crucial for housing sensitive electronic parts. The precision cutting capabilities of these machines streamline production processes, leading to lower operational costs and improved product quality. Buyers should prioritize sourcing machines with specific features such as adequate enclosure size and material specifications to ensure compliance with industry standards.
In What Ways Are Small Metal Laser Cutters Used in Construction?
In the construction industry, small metal laser cutters are employed to fabricate metal structures, ensuring improved accuracy and reduced lead times for projects. These cutters facilitate the production of custom metal parts that fit specific building requirements, enhancing the overall efficiency of construction processes. When sourcing these machines, buyers should consider the cutting area dimensions and power requirements, as well as the portability of the equipment for on-site use.
How Are Small Metal Laser Cutters Transforming the Signage and Advertising Sector?
The signage and advertising industry benefits from small metal laser cutters by producing custom metal signs that feature high-quality finishes and complex shapes. These machines enable businesses to create unique branding elements that stand out in competitive markets. Buyers should pay attention to material types compatible with the laser cutter, as well as the machine’s ability to support bulk orders, ensuring they can meet customer demands effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small metal laser cutter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Power Supply Limitations for Laser Cutters
The Problem: Many businesses, especially in regions with less stable power infrastructure, face challenges when sourcing a small metal laser cutter that requires specific power configurations. For instance, a buyer in Nigeria may encounter difficulties in finding a machine that operates efficiently on single-phase power, as many high-capacity laser cutters necessitate three-phase power. This limitation can lead to increased setup costs and delays, as well as potential downtime if the electrical requirements are not met.
The Solution: When considering a small metal laser cutter, buyers should prioritize models that operate on single-phase power, such as those offering 1kW to 2kW configurations. These machines are particularly advantageous for companies in regions with power constraints, as they can be easily integrated into existing electrical systems without requiring extensive upgrades. Additionally, potential buyers should consult with suppliers to assess the compatibility of laser cutters with local power conditions, and consider investing in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) or voltage stabilizers to ensure consistent operation. Engaging with local experts or technicians during the setup phase can further mitigate risks associated with power supply issues.
Scenario 2: Achieving Precision in Diverse Metal Thicknesses
The Problem: B2B buyers often need to cut a variety of metal types and thicknesses, from thin aluminum sheets to thicker stainless steel. The challenge arises when a laser cutter cannot accommodate this diverse range, leading to inefficient workflows and suboptimal cut quality. For example, a manufacturer in South America may need a versatile cutting solution but find that their chosen machine can only handle a limited thickness, resulting in the need for multiple cutters or outsourcing.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should look for small metal laser cutters that offer adjustable power settings and a wide cutting capacity. Machines with features like automatic height adjustment and advanced focusing technology can adapt to varying thicknesses and ensure precise cuts. It’s crucial to request detailed specifications from suppliers, including maximum cutting capacities for different metals, and to seek demonstrations or trials before purchase. Additionally, investing in training for operators can enhance their ability to optimize settings for different materials, ultimately leading to better productivity and reduced material waste.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety and Compliance in Laser Operations
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern when operating laser cutting machines, particularly in industrial settings. Buyers must navigate regulations and standards that dictate safe practices for laser operations. For instance, a company in Germany may be apprehensive about potential hazards such as stray radiation or fumes generated during cutting, which can pose health risks to employees and lead to costly compliance violations.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize small metal laser cutters that come with comprehensive safety features, such as fully enclosed designs, proper ventilation systems, and integrated fume extraction units. These features significantly reduce the risk of exposure to harmful emissions and stray laser light. It’s also advisable to consult with local regulatory bodies to understand specific compliance requirements for laser operations in their area. Implementing a robust training program for staff on safety protocols and emergency procedures can further safeguard operations. Regular maintenance checks and using protective equipment will also enhance workplace safety and ensure compliance with health standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small metal laser cutter
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Small Metal Laser Cutters?
When selecting materials for small metal laser cutting applications, understanding the properties and performance characteristics of each material is crucial for achieving optimal results. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
Carbon Steel: A Versatile Choice
Carbon steel is widely used in various industries due to its excellent strength and affordability. It typically exhibits high tensile strength and good weldability, making it suitable for structural applications. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, which can limit its longevity in certain environments.
