Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shop drawings software
In the fast-evolving landscape of construction and manufacturing, sourcing effective shop drawings software is a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the need for precision, compliance, and efficiency in shop drawings cannot be overstated. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the various types of shop drawings software available, their applications across different sectors, and crucial factors for supplier vetting and cost considerations.
Understanding the nuances of shop drawings software is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. From integrated Building Information Modeling (BIM) solutions to specialized CAD programs tailored for millwork or structural engineering, this guide equips buyers with the insights needed to navigate the global market effectively.
Moreover, we highlight the unique challenges faced by businesses in regions like Brazil and Germany, providing context-specific solutions that enhance operational efficiency and compliance with local regulations. By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement processes, ensuring they select software that not only meets their technical requirements but also aligns with their strategic goals. Ultimately, this resource empowers companies to optimize their design workflows, reduce errors, and improve collaboration across teams and stakeholders.
Understanding shop drawings software Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated BIM Software | Combines design, analysis, and detailing in one platform | Structural engineering, architectural projects | Pros: Streamlined workflow, enhanced collaboration; Cons: Higher initial investment, complexity in training. |
| CAD Software for Millwork | Specialized tools for millwork design and detailing | Cabinetry, furniture, and custom woodworking | Pros: Precision in design, industry-standard tools; Cons: May require extensive training, software compatibility issues. |
| 3D Modeling Software | Offers advanced visualization and dimensioning capabilities | Product design, prototype development | Pros: Realistic visualizations, improved client presentations; Cons: Can be resource-intensive, requires powerful hardware. |
| Structural Analysis Software | Focused on load analysis and structural integrity | Engineering, construction, and safety assessments | Pros: Ensures compliance with regulations, detailed analysis; Cons: Often limited to structural applications, can be costly. |
| Specialized Furniture Design Software | Tailored for the woodworking industry, with specific features for furniture design | Custom furniture manufacturing, cabinetry | Pros: User-friendly for woodworkers, optimized for furniture-specific tasks; Cons: Limited to furniture applications, may lack broader design tools. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Integrated BIM Software for Shop Drawings?
Integrated BIM (Building Information Modeling) software is characterized by its ability to unify various aspects of design, including structural analysis, architectural design, and detailing into a single platform. This type of software is particularly suitable for large-scale structural engineering and architectural projects, where collaboration between different disciplines is crucial. For B2B buyers, key purchasing considerations include the software’s ability to facilitate real-time collaboration among teams, its compatibility with existing systems, and the potential for long-term cost savings through efficiency gains.
How Does CAD Software for Millwork Differ from Other Options?
CAD software tailored for millwork emphasizes precision and the ability to produce detailed shop drawings specific to cabinetry and furniture design. This software is primarily used in the woodworking industry and is crucial for creating accurate millwork drawings. B2B buyers should consider the software’s ease of use, integration capabilities with other systems, and the level of support provided for training and troubleshooting. While CAD software can be a significant investment, its ability to enhance accuracy and efficiency in production can lead to substantial returns.
Why Choose 3D Modeling Software for Shop Drawings?
3D modeling software provides advanced visualization tools that allow for detailed dimensioning and realistic representations of designs. It is particularly beneficial in product design and prototype development, where visual accuracy is essential for client presentations and approvals. B2B buyers should assess the software’s rendering capabilities, user interface, and compatibility with other design tools. While 3D modeling software can be resource-intensive, the ability to showcase designs in an engaging way can justify the investment.
What are the Benefits of Using Structural Analysis Software?
Structural analysis software is designed to evaluate the integrity and safety of structures under various loads and conditions. This type of software is essential for engineering and construction firms that must comply with safety regulations. Key considerations for B2B buyers include the software’s ability to perform comprehensive analyses, ease of use, and the level of technical support available. While it may be limited to structural applications, the insights gained from using this software can prevent costly design flaws and ensure compliance with industry standards.
How Does Specialized Furniture Design Software Meet Industry Needs?
Specialized furniture design software is crafted specifically for the woodworking sector, providing features that cater to furniture design and production. This software is user-friendly and optimized for tasks specific to woodworkers, making it ideal for custom furniture manufacturing and cabinetry. When considering this software, B2B buyers should look for features that enhance design efficiency, ease of use, and customer support. Although it may lack broader design capabilities, its focus on furniture design can greatly enhance productivity and accuracy in this niche market.
