Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small metal cutting laser
The global market for small metal cutting lasers presents a unique opportunity for businesses looking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities. However, navigating this landscape can be challenging, particularly when sourcing the right equipment that meets specific operational needs. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly turn to fiber laser technology for precision metal cutting, understanding the nuances of this market is essential for informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into various types of small metal cutting lasers, their applications across different sectors, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. From assessing power requirements and cutting capabilities to evaluating cost-effectiveness and potential return on investment, we equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make strategic choices. Whether you are in Nigeria, Vietnam, or elsewhere, this guide aims to demystify the selection process, ensuring that businesses can confidently invest in technology that enhances productivity and competitiveness.
By empowering buyers with actionable information, we pave the way for successful investments in small metal cutting lasers, enabling companies to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.
Understanding small metal cutting laser Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Enclosed Fiber Laser | Up to 2kW power, fully enclosed, compact design | Monograms, jewelry, automotive components | Pros: Space-efficient, safe operation. Cons: Limited cutting size. |
| Entry-Level Fiber Laser Cutter | User-friendly, various power options (up to 6kW) | Signs, logos, personalized parts | Pros: Affordable for startups, easy to learn. Cons: May lack advanced features. |
| Open Bed Fiber Laser | Larger work area, customizable configurations | Industrial applications, larger metal sheets | Pros: Versatile for large projects. Cons: Requires more space and safety measures. |
| High-Power Fiber Laser | Customizable power (up to 20kW), high-speed cutting | Heavy manufacturing, complex metal parts | Pros: Efficient for high-volume production. Cons: Higher upfront investment. |
| Desktop Laser Cutter | Compact, desktop size, lower power (up to 1500W) | Hobbyists, small businesses | Pros: Affordable, space-saving. Cons: Limited to thinner materials. |
What are the Characteristics of Compact Enclosed Fiber Lasers?
Compact enclosed fiber lasers are designed for small-scale operations, offering up to 2kW of power in a fully enclosed setup. Their compact design makes them suitable for businesses with limited space. They are particularly effective for cutting intricate designs in materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and even precious metals like gold and silver. B2B buyers should consider the balance between power and cutting area, as this type is best for smaller projects but may limit larger applications.
How Do Entry-Level Fiber Laser Cutters Cater to Beginners?
Entry-level fiber laser cutters are tailored for newcomers to metal fabrication, featuring user-friendly interfaces and options ranging from 1500W to 6000W. These machines are ideal for small businesses and hobbyists looking to produce signs, logos, and personalized items. Key purchasing considerations include budget constraints and the machine’s ability to handle various materials. While they offer an accessible entry point, buyers should be aware that these models may lack some advanced functionalities found in higher-end machines.
What Advantages Do Open Bed Fiber Lasers Offer for Larger Projects?
Open bed fiber lasers provide a larger working area, allowing for the cutting of bigger metal sheets, which is beneficial for industrial applications. These machines can be customized to meet specific operational needs, making them versatile for various projects. B2B buyers must assess the space available for installation and consider additional safety measures, as open designs expose operators to laser emissions. While they excel in flexibility, the need for a larger footprint and enhanced safety protocols can be a drawback.
Why Choose High-Power Fiber Lasers for Heavy Manufacturing?
High-power fiber lasers, with capabilities of up to 20kW, are designed for high-volume production environments where efficiency is paramount. They are suitable for cutting complex metal parts in heavy manufacturing sectors. Buyers should evaluate their production needs against the higher initial investment required for these machines. The return on investment can be significant for businesses that require rapid cutting speeds and the ability to handle thick materials, making them a smart choice for established companies.
How Do Desktop Laser Cutters Serve Small Businesses and Hobbyists?
Desktop laser cutters are compact and affordable, making them a popular choice for small businesses and hobbyists. With power options typically up to 1500W, they can handle thinner materials effectively. These machines are ideal for creating personalized products, but buyers should consider their limitations regarding material thickness and cutting speed. While they offer an economical entry into laser cutting, they may not suffice for larger-scale operations or more demanding applications.
