Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for single phase cnc mill
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, sourcing a reliable single-phase CNC mill presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re a small workshop in Africa, a burgeoning manufacturer in South America, or an established enterprise in Europe, the need for precision machining at an affordable price is universal. This guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the global market for single-phase CNC mills, addressing key factors such as machine types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
Understanding the diverse functionalities and specifications of single-phase CNC mills is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. With options ranging from compact models ideal for tight spaces to more versatile machines capable of handling various materials, knowing what suits your operational needs can significantly enhance productivity. This guide will empower buyers by providing insights into the capabilities of different CNC mills, the importance of technical support, and the value of long-term partnerships with suppliers.
As we delve into the specifics of the single-phase CNC mill market, our aim is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to confidently evaluate your options. By the end of this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to make strategic decisions that align with your business goals, ultimately driving growth and innovation in your manufacturing operations.
Understanding single phase cnc mill Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tormach 1100M | Compact design, high-speed machining, customizable accessories | Prototyping, small batch production | Pros: Affordable, user-friendly, adaptable. Cons: Limited to smaller workpieces. |
| Haas Mini Mill | 40-taper spindle, compact footprint, versatile tooling options | Tooling, mold making, educational use | Pros: High precision, reliable, extensive support. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Grizzly G0704 | Budget-friendly, basic features, user-friendly setup | Hobbyist machining, small workshops | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to learn. Cons: Limited capabilities for complex tasks. |
| Sieg X2D | Lightweight, portable, suitable for small shops | DIY projects, light machining | Pros: Affordable, compact, good for beginners. Cons: Limited power and size. |
| CNC Masters Mill | Solid construction, versatile for various materials | Manufacturing, educational facilities | Pros: Robust, capable of handling tough materials. Cons: Requires more space, higher maintenance. |
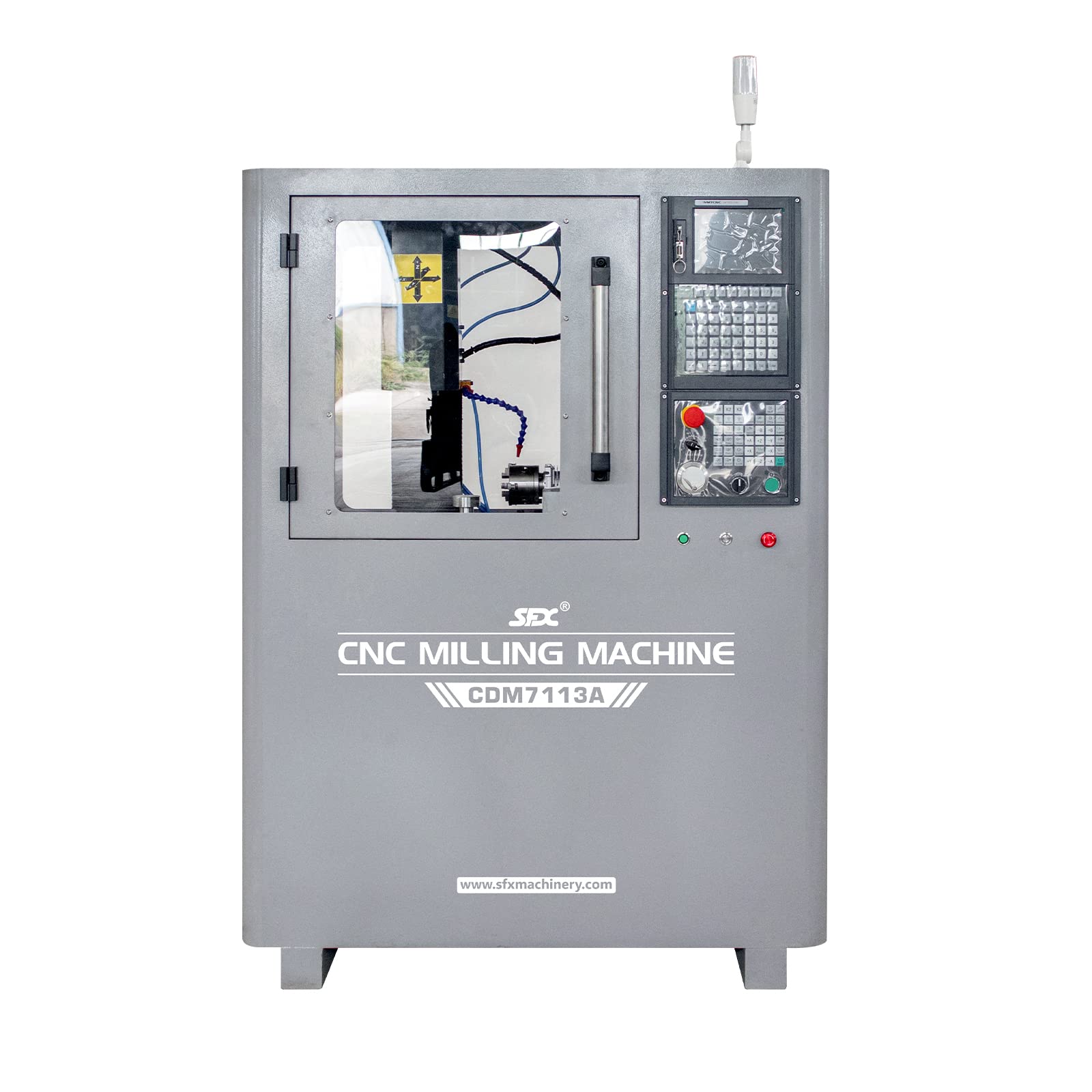
What are the Key Characteristics of the Tormach 1100M CNC Mill?