Pros:
– Cost-effective and widely available.
– High strength-to-weight ratio.
– Excellent for structural applications.
Cons:
– Susceptible to rust and corrosion without protective coatings.
– Requires surface treatment to enhance durability.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36 is vital. Buyers should also consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance the material’s lifespan.
Stainless Steel: Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It maintains its integrity in harsh environments, making it ideal for applications in the food and medical industries. The material is also easy to clean, which is a significant advantage in hygiene-sensitive applications.
Pros:
– Excellent corrosion resistance.
– Long-lasting and low maintenance.
– Suitable for high-temperature applications.
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to carbon steel.
– More challenging to cut due to its toughness.
For buyers in Europe, compliance with DIN standards, such as DIN 1.4301 for austenitic stainless steel, is essential. The higher cost may be offset by the material’s longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and excellent machinability. It is commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications due to its strength-to-weight ratio. Aluminum also offers good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to handle.
– Good corrosion resistance, especially when treated.
– Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons:
– Generally more expensive than carbon steel.
– Softer than other metals, which can affect durability in certain applications.
International buyers should consider the common standards for aluminum, such as JIS H 4000 in Japan or EN 573 in Europe. The cost may be a consideration, but the benefits in specific applications often justify the investment.
Copper: High Conductivity for Specialized Applications
Copper is renowned for its electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical components and heat exchangers. While it is not as strong as steel, its unique properties make it invaluable in specific applications.
Pros:
– Exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity.
– Naturally antimicrobial, making it suitable for medical applications.
– Easy to work with and form.
Cons:
– High cost compared to other metals.
– Prone to tarnishing and corrosion without proper treatment.
Buyers from the Middle East, where copper is commonly used in electrical applications, should ensure compliance with local electrical standards. The investment in copper can be justified by its performance benefits in specialized applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Small Metal Laser Cutters
| Material | Typical Use Case for small metal laser cutter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to rust | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and cutting difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and good machinability | More expensive and softer | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical components, heat exchangers | Exceptional conductivity | High cost and prone to tarnishing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of material choice for small metal laser cutting applications. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small metal laser cutter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Small Metal Laser Cutters?
The manufacturing process of small metal laser cutters involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality machines capable of meeting diverse cutting needs. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Processed?
The first step in manufacturing small metal laser cutters is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-grade metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Suppliers should emphasize the quality of the raw materials, as this directly influences the machine’s performance and longevity.
Once the materials are sourced, they undergo cutting, bending, and machining processes to create components like the frame, cutting head, and other structural elements. Advanced techniques, such as water jet cutting or CNC machining, may be utilized to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used for Component Shaping?
After material preparation, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the components through processes like laser cutting, punching, and welding. The use of laser cutting technology ensures that parts are accurately shaped with minimal kerf, enhancing the overall quality of the machine.
Welding techniques, including TIG or MIG welding, are employed to join metal parts securely, ensuring structural integrity. Manufacturers often use robotic welding systems to enhance precision and speed while maintaining consistent quality.
Assembly: How Are Components Brought Together?
The assembly stage is crucial in the manufacturing process, where all individual components are brought together to create the final product. This typically involves the installation of electrical and mechanical systems, including the laser source, motion systems, and control panels.
Quality checks are integral during assembly. Components are often tested for alignment and functionality before final assembly, ensuring that the machine operates as intended. Using modular designs can facilitate easier assembly and maintenance, which is advantageous for both manufacturers and end-users.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure Aesthetic and Functional Quality?
Finishing processes enhance both the aesthetic appeal and durability of the laser cutters. Techniques such as powder coating, anodizing, or plating are employed to provide protection against corrosion and wear. Additionally, these processes contribute to the machine’s visual appeal, which can be a selling point in the competitive B2B market.
Final inspections are conducted to ensure that all components meet specified standards and are free from defects. This attention to detail is vital for ensuring customer satisfaction and long-term reliability.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Small Metal Laser Cutters?