Key Industrial Applications of small metal cutting laser
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of small metal cutting laser | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Cutting automotive panels and components | Enhances production efficiency and reduces waste | Consider power capacity for material thickness; ensure compatibility with existing systems. |
| Jewelry and Fashion | Creating intricate jewelry designs | Allows for high precision and customization | Look for machines with fine cutting capabilities and quick setup times. |
| Electronics | Fabricating enclosures and electronic components | Improves design flexibility and reduces lead times | Ensure the machine can handle various metal types and has a reliable supply chain for parts. |
| Industrial Signage | Producing metal signs and branding elements | Increases brand visibility and customer engagement | Evaluate the machine’s ability to cut various thicknesses and its operational safety features. |
| Home Appliances | Cutting parts for appliances like ovens and fridges | Streamlines production and enhances product quality | Assess the machine’s energy efficiency and maintenance requirements. |
How is Small Metal Cutting Laser Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, small metal cutting lasers are essential for producing precise automotive panels and components. These lasers allow manufacturers to cut through various metals with extreme accuracy, which is crucial for fitting parts together seamlessly. By using these machines, businesses can significantly reduce material waste and production times, leading to increased operational efficiency. International buyers should consider the laser’s power capacity to handle different material thicknesses and ensure compatibility with their existing manufacturing systems.
What Role Does Small Metal Cutting Laser Play in Jewelry and Fashion?
In the jewelry sector, small metal cutting lasers are utilized to create intricate designs and personalized pieces. The precision of these lasers enables jewelers to execute complex patterns that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional cutting methods. This technology not only enhances creativity but also allows for rapid production of customized items, meeting consumer demand for unique products. Buyers should focus on machines that offer fine cutting capabilities and quick setup times to maximize their investment.
How is Small Metal Cutting Laser Beneficial for Electronics Fabrication?
Small metal cutting lasers are increasingly used in the electronics industry for fabricating enclosures and components. These lasers provide the flexibility to cut various materials, including aluminum and stainless steel, which are commonly used in electronic devices. By adopting this technology, manufacturers can enhance their design capabilities and significantly reduce lead times for product development. International buyers need to ensure that the laser cutter can accommodate the diverse range of metals used in electronics and has a reliable supply chain for parts and maintenance.
What Advantages Does Small Metal Cutting Laser Offer in Industrial Signage?
In the realm of industrial signage, small metal cutting lasers are employed to produce high-quality metal signs and branding elements. The precision of laser cutting allows for detailed designs and sharp edges, which enhance the visibility and appeal of signage. This technology not only improves brand visibility but also enables companies to quickly adapt to changing marketing needs. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s ability to cut various thicknesses of metal and its operational safety features to ensure a safe and efficient production process.
How Does Small Metal Cutting Laser Improve Production in Home Appliances?
Small metal cutting lasers are vital in the home appliance industry for cutting parts used in products like ovens and refrigerators. The ability to quickly and accurately cut metal components streamlines production processes, resulting in higher quality products and reduced manufacturing costs. Additionally, these lasers can work with a variety of materials, allowing for greater flexibility in design. Buyers should assess the energy efficiency of the machine and consider its maintenance requirements to ensure long-term operational success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small metal cutting laser’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating High Initial Investment Costs
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, especially small businesses or startups, the initial investment in a small metal cutting laser can be daunting. The cost ranges significantly, with some models priced at $17,000 or more. Buyers often feel uncertain about whether this investment will yield sufficient returns, particularly when compared to outsourcing metal cutting services that might seem less capital-intensive in the short term. Additionally, the need for skilled operators and maintenance further complicates the decision-making process.
The Solution: To alleviate concerns about high initial costs, potential buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis. This includes evaluating the volume of work they currently outsource and projecting how much they could save by bringing metal cutting in-house. Researching models that offer flexible financing options or leasing arrangements can also help mitigate upfront costs. Furthermore, buyers should consider smaller, entry-level machines that still provide high precision and efficiency without breaking the bank. Engaging with suppliers for demonstrations can also provide insight into the machine’s capabilities and potential ROI, helping buyers make informed decisions.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Technical Complexity and Usability Issues
The Problem: Many users of small metal cutting lasers encounter challenges related to the complexity of operation and programming. This is particularly true for businesses that may not have a dedicated technician or engineer. The steep learning curve associated with sophisticated laser cutting software and the nuances of machine operation can lead to frustration and inefficiencies, ultimately impacting productivity.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize machines that come with user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive training support. Look for models that offer intuitive software with clear documentation and customer support. Additionally, investing in initial training sessions with the supplier can be invaluable. Many manufacturers provide training as part of the purchase, which can help operators become proficient more quickly. It’s also beneficial to seek out community forums or online resources where users share tips and troubleshooting advice, creating a support network that can help navigate common challenges.