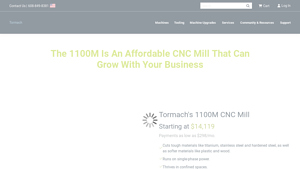
The Tormach 1100M is designed for small businesses that require a compact yet powerful milling solution. Its ability to cut tough materials such as titanium and stainless steel makes it ideal for prototyping and small batch production. Key features include a user-friendly interface and customizable accessories, allowing businesses to scale operations as needed. Buyers should consider the machine’s footprint and adaptability to ensure it fits within their operational constraints.
How Does the Haas Mini Mill Stand Out in the Market?
The Haas Mini Mill is recognized for its precision and reliability, making it suitable for various applications, including tooling and mold making. With a 40-taper spindle and versatile tooling options, it caters to industries that demand high-quality finishes. While the initial investment may be higher than other options, the extensive support network and solid construction justify the cost for businesses focused on long-term production.
Why is the Grizzly G0704 a Popular Choice for Small Workshops?
The Grizzly G0704 is an economical option for hobbyists and small workshops. Its user-friendly setup and budget-friendly price point make it accessible for those new to CNC milling. However, its limited capabilities may restrict its use for more complex machining tasks. Businesses should weigh the cost against potential growth in machining needs when considering this mill.
What Makes the Sieg X2D Ideal for DIY Projects?
The Sieg X2D is lightweight and portable, making it an excellent choice for DIY enthusiasts and small shops. Its affordability and compact size appeal to those who may not require heavy-duty machining capabilities. While it excels in basic tasks, its limited power might deter businesses seeking to tackle more demanding projects. Buyers should evaluate their specific project requirements before making a purchase.
How Does the CNC Masters Mill Meet Diverse Industrial Needs?
The CNC Masters Mill features solid construction and versatility, suitable for a range of materials and applications. It serves well in manufacturing and educational settings, providing robust performance for more challenging tasks. Despite its advantages, the machine requires more space and may incur higher maintenance costs. Organizations should consider their operational space and budget before opting for this mill.
Key Industrial Applications of single phase cnc mill
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of single phase cnc mill | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Component machining for aircraft parts | Precision machining reduces weight while maintaining strength | Ensure compliance with international aerospace standards |
| Automotive | Production of custom parts and prototypes | Enhances innovation with rapid prototyping capabilities | Look for mills with flexible tooling options and quick setup |
| Electronics | Fabrication of circuit boards and enclosures | Improved design accuracy and reduced production costs | Seek mills that support intricate designs and small tolerances |
| Metal Fabrication | Production of specialized tools and fixtures | Increases operational efficiency and reduces lead times | Consider machines with robust material handling capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of surgical instruments and implants | Ensures high-quality standards for safety and effectiveness | Verify certifications and quality control measures in sourcing |
How Is a Single Phase CNC Mill Used in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, single phase CNC mills are utilized for machining lightweight, high-strength components essential for aircraft. These mills can handle tough materials like titanium and aluminum, ensuring precision in every cut. The ability to produce complex geometries helps manufacturers meet stringent regulatory standards while optimizing performance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize machines that comply with aerospace certification requirements, ensuring they can produce parts that meet both safety and performance criteria.
What Role Does a Single Phase CNC Mill Play in Automotive Prototyping?
Automotive manufacturers often rely on single phase CNC mills for producing custom parts and prototypes. These machines enable rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to test designs quickly and efficiently. The flexibility of CNC milling can lead to innovative solutions while reducing time-to-market for new vehicles. International buyers should consider sourcing mills that offer versatile tooling systems and robust software support to facilitate design changes and adaptations throughout the prototyping phase.
