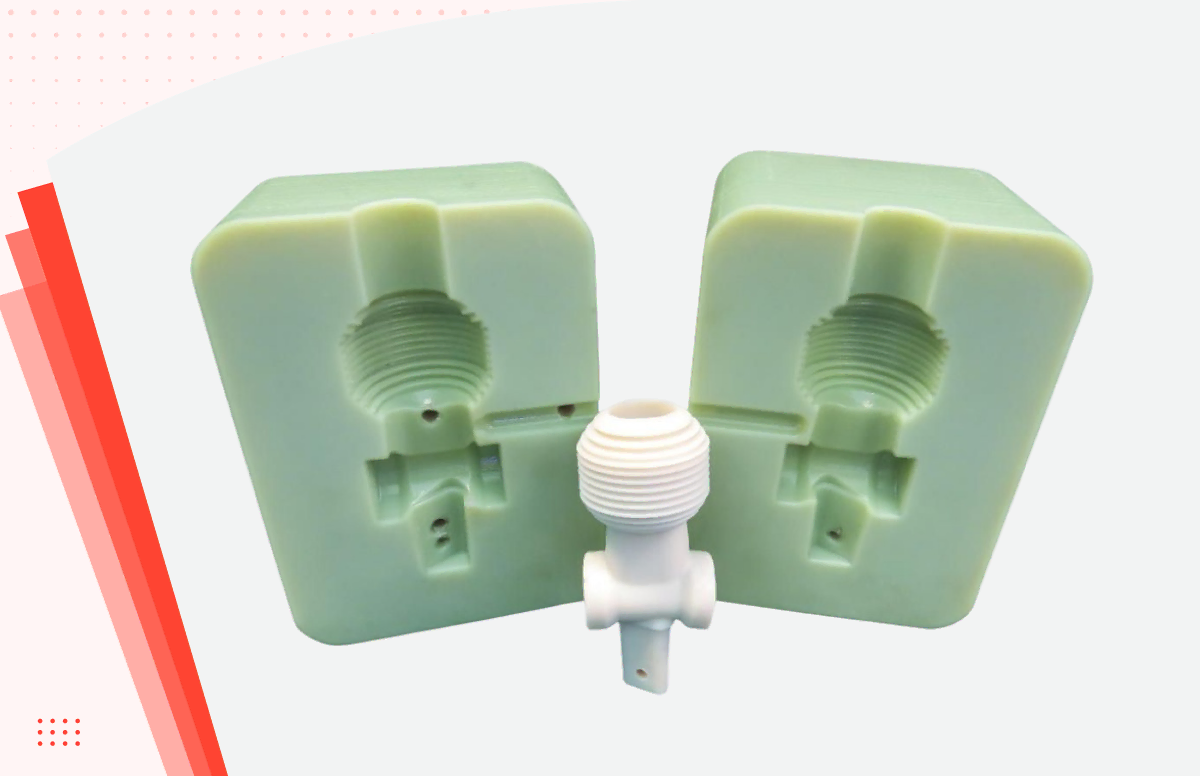
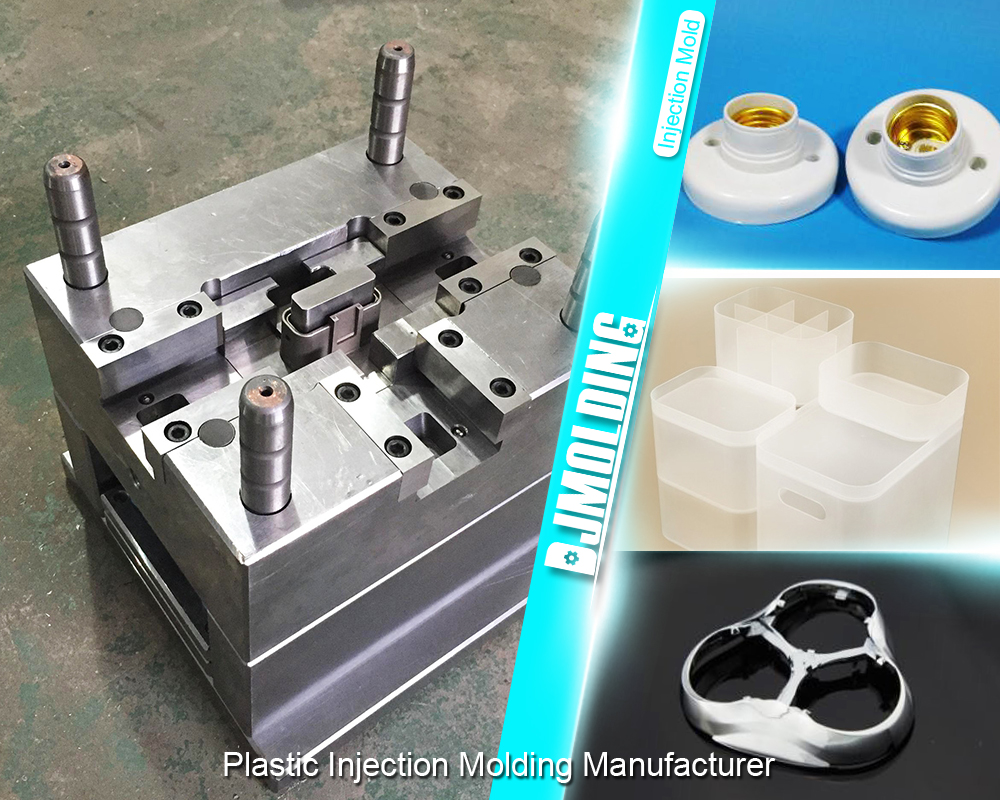
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small batch injection molding
In today’s fast-paced global market, sourcing small batch injection molding solutions poses a significant challenge for manufacturers looking to innovate while managing costs. Traditional injection molding services often require high minimum order quantities, making it difficult for businesses, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America, to access the specialized parts they need for prototypes or limited production runs. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of small batch injection molding, addressing key factors such as types of molds, applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By delving into the intricacies of small batch injection molding, this guide empowers international B2B buyers from regions like Europe, Brazil, and Saudi Arabia to make informed purchasing decisions. You’ll discover the advantages of opting for short run injection molding, including lower minimum order requirements, faster turnaround times, and cost savings. Furthermore, we will explore how to effectively evaluate potential suppliers to ensure quality and reliability in your production processes.