Key Industrial Applications of shop drawings software
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shop drawings software | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural Engineering Drawings | Enhances accuracy in construction, reducing rework costs. | Integration with BIM, local code compliance, user training. |
| Manufacturing | Millwork and Furniture Production | Streamlines production processes, ensuring precise cuts. | Compatibility with CNC machines, ease of use, scalability. |
| Architectural Design | Detailed Architectural Plans | Facilitates clear communication between stakeholders. | Customization options, collaborative features, multi-language support. |
| HVAC and MEP Systems | Ductwork and Piping Layouts | Optimizes space usage and reduces installation errors. | Integration with HVAC systems, local standards adherence. |
| Steel Fabrication | Steel Connection and Assembly Drawings | Improves fabrication efficiency and safety compliance. | Material specifications, design flexibility, software support. |
How is Shop Drawings Software Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, shop drawings software is essential for creating detailed structural engineering drawings. These drawings serve as a bridge between design and actual construction, ensuring that the plans are executed accurately. By utilizing integrated Building Information Modeling (BIM), firms can enhance accuracy, minimize costly rework, and ensure compliance with local building codes. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should prioritize software that offers local code compliance features and user-friendly interfaces to facilitate quick onboarding.
What Role Does Shop Drawings Software Play in Manufacturing?
For manufacturers, particularly in millwork and furniture production, shop drawings software is crucial for generating precise production specifications. This software automates the creation of detailed drawings that dictate exact dimensions and materials required, which significantly streamlines the production process. By reducing human error, businesses can achieve higher quality outputs and optimize material use. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should consider software that integrates seamlessly with CNC machines, providing a direct link between design and manufacturing.
How Does Shop Drawings Software Benefit Architectural Design?
In architectural design, shop drawings software allows architects to produce detailed plans that communicate design intent clearly to contractors and clients. This clarity minimizes misunderstandings and misinterpretations during the construction phase. The software’s capability to generate 3D models and detailed visualizations is particularly beneficial for international collaborations, as it aids in overcoming language barriers. When sourcing software, buyers should look for customization options and features that support collaborative workflows.
What Advantages Does Shop Drawings Software Offer for HVAC and MEP Systems?
Shop drawings software is vital for the HVAC and Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) sectors, where precise ductwork and piping layouts are critical. The software allows for the optimization of space usage, ensuring that installations fit within the designated areas without conflicts. This is particularly important in densely populated regions or older buildings. Buyers should focus on software that integrates well with existing HVAC systems and adheres to local standards to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
How is Shop Drawings Software Used in Steel Fabrication?
In steel fabrication, shop drawings software is indispensable for creating detailed connection and assembly drawings. These drawings improve the efficiency of the fabrication process and ensure that safety standards are met. By providing accurate specifications, the software reduces the risk of costly mistakes during assembly. Buyers in the steel industry should consider software that offers flexibility in design and material specifications, as well as robust support for ongoing technical issues.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘shop drawings software’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Integration Across Teams
The Problem: In a globalized business environment, many B2B buyers face the challenge of ensuring seamless collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors. When different teams use disparate software for creating shop drawings, the risk of miscommunication increases. For example, a structural engineer may draft a design in one software, while the architectural team might use another, leading to inconsistencies that can delay projects and escalate costs. This lack of integration not only hampers efficiency but also frustrates team members who are striving to deliver quality results.
The Solution: To overcome this integration challenge, businesses should prioritize shop drawing software that offers an all-in-one solution with integrated Building Information Modeling (BIM) capabilities. Tools like ideCAD Structural provide a centralized platform that combines architectural design, structural analysis, and detailing within one software. By investing in such integrated solutions, teams can work on a single version of the project, ensuring that any changes made are automatically updated across the board. Additionally, conducting regular training sessions can enhance the team’s proficiency in using the software, leading to improved communication and collaboration.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Generating Accurate Drawings
The Problem: Another prevalent pain point is the complexity involved in generating accurate and detailed shop drawings. Many B2B buyers find themselves frustrated when their software does not automatically update dimensions or fails to produce drawings that meet industry standards. This often results in time-consuming revisions and increased labor costs. For instance, a contractor might spend hours manually adjusting dimensions after the software generates an imprecise drawing, which can lead to delays and potential project overruns.