Scenario 3: Addressing Safety and Compliance Concerns
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern when operating small metal cutting lasers, as improper use can lead to accidents or compliance issues with local regulations. Businesses in regions like Africa and the Middle East may face additional challenges due to varying standards and the necessity for safety certifications. This can create a barrier to purchasing, as buyers fear the consequences of non-compliance or unsafe working conditions.
The Solution: Buyers should focus on sourcing machines that meet international safety standards and come with comprehensive safety features, such as fully enclosed designs and proper ventilation systems. It’s advisable to consult local regulations regarding laser operation and ensure the chosen equipment complies with those standards. Furthermore, implementing a robust safety training program for all operators is essential. Regular safety audits and maintenance checks can help ensure that the equipment remains compliant and safe to operate. Engaging with suppliers who offer certification and ongoing support can also provide peace of mind, ensuring that safety remains a top priority.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small metal cutting laser
What Are the Key Materials for Small Metal Cutting Lasers?
When selecting materials for small metal cutting lasers, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various metals is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring product suitability. Here, we analyze four common materials used in conjunction with small metal cutting lasers, focusing on their characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Laser Cutting Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and durability, making it a popular choice in various industries. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,600°F (870°C) and offers excellent mechanical properties. The primary advantages include its strength and aesthetic appeal, as it can be polished to a high finish. However, it can be more expensive than other metals, and its thickness can complicate the cutting process, requiring higher laser power.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is essential. This material is widely used in food processing, automotive, and medical applications, which may have specific regulatory requirements.
What Benefits Does Aluminum Offer for Laser Cutting?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. It is relatively easy to cut with lasers, especially in thicknesses of 2-3mm, and is cost-effective compared to stainless steel. However, aluminum can produce a rough edge when cut, necessitating additional finishing processes.
International buyers should consider the common standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum alloys. Its applications span aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods, where weight reduction is critical.
Why Is Carbon Steel a Preferred Choice for Many Industries?
Carbon steel is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness. It can handle high-temperature applications and is relatively easy to cut with lasers, particularly in thicknesses up to 12mm. However, it is prone to rust and corrosion, which may require protective coatings or treatments.
B2B buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural carbon steel. This material is often used in construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries, where durability is paramount.
How Does Copper Compare in Laser Cutting Applications?
Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electrical components and heat exchangers. While it can be cut with lasers, its reflective nature poses challenges, requiring specific laser settings to achieve clean cuts. Copper is more expensive than carbon steel and aluminum, which may deter some buyers.
For international buyers, adherence to standards like ASTM B152 for copper sheet and plate is vital. Its applications are primarily in electrical and plumbing industries, where conductivity is essential.
Summary of Material Selection for Small Metal Cutting Lasers
| Material | Typical Use Case for small metal cutting laser | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, automotive, medical | Corrosion resistance, durability | Higher cost, cutting complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Lightweight, cost-effective | Rough edges, requires finishing | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, manufacturing, automotive | High strength, cost-effective | Prone to rust, may need coatings | Low |
| Copper | Electrical components, heat exchangers | Excellent conductivity | Reflective nature, high cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used with small metal cutting lasers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small metal cutting laser
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Small Metal Cutting Lasers?
The manufacturing process of small metal cutting lasers involves several key stages that ensure the machines are both effective and reliable. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting high-quality materials suitable for laser cutting systems. Common materials include stainless steel for structural components, aluminum for lightweight parts, and specialized alloys for high-performance lasers. The materials are often subjected to thorough inspection to verify their quality, ensuring they meet specifications before proceeding to the next stage.
-
Forming: This stage includes machining processes such as CNC milling, laser cutting, and bending to shape the components. Advanced techniques like waterjet cutting may also be employed for precision parts. During this phase, manufacturers utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software to optimize the designs, ensuring that each component fits perfectly within the overall assembly.
-
Assembly: In the assembly stage, all components, including the laser source, optics, and motion systems, are brought together. Careful attention is paid to the alignment and integration of these components to achieve optimal performance. Manufacturers often employ automation technologies, such as robotic arms, for accurate and efficient assembly, minimizing the risk of human error.
