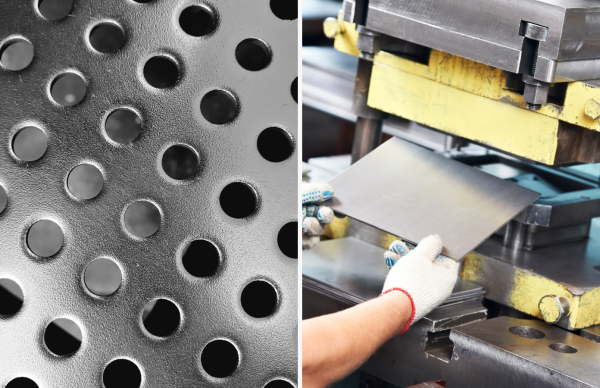
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sheet punching
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, sourcing reliable sheet punching services can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Brazil and Germany) strive to optimize production processes, understanding the intricacies of sheet metal punching becomes essential. This guide is designed to equip decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market for sheet punching, addressing critical aspects such as various punching techniques, applications across diverse sectors, and methods for vetting potential suppliers.
Our comprehensive resource delves into the types of sheet punching operations available, from traditional mechanical presses to advanced CNC systems, each offering unique benefits and capabilities. We explore the wide array of applications, highlighting how sheet metal punching is integral to industries ranging from automotive to aerospace, electronics, and beyond. Additionally, this guide provides insights into cost considerations, allowing buyers to make informed financial decisions while maximizing efficiency.
By leveraging the information presented in this guide, international B2B buyers can confidently identify the right sheet punching solutions tailored to their needs. With a focus on actionable insights and practical strategies, we empower you to forge successful partnerships and drive your manufacturing capabilities forward in a competitive global landscape.
Understanding sheet punching Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Punching | Utilizes a punch and die to create precise holes and shapes. | Automotive, aerospace, electronics | Pros: High speed, accuracy. Cons: Noise and waste. |
| Nibbling | Involves overlapping punches to create irregular shapes. | Custom parts, HVAC components | Pros: Flexibility for complex shapes. Cons: Slower process. |
| CNC Punching | Computer-controlled for high precision and repeatability. | Mass production, intricate designs | Pros: Extremely accurate, automated. Cons: Initial setup cost. |
| Punch Laser Hybrid | Combines punching and laser cutting for complex geometries. | Prototyping, custom fabrication | Pros: Versatile, efficient for varying shapes. Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| Embossing | Creates raised or recessed designs on the sheet metal. | Decorative panels, labels, signage | Pros: Adds aesthetic value, precise detail. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Standard Punching?
Standard punching is characterized by its straightforward process of using a punch and die to create holes and shapes in sheet metal. This method is well-suited for high-volume production across various industries, including automotive and aerospace, where precision and speed are critical. B2B buyers should consider the equipment’s noise levels and potential waste, which can affect operational efficiency and costs.
How Does Nibbling Differ and When Is It Used?
Nibbling allows for the creation of irregular shapes by overlapping punches, making it ideal for custom parts and HVAC components. This method offers flexibility in design, accommodating complex geometries that standard punching may not handle effectively. However, the slower processing speed may necessitate longer lead times, which buyers should factor into project timelines.
Why Choose CNC Punching for Mass Production?
CNC punching leverages computer technology to achieve high precision and repeatability, making it an excellent choice for mass production and intricate designs. This method is especially valuable for manufacturers requiring consistent quality across large batches. While the initial setup costs may be higher due to the technology involved, the long-term benefits of reduced labor and material waste can justify the investment.
What Advantages Does a Punch Laser Hybrid Provide?
The punch laser hybrid technique combines the strengths of both punching and laser cutting, allowing for the efficient production of complex shapes. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for prototyping and custom fabrication, where varied designs are often required. Buyers should be aware of the higher operational costs associated with this technology, but the ability to switch between processes can significantly enhance productivity.
In What Scenarios Is Embossing Most Effective?