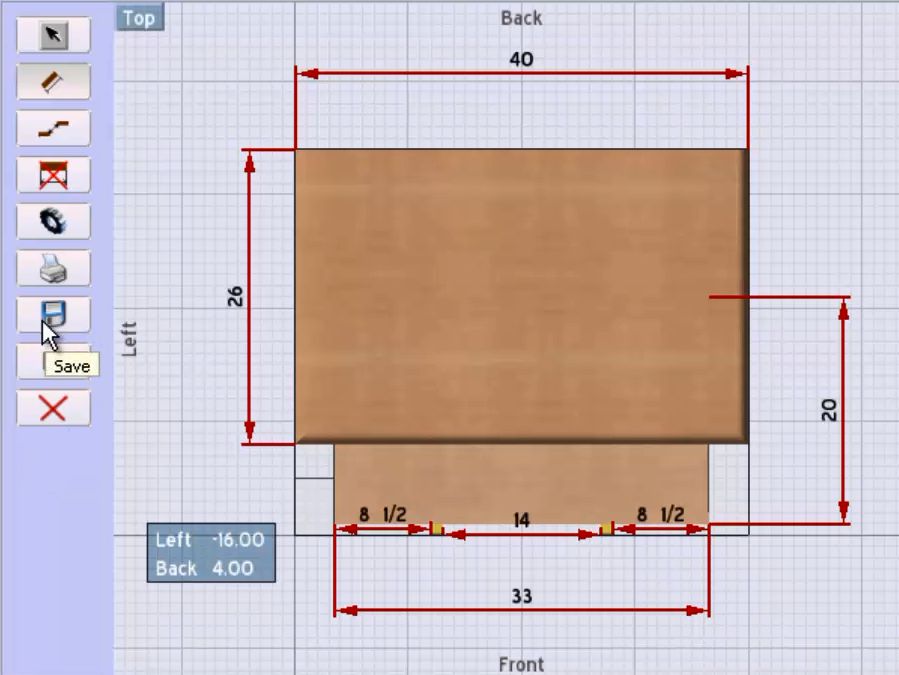
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should seek out shop drawing software that automates the generation of drawings based on real-time project data. Solutions like SketchList 3D allow users to create dimensioned drawings directly from their designs, ensuring accuracy and compliance with specified requirements. By utilizing features such as automatic dimensioning and easy-to-navigate interfaces, teams can streamline the drawing process significantly. Implementing a standardized workflow that includes regular quality checks on generated drawings can further enhance accuracy and reduce the need for revisions.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Standards
The Problem: Compliance with local building codes and regulations poses a significant hurdle for many B2B buyers in the construction and engineering sectors. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, where regulations can vary greatly, ensuring that shop drawings adhere to the necessary standards is crucial. Failure to do so can result in costly rework, fines, or even project shutdowns. Buyers often find it daunting to keep track of multiple codes and standards, leading to compliance issues that can jeopardize project timelines.
The Solution: To effectively navigate compliance challenges, businesses should select shop drawing software that includes automated code-checking features. Programs like ideCAD Structural offer integrated tools that automatically verify designs against local codes and regulations, significantly reducing the burden on project teams. Buyers should also consider consulting with local experts or regulatory bodies when setting up their software to ensure that all necessary standards are incorporated into their workflows. Regular updates and training on compliance requirements can further empower teams, enabling them to create shop drawings that are not only accurate but also compliant with the latest regulations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shop drawings software
What Are the Key Materials Used in Shop Drawings Software?
When selecting shop drawings software, understanding the materials that underpin the software’s functionality is essential. The choice of materials impacts performance, compatibility, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the development of shop drawings software, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural applications. It has excellent temperature and pressure ratings, which are critical in engineering contexts.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability ensures long-lasting performance, but it can be susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires precise cutting and welding techniques. Its cost can vary, but it generally falls in the medium to high range.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various construction methods makes it ideal for detailed structural drawings. However, its weight may require specific handling and transportation considerations.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as EN 1993 (Eurocode 3) for steel structures. In Africa and South America, local regulations may vary significantly, impacting the choice of steel grades.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. It has good thermal and electrical conductivity, which can be beneficial in certain design contexts.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight and high strength-to-weight ratio, which simplifies handling and installation. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various finishes allows for aesthetic flexibility in designs. However, its lower tensile strength compared to steel may limit its use in heavy structural applications.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is crucial for international buyers. In Brazil and Germany, adherence to local standards can affect project timelines and costs.
3. Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offer excellent corrosion resistance and are lightweight. They also have good thermal stability, making them suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for rapid prototyping and design iterations. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications, and their durability can be less than that of metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic materials are often used for non-structural components in shop drawings, such as fittings and fixtures. Their compatibility with various media is generally high, but they may not withstand extreme temperatures.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa should consider local availability and recycling regulations, which can impact long-term sustainability.
4. Wood
Key Properties: Wood is a natural material known for its aesthetic appeal and versatility. It has good insulation properties and can be treated for enhanced durability against pests and moisture.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of wood is its sustainability and ease of use in design. However, it can be prone to warping and requires careful handling during manufacturing. The cost can vary widely depending on the type of wood used.