How Is a Single Phase CNC Mill Beneficial for Electronics Fabrication?
In electronics, single phase CNC mills are instrumental in fabricating circuit boards and enclosures with high precision. The ability to achieve intricate designs and small tolerances is crucial for the reliability of electronic devices. By using CNC mills, manufacturers can streamline their production processes, reducing costs and improving product quality. Buyers should look for mills that support advanced programming capabilities and have a strong track record in producing electronic components to ensure compatibility with their production needs.
Why Choose a Single Phase CNC Mill for Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication businesses utilize single phase CNC mills to produce specialized tools and fixtures tailored to specific projects. These machines enhance operational efficiency by allowing for quick setup and high throughput. They can handle a variety of materials, from soft metals to hardened steel, making them versatile for different applications. When sourcing, businesses should focus on mills that offer strong material handling capabilities and customizable features to adapt to diverse fabrication tasks.
How Do Single Phase CNC Mills Support Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, precision is paramount, and single phase CNC mills are essential for manufacturing surgical instruments and implants. These machines ensure that products meet high-quality standards necessary for patient safety and effectiveness. The ability to produce complex shapes and maintain tight tolerances is critical in this industry. Buyers should verify that potential suppliers adhere to stringent medical manufacturing regulations and quality control processes to ensure the safety and reliability of their products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘single phase cnc mill’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Power Supply Constraints for Small Workshops
The Problem: Many small businesses, especially in regions with unstable power supply or limited infrastructure, often face challenges when operating CNC mills that require three-phase power. This limitation can hinder production capabilities, as these businesses may not have the resources or technical expertise to upgrade their electrical systems. As a result, they may be forced to either invest in costly electrical upgrades or forgo purchasing CNC machinery altogether, missing out on potential efficiency gains and competitive advantages.
The Solution: Opting for a single-phase CNC mill, such as the Tormach 1100M, can be a game changer for these businesses. This machine operates on standard single-phase power, making it accessible for smaller workshops and facilities with limited electrical infrastructure. When sourcing a single-phase CNC mill, buyers should ensure the machine meets their specific power requirements—typically 208-240 Vac and 20 A breaker. Additionally, investing in a machine with flexible power requirements and the ability to handle a range of materials, including metals and plastics, can provide significant versatility in production. It is also advisable to consult with local suppliers and electrical engineers to evaluate the existing power setup and receive guidance on any necessary modifications to ensure optimal operation.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Machine Operation and Programming
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the steep learning curve associated with operating CNC machines. Many manufacturers, particularly in emerging markets, struggle to find skilled operators who are proficient in complex programming languages like G-code. This knowledge gap can lead to decreased productivity, increased machine downtime, and costly errors in production processes, ultimately affecting the bottom line.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, businesses should invest in CNC mills that offer user-friendly control systems and accessible programming tools. For example, the Tormach 1100M features the PathPilot controller, which provides an intuitive, touchscreen-friendly interface and built-in conversational programming capabilities. This allows operators to create and edit programs on the fly without deep programming knowledge. Furthermore, companies can benefit from investing in training programs for their staff, including online courses or workshops that focus on CNC operation and programming basics. Establishing a mentorship system where experienced operators train newer employees can also facilitate knowledge transfer and enhance overall team proficiency.
Scenario 3: Need for Scalability and Upgradability
The Problem: As businesses grow, their production needs often evolve, requiring machinery that can adapt to increased demands without necessitating a complete overhaul. Many companies face the dilemma of purchasing a CNC mill that may become obsolete or inadequate as their production requirements expand, leading to further capital expenditures and operational disruptions.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize CNC mills that offer scalability and the option for future upgrades. The Tormach 1100M, for instance, is designed with adaptability in mind, allowing businesses to enhance their machines with additional accessories like automatic tool changers and multi-axis capabilities. When sourcing a single-phase CNC mill, it is crucial to assess the manufacturer’s offerings for modular components and upgrades. Engaging with vendors who provide long-term support and a clear roadmap for enhancements can ensure that the chosen equipment remains relevant and capable of meeting future production needs. Additionally, businesses should conduct regular assessments of their operational goals and align them with machine capabilities to ensure they are making informed decisions about upgrades and expansions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for single phase cnc mill
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Single Phase CNC Mills?
When selecting materials for single phase CNC mills, it is crucial to consider their properties that directly impact performance. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and plastic. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its application in CNC milling.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Aluminum is widely used in CNC milling due to its excellent machinability and lightweight nature. It has a low density, which makes it easy to handle and reduces wear on tooling. Key properties include good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, easy to machine, and offers a good strength-to-weight ratio.