Embossing is a specialized punching technique that creates raised or recessed designs, making it ideal for decorative panels, labels, and signage. Its capacity for producing precise details adds aesthetic value to products, catering to industries that prioritize design. However, buyers should note that embossing is limited to specific applications and may not be suitable for all sheet metal processing needs.
Key Industrial Applications of sheet punching
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sheet punching | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing car body components | High-speed production with precise tolerances | Consider the tonnage capacity of the punching machines |
| Aerospace | Production of aircraft structural components | Lightweight and robust parts that meet strict regulations | Ensure compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Electronics | Creation of enclosures for electronic devices | Cost-effective and efficient production of complex shapes | Look for suppliers with advanced CNC capabilities |
| HVAC | Fabrication of ductwork and HVAC components | Enhanced energy efficiency and reduced installation time | Evaluate material compatibility and tooling options |
| Furniture | Production of decorative and functional metal parts | Customization and aesthetic appeal for diverse applications | Assess design flexibility and finishing options available |
How is Sheet Punching Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, sheet punching is extensively used to manufacture car body components such as chassis, panels, and brackets. This process allows for high-speed production while maintaining precise tolerances essential for vehicle safety and performance. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust machinery capable of handling high tonnage, as this ensures the ability to work with thicker materials. Additionally, understanding local regulations and quality standards is crucial to avoid compliance issues.
What Role Does Sheet Punching Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, sheet punching is critical for producing lightweight yet strong components like wing structures and fuselage parts. The need for rigorous adherence to safety and performance standards makes precision a top priority. Buyers in this sector must seek suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international aerospace standards, such as AS9100. Additionally, the ability to provide traceability for materials used is a significant consideration in sourcing decisions.
Why is Sheet Punching Important for Electronics?
The electronics industry utilizes sheet punching to create enclosures and chassis for devices, enabling cost-effective and efficient production of complex shapes. This method allows for rapid prototyping and customization, which are essential in a fast-paced market. Buyers should focus on suppliers that offer advanced CNC punching capabilities to ensure high precision and repeatability. Furthermore, understanding the specific material requirements, such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, is essential for product performance.
How Does Sheet Punching Benefit HVAC Applications?
In HVAC applications, sheet punching is employed to fabricate ductwork and components that enhance system efficiency. The process allows for precise mounting holes and openings that facilitate quick installation and optimal airflow. Businesses should consider sourcing from manufacturers who can provide high-quality materials and tooling options suitable for HVAC systems. Additionally, evaluating the supplier’s ability to produce custom sizes and shapes can lead to improved project outcomes.
What Advantages Does Sheet Punching Offer in Furniture Production?
In the furniture industry, sheet punching is used to create both decorative and functional metal parts, enhancing product aesthetics and utility. This application allows for high levels of customization, catering to diverse consumer preferences. Buyers should assess suppliers based on their design flexibility and finishing options to ensure that the final products meet market demands. Additionally, understanding production lead times and minimum order quantities can help in managing inventory effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sheet punching’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality in Punching Operations
The Problem: A manufacturer in Brazil is struggling with inconsistent quality in their sheet metal punching operations. Despite using the same equipment and materials, the parts produced show varying hole sizes and edge finishes, leading to increased waste and rework. This inconsistency results in delays in production and ultimately affects customer satisfaction, as clients receive parts that do not meet their specifications.
The Solution: To address this challenge, the manufacturer should invest in advanced CNC punching technology that allows for precise control over punching parameters. Regular calibration of the punching machines is essential to maintain accuracy. Additionally, implementing a robust quality control process, including the use of digital measuring tools, can help monitor and ensure that each batch of products meets the required tolerances. Engaging with a reputable supplier who can provide high-quality punch and die sets tailored to specific applications is also crucial. This not only enhances the repeatability of the punching process but also reduces the risk of defects, leading to better overall product quality.