Impact on Application: Wood is often used in furniture and cabinetry designs, making it suitable for detailed shop drawings in the woodworking industry. Its compatibility with various finishes allows for creative flexibility.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ISO 3349 for wood-based panels is important for international buyers. In South America and Africa, local species availability can influence material choice and project feasibility.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Shop Drawings Software
| Material | Typical Use Case for shop drawings software | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural engineering drawings | High durability and strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium to High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | Medium to High |
| Plastic | Non-structural components | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Less durable under heavy loads | Low to Medium |
| Wood | Furniture and cabinetry designs | Aesthetic appeal and sustainability | Prone to warping and pests | Low to Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the materials relevant to shop drawings software, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, compliance, and cost considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shop drawings software
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Shop Drawings Software?
The manufacturing process for shop drawings software involves several critical stages designed to ensure the final product meets the specific needs of B2B clients. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs distinct techniques that contribute to the software’s overall functionality and usability.
Material Preparation
In the context of software development, material preparation refers to gathering the necessary technical requirements and user feedback that inform the software’s design. This involves conducting market research to identify the needs of potential users in various industries, including construction, architecture, and manufacturing. Key techniques at this stage include user surveys, interviews, and competitive analysis, which help in defining the software specifications.
Forming
Forming is the stage where the software’s architecture and codebase are developed. This process typically uses programming languages and development frameworks suited to the software’s intended functionalities. Agile development methodologies are commonly employed, allowing for iterative testing and refinement based on user feedback. Techniques such as version control and continuous integration are crucial, ensuring that code changes do not disrupt existing functionalities.
Assembly
Assembly involves integrating various software components, such as the user interface (UI), backend services, and databases. This stage emphasizes ensuring that all parts of the software work seamlessly together. Techniques such as modular programming and application programming interfaces (APIs) are essential, enabling different components to communicate effectively. Rigorous integration testing is performed to identify any discrepancies or bugs that could affect performance.
Finishing
The finishing stage encompasses final testing and polishing of the software before it is released to the market. This includes performance testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), and debugging. Techniques such as load testing and stress testing are used to ensure the software can handle expected user volumes and complex operations. Additionally, this stage involves preparing user documentation and support materials, which are vital for successful implementation.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Shop Drawings Software?
Quality assurance (QA) in shop drawings software is pivotal in ensuring that the product meets the required standards and functions correctly. This process typically adheres to international standards such as ISO 9001, which sets criteria for a quality management system, and industry-specific certifications like CE and API, relevant in construction and engineering contexts.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical to maintaining high standards throughout the software development lifecycle. The main checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, the initial requirements and design specifications are reviewed to ensure they meet the established standards. This includes assessing user feedback and ensuring all necessary features are included.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the development phase, regular reviews and testing are conducted to identify and rectify any issues early in the process. This includes code reviews and unit testing to ensure that individual components function correctly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This is the last checkpoint before the software is released. Comprehensive testing, including functional testing, regression testing, and system testing, is performed to ensure that the software meets all specifications and is free of critical bugs.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Shop Drawings Software Development?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the software’s quality and performance. Common approaches include:
-
Automated Testing: This method uses scripts and tools to execute tests automatically, allowing for efficient and consistent testing across various software components.
-
Manual Testing: Human testers conduct this type of testing to evaluate the software’s usability, functionality, and performance. Testers simulate real-world scenarios to identify potential issues that automated tests may overlook.
-
Performance Testing: This method assesses how the software performs under varying loads and conditions. It helps identify bottlenecks and ensures that the software can handle the expected number of users and transactions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control measures. Here are several ways to verify supplier QC:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s processes can help assess compliance with quality standards. This includes reviewing documentation, process flows, and testing results.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including test results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important for international transactions where standards may vary.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control and certification nuances. These include:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific quality standards and regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
-
Language and Documentation Barriers: Ensure that all quality control documentation is available in a language that is easily understood by all stakeholders. This is crucial for effective communication and understanding of quality processes.