Equipped with the insights presented in this guide, you can navigate the complexities of small batch injection molding with confidence, ensuring that your business remains competitive and responsive to market demands. Whether you are a product developer or a procurement officer, understanding the nuances of this manufacturing technique will enhance your ability to deliver high-quality products that meet your customers’ needs.
Understanding small batch injection molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Molds | Cost-effective, quick turnaround, suitable for low volume runs | Prototyping, specialty parts | Pros: Lower costs, fast production. Cons: Limited lifespan compared to steel molds. |
| Steel Molds | Higher durability, suitable for larger quantities | Short-run production, automotive | Pros: Longer lifespan, better for precision. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Prototype Molding | Focused on creating functional prototypes for testing | Product development, market testing | Pros: Rapid iteration, production-quality parts. Cons: May not suit high-volume needs. |
| Insert Molding | Incorporates metal or other materials into plastic components | Electronics, medical devices | Pros: Enhanced functionality, reduced assembly costs. Cons: Complexity can increase costs. |
| Multi-Cavity Molding | Produces multiple parts in a single cycle for efficiency | High-demand prototypes, consumer goods | Pros: Cost efficiency at higher volumes. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
What Are the Characteristics of Aluminum Molds in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Aluminum molds are a popular choice for small batch injection molding due to their cost-effectiveness and quicker turnaround times. These molds can produce parts in low quantities, typically under 10,000, making them ideal for prototyping and specialty applications. They are easier to machine, allowing for faster modifications and iterations. However, buyers should consider that while aluminum molds are less expensive, they have a shorter lifespan compared to steel molds, which may necessitate replacements sooner than anticipated.
How Do Steel Molds Compare in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Steel molds are known for their durability and are suitable for small to moderate production runs. They can handle larger quantities, offering a good balance between cost and longevity. Steel molds are particularly advantageous in applications requiring high precision, such as automotive and aerospace components. However, the initial investment for steel molds is higher, which could be a deterrent for businesses only needing limited quantities. Buyers must weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits of mold durability.
What Are the Advantages of Prototype Molding for B2B Buyers?
Prototype molding focuses on creating functional prototypes that allow businesses to test and validate designs before full-scale production. This method is particularly beneficial for product development and market testing, as it enables rapid iterations and adjustments. The parts produced are often of production quality, making them suitable for real-world applications. However, while prototype molding is excellent for testing, it may not be the best option for companies expecting high-volume production, as costs can escalate with increased demand.
How Does Insert Molding Enhance Product Functionality?
Insert molding is a technique that integrates metal components or other materials into plastic parts during the injection molding process. This method is particularly useful in industries such as electronics and medical devices, where enhanced functionality is critical. By reducing the need for additional assembly, insert molding can lower overall production costs. However, the complexity of designing these molds can lead to higher initial costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their specific needs and budget constraints.
When Should B2B Buyers Consider Multi-Cavity Molding?
Multi-cavity molding allows for the production of multiple parts within a single mold cycle, significantly increasing efficiency for businesses with higher demand. This method is particularly advantageous for consumer goods and products that require consistent quality across larger batches. While multi-cavity molds can reduce the cost per unit at higher volumes, the initial setup costs can be substantial. B2B buyers should consider their production forecasts and budget when deciding if multi-cavity molding aligns with their operational strategy.