Scenario 2: High Operating Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem: A sheet metal fabricator in Germany is facing high operating costs due to inefficient punching processes. The current manual setup and operation of punching machines are time-consuming, leading to longer lead times and increased labor costs. Furthermore, the excessive wear on tools from improper handling is resulting in frequent replacements, adding to the overall expenses.
The Solution: To optimize the punching process and reduce costs, the fabricator should consider transitioning to fully automated punch presses that can handle complex designs with minimal human intervention. This technology not only speeds up production but also significantly reduces the risk of operator errors. Additionally, investing in a preventive maintenance program can extend the life of the punching tools. Training operators on best practices for handling and setting up the machines can minimize wear and tear, ultimately reducing replacement costs. By analyzing and streamlining the entire workflow, the fabricator can identify bottlenecks and improve efficiency, leading to lower operating costs and faster turnaround times.
Scenario 3: Material Waste and Environmental Concerns
The Problem: A company in South Africa is grappling with substantial material waste during the sheet punching process, which not only inflates production costs but also raises environmental concerns. The inefficiency arises from poor layout planning and incorrect punching patterns, leading to excessive scrap metal that could otherwise be utilized.
The Solution: To mitigate waste, the company should invest in software solutions that optimize nesting layouts for sheet metal components. These programs can analyze the parts to be punched and suggest the most efficient arrangements to minimize scrap. Additionally, conducting a thorough review of the punching patterns and adjusting them according to the material’s dimensions can significantly reduce waste. Collaborating with suppliers who offer recycling services for scrap metal can also turn a potential liability into an asset. By adopting sustainable practices, the company can not only lower costs but also enhance its brand reputation as an environmentally conscious manufacturer.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sheet punching
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Sheet Punching?
When selecting materials for sheet punching, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Copper.
How Does Mild Steel Perform in Sheet Punching Applications?
Mild steel is a popular choice for sheet punching due to its excellent machinability and ductility. It typically has a tensile strength of around 400-550 MPa and can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures. Mild steel exhibits good weldability and can be easily formed into various shapes.
Pros: Mild steel is cost-effective, making it suitable for high-volume production. Its durability and strength make it ideal for applications requiring structural integrity, such as automotive parts and construction materials.
Cons: However, mild steel is prone to corrosion without proper coating or treatment, limiting its use in environments exposed to moisture. Additionally, it may require secondary finishing processes to achieve desired surface qualities.
Impact on Application: Mild steel is compatible with a wide range of media, but its susceptibility to rust can be a concern in humid climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel for Sheet Punching?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it a preferred material in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. With a tensile strength ranging from 500 to 800 MPa, it can withstand harsh environments and high temperatures.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of products. It also offers excellent aesthetic properties, making it suitable for visible components.
Cons: The main drawback is its higher cost compared to mild steel and aluminum. Additionally, its hardness can complicate the punching process, requiring specialized tooling and machinery.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, especially in Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4301 is crucial for ensuring quality and performance in applications involving food and medical equipment.
Why Choose Aluminum for Sheet Punching Projects?
Aluminum is lightweight and highly malleable, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength. It has a tensile strength of about 200-300 MPa, and its natural corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easy handling and transportation, reducing shipping costs. Its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity makes it suitable for electronic components and HVAC systems.
Cons: However, aluminum is generally less durable than steel, which can be a concern for high-stress applications. It is also more expensive than mild steel, which may affect budget considerations.
Impact on Application: In regions like South America and Africa, where lightweight materials are often preferred for transportation and logistics, aluminum’s properties align well with local market needs.
What Advantages Does Copper Offer in Sheet Punching?
Copper is known for its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a vital material in electrical applications. It has a tensile strength of around 210-300 MPa and is highly ductile, allowing for intricate designs.
Pros: Copper’s primary advantage is its conductivity, which is essential for electrical components. Its resistance to corrosion also makes it suitable for plumbing and HVAC applications.