Cons: It is less durable than steel and can deform under high pressure or temperature.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, but its softness may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that their suppliers can meet local quality standards.
Stainless Steel: The Durable Workhorse
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for CNC milling applications that require longevity and reliability. Its key properties include high tensile strength and resistance to oxidation, which are critical in harsh environments.
Pros: Stainless steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Cons: It is more challenging to machine than aluminum, which can increase manufacturing costs and time.
Impact on Application: Ideal for parts exposed to moisture or chemicals, stainless steel is often used in food processing and medical equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with international standards like ASTM A276 or JIS G4303, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Titanium: The High-Performance Material
Titanium offers a unique combination of strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance. It is particularly valued in aerospace and medical applications where performance is critical. Key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent biocompatibility.
Pros: Titanium is incredibly strong and resistant to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
Cons: It is more expensive than aluminum and stainless steel, and machining can be complex due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Titanium is suitable for high-performance applications, including aerospace components and surgical instruments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with aerospace standards (e.g., ASTM B348) is vital for buyers in regions like the Middle East, where aerospace industries are growing.
Plastic: The Versatile Option
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC milling for lightweight and cost-effective solutions. They offer good chemical resistance and can be easily molded into complex shapes.
Pros: Plastics are inexpensive and can be machined quickly, making them suitable for prototyping and low-volume production.
Cons: They generally lack the strength and durability of metals, which can limit their applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for non-structural components and are compatible with various media, but they may not withstand high temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with local environmental regulations, particularly in Europe, where regulations can be stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Single Phase CNC Mills
| Material | Typical Use Case for single phase cnc mill | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable under high stress | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and medical equipment | High durability and corrosion resistance | More challenging to machine | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace components and surgical tools | Exceptional strength and performance | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Plastic | Prototyping and low-volume production | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited strength and durability | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for single phase cnc mill
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Single Phase CNC Mill?
Manufacturing a single phase CNC mill involves several critical stages that ensure both functionality and quality. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first step in manufacturing a CNC mill is selecting the appropriate materials. Common choices include high-grade steel and aluminum, which offer durability and precision. These materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specified standards.
Once the materials are selected, they are cut to size using water jet or laser cutting techniques. This precision cutting is essential for ensuring that each component fits perfectly during assembly. After cutting, the materials are subjected to treatments like heat treatment or surface hardening to enhance their mechanical properties, which is crucial for the longevity of the machine.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted for CNC Mills?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the CNC mill. Techniques such as machining, milling, and turning are employed to achieve the desired dimensions and tolerances. For instance, components like the base, column, and table are machined to precise specifications to ensure stability and accuracy during operation.
Advanced CNC machines are often used in this stage to enhance precision. These machines can perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing the risk of error and improving efficiency. The integration of CAD/CAM software also streamlines this process by allowing for digital simulations before actual machining begins.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final CNC mill unit. This stage requires skilled technicians who ensure that each part is correctly aligned and secured. The assembly process includes installing the spindle, motor, and control systems, as well as integrating software interfaces like PathPilot®.
Quality checks are performed at various points during assembly. This includes verifying that all components are free from defects and function as intended. Using jigs and fixtures can help maintain the accuracy of assembly, ensuring that the final product meets design specifications.
How Is the Finishing Process Performed to Ensure Quality?
The finishing process enhances both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the CNC mill. This may involve surface treatments such as anodizing or painting to protect against corrosion and wear. Precision grinding may also be used to achieve fine tolerances on critical surfaces.
Final inspections are crucial during this stage. Each machine undergoes a thorough quality assurance check to ensure it meets the required standards before shipping. This includes operational testing to verify that all components function harmoniously.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for CNC Mills?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing process of CNC mills. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers follow best practices in quality management. This certification indicates that the manufacturer has established a systematic approach to managing processes, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
How Do Industry-Specific Standards Impact Quality Control?
In addition to ISO standards, manufacturers may also need to comply with industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for compliance with European safety standards or API (American Petroleum Institute) for those operating in the oil and gas sector. These certifications require rigorous testing and documentation, which can add layers of quality assurance to the manufacturing process.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Mill Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical to ensuring that each CNC mill meets the required specifications. Typically, these checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide documentation demonstrating that materials meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, components are continually inspected. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and functionality at various stages of production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, the entire CNC mill undergoes operational testing and final inspection. This ensures that the machine operates as intended and meets all quality standards before it is shipped to the customer.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for CNC Mills?