Quality assurance is a pivotal aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. Buyers should be aware of these standards to make informed purchasing decisions.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
One of the primary international standards relevant to small metal laser cutters is ISO 9001. This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Manufacturers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high-quality standards throughout the production process.
Additionally, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding local certification requirements is crucial, as these may vary significantly.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet specified standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet quality specifications before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to identify any deviations from quality standards. This can include checking dimensions, alignment, and welding quality.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing to verify functionality, performance, and safety. This may involve operational tests, calibration, and performance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international buyers, especially from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance is paramount. Here are actionable steps to ensure that suppliers meet quality standards:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting regular supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and certifications to verify compliance with international standards. On-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality control measures implemented by suppliers.
How Can Buyers Leverage Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. These inspectors can assess both the raw materials and the final products, ensuring compliance with specified standards. This is particularly beneficial for buyers who may not have the capability to perform detailed inspections themselves.
What Documentation Should Buyers Request?
When evaluating potential suppliers, buyers should request comprehensive documentation, including:
- Quality Management System (QMS) documentation: This should outline the manufacturer’s processes for maintaining quality.
- Certificates of compliance: These documents verify that the products meet specific standards, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking.
- Test reports: Detailed reports from testing conducted during various manufacturing stages can provide assurance of product quality.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Impact International B2B Transactions?
Quality control nuances can significantly impact international B2B transactions. Buyers must be aware of regional standards and certifications that may differ from their own. For instance, a product compliant with European standards may not automatically meet the requirements in Africa or South America.
Understanding these nuances can prevent costly delays, fines, or product recalls. B2B buyers should engage in thorough research and maintain open lines of communication with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding of quality expectations and compliance requirements.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for small metal laser cutters is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and verification practices, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small metal laser cutter’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, sourcing a small metal laser cutter can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides a structured checklist to help international B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that you select the right equipment tailored to your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific cutting requirements is essential. Consider the types of materials you will be working with, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper, and their respective thicknesses. Additionally, evaluate the required cutting area dimensions and the desired power output (e.g., 1kW to 20kW) to ensure the machine meets your production needs.
Step 2: Evaluate Supplier Reputation and Experience
Choosing a reputable supplier is critical to ensuring quality and reliability. Research potential suppliers’ backgrounds, focusing on their experience in the industry and customer feedback. Look for case studies or testimonials from companies in similar markets to gauge their performance and service levels.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your potential suppliers comply with international standards, such as ISO certifications and CE marking, which indicate adherence to safety and quality regulations. This step is vital for safeguarding your investment and ensuring that the equipment meets operational safety requirements.
Step 4: Assess Maintenance and Support Services
Inquire about the maintenance options and technical support offered by the supplier. A good supplier should provide a clear maintenance schedule and readily available technical assistance. Assess the warranty terms, including parts and labor, and check if extended warranties are available to cover potential future repairs.
Step 5: Request Product Demonstrations
Before making a final decision, request live demonstrations of the equipment. This allows you to evaluate the machine’s performance in real-time and assess its user-friendliness. Pay attention to the machine’s cutting speed, precision, and any automated features that enhance operational efficiency.
Step 6: Compare Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While the initial purchase price is important, consider the total cost of ownership over the machine’s lifespan. Factor in operational costs, including energy consumption, maintenance expenses, and potential downtime. Some machines may have lower upfront costs but higher operational expenses, affecting your overall budget.
Step 7: Explore Financing Options and Payment Terms
Investigate financing options available through suppliers or third-party lenders. Flexible payment terms can ease budget constraints and make the purchase more manageable. Ensure you understand all terms before committing, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and any hidden fees.