Cons: The main limitation is its cost, which is significantly higher than that of steel and aluminum. Additionally, copper’s softness can lead to wear on punching tools, necessitating more frequent replacements.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, particularly in Europe, compliance with standards like ASTM B152 is essential for ensuring quality in electrical applications. The high cost may limit its use in low-margin projects.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Sheet Punching
| Material | Typical Use Case for sheet punching | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Automotive parts, construction materials | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Corrosion resistant and long-lasting | Higher cost and requires specialized tooling | High |
| Aluminum | Electronic components, HVAC systems | Lightweight and good conductivity | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical components, plumbing | Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance | High cost and tool wear | High |
This guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for sheet punching, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sheet punching
What Are the Key Stages in the Sheet Punching Manufacturing Process?
Sheet punching is a critical manufacturing process that transforms flat sheets of metal into components with precise shapes and features. The process generally consists of several main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital in ensuring the final product meets quality and performance standards.
How is Material Prepared for Sheet Punching?
The first step involves selecting the right type of sheet metal based on the application’s requirements. Common materials include mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, each offering different properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weight.
Once the material is selected, it is cut to the required dimensions using shearing or laser cutting. This initial preparation ensures that the sheets are uniform in size and free from defects. Additionally, the sheets may undergo a cleaning process to remove any oils, dirt, or debris that could affect the punching process.
What Techniques Are Used During the Forming Stage?
The forming stage is where the actual punching occurs. A punch and die set is used to create holes or shapes in the sheet metal. The process can be performed using various types of presses, such as mechanical or hydraulic presses, which apply significant force to ensure clean cuts.
Modern manufacturing often utilizes CNC turret punch presses, which provide high precision and efficiency. These machines can handle multiple tools, allowing for complex shapes and features to be created in a single setup. The ability to quickly change tools enhances production flexibility, making it easier to adapt to varying design specifications.
How Does the Assembly Process Fit into Sheet Punching?
In many cases, punched components require assembly with other parts to create a final product. This could involve welding, fastening, or integrating with other manufacturing processes. For instance, punched panels in automotive applications may be assembled into larger structures or systems.
Effective coordination between the punching operation and subsequent assembly processes is critical. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have streamlined operations to maintain production efficiency and reduce lead times.
What Are the Finishing Techniques After Punching?
After the punching process, components often require finishing to enhance their appearance and functionality. Common finishing techniques include deburring, which removes sharp edges created during punching, and surface treatments like powder coating or anodizing for corrosion resistance.
Quality assurance during the finishing stage is essential to ensure that the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Buyers should inquire about the specific finishing processes their suppliers utilize and any certifications related to these processes.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance in Sheet Punching?
Quality assurance is paramount in the sheet punching industry, especially for B2B buyers. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality across their operations. This standard focuses on quality management systems and continuous improvement, which are crucial for meeting customer expectations.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for safety and compliance in the European market, and API standards for the oil and gas sector, may also apply. Buyers should verify that their suppliers are compliant with these standards to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Sheet Punching Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital throughout the sheet punching process. Key QC stages typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. Any defective materials should be rejected before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the punching process, operators should conduct regular inspections to monitor the quality of punched parts. This can include checking dimensions, hole quality, and overall appearance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a thorough inspection of finished products is essential. This may involve dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections to ensure that all specifications are met.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should implement several verification strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes and adherence to international standards. These audits should assess the entire manufacturing process, from material sourcing to final inspection.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC procedures, inspection results, and any certifications obtained. This transparency allows buyers to assess the reliability and consistency of the supplier’s output.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. These inspectors can conduct random checks and offer detailed reports on compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of certain nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices regarding quality assurance. Buyers should be aware of these differences and communicate their quality expectations clearly.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, while other regions may have different compliance requirements.