-
Variability in Supplier Capabilities: Suppliers from different regions may have varying levels of expertise and access to technology. Buyers should assess the supplier’s capabilities and experience in delivering quality software that meets international standards.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for shop drawings software is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable, high-quality solutions. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and organizational standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘shop drawings software’
Introduction
Choosing the right shop drawings software is critical for ensuring precision and efficiency in your construction or manufacturing projects. This guide serves as a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in identifying the most suitable software solutions tailored to their specific needs, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your software selection process. Identify the specific features you need, such as integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM), compatibility with existing systems, or support for various materials like steel and concrete. Documenting these requirements will help you filter options that do not meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Assess User-Friendliness and Training Needs
The usability of the software can significantly impact your team’s productivity. Investigate whether the software offers intuitive interfaces and robust customer support. Additionally, consider the availability of training resources, such as tutorials or webinars, which can facilitate a smoother transition and empower your team to maximize the software’s capabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Software Integration Capabilities
Modern construction and design processes often require various tools to work seamlessly together. Ensure that the software can integrate with other essential applications, such as CAD software or project management tools. Look for solutions that provide APIs or built-in features for data sharing to streamline workflows and reduce manual errors.
Step 4: Check for Industry-Specific Features
Different industries may require unique functionalities. For example, if you are in the woodworking sector, look for software that excels in creating detailed millwork shop drawings. Evaluate whether the software includes templates, dimensioning tools, or material optimization features relevant to your industry to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Step 5: Review Supplier Reputation and Support
Before finalizing your choice, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from businesses similar to yours. A reliable supplier should offer responsive customer support and regular updates, ensuring that you receive ongoing assistance and improvements to the software.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Hands-on experience with the software can provide invaluable insights into its functionality. Request demonstrations or free trials from suppliers to assess how well the software meets your needs. Pay attention to aspects such as ease of use, the quality of output, and the speed of processes during these trials.
Step 7: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Finally, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with the software. Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate ongoing costs, including maintenance fees, training expenses, and any additional modules you may need. A clear understanding of TCO will help you make a more informed financial decision that aligns with your budget and expected ROI.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing shop drawings software and make a well-informed decision that enhances your operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shop drawings software Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Shop Drawings Software?
When sourcing shop drawings software, several key cost components should be carefully analyzed. These include:
-
Materials: This refers to the software’s core features and functionalities. High-quality shop drawings software often integrates Building Information Modeling (BIM) capabilities, structural analysis, and detailing features, which can significantly influence the cost.
-
Labor: The cost of labor encompasses both the development of the software and the support provided to users. Consider the availability of customer service and technical support, as these factors contribute to the overall value of the software.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with producing the software, such as infrastructure, software maintenance, and regular updates. Understanding how often the software is updated can help gauge ongoing costs.
-
Tooling: In the context of software, tooling refers to the tools and libraries integrated within the software that facilitate design and drafting processes. Comprehensive tools may come at a higher initial cost but can save time and resources in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): The reliability and accuracy of the software are crucial, especially for industries that demand high precision, such as construction and engineering. Higher QC standards often result in increased costs but can prevent costly errors.
-
Logistics: While less relevant in software, logistics can include the distribution model of the software (cloud-based vs. on-premises) and associated costs for implementation and training.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a margin into their pricing, which can vary depending on the software’s brand reputation, market demand, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Shop Drawings Software?
Several factors can influence the pricing of shop drawings software:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases or long-term contracts may lead to discounts. Buyers should inquire about volume pricing options.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features tailored to specific industry needs can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Software that meets certain industry standards or certifications may command higher prices. However, investing in certified software can enhance reliability and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers often provide more robust support and features, justifying a higher price.
-
Incoterms: While generally more applicable to physical goods, understanding Incoterms can be beneficial for software solutions that require installation or implementation services.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Negotiate Better Pricing for Shop Drawings Software?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several tips can enhance negotiation strategies:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the price range for comparable software can empower buyers during negotiations. Investigate competitors and available alternatives.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, updates, and training. A lower upfront cost might lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Negotiate on Additional Services: Look for opportunities to negotiate not just on price, but also on value-added services such as training, support, or extended warranties.
-
Consider Payment Terms: Flexible payment options can provide financial relief, especially for buyers in emerging markets. Discussing payment terms can lead to better cash flow management.