Key Industrial Applications of small batch injection molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of small batch injection molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Production of specialized surgical instruments | Enables rapid prototyping and production of custom tools, reducing time-to-market for critical devices. | Ensure compliance with ISO standards and material certifications for safety. |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of prototype components for vehicle testing | Facilitates quick iterations of parts, allowing for faster testing and validation of new designs. | Look for suppliers with expertise in automotive-grade materials and precision molding. |
| Aerospace | Creation of lightweight, precision components | Supports the development of high-performance parts with stringent weight and safety requirements. | Verify supplier capabilities in producing high-tolerance molds and parts. |
| Consumer Electronics | Development of custom housings and enclosures | Offers flexibility to adapt designs based on user feedback and market trends, enhancing product appeal. | Consider suppliers’ lead times and ability to handle varying production volumes. |
| Industrial Equipment | Production of specialized tooling and fixtures | Reduces costs associated with tooling by allowing for small batch runs, optimizing manufacturing processes. | Assess the supplier’s ability to provide durable molds and rapid turnaround times. |
How is Small Batch Injection Molding Used in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical sector, small batch injection molding is crucial for producing specialized surgical instruments and components that require high precision. Manufacturers often face the challenge of rapidly developing prototypes to meet regulatory standards and market demands. Small batch production allows for quick iterations, enabling companies to refine their designs based on feedback without incurring high costs associated with large-scale production. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers who comply with ISO standards and can guarantee the use of biocompatible materials.
What Role Does Small Batch Injection Molding Play in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry benefits significantly from small batch injection molding when it comes to manufacturing prototype components for testing new vehicle designs. This method allows for the rapid production of parts that are essential for performance testing and validation. With the automotive market’s fast-paced nature, the ability to quickly iterate on designs can lead to enhanced vehicle features and safety. Buyers in regions like South America and Europe should seek suppliers with expertise in automotive-grade materials and a proven track record of precision molding to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards.
Why is Small Batch Injection Molding Important for Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, the demand for lightweight and precise components is paramount. Small batch injection molding facilitates the production of specialized parts that meet stringent weight and safety requirements. This process allows manufacturers to test and validate new designs quickly, which is essential in an industry where performance is critical. Buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers possess the capability to produce high-tolerance molds and parts, as well as adhere to rigorous aerospace standards.
How Does Small Batch Injection Molding Enhance Consumer Electronics Development?
For the consumer electronics sector, small batch injection molding is instrumental in developing custom housings and enclosures that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. This flexibility allows companies to adapt their designs based on user feedback and market trends, significantly enhancing product appeal. International buyers should consider suppliers with efficient lead times and the capability to manage varying production volumes to stay competitive in this rapidly evolving market.
In What Ways Does Small Batch Injection Molding Support Industrial Equipment Production?
Small batch injection molding is particularly advantageous in the industrial equipment sector, where specialized tooling and fixtures are often required. This method reduces costs associated with tooling by allowing for small batch runs, optimizing manufacturing processes while maintaining quality. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should assess suppliers based on their ability to provide durable molds and rapid turnaround times, ensuring that production schedules are met without compromising quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small batch injection molding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Minimum Order Requirements Stifling Innovation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant hurdles when suppliers impose high minimum order quantities, often in the hundreds or thousands of units. This poses a major challenge for companies aiming to produce specialized components or prototypes. For instance, a medical device manufacturer may want to test a new product’s viability but is deterred by a supplier’s requirement for an order of 10,000 units. This not only escalates costs but also limits their ability to innovate and adapt quickly to market demands.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, B2B buyers should seek suppliers that specialize in small batch injection molding, which offers flexibility with no minimum order quantities. By partnering with manufacturers that focus on short-run production, companies can order as few as 100 parts, enabling them to prototype and test designs without incurring unnecessary expenses. When sourcing these suppliers, it’s crucial to evaluate their track record in rapid turnaround times and production quality. Engaging in open communication about specific project needs can also help ensure that the supplier is aligned with your innovation goals. This approach allows for a more iterative design process, facilitating quicker adjustments based on testing feedback and market demands.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times Delaying Product Launch
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the prolonged lead times associated with traditional injection molding processes. A company in the automotive sector may find itself waiting several months to receive tooling and initial parts, causing delays in product development and time-to-market. These delays can lead to lost opportunities, especially in industries where speed is critical to maintaining a competitive edge.
The Solution: To address long lead times, buyers should consider leveraging small batch injection molding services that prioritize speed. Many providers offer rapid prototyping options with production-quality outputs, significantly reducing the wait time to just a few days. Buyers should look for manufacturers that utilize aluminum molds for short runs, which are not only cost-effective but also faster to produce than hardened steel molds. Additionally, establishing a relationship with suppliers who have dedicated capacities for short runs can ensure that your projects receive the attention and promptness required to meet tight deadlines. Clearly outlining project timelines and expectations during the initial discussions can further streamline the process, fostering a partnership focused on efficiency and responsiveness.
Scenario 3: Quality Assurance Concerns with Prototyping
The Problem: B2B buyers often face quality assurance challenges when transitioning from prototype to production. A product engineer may find that components produced through traditional prototyping methods, such as 3D printing, do not meet the stringent quality standards required for end-use applications. This inconsistency can lead to costly redesigns and delays in securing regulatory approvals, particularly in sectors like medical devices or aerospace.