-
Finishing: The finishing process involves surface treatments and coatings to enhance durability and performance. Techniques such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting may be used to protect against corrosion and wear. This stage also includes rigorous cleaning processes to remove any contaminants that could affect performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Small Metal Cutting Laser Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of small metal cutting lasers to ensure that they meet international standards and customer expectations. Various quality control (QC) measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
-
International and Industry-Specific Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with CE marking requirements is also common in Europe, indicating that the product meets safety and environmental standards. For certain applications, additional certifications, such as API for oil and gas equipment, may be required.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: The QC process typically includes several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor processes and component quality.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough final inspection is performed to ensure the entire system operates correctly and meets predefined performance criteria. -
Common Testing Methods: Manufacturers employ various testing methods to verify the performance and reliability of the laser systems. These may include:
– Functional Testing: Ensuring that the laser cutting machine operates as intended under various conditions.
– Precision Testing: Measuring the accuracy of cuts and the repeatability of operations.
– Safety Testing: Verifying that safety features are functional and meet regulatory requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and adherence to international standards. This allows buyers to assess the supplier’s capability to deliver consistent quality.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Documentation: Buyers should ask for documentation related to quality control processes, including test reports, inspection records, and certificates of compliance with relevant standards. This documentation serves as a reference for the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, providing an added layer of confidence for buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges regarding quality control. Understanding these nuances is essential for successful procurement.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding laser equipment. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements in their region, such as safety standards, emissions regulations, and electrical codes. Ensuring that suppliers comply with these regulations is vital to avoid legal and operational issues.
-
Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences can impact communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication and set mutual expectations regarding product specifications, timelines, and quality standards to mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Logistical Challenges: Transporting equipment internationally can pose risks to quality, especially if not handled correctly. Buyers should work with suppliers who understand the logistics of shipping sensitive equipment and can provide assurance of safe packaging and handling.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing small metal cutting lasers, ensuring they invest in reliable and high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small metal cutting laser’
In today’s competitive marketplace, sourcing a small metal cutting laser requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure you make an informed decision. This guide provides a structured checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively.
-
Identify Your Cutting Requirements
Understanding your specific cutting needs is crucial. Consider the types of metals you will be cutting—such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper—and the thickness range required for your projects. This information will guide you in selecting a laser with the appropriate power and capabilities, ensuring that it meets your operational demands. -
Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications necessary for your operations. This includes laser power (typically ranging from 1kW to 20kW), cutting speed, and accuracy. Make sure to specify features like auto-height adjustment and cooling systems, as these can significantly impact cutting efficiency and quality. -
Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that showcase their experience in your industry. Additionally, seek testimonials or references from similar businesses to gauge supplier reliability and customer satisfaction. -
Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers meet industry standards and certifications, such as CE, ISO, or specific safety regulations relevant to your region. Certification not only assures quality but also compliance with safety standards, which is essential for operational legitimacy and risk management. -
Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the after-sales support provided by the supplier, including technical assistance, maintenance services, and training programs. A solid warranty—ideally covering parts and labor for at least one year—can save you significant costs and downtime in the long run. Consider the availability of extended warranties for critical components as well. -
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes the initial purchase price, operational costs (energy consumption, maintenance), and potential downtime. Small metal cutting lasers can offer substantial ROI, especially when compared to outsourcing cutting services. Factor in how quickly you can expect the machine to pay for itself based on your production needs. -
Request Demonstrations or Trials
Before finalizing your purchase, request a live or virtual demonstration of the laser cutting machine. This allows you to see the equipment in action, assess its performance, and clarify any technical queries. Some suppliers may offer trial periods or sample cutting to ensure the machine meets your requirements.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for small metal cutting lasers, ensuring they choose the right equipment for their operational needs while minimizing risks and maximizing value.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small metal cutting laser Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of small metal cutting lasers, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Small Metal Cutting Lasers?
The cost structure of small metal cutting lasers typically includes several key components:
-
Materials: The primary material costs involve the laser source (fiber optics), structural components, and electronics. Higher-quality materials can significantly impact the price, with advanced options like IPG or Raycus lasers being more expensive but offering better efficiency and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct manufacturing labor and any skilled technicians required for assembly and quality control. In regions with lower labor costs, such as some parts of Africa and South America, these expenses may be reduced, potentially lowering the overall price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, which is particularly important for suppliers aiming to remain competitive.