-
Leverage International Buying Power: Buyers from regions with growing economies may have leverage in negotiations, especially if they can commit to long-term contracts or larger purchases.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for shop drawings software can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes directly from suppliers and consider all cost components to make informed decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing shop drawings software With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Shop Drawings Software for B2B Buyers
In the realm of architectural and engineering design, the efficiency and accuracy of shop drawings are crucial for project success. While dedicated shop drawings software provides a streamlined approach to creating these drawings, there are alternative solutions available that can also meet the needs of businesses in diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section compares traditional shop drawings software with other viable methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Shop Drawings Software | CAD Software | Manual Drafting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy; automates drawing generation and updates. | Moderate to high accuracy; dependent on user skill and software capabilities. | Varies significantly; highly dependent on the drafter’s expertise. |
| Cost | Subscription-based; can be costly depending on features. | Initial purchase can be high; maintenance and updates may add costs. | Low initial costs; however, labor-intensive and time-consuming. |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly interfaces; quick onboarding with training resources. | Steeper learning curve; requires training to master. | Intuitive for skilled drafters; lacks efficiency tools. |
| Maintenance | Regular updates and support provided by vendors. | Varies by software; some require significant updates and troubleshooting. | Minimal maintenance but requires continuous skilled labor. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex projects requiring high collaboration and integration. | Suitable for detailed technical drawings across various industries. | Best for small projects or when digital tools are unavailable. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of CAD Software as an Alternative?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is a popular alternative to dedicated shop drawings software, particularly for firms involved in various engineering and design projects. CAD tools like AutoCAD are widely used due to their versatility and ability to create detailed technical drawings.
Pros:
– High customization and flexibility for different types of design work.
– Strong industry support and a vast resource pool for training and troubleshooting.
Cons:
– Requires a higher skill level to utilize effectively, which may necessitate additional training for staff.
– Can be costly due to licensing fees and the need for powerful hardware.
How Does Manual Drafting Compare as an Alternative?
Manual drafting represents a traditional approach to creating shop drawings. While this method has been largely replaced by digital solutions, it remains a feasible option for some businesses, especially in areas with limited access to technology.
Pros:
– Low initial costs as it primarily requires basic drafting tools (pencil, paper, ruler).
– Intuitive for experienced drafters who prefer a hands-on approach.
Cons:
– Time-consuming and labor-intensive, leading to potential delays in project timelines.
– Higher likelihood of errors due to manual processes, which can affect project accuracy.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
When selecting the appropriate solution for creating shop drawings, B2B buyers should consider their specific project requirements, budget constraints, and team capabilities. For organizations needing high accuracy and collaboration on complex projects, investing in dedicated shop drawings software may be the best choice. Conversely, if budget constraints are significant, or if the projects are relatively simple, CAD software or even manual drafting could suffice. Evaluating the pros and cons of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shop drawings software
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Shop Drawings Software?
When selecting shop drawings software, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that it meets the demands of complex projects. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM)
A primary technical feature of modern shop drawings software is its ability to integrate with BIM systems. This integration enables seamless collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors, facilitating real-time updates and reducing errors. For B2B buyers, this means enhanced efficiency and accuracy in project execution, ultimately leading to cost savings.
2. Detail Level and Dimensioning Capabilities
The software should allow users to create detailed and dimensioned drawings, which are vital for accurate fabrication and assembly. High-quality dimensioning tools enable precise measurements, ensuring that all components fit together correctly. This is particularly important for international buyers who may work with diverse standards and regulations.
3. Code Compliance Automation
Automated code compliance checks within the software can significantly reduce the risk of costly rework. This feature ensures that all designs adhere to relevant building codes and regulations, which is essential for projects in different regions, such as Europe and Africa. Ensuring compliance not only mitigates legal risks but also enhances the credibility of the business.
4. Customization and User Interface
User-friendly interfaces and customizable templates allow teams to adapt the software to their specific workflow and project requirements. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced environments, as it enables rapid adjustments and improvements in productivity.
5. Export and Reporting Features
The ability to easily export drawings into various formats (such as PDF, DWG, or DXF) and generate comprehensive reports is crucial for communication and collaboration among stakeholders. This functionality supports the sharing of information across different platforms and ensures that all parties have access to the most current data.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Shop Drawings Software?
Understanding industry jargon is equally important for effective communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of shop drawings software, an OEM might provide specialized components or tools integrated into the software, enhancing its functionality for specific industries.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For software solutions, understanding MOQ is essential when negotiating licenses or subscriptions, as it can affect the overall budget and project scalability.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to invite suppliers to submit price proposals for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for shop drawings software can help compare features and pricing from different vendors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for ensuring smooth negotiations and understanding shipping, insurance, and liability clauses.
5. SaaS (Software as a Service)
This term describes software that is hosted in the cloud and accessed via the internet, rather than installed locally on a device. SaaS solutions for shop drawings software often provide flexibility, scalability, and ease of access, making them an attractive option for businesses with distributed teams.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting shop drawings software that aligns with their operational needs and project requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the shop drawings software Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Shop Drawings Software?
The shop drawings software market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary drivers is the increasing adoption of Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology, which enhances collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Brazil and Germany, where construction projects are becoming increasingly complex, necessitating sophisticated software solutions that integrate various design and engineering functions.