By following these steps, you can confidently navigate the procurement process for a small metal laser cutter, ensuring that you select a machine that aligns with your business objectives and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small metal laser cutter Sourcing
When sourcing small metal laser cutters, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for making informed decisions. The cost components and price influencers can significantly impact the overall investment and operational efficiency.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Small Metal Laser Cutters?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in manufacturing small metal laser cutters includes the raw materials required for the machine, such as metals, lasers, and electronic components. High-quality materials can enhance performance but also increase costs. Suppliers often provide different grades of materials, which can affect durability and cutting efficiency.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for assembling and maintaining laser cutters. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location and the level of expertise required. In regions like Europe, labor may be more expensive compared to emerging markets in Africa or South America, potentially influencing total costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and operational scale. Efficient manufacturers may have lower overheads, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be required for the production of laser cutters. The cost associated with these tools can be substantial, especially if custom tooling is needed for specialized configurations. Buyers should consider this when evaluating total costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures the reliability and efficiency of the laser cutters. While this can add to initial costs, it can significantly reduce long-term operational issues and maintenance costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and insurance can add to the total expenditure. The complexity of international shipping can lead to variations in logistics costs, particularly when sourcing from suppliers in different continents.
-
Margin: Manufacturers will typically include a profit margin in the pricing. Understanding the market dynamics and the supplier’s positioning can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Small Metal Laser Cutters?
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly influence pricing. Larger orders often benefit from bulk discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customization options, such as power levels or additional features, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials or certified components often come at a premium. Certifications can also influence pricing, especially if compliance with international standards is necessary.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and relationship can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records might charge more but offer better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly impact the final cost. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate responsibilities and costs related to shipping, insurance, and handling, which can add to the total expense.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage the competition among suppliers to negotiate better pricing. Understanding market rates and being clear about your needs can lead to favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the purchase price but also operating costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower TCO if the equipment is more efficient and reliable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties that can affect costs when sourcing from different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Obtain comprehensive quotes that break down all cost components. This transparency helps in comparing offers and understanding the rationale behind pricing.
Conclusion
While sourcing small metal laser cutters, a detailed analysis of cost components and pricing influencers is essential for optimizing your investment. By understanding the intricacies of the cost structure, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. Always consult multiple suppliers and consider the long-term implications of your purchase to achieve the best possible outcome.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small metal laser cutter With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Metal Cutting
When considering investment in metal cutting technologies, it is essential to evaluate not just the small metal laser cutter but also viable alternatives. Each method presents unique advantages and drawbacks based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. This analysis aims to help B2B buyers identify the most suitable option for their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Small Metal Laser Cutter | Water Jet Cutting System | Plasma Cutting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with minimal kerf (≤25µm); suitable for thin to medium thickness metals (up to 12mm) | Excellent for thick materials; high versatility in cutting various materials | Fast cutting speed; less precision; ideal for thicker metals (up to 50mm) |
| Cost | Initial investment $35,000 – $65,000; lower operational costs | Higher initial cost (up to $100,000); higher operational costs due to water and abrasive materials | Lower initial cost ($15,000 – $30,000); higher operational costs due to consumables |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic electrical setup; limited training needed | More complex setup; may require specialized training for operation | Relatively easy to set up; minimal training for basic operation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; long-lasting fiber source (over 50,000 hours) | Moderate maintenance; needs regular water and abrasive management | Higher maintenance due to consumables; frequent nozzle replacements |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for detailed work, intricate designs, and small to medium parts | Best for thick materials and large-scale cutting applications | Suitable for rapid cutting of thicker metals in less detailed projects |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Water Jet Cutting System
Water jet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to cut through various substances, including metals. The primary advantage is its ability to handle thicker materials without altering their physical properties, making it ideal for applications in industries such as aerospace and construction. However, the operational costs can be significant due to the need for abrasives and water management, and the initial investment can be higher than that of a small metal laser cutter.
Plasma Cutting System
Plasma cutting involves using a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through electrically conductive materials. It is favored for its speed, making it a cost-effective solution for high-volume projects. However, the precision is generally lower compared to laser cutting, making it less suitable for intricate designs. Plasma cutting systems are typically cheaper upfront, but ongoing costs can accumulate due to frequent replacement of consumables like nozzles and electrodes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate metal cutting solution hinges on understanding your operational requirements and budget constraints. A small metal laser cutter is ideal for businesses focusing on precision and intricate designs, especially in fields such as jewelry and automotive components. In contrast, water jet systems excel in heavy-duty applications requiring thickness, while plasma cutters offer speed for less detailed work. By carefully assessing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their production goals and financial parameters.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small metal laser cutter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Small Metal Laser Cutters?