-
Tooling: The setup and maintenance of tooling for manufacturing lasers can add to the cost. Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can increase the initial investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes are essential, especially for machines that will perform precision cutting. The costs associated with QC can vary depending on the standards being adhered to, such as ISO certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, especially for international transactions. Factors such as the weight of the machinery, shipping distance, and chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) significantly influence these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins vary widely based on brand reputation, market position, and competitive landscape. Established brands may command higher prices due to perceived value and reliability.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Small Metal Cutting Laser Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of small metal cutting lasers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower unit prices. Negotiating for minimum order quantities can yield significant savings, particularly for large businesses.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as higher power outputs or specialized cutting capabilities can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these features align with their operational needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials affects both performance and price. Additionally, lasers that come with certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) may carry a premium due to the assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capacity can influence pricing. Engaging with multiple suppliers may uncover competitive pricing options.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, the following strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating better terms, such as payment plans, warranties, and service agreements. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A more expensive machine may offer greater long-term savings through efficiency and reliability.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations can affect overall costs. Staying informed about these factors can help you make better purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of small metal cutting lasers is essential for B2B buyers. By considering key cost components, price influencers, and employing strategic purchasing tips, companies can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that indicative prices can vary widely based on the specifics of each deal, so thorough research and engagement with suppliers are critical.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small metal cutting laser With Other Solutions
In the realm of metal cutting, businesses often seek solutions that not only meet their production requirements but also align with their operational capabilities and budget. The small metal cutting laser is a popular choice due to its precision and efficiency, but several alternative technologies can also achieve similar results. This analysis will compare small metal cutting lasers with water jet cutting and plasma cutting methods, providing valuable insights for B2B buyers in various markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
| Comparison Aspect | Small Metal Cutting Laser | Water Jet Cutting | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; cuts up to 0.5″ thick steel; rapid speeds (up to 25m/min) | Moderate precision; can cut thicker materials; slower than lasers | Good for thick materials; faster than water jet; less precision |
| Cost | $17,000 – $65,000 depending on power and features | $40,000 – $100,000 for machines; high operational costs due to water and abrasives | $30,000 – $70,000 for machines; lower operational costs than water jet |
| Ease of Implementation | Compact, easy to set up; requires minimal training | Requires significant space for water tanks; training needed for operation | Moderate setup; requires training for skilled operation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; solid-state lasers have long life | High maintenance; water and abrasives can cause wear | Moderate maintenance; consumables need regular replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium businesses needing precision in cutting thin metals | Best for cutting thick materials or those sensitive to heat | Suitable for heavy-duty applications and thicker metals |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Water Jet Cutting?
Water jet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through materials. One of the primary advantages of this method is its ability to cut thicker materials without inducing heat-affected zones, making it ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures. However, the operational costs can be significant due to water and abrasive usage, and the machinery typically requires a larger physical footprint and more maintenance compared to small metal cutting lasers. Additionally, water jet cutting is generally slower than laser cutting, which may impact production efficiency.
How Does Plasma Cutting Compare?
Plasma cutting employs a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and remove material, making it effective for cutting thick metals. It is generally faster than water jet cutting and can handle a variety of metal types, including stainless steel and aluminum. However, plasma cutting lacks the precision of laser cutting, which can lead to rough edges and the need for secondary finishing processes. Additionally, plasma cutters often require skilled operators to ensure quality cuts and safety, making initial training a consideration for businesses.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Metal Cutting Solution?
When evaluating metal cutting solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, including the types of materials they cut, production volumes, and budget constraints. Small metal cutting lasers offer high precision and efficiency for thin metals and are ideal for small to medium businesses. In contrast, water jet cutting is better suited for thicker materials that are heat-sensitive, while plasma cutting is advantageous for high-speed operations on thicker metals but may require additional finishing work. By carefully assessing the pros and cons of each method, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production goals and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small metal cutting laser
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Small Metal Cutting Lasers?
When evaluating small metal cutting lasers, understanding their technical specifications is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Laser Power (kW)
The laser power, measured in kilowatts (kW), directly impacts the cutting speed and thickness of the materials that can be processed. For instance, a 1kW laser typically cuts through 6mm carbon steel, while a 2kW laser can handle up to 12mm. Higher power lasers allow for faster production times and the ability to work with thicker materials, which can significantly improve operational efficiency and productivity.