Another notable trend is the rise of cloud-based solutions, which provide flexibility and scalability for businesses looking to streamline their operations. These platforms allow for real-time collaboration across different geographical locations, crucial for international projects. Additionally, the demand for automation in the drafting process is growing, as businesses seek to reduce manual errors and accelerate project timelines. This is particularly beneficial for firms in regions with rapid urbanization, where timely project delivery is essential to meet the growing infrastructure needs.
Moreover, there is a noticeable shift towards mobile accessibility in shop drawing software. As more professionals work remotely or in the field, having access to software applications on mobile devices is becoming increasingly important. This trend is aligning with the global push towards digital transformation in the construction and engineering sectors.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Shop Drawings Software?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have emerged as critical considerations for B2B buyers in the shop drawings software sector. The environmental impact of construction practices is under scrutiny, leading to a demand for software solutions that facilitate sustainable design practices. This includes features that help designers optimize material usage, minimize waste, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are gaining prominence as businesses recognize the importance of transparency and accountability. Buyers are increasingly favoring software providers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, whether through the use of eco-friendly materials or by obtaining ‘green’ certifications. Such certifications can enhance a company’s reputation and align with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible practices.
In addition to software features that promote sustainability, the choice of materials and processes used in the development of shop drawings software also plays a role. Providers that prioritize sustainable practices in their operations can attract a broader customer base, particularly in regions where environmental concerns are paramount, such as Europe.
How Has Shop Drawings Software Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of shop drawings software has been marked by significant advancements in technology and user needs. Initially, these tools were primarily focused on manual drafting, which was often time-consuming and prone to errors. The introduction of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) revolutionized the sector, allowing for more precise and efficient drawing processes.
As the industry progressed, the integration of BIM technology transformed shop drawings software into comprehensive solutions that combine design, analysis, and detailing in one platform. This integration is particularly beneficial for B2B buyers, as it facilitates collaboration among various stakeholders in construction projects, leading to improved project outcomes.
Today, the focus is shifting towards cloud-based solutions and mobile accessibility, further enhancing the versatility and usability of shop drawings software. This trajectory illustrates how the industry is continuously adapting to meet the evolving demands of international buyers, making it imperative for businesses to stay informed about these trends to remain competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shop drawings software
-
How do I choose the right shop drawings software for my business?
Choosing the right shop drawings software involves evaluating your specific needs, such as the type of projects you handle and the level of integration required with other tools. Look for software that supports Building Information Modeling (BIM) for seamless collaboration across teams. Additionally, consider user-friendly interfaces, customer support, and compatibility with existing systems. Research reviews and case studies from similar businesses to gauge effectiveness and efficiency. Finally, take advantage of free trials to test the software in real-world scenarios before making a commitment. -
What features should I look for in shop drawings software?
Key features to seek in shop drawings software include robust drafting tools, integrated BIM capabilities, automated dimensioning, and customizable templates. Ensure the software offers collaboration features to facilitate communication among stakeholders and supports various file formats for easy sharing. Look for code compliance and automated reporting functionalities to streamline your workflow. User support and training resources are also crucial, especially for teams unfamiliar with advanced software solutions. -
What is the best software for creating shop drawings in the construction industry?
The best software for creating shop drawings in the construction industry often includes solutions like ideCAD Structural, AutoCAD, and SketchList3D. These programs provide comprehensive tools for structural analysis, detailing, and integrated architectural design. When selecting software, consider factors such as the complexity of your projects, ease of use, and the specific features you require. Opt for software that allows for easy collaboration and integrates well with other tools in your workflow. -
How can I ensure the quality of shop drawings produced by the software?
To ensure high-quality shop drawings, choose software with built-in quality assurance features, such as automated code checking and error detection. Regularly review and update your templates to reflect industry standards and best practices. Implement a feedback loop where team members can review and provide input on generated drawings. Additionally, training your staff to utilize the software effectively will enhance the overall quality of the outputs. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by shop drawings software suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, monthly subscriptions, or annual licensing fees. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment plans based on your business’s cash flow needs. Always clarify terms before signing contracts, including any additional costs for upgrades, training, or technical support. Understanding these terms will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for shop drawings software licenses?
Many shop drawings software suppliers do not have a minimum order quantity for licenses, especially for cloud-based solutions. However, if you are looking for on-premise licenses, some vendors may have MOQ requirements, typically ranging from 5 to 10 licenses. It’s essential to inquire directly with suppliers about their specific policies. Additionally, consider group purchasing options if your organization has multiple departments needing access. -
How can I vet suppliers of shop drawings software in international markets?