-
Supply Chain Dynamics: International shipping can introduce risks related to material handling and product integrity. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that products are packaged and shipped in a manner that maintains quality.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in sheet punching is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside rigorous quality control measures, companies can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sheet punching’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of B2B manufacturing, sourcing high-quality sheet punching services can significantly impact your production efficiency and product quality. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international buyers navigate the sourcing process effectively, ensuring you select the right partners for your sheet metal punching needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensure that the punched parts meet your requirements. Consider factors such as the type of material, thickness, tolerances, and the complexity of shapes needed. Documenting these details will help streamline communication with potential suppliers and avoid misunderstandings later on.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Understanding industry standards relevant to sheet metal punching is crucial for compliance and quality assurance. Look for suppliers who adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Compliance not only ensures product quality but also helps maintain regulatory standards in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and expertise. Pay attention to their production capabilities, machinery, and experience in handling specific materials or complex designs.
Step 4: Assess Technological Capabilities
The technology used in sheet punching can significantly affect the quality and efficiency of the production process. Ensure that the suppliers utilize modern CNC punch presses and other advanced technologies that offer precision and fast turnaround times. Inquire about their ability to integrate punching with other processes, such as laser cutting, for enhanced versatility.
Step 5: Verify Quality Control Processes
A robust quality control system is essential for maintaining product integrity. Inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes, including in-process inspections and final product evaluations. Understanding their approach to quality control can help you minimize risks associated with defects and rework.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples or conduct trial runs to evaluate the quality of their work. This step allows you to assess the accuracy of the punched parts and ensure they meet your specifications. Analyzing samples can also help you identify any potential issues before placing a larger order.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Establish Clear Communication
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms that align with your business goals. Discuss lead times, payment terms, and delivery schedules to avoid any future complications. Establishing clear lines of communication is crucial for addressing any issues that may arise during the production process, ensuring a smooth partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing sheet punching services, ultimately enhancing their manufacturing processes and product offerings.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sheet punching Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sheet Punching Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with sheet punching, various components contribute to the overall expenditure. Understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in sheet punching is the material itself. Prices can fluctuate based on the type of metal (e.g., steel, aluminum, stainless steel) and its thickness. For instance, high-strength materials may incur higher costs but can enhance product durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and the complexity of the project. Automated processes reduce labor needs but may require skilled technicians for setup and maintenance. In regions like Europe and North America, labor costs tend to be higher compared to emerging markets in Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the fixed and variable costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility depreciation. Efficient production systems can help mitigate overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial investment in punches and dies, which can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific projects will increase these costs. Buyers should consider whether standard tooling can be utilized for their needs to reduce expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality output requires investment in QC processes. This might involve inspections, testing equipment, and certifications. Quality assurance is critical, especially in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where compliance with strict standards is mandatory.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely, influenced by distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers should factor in logistics when evaluating total costs, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Factors Influence Pricing in Sheet Punching?
Pricing in sheet punching is influenced by multiple factors that buyers must consider to optimize their sourcing strategy.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also affect pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique designs or complex specifications can lead to increased costs. Standardized designs typically incur lower costs due to the use of existing tooling.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the initial cost but also the long-term performance and maintenance of the finished product. Higher quality materials may result in better pricing over time due to durability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications (like ISO) may charge a premium. However, this can be justified by the assurance of consistent quality and compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality and service, but at a higher price.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipment dictate who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage their total costs effectively.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sheet Punching?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing sheet punching services, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices and terms, especially for large orders. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and logistics in your TCO analysis to make a more informed decision.
-
Research Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of local market conditions, import duties, and tariffs that can affect final costs.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize software tools for inventory management and procurement to streamline operations and reduce costs.