2. Cutting Speed (m/min)
Cutting speed, expressed in meters per minute (m/min), indicates how quickly the laser can cut through materials. A typical small metal cutting laser might operate at speeds up to 25m/min. High cutting speeds enhance throughput, enabling businesses to complete more jobs in less time, ultimately leading to higher profitability.
3. Positioning Accuracy (mm)
Positioning accuracy refers to the precision with which the laser can position itself during operation, often indicated in millimeters (mm). For example, a laser with a positioning accuracy of ±0.03mm ensures tight tolerances are maintained in the final product. This is crucial for industries requiring high precision, such as electronics and aerospace, where even minor deviations can lead to costly errors.
4. Material Compatibility
Small metal cutting lasers are designed to work with a variety of materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and more. Understanding the compatible materials is essential for businesses that require versatility in their cutting operations. For instance, some machines may efficiently cut titanium or copper, expanding their applicability across different industries.
5. Cooling System
The cooling system is critical for maintaining optimal operating temperatures during laser cutting. Most small metal cutting lasers use refrigerated water cooling to prevent overheating and ensure consistent performance. A reliable cooling system extends the lifespan of the laser and reduces maintenance costs, which is an essential consideration for B2B buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Small Metal Cutting Lasers?
Familiarity with industry jargon can help B2B buyers navigate negotiations and contracts more effectively. Here are some common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser cutting machines, understanding whether the equipment comes from an OEM can indicate quality assurance and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. It can also impact cash flow, especially for startups or small businesses.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit bids from suppliers for specific products or services. Understanding the RFQ process can help buyers secure competitive pricing and favorable terms for their laser cutting equipment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps in understanding shipping, insurance, and liability during the purchase process.
5. Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the machine and the terms for repair or replacement. Knowing the warranty details can help buyers assess the long-term viability and support options available for their investment.
By understanding these essential technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in small metal cutting lasers, ensuring they choose equipment that meets their specific operational needs and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small metal cutting laser Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Small Metal Cutting Laser Market?
The small metal cutting laser market is currently experiencing robust growth, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision manufacturing, and a shift towards automation. As global industries prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness, fiber laser technology has emerged as a preferred choice due to its superior cutting speed and precision compared to traditional methods. This shift is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in emerging markets such as Nigeria and Vietnam, where the need for high-quality manufacturing solutions is on the rise.
Moreover, the compact nature of small metal cutting lasers makes them accessible for small to medium enterprises (SMEs) looking to establish in-house metal fabrication capabilities. This is a significant trend among buyers in Africa and South America, where outsourcing metal cutting services can be prohibitively expensive. Additionally, the increasing availability of affordable entry-level models, such as the ST-FC1390, is democratizing access to advanced cutting technology, enabling more businesses to innovate and compete.
Emerging technologies, including AI and IoT, are also influencing sourcing trends in this sector. These technologies enhance machine capabilities, providing predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, which are critical for optimizing operational efficiency. B2B buyers should consider these advancements when sourcing small metal cutting lasers to ensure they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Small Metal Cutting Laser Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in the sourcing of small metal cutting lasers, as businesses increasingly recognize the importance of minimizing their environmental impact. The metal fabrication industry is traditionally associated with significant waste and energy consumption, but modern laser cutting solutions are designed to be more energy-efficient, significantly reducing their carbon footprint. For instance, fiber lasers consume less power while delivering high cutting speeds, which not only lowers operational costs but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction among B2B buyers, who are now more conscientious about the supply chains of the machinery they purchase. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize ethical practices, including fair labor conditions and sustainable material sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential considerations for buyers looking to ensure that their suppliers adhere to high standards of environmental and social responsibility.
As B2B buyers evaluate their options, they should prioritize suppliers who offer green certifications and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, as this not only enhances their brand reputation but can also lead to long-term cost savings through efficient resource utilization.
What Is the Evolution of Small Metal Cutting Lasers and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of small metal cutting lasers has transformed the landscape of metal fabrication. Initially, laser cutting technology was primarily accessible to large-scale manufacturers due to high costs and complex operational requirements. However, advancements in laser technology, particularly the development of fiber lasers in the last decade, have made these machines more compact, affordable, and user-friendly.
Today, small metal cutting lasers are equipped with features that cater specifically to the needs of SMEs and individual entrepreneurs. The introduction of entry-level models, like those with varying power options from 1kW to 6kW, has opened up opportunities for businesses to engage in precision metal cutting without the need for extensive capital investment. This evolution is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where there is a growing emphasis on local production capabilities and reducing reliance on outsourcing.