Testing methods vary based on the component being assessed, but common approaches include:
-
Functional Testing: Verifying the operational performance of the CNC mill, including speed, accuracy, and control response.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspections ensure that internal structures are free from defects without damaging the components.
-
Calibration: Ensuring that the CNC mill is accurately calibrated for precision machining. This often involves using precision measuring tools to validate machine settings.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Periodically visiting the manufacturing site allows buyers to assess the quality management systems in place. An audit can reveal adherence to international standards and the effectiveness of QC processes.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their QC processes, including documentation of testing methods and results. This transparency builds trust and confidence in the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the CNC mill’s quality. This is particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with the local market or manufacturing practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. For example, while ISO 9001 is widely recognized, local compliance requirements may differ significantly.
Understanding the specific certification and compliance requirements for the destination market is critical. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers can meet these requirements to avoid potential legal or operational issues. Additionally, being informed about the supplier’s reputation within their local market can provide insights into their reliability and commitment to quality.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for single phase CNC mills is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on the entire lifecycle from material preparation to final inspection, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they partner with reliable manufacturers capable of delivering high-quality machinery tailored to their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘single phase cnc mill’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring a single-phase CNC mill. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, having the right equipment is critical for enhancing productivity, ensuring precision, and meeting market demands. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of selecting a CNC mill that meets your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific technical requirements of your operations is the first step in sourcing a single-phase CNC mill. Identify the materials you will be machining, such as metals or plastics, and the complexity of the parts you intend to produce. Key specifications to consider include:
– Spindle Power and Speed: Ensure the mill can handle the materials you will work with.
– Travel Dimensions: Assess the size of parts to confirm the mill can accommodate them.
Step 2: Determine Your Budget
Establishing a clear budget is crucial in the sourcing process. Consider not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational costs such as maintenance, tooling, and potential upgrades. Look for options that offer:
– Transparent Pricing: Ensure there are no hidden fees.
– Financing Options: Some suppliers provide flexible payment plans, which can be beneficial for managing cash flow.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Research their market reputation, customer service, and product reliability. Key actions include:
– Requesting References: Ask for testimonials or case studies from other businesses in your industry.
– Assessing Certifications: Verify that the supplier meets international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications).
Step 4: Inspect Machine Features and Capabilities
Review the features and capabilities of the CNC mills on your shortlist. Look for machines that offer:
– User-Friendly Controls: An intuitive interface can shorten the learning curve for your team.
– Upgrade Options: Choose models that allow for future enhancements, such as automatic tool changers or advanced software.
Step 5: Inquire About Warranty and Support
Understanding the warranty and support offered by the supplier can save you significant costs down the line. Important aspects to consider include:
– Warranty Length and Coverage: Look for comprehensive warranties that cover critical components.
– Technical Support Availability: Ensure that the supplier provides accessible support channels for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Step 6: Consider Assembly and Installation Services
Many suppliers offer assembly and installation services, which can be particularly beneficial if your team lacks the expertise. Evaluate:
– Turnkey Solutions: Some suppliers can provide fully assembled machines ready for immediate use.
– Installation Training: Consider whether the supplier offers training for your staff to maximize the machine’s capabilities.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected a supplier and model, carefully review the purchase agreement. Ensure that it includes:
– Delivery Terms: Confirm the timeline and conditions for delivery.
– Payment Terms: Clarify payment schedules and any potential penalties for late payments.
By following this checklist, you can confidently navigate the process of sourcing a single-phase CNC mill that aligns with your business goals and operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for single phase cnc mill Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Single Phase CNC Mill?
When sourcing a single phase CNC mill, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and electronics significantly influences the overall price. High-quality materials that meet industry standards will typically incur higher costs but result in better durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled machinists, assembly workers, and engineers involved in the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs may affect the pricing, while countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower these costs, making the final product more affordable.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs cover the necessary equipment and fixtures required for machining operations. Custom tooling may be required for specialized parts, impacting the overall budget.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures is essential to ensure the reliability and precision of CNC mills. While this may add to the initial costs, it reduces the risk of defects and recalls.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and import duties can greatly influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and investment in innovation. Understanding this margin can aid in negotiation.
What Influences the Pricing of a Single Phase CNC Mill?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure of single phase CNC mills:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, making it advantageous for businesses planning to scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines with specific features or capabilities will generally cost more than standard models. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications (such as ISO compliance) can impact costs. Higher-grade materials and certifications often justify a premium price due to the assurance of quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their brand value and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who bears the cost and risk during transportation. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can lead to different cost implications.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for CNC Mills?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing a single phase CNC mill, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding the market rates for CNC mills helps in making informed purchasing decisions and negotiating better prices.