The Solution: To ensure high-quality prototypes, it is advisable for buyers to utilize small batch injection molding for their prototyping needs. This method provides production-grade materials and surface finishes that are comparable to those of mass-produced items. When selecting a supplier, buyers should inquire about their quality control processes, including first article inspections and capability reports, which can assure them of the molds’ integrity and performance. Additionally, collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can help address potential quality issues early on. By choosing a partner experienced in small batch injection molding, companies can achieve reliable prototypes that facilitate smoother transitions to full-scale production, ultimately saving time and resources in the long run.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small batch injection molding
What Are the Key Materials for Small Batch Injection Molding?
When it comes to small batch injection molding, selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring product performance and meeting specific application requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials used in this process: ABS, Polypropylene (PP), Nylon (PA), and Polycarbonate (PC). Each of these materials has unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact the final product.
How Does ABS Perform in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its strength and impact resistance. It has a temperature rating of approximately 80°C (176°F) and exhibits good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: ABS is relatively inexpensive and easy to process, which makes it an excellent choice for prototypes and low-volume production. It also offers good surface finish and is available in various colors.
Cons: However, ABS has lower heat resistance compared to other materials, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, it can be prone to stress cracking under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: ABS is compatible with a range of media, including household chemicals, but may not be suitable for applications involving high temperatures or harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile strength. Additionally, they should consider the availability of ABS in their local markets to avoid supply chain disruptions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene is another popular choice for small batch injection molding due to its excellent chemical resistance and low density. It has a temperature rating of about 100°C (212°F) and is known for its fatigue resistance.
Pros: The lightweight nature of PP makes it cost-effective for shipping and handling. It also boasts good impact resistance and can be easily molded into complex shapes.
Cons: On the downside, PP has lower tensile strength compared to ABS and may not be suitable for applications requiring high structural integrity. Its surface finish can also be less appealing than that of other materials.
Impact on Application: PP is ideal for applications involving moisture or chemical exposure, such as packaging and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ISO 1873 is essential for PP applications. Buyers should also be aware of the environmental regulations regarding plastic use in their respective regions.
Why Choose Nylon (PA) for Small Batch Injection Molding?
Nylon, or Polyamide (PA), is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and offers good resistance to wear and abrasion.
Pros: Nylon is suitable for applications requiring high strength and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive and industrial components. It also has good chemical resistance, particularly against oils and fuels.
Cons: However, Nylon can absorb moisture, which may affect its dimensional stability and mechanical properties. It is also more expensive than ABS and PP.
Impact on Application: Nylon is particularly effective in applications requiring high wear resistance, such as gears and bearings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D4066 for Nylon applications. Additionally, they should consider the availability of Nylon grades suitable for their specific applications.
What Makes Polycarbonate (PC) a Preferred Material?
Polycarbonate is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 135°C (275°F) and is often used in applications requiring transparency and durability.
Pros: The ability of PC to resist high impacts makes it suitable for safety applications, such as eyewear and protective equipment. It also offers excellent dimensional stability.
Cons: However, PC is more expensive than other materials and can be prone to scratching unless treated with a protective coating. It also has lower chemical resistance compared to Nylon.
Impact on Application: PC is ideal for applications that require transparency and high impact resistance, such as lenses and safety shields.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ISO 11963 for safety applications. Understanding local regulations regarding the use of polycarbonate is also crucial.
Summary of Material Selection for Small Batch Injection Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for small batch injection molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Prototypes, consumer products | Cost-effective and easy to process | Lower heat resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene | Packaging, automotive components | Lightweight and good chemical resistance | Lower tensile strength | Low |
| Nylon | Gears, bearings, industrial components | High strength and wear resistance | Moisture absorption affects stability | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Safety eyewear, protective equipment | Exceptional impact resistance | Higher cost and prone to scratching | High |
By understanding the properties and implications of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small batch injection molding
What Are the Key Stages of the Small Batch Injection Molding Manufacturing Process?
Small batch injection molding is a streamlined process designed to produce high-quality plastic parts in limited quantities, making it an attractive option for businesses needing flexibility and efficiency. Understanding the main stages of this manufacturing process is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in this technology.
How Is Material Prepared for Injection Molding?
The first step in the small batch injection molding process involves material preparation. This typically includes selecting the appropriate thermoplastic material based on the application requirements. Common materials include ABS, polycarbonate, and polypropylene, each offering distinct properties such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
Once the material is chosen, it is dried to remove moisture, which is critical for maintaining the quality of the final product. Moisture can lead to defects during the molding process, such as bubbles or weak spots. The dried pellets are then fed into a hopper connected to the injection molding machine.
What Does the Forming Stage Involve?
The forming stage is where the actual molding takes place. In this stage, the dried plastic material is heated until it reaches a molten state. This molten material is then injected into a pre-designed mold under high pressure. The choice of mold material—often aluminum for small batch production—affects both the cost and durability of the mold.