-
Assess Supplier Capabilities: Ensure that the chosen supplier can meet your specific requirements without compromising on quality or delivery timelines.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for sheet punching can vary based on numerous factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and terms that align with their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sheet punching With Other Solutions
When evaluating manufacturing processes, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to explore various alternatives to sheet punching. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting factors such as production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and application suitability. Below, we compare sheet punching with laser cutting and water jet cutting, two prevalent alternatives in the sheet metal processing industry.
| Comparison Aspect | Sheet Punching | Laser Cutting | Water Jet Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed production, precise holes | Excellent for complex shapes; slower than punching | Slower than both; good for thick materials |
| Cost | Low tooling costs; economical for high volumes | Higher setup and operational costs | Moderate costs; requires more maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tooling; setup can be complex | Requires training for setup; versatile applications | Setup is straightforward; minimal tooling needed |
| Maintenance | Low; regular inspections needed | Medium; lens cleaning and focus adjustments required | High; frequent maintenance due to abrasives |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of simple shapes | Complex geometries and intricate designs | Thick materials and sensitive surfaces |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting Compared to Sheet Punching?
Laser cutting is renowned for its ability to produce complex shapes and intricate designs with high precision. The versatility of laser technology allows it to handle various materials, including metals, plastics, and even wood. However, the trade-off is a higher operational cost and slower processing speeds compared to sheet punching, making it less ideal for high-volume production of simpler shapes. For applications that require fine detailing, laser cutting shines, but for bulk manufacturing where speed and cost are critical, it may not be the best option.
How Does Water Jet Cutting Stack Up Against Sheet Punching?
Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through materials. This method excels in handling thicker materials without thermal distortion, making it suitable for sensitive components. While water jet cutting provides a clean edge and does not introduce heat into the material, it typically operates at a slower pace than both sheet punching and laser cutting. The maintenance costs can also be higher due to the wear and tear on the equipment from the abrasives. However, for applications requiring precision in thicker materials, water jet cutting can be a viable alternative.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between sheet punching and its alternatives, B2B buyers should assess their specific production needs, including volume, complexity of designs, material types, and budget constraints. If the goal is to manufacture high volumes of simple components quickly and cost-effectively, sheet punching is likely the best choice. Conversely, for projects that demand intricate designs or thicker materials, laser or water jet cutting might be more appropriate despite higher costs. Understanding the nuances of each method will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and production requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sheet punching
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Sheet Punching?
Understanding the critical specifications in sheet punching is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that their manufacturing processes meet quality and efficiency standards. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific type of metal used in sheet punching, such as mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum. Each grade has unique properties that affect its machinability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring the durability and performance of the punched parts, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace where material failure can have serious implications.
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a part’s dimensions. In sheet punching, maintaining tight tolerances is vital for ensuring that parts fit together accurately in assemblies. Specifications often require tolerances in the range of ±0.1 mm or tighter, depending on the application. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can influence production costs and the final quality of the assembled products.
Punching Capacity
Punching capacity refers to the maximum thickness of material that a punch press can effectively process. This property is significant for buyers looking to punch thicker materials, as it directly impacts the choice of machinery and tooling. A higher punching capacity often correlates with increased production capabilities but may also involve higher initial investment costs.
Production Speed
This property indicates how quickly a punch press can complete a punching operation, typically measured in strokes per minute (SPM). Faster production speeds can lead to lower operational costs and increased throughput, making it a critical factor for buyers aiming to optimize their manufacturing processes. Understanding production speed helps companies align their capabilities with market demand.
Edge Quality
Edge quality describes the finish and cleanliness of the cut edges of punched parts. High-quality edges require less secondary processing, such as deburring, which saves time and costs. For B2B buyers, ensuring good edge quality is essential for maintaining the aesthetic and functional aspects of the final product.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Sheet Punching?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms relevant to sheet punching:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of sheet punching, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can meet specific manufacturing needs while adhering to industry standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage their inventory and production schedules effectively. It can also influence purchasing decisions and budgeting for projects.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request price quotes for specific quantities of materials or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing them to compare prices and terms from different suppliers.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in international transactions, as they clarify shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to automate tasks like sheet punching. Understanding CNC capabilities can help buyers evaluate potential suppliers based on their technological sophistication and the precision of their operations.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline their purchasing processes, and establish effective partnerships in the sheet punching industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sheet punching Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Sheet Punching?