When considering the purchase of a small metal laser cutter, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that it meets the operational needs of your business. Below are essential specifications to evaluate:
1. Laser Power
Laser power, typically measured in watts (W), directly influences the cutting speed and thickness of materials the machine can handle. For instance, a 1kW laser can cut up to 6mm of carbon steel, while a 2kW laser can handle up to 12mm. Higher wattage means faster processing and the ability to cut thicker materials, making it vital for businesses that require high throughput.
2. Cutting Speed
Measured in meters per minute (m/min), cutting speed refers to how quickly the laser cutter can process materials. A machine with a maximum cutting speed of 25 m/min can significantly reduce production time. For B2B buyers, understanding cutting speed helps in assessing the machine’s efficiency and its potential return on investment (ROI).
3. Material Compatibility
Small metal laser cutters should be compatible with various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Knowing the range of materials that can be processed allows businesses to diversify their offerings and meet customer demands across different sectors.
4. Tolerance and Accuracy
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. High-precision machines offer tolerances of ±0.03mm or better, which is essential for applications requiring intricate designs, such as automotive components and jewelry. Accurate machines minimize waste and rework, which is crucial for maintaining profitability.
5. Cooling System
The cooling system, often water-cooled, plays a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Effective cooling prevents overheating, thereby extending the machine’s lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. Buyers should consider the cooling method when evaluating performance and reliability.
6. Enclosure Type
Laser cutters may come as open or fully enclosed systems. Enclosed systems enhance safety by containing stray radiation and reducing noise, making them suitable for environments where operator safety is a priority. Understanding the enclosure type can influence the decision based on workplace regulations and safety standards.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing a Small Metal Laser Cutter?
Navigating the procurement process involves familiarizing oneself with common industry terminology. Here are key terms to understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of laser cutters, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the equipment being purchased.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For small metal laser cutters, understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses that may not require large volumes initially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for a price quote on specific products or services. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to initiate the purchasing process and ensure they receive competitive pricing for their laser cutter needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing equipment from different countries, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. Knowing the lead time for a small metal laser cutter is important for planning production schedules and managing customer expectations.
6. Warranty and Service Agreements
These agreements outline the support a buyer can expect post-purchase, including repair services and parts replacement. Understanding warranty terms is essential for assessing the long-term reliability and operational costs associated with the laser cutter.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small metal laser cutter Sector
What are the Global Drivers and Current Trends in the Small Metal Laser Cutter Market?
The small metal laser cutter market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As global industries evolve, the need for efficient and versatile cutting solutions is paramount. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly adopting small metal laser cutters for their ability to handle complex designs and materials with minimal waste.
Emerging technologies, such as automation and IoT (Internet of Things), are reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers are seeking machines that integrate with existing production lines, offering real-time data analytics and remote monitoring capabilities. Moreover, advancements in fiber laser technology provide higher efficiency and lower operating costs, making these systems attractive for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities. For instance, systems with customizable power options allow businesses to scale operations according to their specific needs, a critical factor for companies operating in fluctuating markets.
Furthermore, the demand for compact and enclosed laser systems is rising, especially in urban areas where space is limited. These systems not only maximize efficiency but also ensure compliance with safety regulations, appealing to international buyers focused on workplace safety and environmental standards.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions for Small Metal Laser Cutters?
Sustainability is becoming a central consideration for international B2B buyers in the small metal laser cutter sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to seek solutions that minimize waste and energy consumption. Laser cutting technology is inherently more efficient than traditional cutting methods, producing less scrap material and requiring less energy. This efficiency aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable production practices.
Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability. This includes evaluating suppliers based on their use of environmentally friendly materials, energy-efficient operations, and adherence to green certifications. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, are becoming crucial for suppliers aiming to attract eco-conscious buyers.