After the molten plastic fills the mold, it is allowed to cool and solidify. This cooling period is crucial, as it determines the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the final part. For small batch injection molding, the cooling time is generally shorter than in traditional mass production, allowing for quicker turnaround times.
How Are Parts Assembled and Finished?
Once the parts are ejected from the mold, they may undergo further assembly or finishing processes. This could include trimming excess material, surface treatment, or painting, depending on the specifications of the end product. For products requiring high aesthetic quality or functional enhancements, additional processes like plating or coating can be employed.
Finishing touches are essential to meet the standards expected in various industries, such as automotive or medical devices, where precision and quality are non-negotiable.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the small batch injection molding process, ensuring that the final products meet required specifications and standards. B2B buyers must understand how to evaluate the quality control measures employed by their suppliers.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards play a pivotal role in maintaining quality throughout the manufacturing process. ISO 9001 is the most recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers adhere to consistent quality practices. For specialized industries, additional certifications may be relevant:
- ISO 13485: Essential for medical devices.
- ISO 14001: Focuses on environmental management.
- TS 16949: Specific to the automotive industry.
Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of these certifications, giving buyers confidence in their quality assurance processes.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure defects are identified and corrected promptly. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the molding process to detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspections of finished products to confirm they meet all design and quality specifications.
These checkpoints help to minimize the risk of defects and ensure that only high-quality parts are delivered to the client.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of molded parts. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing protocols used by their suppliers:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that parts meet specified dimensions using calipers and gauges.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, discoloration, or other visible issues.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility through standardized tests.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that the part performs as intended in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When selecting a supplier for small batch injection molding, B2B buyers should perform due diligence to ensure robust quality control practices. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation detailing the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes, along with any corrective actions taken in response to defects.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to independently verify the quality of the parts before shipment, particularly for high-stakes industries like automotive and medical.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control can significantly impact sourcing decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements for products, especially in the medical and automotive sectors. Buyers should ensure suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Quality expectations can vary widely across cultures. Buyers should communicate their quality expectations clearly and ensure that suppliers are aligned with these standards.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International shipping can introduce additional risks, such as damage during transport. Quality control measures should extend to packaging and logistics to ensure parts arrive in optimal condition.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product quality in the realm of small batch injection molding.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small batch injection molding’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement process for small batch injection molding can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you select a supplier that meets your specific needs while maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful small batch injection molding project. This includes dimensions, tolerances, material types, and any surface finish requirements. Precise specifications will help suppliers provide accurate quotes and reduce the risk of costly revisions later in the production process.
Step 2: Determine Your Production Volume Needs
Identify the exact quantity you need for your initial production run. Small batch injection molding is ideal for orders ranging from fewer than 100 to around 10,000 parts. Understanding your volume requirements will guide your choice between short-run and production tooling options, ultimately impacting cost and lead time.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with experience in your specific market, as this can indicate their understanding of unique challenges and regulatory requirements.
- Check for Industry Certifications: Ensure the supplier holds relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 13485 for medical devices, if applicable.
- Review Their Portfolio: Examine previous projects to assess their capability to meet your quality standards.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that break down costs associated with tooling, production, and lead times. A transparent quote allows for better comparison and negotiation.
- Look for Hidden Costs: Ensure that quotes include all potential costs, such as shipping, taxes, and any additional fees for tooling changes or revisions.
- Assess Lead Times: Understand the expected turnaround time and how it aligns with your project timelines.
Step 5: Assess Tooling Options and Lifespan
Discuss the types of molds available, such as aluminum or steel, and their respective lifespans. Aluminum molds are often used for small batch production due to their lower cost and faster turnaround times, making them suitable for orders under 10,000 pieces.
- Understand Warranty Terms: Check warranty options for the molds and the expected number of shots they can produce before replacement is necessary.
- Evaluate Flexibility: Inquire about the supplier’s ability to adapt the tooling for future iterations or modifications.
Step 6: Establish Communication Protocols
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear lines of communication with your supplier to facilitate updates, feedback, and issue resolution.
- Set Up Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular meetings to discuss project status, address concerns, and make timely adjustments.
- Utilize Project Management Tools: Consider using project management software to track progress and share documentation efficiently.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement
Before proceeding, ensure all terms are clearly defined in a formal contract. This should include specifications, lead times, payment terms, and any contingencies for changes.
- Review Terms Carefully: Pay close attention to clauses regarding quality assurance, penalties for late delivery, and dispute resolution.
- Involve Legal Advisors if Necessary: If you’re dealing with a significant investment or complex terms, consult with legal experts to ensure your interests are protected.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing small batch injection molding services, ensuring a successful partnership with your chosen supplier.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small batch injection molding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Small Batch Injection Molding?