The sheet punching sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by technological advancements and global market shifts. Automation and Industry 4.0 technologies are at the forefront, enhancing production efficiency through the integration of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems. These technologies allow for precision, repeatability, and the ability to handle complex geometries, catering to diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Moreover, as international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their manufacturing processes, there is a growing trend towards hybrid solutions that combine punching with laser cutting. This flexibility allows manufacturers to produce both high volumes of standardized parts and intricate custom designs, meeting varying client demands.
Sourcing trends are also evolving. B2B buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate robust supply chain resilience. This includes diversifying their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and fluctuations in material costs. Countries like Brazil and Germany are leading in adopting sustainable practices, prompting suppliers to align their offerings with environmentally friendly materials and processes.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated in Sheet Punching?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sheet punching industry, influencing procurement decisions among B2B buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. As a result, companies are prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable practices, such as minimizing scrap through precision punching and utilizing recycled materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers are increasingly aware of the social implications of their supply chains and are seeking out partners who adhere to ethical labor practices and fair trade principles. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming essential benchmarks for suppliers. Moreover, the adoption of “green” materials, such as biodegradable or recyclable metals, is gaining traction, aligning with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
How Has the Sheet Punching Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the sheet punching industry has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in manufacturing paradigms. Initially, sheet metal punching was a manual, labor-intensive process. However, the introduction of hydraulic and mechanical presses revolutionized the industry, enabling faster production rates and higher precision.
As technology progressed, CNC technology emerged, allowing for automated and highly accurate punching operations. The integration of laser technology further enhanced the capabilities of punching machines, allowing for intricate designs and varied applications. This evolution has not only improved efficiency but also expanded the range of materials and thicknesses that can be processed, making sheet punching a versatile solution for modern manufacturing challenges.
In conclusion, international B2B buyers in the sheet punching sector must navigate these dynamic market trends, emphasizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, while leveraging technological advancements to maintain competitive advantages in a global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sheet punching
-
How do I solve quality issues in sheet punching?
Quality issues in sheet punching can arise from tool wear, incorrect machine settings, or material inconsistencies. To solve these problems, regularly inspect and maintain your punch and die tooling, ensuring they are sharp and in good condition. Implement strict quality control measures to monitor the thickness and composition of your sheet metal. Additionally, invest in training for operators on best practices and troubleshooting techniques to quickly address any arising issues. -
What is the best type of punching machine for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, CNC turret punch presses are often the best choice. These machines offer rapid cycle times, high precision, and the ability to handle various materials and thicknesses. Their automation capabilities allow for quick tool changes, making them efficient for large runs of identical parts. When selecting a machine, consider your specific production needs, including the types of shapes you require and the materials you’ll be working with. -
How can I customize sheet punching services to fit my specific needs?
Customization in sheet punching can be achieved by communicating your design specifications clearly to your supplier. Discuss the desired shapes, sizes, and tolerances, as well as any additional features like embossing or deburring. Many suppliers offer tailored tooling options, so inquire about their capabilities for custom punches and dies. It’s also beneficial to provide prototypes or CAD drawings to ensure your requirements are met accurately. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for sheet punching services?
Minimum order quantities for sheet punching can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand pieces. It’s essential to discuss MOQs during your initial conversations with suppliers, as some may be flexible depending on your specific needs or the potential for future orders. Be sure to assess your production requirements to find a supplier that aligns with your volume expectations. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing sheet punching services internationally?
Payment terms for international sheet punching services typically include options like advance payment, partial payment upfront, or payment upon delivery. Commonly accepted methods include bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment platforms like PayPal. It’s vital to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your financial practices and cash flow requirements. Always confirm the currency of payment to avoid exchange rate issues. -
How do I vet potential suppliers for sheet punching services?
To vet potential suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry through reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, certifications (such as ISO), and adherence to safety standards. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible, or conducting virtual audits to assess their processes and equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing punched sheet metal parts?