-
Leverage Relationships with Suppliers: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms, discounts, and insights into upcoming innovations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but also the long-term expenses associated with maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower TCO.
-
Explore Financing Options: Many suppliers offer financing solutions that can alleviate upfront costs. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with budget constraints.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should consider currency fluctuations, import taxes, and tariffs that may affect the final pricing of CNC mills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sourcing a single phase CNC mill involves a multifaceted cost structure influenced by various factors. By understanding these components and leveraging effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. As always, it’s advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any purchases, keeping in mind that prices can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing single phase cnc mill With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Single Phase CNC Mills: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of precision machining, selecting the right equipment is crucial for optimizing production and meeting specific operational needs. While single-phase CNC mills offer various benefits, including affordability and ease of use, several alternative solutions can also achieve similar goals. This analysis compares single-phase CNC mills with two viable alternatives: multi-phase CNC mills and manual machining techniques.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Single Phase CNC Mill | Multi-Phase CNC Mill | Manual Machining Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Suitable for light to medium tasks; lower torque | Higher torque and speed, suitable for heavier materials | Labor-intensive; dependent on operator skill |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment (e.g., Tormach 1100M starts at $14,119) | Higher upfront costs; often requires additional infrastructure | Low equipment costs but high labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to set up; can be operational in confined spaces | More complex setup; requires three-phase power | Requires skilled labor for setup and operation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; user-friendly design | Higher maintenance due to complexity | Variable maintenance; depends on machine age and usage |
| Best Use Case | Small shops, prototyping, and light production | Large-scale manufacturing and heavy-duty applications | Custom, one-off projects and repairs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Multi-Phase CNC Mills
Multi-phase CNC mills, operating on three-phase power, offer higher performance compared to single-phase models. They can handle heavier materials and more complex machining tasks, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing environments. However, the initial investment is significantly higher, and they require a robust power supply infrastructure. Maintenance can also be more demanding due to their complexity. For businesses focused on high-volume production and capable of investing in infrastructure, multi-phase CNC mills are a strong alternative.
Manual Machining Techniques
Manual machining involves traditional methods where skilled operators use lathes, mills, and other equipment to create parts. While this method requires minimal initial investment, it is heavily reliant on the skill level of the machinists. The performance is variable; high-quality outputs depend on the operator’s expertise. This technique can be beneficial for custom, low-volume projects where flexibility is needed. However, it tends to be labor-intensive and less efficient than CNC options, making it less suitable for businesses aiming for scalability and consistency.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
When deciding between a single-phase CNC mill and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and production goals. Single-phase CNC mills are excellent for small to medium-sized operations seeking affordability and ease of use. In contrast, multi-phase CNC mills are ideal for larger manufacturers requiring high performance and the ability to work with tough materials. Meanwhile, manual machining may be appropriate for specialized projects that demand a personal touch and craftsmanship. Ultimately, aligning the choice of equipment with the company’s strategic objectives will ensure optimal production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for single phase cnc mill
What Are the Key Technical Specifications of a Single Phase CNC Mill?
Understanding the technical specifications of a single phase CNC mill is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the essential properties:
1. Spindle Power
Spindle power is typically measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW) and indicates the milling machine’s capability to handle different materials. For instance, a 2 HP spindle can effectively cut through materials like aluminum and plastics, while a higher power rating might be necessary for tougher materials such as titanium or stainless steel. This specification is vital for businesses aiming to process a diverse range of materials.
2. Maximum Speed
The maximum speed of a CNC mill, often expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM), directly affects the quality and efficiency of the machining process. For instance, a mill with a maximum speed of 7500 RPM allows for faster cutting rates and finer finishes. Understanding this specification helps businesses assess the machine’s suitability for their production needs.
3. Travel Dimensions (X, Y, Z Axes)
The travel dimensions refer to the maximum movement the machine can achieve along each axis. For example, a travel dimension of 18 inches on the X-axis, 11 inches on the Y-axis, and 16.25 inches on the Z-axis determines the size of the workpieces that can be machined. This specification is crucial for businesses that require machining of larger components.
4. Weight Capacity
Each CNC mill has a maximum weight capacity it can support on its table. For example, a machine with a 500 lbs capacity can handle substantial workpieces, which is essential for industries like aerospace or automotive where heavy components are common. Understanding this specification ensures that the chosen machine can handle specific production tasks.