Additionally, the trend toward using recyclable and sustainable materials is influencing product design. Manufacturers are exploring options for biodegradable or recyclable components in their machines, appealing to a market that values environmental responsibility. As these trends evolve, businesses that prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies will not only enhance their market reputation but also align with regulatory pressures and consumer expectations for greener manufacturing practices.
What is the Historical Context of Small Metal Laser Cutters in B2B Manufacturing?
The evolution of small metal laser cutters has been marked by significant technological advancements since their inception in the late 20th century. Originally, laser cutting technology was predominantly utilized in large industrial applications due to the high costs and space requirements of the machinery. However, as technology progressed, the development of compact and cost-effective laser systems made it feasible for small to medium enterprises (SMEs) to adopt these cutting solutions.
By the early 2000s, the introduction of fiber laser technology revolutionized the market, offering enhanced efficiency, lower operational costs, and superior cutting quality compared to traditional CO2 lasers. This shift allowed for greater versatility, enabling businesses to cut a wider range of materials, including metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and even non-metals, thereby expanding market opportunities.
Today, small metal laser cutters are essential tools for a variety of industries, facilitating rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing. Their ability to produce intricate designs with high precision has made them indispensable in sectors such as jewelry making, automotive components, and decorative metalwork. As the market continues to evolve, ongoing innovations promise to further enhance the capabilities and applications of small metal laser cutting technology, solidifying its role in modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small metal laser cutter
-
How do I choose the right small metal laser cutter for my business needs?
Selecting the right small metal laser cutter involves evaluating your production requirements, including the materials you intend to cut, thickness, and precision levels needed. Consider factors such as laser power (1kW to 20kW options), cutting speed, and the types of metals involved (stainless steel, aluminum, etc.). Additionally, assess the machine’s footprint and whether you need a fully enclosed design for safety. Consulting with suppliers about your specific applications can help you identify the best machine suited for your operations. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing a small metal laser cutter internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payment, deposits (usually 30-50%), and balance upon delivery or installation. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in the transaction. Consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for large investments. Always clarify any additional costs like shipping, taxes, and duties before finalizing the payment agreement. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) when sourcing small metal laser cutters?
MOQs for small metal laser cutters can differ significantly based on the manufacturer and the customization required. Some suppliers may accept single-unit orders, especially for standard models, while others may set an MOQ of 2-5 units to offset production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their policies. Always consider your budget and storage capabilities when determining the number of units to order. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including reviews, certifications, and previous client experiences. Request samples or demonstrations of the laser cutter to evaluate performance. Establish clear quality standards and specifications before placing an order. It may also be beneficial to include a clause in your purchase agreement that outlines quality checks and guarantees, as well as the processes for handling defects or non-conformities. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing a small metal laser cutter?
Logistics play a crucial role in importing a small metal laser cutter. Key considerations include shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance, and potential tariffs or duties. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, to facilitate customs processing. Engage a reliable freight forwarder who understands international regulations and can assist with the logistics to minimize delays and additional costs. -
What types of materials can be cut with a small metal laser cutter?
Small metal laser cutters are versatile and can cut various materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, copper, and even some non-metals with the right configuration. The thickness of the materials that can be cut will depend on the laser power, with typical capabilities ranging from 1.5mm to 12mm for metals. Understanding the specific materials you will work with is crucial for selecting a machine with the appropriate power and cutting capabilities. -
How do I evaluate the reliability of a laser cutter supplier?
Evaluating the reliability of a laser cutter supplier involves examining their track record, years in business, and customer feedback. Look for suppliers that offer warranties and after-sales support, as these are indicators of their confidence in their product. Request references from previous clients and consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible. Additionally, verify their compliance with international manufacturing standards, which can provide assurance of their operational quality. -
What are the advantages of owning a small metal laser cutter versus outsourcing cutting services?