In summary, the small metal cutting laser sector has evolved to meet the demands of a dynamic market, offering innovative solutions that enhance productivity while promoting sustainability and ethical practices. B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small metal cutting laser
-
How do I choose the right small metal cutting laser for my business needs?
Selecting the right small metal cutting laser involves assessing your specific cutting requirements, including the types of materials you will work with, the thickness of those materials, and the required precision. It’s essential to consider the laser’s power options, speed, and cutting capabilities. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s size and whether it fits your workspace. Lastly, consider the manufacturer’s reputation, warranty, and support services, as these can significantly impact your operational efficiency. -
What is the best small metal cutting laser for beginners?
For beginners, entry-level small metal cutting lasers like the ST-FC1390 are highly recommended due to their user-friendly design and affordability. These machines typically come with lower power options, making them suitable for cutting thin metals such as stainless steel and aluminum. Features like a fully enclosed design enhance safety, while intuitive controls facilitate a shorter learning curve. Always ensure that the machine meets your specific cutting needs while remaining within your budget. -
What are the typical lead times for small metal cutting laser orders?
Lead times for small metal cutting lasers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, customization options, and current demand. Generally, you can expect a lead time ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Customization, such as specific power levels or additional features, may extend the timeline. It’s advisable to communicate directly with your supplier for precise estimates and to factor in additional time for shipping, especially for international orders. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing a small metal cutting laser?
To ensure quality assurance, start by sourcing from reputable manufacturers with established credentials and industry experience. Request certifications such as CE or ISO to verify compliance with international standards. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, as these reflect the manufacturer’s confidence in their products. Finally, consider visiting the facility for a live demonstration to assess the machine’s performance and quality firsthand. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing small metal cutting lasers internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of small metal cutting lasers typically include options like a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letter of credit terms, depending on the transaction size and relationship with the buyer. Always clarify these terms in your initial negotiations to avoid misunderstandings later on. -
What are the common logistics and shipping considerations for small metal cutting lasers?
When importing small metal cutting lasers, consider logistics such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance, and potential tariffs or duties. Ensure that the supplier provides proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. It’s also important to factor in delivery times and choose a shipping method that aligns with your project timeline. Engaging a freight forwarder can simplify the process and help navigate the complexities of international shipping. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing small metal cutting lasers internationally?
Vetting suppliers involves conducting thorough research on their business history, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and check for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or attending trade shows to establish personal connections. Online platforms and trade associations can also provide valuable insights into a supplier’s reliability. -
What customization options are available for small metal cutting lasers?