Understanding the cost structure of small batch injection molding is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of plastic resin significantly affects pricing. Common materials like ABS or polycarbonate are generally less expensive than specialized composites. Prices can vary based on market conditions, with fluctuations in oil prices impacting polymer costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass not only the workforce directly involved in molding but also the skilled technicians needed for setup and quality assurance. Geographic location plays a critical role; for instance, labor costs may be lower in some regions of South America compared to Europe.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes operational costs such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. Overhead can be higher for suppliers in regions with stricter regulations or higher taxes.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary widely based on complexity and material. Aluminum molds are often used for short runs and are less expensive than steel molds, but they have a limited lifespan (typically 2,000 to 10,000 shots). Buyers must consider the trade-off between upfront costs and longevity.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specifications requires investment in quality assurance processes. This could involve additional testing and inspections, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must be factored in, especially for international transactions. These costs can vary based on distance, weight, and chosen Incoterms, which define responsibilities between buyer and seller.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their risks and profits. This can range from 10% to 30%, depending on the supplier’s position in the market and the complexity of the project.
What Influences Pricing in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Several factors influence the pricing of small batch injection molding, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: While short-run services often have no minimum order quantities (MOQ), pricing per unit can decrease with higher volumes. Buyers should assess their needs to find the most cost-effective solution.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts with intricate designs or specific tolerances will incur additional costs. Buyers should provide detailed specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the initial cost but also long-term performance and suitability for the intended application.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring industry certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) will typically cost more due to the additional testing and compliance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can also impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer superior quality and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms determine who bears the shipping costs and risks. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics expenses effectively.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing in Small Batch Injection Molding?
International B2B buyers can implement several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the unit price, consider the total cost of ownership, including shipping, quality control, and potential rework. This holistic view can lead to better long-term decisions.
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Even if a project starts with a low quantity, discuss future orders to negotiate better rates. Suppliers are often more willing to lower prices for guaranteed repeat business.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide a clearer picture of market rates and help in negotiating favorable terms.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, making the overall project more efficient.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers must be aware of specific pricing nuances when sourcing small batch injection molding services. Currency fluctuations can affect overall costs, as can trade tariffs and import duties. Additionally, cultural differences in negotiation styles may influence pricing discussions. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and more favorable pricing structures over time.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for small batch injection molding can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small batch injection molding With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Small Batch Injection Molding
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly for businesses seeking to produce specialty parts or prototypes, small batch injection molding offers a unique solution. However, it is essential to explore alternatives that may align better with specific project requirements. This section compares small batch injection molding against other viable manufacturing methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Small Batch Injection Molding | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, production-grade parts | Good for prototypes, variable quality | High precision, excellent surface finish |
| Cost | Moderate for low quantities; tooling costs apply | Low initial costs, but can be high per unit at scale | Higher cost per part; setup can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires tooling, longer lead times for setup | Quick setup, minimal tooling needed | Setup can be complex; requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Moderate; tooling needs to be replaced after use | Low; no moving parts | High; requires regular maintenance of machines |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping and low-volume production of functional parts | Rapid prototyping, complex geometries | High precision parts, low to medium volume production |
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
3D Printing
3D printing has gained popularity for its ability to produce complex geometries and rapid prototyping capabilities. The major advantage of this method is its minimal setup cost and flexibility in design changes. However, while the initial costs can be lower, the price per unit can escalate with larger production runs, making it less economical for high-volume needs. Additionally, the surface finish and material strength may not match the quality of parts produced through small batch injection molding, which can be a concern for end-use applications.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is another alternative that excels in producing highly precise parts. It is particularly beneficial when tolerances are critical and surface finish is paramount. While it offers exceptional quality, the setup costs can be substantial, and the process is generally slower than injection molding. Moreover, CNC machining is best suited for metal parts rather than plastics, which may limit its application in certain industries. The maintenance and operational expertise required also add to its complexity, making it less accessible for smaller businesses or projects.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing method, B2B buyers should consider their specific project requirements, including production volume, budget constraints, and desired part characteristics. Small batch injection molding is ideal for high-quality, low-volume production, particularly when functional prototypes are needed. In contrast, 3D printing serves well for rapid iterations and complex designs, while CNC machining is the go-to for precision and metal applications. By weighing these factors, buyers can effectively align their manufacturing choice with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small batch injection molding
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Small Batch Injection Molding?
In the realm of small batch injection molding, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic or polymer used in the injection molding process, such as ABS, polycarbonate, or nylon. Each material has unique properties, including strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance. For buyers, selecting the right material is essential for ensuring that the final product meets performance requirements and regulatory standards, especially in industries like medical and automotive.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a part’s dimensions. In small batch injection molding, tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.005 inches) are often required to ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Understanding tolerances is vital for buyers to avoid costly rework or production delays, particularly when parts are intended for assembly or critical applications.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to produce a single part, encompassing injection, cooling, and ejection phases. In small batch production, shorter cycle times can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Buyers should assess cycle times to align production schedules with market demand, thereby optimizing inventory management and cash flow.
4. Mold Life
Mold life refers to the expected number of cycles a mold can produce before wear and tear necessitates replacement or repair. In small batch injection molding, aluminum molds typically have a shorter life than steel molds, which can last for tens of thousands of cycles. Understanding mold life helps buyers evaluate the cost-effectiveness of their investment, especially when considering the volume of parts required over time.
5. Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture of a molded part’s surface, which can range from smooth to textured. The desired finish often depends on the application; for example, cosmetic parts may require a high-gloss finish, while functional components might prioritize grip or durability. Buyers must specify surface finish requirements to ensure that the final product meets aesthetic and functional criteria.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Small Batch Injection Molding?
Navigating the landscape of small batch injection molding involves familiarity with specific industry jargon. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of injection molding, OEMs often source molded components to integrate into their products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential partners and streamline their supply chains.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to produce or sell. In small batch injection molding, many suppliers have low MOQs, allowing businesses to order only what they need for prototypes or limited production runs. This flexibility is advantageous for companies testing new designs or entering new markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. In small batch injection molding, issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare costs, lead times, and service capabilities, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border procurement, as they outline who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and the completion of delivery. In small batch injection molding, lead times can vary significantly based on factors like mold design and production capacity. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning product launches and inventory levels to ensure timely market entry.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make better-informed decisions in the small batch injection molding landscape, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small batch injection molding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting Small Batch Injection Molding?
The small batch injection molding market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for customized and specialized parts across various industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. International B2B buyers, particularly from emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers that can offer flexible production capabilities with no minimum order quantities. This shift is partly due to the need for rapid prototyping and product development, which has become crucial in a fast-paced market environment where time-to-market can determine competitive advantage.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. The integration of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and CNC machining, alongside small batch injection molding, is enabling companies to streamline their production processes. This hybrid approach allows for quicker iterations and a more agile response to changing market demands. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms for sourcing and supply chain management is providing B2B buyers with enhanced transparency and the ability to compare suppliers globally, thus driving better decision-making.
Furthermore, international trade dynamics are influencing sourcing strategies. Trade agreements and tariffs can impact the cost and accessibility of materials and services, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about geopolitical factors that may affect their supply chains. As a result, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate resilience and adaptability in their operations.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Small Batch Injection Molding Industry?
Sustainability has become a key consideration for B2B buyers in the small batch injection molding sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Buyers are looking for suppliers that use eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes, which not only reduces their carbon footprint but also aligns with corporate social responsibility goals.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers are increasingly aware of the social implications of their supply chains and are seeking suppliers who maintain high ethical standards in labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to ethical labor practices are becoming prerequisites for supplier selection.
The use of recyclable and biodegradable materials in small batch injection molding is gaining traction, providing an avenue for companies to enhance their sustainability profiles. Suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices are likely to stand out in a crowded marketplace, appealing to buyers who prioritize environmental responsibility.
How Has the Small Batch Injection Molding Process Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of small batch injection molding can be traced back to the growing need for flexibility and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing. Traditionally, injection molding required large minimum order quantities, which often posed challenges for companies looking to produce specialized or prototype parts. However, advancements in tooling technology, particularly the development of aluminum molds, have significantly reduced production costs and lead times, making small batch production more accessible.
The shift towards smaller production runs has allowed manufacturers to pivot quickly in response to market demands, fostering innovation and experimentation. As a result, small batch injection molding has become a vital process for industries that prioritize rapid prototyping and product development. This evolution continues to shape the strategies of international B2B buyers, as they seek partners who can provide high-quality, customized solutions with the agility required in today’s competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small batch injection molding
-
How do I solve high minimum order quantity issues in injection molding?
High minimum order quantities can be a significant barrier for businesses looking to produce specialized parts. Short batch injection molding is an effective solution, allowing you to order as few as 100 pieces. This flexibility helps manage costs and inventory while enabling rapid prototyping and testing. By selecting a supplier that specializes in short runs, you can optimize your production process and mitigate the risks associated with overproduction. -
What is the best approach for sourcing small batch injection molding suppliers?
When sourcing suppliers for small batch injection molding, prioritize those with a proven track record in quality and customer service. Look for ISO certifications, client testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their capability in handling short runs. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer flexibility in order quantities and rapid turnaround times, as this can significantly enhance your product development cycle. -
How can I customize my small batch injection molded parts?
Customization in small batch injection molding is highly feasible. Discuss your specific design requirements with potential suppliers, including material selection, part geometry, and surface finish. Many suppliers offer design assistance to optimize your parts for manufacturability. Ensure that your supplier has the capability to adapt to changes during the production process, as iterative design adjustments are common in small batch projects. -
What are the payment terms typically offered for small batch injection molding?
Payment terms for small batch injection molding can vary by supplier, but common practices include upfront deposits followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established clients. Always clarify payment structures before initiating a project, and consider the financial implications of your order quantities to maintain cash flow. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from my injection molding supplier?
A reputable injection molding supplier should implement stringent quality assurance measures, including first article inspections, process capability assessments, and regular quality audits. Ask about their methodologies for maintaining consistency and meeting specifications, such as statistical process control (SPC). It’s beneficial to choose suppliers with relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) to ensure they adhere to industry standards. -
How does international trade impact small batch injection molding sourcing?