Owning a small metal laser cutter provides several advantages, including cost savings in the long run, faster turnaround times, and greater control over production quality. By cutting in-house, businesses can respond more quickly to customer demands and reduce dependency on third-party services, which often come with high hourly rates. Furthermore, having a laser cutter allows for greater flexibility in design iterations and the ability to experiment with new projects without incurring additional costs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Small Metal Laser Cutter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
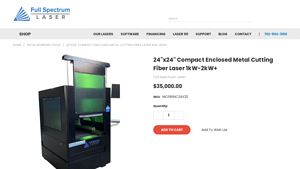
1. FS Laser – 24×24 Compact Enclosed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: 24″x24″ Compact Enclosed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser 1kW-2kW+
– MSRP: $35,000.00
– SKU: MCFBENC24X20
– Wattage Options: 1 kW, 1.5 kW, 2 kW
– Dust Collector Options: None, MC Series Industrial Dust Collector X4 (+$15,000), MC Series Industrial Dust Collector X6 (+$20,000)
– External Dimensions: 56″ X 48″ X 82″
– Cutting Capacity:
– 1kW: Up to 6mm carbon steel, 3mm stainless, 1.5mm aluminum
– 1.5…
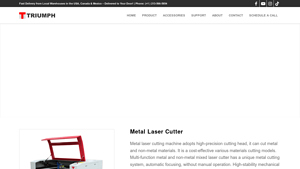
2. Triumph – Metal & Non-Metal Laser Cutter
Domain: triumphlaser.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Metal & Non Metal Laser Cutter
Key Features:
– High-speed multifunctional laser cutting machine
– Capable of cutting both metal and non-metal materials
– High-precision cutting head with automatic focusing
– Unique metal cutting system for mixed materials
– High-stability mechanical structure with smooth CNC movement
– Super strong beam with narrow slit and smooth edge
– Dynamic Focu…
3. PlasmaPro – Precision Metal Cutter
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Looking for a small footprint machine to cut through 1/4″ or less metal (brass, stainless, carbon steel, aluminum). Current needs are for cutting at least 1/4″ thickness, but thicker cuts would be acceptable. Interested in options around $50,000 for cutting 1/8″ or 3/32″ material. Suggestions for laser types include 2000 watt or more fiber lasers for thicker materials, and CO2 lasers outfitted wit…
4. LightObject – RANGER III
Domain: lightobject.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”RANGER III”,”size”:”600×380 (24\”x15\”)”,”type”:”Laser Desktop”,”price”:”$3,939.00″,”original_price”:”$5,200.00″,”stock”:”Only 2 left in stock”},{“name”:”SOLO II”,”size”:”500×300 (19\” x 11.8\”)”,”type”:”Laser Desktop W/O Z table”,”price”:”$2,990.00″},{“name”:”MAX renewed MSFC-1500W”,”type”:”fiber laser source”,”price”:”$2,350.00″},{“name”:”MAX renewed 1000W”,”type”:”fiber la…
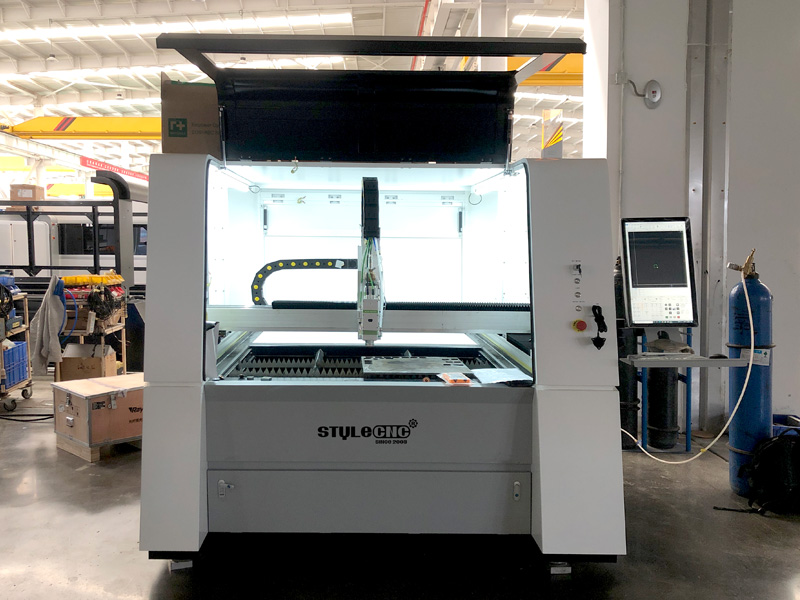
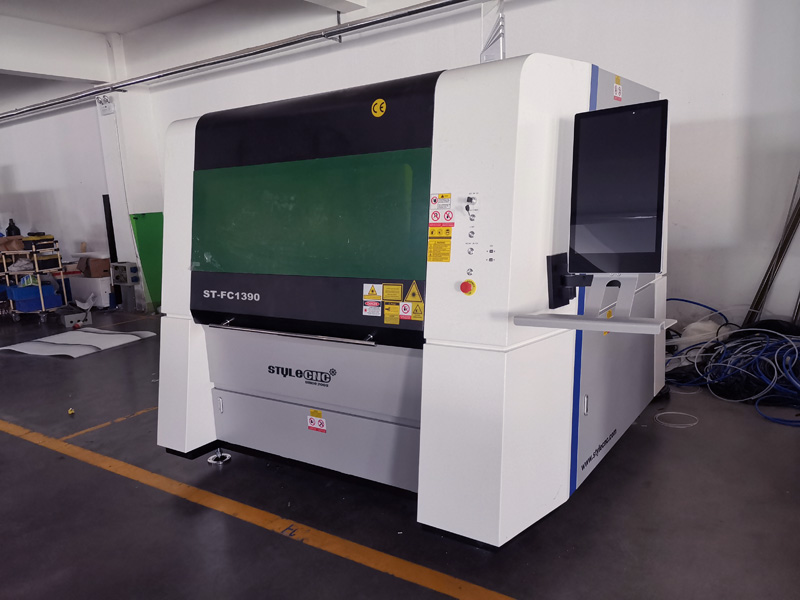
5. STYLECNC – Entry Level Small Metal Laser Cutter