5. Power Requirements
CNC mills operating on single-phase power typically require specific voltage and amperage ratings. A common requirement might be 208-240 Vac with a 20 A breaker. This is essential for buyers to consider in their facility setup to ensure compatibility with existing electrical systems.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Single Phase CNC Mills?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers looking for reliable sources of replacement parts or upgrades for their CNC mills.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers who need to manage inventory costs and ensure that they meet purchasing requirements without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price quotes on specified products or services. It is a vital step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare costs and services from multiple suppliers before making a decision.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for effective inventory management and ensuring production schedules are met.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in single phase CNC mills, ultimately optimizing their operations and enhancing productivity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the single phase cnc mill Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing the Single Phase CNC Mill Sector?
The single phase CNC mill market is witnessing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increasing demand for precision engineering and customized manufacturing solutions is at the forefront. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are experiencing an upsurge in small to medium enterprises (SMEs) that require versatile and affordable CNC solutions, making single phase mills particularly appealing. The rise of Industry 4.0 has also fostered a technological revolution, with businesses increasingly adopting smart manufacturing practices. Buyers are seeking CNC mills that not only perform efficiently but also integrate easily with advanced software systems for enhanced operational control.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards modular and adaptable CNC milling solutions that allow businesses to scale operations without substantial upfront investments. As firms prioritize flexibility, CNC mills with capabilities to handle a variety of materials—from metals like titanium and stainless steel to plastics—are becoming essential. Additionally, innovations in user-friendly interfaces, such as conversational programming, are making CNC technology accessible to a broader audience, including those with limited technical expertise.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Single Phase CNC Mill Market?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point for B2B buyers in the CNC milling sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led to a heightened awareness of ethical sourcing and responsible production practices. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, utilizing eco-friendly materials and minimizing waste in their manufacturing processes.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is also rising. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming standard requirements for suppliers, reflecting a commitment to sustainable practices. For single phase CNC mills, this may involve the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient machinery that reduces carbon footprints. B2B buyers should consider not only the performance and cost of CNC mills but also the environmental credentials of their suppliers, as these factors increasingly influence purchasing decisions.
How Has the Single Phase CNC Mill Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the single phase CNC mill sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and a shift towards more user-friendly solutions. Historically, CNC milling machines were primarily designed for large-scale industrial applications, often requiring three-phase power. However, the growing need for affordable and accessible manufacturing solutions has spurred the development of single phase CNC mills, catering specifically to SMEs and educational institutions.
Over the years, manufacturers have made strides in enhancing the capabilities of these machines, integrating advanced control systems and software that simplify operations. The introduction of features such as high-speed machining and built-in programming tools has made CNC technology more approachable for businesses across various sectors. This evolution not only reflects the changing demands of the market but also underscores the importance of innovation in maintaining competitiveness in the global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of single phase cnc mill
-
How do I choose the right single phase CNC mill for my business needs?
Choosing the right single phase CNC mill involves assessing your specific production requirements, including material types, part sizes, and production volume. Start by evaluating the machine’s specifications, such as spindle power, maximum feed rates, and table dimensions. Consider the software compatibility and ease of use, as well as the availability of upgrades and accessories. Additionally, consult with suppliers to understand their after-sales support and warranty options, which can be crucial for long-term operational efficiency. -
What is the best way to evaluate suppliers of single phase CNC mills?
To evaluate suppliers, begin by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and testimonials to gauge their reliability. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, especially if you’re importing to regions like Africa or South America. Request references from other buyers and assess their response time and customer service during your inquiry. A reputable supplier should also provide clear information about warranty, support, and maintenance services. -
What customization options are available for single phase CNC mills?
Many manufacturers offer customization options such as enhanced spindle speeds, tool changers, and specialized software features. You can also request modifications to accommodate specific materials or production processes. When discussing customization, ensure that the supplier provides detailed specifications and timelines. Additionally, inquire if they offer training or support for the customized features, as this can significantly impact your operational efficiency. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing a single phase CNC mill?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upon order placement and the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans, which can help manage cash flow. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, especially for international transactions. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
What should I consider regarding logistics when importing a CNC mill?
Logistics is a critical aspect of importing CNC mills. Consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive shipping options and is familiar with the import regulations in your country. It may also be beneficial to work with logistics companies that specialize in heavy machinery to handle transportation and installation. Additionally, confirm that the machine’s packaging is suitable for international shipping to prevent damage during transit. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my CNC mill?