When importing punched sheet metal parts, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Choose a reliable logistics partner who understands international shipping and can navigate customs efficiently. Ensure that all documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, is accurate and complete to avoid delays. Additionally, consider lead times for production and shipping to align with your project timelines. -
How can I ensure consistent quality in my sheet punching orders?
To ensure consistent quality in your sheet punching orders, establish a clear communication channel with your supplier regarding specifications and expectations. Implement a quality assurance process that includes regular inspections of the produced parts, both during and after production. Use statistical process control (SPC) methods to monitor production consistency and address any deviations promptly. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate continuous improvement efforts and quality alignment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Sheet Punching Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Codinter – Sheet Metal Punching Solutions
Domain: codinter.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Sheet metal punching is a manufacturing process that uses a punch and dies to create holes and other features in sheet metal. Key features include: 1. Punch and die: The punch tool presses into the sheet metal resting on the die cavity, shearing the material to create desired holes or shapes. 2. Press machine: Hydraulic or mechanical presses provide high force for the punching operation. 3. Fast t…
2. Trumpf – Punching and Nibbling Solutions
Domain: trumpf.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Punching and nibbling are processes used in sheet metal processing. Punching involves cutting through a sheet in a single stroke, creating geometrically perfect shapes such as round holes. The process occurs in four phases: deformation, cutting, breaking along the cut contour, and ejection of the punched piece (slug). Punching machines can also create outer contours and are suitable for repeating …
3. Harsle – Sheet Metal Punching Solutions
Domain: harsle.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Sheet metal punching is a manufacturing process used to create holes, slots, or custom shapes in metal sheets. It involves applying force using a punch press machine equipped with specially designed tools—punches and dies—to cut through metal sheets efficiently and precisely. Key benefits include high precision and consistency, cost-effectiveness for mass production, and minimal waste material. St…
4. VandF – Sheet Metal Punching Rules
Domain: vandf.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Punching Rules: 1. Punched holes have different diameters on the top and bottom sides due to die clearance. 2. The top hole diameter matches the punch diameter, while the bottom is larger due to the die. 3. Die clearances range for materials from 0.4mm to 5.0mm thick. 4. The hole cross-section is a two-stage taper: the first 25%-33% is parallel, the remaining 75%-67% tapers to the die …
5. Trick Tools – Portable Punch Kit
Domain: trick-tools.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Trick Tools – Portable Punch Kit, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Meta Fab – Metal Fabrication Services
Domain: metafab.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Meta Fab offers metal fabrication services, specializing in processes such as metal punching and shearing. Metal punching involves creating holes in sheets of metal using punch presses, which can be hand-powered or CNC-controlled. Hand-powered punch presses are suitable for light metalwork and decorative projects, while CNC-controlled punch presses provide precision and speed for high-level produc…
7. Minifaber – Sheet Metal Punching Solutions
Domain: minifaber.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Sheet metal punching is a common processing method using automatic CNC machines, involving punches and dies to create holes of various shapes and sizes. It can punch almost all metals, including iron, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and special alloys, making it versatile for industries like engineering, pharmaceuticals, automotive, manufacturing, electronics, and textiles. Different pun…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sheet punching
As the global demand for precision-engineered components continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of sheet punching services has become a critical consideration for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the speed, accuracy, and versatility of sheet metal punching, companies can optimize production processes and reduce overall costs. The ability to accommodate various materials and thicknesses further enhances its appeal across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Investing in high-quality punching equipment and maintaining strong supplier relationships can lead to significant competitive advantages. Buyers must prioritize sourcing partners that not only offer advanced technology but also adhere to stringent quality and safety standards. This ensures that the punched components meet the necessary specifications while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Looking ahead, the integration of automation and smart technologies into sheet punching operations will likely redefine industry standards. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should stay informed about these trends and be proactive in adapting their sourcing strategies. Embrace innovation and partner with forward-thinking suppliers to ensure your business remains at the forefront of this dynamic market. Engage with local and international vendors today to harness the full potential of sheet punching in your production processes.