To vet suppliers in international markets, start by checking their reputation through reviews and testimonials from other businesses. Look for certifications or partnerships with industry standards organizations. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to meet suppliers face-to-face and assess their offerings. Additionally, request product demonstrations and trial versions to evaluate functionality before making a commitment. Networking with other professionals can provide insights into reliable suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when purchasing shop drawings software?
When purchasing shop drawings software, consider the logistics of software deployment, including installation, updates, and technical support. Ensure that the supplier offers timely support for international clients, especially if you face challenges related to time zones. Additionally, assess the cloud infrastructure, as this will impact data accessibility and security. Be aware of any potential import taxes or regulations if you are acquiring physical licenses or hardware associated with the software.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Shop Drawings Software Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. idecad – Integrated Structural Engineering Software
Domain: idecad.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Shop Drawings Software with Integrated Design for Structural Engineering, including Integrated Architectural Design. Features include Integrated Shop Drawing Workflow, Structural Analysis, Structural Design, and Structural Detailing for Concrete and Steel Buildings. Offers All-in-One Structural Engineering Software with Building Information Modeling (BIM) tools. Key functionalities include intelli…
2. SketchList3D – Woodworking Design Software
Domain: sketchlist.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: SketchList3D woodworking design software allows users to create detailed and dimensioned shop drawings. Key features include automatic addition of objects to shop drawings, parts list, purchase list, and optimized layout diagram upon object addition. Users can create shop drawings at various levels: project level for assemblies, assembly level for dimensions of doors, drawers, and hardware, and co…
3. DraftSight – 2D CAD & 3D Design Software
Domain: draftsight.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: DraftSight is a 2D CAD drafting and 3D design software developed by the makers of SOLIDWORKS. It offers productivity tools and an API for creating, editing, viewing, and sharing 2D and 3D DWG files. The software features a familiar and easy-to-learn interface, making it suitable for architects, engineers, designers, and hobbyists. DraftSight provides various licensing options including Premium ($5…
4. Signs101 – Shop Drawing Software Solutions
Domain: signs101.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Looking for suggestions on software for shop drawings. Currently using Illustrator, which is not practical for managing details like sizing and finishes. Seeking a program or plugin that allows importing multiple sets of variable data from a custom workflow platform. Company size: 20-30 employees, focusing on one-off jobs and larger projects with 50+ sign types needing individual shop drawings. Pr…
5. CabWriter – Cabinet Shop Drawing Software
Domain: cabwritersoftware.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: CabWriter integrates with SketchUp to create detailed shop drawings necessary for cabinet construction. Key features include: 3D model visualization, detailed shop drawings with elevations, sections, dimensions, hatching, symbols, and professional title blocks. Requires SketchUp Pro for robust dimensioning and layout capabilities, utilizing LayOut for linking scenes and creating sheets. Automatic …
6. WoodWeb – Software Solutions for Design and Drafting
Domain: woodweb.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Software options discussed include DesignCAD 3D for shop drawings, eCabinets for presentation drawings, and CutLists Plus for cut lists. Contributors recommend basic drafting programs like Intellicad products or AutoCAD LT for producing fully dimensioned custom elevations and plan views. Chief Architect is also mentioned positively. The focus is on producing CAD shops that resemble hand-drawn desi…
7. SmartDraw – Professional 2D Drawing Software
Domain: smartdraw.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: SmartDraw is a professional 2D drawing and design software that offers a range of features including easy-to-use tools for creating 2D drawings, thousands of professionally designed symbols for various types of drawings (architectural, engineering, mechanical, electrical, P&ID, HVAC), the ability to draw and print to scale, integration with Microsoft Office and Google Workspace, compatibility with…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shop drawings software
In the evolving landscape of shop drawings software, strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical factor for B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and accuracy. By investing in integrated solutions that combine structural analysis, design, and detailing, companies can streamline workflows and reduce errors. This is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse project requirements demand robust and adaptable software capabilities.
The value of shop drawings software extends beyond mere drafting; it encompasses enhanced collaboration through Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the automation of code compliance checks. These features not only facilitate compliance with local regulations but also improve project timelines and cost management. As competition intensifies, leveraging advanced software tools will be pivotal in driving business growth and meeting client expectations.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate their current software solutions critically. Consider initiating trials of leading platforms to assess their fit for your specific needs. Embrace the opportunity to innovate your processes and position your business for success in the global market. Investing in the right shop drawings software today can pave the way for a more efficient and profitable tomorrow.