International trade can significantly influence sourcing decisions for small batch injection molding. Factors such as tariffs, shipping costs, and import regulations may affect overall project costs and timelines. It’s essential to understand the trade agreements between your country and the supplier’s location, as well as any potential impacts on lead times. Establishing a local presence or working with suppliers familiar with your region can mitigate these challenges. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for small batch injection molded parts?
Logistics play a crucial role in the success of your small batch injection molding project. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and the supplier’s location relative to your operations. Effective communication with your supplier about shipping schedules and potential delays can help you manage expectations. Additionally, inquire about their capabilities for handling customs clearance and documentation, especially for international shipments. -
How quickly can I expect turnaround times for small batch injection molding?
Turnaround times for small batch injection molding can vary, but many suppliers offer rapid production capabilities, often completing projects in as little as two days. Factors influencing lead times include mold design complexity, material availability, and the supplier’s current workload. Ensure you communicate your timeline needs upfront, and choose a supplier with a dedicated short-run capacity to meet your project deadlines efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Small Batch Injection Molding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. RevPart – Short Run Injection Molding
Domain: revpart.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Short run injection molding allows for lower minimum order quantities, with runs as low as less than 100 pieces. It offers faster turnaround times, with fulfillment in as little as two days, and reduced costs compared to standard production molding. RevPart provides two types of prototype molds: an aluminum mold with a 2,000 shot warranty and a 718 steel mold with a 10,000 shot warranty. This serv…
2. Reddit – Two-Piece Shell Assembly
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The product is a two-piece shell with 3-4 countersunk recesses for screws on one side and corresponding bosses for threading. It includes standoffs for a PCB and features for positioning a battery. The dimensions are approximately 80mm x 40mm with wall thickness normalized at 1.3-2.2mm. The estimated costs for tooling range from $5-12K USD, with part costs between $3-5 USD, leading to a total esti…
3. Thunderbird Molding – Custom Plastic Injection Parts
Domain: thunderbird-molding.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: High-quality custom plastic injection molded parts at low volumes; specialized in short-run, low-volume production; equipped with quick-mold-change systems and Master Unit Dies; over 800 active molds in-house; proprietary batch molding procedures; one-touch exchange of die; low-volume production using carbon printing; 3D-printing capabilities for prototyping and low-volume production; focus on hig…
4. Midwest Mold – Low Volume Plastic Injection Molding
Domain: midwestmold.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Midwest Mold specializes in low volume plastic injection molding, ideal for projects requiring less than 10,000 pieces per year. They offer rapid tooling and prototyping services with a focus on speed, flexibility, and quality. The company utilizes aluminum injection molds, which can save 5%-30% in tooling costs and reduce cycle times by up to 40% compared to steel molds. They have in-house plasti…
5. Makerverse – Low-Volume Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: makerverse.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Low-volume injection molding is a manufacturing process ideal for producing limited quantities of custom parts and prototypes, typically ranging from 100 to 10,000 parts. It is cost-effective, with lower upfront tooling costs compared to high-volume production, allowing for faster time to market and flexibility in design adjustments. Common materials used include ABS, polycarbonate, polypropylene,…
6. Globalspec – Industry Insights
Domain: cr4.globalspec.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Globalspec – Industry Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Omega Plastics – Custom Mold Design Services
Domain: opinc.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Injection Molding Design services at Omega Plastics focus on collaboration to develop and optimize custom mold designs. Key aspects include: 1. Custom Mold Design: Involves creating a model of the part, defining its size, shape, and features. 2. Moldflow® Simulation: Utilizes software to predict plastic flow and identify potential issues like air traps and weld lines. 3. Manufacturing Process: Inc…
8. The Tool Room – Short Run Plastic Injection Molding
Domain: thetoolroom.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Short run plastic injection molding allows for lower minimum order quantities, starting from as few as 100 parts. It is suitable for prototypes, small marketing production, custom components for specialty automotive or medical applications, and high-end appliances or technology. The process utilizes similar resins as high-volume molding, ensuring high-quality results despite low volume needs. The …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small batch injection molding
In conclusion, small batch injection molding emerges as a pivotal solution for businesses seeking flexibility and cost efficiency in their production processes. By lowering minimum order requirements and enabling rapid prototyping, companies can respond swiftly to market demands without incurring prohibitive costs. This method not only accelerates product development cycles but also ensures that manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards, critical for industries such as medical, automotive, and aerospace.
Strategic sourcing in small batch injection molding allows international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to leverage local suppliers who understand their unique market needs. As global supply chains evolve, investing in local partnerships can enhance responsiveness and mitigate risks associated with longer lead times.
Looking forward, the future of small batch injection molding is promising, with advancements in technology and materials paving the way for even greater efficiencies. Now is the time for B2B buyers to explore this innovative manufacturing method, ensuring they remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic landscape. Engage with trusted suppliers today to harness the benefits of small batch injection molding and elevate your production capabilities.