To ensure quality assurance, inquire about the manufacturer’s QA processes during production. Request documentation of inspections and certifications that verify compliance with industry standards. It’s also advisable to perform a pre-shipment inspection if possible. Establish clear acceptance criteria for the machine’s performance upon delivery, and consider a warranty that covers defects and operational failures. Regular maintenance and service agreements can further enhance the longevity and reliability of your CNC mill. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for CNC mills?
Minimum order quantities can vary based on the manufacturer and specific machine models. Some suppliers may have an MOQ for bulk orders to ensure cost-effectiveness, while others might offer single units for smaller operations. When discussing your needs, be transparent about your production volume to negotiate favorable terms. It’s also worth exploring potential discounts for larger orders or bundled purchases that include accessories or tooling. -
What factors should I consider for maintenance of a single phase CNC mill?
Maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of your CNC mill. Regularly scheduled servicing, including lubrication, calibration, and software updates, can prevent costly breakdowns. Review the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations and consider training your staff on basic troubleshooting and upkeep. Additionally, inquire about the availability of spare parts and the supplier’s response time for service requests, as these factors can significantly impact your machine’s operational downtime.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Single Phase Cnc Mill Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tormach – 1100M CNC Milling Machine
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Tormach 1100M CNC Milling Machine”, “Starting Price”: “$14,119”, “Payment Options”: “Payments as low as $298/mo”, “Material Capability”: “Cuts tough materials like titanium, stainless steel, and hardened steel, as well as softer materials like plastic and wood”, “Power Requirements”: “Single-phase 208-240 Vac, 50/60 Hz, 20 A Breaker, NEMA 6-20R Receptacle”, “Dimensions”: {“Table …
2. Haas – TM1 Toolroom Mill
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, Haas – TM1 Toolroom Mill, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Tormach – 1100M & 770 CNC Machines
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Tormach 1100M – Ideal for machining knives from aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel. Requires 120V to 220V transformer, max 20A-25A power. Features include ATC (Automatic Tool Change) and a spindle speed of at least 10,000 RPM. 2. Tormach 770 – Mentioned as a first CNC machine, appreciated for its ease of use. 3. Hurco – Recommended for conversational programming, known for being accurate a…
4. Haas CNC – Mini Mill
Domain: haascnc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haas CNC – Mini Mill, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Model Engineer – Milling Machine Insights
Domain: model-engineer.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Single phase milling machine recommendations discussed in a forum with mentions of specific models like Warco WM250 and Centec 2B. Users share experiences with single phase and three phase machines, highlighting preferences for older technology and the reliability of three phase motors. The conversation includes insights on motor types, efficiency, and the importance of mechanical condition over m…
6. Mycncuk – 240V CNC Milling Machine
Domain: mycncuk.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: 240V single phase CNC milling machine; suitable for machining small detailed parts up to 150mm square tool steel; preference for installation in a garage; considerations for rigidity and spindle speeds; advice on focusing on specific functions for the machine.
7. SYIL – SYIL X7 Small CNC Mill
Domain: us.syil.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “SYIL X7”, “Type”: “Small CNC Mill”, “Axis Travels”: {“X travel”: “400 mm (15.7 inches)”, “Y travel”: “300 mm (11.8 inches)”, “Z travel”: “380 mm (14.9 inches)”}, “Table Size”: {“Dimensions”: “700 mm x 300 mm (27.56″ x 11.81″)”, “Max Table Load”: “150 kg (330 lb)”, “T-slots”: {“Number”: 3, “Size”: “14 mm”, “Distance”: “100 mm”}}, “Spindle”: {“Type”: “BT30”, “Max Speed”: “12,000 rp…
8. {product_details:MSC Industrial – Industrial Supplies and Solutions}
Domain: mscdirect.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: CRITICAL: You MUST output ONLY the JSON object, with no other text, commentary, or markdown formatting. The entire response must be a single, valid JSON object like this: {“product_details”: “string”}. If no info is found, use an empty string for the value.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for single phase cnc mill
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Single Phase CNC Mills?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of single-phase CNC mills presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, especially in developing markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The versatility and affordability of models like the Tormach 1100M or Haas Mini Mill make them ideal for small to medium enterprises looking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities without significant capital investment. These machines not only accommodate a range of materials but also support future upgrades and integrations, which is crucial for businesses aiming for long-term growth.
Furthermore, the importance of understanding local power requirements and operational support cannot be overstated. Buyers should leverage partnerships with reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive support, including training and after-sales service, to ensure seamless operations.
As industries evolve and demand for precision machining increases, investing in the right single-phase CNC mill can position your business competitively. Embrace this technological shift and explore options that align with your operational needs. The future of manufacturing is here; make the strategic decision to invest wisely and watch your business thrive.