Customization options for small metal cutting lasers may include variations in laser power (ranging from 1kW to over 20kW), bed size, and additional features like automated height adjustment or specific software integrations. Some manufacturers also offer tailored solutions for unique cutting requirements or material types. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand available customizations and their associated costs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Small Metal Cutting Laser Manufacturers & Suppliers List
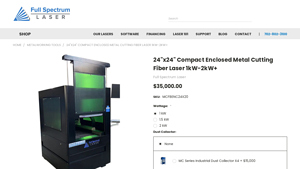
1. FS Laser – 24×24 Compact Enclosed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “24”x24″ Compact Enclosed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser”,”Power Options”: “1 kW, 1.5 kW, 2 kW (up to 20 kW custom)”,”Cutting Capacity”: {“1 kW”: “Up to 6mm carbon steel, 3mm stainless, 1.5mm aluminum”,”1.5 kW”: “Up to 9mm carbon steel, 4.5mm stainless, 2.25mm aluminum”,”2 kW”: “Up to 12mm carbon steel, 6mm stainless, 3mm aluminum”},”Max Cutting Speed”: “25m/min”,”Positioning Accuracy”…
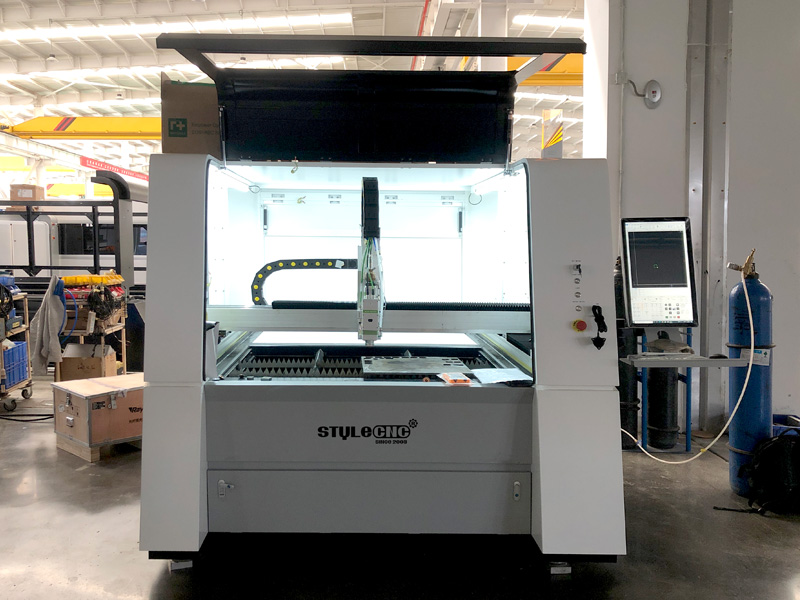
2. STYLECNC – Entry Level Small Metal Laser Cutter
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Entry Level Small Metal Laser Cutter for Beginners – STYLECNC
Model: ST-FC1390
Laser Source: Raycus, IPG, MAX, RECI
Power Options: 1500W, 2000W, 3000W, 6000W
Price: $17,000 (Standard Edition) / $31,000 (Pro Edition)
Stock: 180 Units Available Monthly
Warranty: One-Year Limited Warranty (Extended Warranties Available)
Working Area: 1300mm x 900mm
Repeat Positioning Accuracy: ±0.008mm
Maximum Speed:…
3. Kern – Metal Cutting Laser Systems
Domain: kernlasers.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Kern’s metal cutting laser systems allow for accurate cutting of sheet metal including stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Key features include an Automatic Focusing Height Follower for optimal cutting, a protective cover lens (K-Lens for CO2 machines, F-Lens for fiber systems), and a durable steel grid work metal cutting table. Advanced KCAM Laser Software provides control o…
4. LightObject – RANGER III
Domain: lightobject.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”RANGER III”,”size”:”600×380 (24\”x15\”)”,”type”:”Laser Desktop”,”price”:”$3,939.00″,”original_price”:”$5,200.00″,”stock”:”Only 1 left in stock”},{“name”:”SOLO II”,”size”:”500×300 (19\” x 11.8\”)”,”type”:”Laser Desktop W/O Z table”,”price”:”$2,990.00″,”original_price”:”$2,250.00″,”stock”:”Only 2 left in stock”},{“name”:”MAX renewed MSFC-1500W”,”type”:”fiber laser source”,”pric…
5. ACCU STAR – Fiber Laser Sheet Metal Cutting Machine
Domain: bescutter.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: ACCU STAR 5’x10′ |1000 – 2000W | Fiber Laser Sheet Metal Cutting Machine from 7000000 12000000 / per; ACCU STAR 5′ x20′ | 1500-2000W | Fiber Laser Metal Sheet Cutting Machine from 11000000 10000000 / per; SPACE SAVER 5’x10′ | 1500W – 4000W IPG | Fiber Laser Metal Sheet Cutting Machine from 12500000 12500000 / per; SMART CUBE 51″x51″ | 2000W – 4000W | Fiber Laser Metal Sheet Cutter from 9000000 15…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small metal cutting laser
In the evolving landscape of metal fabrication, small metal cutting lasers present an invaluable opportunity for businesses across various sectors. By investing in these advanced tools, companies can achieve precision cutting, enhance operational efficiency, and significantly reduce costs associated with outsourcing. The compact and powerful design of machines, such as the 24″x24″ fiber laser, allows for versatile applications ranging from automotive components to intricate jewelry designs, making them suitable for both startups and established enterprises.
Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in maximizing the benefits of these technologies. By carefully selecting suppliers who provide quality, reliability, and competitive pricing, businesses can ensure a solid return on investment. It is essential for international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to leverage global logistics and partnerships to access the best machinery suited to their specific needs.
As the demand for customized metal products continues to grow, now is the time for B2B buyers to act. Investing in a small metal cutting laser not only positions your business for success but also prepares you for the future of manufacturing. Explore your options today and take the next step towards enhancing your production capabilities.