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Entry Level Small Metal Laser Cutter for Beginners – STYLECNC Model: ST-FC1390 Laser Source: Raycus, IPG, MAX, RECI Power Options: 1500W, 2000W, 3000W, 6000W Price: $17,000 (Standard Edition) / $31,000 (Pro Edition) Stock: 180 Units Available Monthly Warranty: One-Year Limited Warranty for Entire Machine (Extended Warranties Available for Major Parts) Working Area: 1300mm x 900mm Repeat Positionin…
6. OMTech – Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Best Fiber Laser Cutting Machine for Metal Fabrication, OMTech Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines, FC22 1500W Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC22-C 1500W Open Metal Laser Cutting Machine, FC-105 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, FC-44 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine, Easy Financing with Clicklease – No Credit Needed, Price Match Guarantee, Customization options available, Power capacities ranging fr…
7. LightBurn – Desktop Laser Cutting Solutions
Domain: forum.lightburnsoftware.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Desktop laser cutter for metal up to 3mm thick; 1kW fiber laser recommended for cutting; 500W models claim to cut 3mm stainless; desktop solutions available for aluminum; X-Carve CNC frame compatibility; 20W fiber laser and Glowforge mentioned; need for sharp inside corners noted.
8. MechMate – Laser Cutting Solutions
Domain: mechmate.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutting for Metal: A Beginner’s Guide – CNC laser cutting technology uses a high-power laser beam guided by computer instructions to cut or engrave materials with high accuracy and precision. Commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and construction. The fiber laser cutter is a CNC laser cutting system for metal, offering high cutting quality, speed, p…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small metal laser cutter
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business with Small Metal Laser Cutters?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of small metal laser cutters presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By investing in advanced laser cutting technology, businesses can achieve remarkable precision and speed, significantly improving their production capabilities. The ability to cut various metals with minimal waste not only increases profitability but also positions companies competitively in their respective markets.
Moreover, as manufacturers increasingly adopt energy-efficient solutions, sourcing high-quality equipment can lead to substantial long-term savings. For companies in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the potential return on investment is compelling, especially when considering the high hourly rates charged by third-party cutting services.
As you explore options for small metal laser cutters, consider partnering with reputable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions to meet your specific needs. The future of metal cutting is bright, and with the right equipment, your business can thrive. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy today to position your company for success in an evolving marketplace.